|
Proteome
A proteome is the entire set of proteins that is, or can be, expressed by a genome, cell, tissue, or organism at a certain time. It is the set of expressed proteins in a given type of cell or organism, at a given time, under defined conditions. Proteomics is the study of the proteome. Types of proteomes While proteome generally refers to the proteome of an organism, multicellular organisms may have very different proteomes in different cells, hence it is important to distinguish proteomes in cells and organisms. A cellular proteome is the collection of proteins found in a particular cell (biology), cell type under a particular set of environmental conditions such as exposure to hormone, hormone stimulation. It can also be useful to consider an organism's complete proteome, which can be conceptualized as the complete set of proteins from all of the various cellular proteomes. This is very roughly the protein equivalent of the genome. The term ''proteome'' has also been used to r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteomics
Proteomics is the large-scale study of proteins. Proteins are vital macromolecules of all living organisms, with many functions such as the formation of structural fibers of muscle tissue, enzymatic digestion of food, or synthesis and replication of DNA. In addition, other kinds of proteins include antibodies that protect an organism from infection, and hormones that send important signals throughout the body. The proteome is the entire set of proteins produced or modified by an organism or system. Proteomics enables the identification of ever-increasing numbers of proteins. This varies with time and distinct requirements, or stresses, that a cell or organism undergoes. Proteomics is an interdisciplinary domain that has benefited greatly from the genetic information of various genome projects, including the Human Genome Project. It covers the exploration of proteomes from the overall level of protein composition, structure, and activity, and is an important component of function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marc Wilkins (geneticist)
Marc R. Wilkins is an Australian scientist who is credited with the defining the concept of the proteome. Wilkins is a Professor in the School of Biotechnology and Biomolecular Sciences at the University of New South Wales, Sydney. Wilkins coined the term proteome in 1994 whilst developing the concept as a PhD student at Macquarie University, Sydney, Australia, describing it as the 'PROTein complement expressed by a genOME'. The term is a generalisation of the concept of the genome to encompass the set of all proteins that can be produced through the genome through alternative splicing and post-transcriptional modification of messenger RNA. Career Wilkins held a post-doctoral fellowship from 1995–1997 at the University of Geneva, Switzerland, working with Prof Denis Hochstrasser and Dr Amos Bairoch. He co-developed many of the protein analysis tools available on the ExPASy web server. He subsequently served as a senior post-doctoral fellow in the Australian Proteome Analysi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondrion
A mitochondrion () is an organelle found in the cell (biology), cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double lipid bilayer, membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy. They were discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1857 in the voluntary muscles of insects. The term ''mitochondrion'', meaning a thread-like granule, was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. The mitochondrion is popularly nicknamed the "powerhouse of the cell", a phrase popularized by Philip Siekevitz in a 1957 ''Scientific American'' article of the same name. Some cells in some multicellular organisms lack mitochondria (for example, mature mammalian red blood cells). The multicellular animal ''Henneguya zschokkei, Henneguya salminicola'' is known to have retained mitochondrion-related organelles despite a complete loss of their mitochondrial genome. A large number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
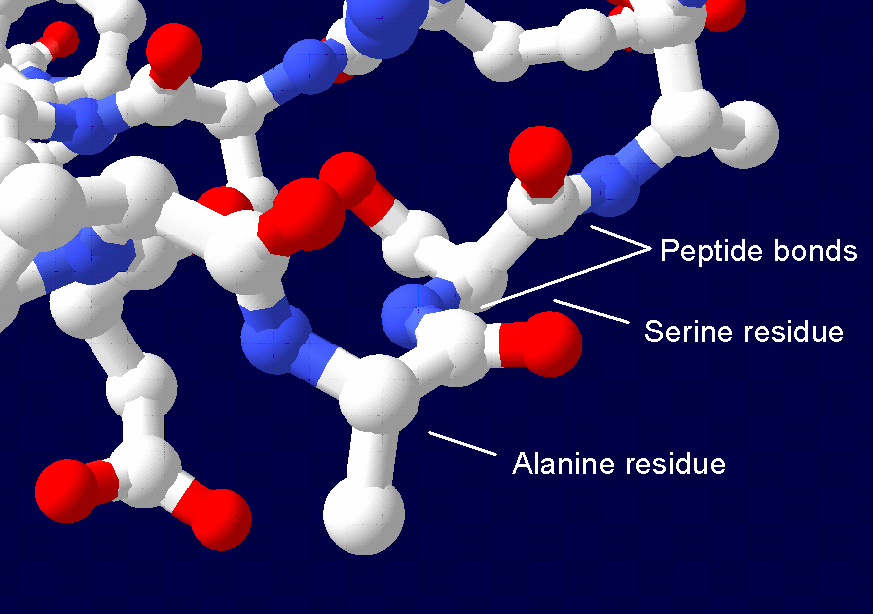
Protein Patterns And Diagnosis
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolomics Schema
Metabolomics is the scientific study of chemical processes involving metabolites, the small molecule substrates, intermediates, and products of cell metabolism. Specifically, metabolomics is the "systematic study of the unique chemical fingerprints that specific cellular processes leave behind", the study of their small-molecule metabolite profiles. The metabolome represents the complete set of metabolites in a biological cell, tissue, organ, or organism, which are the end products of cellular processes. Messenger RNA (mRNA), gene expression data, and proteomics, proteomic analyses reveal the set of gene products being produced in the cell, data that represents one aspect of cellular function. Conversely, metabolic profiling can give an instantaneous snapshot of the physiology of that cell, and thus, metabolomics provides a direct "functional readout of the physiological state" of an organism. There are indeed quantifiable correlations between the metabolome and the other cellular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apolipoprotein A1
Apolipoprotein AI (Apo-AI) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''APOA1'' gene. As the major component of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles, it has a specific role in lipid metabolism. Structure ''APOA1'' is located on chromosome 11, with its specific location being 11q23-q24. The gene contains 4 exons. The encoded apolipoprotein AI, is a 28.1 kDa protein composed of 243 amino acids; 21 peptides have been observed through mass spectrometry data. Due to alternative splicing, there exists multiple transcript variants of ''APOA1'', including at least one which encodes a Apo-AI preprotein. Function Apolipoprotein AI is the major protein component of high density lipoprotein (HDL) particles in plasma. Chylomicrons secreted from the intestinal enterocyte also contain Apo-AI, but it is quickly transferred to HDL in the bloodstream. The protein, as a component of HDL particles, enables efflux of fat molecules by accepting fats from within cells (including macro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Evolution
Viral evolution is a subfield of evolutionary biology and virology concerned with the evolution of viruses. Viruses have short generation times, and many—in particular RNA viruses—have relatively high mutation rates (on the order of one point mutation or more per genome per round of replication). Although most viral mutations confer no benefit and often even prove deleterious to viruses, the rapid rate of viral mutation combined with natural selection allows viruses to quickly adapt to changes in their host environment. In addition, because viruses typically produce many copies in an infected host, mutated genes can be passed on to many offspring quickly. Although the chance of mutations and evolution can change depending on the type of virus (e.g., double stranded DNA, double stranded RNA, or single stranded DNA), viruses overall have high chances for mutations. Viral evolution is an important aspect of the epidemiology of viral diseases such as influenza ( influenza viru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus
''Bacillus'', from Latin "bacillus", meaning "little staff, wand", is a genus of Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria, a member of the phylum ''Bacillota'', with 266 named species. The term is also used to describe the shape (rod) of other so-shaped bacteria; and the plural ''Bacilli'' is the name of the class of bacteria to which this genus belongs. ''Bacillus'' species can be either obligate aerobes which are dependent on oxygen, or facultative anaerobes which can survive in the absence of oxygen. Cultured ''Bacillus'' species test positive for the enzyme catalase if oxygen has been used or is present. ''Bacillus'' can reduce themselves to oval endospores and can remain in this dormant state for years. The endospore of one species from Morocco is reported to have survived being heated to 420 °C. Endospore formation is usually triggered by a lack of nutrients: the bacterium divides within its cell wall, and one side then engulfs the other. They are not true spores (i.e. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a ''mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures. A mass spectrum is a type of plot of the ion signal as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. These spectra are used to determine the elemental or isotopic signature of a sample, the masses of particles and of molecules, and to elucidate the chemical identity or structure of molecules and other chemical compounds. In a typical MS procedure, a sample, which may be solid, liquid, or gaseous, is ionization, ionized, for example by bombarding it with a Electron ionization, beam of electrons. This may cause some of the sample's molecules to break up into positively charged fragments or simply become positively charged without fragmenting. These ions (fragmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colon Cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel movements, weight loss, abdominal pain and fatigue. Most colorectal cancers are due to lifestyle factors and genetic disorders. Risk factors include diet, obesity, smoking, and lack of physical activity. Dietary factors that increase the risk include red meat, processed meat, and alcohol. Another risk factor is inflammatory bowel disease, which includes Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Some of the inherited genetic disorders that can cause colorectal cancer include familial adenomatous polyposis and hereditary non-polyposis colon cancer; however, these represent less than 5% of cases. It typically starts as a benign tumor, often in the form of a polyp, which over time becomes cancerous. Colorectal cancer may be diagnosed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellular Differentiation
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a stem cell changes from one type to a differentiated one. Usually, the cell changes to a more specialized type. Differentiation happens multiple times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Metabolic composition, however, gets dramatically altered where st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |