|
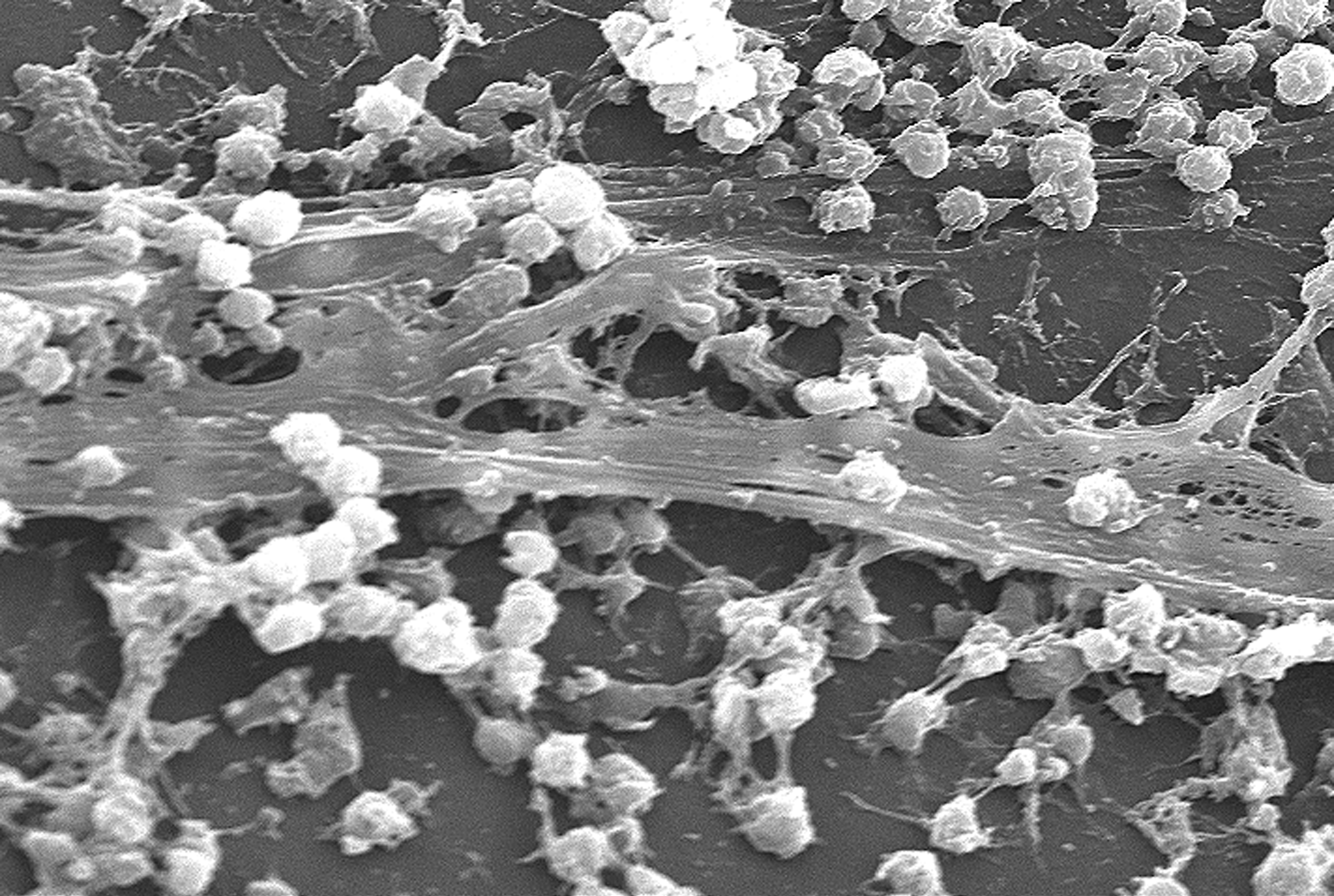
Extracellular Polymeric Substance
Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) are biopolymer, natural polymers of molecular mass, high molecular weight secreted by microorganisms into their environment. EPS establish the functional and structural integrity of biofilms, and are considered the fundamental component that determines the physicochemical properties of a biofilm. EPS in the matrix of biofilms provides compositional support and protection of microbial communities from the harsh environments. Components of EPS can be of different classes of polysaccharides, lipids, nucleic acids, proteins, lipopolysaccharides, and minerals. Components EPS are mostly composed of polysaccharides (exopolysaccharides) and proteins, but include other macromolecules such as DNA, lipids and Humic acid, humic substances. EPS are the construction material of bacterial settlements and either remain attached to the cell's outer surface, or are secreted into its growth medium. These compounds are important in biofilm formation and cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
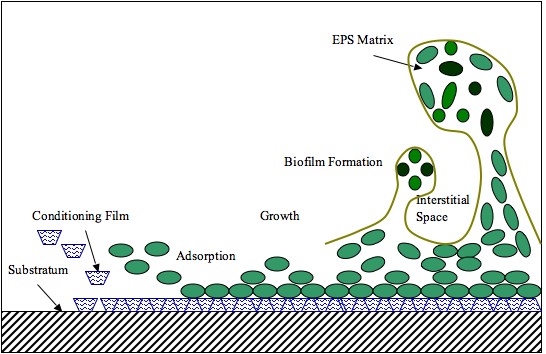
Biofilm Formation
A biofilm is a syntrophic community of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs). The cells within the biofilm produce the EPS components, which are typically a polymeric combination of extracellular polysaccharides, proteins, lipids and DNA. Because they have a three-dimensional structure and represent a community lifestyle for microorganisms, they have been metaphorically described as "cities for microbes". Biofilms may form on living (biotic) or non-living (abiotic) surfaces and can be common in natural, industrial, and hospital settings. They may constitute a microbiome or be a portion of it. The microbial cells growing in a biofilm are physiologically distinct from planktonic cells of the same organism, which, by contrast, are single cells that may float or swim in a liquid medium. Biofilms ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyruvate
Pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) is the simplest of the alpha-keto acids, with a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group. Pyruvate, the conjugate base, CH3COCOO−, is an intermediate in several metabolic pathways throughout the cell. Pyruvic acid can be made from glucose through glycolysis, converted back to carbohydrates (such as glucose) via gluconeogenesis, or converted to fatty acids through a reaction with acetyl-CoA. It can also be used to construct the amino acid alanine and can be converted into ethanol or lactic acid via fermentation. Pyruvic acid supplies energy to cells through the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle) when oxygen is present ( aerobic respiration), and alternatively ferments to produce lactate when oxygen is lacking. Chemistry In 1834, Théophile-Jules Pelouze distilled tartaric acid and isolated glutaric acid and another unknown organic acid. Jöns Jacob Berzelius characterized this other acid the following year and na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xylose
Xylose ( , , "wood") is a sugar first isolated from wood, and named for it. Xylose is classified as a monosaccharide of the aldopentose type, which means that it contains five carbon atoms and includes an aldehyde functional group. It is derived from hemicellulose, one of the main constituents of biomass. Like most sugars, it can adopt several structures depending on conditions. With its free aldehyde group, it is a reducing sugar. Structure The acyclic form of xylose has chemical formula . The cyclic hemiacetal isomers are more prevalent in solution and are of two types: the pyranoses, which feature six-membered rings, and the furanoses, which feature five-membered rings (with a pendant group). Each of these rings is subject to further isomerism, depending on the relative orientation of the anomeric hydroxy group. The dextrorotary form, -xylose, is the one that usually occurs endogenously in living things. A levorotary form, -xylose, can be synthesized. Occurren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. It is used by plants to make cellulose, the most abundant carbohydrate in the world, for use in cell walls, and by all living Organism, organisms to make adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used by the cell as energy. In energy metabolism, glucose is the most important source of energy in all organisms. Glucose for metabolism is stored as a polymer, in plants mainly as amylose and amylopectin, and in animals as glycogen. Glucose circulates in the blood of animals as blood sugar. The naturally occurring form is -glucose, while its Stereoisomerism, stereoisomer L-glucose, -glucose is produced synthetically in comparatively small amounts and is less biologicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactose
Galactose (, ''wikt:galacto-, galacto-'' + ''wikt:-ose#Suffix 2, -ose'', ), sometimes abbreviated Gal, is a monosaccharide sugar that is about as sweetness, sweet as glucose, and about 65% as sweet as sucrose. It is an aldohexose and a C-4 epimer of glucose. A galactose molecule linked with a glucose molecule forms a lactose molecule. Galactan is a polymeric form of galactose found in hemicellulose, and forming the core of the galactans, a class of natural polymeric carbohydrates. D-Galactose is also known as brain sugar since it is a component of glycoproteins (oligosaccharide-protein compounds) found in Nerve tissue, nerve tissue. Etymology The word ''galactose'' was coined by Charles Weissman in the mid-19th century and is derived from Greek language, Greek , , and the generic chemical suffix for sugars ''-ose''. The etymology is comparable to that of the word ''lactose'' in that both contain roots meaning "milk sugar". Lactose is a disaccharide of galactose plus glucose. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomineralization
Biomineralization, also written biomineralisation, is the process by which living organisms produce minerals, often resulting in hardened or stiffened '' mineralized tissues''. It is an extremely widespread phenomenon: all six taxonomic kingdoms contain members that can form minerals, and over 60 different minerals have been identified in organisms. Examples include silicates in algae and diatoms, carbonates in invertebrates, and calcium phosphates and carbonates in vertebrates. These minerals often form structural features such as sea shells and the bone in mammals and birds. Organisms have been producing mineralized skeletons for the past 550 million years. Calcium carbonates and calcium phosphates are usually crystalline, but silica organisms (such as sponges and diatoms) are always non-crystalline minerals. Other examples include copper, iron, and gold deposits involving bacteria. Biologically formed minerals often have special uses such as magnetic sensors in magnetota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticancer
An anticarcinogen (also known as a carcinopreventive agent) is a substance that counteracts the effects of a carcinogen or inhibits the development of cancer. Anticarcinogens are different from anticarcinoma agents (also known as anticancer or anti-neoplastic agents) in that anticarcinoma agents are used to selectively destroy or inhibit cancer cells ''after'' cancer has developed. Interest in anticarcinogens is motivated primarily by the principle that it is preferable to prevent disease ( preventive medicine) than to have to treat it ( rescue medicine). In theory, anticarcinogens may act via different mechanisms including enhancement of natural defences against cancer, deactivation of carcinogens, and blocking the mechanisms by which carcinogens act (such as free radical damage to DNA). Confirmation that a substance possesses anticarcinogenic activity requires extensive ''in vitro'', '' in vivo'', and clinical investigation. Health claims for anticarcinogens are regulated b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibacterial
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of such infections. They may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the ones which cause the common cold or influenza. Drugs which inhibit growth of viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals. Antibiotics are also not effective against fungi. Drugs which inhibit growth of fungi are called antifungal drugs. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thickening Agent
A thickening agent or thickener is a substance which can increase the viscosity of a liquid without substantially changing its other properties. Edible thickeners are commonly used to thicken sauces, soups, and puddings without altering their taste; thickeners are also used in paints, inks, explosives, and cosmetics. Thickeners may also improve the suspension of other ingredients or emulsions which increases the stability of the product. Thickening agents are often regulated as food additives and as cosmetics and personal hygiene product ingredients. Some thickening agents are gelling agents (gellants), forming a gel, dissolving in the liquid phase as a colloid mixture that forms a weakly cohesive internal structure. Others act as mechanical thixotropic additives with discrete particles adhering or interlocking to resist strain. Thickening agents can also be used when a medical condition such as dysphagia causes difficulty in swallowing. Some of these people may benefit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria ( ) are a group of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological energy via oxygenic photosynthesis. The name "cyanobacteria" () refers to their bluish green (cyan) color, which forms the basis of cyanobacteria's informal common name, blue-green algae. Cyanobacteria are probably the most numerous taxon to have ever existed on Earth and the first organisms known to have produced oxygen, having appeared in the middle Archean eon and apparently originated in a freshwater or terrestrial environment. Their photopigments can absorb the red- and blue-spectrum frequencies of sunlight (thus reflecting a greenish color) to split water molecules into hydrogen ions and oxygen. The hydrogen ions are used to react with carbon dioxide to produce complex organic compounds such as carbohydrates (a process known as carbon fixation), and the oxygen is released as a byproduct. By continuously producing and releasing oxygen over billions of years, cyanobacte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Algae
Red algae, or Rhodophyta (, ; ), make up one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta comprises one of the largest Phylum, phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 recognized species within over 900 Genus, genera amidst ongoing taxonomic revisions. The majority of species (6,793) are Florideophyceae, and mostly consist of multicellular, ocean, marine algae, including many notable seaweeds. Red algae are abundant in marine habitats. Approximately 5% of red algae species occur in freshwater environments, with greater concentrations in warmer areas. Except for two coastal cave dwelling species in the asexual class Cyanidiophyceae, no terrestrial species exist, which may be due to an evolutionary bottleneck in which the last common ancestor lost about 25% of its core genes and much of its evolutionary plasticity. Red algae form a distinct group characterized by eukaryotic cells without flagella and centrioles, chloroplasts without external endoplasmic reticulum or unstack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Wall
A cell wall is a structural layer that surrounds some Cell type, cell types, found immediately outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. Primarily, it provides the cell with structural support, shape, protection, and functions as a selective barrier. Another vital role of the cell wall is to help the cell withstand osmotic pressure and mechanical stress. While absent in many eukaryotes, including animals, cell walls are prevalent in other organisms such as fungi, algae and plants, and are commonly found in most Prokaryote, prokaryotes, with the exception of Mollicutes, mollicute bacteria. The composition of cell walls varies across taxonomic groups, species, cell type, and the cell cycle. In Embryophyte, land plants, the primary cell wall comprises Polysaccharide, polysaccharides like cellulose, hemicelluloses, and pectin. Often, other Polymer, polymers such as lignin, suberin or cutin are anchored to or embedded in plant cell walls. Algae exhibit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |