|
Sublimation (phase Transition)
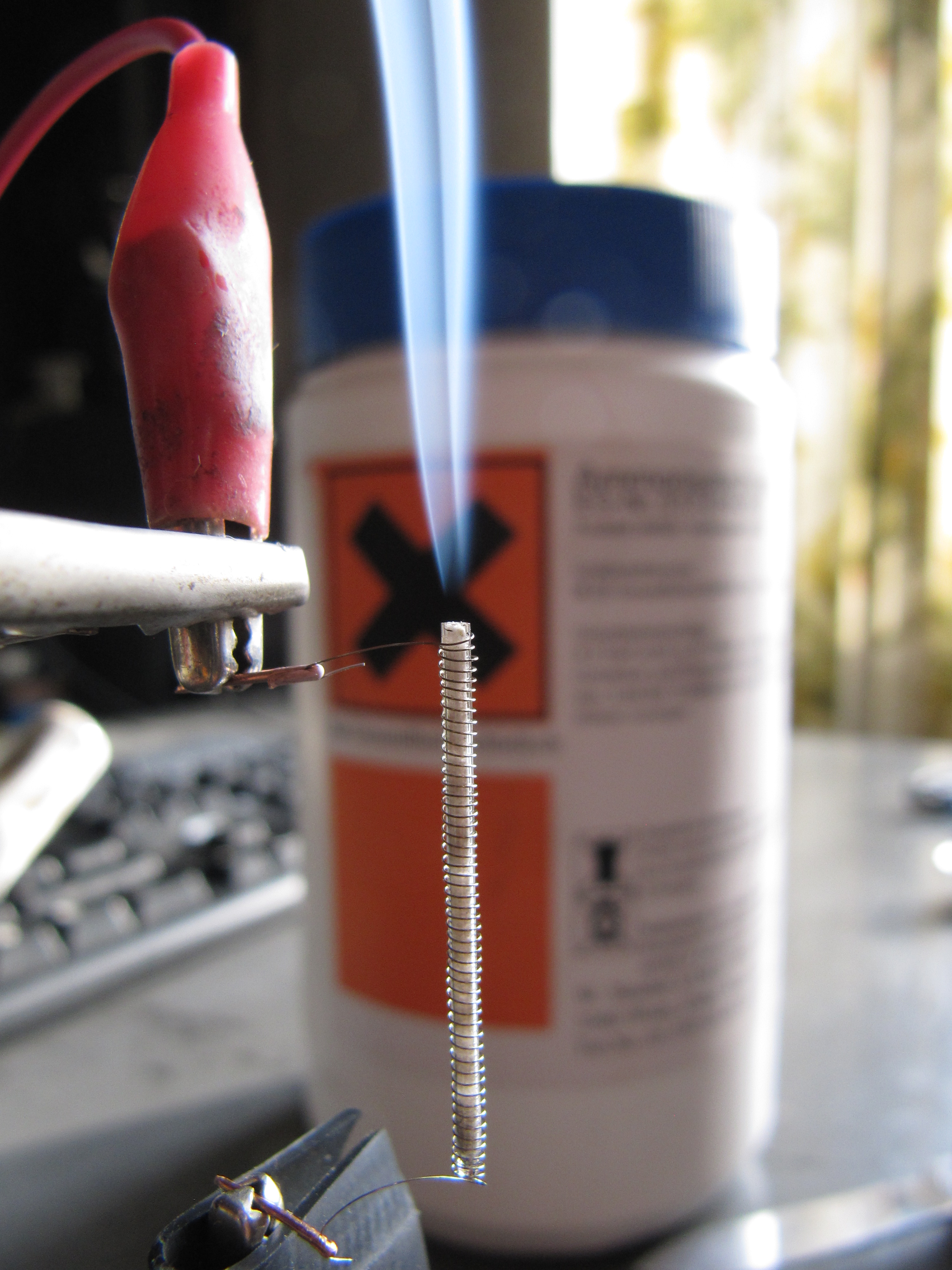
Sublimation is the Phase transition, transition of a substance directly from the solid to the gas state, without passing through the liquid state. The verb form of sublimation is ''sublime'', or less preferably, ''sublimate''. ''Sublimate'' also refers to the product obtained by sublimation. The point at which sublimation occurs rapidly (for further details, see #False correspondence with vaporization, below) is called critical sublimation point, or simply sublimation point. Notable examples include sublimation of dry ice at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, and that of solid iodine with heating. The reverse process of sublimation is deposition (phase transition), ''deposition'' (also called ''desublimation''), in which a substance passes directly from a gas to a solid phase, without passing through the liquid state. Technically, all solids may sublime, though most sublime at extremely low rates that are hardly detectable under usual conditions. At standard condi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is notoriously toxic. It occurs naturally in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. It has various Allotropes of arsenic, allotropes, but only the grey form, which has a metallic appearance, is important to industry. The primary use of arsenic is in alloys of lead (for example, in car batteries and ammunition). Arsenic is also a common n-type dopant in semiconductor electronic devices, and a component of the III–V compound semiconductor gallium arsenide. Arsenic and its compounds, especially the trioxide, are used in the production of pesticides, treated wood products, herbicides, and insecticides. These applications are declining with the increasing recognition of the persistent tox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonium Chloride
Ammonium chloride is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula , also written as . It is an ammonium salt of hydrogen chloride. It consists of ammonium cations and chloride anions . It is a white crystalline salt (chemistry), salt that is highly soluble in water. Solutions of ammonium chloride are mildly acidic. In its naturally occurring mineralogic form, it is known as salammoniac. The mineral is commonly formed on burning coal dumps from condensation of coal-derived gases. It is also found around some types of volcanic vents. It is mainly used as fertilizer and a flavouring agent in Salty liquorice, some types of liquorice. It is a product of the reaction of hydrochloric acid and ammonia. Production It is a product of the Solvay process used to produce sodium carbonate: :CO2 + 2 NH3 + 2 NaCl + H2O → 2 NH4Cl + Na2CO3 Not only is that method the principal one for the manufacture of ammonium chloride, but also it is used to minimize ammonia release in some ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Of Matter
In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and Plasma (physics), plasma. Different states are distinguished by the ways the component particles (atoms, molecules, ions and electrons) are arranged, and how they behave collectively. In a solid, the particles are tightly packed and held in fixed positions, giving the material a definite shape and volume. In a liquid, the particles remain close together but can move past one another, allowing the substance to maintain a fixed volume while adapting to the shape of its container. In a gas, the particles are far apart and move freely, allowing the substance to expand and fill both the shape and volume of its container. Plasma is similar to a gas, but it also contains charged particles (ions and free electrons) that move independently and respond to electric and magnetic fields. Beyond the classical states of matter, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Change
Physical changes are changes affecting the form of a chemical substance, but not its chemical composition. Physical changes are used to separate mixtures into their component compounds, but can not usually be used to separate compounds into chemical elements or simpler compounds.Zumdahl, Steven S. and Zumdahl, Susan A. (2000), ''Chemistry,'' Houghton Mifflin, 5th ed., p. 27 Physical changes occur when objects or substances undergo a change that does not change their chemical composition. This contrasts with the concept of chemical change in which the composition of a substance changes or one or more substances combine or break up to form new substances. In general a physical change is reversible using physical means. For example, salt dissolved in water can be recovered by allowing the water to evaporate. A physical change involves a change in physical properties. Examples of physical properties include melting, transition to a gas, change of strength, change of dura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boiling
Boiling or ebullition is the rapid phase transition from liquid to gas or vapor, vapour; the reverse of boiling is condensation. Boiling occurs when a liquid is heated to its boiling point, so that the vapour pressure of the liquid is equal to the pressure exerted on the liquid by the Standard atmosphere (unit), surrounding atmosphere. Boiling and evaporation are the two main forms of liquid vapourization. There are two main types of boiling: nucleate boiling, where small bubbles of vapour form at discrete points; and critical heat flux boiling, where the boiling surface is heated above a certain critical temperature and a film of vapour forms on the surface. Transition boiling is an intermediate, unstable form of boiling with elements of both types. The boiling point of water is 100 °C or 212 °F but is lower with the decreased atmospheric pressure found at higher altitudes. Boiling water is used as a method of making it potable by killing Microorganism, microbes an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaporization
Vaporization (or vapo(u)risation) of an element or compound is a phase transition from the liquid phase to vapor. There are two types of vaporization: evaporation and boiling. Evaporation is a surface phenomenon, whereas boiling is a bulk phenomenon (a phenomenon in which the whole object or substance is involved in the process). Evaporation Evaporation is a phase transition from the liquid phase to vapor (a state of substance below critical temperature) that occurs at temperatures below the boiling temperature at a given pressure. Evaporation occurs ''on the surface''. Evaporation only occurs when the partial pressure of vapor of a substance is less than the equilibrium vapor pressure. For example, due to constantly decreasing pressures, vapor pumped out of a solution will eventually leave behind a cryogenic liquid. Boiling Boiling is also a phase transition from the liquid phase to gas phase, but boiling is the formation of vapor as bubbles of vapor ''below the surface'' of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enthalpy Of Vaporization
In thermodynamics, the enthalpy of vaporization (symbol ), also known as the (latent) heat of vaporization or heat of evaporation, is the amount of energy (enthalpy) that must be added to a liquid substance to transform a quantity of that substance into a gas. The enthalpy of vaporization is a function of the pressure and temperature at which the transformation (vaporization or evaporation) takes place. The enthalpy of vaporization is often quoted for the normal boiling temperature of the substance. Although tabulated values are usually corrected to 298 K, that correction is often smaller than the uncertainty in the measured value. The heat of vaporization is temperature-dependent, though a constant heat of vaporization can be assumed for small temperature ranges and for reduced temperature . The heat of vaporization diminishes with increasing temperature and it vanishes completely at a certain point called the critical temperature (). Above the critical temperature, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enthalpy Of Fusion
In thermodynamics, the enthalpy of fusion of a substance, also known as (latent) heat of fusion, is the change in its enthalpy resulting from providing energy, typically heat, to a specific quantity of the substance to change its state from a solid to a liquid, at constant pressure. The enthalpy of fusion is the amount of energy required to convert one mole of solid into liquid. For example, when melting 1 kg of ice (at 0 °C under a wide range of pressures), 333.55 kJ of energy is absorbed with no temperature change. The heat of solidification (when a substance changes from liquid to solid) is equal and opposite. This energy includes the contribution required to make room for any associated change in volume by displacing its environment against ambient pressure. The temperature at which the phase transition occurs is the melting point or the freezing point, according to context. By convention, the pressure is assumed to be unless otherwise specified. Overview T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enthalpy Of Sublimation
In thermodynamics, the enthalpy of sublimation, or heat of sublimation, is the heat required to sublimate (change from solid to gas) one mole of a substance at a given combination of temperature and pressure, usually standard temperature and pressure (STP). It is equal to the cohesive energy of the solid. For elemental metals, it is also equal to the standard enthalpy of formation of the gaseous metal atoms. The heat of sublimation is usually expressed in kJ/mol, although the less customary kJ/kg is also encountered. Sublimation enthalpies See also * Heat * Sublimation (chemistry) * Phase transition In physics, chemistry, and other related fields like biology, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic Sta ... * Clausius-Clapeyron equation References {{DEFAULTSORT:Enthalpy Of Sublimation Enthalpy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endothermic
An endothermic process is a chemical or physical process that absorbs heat from its surroundings. In terms of thermodynamics, it is a thermodynamic process with an increase in the enthalpy (or internal energy ) of the system.Oxtoby, D. W; Gillis, H.P., Butler, L. J. (2015). ''iarchive:principlesofmode0000oxto, Principle of Modern Chemistry'', Brooks Cole. p. 617. In an endothermic process, the heat that a system absorbs is thermal energy transfer into the system. Thus, an endothermic reaction generally leads to an increase in the temperature of the system and a decrease in that of the surroundings. The term was coined by 19th-century French chemist Marcellin Berthelot. The term ''endothermic'' comes from the Greek language, Greek ἔνδον (''endon'') meaning 'within' and θερμ- (''therm'') meaning 'hot' or 'warm'. An endothermic process may be a chemical process, such as dissolving ammonium nitrate () in water (), or a physical process, such as the melting of ice cubes. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermolecular Force
An intermolecular force (IMF; also secondary force) is the force that mediates interaction between molecules, including the electromagnetic forces of attraction or repulsion which act between atoms and other types of neighbouring particles (e.g. atoms or ions). Intermolecular forces are weak relative to intramolecular forces – the forces which hold a molecule together. For example, the covalent bond, involving sharing electron pairs between atoms, is much stronger than the forces present between neighboring molecules. Both sets of forces are essential parts of force fields frequently used in molecular mechanics. The first reference to the nature of microscopic forces is found in Alexis Clairaut's work ''Théorie de la figure de la Terre,'' published in Paris in 1743. Other scientists who have contributed to the investigation of microscopic forces include: Laplace, Gauss, Maxwell, Boltzmann and Pauling. Attractive intermolecular forces are categorized into the following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |