cerium on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cerium is a
 Four allotropic forms of cerium are known to exist at standard pressure and are given the common labels of α to δ:
* The high-temperature form, δ-cerium, has a bcc (
Four allotropic forms of cerium are known to exist at standard pressure and are given the common labels of α to δ:
* The high-temperature form, δ-cerium, has a bcc (
 The compound ceric ammonium nitrate (CAN) is the most common cerium compound encountered in the laboratory. The six nitrate ligands bind as bidentate ligands. The complex is 12-coordinate, a high coordination number which emphasizes the large size of the Ce4+ ion. CAN is a popular oxidant in
The compound ceric ammonium nitrate (CAN) is the most common cerium compound encountered in the laboratory. The six nitrate ligands bind as bidentate ligands. The complex is 12-coordinate, a high coordination number which emphasizes the large size of the Ce4+ ion. CAN is a popular oxidant in
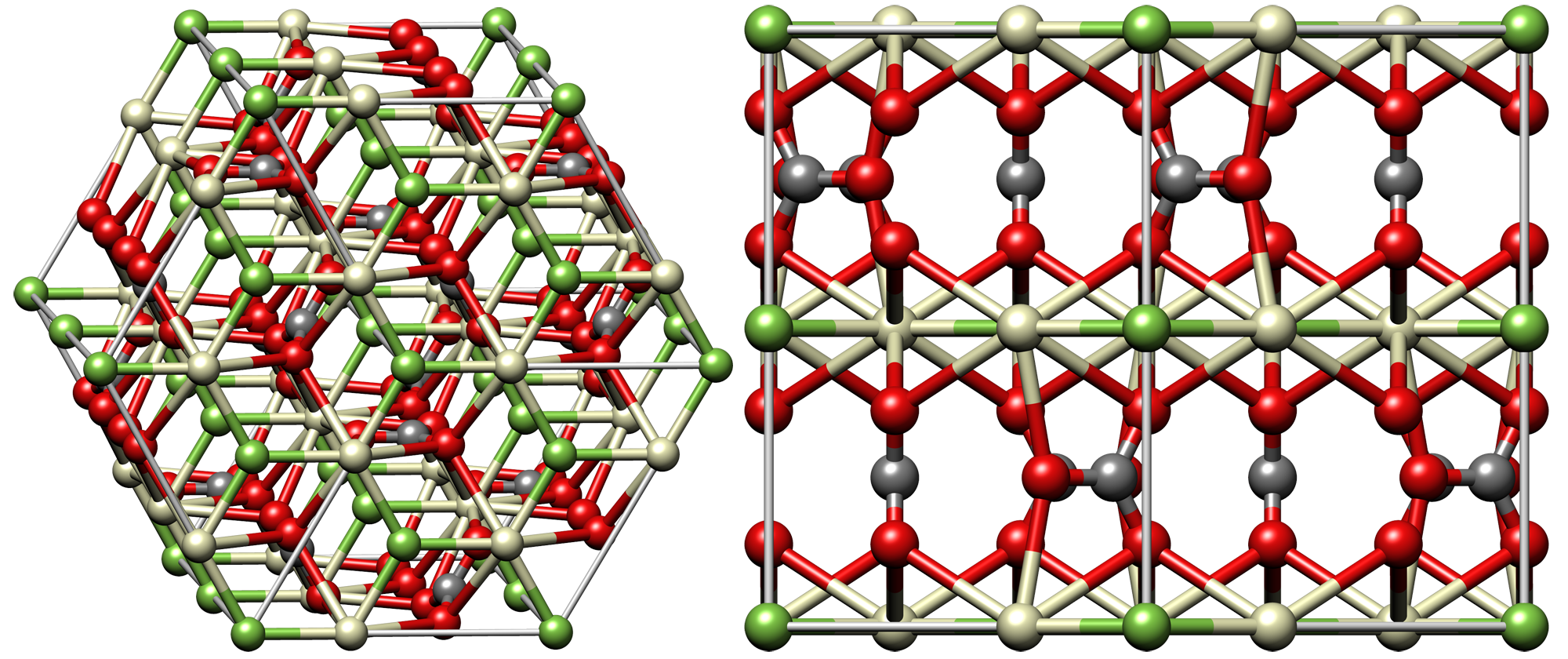 Bastnäsite, LnCOF, is usually lacking in
Bastnäsite, LnCOF, is usually lacking in
 Cerium has two main applications, both of which use CeO2. The industrial application of ceria is for polishing, especially chemical-mechanical planarization (CMP). In its other main application, CeO2 is used to decolorize glass. It functions by converting green-tinted ferrous impurities to nearly colorless ferric oxides. Ceria has also been used as a substitute for its radioactive congener thoria, for example in the manufacture of electrodes used in gas tungsten arc welding, where cerium as an alloying element improves arc stability and ease of starting while decreasing burn-off.
Cerium has two main applications, both of which use CeO2. The industrial application of ceria is for polishing, especially chemical-mechanical planarization (CMP). In its other main application, CeO2 is used to decolorize glass. It functions by converting green-tinted ferrous impurities to nearly colorless ferric oxides. Ceria has also been used as a substitute for its radioactive congener thoria, for example in the manufacture of electrodes used in gas tungsten arc welding, where cerium as an alloying element improves arc stability and ease of starting while decreasing burn-off.
. nanopartikel.info (2011-02-02) The most commonly used example is cerium(III)-doped yttrium aluminium garnet (Ce:YAG) which emits green to yellow-green light (550–530 nm) and also behaves as a scintillator.
chemical element
A chemical element is a chemical substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons. The number of protons is called the atomic number of that element. For example, oxygen has an atomic number of 8: each oxygen atom has 8 protons in its ...
; it has symbol
A symbol is a mark, Sign (semiotics), sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, physical object, object, or wikt:relationship, relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by cr ...
Ce and atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of its atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei composed of protons and neutrons, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of pro ...
58. It is a soft, ductile
Ductility refers to the ability of a material to sustain significant plastic deformation before fracture. Plastic deformation is the permanent distortion of a material under applied stress, as opposed to elastic deformation, which is reversi ...
, and silvery-white metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated wit ...
that tarnishes when exposed to air. Cerium is the second element in the lanthanide series, and while it often shows the oxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical Electrical charge, charge of an atom if all of its Chemical bond, bonds to other atoms are fully Ionic bond, ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons ...
of +3 characteristic of the series, it also has a stable +4 state that does not oxidize water. It is considered one of the rare-earth elements. Cerium has no known biological role in humans but is not particularly toxic, except with intense or continued exposure.
Despite always occurring in combination with the other rare-earth elements in minerals such as those of the monazite and bastnäsite groups, cerium is easy to extract from its ores, as it can be distinguished among the lanthanides by its unique ability to be oxidized to the +4 state in aqueous solution. It is the most common of the lanthanides, followed by neodymium
Neodymium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is the fourth member of the lanthanide series and is considered to be one of the rare-earth element, rare-earth metals. It is a hard (physics), hard, sli ...
, lanthanum, and praseodymium. Its estimated abundance in the Earth's crust is 68 ppm.
Cerium was the first of the lanthanides to be discovered, in Bastnäs, Sweden. It was discovered by Jöns Jakob Berzelius and Wilhelm Hisinger in 1803, and independently by Martin Heinrich Klaproth in Germany in the same year. In 1839 Carl Gustaf Mosander separated cerium(III) oxide from other rare earths, and in 1875 William Francis Hillebrand became the first to isolate the metal. Today, cerium and its compounds have a variety of uses: for example, cerium(IV) oxide is used to polish glass and is an important part of catalytic converter
A catalytic converter part is an vehicle emissions control, exhaust emission control device which converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalysis, catalyzing a redox ...
s. Cerium metal is used in ferrocerium lighters for its pyrophoric properties. Cerium-doped YAG phosphor is used in conjunction with blue light-emitting diode
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (corre ...
s to produce white light in most commercial white LED light sources.
Characteristics
Physical
Cerium is the second element of the lanthanide series. In the periodic table, it appears between the lanthanides lanthanum to its left and praseodymium to its right, and above theactinide
The actinide () or actinoid () series encompasses at least the 14 metallic chemical elements in the 5f series, with atomic numbers from 89 to 102, actinium through nobelium. Number 103, lawrencium, is also generally included despite being part ...
thorium
Thorium is a chemical element; it has symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is a weakly radioactive light silver metal which tarnishes olive grey when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft, malleable, and ha ...
. It is a ductile
Ductility refers to the ability of a material to sustain significant plastic deformation before fracture. Plastic deformation is the permanent distortion of a material under applied stress, as opposed to elastic deformation, which is reversi ...
metal with a hardness similar to that of silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
. Its 58 electrons are arranged in the configuration ef5d6s, of which the four outer electrons are valence electrons. The 4f, 5d, and 6s energy levels are very close to each other, and the transfer of one electron to the 5d shell is due to strong interelectronic repulsion in the compact 4f shell. This effect is overwhelmed when the atom is positively ionised; thus Ce on its own has instead the regular configuration ef, although in some solid solutions it may be ef5d. Most lanthanides can use only three electrons as valence electrons, as afterwards the remaining 4f electrons are too strongly bound: cerium is an exception because of the stability of the empty f-shell in Ce and the fact that it comes very early in the lanthanide series, where the nuclear charge is still low enough until neodymium
Neodymium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is the fourth member of the lanthanide series and is considered to be one of the rare-earth element, rare-earth metals. It is a hard (physics), hard, sli ...
to allow the removal of the fourth valence electron by chemical means.
Cerium has a variable electronic structure. The energy of the 4f electron is nearly the same as that of the outer 5d and 6s electrons that are delocalized in the metallic state, and only a small amount of energy is required to change the relative occupancy of these electronic levels. This gives rise to dual valence states. For example, a volume change of about 10% occurs when cerium is subjected to high pressures or low temperatures. In its high pressure phase (α-Cerium), the 4f electrons are also delocalized and itinerate, as opposed to localized 4f electrons in low pressure phase (γ-Cerium). It appears that the valence changes from about 3 to 4 when it is cooled or compressed.
Chemical properties of the element
Like the other lanthanides, cerium metal is a goodreducing agent
In chemistry, a reducing agent (also known as a reductant, reducer, or electron donor) is a chemical species that "donates" an electron to an (called the , , , or ).
Examples of substances that are common reducing agents include hydrogen, carbon ...
, having standard reduction potential of ''E'' = −2.34 V for the Ce/Ce couple. It tarnishes in air, forming a passivating oxide layer like iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
rust. A centimeter-sized sample of cerium metal corrodes completely in about a year. More dramatically, metallic cerium can be highly pyrophoric:
:
Being highly electropositive, cerium reacts with water. The reaction is slow with cold water but speeds up with increasing temperature, producing cerium(III) hydroxide and hydrogen gas:
:
Allotropes
 Four allotropic forms of cerium are known to exist at standard pressure and are given the common labels of α to δ:
* The high-temperature form, δ-cerium, has a bcc (
Four allotropic forms of cerium are known to exist at standard pressure and are given the common labels of α to δ:
* The high-temperature form, δ-cerium, has a bcc (body-centered cubic
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the Crystal structure#Unit cell, unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals.
There ...
) crystal structure and exists above 726 °C.
* The stable form below 726 °C to approximately room temperature is γ-cerium, with an fcc (face-centered cubic
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals.
There are three main varieties o ...
) crystal structure.
* The DHCP (double hexagonal close-packed) form β-cerium is the equilibrium structure approximately from room temperature to −150 °C.
* The fcc form α-cerium is stable below about −150 °C; it has a density of 8.16 g/cm.
* Other solid phases occurring only at high pressures are shown on the phase diagram.
* Both γ and β forms are quite stable at room temperature, although the equilibrium transformation temperature is estimated at 75 °C.
At lower temperatures the behavior of cerium is complicated by the slow rates of transformation. Transformation temperatures are subject to substantial hysteresis and values quoted here are approximate. Upon cooling below −15 °C, γ-cerium starts to change to β-cerium, but the transformation involves a volume increase and, as more β forms, the internal stresses build up and suppress further transformation. Cooling below approximately −160 °C will start formation of α-cerium but this is only from remaining γ-cerium. β-cerium does not significantly transform to α-cerium except in the presence of stress or deformation. At atmospheric pressure, liquid cerium is more dense than its solid form at the melting
point.
Isotopes
Naturally occurring cerium is made up of four isotopes: Ce (0.19%), Ce (0.25%), Ce (88.4%), and Ce (11.1%). All four are observationally stable, though the light isotopes Ce and Ce are theoretically expected to undergo double electron capture to isotopes of barium, and the heaviest isotope 142Ce is expected to undergo double beta decay to 142Nd or alpha decay to 138Ba. Thus, 140Ce is the only theoreticallystable isotope
Stable nuclides are Isotope, isotopes of a chemical element whose Nucleon, nucleons are in a configuration that does not permit them the surplus energy required to produce a radioactive emission. The Atomic nucleus, nuclei of such isotopes are no ...
. None of these decay modes have yet been observed, though the double beta decay of 136Ce, 138Ce, and 142Ce have been experimentally searched for. The current experimental limits for their half-lives are:
:136Ce: >3.8×1016 y
:138Ce: >5.7×1016 y
:142Ce: >5.0×1016 y
All other cerium isotopes are synthetic and radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is conside ...
. The most stable of them are 144Ce with a half-life of 284.9 days, 139Ce with a half-life of 137.6 days, and 141Ce with a half-life of 32.5 days. All other radioactive cerium isotopes have half-lives under four days, and most of them have half-lives under ten minutes. The isotopes between 140Ce and 144Ce inclusive occur as fission products of uranium
Uranium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Ura ...
. The primary decay mode of the isotopes lighter than 140Ce is inverse beta decay or electron capture
Electron capture (K-electron capture, also K-capture, or L-electron capture, L-capture) is a process in which the proton-rich nucleus of an electrically neutral atom absorbs an inner atomic electron, usually from the K or L electron shells. Th ...
to isotopes of lanthanum, while that of the heavier isotopes is beta decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron), transforming into an isobar of that nuclide. For example, beta decay of a neutron ...
to isotopes of praseodymium. Some isotopes of neodymium
Naturally occurring neodymium (60Nd) is composed of five stable isotopes, 142Nd, 143Nd, 145Nd, 146Nd and 148Nd, with 142Nd being the most abundant (27.2% natural abundance), and two long-lived radioisotopes, 144Nd and 150Nd. In all, 35 radioisotop ...
can alpha decay
Alpha decay or α-decay is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle (helium nucleus). The parent nucleus transforms or "decays" into a daughter product, with a mass number that is reduced by four and an a ...
or are predicted to decay to isotopes of cerium.
The rarity of the proton-rich 136Ce and 138Ce is explained by the fact that they cannot be made in the most common processes of stellar nucleosynthesis
In astrophysics, stellar nucleosynthesis is the creation of chemical elements by nuclear fusion reactions within stars. Stellar nucleosynthesis has occurred since the original creation of hydrogen, helium and lithium during the Big Bang. As a ...
for elements beyond iron, the s-process (slow neutron capture
Neutron capture is a nuclear reaction in which an atomic nucleus and one or more neutrons collide and merge to form a heavier nucleus. Since neutrons have no electric charge, they can enter a nucleus more easily than positively charged protons, wh ...
) and the r-process
In nuclear astrophysics, the rapid neutron-capture process, also known as the ''r''-process, is a set of nuclear reactions that is responsible for nucleosynthesis, the creation of approximately half of the Atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei Heavy meta ...
(rapid neutron capture). This is so because they are bypassed by the reaction flow of the s-process, and the r-process nuclides are blocked from decaying to them by more neutron-rich stable nuclides. Such nuclei are called p-nuclei, and their origin is not yet well understood: some speculated mechanisms for their formation include proton capture as well as photodisintegration
Photodisintegration (also called phototransmutation, or a photonuclear reaction) is a nuclear process in which an atomic nucleus absorbs a high-energy gamma ray, enters an excited state, and immediately decays by emitting a subatomic particle. The ...
. 140Ce is the most common isotope of cerium, as it can be produced in both the s- and r-processes, while 142Ce can only be produced in the r-process. Another reason for the abundance of 140Ce is that it is a magic nucleus, having a closed neutron shell (it has 82 neutrons), and hence it has a very low cross section towards further neutron capture. Although its proton number of 58 is not magic, it is granted additional stability, as its eight additional protons past the magic number 50 enter and complete the 1g proton orbital. The abundances of the cerium isotopes may differ very slightly in natural sources, because Ce and Ce are the daughters of the long-lived primordial radionuclides La and Nd, respectively.
Compounds
Cerium exists in two main oxidation states, Ce(III) and Ce(IV). This pair of adjacent oxidation states dominates several aspects of the chemistry of this element. Cerium(IV) aqueous solutions may be prepared by reacting cerium(III) solutions with the strong oxidizing agents peroxodisulfate or bismuthate. The value of ''E''(Ce/Ce) varies widely depending on conditions due to the relative ease of complexation and hydrolysis with various anions, although +1.72 V is representative. Cerium is the only lanthanide which has important aqueous and coordination chemistry in the +4 oxidation state.Halides
Cerium forms all four trihalides CeX (X = F, Cl, Br, I) usually by reaction of the oxides with the hydrogen halides. The anhydrous halides are pale-colored, paramagnetic, hygroscopic solids. Upon hydration, the trihalides convert to complexes containing aquo complexes e(HO) Unlike most lanthanides, Ce forms a tetrafluoride, a white solid. It also forms a bronze-colored diiodide, which has metallic properties. Aside from the binary halide phases, a number of anionic halide complexes are known. The fluoride gives the Ce(IV) derivatives and . The chloride gives the orange .Oxides and chalcogenides
Cerium(IV) oxide ("ceria") has the fluorite structure, similarly to the dioxides of praseodymium andterbium
Terbium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Tb and atomic number 65. It is a silvery-white, rare earth element, rare earth metal that is malleable and ductile. The ninth member of the lanthanide series, terbium is a fairly ele ...
. Ceria is a nonstoichiometric compound, meaning that the real formula is CeO, where x is about 0.2. Thus, the material is not perfectly described as Ce(IV). Ceria reduces to cerium(III) oxide with hydrogen gas. Many nonstoichiometric chalcogen
The chalcogens (ore forming) ( ) are the chemical elements in group 16 of the periodic table. This group is also known as the oxygen family. Group 16 consists of the elements oxygen (O), sulfur (S), selenium (Se), tellurium (Te), and the rad ...
ides are also known, along with the trivalent CeZ (Z = S, Se, Te). The monochalcogenides CeZ conduct electricity and would better be formulated as CeZe. While CeZ are known, they are polychalcogenides with cerium(III): cerium(IV) derivatives of S, Se, and Te are unknown.
Cerium(IV) complexes
 The compound ceric ammonium nitrate (CAN) is the most common cerium compound encountered in the laboratory. The six nitrate ligands bind as bidentate ligands. The complex is 12-coordinate, a high coordination number which emphasizes the large size of the Ce4+ ion. CAN is a popular oxidant in
The compound ceric ammonium nitrate (CAN) is the most common cerium compound encountered in the laboratory. The six nitrate ligands bind as bidentate ligands. The complex is 12-coordinate, a high coordination number which emphasizes the large size of the Ce4+ ion. CAN is a popular oxidant in organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a branch of chemical synthesis concerned with the construction of organic compounds. Organic compounds are molecules consisting of combinations of covalently-linked hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms. Within the gen ...
, both as a stoichiometric reagent and as a catalyst. It is inexpensive, stable in air, easily handled, and of low toxicity. It operates by one-electron redox. Cerium nitrates also form 4:3 and 1:1 complexes with 18-crown-6 (the ratio referring to that between the nitrate and the crown ether). Classically, CAN is a primary standard for quantitative analysis. Cerium(IV) salts, especially cerium(IV) sulfate, are often used as standard reagents for volumetric analysis
Titration (also known as titrimetry and volumetric analysis) is a common laboratory method of Quantitative research, quantitative Analytical chemistry, chemical analysis to determine the concentration of an identified analyte (a substance to be ...
in cerimetric titrations.
Due to ligand-to-metal charge transfer, aqueous cerium(IV) ions are orange-yellow. Aqueous cerium(IV) is metastable in water and is a strong oxidizing agent that oxidizes hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid or spirits of salt, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride (HCl). It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungency, pungent smell. It is classified as a acid strength, strong acid. It is ...
to give chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between ...
gas. In the Belousov–Zhabotinsky reaction, cerium oscillates between the +4 and +3 oxidation states to catalyze the reaction.
Organocerium compounds
Organocerium chemistry is similar to that of the other lanthanides, often involving complexes of cyclopentadienyl and cyclooctatetraenyl ligands. Cerocene adopts theuranocene
Uranocene, U(C8H8)2, is an organouranium compound composed of a uranium atom sandwiched between two cyclooctatetraene, cyclooctatetraenide rings. It was one of the first Organoactinide chemistry, organoactinide compounds to be synthesized. It is a ...
molecular structure. The 4f electron in cerocene is poised ambiguously between being localized and delocalized and this compound is considered intermediate-valent.
Alkyl
In organic chemistry, an alkyl group is an alkane missing one hydrogen.
The term ''alkyl'' is intentionally unspecific to include many possible substitutions.
An acyclic alkyl has the general formula of . A cycloalkyl group is derived from a cy ...
, alkynyl, and alkenyl organocerium derivatives are prepared from the transmetallation of the respective organolithium or Grignard reagents, and are more nucleophilic but less basic than their precursors.
History
Cerium was discovered in Bastnäs in Sweden by Jöns Jakob Berzelius and Wilhelm Hisinger, and independently in Germany by Martin Heinrich Klaproth, both in 1803. Cerium was named by Berzelius after the asteroid Ceres, formally 1 Ceres, discovered two years earlier. Ceres was initially considered to be a planet at the time. The asteroid is itself named after the Roman goddess Ceres, goddess of agriculture, grain crops, fertility and motherly relationships. Cerium was originally isolated in the form of its oxide, which was named ''ceria'', a term that is still used. The metal itself was too electropositive to be isolated by then-current smelting technology, a characteristic of rare-earth metals in general. After the development ofelectrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry concerned with the relationship between Electric potential, electrical potential difference and identifiable chemical change. These reactions involve Electron, electrons moving via an electronic ...
by Humphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet (17 December 177829 May 1829) was a British chemist and inventor who invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp. He is also remembered for isolating, by using electricity, several Chemical element, e ...
five years later, the earths soon yielded the metals they contained. Ceria, as isolated in 1803, contained all of the lanthanides present in the cerite ore from Bastnäs, Sweden, and thus only contained about 45% of what is now known to be pure ceria. It was not until Carl Gustaf Mosander succeeded in removing lanthana and "didymia" in the late 1830s that ceria was obtained pure. Wilhelm Hisinger was a wealthy mine-owner and amateur scientist, and sponsor of Berzelius. He owned and controlled the mine at Bastnäs, and had been trying for years to find out the composition of the abundant heavy gangue rock (the "Tungsten of Bastnäs", which despite its name contained no tungsten
Tungsten (also called wolfram) is a chemical element; it has symbol W and atomic number 74. It is a metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively in compounds with other elements. It was identified as a distinct element in 1781 and first ...
), now known as cerite, that he had in his mine. Mosander and his family lived for many years in the same house as Berzelius, and Mosander was undoubtedly persuaded by Berzelius to investigate ceria further.
The element played a role in the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development program undertaken during World War II to produce the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States in collaboration with the United Kingdom and Canada.
From 1942 to 1946, the ...
, where cerium compounds were investigated in the Berkeley site as materials for crucibles for uranium
Uranium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Ura ...
and plutonium
Plutonium is a chemical element; it has symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is a silvery-gray actinide metal that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four ...
casting. For this reason, new methods for the preparation and casting of cerium were developed within the scope of the Ames daughter project (now the Ames Laboratory). Production of extremely pure cerium in Ames commenced in mid-1944 and continued until August 1945.
Occurrence and production
Cerium is the most abundant of all the lanthanides and the 25th most abundant element, making up 68 ppm of the Earth's crust. This value is the same ofcopper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
, and cerium is even more abundant than common metals such as lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
(13 ppm) and tin (2.1 ppm). Thus, despite its position as one of the so-called rare-earth metal
The rare-earth elements (REE), also called the rare-earth metals or rare earths, and sometimes the lanthanides or lanthanoids (although scandium and yttrium, which do not belong to this series, are usually included as rare earths), are a set of ...
s, cerium is actually not rare at all. Cerium content in the soil varies between 2 and 150 ppm, with an average of 50 ppm; seawater contains 1.5 parts per trillion of cerium. Cerium occurs in various minerals, but the most important commercial sources are the minerals of the monazite and bastnäsite groups, where it makes up about half of the lanthanide content. Monazite-(Ce) is the most common representative of the monazites, with "-Ce" being the Levinson suffix informing on the dominance of the particular REE element representative. Also the cerium-dominant bastnäsite-(Ce) is the most important of the bastnäsites. Cerium is the easiest lanthanide to extract from its minerals because it is the only one that can reach a stable +4 oxidation state in aqueous solution. Because of the decreased solubility of cerium in the +4 oxidation state, cerium is sometimes depleted from rocks relative to the other rare-earth elements and is incorporated into zircon, since Ce4+ and Zr4+ have the same charge and similar ionic radii. In extreme cases, cerium(IV) can form its own minerals separated from the other rare-earth elements, such as cerianite-(Ce) and .
 Bastnäsite, LnCOF, is usually lacking in
Bastnäsite, LnCOF, is usually lacking in thorium
Thorium is a chemical element; it has symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is a weakly radioactive light silver metal which tarnishes olive grey when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft, malleable, and ha ...
and the heavy lanthanides beyond samarium and europium
Europium is a chemical element; it has symbol Eu and atomic number 63. It is a silvery-white metal of the lanthanide series that reacts readily with air to form a dark oxide coating. Europium is the most chemically reactive, least dense, and soft ...
, and hence the extraction of cerium from it is quite direct. First, the bastnäsite is purified, using dilute hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid or spirits of salt, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride (HCl). It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungency, pungent smell. It is classified as a acid strength, strong acid. It is ...
to remove calcium carbonate
Calcium carbonate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is a common substance found in Rock (geology), rocks as the minerals calcite and aragonite, most notably in chalk and limestone, eggshells, gastropod shells, shellfish skel ...
impurities. The ore is then roasted in the air to oxidize it to the lanthanide oxides: while most of the lanthanides will be oxidized to the sesquioxides , cerium will be oxidized to the dioxide CeO. This is insoluble in water and can be leached out with 0.5 M hydrochloric acid, leaving the other lanthanides behind.
The procedure for monazite, , which usually contains all the rare earths, as well as thorium, is more involved. Monazite, because of its magnetic properties, can be separated by repeated electromagnetic separation. After separation, it is treated with hot concentrated sulfuric acid to produce water-soluble sulfates of rare earths. The acidic filtrates are partially neutralized with sodium hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions .
Sodium hydroxide is a highly corrosive base (chemistry), ...
to pH 3–4. Thorium precipitates out of solution as hydroxide and is removed. After that, the solution is treated with ammonium oxalate
Ammonium oxalate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . Its formula is often written as or . It is an ammonium salt of oxalic acid. It consists of ammonium cations () and oxalate anions (). The structure of ammonium oxalate is . A ...
to convert rare earths to their insoluble oxalates. The oxalates are converted to oxides by annealing. The oxides are dissolved in nitric acid, but cerium oxide is insoluble in HNO3 and hence precipitates out. Care must be taken when handling some of the residues as they contain 228Ra, the daughter of 232Th, which is a strong gamma emitter.
Applications
 Cerium has two main applications, both of which use CeO2. The industrial application of ceria is for polishing, especially chemical-mechanical planarization (CMP). In its other main application, CeO2 is used to decolorize glass. It functions by converting green-tinted ferrous impurities to nearly colorless ferric oxides. Ceria has also been used as a substitute for its radioactive congener thoria, for example in the manufacture of electrodes used in gas tungsten arc welding, where cerium as an alloying element improves arc stability and ease of starting while decreasing burn-off.
Cerium has two main applications, both of which use CeO2. The industrial application of ceria is for polishing, especially chemical-mechanical planarization (CMP). In its other main application, CeO2 is used to decolorize glass. It functions by converting green-tinted ferrous impurities to nearly colorless ferric oxides. Ceria has also been used as a substitute for its radioactive congener thoria, for example in the manufacture of electrodes used in gas tungsten arc welding, where cerium as an alloying element improves arc stability and ease of starting while decreasing burn-off.
Gas mantles and pyrophoric alloys
The first use of cerium was in gas mantles, invented by Austrian chemist Carl Auer von Welsbach. In 1885, he had previously experimented with mixtures ofmagnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
, lanthanum, and yttrium oxides, but these gave green-tinted light and were unsuccessful. Six years later, he discovered that pure thorium oxide produced a much better, though blue, light, and that mixing it with cerium dioxide resulted in a bright white light. Cerium dioxide also acts as a catalyst for the combustion of thorium oxide.
This resulted in commercial success for von Welsbach and his invention, and created great demand for thorium. Its production resulted in a large amount of lanthanides being simultaneously extracted as by-products. Applications were soon found for them, especially in the pyrophoric alloy known as " mischmetal" composed of 50% cerium, 25% lanthanum, and the remainder being the other lanthanides, that is used widely for lighter flints. Usually iron is added to form the alloy ferrocerium, also invented by von Welsbach. Due to the chemical similarities of the lanthanides, chemical separation is not usually required for their applications, such as the addition of mischmetal to steel as an inclusion modifier to improve mechanical properties, or as catalysts for the cracking of petroleum. This property of cerium saved the life of writer Primo Levi at the Auschwitz concentration camp
Auschwitz, or Oświęcim, was a complex of over 40 Nazi concentration camps, concentration and extermination camps operated by Nazi Germany in Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany, occupied Poland (in a portion annexed into Germany in 1939) d ...
, when he found a supply of ferrocerium alloy and bartered it for food.Pigments and phosphors
The photostability ofpigment
A pigment is a powder used to add or alter color or change visual appearance. Pigments are completely or nearly solubility, insoluble and reactivity (chemistry), chemically unreactive in water or another medium; in contrast, dyes are colored sub ...
s can be enhanced by the addition of cerium, as it provides pigments with lightfastness and prevents clear polymers from darkening in sunlight. An example of a cerium compound used on its own as an inorganic pigment is the vivid red cerium(III) sulfide (cerium sulfide red), which stays chemically inert up to very high temperatures. The pigment is a safer alternative to lightfast but toxic cadmium selenide-based pigments. The addition of cerium oxide to older cathode-ray tube
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns, which emit electron beams that are manipulated to display images on a phosphorescent screen. The images may represent electrical waveforms on an oscilloscope, a ...
television glass plates was beneficial, as it suppresses the darkening effect from the creation of F-center defects due to the continuous electron bombardment during operation. Cerium is also an essential component as a dopant
A dopant (also called a doping agent) is a small amount of a substance added to a material to alter its physical properties, such as electrical or optics, optical properties. The amount of dopant is typically very low compared to the material b ...
for phosphor
A phosphor is a substance that exhibits the phenomenon of luminescence; it emits light when exposed to some type of radiant energy. The term is used both for fluorescent or phosphorescent substances which glow on exposure to ultraviolet or ...
s used in CRT TV screens, fluorescent lamps, and later white light-emitting diodes.Cerium dioxide. nanopartikel.info (2011-02-02) The most commonly used example is cerium(III)-doped yttrium aluminium garnet (Ce:YAG) which emits green to yellow-green light (550–530 nm) and also behaves as a scintillator.
Other uses
Cerium salts, such as the sulfides Ce2S3 and Ce3S4, were considered during theManhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development program undertaken during World War II to produce the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States in collaboration with the United Kingdom and Canada.
From 1942 to 1946, the ...
as advanced refractory materials
In materials science, a refractory (or refractory material) is a material that is resistant to Thermal decomposition, decomposition by heat or chemical attack and that retains its strength and rigidity at high temperatures. They are Inorganic c ...
for the construction of crucibles which could withstand the high temperatures and strongly reducing conditions when casting plutonium metal. Despite desirable properties, these sulfides were never widely adopted due to practical issues with their synthesis. Cerium is used as alloying element in aluminium to create castable eutectic aluminium alloys
An aluminium alloy (British English, UK/International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, IUPAC) or aluminum alloy (North American English, NA; see American and British English spelling differences, spelling differences) is an alloy in which al ...
with 6–16 wt.% Ce, to which other elements such as Mg, Ni, Fe and Mn can be added. These Al-Ce alloys have excellent high temperature strength and are suitable for automotive applications (e.g. in cylinder heads). Other alloys of cerium include Pu-Ce and Pu-Ce-Co plutonium alloys, which have been used as nuclear fuel
Nuclear fuel refers to any substance, typically fissile material, which is used by nuclear power stations or other atomic nucleus, nuclear devices to generate energy.
Oxide fuel
For fission reactors, the fuel (typically based on uranium) is ...
.
Other automotive applications for the lower sesquioxide are as a catalytic converter
A catalytic converter part is an vehicle emissions control, exhaust emission control device which converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalysis, catalyzing a redox ...
for the oxidation of CO and NO emissions in the exhaust gases from motor vehicles.
Biological role and precautions
The early lanthanides have been found to be essential to some methanotrophic bacteria living in volcanic mudpots, such as '' Methylacidiphilum fumariolicum'': lanthanum,cerium
Cerium is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Ce and atomic number 58. It is a hardness, soft, ductile, and silvery-white metal that tarnishes when exposed to air. Cerium is the second element in the lanthanide series, and while it ...
, praseodymium, and neodymium
Neodymium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is the fourth member of the lanthanide series and is considered to be one of the rare-earth element, rare-earth metals. It is a hard (physics), hard, sli ...
are about equally effective. Cerium is otherwise not known to have biological role in any other organisms, but is not very toxic either; it does not accumulate in the food chain to any appreciable extent. Because it often occurs together with calcium in phosphate minerals, and bones are primarily calcium phosphate, cerium can accumulate in bones in small amounts that are not considered dangerous.
Cerium nitrate is an effective topical antimicrobial treatment for third-degree burns, although large doses can lead to cerium poisoning and methemoglobinemia
Methemoglobinemia, or methaemoglobinaemia, is a condition of elevated methemoglobin in the blood. Symptoms may include headache, dizziness, shortness of breath, nausea, poor muscle coordination, and blue-colored skin (cyanosis). Complications ma ...
.
Like all rare-earth metals, cerium is of low to moderate toxicity. A strong reducing agent, it ignites spontaneously in air at 65 to 80 °C. Fumes from cerium fires are toxic. Cerium reacts with water to produce hydrogen gas, and thus cerium fires can only be effectively extinguished using class D dry powder extinguishing media. Workers exposed to cerium have experienced itching, sensitivity to heat, and skin lesions. Cerium is not toxic when eaten, but animals injected with large doses of cerium have died due to cardiovascular collapse. Cerium is more dangerous to aquatic organisms because it damages cell membranes; it is not very soluble in water and can cause environmental contamination.
Cerium oxide, the most prevalent cerium compound in industrial applications, is not regulated in the United States by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA; ) is a regulatory agency of the United States Department of Labor that originally had federal visitorial powers to inspect and examine workplaces. The United States Congress established ...
(OSHA) as a hazardous substance. In Russia, its occupational exposure limit is 5 mg/m. Elemental cerium has no established occupational or permissible exposure limits by the OSHA or American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists, though it is classified as a flammable solid and regulated as such under the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals. Toxicological reports on cerium compounds have noted their cytotoxicity
Cytotoxicity is the quality of being toxic to cells. Examples of toxic agents are toxic metals, toxic chemicals, microbe neurotoxins, radiation particles and even specific neurotransmitters when the system is out of balance. Also some types of d ...
and contributions to pulmonary interstitial fibrosis in workers.
References
Bibliography
* {{Authority control Chemical elements Chemical elements with double hexagonal close-packed structure Lanthanides Reducing agents Pyrophoric materials Materials that expand upon freezing