Carbon fixation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Biological carbon fixation, or сarbon assimilation, is the
Biological carbon fixation, or сarbon assimilation, is the
ecosystem dynamics
climate regulation, and the sustainability of life on Earth. Organisms that grow by fixing carbon, such as most
 The primary form of fixed inorganic carbon is carbon dioxide (CO2). It is estimated that approximately 250 billion tons of carbon dioxide are converted by photosynthesis annually, nearly one half in the oceans and a bit more in terrestrial environments. The majority of the fixation in terrestrial environments occurs in the tropics. The gross amount of carbon dioxide fixed is much larger since approximately 40% is consumed by respiration following photosynthesis. Historically, it is estimated that approximately 2×1011 billion tons of carbon has been fixed since the origin of life.
The primary form of fixed inorganic carbon is carbon dioxide (CO2). It is estimated that approximately 250 billion tons of carbon dioxide are converted by photosynthesis annually, nearly one half in the oceans and a bit more in terrestrial environments. The majority of the fixation in terrestrial environments occurs in the tropics. The gross amount of carbon dioxide fixed is much larger since approximately 40% is consumed by respiration following photosynthesis. Historically, it is estimated that approximately 2×1011 billion tons of carbon has been fixed since the origin of life.
 The organisms the Calvin cycle is found in are plants, algae,
The organisms the Calvin cycle is found in are plants, algae,

Formulas for triose and TP are C2H3O2-CH2OH and C2H3O2-CH2OPO32− + 2 H+.
 The first cycle is a way of synthesis of glyoxylate. During this cycle, two equivalents of
The first cycle is a way of synthesis of glyoxylate. During this cycle, two equivalents of  In the second cycle, glyoxylate is approximately one equivalent of propionyl-CoA forming methylamalonyl-CoA. This, in turn, is then converted through a series of reactions into citramalyl-CoA. The citramalyl-CoA is split into pyruvate and acetyl-CoA thanks to the enzyme MMC lyase. The pyruvate is released at this point, while the acetyl-CoA is reused and carboxylated again at malonyl-CoA, thus reconstituting the cycle.
A total of 19 reactions are involved in the 3-hydroxypropionate bicycle, and 13 multifunctional enzymes are used. The multi-functionality of these enzymes is an important feature of this pathway which thus allows the fixation of three bicarbonate molecules.
It is a costly pathway: 7 ATP molecules are consumed to synthesise the new pyruvate and 3 ATP for the phosphate triose.
An important characteristic of this cycle is that it allows the co-assimilation of numerous compounds, making it suitable for the mixotrophic organisms.
In the second cycle, glyoxylate is approximately one equivalent of propionyl-CoA forming methylamalonyl-CoA. This, in turn, is then converted through a series of reactions into citramalyl-CoA. The citramalyl-CoA is split into pyruvate and acetyl-CoA thanks to the enzyme MMC lyase. The pyruvate is released at this point, while the acetyl-CoA is reused and carboxylated again at malonyl-CoA, thus reconstituting the cycle.
A total of 19 reactions are involved in the 3-hydroxypropionate bicycle, and 13 multifunctional enzymes are used. The multi-functionality of these enzymes is an important feature of this pathway which thus allows the fixation of three bicarbonate molecules.
It is a costly pathway: 7 ATP molecules are consumed to synthesise the new pyruvate and 3 ATP for the phosphate triose.
An important characteristic of this cycle is that it allows the co-assimilation of numerous compounds, making it suitable for the mixotrophic organisms.
/ref> These substances help bind together soil particles,Soil Science Society of America (SSSA). Physical Properties of Soil – Soil Texture
/ref> forming aggregates that protect organic carbon from microbial decomposition and physical
 Biological carbon fixation, or сarbon assimilation, is the
Biological carbon fixation, or сarbon assimilation, is the process
A process is a series or set of activities that interact to produce a result; it may occur once-only or be recurrent or periodic.
Things called a process include:
Business and management
* Business process, activities that produce a specific s ...
by which living organisms convert inorganic carbon (particularly carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
, ) to organic compounds
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-co ...
. These organic compounds are then used to store energy
Energy () is the physical quantity, quantitative physical property, property that is transferred to a physical body, body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of Work (thermodynamics), work and in the form of heat and l ...
and as structures for other biomolecules
A biomolecule or biological molecule is loosely defined as a molecule produced by a living organism and essential to one or more typically biological processes. Biomolecules include large macromolecules such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipi ...
. Carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
is primarily fixed through photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabo ...
, but some organisms use chemosynthesis in the absence of sunlight
Sunlight is the portion of the electromagnetic radiation which is emitted by the Sun (i.e. solar radiation) and received by the Earth, in particular the visible spectrum, visible light perceptible to the human eye as well as invisible infrare ...
. Chemosynthesis is carbon fixation driven by chemical energy rather than from sunlight.
The process of biological carbon fixation plays a crucial role in the global carbon cycle
The carbon cycle is a part of the biogeochemical cycle where carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of Earth. Other major biogeochemical cycles include the nitrogen cycle and the water cycl ...
, as it serves as the primary mechanism for removing from the atmosphere and incorporating it into living biomass. The primary production
In ecology, primary production is the synthesis of organic compounds from atmospheric or aqueous carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through ...
of organic compounds allows carbon to enter the biosphere
The biosphere (), also called the ecosphere (), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be termed the zone of life on the Earth. The biosphere (which is technically a spherical shell) is virtually a closed system with regard to mat ...
. Carbon is considered essential for life as a base element for building organic compounds. The flow of carbon from the Earth's atmosphere, oceans and lithosphere into lifeforms and then back into the air, water and soil is one of the key biogeochemical cycles (or nutrient cycles). Understanding biological carbon fixation is essential for comprehendinecosystem dynamics
climate regulation, and the sustainability of life on Earth. Organisms that grow by fixing carbon, such as most
plants
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria to produce sugars f ...
and algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthesis, photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular ...
, are called autotrophs. These include photoautotrophs (which use sunlight) and lithoautotrophs (which use inorganic oxidation). Heterotrophs
A heterotroph (; ) is an organism that cannot produce its own food, instead taking nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter. In the food chain, heterotrophs are primary, secondary and tertiary consumers, but ...
, such as animals
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a ...
and fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
, are not capable of carbon fixation but are able to grow by consuming the carbon fixed by autotrophs or other heterotrophs.
Seven natural autotrophic carbon fixation pathways are currently known. They are the: i) Calvin-Benson-Bassham (Calvin Cycle), ii) Reverse Krebs (rTCA) cycle, iii) the reductive acetyl-CoA (Wood-Ljungdahl pathway), iv) 3-hydroxy propionate -HPbicycle, v) 3-hydroypropionate/4- hydroxybutyrate (3-HP/4-HB) cycle, vi) the dicarboxylate/ 4-hydroxybutyrate (DC/4-HB) cycle, and vii) the reductive glycine (rGly) pathway. "Fixed carbon," "reduced carbon," and "organic carbon" may all be used interchangeably to refer to various organic compounds.
Net vs. gross CO2 fixation
 The primary form of fixed inorganic carbon is carbon dioxide (CO2). It is estimated that approximately 250 billion tons of carbon dioxide are converted by photosynthesis annually, nearly one half in the oceans and a bit more in terrestrial environments. The majority of the fixation in terrestrial environments occurs in the tropics. The gross amount of carbon dioxide fixed is much larger since approximately 40% is consumed by respiration following photosynthesis. Historically, it is estimated that approximately 2×1011 billion tons of carbon has been fixed since the origin of life.
The primary form of fixed inorganic carbon is carbon dioxide (CO2). It is estimated that approximately 250 billion tons of carbon dioxide are converted by photosynthesis annually, nearly one half in the oceans and a bit more in terrestrial environments. The majority of the fixation in terrestrial environments occurs in the tropics. The gross amount of carbon dioxide fixed is much larger since approximately 40% is consumed by respiration following photosynthesis. Historically, it is estimated that approximately 2×1011 billion tons of carbon has been fixed since the origin of life.
Overview of the carbon fixation cycles
Seven autotrophic carbon fixation pathways are known: the Calvin Cycle, the Reverse Krebs Cycle, the reductive acetyl-CoA, the 3-HP bicycle, the 3-HP/4-HB cycle, the DC/4-HB cycles, and the reductive glycine pathway. The organisms the Calvin cycle is found in are plants, algae,
The organisms the Calvin cycle is found in are plants, algae, cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria ( ) are a group of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological energy via oxygenic photosynthesis. The name "cyanobacteria" () refers to their bluish green (cyan) color, which forms the basis of cyanobacteri ...
, aerobic proteobacteria, and purple bacteria. The Calvin cycle fixes carbon in the chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle, organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant cell, plant and algae, algal cells. Chloroplasts have a high concentration of chlorophyll pigments which captur ...
s of plants and algae, and in the cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria ( ) are a group of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological energy via oxygenic photosynthesis. The name "cyanobacteria" () refers to their bluish green (cyan) color, which forms the basis of cyanobacteri ...
. It also fixes carbon in the anoxygenic photosynthesis in one type of Pseudomonadota
Pseudomonadota (synonym "Proteobacteria") is a major phylum of gram-negative bacteria. Currently, they are considered the predominant phylum within the domain of bacteria. They are naturally found as pathogenic and free-living (non- parasitic) ...
called purple bacteria, and in some non-phototrophic Pseudomonadota.
Of the other autotrophic pathways, three are known only in bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
(the reductive citric acid cycle, the 3-hydroxypropionate cycle, and the reductive glycine pathway), two only in archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
(two variants of the 3-hydroxypropionate cycle), and one in both bacteria and archaea (the reductive acetyl CoA pathway). Sulfur- and hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria often use the Calvin cycle or the reductive citric acid cycle.
List of pathways
Calvin cycle
The Calvin cycle accounts for 90% of biological carbon fixation. Consumingadenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleoside triphosphate that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cell (biology), cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known ...
(ATP) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH), the Calvin cycle in plants accounts for the predominance of carbon fixation on land. In algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthesis, photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular ...
and cyanobacteria, it accounts for the dominance of carbon fixation in the oceans. The Calvin cycle converts carbon dioxide into sugar, as triose phosphate (TP), which is glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (GAP) together with dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP):
: 3 CO2 + 12 e− + 12 H+ + Pi → TP + 4 H2O
An alternative perspective accounts for NADPH (source of e−) and ATP:
: 3 CO2 + 6 NADPH + 6 H+ + 9 ATP + 5 H2O → TP + 6 NADP+ + 9 ADP + 8 Pi
The formula for inorganic phosphate (Pi) is HOPO32− + 2 H+.Formulas for triose and TP are C2H3O2-CH2OH and C2H3O2-CH2OPO32− + 2 H+.

Reverse Krebs cycle
The reverse Krebs cycle, also known as the reverse TCA cycle (rTCA) or reductive citric acid cycle, is an alternative to the standard Calvin-Benson cycle for carbon fixation. It has been found in strict anaerobic or microaerobicbacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
(as '' Aquificales'') and anaerobic archea. It was discovered by Evans, Buchanan and Arnon in 1966 working with the photosynthetic green sulfur bacterium ''Chlorobium limicola''. In particular, it is one of the most used pathways in hydrothermal vents by the Campylobacterota. This feature allows primary production
In ecology, primary production is the synthesis of organic compounds from atmospheric or aqueous carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through ...
in the ocean's aphotic environments, or "dark primary production." Without it, there would be no primary production in aphotic environments, which would lead to habitats without life.
The cycle involves the biosynthesis
Biosynthesis, i.e., chemical synthesis occurring in biological contexts, is a term most often referring to multi-step, enzyme-Catalysis, catalyzed processes where chemical substances absorbed as nutrients (or previously converted through biosynthe ...
of acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA (acetyl coenzyme A) is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidation, o ...
from two molecules of CO2. The key steps of the reverse Krebs cycle are:
* Oxaloacetate to malate
Malic acid is an organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a dicarboxylic acid that is made by all living organisms, contributes to the sour taste of fruits, and is used as a food additive. Malic acid has two stereoisomeric forms ( ...
, using NADH + H+
*:
* Fumarate to succinate, catalyzed by an oxidoreductase, Fumarate reductase
*:
* Succinate to succinyl-CoA, an ATP-dependent step
*:
* Succinyl-CoA to alpha-ketoglutarate, using one molecule of CO2
*:
* Alpha-ketoglutarate to isocitrate, using NADPH + H+ and another molecule of CO2
*:
* Citrate converted into oxaloacetate and acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA (acetyl coenzyme A) is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidation, o ...
, this is an ATP dependent step and the key enzyme is the ATP citrate lyase
*:
This pathway is cyclic due to the regeneration of the oxaloacetate.
The bacteria Gammaproteobacteria and '' Riftia pachyptila'' switch from the Calvin-Benson cycle to the rTCA cycle in response to concentrations of H2S.

Reductive acetyl CoA pathway
The reductive acetyl CoA pathway (CoA) pathway, also known as the Wood-Ljungdahl pathway uses CO2 as electron acceptor and carbon source, and H2 as an electron donor to form acetic acid. This metabolism is widespread within the phylumBacillota
The Bacillota (synonym Firmicutes) are a phylum of bacteria, most of which have Gram-positive cell wall structure. They have round cells, called cocci (singular coccus), or rod-like forms (bacillus). A few Bacillota, such as '' Megasphaera'', ...
, especially in the Clostridia
The Clostridia are a highly polyphyletic class of Bacillota, including '' Clostridium'' and other similar genera. They are distinguished from the Bacilli by lacking aerobic respiration. They are obligate anaerobes and oxygen is toxic to them ...
.
The pathway is also used by methanogen
Methanogens are anaerobic archaea that produce methane as a byproduct of their energy metabolism, i.e., catabolism. Methane production, or methanogenesis, is the only biochemical pathway for Adenosine triphosphate, ATP generation in methanogens. A ...
s, which are mainly Euryarchaeota
Methanobacteriota is a phylum in the domain Archaea.
Taxonomy
The phylum ''Methanobacteriota'' was introduced to prokaryotic nomenclature in 2023. It contains following classes:
*Archaeoglobi Garrity & Holt (2002)
*Halobacteria Grant ''et al ...
, and several anaerobic chemolithoautotrophs, such as sulfate-reducing bacteria and archaea. It is probably performed also by the Brocadiales, an order of Planctomycetota that oxidize ammonia in anaerobic conditions. Hydrogenotrophic methanogenesis, which is only found in certain archaea and accounts for 80% of global methanogenesis, is also based on the reductive acetyl CoA pathway.
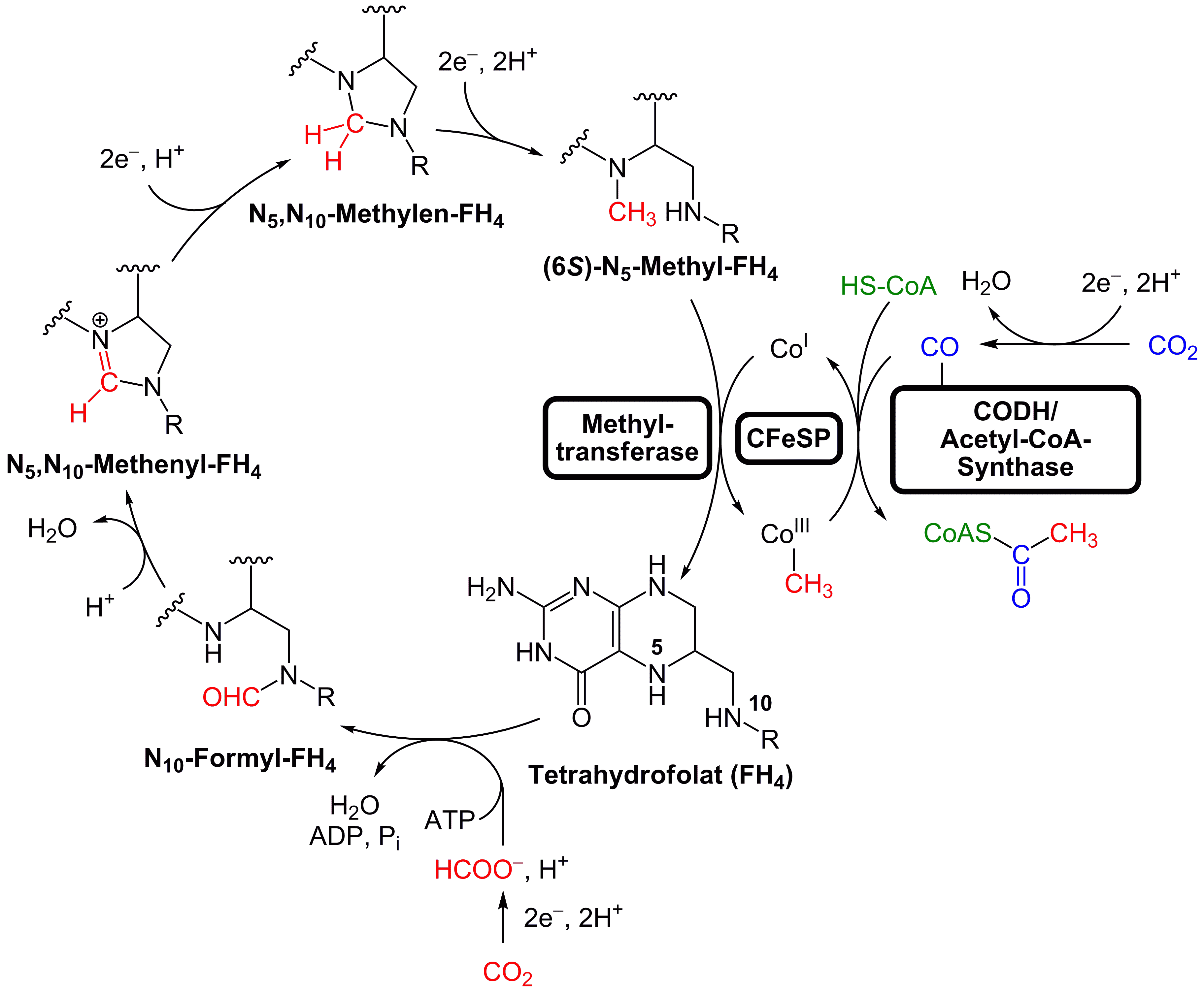
The Carbon Monoxide Dehydrogenase/ Acetyl-CoA Synthase is the oxygen-sensitive enzyme that permits the reduction of CO2 to CO and the synthesis of acetyl-CoA in several reactions.
One branch of this pathway, the methyl branch, is similar but non-homologous between bacteria and archaea. In this branch happens the reduction of CO2 to a methyl residue bound to a cofactor. The intermediates are formate for bacteria and formyl-methanofuran for archaea, and also the carriers, tetrahydrofolate and tetrahydropterins respectively in bacteria and archaea, are different, such as the enzymes forming the cofactor-bound methyl group.
Otherwise, the carbonyl branch is homologous between the two domains and consists of the reduction of another molecule of CO2 to a carbonyl residue bound to an enzyme, catalyzed by the CO dehydrogenase/acetyl-CoA synthase. This key enzyme is also the catalyst for the formation of acetyl-CoA starting from the products of the previous reactions, the methyl and the carbonyl residues.
This carbon fixation pathway requires only one molecule of ATP for the production of one molecule of pyruvate, which makes this process one of the main choice for chemolithoautotrophs limited in energy and living in anaerobic conditions.
3-Hydroxypropionate -HPbicycle
The 3-hydroxypropionate bicycle, also known as 3-HP/malyl-CoA cycle, discovered only in 1989, is utilized by green non-sulfur phototrophs of Chloroflexaceae family, including the maximum exponent of this family '' Chloroflexus auranticus'' by which this way was discovered and demonstrated. The 3-hydroxypropionate bicycle is composed of two cycles, and the name of this way comes from the 3-hydroxypropionate, which corresponds to an intermediate characteristic of it.bicarbonate
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula .
Bicarbonate serves a crucial bioche ...
are fixed by the action of two enzymes: the acetyl-CoA carboxylase catalyzes the carboxylation of the acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA and propionyl-CoA carboxylase catalyses the carboxylation of propionyl-CoA to methylamalonyl-CoA. From this point, a series of reactions lead to the formation of glyoxylate, which will thus become part of the second cycle.
Cycles related to the 3-hydroxypropionate cycle
A variant of the 3-hydroxypropionate cycle was found to operate in the aerobic extreme thermoacidophile archaeon ''Metallosphaera sedula''. This pathway is called the 3-hydroxypropionate/4-hydroxybutyrate (3-HP/4-HB) cycle. Yet another variant of the 3-hydroxypropionate cycle is the dicarboxylate/4-hydroxybutyrate (DC/4-HB) cycle. It was discovered in anaerobic archaea. It was proposed in 2008 for the hyperthermophile archeon ''Ignicoccus hospitalis''.Enoyl-CoA carboxylases/reductases
fixation is catalyzed by enoyl-CoA carboxylases/reductases.Non-autotrophic pathways
Although no heterotrophs use carbon dioxide in biosynthesis, some carbon dioxide is incorporated in their metabolism. Notably pyruvate carboxylase consumes carbon dioxide (as bicarbonate ions) as part ofgluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis (GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the biosynthesis of glucose from certain non-carbohydrate carbon substrates. It is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. In verte ...
, and carbon dioxide is consumed in various anaplerotic reactions.
6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase catalyzes the reductive carboxylation of ribulose 5-phosphate to 6-phosphogluconate in ''E. coli'' under elevated CO2 concentrations.
Carbon isotope discrimination
Some carboxylases, particularly RuBisCO, preferentially bind the lighter carbon stable isotopecarbon-12
Carbon-12 (12C) is the most abundant of the two stable isotopes of carbon ( carbon-13 being the other), amounting to 98.93% of element carbon on Earth; its abundance is due to the triple-alpha process by which it is created in stars. Carbon-1 ...
over the heavier carbon-13
Carbon-13 (13C) is a natural, stable isotope of carbon with a nucleus containing six protons and seven neutrons. As one of the environmental isotopes, it makes up about 1.1% of all natural carbon on Earth.
Detection by mass spectrometry
A m ...
. This is known as carbon isotope discrimination and results in carbon-12 to carbon-13 ratios in the plant that are higher than in the free air. Measurement of this isotopic ratio is important in the evaluation of water use efficiency in plants, and also in assessing the possible or likely sources of carbon in global carbon cycle studies.
Biological carbon fixation in soils
In addition to photosynthetic and chemosynthetic processes, biological carbon fixation occurs in soil through the activity of microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. These soil microbes play a crucial role in the global carbon cycle by sequestering carbon from decomposed organic matter and recycling it back into the soil, thereby contributing to soil fertility and ecosystem productivity. In soil environments, organic matter derived from dead plant and animal material undergoesdecomposition
Decomposition is the process by which dead organic substances are broken down into simpler organic or inorganic matter such as carbon dioxide, water, simple sugars and mineral salts. The process is a part of the nutrient cycle and is ess ...
, a process carried out by a diverse community of microorganisms. During decomposition, complex organic compounds are broken down into simpler molecules by the action of enzymes produced by bacteria, fungi, and other soil organisms. As organic matter is decomposed, carbon is released in various forms, including carbon dioxide () and dissolved organic carbon (DOC).
However, not all the carbon released during decomposition is immediately lost to the atmosphere; a significant portion is retained in the soil through processes collectively known as soil carbon sequestration. Soil microbes, mainly bacteria and fungi, play a pivotal role in this process by incorporating decomposed organic carbon into their biomass or by facilitating the formation of stable organic compounds, such as humus
In classical soil science, humus is the dark organic matter in soil that is formed by the decomposition of plant and animal matter. It is a kind of soil organic matter. It is rich in nutrients and retains moisture in the soil. Humus is the Lati ...
and soil organic matter
Soil organic matter (SOM) is the organic matter component of soil, consisting of plant and animal detritus at various stages of decomposition, cells and tissues of soil microbes, and substances that soil microbes synthesize. SOM provides numerou ...
.
One key mechanism by which soil microbes sequester carbon is through microbial biomass production. Bacteria and fungi assimilate carbon from decomposed organic matter into their cellular structures as they grow and reproduce. This microbial biomass serves as a reservoir for stored carbon in the soil, effectively sequestering carbon from the atmosphere.
Additionally, soil microbes contribute to the formation of stable soil organic matter through the synthesis of extracellular polymers, enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
s, and other biochemical compounds.LibreTexts Biology, 3.4: Biochemical compounds/ref> These substances help bind together soil particles,Soil Science Society of America (SSSA). Physical Properties of Soil – Soil Texture
/ref> forming aggregates that protect organic carbon from microbial decomposition and physical
erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as Surface runoff, water flow or wind) that removes soil, Rock (geology), rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust#Crust, Earth's crust and then sediment transport, tran ...
. Over time, these aggregates accumulate in the soil, forming soil organic matter, which can persist for centuries to millennia.
The sequestration of carbon in soil not only helps mitigate the accumulation of atmospheric and mitigate climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
but also enhances soil fertility, water retention, and nutrient cycling
A nutrient cycle (or ecological recycling) is the movement and exchange of inorganic and organic matter back into the production of matter. Energy flow is a unidirectional and noncyclic pathway, whereas the movement of mineral nutrients is cyc ...
, thereby supporting plant growth and ecosystem productivity. Consequently, understanding the role of soil microbes in biological carbon fixation is essential for managing soil health
Soil health is a state of a soil meeting its range of ecosystem functions as appropriate to its environment. In more colloquial terms, the health of soil arises from favorable interactions of all soil components (living and non-living) that belong ...
, mitigating climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
, and promoting sustainable land management practices.
Biological carbon fixation is a fundamental process that sustains life on Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
by regulating atmospheric levels, supporting the growth of plants and other photosynthetic organisms, and maintaining ecological balance.
See also
* Blue carbon *Nitrogen fixation
Nitrogen fixation is a chemical process by which molecular dinitrogen () is converted into ammonia (). It occurs both biologically and abiological nitrogen fixation, abiologically in chemical industry, chemical industries. Biological nitrogen ...
* Oxygen cycle
* Biogeochemical cycles
References
Further reading
* * * * * * {{MetabolismMap Photosynthesis Carbon Metabolic pathways Atmospheric chemistry Microbiology