Congested Lungs on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the
 Pneumonia is due to infections caused primarily by bacteria or viruses and less commonly by fungi and parasites. Although more than 100 strains of infectious agents have been identified, only a few are responsible for the majority of cases. Mixed infections with both viruses and bacteria may occur in roughly 45% of infections in children and 15% of infections in adults. A causative agent may not be isolated in about half of cases despite careful testing. In an active population-based surveillance for community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization in five hospitals in Chicago and Nashville from January 2010 through June 2012, 2259 patients were identified who had radiographic evidence of pneumonia and specimens that could be tested for the responsible pathogen. Most patients (62%) had no detectable pathogens in their sample, and unexpectedly, respiratory viruses were detected more frequently than bacteria. Specifically, 23% had one or more viruses, 11% had one or more bacteria, 3% had both bacterial and viral pathogens, and 1% had a fungal or mycobacterial infection. "The most common pathogens were
Pneumonia is due to infections caused primarily by bacteria or viruses and less commonly by fungi and parasites. Although more than 100 strains of infectious agents have been identified, only a few are responsible for the majority of cases. Mixed infections with both viruses and bacteria may occur in roughly 45% of infections in children and 15% of infections in adults. A causative agent may not be isolated in about half of cases despite careful testing. In an active population-based surveillance for community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization in five hospitals in Chicago and Nashville from January 2010 through June 2012, 2259 patients were identified who had radiographic evidence of pneumonia and specimens that could be tested for the responsible pathogen. Most patients (62%) had no detectable pathogens in their sample, and unexpectedly, respiratory viruses were detected more frequently than bacteria. Specifically, 23% had one or more viruses, 11% had one or more bacteria, 3% had both bacterial and viral pathogens, and 1% had a fungal or mycobacterial infection. "The most common pathogens were
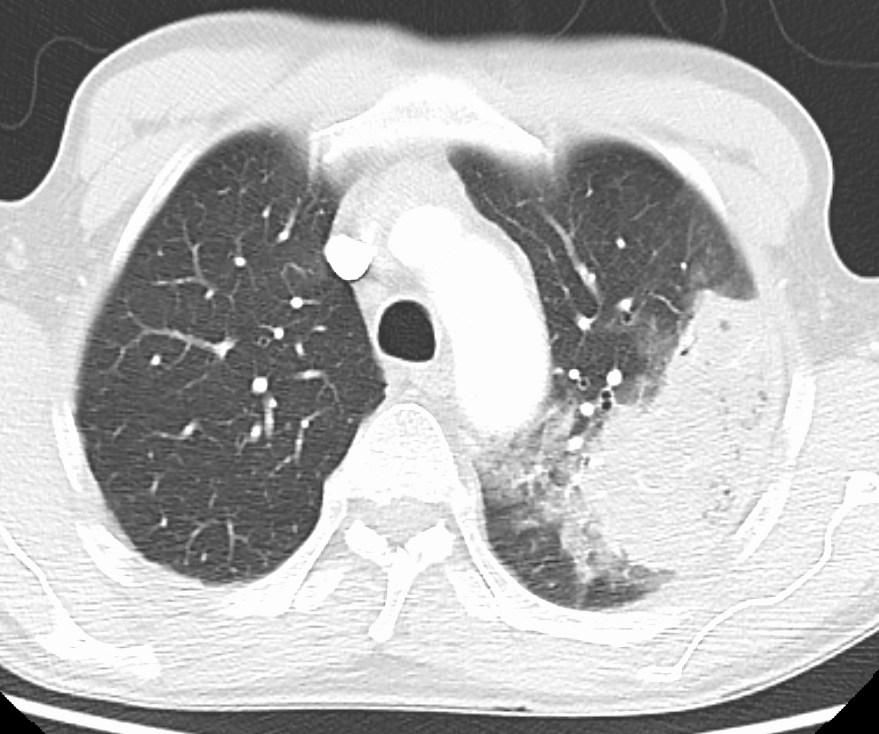 Bacteria are the most common cause of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), with '' Streptococcus pneumoniae'' isolated in nearly 50% of cases. Other commonly isolated bacteria include '' Haemophilus influenzae'' in 20%, '' Chlamydophila pneumoniae'' in 13%, and '' Mycoplasma pneumoniae'' in 3% of cases; ''
Bacteria are the most common cause of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), with '' Streptococcus pneumoniae'' isolated in nearly 50% of cases. Other commonly isolated bacteria include '' Haemophilus influenzae'' in 20%, '' Chlamydophila pneumoniae'' in 13%, and '' Mycoplasma pneumoniae'' in 3% of cases; ''
 In adults, viruses account for about one third of pneumonia cases, and in children for about 15% of them. Commonly implicated agents include rhinoviruses,
In adults, viruses account for about one third of pneumonia cases, and in children for about 15% of them. Commonly implicated agents include rhinoviruses,
 Pneumonia frequently starts as an upper respiratory tract infection that moves into the lower respiratory tract. It is a type of pneumonitis (lung inflammation). The normal flora of the upper airway give protection by competing with pathogens for nutrients. In the lower airways, reflexes of the glottis, actions of
Pneumonia frequently starts as an upper respiratory tract infection that moves into the lower respiratory tract. It is a type of pneumonitis (lung inflammation). The normal flora of the upper airway give protection by competing with pathogens for nutrients. In the lower airways, reflexes of the glottis, actions of

 A
A
File:UOTW 34 - Ultrasound of the Week 1.webm, Pneumonia seen by ultrasound
File:UOTW 34 - Ultrasound of the Week 2.webm, Pneumonia seen by ultrasound
File:UOTW 34 - Ultrasound of the Week 3.jpg, Pneumonia seen by ultrasound
File:RtPneuKidMark.png, Right middle lobe pneumonia in a child as seen on plain X-ray
 In pneumonia, a pleural effusion, collection of fluid may form in the pleural cavity, space that surrounds the lung. Occasionally, microorganisms will infect this fluid, causing an pleural empyema, empyema. To distinguish an empyema from the more common simple parapneumonic effusion, the fluid may be collected with a needle (thoracentesis), and examined. If this shows evidence of empyema, complete drainage of the fluid is necessary, often requiring a chest tube, drainage catheter. In severe cases of empyema, Decortication, surgery may be needed. If the infected fluid is not drained, the infection may persist, because antibiotics do not penetrate well into the pleural cavity. If the fluid is sterile, it must be drained only if it is causing symptoms or remains unresolved.
In rare circumstances, bacteria in the lung will form a pocket of infected fluid called a
In pneumonia, a pleural effusion, collection of fluid may form in the pleural cavity, space that surrounds the lung. Occasionally, microorganisms will infect this fluid, causing an pleural empyema, empyema. To distinguish an empyema from the more common simple parapneumonic effusion, the fluid may be collected with a needle (thoracentesis), and examined. If this shows evidence of empyema, complete drainage of the fluid is necessary, often requiring a chest tube, drainage catheter. In severe cases of empyema, Decortication, surgery may be needed. If the infected fluid is not drained, the infection may persist, because antibiotics do not penetrate well into the pleural cavity. If the fluid is sterile, it must be drained only if it is causing symptoms or remains unresolved.
In rare circumstances, bacteria in the lung will form a pocket of infected fluid called a

 Pneumonia is a common illness affecting approximately 450 million people a year and occurring in all parts of the world. It is a major cause of death among all age groups resulting in 4 million deaths (7% of the world's total death) yearly. Rates are greatest in children less than five, and adults older than 75 years. It occurs about five times more frequently in the developing world than in the developed world. Viral pneumonia accounts for about 200 million cases. In the United States, as of 2009, pneumonia is the 8th leading cause of death.
Pneumonia is a common illness affecting approximately 450 million people a year and occurring in all parts of the world. It is a major cause of death among all age groups resulting in 4 million deaths (7% of the world's total death) yearly. Rates are greatest in children less than five, and adults older than 75 years. It occurs about five times more frequently in the developing world than in the developed world. Viral pneumonia accounts for about 200 million cases. In the United States, as of 2009, pneumonia is the 8th leading cause of death.
 Pneumonia has been a common disease throughout human history. The word is from Greek πνεύμων (pneúmōn) meaning "lung". The symptoms were described by Hippocrates (–370 BC): "Peripneumonia, and pleuritic affections, are to be thus observed: If the fever be acute, and if there be pains on either side, or in both, and if expiration be if cough be present, and the sputa expectorated be of a blond or livid color, or likewise thin, frothy, and florid, or having any other character different from the common... When pneumonia is at its height, the case is beyond remedy if he is not purged, and it is bad if he has dyspnoea, and urine that is thin and acrid, and if sweats come out about the neck and head, for such sweats are bad, as proceeding from the suffocation, rales, and the violence of the disease which is obtaining the upper hand." However, Hippocrates referred to pneumonia as a disease "named by the ancients". He also reported the results of surgical drainage of empyemas. Maimonides (1135–1204 AD) observed: "The basic symptoms that occur in pneumonia and that are never lacking are as follows: acute fever, sticking pleuritic pain in the side, short rapid breaths, serrated pulse and cough."Maimonides, ''Fusul Musa'' ("''Pirkei Moshe''"). This clinical description is quite similar to those found in modern textbooks, and it reflected the extent of medical knowledge through the Middle Ages into the 19th century.
Edwin Klebs was the first to observe bacteria in the airways of persons having died of pneumonia in 1875. Initial work identifying the two common bacterial causes, ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' and ''Klebsiella pneumoniae'', was performed by Carl Friedländer and Albert Fraenkel (1848–1916), Albert Fraenkel in 1882 and 1884, respectively. Friedländer's initial work introduced the Gram staining, Gram stain, a fundamental laboratory test still used today to identify and categorize bacteria. Christian Gram's paper describing the procedure in 1884 helped to differentiate the two bacteria, and showed that pneumonia could be caused by more than one microorganism. In 1887, Jaccond demonstrated pneumonia may be caused by opportunistic bacteria always present in the lung.
Sir William Osler, known as "the father of modern medicine", appreciated the death and disability caused by pneumonia, describing it as the "captain of the men of death" in 1918, as it had overtaken tuberculosis as one of the leading causes of death in this time. This phrase was originally coined by John Bunyan in reference to "consumption" (tuberculosis). Osler also described pneumonia as "the old man's friend" as death was often quick and painless when there were much slower and more painful ways to die.
Viral pneumonia was first described by Hobart Reimann in 1938. Reimann, Chairman of the Department of Medicine at Thomas Jefferson University, Jefferson Medical College, had established the practice of routinely typing the pneumococcal organism in cases where pneumonia presented. Out of this work, the distinction between viral and bacterial strains was noticed.
Several developments in the 1900s improved the outcome for those with pneumonia. With the advent of penicillin and other antibiotics, modern surgical techniques, and intensive care in the 20th century, mortality from pneumonia, which had approached 30%, dropped precipitously in the developed world. Vaccination of infants against '' Haemophilus influenzae'' type B began in 1988 and led to a dramatic decline in cases shortly thereafter. Vaccination against ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' in adults began in 1977, and in children in 2000, resulting in a similar decline.
Pneumonia has been a common disease throughout human history. The word is from Greek πνεύμων (pneúmōn) meaning "lung". The symptoms were described by Hippocrates (–370 BC): "Peripneumonia, and pleuritic affections, are to be thus observed: If the fever be acute, and if there be pains on either side, or in both, and if expiration be if cough be present, and the sputa expectorated be of a blond or livid color, or likewise thin, frothy, and florid, or having any other character different from the common... When pneumonia is at its height, the case is beyond remedy if he is not purged, and it is bad if he has dyspnoea, and urine that is thin and acrid, and if sweats come out about the neck and head, for such sweats are bad, as proceeding from the suffocation, rales, and the violence of the disease which is obtaining the upper hand." However, Hippocrates referred to pneumonia as a disease "named by the ancients". He also reported the results of surgical drainage of empyemas. Maimonides (1135–1204 AD) observed: "The basic symptoms that occur in pneumonia and that are never lacking are as follows: acute fever, sticking pleuritic pain in the side, short rapid breaths, serrated pulse and cough."Maimonides, ''Fusul Musa'' ("''Pirkei Moshe''"). This clinical description is quite similar to those found in modern textbooks, and it reflected the extent of medical knowledge through the Middle Ages into the 19th century.
Edwin Klebs was the first to observe bacteria in the airways of persons having died of pneumonia in 1875. Initial work identifying the two common bacterial causes, ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' and ''Klebsiella pneumoniae'', was performed by Carl Friedländer and Albert Fraenkel (1848–1916), Albert Fraenkel in 1882 and 1884, respectively. Friedländer's initial work introduced the Gram staining, Gram stain, a fundamental laboratory test still used today to identify and categorize bacteria. Christian Gram's paper describing the procedure in 1884 helped to differentiate the two bacteria, and showed that pneumonia could be caused by more than one microorganism. In 1887, Jaccond demonstrated pneumonia may be caused by opportunistic bacteria always present in the lung.
Sir William Osler, known as "the father of modern medicine", appreciated the death and disability caused by pneumonia, describing it as the "captain of the men of death" in 1918, as it had overtaken tuberculosis as one of the leading causes of death in this time. This phrase was originally coined by John Bunyan in reference to "consumption" (tuberculosis). Osler also described pneumonia as "the old man's friend" as death was often quick and painless when there were much slower and more painful ways to die.
Viral pneumonia was first described by Hobart Reimann in 1938. Reimann, Chairman of the Department of Medicine at Thomas Jefferson University, Jefferson Medical College, had established the practice of routinely typing the pneumococcal organism in cases where pneumonia presented. Out of this work, the distinction between viral and bacterial strains was noticed.
Several developments in the 1900s improved the outcome for those with pneumonia. With the advent of penicillin and other antibiotics, modern surgical techniques, and intensive care in the 20th century, mortality from pneumonia, which had approached 30%, dropped precipitously in the developed world. Vaccination of infants against '' Haemophilus influenzae'' type B began in 1988 and led to a dramatic decline in cases shortly thereafter. Vaccination against ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' in adults began in 1977, and in children in 2000, resulting in a similar decline.
lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of t ...
primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli Alveolus (; pl. alveoli, adj. alveolar) is a general anatomical term for a concave cavity or pit.
Uses in anatomy and zoology
* Pulmonary alveolus, an air sac in the lungs
** Alveolar cell or pneumocyte
** Alveolar duct
** Alveolar macrophage
* ...
. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain
Chest pain is pain or discomfort in the chest, typically the front of the chest. It may be described as sharp, dull, pressure, heaviness or squeezing. Associated symptoms may include pain in the shoulder, arm, upper abdomen, or jaw, along with n ...
, fever, and difficulty breathing
Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing disc ...
. The severity of the condition is variable.
Pneumonia is usually caused by infection with viruses or bacteria, and less commonly by other microorganisms. Identifying the responsible pathogen can be difficult. Diagnosis is often based on symptoms and physical examination. Chest X-ray
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in med ...
s, blood tests, and culture of the sputum
Sputum is mucus that is coughed up from the lower airways (the trachea and bronchi). In medicine, sputum samples are usually used for a naked eye examination, microbiological investigation of respiratory infections and cytological investigations ...
may help confirm the diagnosis. The disease may be classified by where it was acquired, such as community- or hospital-acquired or healthcare-associated pneumonia.
Risk factors for pneumonia include cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. O ...
, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), sickle cell disease, asthma, diabetes, heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, a ...
, a history of smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is burned and the resulting smoke is typically breathed in to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, which have bee ...
, a poor ability to cough (such as following a stroke
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functionin ...
), and a weak immune system.
Vaccines to prevent certain types of pneumonia (such as those caused by '' Streptococcus pneumoniae'' bacteria, linked to influenza
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptoms ...
, or linked to COVID-19) are available. Other methods of prevention include hand washing to prevent infection, not smoking, and social distancing.
Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Pneumonia believed to be due to bacteria is treated with antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of ...
s. If the pneumonia is severe, the affected person is generally hospitalized. Oxygen therapy
Oxygen therapy, also known as supplemental oxygen, is the use of oxygen as medical treatment. Acute indications for therapy include hypoxemia (low blood oxygen levels), carbon monoxide toxicity and cluster headache. It may also be prophylactica ...
may be used if oxygen levels are low.
Each year, pneumonia affects about 450 million people globally (7% of the population) and results in about 4 million deaths. With the introduction of antibiotics and vaccines in the 20th century, survival has greatly improved. Nevertheless, pneumonia remains a leading cause of death
The following is a list of the causes of human deaths worldwide for different years arranged by their associated mortality rates. In 2002, there were about 57 million deaths. In 2005, according to the World Health Organization (WHO) using the I ...
in developing countries, and also among the very old, the very young, and the chronically ill. Pneumonia often shortens the period of suffering among those already close to death and has thus been called "the old man's friend".
Signs and symptoms
People with infectious pneumonia often have a productive cough, fever accompanied by shaking chills, shortness of breath, sharp or stabbingchest pain
Chest pain is pain or discomfort in the chest, typically the front of the chest. It may be described as sharp, dull, pressure, heaviness or squeezing. Associated symptoms may include pain in the shoulder, arm, upper abdomen, or jaw, along with n ...
during deep breaths, and an increased rate of breathing. In elderly people, confusion may be the most prominent sign.
The typical signs and symptoms in children under five are fever, cough, and fast or difficult breathing. Fever is not very specific, as it occurs in many other common illnesses and may be absent in those with severe disease, malnutrition or in the elderly. In addition, a cough is frequently absent in children less than 2 months old. More severe signs and symptoms in children may include blue-tinged skin, unwillingness to drink, convulsions, ongoing vomiting, extremes of temperature, or a decreased level of consciousness.
Bacterial and viral cases of pneumonia usually result in similar symptoms. Some causes are associated with classic, but non-specific, clinical characteristics. Pneumonia caused by '' Legionella'' may occur with abdominal pain, diarrhea, or confusion. Pneumonia caused by '' Streptococcus pneumoniae'' is associated with rusty colored sputum. Pneumonia caused by '' Klebsiella'' may have bloody sputum often described as "currant jelly". Bloody sputum (known as hemoptysis) may also occur with tuberculosis, Gram-negative pneumonia, lung abscess
Lung abscess is a type of liquefactive necrosis of the lung tissue and formation of cavities (more than 2 cm) containing necrotic debris or fluid caused by microbial infection.
This pus-filled cavity is often caused by aspiration, which may ...
es and more commonly acute bronchitis
Acute bronchitis, also known as a chest cold, is short-term bronchitis – inflammation of the bronchi (large and medium-sized airways) of the lungs. The most common symptom is a cough. Other symptoms include coughing up mucus, wheezing, shortne ...
. Pneumonia caused by '' Mycoplasma pneumoniae'' may occur in association with swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck, joint pain, or a middle ear infection
Otitis media is a group of inflammatory diseases of the middle ear. One of the two main types is acute otitis media (AOM), an infection of rapid onset that usually presents with ear pain. In young children this may result in pulling at the ear, ...
. Viral pneumonia presents more commonly with wheezing than bacterial pneumonia. Pneumonia was historically divided into "typical" and "atypical" based on the belief that the presentation predicted the underlying cause. However, evidence has not supported this distinction, therefore it is no longer emphasized.
Cause
 Pneumonia is due to infections caused primarily by bacteria or viruses and less commonly by fungi and parasites. Although more than 100 strains of infectious agents have been identified, only a few are responsible for the majority of cases. Mixed infections with both viruses and bacteria may occur in roughly 45% of infections in children and 15% of infections in adults. A causative agent may not be isolated in about half of cases despite careful testing. In an active population-based surveillance for community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization in five hospitals in Chicago and Nashville from January 2010 through June 2012, 2259 patients were identified who had radiographic evidence of pneumonia and specimens that could be tested for the responsible pathogen. Most patients (62%) had no detectable pathogens in their sample, and unexpectedly, respiratory viruses were detected more frequently than bacteria. Specifically, 23% had one or more viruses, 11% had one or more bacteria, 3% had both bacterial and viral pathogens, and 1% had a fungal or mycobacterial infection. "The most common pathogens were
Pneumonia is due to infections caused primarily by bacteria or viruses and less commonly by fungi and parasites. Although more than 100 strains of infectious agents have been identified, only a few are responsible for the majority of cases. Mixed infections with both viruses and bacteria may occur in roughly 45% of infections in children and 15% of infections in adults. A causative agent may not be isolated in about half of cases despite careful testing. In an active population-based surveillance for community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization in five hospitals in Chicago and Nashville from January 2010 through June 2012, 2259 patients were identified who had radiographic evidence of pneumonia and specimens that could be tested for the responsible pathogen. Most patients (62%) had no detectable pathogens in their sample, and unexpectedly, respiratory viruses were detected more frequently than bacteria. Specifically, 23% had one or more viruses, 11% had one or more bacteria, 3% had both bacterial and viral pathogens, and 1% had a fungal or mycobacterial infection. "The most common pathogens were human rhinovirus
The rhinovirus (from the grc, ῥίς, rhis "nose", , romanized: "of the nose", and the la, vīrus) is the most common viral infectious agent in humans and is the predominant cause of the common cold. Rhinovirus infection proliferates in tem ...
(in 9% of patients), influenza virus (in 6%), and ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' (in 5%)."
The term ''pneumonia'' is sometimes more broadly applied to any condition resulting in inflammation of the lungs (caused for example by autoimmune disease
An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a functioning body part. At least 80 types of autoimmune diseases have been identified, with some evidence suggesting that there may be more than 100 types. Nearly a ...
s, chemical burns or drug reactions); however, this inflammation is more accurately referred to as pneumonitis.
Factors that predispose to pneumonia include smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is burned and the resulting smoke is typically breathed in to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, which have bee ...
, immunodeficiency
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromisation, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that a ...
, alcoholism, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, sickle cell disease (SCD), asthma, chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of kidney disease in which a gradual loss of kidney function occurs over a period of months to years. Initially generally no symptoms are seen, but later symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vo ...
, liver disease, and biological aging
Senescence () or biological aging is the gradual deterioration of functional characteristics in living organisms. The word ''senescence'' can refer to either cellular senescence or to senescence of the whole organism. Organismal senescence inv ...
. Additional risks in children include not being breastfed, exposure to cigarette smoke and other air pollution, malnutrition, and poverty. The use of acid-suppressing medications – such as proton-pump inhibitors or H2 blockers – is associated with an increased risk of pneumonia. Approximately 10% of people who require mechanical ventilation develop ventilator-associated pneumonia
Ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) is a type of lung infection that occurs in people who are on mechanical ventilation breathing machines in hospitals. As such, VAP typically affects critically ill persons that are in an intensive care unit (I ...
, and people with a gastric feeding tube
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach is ...
have an increased risk of developing aspiration pneumonia. For people with certain variants of the FER gene, the risk of death is reduced in sepsis caused by pneumonia. However, for those with TLR6 variants, the risk of getting Legionnaires' disease
Legionnaires' disease is a form of atypical pneumonia caused by any species of ''Legionella'' bacteria, quite often '' Legionella pneumophila''. Signs and symptoms include cough, shortness of breath, high fever, muscle pains, and headaches. Naus ...
is increased.
Bacteria
 Bacteria are the most common cause of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), with '' Streptococcus pneumoniae'' isolated in nearly 50% of cases. Other commonly isolated bacteria include '' Haemophilus influenzae'' in 20%, '' Chlamydophila pneumoniae'' in 13%, and '' Mycoplasma pneumoniae'' in 3% of cases; ''
Bacteria are the most common cause of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), with '' Streptococcus pneumoniae'' isolated in nearly 50% of cases. Other commonly isolated bacteria include '' Haemophilus influenzae'' in 20%, '' Chlamydophila pneumoniae'' in 13%, and '' Mycoplasma pneumoniae'' in 3% of cases; ''Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive ...
''; '' Moraxella catarrhalis''; and ''Legionella pneumophila
''Legionella pneumophila'' is a thin, aerobic, pleomorphic, flagellated, non-spore-forming, Gram-negative bacterium of the genus ''Legionella''. ''L. pneumophila'' is the primary human pathogenic bacterium in this group and is the causative age ...
''. A number of drug-resistant
Drug resistance is the reduction in effectiveness of a medication such as an antimicrobial or an antineoplastic in treating a disease or condition. The term is used in the context of resistance that pathogens or cancers have "acquired", that is, ...
versions of the above infections are becoming more common, including drug-resistant ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' (DRSP) and methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA).
The spreading of organisms is facilitated by certain risk factors. Alcoholism is associated with ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', anaerobic organism
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require molecular oxygen for growth. It may react negatively or even die if free oxygen is present. In contrast, an aerobic organism (aerobe) is an organism that requires an oxygenate ...
s, and ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''; smoking facilitates the effects of ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', ''Haemophilus influenzae'', ''Moraxella catarrhalis'', and ''Legionella pneumophila''. Exposure to birds is associated with '' Chlamydia psittaci''; farm animals with ''Coxiella burnetti
''Coxiella burnetii'' is an obligate intracellular bacterial pathogen, and is the causative agent of Q fever. The genus ''Coxiella'' is morphologically similar to ''Rickettsia'', but with a variety of genetic and physiological differences. ''C. ...
''; aspiration of stomach contents with anaerobic organisms; and cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. O ...
with '' Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' and ''Staphylococcus aureus''. ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' is more common in the winter, and it should be suspected in persons aspirating a large number of anaerobic organisms.
Viruses
 In adults, viruses account for about one third of pneumonia cases, and in children for about 15% of them. Commonly implicated agents include rhinoviruses,
In adults, viruses account for about one third of pneumonia cases, and in children for about 15% of them. Commonly implicated agents include rhinoviruses, coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the com ...
es, influenza virus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), adenovirus
Adenoviruses (members of the family ''Adenoviridae'') are medium-sized (90–100 nm), nonenveloped (without an outer lipid bilayer) viruses with an icosahedral nucleocapsid containing a double-stranded DNA genome. Their name derives from the ...
, and parainfluenza. Herpes simplex virus
Herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2), also known by their taxonomical names ''Human alphaherpesvirus 1'' and '' Human alphaherpesvirus 2'', are two members of the human ''Herpesviridae'' family, a set of viruses that produce viral inf ...
rarely causes pneumonia, except in groups such as newborns, persons with cancer, transplant recipients, and people with significant burns. After organ transplantation or in otherwise immunocompromised persons, there are high rates of cytomegalovirus
''Cytomegalovirus'' (''CMV'') (from ''cyto-'' 'cell' via Greek - 'container' + 'big, megalo-' + -''virus'' via Latin 'poison') is a genus of viruses in the order ''Herpesvirales'', in the family ''Herpesviridae'', in the subfamily ''Betaherpe ...
pneumonia. Those with viral infections may be secondarily infected with the bacteria ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', ''Staphylococcus aureus'', or ''Haemophilus influenzae'', particularly when other health problems are present. Different viruses predominate at different times of the year; during flu season, for example, influenza may account for more than half of all viral cases. Outbreaks of other viruses also occur occasionally, including hantaviruses and coronaviruses. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019), the respiratory illness responsible for the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had a No ...
(SARS-CoV-2) can also result in pneumonia.
Fungi
Fungal pneumonia is uncommon, but occurs more commonly in individuals with weakened immune systems due toAIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual m ...
, immunosuppressive drug
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent activity of the immune system.
Classification
Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified into ...
s, or other medical problems. It is most often caused by '' Histoplasma capsulatum'', ''Blastomyces
''Chrysosporium'' is a genus of hyaline hyphomycetes fungi in the family Onygenaceae.
''Chrysosporium'' colonies are moderately fast-growing, flat, white to tan to beige in color; they often have a powdery or granular surface texture. Hyaline, o ...
'', '' Cryptococcus neoformans'', '' Pneumocystis jiroveci'' (pneumocystis pneumonia
''Pneumocystis'' pneumonia (PCP), also known as ''Pneumocystis jirovecii'' pneumonia (PJP), is a form of pneumonia that is caused by the yeast-like fungus ''Pneumocystis jirovecii''.
''Pneumocystis'' specimens are commonly found in the lungs of ...
, or PCP), and '' Coccidioides immitis''. Histoplasmosis is most common in the Mississippi River basin, and coccidioidomycosis is most common in the Southwestern United States
The Southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest or simply the Southwest, is a geographic and cultural region of the United States that generally includes Arizona, New Mexico, and adjacent portions of California, Colorado, Ne ...
. The number of cases of fungal pneumonia has been increasing in the latter half of the 20th century due to increasing travel and rates of immunosuppression in the population. For people infected with HIV/AIDS, PCP is a common opportunistic infection
An opportunistic infection is an infection caused by pathogens (bacteria, fungi, parasites or viruses) that take advantage of an opportunity not normally available. These opportunities can stem from a variety of sources, such as a weakened immune ...
.
Parasites
A variety of parasites can affect the lungs, including '' Toxoplasma gondii'', ''Strongyloides stercoralis
''Strongyloides stercoralis'' is a human pathogenic parasitism, parasitic nematode, roundworm causing the disease strongyloidiasis. Its common name in the US is threadworm. In the UK and Australia, however, the term ''threadworm'' can also refe ...
'', '' Ascaris lumbricoides'', and '' Plasmodium malariae''.Murray and Nadel (2010). Chapter 37. These organisms typically enter the body through direct contact with the skin, ingestion, or via an insect vector. Except for ''Paragonimus westermani
''Paragonimus westermani'' (Japanese lung fluke or oriental lung fluke) is the most common species of lung fluke that infects humans, causing paragonimiasis. Human infections are most common in eastern Asia and in South America. Paragonimiasis m ...
'', most parasites do not specifically affect the lungs but involve the lungs secondarily to other sites. Some parasites, in particular those belonging to the ''Ascaris'' and ''Strongyloides'' genera, stimulate a strong eosinophilic reaction, which may result in eosinophilic pneumonia. In other infections, such as malaria, lung involvement is due primarily to cytokine-induced systemic inflammation
Chronic systemic inflammation (SI) is the result of release of pro-inflammatory cytokines from immune-related cells and the chronic activation of the innate immune system. It can contribute to the development or progression of certain conditions s ...
. In the developed world, these infections are most common in people returning from travel or in immigrants. Around the world, parasitic pneumonia is most common in the immunodeficient.
Noninfectious
Idiopathic interstitial pneumonia or noninfectious pneumonia is a class of diffuse lung diseases. They includediffuse alveolar damage
Diffuse alveolar damage (DAD) is a histologic term used to describe specific changes that occur to the structure of the lungs during injury or disease. Most often DAD is described in association with the early stages of acute respiratory distress s ...
, organizing pneumonia, nonspecific interstitial pneumonia
Non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) is a form of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia.
Symptoms
Symptoms include cough, difficulty breathing, and fatigue.
Causes
It has been suggested that idiopathic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia ha ...
, lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia, desquamative interstitial pneumonia, respiratory bronchiolitis interstitial lung disease, and usual interstitial pneumonia
Usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) is a form of lung disease characterized by progressive scarring of both lungs. The scarring (fibrosis) involves the pulmonary interstitium (the supporting framework of the lung). UIP is thus classified as a for ...
. Lipoid pneumonia
Lipoid pneumonia is a specific form of lung inflammation (pneumonia) that develops when lipids enter the bronchial tree. The disorder is sometimes called cholesterol pneumonia in cases where that lipid is a factor.
Signs and symptoms
The pneumon ...
is another rare cause due to lipids entering the lung. These lipids can either be inhaled or spread to the lungs from elsewhere in the body.
Mechanisms
 Pneumonia frequently starts as an upper respiratory tract infection that moves into the lower respiratory tract. It is a type of pneumonitis (lung inflammation). The normal flora of the upper airway give protection by competing with pathogens for nutrients. In the lower airways, reflexes of the glottis, actions of
Pneumonia frequently starts as an upper respiratory tract infection that moves into the lower respiratory tract. It is a type of pneumonitis (lung inflammation). The normal flora of the upper airway give protection by competing with pathogens for nutrients. In the lower airways, reflexes of the glottis, actions of complement protein
The complement system, also known as complement cascade, is a part of the immune system that enhances (complements) the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells from an organism, promote inflammation, and at ...
s and immunoglobulin
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the ...
s are important for protection. Micro aspiration of contaminated secretions can infect the lower airways and cause pneumonia. The progress of pneumonia is determined by the virulence of the organism; the amount of organism required to start an infection; and the body's immune response against the infection.
Bacterial
Most bacteria enter the lungs via small aspirations of organisms residing in the throat or nose. Half of normal people have these small aspirations during sleep. While the throat always contains bacteria, potentially infectious ones reside there only at certain times and under certain conditions. A minority of types of bacteria such as ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis
''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (M. tb) is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis. First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch, ''M. tuberculosis'' has an unusual, waxy coating on its c ...
'' and ''Legionella pneumophila
''Legionella pneumophila'' is a thin, aerobic, pleomorphic, flagellated, non-spore-forming, Gram-negative bacterium of the genus ''Legionella''. ''L. pneumophila'' is the primary human pathogenic bacterium in this group and is the causative age ...
'' reach the lungs via contaminated airborne droplets. Bacteria can also spread via the blood. Once in the lungs, bacteria may invade the spaces between cells and between alveoli, where the macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cel ...
s and neutrophils (defensive white blood cell
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cell (biology), cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and de ...
s) attempt to inactivate the bacteria. The neutrophils also release cytokines, causing a general activation of the immune system. This leads to the fever, chills, and fatigue common in bacterial pneumonia. The neutrophils, bacteria, and fluid from surrounding blood vessels fill the alveoli, resulting in the consolidation seen on chest X-ray.
Viral
Viruses may reach the lung by a number of different routes. Respiratory syncytial virus is typically contracted when people touch contaminated objects and then touch their eyes or nose.Murray and Nadel (2010). Chapter 31. Other viral infections occur when contaminated airborne droplets are inhaled through the nose or mouth. Once in the upper airway, the viruses may make their way into the lungs, where they invade the cells lining the airways, alveoli, orlung parenchyma
Parenchyma () is the bulk of functional substance in an animal organ or structure such as a tumour. In zoology it is the name for the tissue that fills the interior of flatworms.
Etymology
The term ''parenchyma'' is New Latin from the word π ...
. Some viruses such as measles and herpes simplex may reach the lungs via the blood. The invasion of the lungs may lead to varying degrees of cell death. When the immune system responds to the infection, even more lung damage may occur. Primarily white blood cell
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cell (biology), cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and de ...
s, mainly mononuclear cell
In immunology, agranulocytes (also known as nongranulocytes or mononuclear leukocytes) are one of the two types of leukocytes (white blood cells), the other type being granulocytes. Agranular cells are noted by the absence of Granule (cell biol ...
s, generate the inflammation. As well as damaging the lungs, many viruses simultaneously affect other organs and thus disrupt other body functions. Viruses also make the body more susceptible to bacterial infections; in this way, bacterial pneumonia can occur at the same time as viral pneumonia.
Diagnosis
Pneumonia is typically diagnosed based on a combination of physical signs and often achest X-ray
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in med ...
. In adults with normal vital signs and a normal lung examination, the diagnosis is unlikely. However, the underlying cause can be difficult to confirm, as there is no definitive test able to distinguish between bacterial and non-bacterial cause. The overall impression of a physician appears to be at least as good as decision rules for making or excluding the diagnosis.
Diagnosis in children
The World Health Organization has defined pneumonia in children clinically based on either a cough or difficulty breathing and a rapid respiratory rate, chest indrawing, or a decreased level of consciousness. A rapid respiratory rate is defined as greater than 60 breaths per minute in children under 2 months old, greater than 50 breaths per minute in children 2 months to 1 year old, or greater than 40 breaths per minute in children 1 to 5 years old. In children, low oxygen levels and lower chest indrawing are more sensitive than hearing chest crackles with astethoscope
The stethoscope is a medical device for auscultation, or listening to internal sounds of an animal or human body. It typically has a small disc-shaped resonator that is placed against the skin, and one or two tubes connected to two earpieces. ...
or increased respiratory rate. Grunting and nasal flaring may be other useful signs in children less than five years old.
Lack of wheezing is an indicator of '' Mycoplasma pneumoniae'' in children with pneumonia, but as an indicator it is not accurate enough to decide whether or not macrolide treatment should be used. The presence of chest pain in children with pneumonia doubles the probability of ''Mycoplasma pneumoniae''.
Diagnosis in adults
In general, in adults, investigations are not needed in mild cases. There is a very low risk of pneumonia if all vital signs andauscultation
Auscultation (based on the Latin verb ''auscultare'' "to listen") is listening to the internal sounds of the body, usually using a stethoscope. Auscultation is performed for the purposes of examining the circulatory and respiratory systems (hea ...
are normal. C-reactive protein (CRP) may help support the diagnosis. For those with CRP less than 20 mg/L without convincing evidence of pneumonia, antibiotics are not recommended.
Procalcitonin
Procalcitonin (PCT) is a peptide precursor of the hormone calcitonin, the latter being involved with calcium homeostasis. It arises once preprocalcitonin is cleaved by endopeptidase. It was first identified by Leonard J. Deftos and Bernard A. Roos ...
may help determine the cause and support decisions about who should receive antibiotics. Antibiotics are encouraged if the procalcitonin level reaches 0.25 μg/L, strongly encouraged if it reaches 0.5 μg/L, and strongly discouraged if the level is below 0.10 μg/L. In people requiring hospitalization, pulse oximetry, chest radiography
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in med ...
and blood test
A blood test is a laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose test or a cholester ...
s – including a complete blood count, serum electrolytes, C-reactive protein level, and possibly liver function tests
Liver function tests (LFTs or LFs), also referred to as a hepatic panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. These tests include prothrombin time (PT/INR), activated partial thromboplastin ti ...
– are recommended.
The diagnosis of influenza-like illness
Influenza-like illness (ILI), also known as flu-like syndrome or flu-like symptoms, is a medical diagnosis of possible influenza or other illness causing a set of common symptoms. These include fever, shivering, chills, malaise, dry cough, lo ...
can be made based on the signs and symptoms; however, confirmation of an influenza infection requires testing. Thus, treatment is frequently based on the presence of influenza in the community or a rapid influenza test.
Physical exam
Physical examination may sometimes reveal low blood pressure, high heart rate, or low oxygen saturation. The respiratory rate may be faster than normal, and this may occur a day or two before other signs. Examination of the chest may be normal, but it may show decreased expansion on the affected side. Harsh breath sounds from the larger airways that are transmitted through the inflamed lung are termedbronchial
A bronchus is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi pronounced (BRAN-KAI) to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. ...
breathing and are heard on auscultation with a stethoscope
The stethoscope is a medical device for auscultation, or listening to internal sounds of an animal or human body. It typically has a small disc-shaped resonator that is placed against the skin, and one or two tubes connected to two earpieces. ...
. Crackles (rales) may be heard over the affected area during inspiration
Inspiration, inspire, or inspired often refers to:
* Artistic inspiration, sudden creativity in artistic production
* Biblical inspiration, the doctrine in Judeo-Christian theology concerned with the divine origin of the Bible
* Creative inspirat ...
. Percussion may be dulled over the affected lung, and increased, rather than decreased, vocal resonance distinguishes pneumonia from a pleural effusion.
Imaging

 A
A chest radiograph
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in med ...
is frequently used in diagnosis. In people with mild disease, imaging is needed only in those with potential complications, those not having improved with treatment, or those in which the cause is uncertain. If a person is sufficiently sick to require hospitalization, a chest radiograph is recommended. Findings do not always match the severity of disease and do not reliably separate between bacterial and viral infection.
X-ray presentations of pneumonia may be classified as lobar pneumonia, bronchopneumonia, lobular pneumonia, and interstitial pneumonia
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD), is a group of respiratory diseases affecting the interstitium (the tissue and space around the alveoli (air sacs)) of the lungs. It concerns alveolar epithelium, pulmona ...
. Bacterial, community-acquired pneumonia classically show lung consolidation
A pulmonary consolidation is a region of normally compressible lung tissue that has filled with liquid instead of air. The condition is marked by induration (swelling or hardening of normally soft tissue) of a normally aerated lung. It is conside ...
of one lung segmental lobe, which is known as lobar pneumonia. However, findings may vary, and other patterns are common in other types of pneumonia. Aspiration pneumonia may present with bilateral opacities primarily in the bases of the lungs and on the right side. Radiographs of viral pneumonia may appear normal, appear hyper-inflated, have bilateral patchy areas, or present similar to bacterial pneumonia with lobar consolidation. Radiologic findings may not be present in the early stages of the disease, especially in the presence of dehydration, or may be difficult to interpret in the obese or those with a history of lung disease. Complications such as pleural effusion may also be found on chest radiographs. Laterolateral chest radiographs can increase the diagnostic accuracy of lung consolidation and pleural effusion.
A CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
can give additional information in indeterminate cases. CT scans can also provide more details in those with an unclear chest radiograph (for example occult
The occult, in the broadest sense, is a category of esoteric supernatural beliefs and practices which generally fall outside the scope of religion and science, encompassing phenomena involving otherworldly agency, such as magic and mysticism a ...
pneumonia in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) and can exclude pulmonary embolism and fungal pneumonia and detect lung abscess
Lung abscess is a type of liquefactive necrosis of the lung tissue and formation of cavities (more than 2 cm) containing necrotic debris or fluid caused by microbial infection.
This pus-filled cavity is often caused by aspiration, which may ...
in those who are not responding to treatments. However, CT scans are more expensive, have a higher dose of radiation, and cannot be done at bedside.
Lung ultrasound
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly imaging techniques) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, muscles ...
may also be useful in helping to make the diagnosis. Ultrasound is radiation free and can be done at bedside. However, ultrasound requires specific skills to operate the machine and interpret the findings. It may be more accurate than chest X-ray.
Microbiology
In people managed in the community, determining the causative agent is not cost-effective and typically does not alter management. For people who do not respond to treatment, sputum culture should be considered, and culture for ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis
''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (M. tb) is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis. First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch, ''M. tuberculosis'' has an unusual, waxy coating on its c ...
'' should be carried out in persons with a chronic productive cough. Microbiological evaluation is also indicated in severe pneumonia, alcoholism, asplenia, immunosuppression, HIV infection, and those being empirically treated for MRSA of pseudomonas. Although positive blood culture and pleural fluid culture definitively establish the diagnosis of the type of micro-organism involved, a positive sputum culture has to be interpreted with care for the possibility of colonisation of respiratory tract. Testing for other specific organisms may be recommended during outbreaks, for public health reasons. In those hospitalized for severe disease, both sputum and blood cultures are recommended, as well as testing the urine for antigens to ''Legionella'' and ''Streptococcus''. Viral infections, can be confirmed via detection of either the virus or its antigens with culture or polymerase chain reaction (PCR), among other techniques. ''Mycoplasma'', ''Legionella'', ''Streptococcus'', and ''Chlamydia'' can also be detected using PCR techniques on bronchoalveolar lavage
Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) (also known as bronchoalveolar washing) is a diagnostic method of the lower respiratory system in which a bronchoscope is passed through the mouth or nose into an appropriate airway in the lungs, with a measured amoun ...
and nasopharyngeal swab. The causative agent is determined in only 15% of cases with routine microbiological tests.
Classification
Pneumonitis refers to lung inflammation; pneumonia refers to pneumonitis, usually due to infection but sometimes non-infectious, that has the additional feature of pulmonary consolidation. Pneumonia is most commonly classified by where or how it was acquired: community-acquired, aspiration, healthcare-associated, hospital-acquired, andventilator-associated pneumonia
Ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) is a type of lung infection that occurs in people who are on mechanical ventilation breathing machines in hospitals. As such, VAP typically affects critically ill persons that are in an intensive care unit (I ...
. It may also be classified by the area of the lung affected: lobar pneumonia, bronchial pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severity of ...
and acute interstitial pneumonia
Acute interstitial pneumonitis is a rare, severe lung disease that usually affects otherwise healthy individuals. There is no known cause or cure.
Acute interstitial pneumonitis is often categorized as both an interstitial lung disease and a form ...
; or by the causative organism. Pneumonia in children may additionally be classified based on signs and symptoms as non-severe, severe, or very severe.
The setting in which pneumonia develops is important to treatment, as it correlates to which pathogens are likely suspects, which mechanisms are likely, which antibiotics are likely to work or fail, and which complications can be expected based on the person's health status.
Community
Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is acquired in the community, outside of health care facilities. Compared with healthcare-associated pneumonia, it is less likely to involvemultidrug-resistant
Multiple drug resistance (MDR), multidrug resistance or multiresistance is antimicrobial resistance shown by a species of microorganism to at least one antimicrobial drug in three or more antimicrobial categories. Antimicrobial categories are c ...
bacteria. Although the latter are no longer rare in CAP, they are still less likely.
Healthcare
Health care–associated pneumonia (HCAP) is an infection associated with recent exposure to thehealth care
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health profe ...
system, including hospitals, outpatient clinics, nursing homes, dialysis Dialysis may refer to:
*Dialysis (chemistry), a process of separating molecules in solution
**Electrodialysis, used to transport salt ions from one solution to another through an ion-exchange membrane under the influence of an applied electric pote ...
centers, chemotherapy treatment, or home care Homecare (also spelled as home care) is health care or supportive care provided by a professional caregiver in the individual home where the patient or client is living, as opposed to care provided in group accommodations like clinics or nursing ho ...
. HCAP is sometimes called MCAP (medical care–associated pneumonia).
People may become infected with pneumonia in a hospital; this is defined as pneumonia not present at the time of admission (symptoms must start at least 48 hours after admission). It is likely to involve hospital-acquired infections, with higher risk of multidrug-resistant
Multiple drug resistance (MDR), multidrug resistance or multiresistance is antimicrobial resistance shown by a species of microorganism to at least one antimicrobial drug in three or more antimicrobial categories. Antimicrobial categories are c ...
pathogens. People in a hospital often have other medical conditions, which may make them more susceptible to pathogens in the hospital.
Ventilator-associated pneumonia
Ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) is a type of lung infection that occurs in people who are on mechanical ventilation breathing machines in hospitals. As such, VAP typically affects critically ill persons that are in an intensive care unit (I ...
occurs in people breathing with the help of mechanical ventilation. Ventilator-associated pneumonia is specifically defined as pneumonia that arises more than 48 to 72 hours after endotracheal intubation.
Differential diagnosis
Several diseases can present with similar signs and symptoms to pneumonia, such as: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, pulmonary edema,bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis is a disease in which there is permanent enlargement of parts of the bronchi, airways of the lung. Symptoms typically include a chronic cough with sputum, mucus production. Other symptoms include shortness of breath, hemoptysis, co ...
, lung cancer, and pulmonary emboli
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include shortness of breath, chest pain particularly upon breathing ...
. Unlike pneumonia, asthma and COPD typically present with wheezing, pulmonary edema presents with an abnormal electrocardiogram, cancer and bronchiectasis present with a cough of longer duration, and pulmonary emboli present with acute onset sharp chest pain and shortness of breath. Mild pneumonia should be differentiated from upper respiratory tract infection (URTI). Severe pneumonia should be differentiated from acute heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, a ...
. Pulmonary infiltrates that resolved after giving mechanical ventilation should point to heart failure and atelectasis rather than pneumonia. For recurrent pneumonia, underlying lung cancer, metastasis, tuberculosis, a foreign bodies, immunosuppression, and hypersensitivity should be suspected.
Prevention
Prevention includes vaccination, environmental measures, and appropriate treatment of other health problems. It is believed that, if appropriate preventive measures were instituted globally, mortality among children could be reduced by 400,000; and, if proper treatment were universally available, childhood deaths could be decreased by another 600,000.Vaccination
Vaccination prevents against certain bacterial and viral pneumonias both in children and adults. Influenza vaccines are modestly effective at preventing symptoms of influenza, The Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends yearly influenza vaccination for every person 6 months and older. Immunizing health care workers decreases the risk of viral pneumonia among their patients. Vaccinations against '' Haemophilus influenzae'' and '' Streptococcus pneumoniae'' have good evidence to support their use. There is strong evidence for vaccinating children under the age of 2 against ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' (pneumococcal conjugate vaccine). Vaccinating children against ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' has led to a decreased rate of these infections in adults, because many adults acquire infections from children. A Pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine, ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' vaccine is available for adults, and has been found to decrease the risk of invasive pneumococcal disease by 74%, but there is insufficient evidence to suggest using the pneumococcal vaccine to prevent pneumonia or death in the general adult population. The CDC recommends that young children and adults over the age of 65 receive the pneumococcal vaccine, as well as older children or younger adults who have an increased risk of getting pneumococcal disease. The pneumococcal vaccine has been shown to reduce the risk of community acquired pneumonia in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, but does not reduce mortality or the risk of hospitalization for people with this condition. People with COPD are recommended by a number of guidelines to have a pneumococcal vaccination. Other vaccines for which there is support for a protective effect against pneumonia include Pertussis vaccine, pertussis, varicella vaccine, varicella, and Measles vaccine, measles.Medications
When influenza outbreaks occur, medications such as amantadine or rimantadine may help prevent the condition, but they are associated with side effects. Zanamivir or oseltamivir decrease the chance that people who are exposed to the virus will develop symptoms; however, it is recommended that potential side effects are taken into account.Other
Smoking cessation and reducing indoor air quality, indoor air pollution, such as that from cooking indoors with wood, crop residues or feces, dung, are both recommended. Smoking appears to be the single biggest risk factor for pneumococcal pneumonia in otherwise-healthy adults. Hand hygiene and coughing into one's sleeve may also be effective preventative measures. Wearing surgical masks by the sick may also prevent illness. Appropriately treating underlying illnesses (such as HIV/AIDS, diabetes mellitus, and malnutrition) can decrease the risk of pneumonia. In children less than 6 months of age, exclusive breast feeding reduces both the risk and severity of disease. In people with HIV/AIDS and a CD4 count of less than 200 cells/uL the antibiotic trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole decreases the risk of ''Pneumocystis pneumonia'' and is also useful for prevention in those that are immunocompromised but do not have HIV. Testing pregnant women for Group B Streptococcus and ''Chlamydia trachomatis'', and administeringantibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of ...
treatment, if needed, reduces rates of pneumonia in infants; preventive measures for HIV transmission from mother to child may also be efficient. Suctioning the mouth and throat of infants with meconium-stained amniotic fluid has not been found to reduce the rate of aspiration pneumonia and may cause potential harm, thus this practice is not recommended in the majority of situations. In the frail elderly good oral health care may lower the risk of aspiration pneumonia, even though there is no good evidence that one approach to mouth care is better than others in preventing nursing home acquired pneumonia. Zinc supplementation in children 2 months to five years old appears to reduce rates of pneumonia.
For people with low levels of vitamin C in their diet or blood, taking vitamin C supplements may be suggested to decrease the risk of pneumonia, although there is no strong evidence of benefit. There is insufficient evidence to recommend that the general population take vitamin C to prevent or treat pneumonia.
For adults and children in the hospital who require a respirator, there is no strong evidence indicating a difference between heat and moisture exchangers and Humidifier, heated humidifiers for preventing pneumonia. There is tentative evidence that laying flat on the back compared to semi-raised increases pneumonia risks in people who are intubated.
Management
Antibiotics by mouth, rest, simple analgesics, and fluids usually suffice for complete resolution. However, those with other medical conditions, the elderly, or those with significant trouble breathing may require more advanced care. If the symptoms worsen, the pneumonia does not improve with home treatment, or complications occur, hospitalization may be required. Worldwide, approximately 7–13% of cases in children result in hospitalization, whereas in the developed world between 22 and 42% of adults with community-acquired pneumonia are admitted. The CURB-65 score is useful for determining the need for admission in adults. If the score is 0 or 1, people can typically be managed at home; if it is 2, a short hospital stay or close follow-up is needed; if it is 3–5, hospitalization is recommended. In children those with Dyspnea, respiratory distress or oxygen saturations of less than 90% should be hospitalized. The utility of chest physiotherapy in pneumonia has not yet been determined. Over-the-counter cough medicine has not been found to be effective, nor has the use of zinc supplementation, zinc in children. There is insufficient evidence for mucolytics. There is no strong evidence to recommend that children who have non-measles related pneumonia take vitamin A supplements. Vitamin D, as of 2018 is of unclear benefit in children. Pneumonia can cause severe illness in a number of ways, and pneumonia with evidence of organ dysfunction may require intensive care unit admission for observation and specific treatment. The main impact is on the respiratory and the circulatory system. Respiratory failure not responding to normal oxygen therapy may require heated humidified high-flow therapy delivered through nasal cannulae, non-invasive ventilation, or in severe cases Mechanical ventilation, invasive ventilation through an endotracheal tube. Regarding circulatory problems as part of sepsis, evidence of poor blood flow or low blood pressure is initially treated with 30 mL/kg of crystalloid solution, crystalloid infused intravenously. In situations where fluids alone are ineffective, Antihypotensive agent, vasopressor medication may be required. For adults with moderate or severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) undergoing mechanical ventilation, there is a reduction in mortality when people proning, lie on their front for at least 12 hours a day. However, this increases the risk of endotracheal tube obstruction and pressure sores.Bacterial
Antibiotics improve outcomes in those with bacterial pneumonia. The first dose of antibiotics should be given as soon as possible. Increased use of antibiotics, however, may lead to the development of Antimicrobial resistance, antimicrobial resistant strains of bacteria. Antibiotic choice depends initially on the characteristics of the person affected, such as age, underlying health, and the location the infection was acquired. Antibiotic use is also associated with side effects such as nausea, diarrhea, dizziness, taste distortion, or headaches. In the UK, Empiric therapy, treatment before culture results with amoxicillin is recommended as the first line for community-acquired pneumonia, with doxycycline or clarithromycin as alternatives. In North America, amoxicillin, doxycycline, and in some areas a macrolide (such as azithromycin or erythromycin) is the first-line outpatient treatment in adults. In children with mild or moderate symptoms, amoxicillin taken by mouth is the first line. The use of fluoroquinolones in uncomplicated cases is discouraged due to concerns about side-effects and generating resistance in light of there being no greater benefit. For those who require hospitalization and caught their pneumonia in the community the use of a β-lactam such as cephazolin plus macrolide such as azithromycin is recommended. A fluoroquinolone may replace azithromycin but is less preferred. Antibiotics by mouth and by injection appear to be similarly effective in children with severe pneumonia. The duration of treatment has traditionally been seven to ten days, but increasing evidence suggests that shorter courses (3–5 days) may be effective for certain types of pneumonia and may reduce the risk of antibiotic resistance. Research in children showed that a shorter, 3-day course of amoxicillin was as effective as a longer, 7-day course for treating pneumonia in this population. For pneumonia that is associated with a ventilator caused by non-fermenting Gram-negative bacilli (NF-GNB), a shorter course of antibiotics increases the risk that the pneumonia will return. Recommendations for hospital-acquired pneumonia include third- and fourth-generation cephalosporins, carbapenems, fluoroquinolones, aminoglycosides, and vancomycin. These antibiotics are often given intravenous therapy, intravenously and used in combination. In those treated in hospital, more than 90% improve with the initial antibiotics. For people with ventilator-acquired pneumonia, the choice of antibiotic therapy will depend on the person's risk of being infected with a strain of bacteria that is Multi-drug resistant bacteria, multi-drug resistant. Once clinically stable, intravenous antibiotics should be switched to oral antibiotics. For those with ''Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) or ''Legionella'' infections, prolonged antibiotics may be beneficial. The addition of corticosteroids to standard antibiotic treatment appears to improve outcomes, reducing death and morbidity for adults with severe community acquired pneumonia, and reducing death for adults and children with non-severe community acquired pneumonia. A 2017 review therefore recommended them in adults with severe community acquired pneumonia. A 2019 guideline however recommended against their general use, unless refractory shock was present. Side effects associated with the use of corticosteroids include high blood sugar. There is some evidence that adding corticosteroids to the standard PCP pneumonia treatment may be beneficial for people who are infected with HIV. The use of granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) along with antibiotics does not appear to reduce mortality and routine use for treating pneumonia is not supported by evidence.Viral
Neuraminidase inhibitors may be used to treat viral pneumonia caused by influenza viruses (influenza A and influenza B). No specific antiviral drug, antiviral medications are recommended for other types of community acquired viral pneumonias including SARS, SARS coronavirus,adenovirus
Adenoviruses (members of the family ''Adenoviridae'') are medium-sized (90–100 nm), nonenveloped (without an outer lipid bilayer) viruses with an icosahedral nucleocapsid containing a double-stranded DNA genome. Their name derives from the ...
, hantavirus, and parainfluenza virus. Influenza A may be treated with rimantadine or amantadine, while influenza A or B may be treated with oseltamivir, zanamivir or peramivir. These are of most benefit if they are started within 48 hours of the onset of symptoms. Many strains of H5N1 influenza A, also known as avian influenza or "bird flu", have shown resistance to rimantadine and amantadine. The use of antibiotics in viral pneumonia is recommended by some experts, as it is impossible to rule out a complicating bacterial infection. The British Thoracic Society recommends that antibiotics be withheld in those with mild disease. The use of corticosteroids is controversial.
Aspiration
In general, Chemical pneumonitis, aspiration pneumonitis is treated conservatively with antibiotics indicated only for aspiration pneumonia. The choice of antibiotic will depend on several factors, including the suspected causative organism and whether pneumonia was acquired in the community or developed in a hospital setting. Common options include clindamycin, a combination of a beta-lactam antibiotic and metronidazole, or an aminoglycoside. Corticosteroids are sometimes used in aspiration pneumonia, but there is limited evidence to support their effectiveness.Follow-up
The British Thoracic Society recommends that a follow-up chest radiograph be taken in people with persistent symptoms, smokers, and people older than 50. American guidelines vary, from generally recommending a follow-up chest radiograph to not mentioning any follow-up.Prognosis
With treatment, most types of bacterial pneumonia will stabilize in 3–6 days. It often takes a few weeks before most symptoms resolve. X-ray findings typically clear within four weeks and mortality is low (less than 1%). In the elderly or people with other lung problems, recovery may take more than 12 weeks. In persons requiring hospitalization, mortality may be as high as 10%, and in those requiring intensive care it may reach 30–50%. Pneumonia is the most common nosocomial infection, hospital-acquired infection that causes death.Murray and Nadel (2010). Chapter 32. Before the advent of antibiotics, mortality was typically 30% in those that were hospitalized. However, for those whose lung condition deteriorates within 72 hours, the problem is usually due to sepsis. If pneumonia deteriorates after 72 hours, it could be due to nosocomial infection or excerbation of other underlying comorbidities. About 10% of those discharged from hospital are readmitted due to underlying co-morbidities such as heart, lung, or neurological disorders, or due to new onset of pneumonia. Complications may occur in particular in the elderly and those with underlying health problems. This may include, among others: empyema,lung abscess
Lung abscess is a type of liquefactive necrosis of the lung tissue and formation of cavities (more than 2 cm) containing necrotic debris or fluid caused by microbial infection.
This pus-filled cavity is often caused by aspiration, which may ...
, bronchiolitis obliterans, acute respiratory distress syndrome, sepsis, and worsening of underlying health problems.Cunha (2010). pp. 6–18.
Clinical prediction rules
Clinical prediction rules have been developed to more objectively predict outcomes of pneumonia. These rules are often used to decide whether to hospitalize the person. * Pneumonia severity index (or ''PSI Score'') * CURB-65 score, which takes into account the severity of symptoms, any underlying diseases, and agePleural effusion, empyema, and abscess
 In pneumonia, a pleural effusion, collection of fluid may form in the pleural cavity, space that surrounds the lung. Occasionally, microorganisms will infect this fluid, causing an pleural empyema, empyema. To distinguish an empyema from the more common simple parapneumonic effusion, the fluid may be collected with a needle (thoracentesis), and examined. If this shows evidence of empyema, complete drainage of the fluid is necessary, often requiring a chest tube, drainage catheter. In severe cases of empyema, Decortication, surgery may be needed. If the infected fluid is not drained, the infection may persist, because antibiotics do not penetrate well into the pleural cavity. If the fluid is sterile, it must be drained only if it is causing symptoms or remains unresolved.
In rare circumstances, bacteria in the lung will form a pocket of infected fluid called a
In pneumonia, a pleural effusion, collection of fluid may form in the pleural cavity, space that surrounds the lung. Occasionally, microorganisms will infect this fluid, causing an pleural empyema, empyema. To distinguish an empyema from the more common simple parapneumonic effusion, the fluid may be collected with a needle (thoracentesis), and examined. If this shows evidence of empyema, complete drainage of the fluid is necessary, often requiring a chest tube, drainage catheter. In severe cases of empyema, Decortication, surgery may be needed. If the infected fluid is not drained, the infection may persist, because antibiotics do not penetrate well into the pleural cavity. If the fluid is sterile, it must be drained only if it is causing symptoms or remains unresolved.
In rare circumstances, bacteria in the lung will form a pocket of infected fluid called a lung abscess
Lung abscess is a type of liquefactive necrosis of the lung tissue and formation of cavities (more than 2 cm) containing necrotic debris or fluid caused by microbial infection.
This pus-filled cavity is often caused by aspiration, which may ...
. Lung abscesses can usually be seen with a chest X-ray but frequently require a chest CT scan to confirm the diagnosis. Abscesses typically occur in aspiration pneumonia, and often contain several types of bacteria. Long-term antibiotics are usually adequate to treat a lung abscess, but sometimes the abscess must be drained by a surgery, surgeon or Interventional radiology, radiologist.
Respiratory and circulatory failure
Pneumonia can cause respiratory failure by triggering acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), which results from a combination of infection and inflammatory response. The lungs quickly fill with fluid and become stiff. This stiffness, combined with severe difficulties extracting oxygen due to the alveolar fluid, may require long periods of mechanical ventilation for survival. Other causes of circulatory failure are hypoxemia, inflammation, and increased coagulability. Sepsis is a potential complication of pneumonia but usually occurs in people with poor immunity or hyposplenism. The organisms most commonly involved are ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', ''Haemophilus influenzae'', and ''Klebsiella pneumoniae''. Other causes of the symptoms should be considered such as a myocardial infarction or a pulmonary embolism.Cunha (2010). pp. 250–51.Epidemiology
Children
In 2008, pneumonia occurred in approximately 156 million children (151 million in the developing world and 5 million in the developed world). In 2010, it resulted in 1.3 million deaths, or 18% of all deaths in those under five years, of which 95% occurred in the developing world. Countries with the greatest burden of disease include India (43 million), China (21 million) and Pakistan (10 million). It is the leading cause of death among children in low income countries. Many of these deaths occur in the neonatal, newborn period. The World Health Organization estimates that one in three newborn infant deaths is due to pneumonia. Approximately half of these deaths can be prevented, as they are caused by the bacteria for which an effective vaccine is available. In 2011, pneumonia was the most common reason for admission to the hospital after an emergency department visit in the U.S. for infants and children.History
 Pneumonia has been a common disease throughout human history. The word is from Greek πνεύμων (pneúmōn) meaning "lung". The symptoms were described by Hippocrates (–370 BC): "Peripneumonia, and pleuritic affections, are to be thus observed: If the fever be acute, and if there be pains on either side, or in both, and if expiration be if cough be present, and the sputa expectorated be of a blond or livid color, or likewise thin, frothy, and florid, or having any other character different from the common... When pneumonia is at its height, the case is beyond remedy if he is not purged, and it is bad if he has dyspnoea, and urine that is thin and acrid, and if sweats come out about the neck and head, for such sweats are bad, as proceeding from the suffocation, rales, and the violence of the disease which is obtaining the upper hand." However, Hippocrates referred to pneumonia as a disease "named by the ancients". He also reported the results of surgical drainage of empyemas. Maimonides (1135–1204 AD) observed: "The basic symptoms that occur in pneumonia and that are never lacking are as follows: acute fever, sticking pleuritic pain in the side, short rapid breaths, serrated pulse and cough."Maimonides, ''Fusul Musa'' ("''Pirkei Moshe''"). This clinical description is quite similar to those found in modern textbooks, and it reflected the extent of medical knowledge through the Middle Ages into the 19th century.
Edwin Klebs was the first to observe bacteria in the airways of persons having died of pneumonia in 1875. Initial work identifying the two common bacterial causes, ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' and ''Klebsiella pneumoniae'', was performed by Carl Friedländer and Albert Fraenkel (1848–1916), Albert Fraenkel in 1882 and 1884, respectively. Friedländer's initial work introduced the Gram staining, Gram stain, a fundamental laboratory test still used today to identify and categorize bacteria. Christian Gram's paper describing the procedure in 1884 helped to differentiate the two bacteria, and showed that pneumonia could be caused by more than one microorganism. In 1887, Jaccond demonstrated pneumonia may be caused by opportunistic bacteria always present in the lung.
Sir William Osler, known as "the father of modern medicine", appreciated the death and disability caused by pneumonia, describing it as the "captain of the men of death" in 1918, as it had overtaken tuberculosis as one of the leading causes of death in this time. This phrase was originally coined by John Bunyan in reference to "consumption" (tuberculosis). Osler also described pneumonia as "the old man's friend" as death was often quick and painless when there were much slower and more painful ways to die.
Viral pneumonia was first described by Hobart Reimann in 1938. Reimann, Chairman of the Department of Medicine at Thomas Jefferson University, Jefferson Medical College, had established the practice of routinely typing the pneumococcal organism in cases where pneumonia presented. Out of this work, the distinction between viral and bacterial strains was noticed.
Several developments in the 1900s improved the outcome for those with pneumonia. With the advent of penicillin and other antibiotics, modern surgical techniques, and intensive care in the 20th century, mortality from pneumonia, which had approached 30%, dropped precipitously in the developed world. Vaccination of infants against '' Haemophilus influenzae'' type B began in 1988 and led to a dramatic decline in cases shortly thereafter. Vaccination against ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' in adults began in 1977, and in children in 2000, resulting in a similar decline.
Pneumonia has been a common disease throughout human history. The word is from Greek πνεύμων (pneúmōn) meaning "lung". The symptoms were described by Hippocrates (–370 BC): "Peripneumonia, and pleuritic affections, are to be thus observed: If the fever be acute, and if there be pains on either side, or in both, and if expiration be if cough be present, and the sputa expectorated be of a blond or livid color, or likewise thin, frothy, and florid, or having any other character different from the common... When pneumonia is at its height, the case is beyond remedy if he is not purged, and it is bad if he has dyspnoea, and urine that is thin and acrid, and if sweats come out about the neck and head, for such sweats are bad, as proceeding from the suffocation, rales, and the violence of the disease which is obtaining the upper hand." However, Hippocrates referred to pneumonia as a disease "named by the ancients". He also reported the results of surgical drainage of empyemas. Maimonides (1135–1204 AD) observed: "The basic symptoms that occur in pneumonia and that are never lacking are as follows: acute fever, sticking pleuritic pain in the side, short rapid breaths, serrated pulse and cough."Maimonides, ''Fusul Musa'' ("''Pirkei Moshe''"). This clinical description is quite similar to those found in modern textbooks, and it reflected the extent of medical knowledge through the Middle Ages into the 19th century.
Edwin Klebs was the first to observe bacteria in the airways of persons having died of pneumonia in 1875. Initial work identifying the two common bacterial causes, ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' and ''Klebsiella pneumoniae'', was performed by Carl Friedländer and Albert Fraenkel (1848–1916), Albert Fraenkel in 1882 and 1884, respectively. Friedländer's initial work introduced the Gram staining, Gram stain, a fundamental laboratory test still used today to identify and categorize bacteria. Christian Gram's paper describing the procedure in 1884 helped to differentiate the two bacteria, and showed that pneumonia could be caused by more than one microorganism. In 1887, Jaccond demonstrated pneumonia may be caused by opportunistic bacteria always present in the lung.
Sir William Osler, known as "the father of modern medicine", appreciated the death and disability caused by pneumonia, describing it as the "captain of the men of death" in 1918, as it had overtaken tuberculosis as one of the leading causes of death in this time. This phrase was originally coined by John Bunyan in reference to "consumption" (tuberculosis). Osler also described pneumonia as "the old man's friend" as death was often quick and painless when there were much slower and more painful ways to die.
Viral pneumonia was first described by Hobart Reimann in 1938. Reimann, Chairman of the Department of Medicine at Thomas Jefferson University, Jefferson Medical College, had established the practice of routinely typing the pneumococcal organism in cases where pneumonia presented. Out of this work, the distinction between viral and bacterial strains was noticed.
Several developments in the 1900s improved the outcome for those with pneumonia. With the advent of penicillin and other antibiotics, modern surgical techniques, and intensive care in the 20th century, mortality from pneumonia, which had approached 30%, dropped precipitously in the developed world. Vaccination of infants against '' Haemophilus influenzae'' type B began in 1988 and led to a dramatic decline in cases shortly thereafter. Vaccination against ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' in adults began in 1977, and in children in 2000, resulting in a similar decline.
Society and culture
Awareness
Due to the relatively low awareness of the disease, 12 November was declared as the annual World Pneumonia Day, a day for concerned citizens and policy makers to take action against the disease, in 2009.Costs
The global economic cost of community-acquired pneumonia has been estimated at $17 billion annually. Other estimates are considerably higher. In 2012 the estimated aggregate costs of treating pneumonia in the United States were $20 billion; the median cost of a single pneumonia-related hospitalization is over $15,000. According to data released by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, average 2012 hospital charges for inpatient treatment of uncomplicated pneumonia in the U.S. were $24,549 and ranged as high as $124,000. The average cost of an emergency room consult for pneumonia was $943 and the average cost for medication was $66. Aggregate annual costs of treating pneumonia in Europe have been estimated at €10 billion.References
Footnotes CitationsBibliography
* *External links
{{Authority control Pneumonia, Articles containing video clips Coronavirus-associated diseases Infectious diseases Respiratory and cardiovascular disorders specific to the perinatal period Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate (full) Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate