Carnot battery on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A Carnot battery is a type of
A Carnot battery is a type of
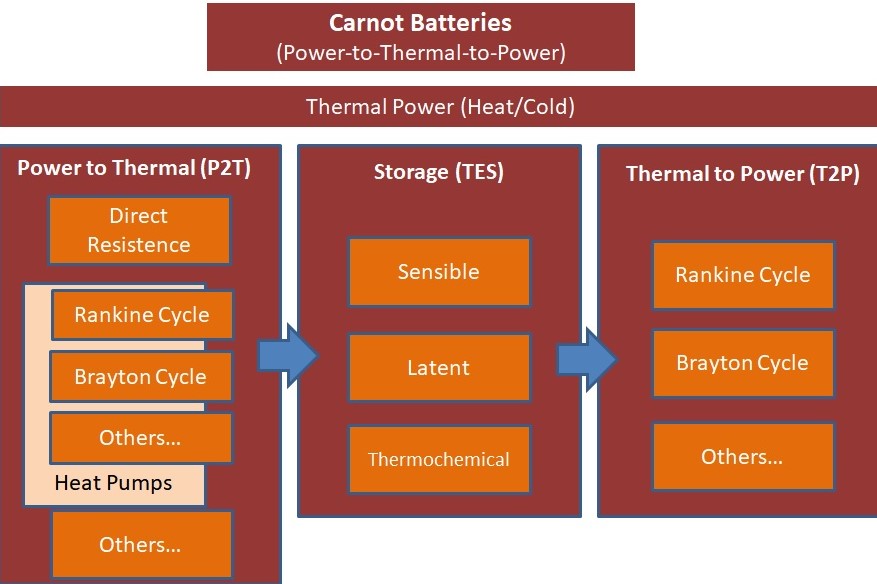 A Carnot battery system can be divided into three parts: Power to Thermal (P2T), Thermal Energy Storage (TES), and Thermal to Power (T2P).
A Carnot battery system can be divided into three parts: Power to Thermal (P2T), Thermal Energy Storage (TES), and Thermal to Power (T2P).
2nd International Workshop on Carnot Batteries, University Stuttgart, September 15-16, 2020
{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201021050040/https://iwcb2020.besl-eventservice.de/ , date=2020-10-21
International Workshop on Carnot Batteries, Stuttgart, Germany, October 9-10, 2018
Energy storage
energy storage
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time to reduce imbalances between energy demand and energy production. A device that stores energy is generally called an Accumulator (energy), accumulator or Batte ...
system that stores electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
in thermal energy storage
Thermal energy storage (TES) is the storage of thermal energy for later reuse. Employing widely different technologies, it allows surplus thermal energy to be stored for hours, days, or months. Scale both of storage and use vary from small t ...
. During the charging process, electricity is converted into heat
In thermodynamics, heat is energy in transfer between a thermodynamic system and its surroundings by such mechanisms as thermal conduction, electromagnetic radiation, and friction, which are microscopic in nature, involving sub-atomic, ato ...
and kept in heat storage. During the discharging process, the stored heat is converted back into electricity.
Fritz Marguerre patented the concept of this technology 100 years ago, but its development was recently revitalized, given the increased use of renewable energies and the need to increase the total recovered energy delivered from such sources. In this context, Andre Thess coined the term "Carnot battery" in 2018, prior to the first International Workshop on Carnot Batteries.
The term "Carnot battery" is derived from Carnot's theorem, which describes the maximum efficiency of conversion of heat energy into mechanical energy
In physical sciences, mechanical energy is the sum of macroscopic potential and kinetic energies. The principle of conservation of mechanical energy states that if an isolated system is subject only to conservative forces, then the mechanical ...
. The word "battery" indicates that the purpose of this technology is to store electricity. The discharge efficiency of Carnot batteries is limited by the Carnot efficiency
A Carnot cycle is an ideal thermodynamic cycle proposed by French physicist Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot, Sadi Carnot in 1824 and expanded upon by others in the 1830s and 1840s. By Carnot's theorem (thermodynamics), Carnot's theorem, it provides ...
. The concept of Carnot batteries covers technologies such as pumped thermal energy storage and liquid air energy storage.
Background
In the transition to low-carbon energy systems, the penetration ofvariable renewable energy
Variable renewable energy (VRE) or intermittent renewable energy sources (IRES) are renewable energy sources that are not dispatchable due to their fluctuating nature, such as wind power and solar power, as opposed to controllable renewable ener ...
in electrical energy systems increases, and this also increases the need for energy storage
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time to reduce imbalances between energy demand and energy production. A device that stores energy is generally called an Accumulator (energy), accumulator or Batte ...
. Currently, most of the new installed energy storage capacity comes from electrochemical batteries, such as lithium-ion batteries. This type of battery is suitable for short-term storage but may not be economical for longer durations due to its high energy capacity costs.
Thermal energy storage can store energy in inexpensive materials, such as water, rocks, and salts. Therefore, the cost for large-scale systems (e.g. gigawatt hours) can be lower than the cost of electrochemical batteries.
The German Aerospace Center (DLR) and University of Stuttgart
The University of Stuttgart () is a research university located in Stuttgart, Germany. It was founded in 1829 and is organized into 10 faculties. It is one of the oldest technical universities in Germany with programs in civil, mechanical, ind ...
have been working on the concept of Carnot batteries that store electricity in high-temperature heat storage since 2014.
In 2018, the name "Carnot battery" was used at the Hannover Messe, one of the world's largest trade fairs, by DLR.
System configuration
 A Carnot battery system can be divided into three parts: Power to Thermal (P2T), Thermal Energy Storage (TES), and Thermal to Power (T2P).
A Carnot battery system can be divided into three parts: Power to Thermal (P2T), Thermal Energy Storage (TES), and Thermal to Power (T2P).
Electricity to heat technology
Electricity can be converted into heat through the use of various technologies. *Resistive heating
Joule heating (also known as resistive heating, resistance heating, or Ohmic heating) is the process by which the passage of an electric current through a conductor produces heat.
Joule's first law (also just Joule's law), also known in countr ...
* Heat pump
A heat pump is a device that uses electricity to transfer heat from a colder place to a warmer place. Specifically, the heat pump transfers thermal energy using a heat pump and refrigeration cycle, cooling the cool space and warming the warm s ...
s as the technology to pump heat from a lower temperature reservoir to a higher temperature. It can be divided into two groups: the reverse Rankine cycle
The Rankine cycle is an idealized thermodynamic cycle describing the process by which certain heat engines, such as steam turbines or reciprocating steam engines, allow mechanical work to be extracted from a fluid as it moves between a heat sour ...
and the reverse Brayton cycle
The Brayton cycle, also known as the Joule cycle, is a thermodynamic cycle that describes the operation of certain heat engines that have air or some other gas as their working fluid.
It is characterized by isentropic process, isentropic compre ...
.
** The reverse Rankine cycle has been widely used in conventional heat pumps.
** The concept of using the Brayton cycle for charging and discharging thermal energy was proposed by Prof. Robert B. Laughlin
Robert Betts Laughlin (born November 1, 1950) is the Anne T. and Robert M. Bass Professor of Physics and Applied Physics at Stanford University. Along with Horst L. Störmer of Columbia University and Daniel C. Tsui of Princeton Universi ...
in 2017.
* Others: In liquid air energy storage systems, the Claude Cycle is used to liquify air. The Lamm–Honigmann process uses thermochemical cycles to convert power to heat.
Thermal energy storage
According to the mechanism to store heat, thermal energy storage can be divided into three types:sensible heat
Sensible heat is heat exchanged by a body or thermodynamic system in which the exchange of heat changes the temperature of the body or system, and some macroscopic variables of the body or system, but leaves unchanged certain other macroscopic vari ...
storage, latent heat
Latent heat (also known as latent energy or heat of transformation) is energy released or absorbed, by a body or a thermodynamic system, during a constant-temperature process—usually a first-order phase transition, like melting or condensation. ...
storage, and thermochemical storage. The storage materials that have been used for Carnot batteries are:
* Hot water
* Molten salt
Molten salt is salt which is solid at standard temperature and pressure but liquified due to elevated temperature. A salt that is liquid even at standard temperature and pressure is usually called a room-temperature ionic liquid, and molten salts ...
* Packed-bed rock
Rock most often refers to:
* Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids
* Rock music, a genre of popular music
Rock or Rocks may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wale ...
s
* Liquid air
Liquid Air was the marque of an automobile planned by Liquid Air Power and Automobile Co. of Boston and New York City in 1899. page 1432
A factory location was acquired in Boston, Massachusetts in 1899 and Liquid Air claimed they would constr ...
* Latent heat thermal energy storage
* Thermochemical materials (pairs of chemicals), such as LiBr/H2O and H2O/NH3
Heat to electricity
Heat can be converted into power through thermodynamic cycles, such as the Rankine cycle or Brayton cycle. Some technologies use the property of semiconductor materials to convert heat into electricity, and those are not considered a Carnot battery because there are no thermodynamic cycles involved in the conversion process, such as thermoelectric materials and the "Sun in a box". The typical technologies are: *Heat engine
A heat engine is a system that transfers thermal energy to do mechanical or electrical work. While originally conceived in the context of mechanical energy, the concept of the heat engine has been applied to various other kinds of energy, pa ...
s
* Steam turbine
A steam turbine or steam turbine engine is a machine or heat engine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work utilising a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Sir Charles Par ...
s
* Gas turbine
A gas turbine or gas turbine engine is a type of Internal combustion engine#Continuous combustion, continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part (known as the gas gene ...
s
* Organic Rankine cycle
In thermal engineering, the organic Rankine cycle (ORC) is a type of thermodynamic cycle. It is a variation of the Rankine cycle named for its use of an organic, high- molecular-mass fluid (compared to water) whose vaporization temperature is l ...
machines
* Lamm-Honigmann process
The Lamm-Honigmann process is a storage and heat to power conversion process that consists of using the effect of vapor pressure depression of a working fluid mixture compared to a pure working fluid of that mixture. This process is named after ...
can convert the stored energy in thermochemical storage into electricity.
These elements can be combined in many ways. An analysis of the combinations found an optimal design with 57% efficiency and an levelized cost of storage (LCOS) of €0.649 ($0.73)/kWh. Efficiency up to 81% is possible.
Advantages and disadvantages
The Carnot battery is known by several other names such as Pumped Thermal Electricity Storage (PTES) or Pumped Heat Electricity Storage (PHES). This relatively new technology has become one of the most promising large-scale energy storage technologies. The main advantages of the Carnot battery are: * Free choice of site; * Small environmental footprint; * Life expectancies of 20–30 years; * Optional low-cost backup capacity; * The components of an underutilized fossil-fueled power plant can be partially reused to build the Carnot batteries unit; The major drawback of this technology is: *The limited roundtrip efficiency 𝜂𝑟𝑜𝑢𝑛𝑑, which relates the electricity 𝑾𝒅𝒊𝒔 delivered during discharge to the electricity 𝑾𝒄𝒉𝒂𝒓 needed to charge the system. Carnot batteries generally aim for a 40-70% efficiency range, significantly lower thanpumped-storage hydroelectricity
Pumped-storage hydroelectricity (PSH), or pumped hydroelectric energy storage (PHES), is a type of hydroelectric energy storage used by electric power systems for load balancing (electrical power), load balancing.
A PSH system stores energy i ...
(65-85%).
Application
Carnot batteries can be used asgrid energy storage
Grid energy storage, also known as large-scale energy storage, are technologies connected to the electrical power grid that store energy for later use. These systems help balance supply and demand by storing excess electricity from variabl ...
to store excess power from variable renewable energy sources and to produce electricity when needed.
Some Carnot battery systems can use the stored heat or cold for other applications, such as district heating
District heating (also known as heat networks) is a system for distributing heat generated in a centralized location through a system of insulated pipes for residential and commercial heating requirements such as space heater, space heating and w ...
and cooling
Cooling is removal of heat, usually resulting in a lower temperature and/or Phase transition, phase change. Temperature lowering achieved by any other means may also be called cooling.
The Heat transfer, transfer of Internal energy, thermal energ ...
for data centers
A data center is a building, a dedicated space within a building, or a group of buildings used to house computer, computer systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and computer data storage, storage systems.
Since IT opera ...
.
Carnot batteries have been proposed as a solution to convert existing coal-fired power plants
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is a type of ...
into a fossil fuel
A fossil fuel is a flammable carbon compound- or hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the buried remains of prehistoric organisms (animals, plants or microplanktons), a process that occurs within geolog ...
-free generation system by replacing the coal fueled boiler. The existing facilities in power plants such as power generation systems and transmission systems can be used.
List of Carnot battery projects
Although the term ''Carnot battery'' is new, many existing technologies can be classified as Carnot batteries. * Liquid air energy storage: Highview Power,University of Birmingham
The University of Birmingham (informally Birmingham University) is a Public university, public research university in Birmingham, England. It received its royal charter in 1900 as a successor to Queen's College, Birmingham (founded in 1825 as ...
* Pumped thermal energy storage: Malta Inc., University of Durham
Durham University (legally the University of Durham) is a collegiate public research university in Durham, England, founded by an Act of Parliament in 1832 and incorporated by royal charter in 1837. It was the first recognised university to ...
* Electric thermal energy storage: Siemens Gamesa
Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy, S.A. was formed in 2017 in a merger of Siemens AG, Siemens' Wind Power division with Gamesa Corporación Tecnológica, S.A.; it is a Spanish-German wind engineering company based in Zamudio, Biscay, Spain. The co ...
, National Renewable Energy Laboratory
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) in the US specializes in the research and development of renewable energy, energy efficiency, energy systems integration, and sustainable transportation. NREL is a federally funded research and ...
* Reversible heat pump / ORC: University of Liège
The University of Liège (), or ULiège, is a major public university of the French Community of Belgium founded in 1817 and based in Liège, Wallonia, Belgium. Its official language is French (language), French.
History
The university was foun ...
* Lamm-Honigmann energy storage: Technische Universität Berlin
(TU Berlin; also known as Berlin Institute of Technology and Technical University of Berlin, although officially the name should not be translated) is a public university, public research university located in Berlin, Germany. It was the first ...
* Carnot battery research: Czech Technical University in Prague
Czech Technical University in Prague (CTU) () is one of the largest universities in the Czech Republic with 8 faculties, and is one of the oldest institutes of technology in Central Europe. It is also the oldest non-military technical universi ...
- UCEEB
See also
*Energy storage
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time to reduce imbalances between energy demand and energy production. A device that stores energy is generally called an Accumulator (energy), accumulator or Batte ...
* Grid energy storage
Grid energy storage, also known as large-scale energy storage, are technologies connected to the electrical power grid that store energy for later use. These systems help balance supply and demand by storing excess electricity from variabl ...
* Thermal energy storage
Thermal energy storage (TES) is the storage of thermal energy for later reuse. Employing widely different technologies, it allows surplus thermal energy to be stored for hours, days, or months. Scale both of storage and use vary from small t ...
References
External links
2nd International Workshop on Carnot Batteries, University Stuttgart, September 15-16, 2020
{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201021050040/https://iwcb2020.besl-eventservice.de/ , date=2020-10-21
International Workshop on Carnot Batteries, Stuttgart, Germany, October 9-10, 2018
Energy storage