Cervical Mucus Plug on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A cervical mucus plug (operculum) is a plug that fills and seals the
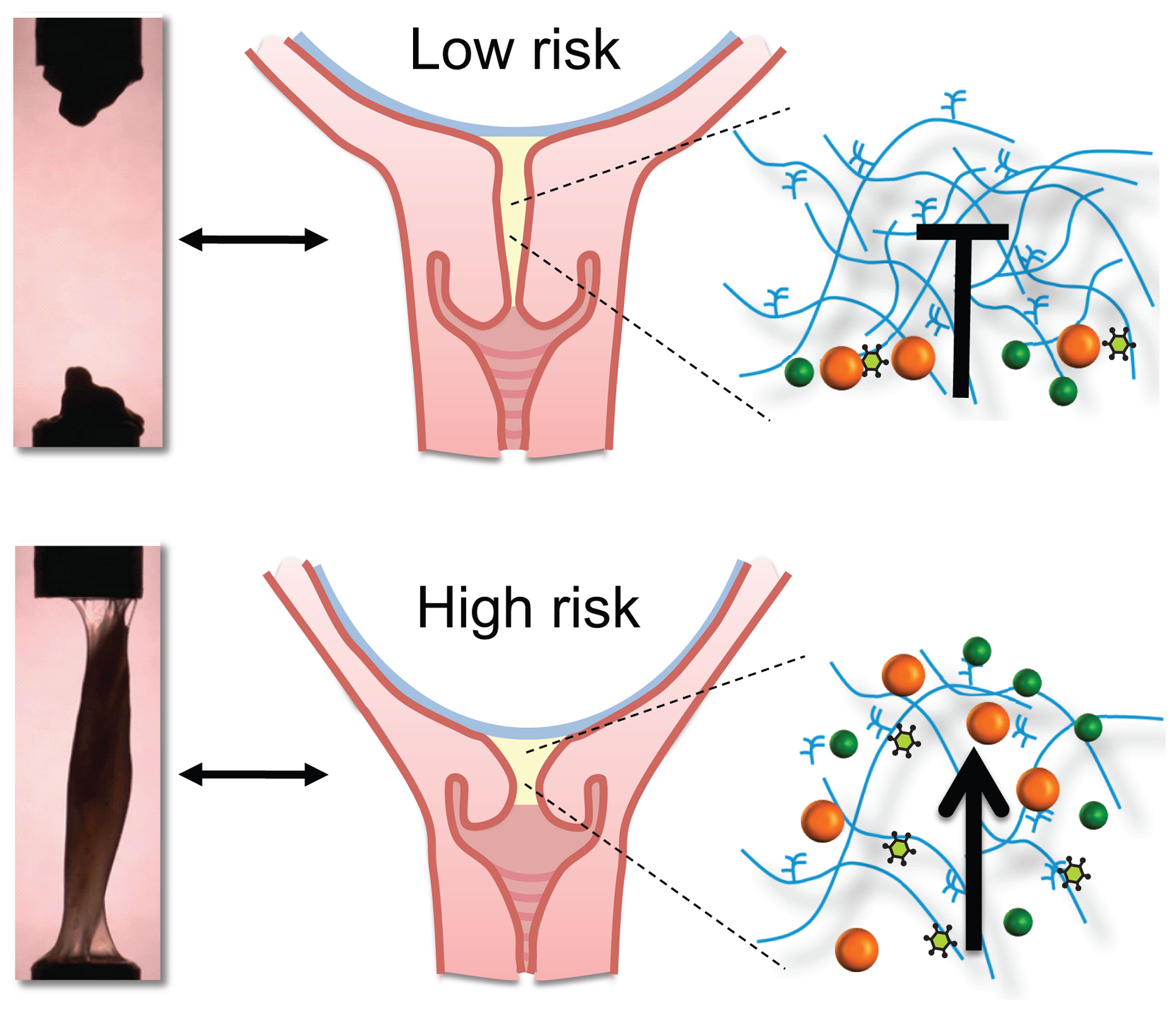 A common complication in pregnancy is preterm birth, as mentioned before. Preterm birth is birth prior to 37 weeks of gestation. In individuals with a higher risk for preterm birth, the CMP is found to be more translucent, extensible, and permeable compared to those at low risk for preterm birth. These individuals also may display shorter cervix which can result in increased risk of
A common complication in pregnancy is preterm birth, as mentioned before. Preterm birth is birth prior to 37 weeks of gestation. In individuals with a higher risk for preterm birth, the CMP is found to be more translucent, extensible, and permeable compared to those at low risk for preterm birth. These individuals also may display shorter cervix which can result in increased risk of
cervical canal
The cervical canal is the spindle-shaped, flattened canal of the cervix which connects the vagina to the main cavity of the uterus in most mammals.
Anatomy
The cervical canal communicates with the uterine cavity via the internal orifice of the ...
during pregnancy. It is formed by a small amount of cervical mucus
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both Serous fluid, serous and muc ...
that condenses to form a cervical mucus plug during pregnancy.
The cervical mucus plug (CMP) acts as a protective barrier by deterring the passage of bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
into the uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', : uteri or uteruses) or womb () is the hollow organ, organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic development, embryonic and prenatal development, f ...
, and contains a variety of antimicrobial agents, including immunoglobulin
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as pathogenic bacteria, bacteria and viruses, includin ...
s, and similar antimicrobial peptides
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), also called host defence peptides (HDPs) are part of the innate immune response found among all classes of life. Fundamental differences exist between Prokaryote, prokaryotic and eukaryota, eukaryotic cells that may ...
to those found in nasal mucus
The nasal mucosa lines the nasal cavity. It is part of the respiratory mucosa, the mucous membrane lining the respiratory tract. The nasal mucosa is intimately adherent to the periosteum or perichondrium of the nasal conchae. It is continuous w ...
.The CMP inhibits the migration of vaginal bacteria towards the uterus, protecting against opportunistic infections that can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease and the onset of preterm labor. Ensuring the presence and proper function of the CMP is essential in reducing severe infections and promoting overall reproductive health.
During pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
, the mucus has viscoelastic
In materials science and continuum mechanics, viscoelasticity is the property of materials that exhibit both Viscosity, viscous and Elasticity (physics), elastic characteristics when undergoing deformation (engineering), deformation. Viscous mate ...
properties and can be described as cloudy, clear, thick, salty and sticky. It holds innate and adaptive immunity properties allowing for protection of the cervical epithelium during pregnancy. Toward the end of the pregnancy, when the cervix thins, some blood is released into the cervix which causes the mucus to become bloody. As the pregnancy progresses into labor, the cervix begins to dilate and the mucus plug is discharged. The plug may come out as a plug, a lump, or simply as increased vaginal discharge
Vaginal discharge is a mixture of liquid, cells, and bacteria that lubricate and protect the vagina. This mixture is constantly produced by the cells of the vagina and cervix, and it exits the body through the vaginal opening. The composition, ...
over several days. Loss of the mucus plug does not necessarily mean that delivery or labor is imminent.
Having intercourse or a vaginal examination can also disturb the mucus plug and cause a pregnant individuals to see some blood-tinged discharge, even when labor does not begin over the next few days.
A cervical mucus plug can allow for identification of an individual's ovulation cycle and serve as fertility indicator. The cervical mucus plug proteome
A proteome is the entire set of proteins that is, or can be, expressed by a genome, cell, tissue, or organism at a certain time. It is the set of expressed proteins in a given type of cell or organism, at a given time, under defined conditions. P ...
changes throughout an individual's menstrual cycle and allows for identification of specific proteins that may represent different stages of ovulation.
Some proteins found within the cervical mucus of patients with endometriosis could serve as potential biomarkers for the disease.
Components
Cervicovaginal mucus is composed of water, gel-forming-mucins (GFMS), and vaginal flora. GMFS are a combination of proteins and other molecules that are responsible for the viscoelastic properties of the mucus. Cervical mucus is formed by secretory cells within the cervical crypts. Mucusglycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide (sugar) chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known a ...
s (mucins) provide structural framework for a CMP, they determine the elasticity and fluid mechanics of a cervical mucus plug.
Function
Mucus within the genital tract serves numerous biological functions such as maintaining mucosa moisture, providing lubrication during intercourse, supporting fertility, and restricting ascending sperm cells during ovulation. The mucus glycoproteins (mucins) mentioned previously have five major components. The first is their ligand function for lectins, adhesion molecules, growth factors, cytokines, and chemokines. Second, they are responsible for binding water in CMPs and determines its hydration state. Third, mucins exclude larger molecules and bacteria which prevents bacterial infections in the lower genital tract. Mucins inhibit diffusion of these large molecules, while smaller molecules can diffuse through the CMP more freely. Fourth, mucins are responsible for the retention of positively charged molecules, while negative charged molecules are repelled and pass through the CMP. This is due to the negatively chargedoligosaccharide
An oligosaccharide (; ) is a carbohydrate, saccharide polymer containing a small number (typically three to ten) of monosaccharides (simple sugars). Oligosaccharides can have many functions including Cell–cell recognition, cell recognition and ce ...
chains in the mucins, which promote retention of the positively charged molecules. Lastly, mucins inhibit viral replication of poxvirus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in vitro. In addition, mucins can also create a communication between the CMP and cervical epithelium.
Antimicrobial properties
The cervical mucus plug (CMP) has a viscoelastic structure which is a gel like. The CMP occupies the cervical canal during pregnancy. It displays potent antimicrobial properties against bacteria such as Staphylococcus saprophyticus, S. aureus, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterococcus faecium, Streptococcus pyogenes, and S. agalactiae. * This plug is recognized as an innate immune defense and plays an important role in safeguarding against infections that may ascend from the vaginal area to the uterus. The ascending infections have been associated with preterm birth. Naturally occurring Lactobacillus species within the cervicovaginal mucus flora offer protection from harmful microbes by producing lactic acid, bacteriocins, and other molecules that lower the pH level and increase mucus viscosity. These changes reduce the adherence of harmful bacteria to the epithelial tissue.Menstrual cycle
Throughout the menstrual cycle, the cervical mucus undergoes distinct changes. During the follicular phase, increasing levels of estrogen result in greater mucus volume and gradual reduction in thickness. Ovulation triggers significant surges in mucus levels due to high expression ofMUC5B
Mucin-5B (MUC-5B) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MUC5B'' gene
and by the ''Muc5b'' gene in the mouse. It is one of the five gel-forming mucins. MUC-5B can be found in whole saliva, normal lung mucus, and cervical mucus. In som ...
which creates a watery consistency that aids sperm mobility into the reproductive tract. In the luteal phase, progesterone leads to a decrease in MUC5B
Mucin-5B (MUC-5B) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MUC5B'' gene
and by the ''Muc5b'' gene in the mouse. It is one of the five gel-forming mucins. MUC-5B can be found in whole saliva, normal lung mucus, and cervical mucus. In som ...
expression, resulting in the thickening of cervical mucus. Immune factors and antimicrobial peptides vary a different stages of the menstrual cycle.
Pregnancy
Healthy pregnancy results in a dense CMP which protects the uterine cavity from infection. Elevated progesterone plasma levels induce cervical mucus to form a more viscous plug called the CMP. One of the most common causes of preterm birth is inflammation induced by the changes in vaginal bacterial flora.Lactobacillus
''Lactobacillus'' is a genus of gram-positive, aerotolerant anaerobes or microaerophilic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacteria. Until 2020, the genus ''Lactobacillus'' comprised over 260 phylogenetically, ecologically, and metabolically div ...
plays an important role in maintaining the vaginal PH by producing lactic acids that protects against infections. Lactobacillus bacteria reduction in the vaginal bacterial flora leads other anaerobic bacteria to grow more easily. It also lead to increased cervical mucus IL-8 and increased preterm birth. Dysbiosis
Dysbiosis (also called dysbacteriosis) is characterized by a disruption to the microbiome resulting in an imbalance in the microbiota, changes in their functional composition and metabolic activities, or a shift in their local distribution. For e ...
occurs when the presence of naturally occurring bacteria such as lactobacilli declines resulting in an increase of harmful bacteria within the vagina. These changes result a CMP that is thin and porous which can leave the uterine compartment susceptible to infection.
Infections of the placenta and amniotic fluid by bacteria found in the vagina have been closely correlated to preterm labor. The CMP of pregnant women is in direct contact with the supracervical region of the chorioamniotic membranes which contain amniotic fluid
The amniotic fluid is the protective liquid contained by the amniotic sac of a gravid amniote. This fluid serves as a cushion for the growing fetus, but also serves to facilitate the exchange of nutrients, water, and biochemical products betwee ...
. This allows direct protection of the fetus.
Complications
Impairment of a CMP may be caused bycervical effacement
Cervical effacement or cervical ripening refers to the thinning and shortening of the cervix. This process occurs during Childbirth, labor to prepare the cervix for dilation to allow the fetus to pass through the vagina. While this is a normal, ph ...
, resulting in loss of the CMP. The CMP's most important task is to protect reproductive organs against infection by microorganisms coming from the vagina. It does so with a variety of polypeptides that have activity against microorganisms and immunoglobulins
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses, including those that cause di ...
. Without protection by the CMP, infection can occur leading to a number of complications.
Preterm birth
 A common complication in pregnancy is preterm birth, as mentioned before. Preterm birth is birth prior to 37 weeks of gestation. In individuals with a higher risk for preterm birth, the CMP is found to be more translucent, extensible, and permeable compared to those at low risk for preterm birth. These individuals also may display shorter cervix which can result in increased risk of
A common complication in pregnancy is preterm birth, as mentioned before. Preterm birth is birth prior to 37 weeks of gestation. In individuals with a higher risk for preterm birth, the CMP is found to be more translucent, extensible, and permeable compared to those at low risk for preterm birth. These individuals also may display shorter cervix which can result in increased risk of intra-amniotic infection
Chorioamnionitis, also known as amnionitis and intra-amniotic infection (IAI), is inflammation of the fetal membranes (amnion and chorion), usually due to bacterial infection. In 2015, a National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Wo ...
. The permeability of the CMP is the most important factor as it can allow for a higher risk for the entrance of foreign particles that are harmful. It seems that those at a higher risk for preterm birth develop a less thick and impermeable CMP during the pregnancy, which in turn allows for the entrance of more foreign particles such as bacteria, which is a known cause of preterm birth.
HPV infections
Dysbiosis in the cervicovaginal microbiota has been closely associated with increased HPV infections. Human papillomaviruses are a type of double-stranded DNA viruses categorized within the Papillomaviridae family. HPV infections are primarily transmitted through sexual contact. A healthy vaginal microbiota plays a crucial role in preventing various urogenital infections including sexually transmitted diseases. However, HPV infection occurs when it inhibits the production of cytokines, leading to changes in the microbial interactions within the cervical microenvironment. Lactobacillus bacteria plays an important role in maintaining the PH of the vagina by producing lactic acid. The lactate generated by lactobacilli elevates the thickness of cervical mucus, creating a barrier that entangles viral particles and hinders papillomavirus from reaching basal keratinocytes, which plays an important role in protection. When lactobacillus bacterias decline, the vaginal microbiota is dominated by non lactobacillus species. This increases the risk of HPV infections.References
{{Reflist Obstetrics Midwifery