Calluses on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
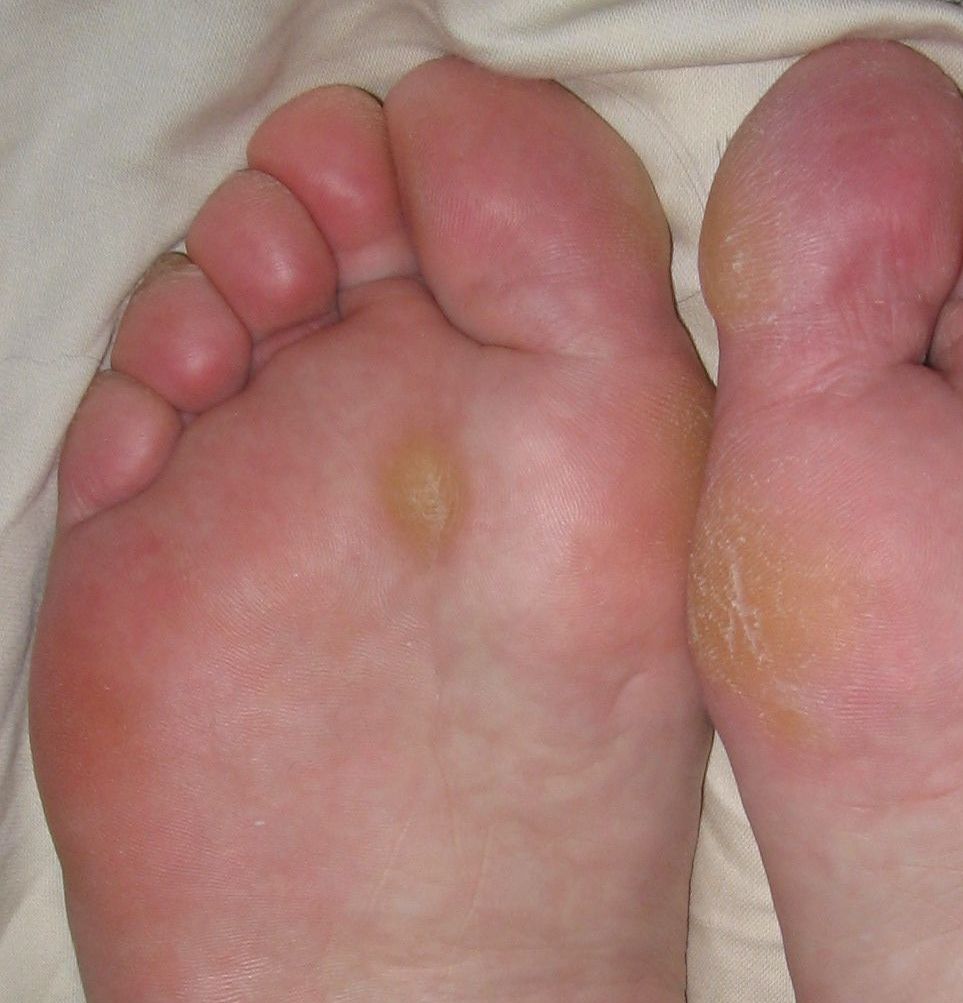 A callus (: calluses) is an area of thickened and sometimes hardened skin that forms as a response to repeated friction, pressure, or other irritation. Since repeated contact is required, calluses are most often found on the feet and hands, but they may occur anywhere on the skin. Some degree of callus, such as on the bottom of the foot, is normal.
Calluses are generally not harmful and help prevent
A callus (: calluses) is an area of thickened and sometimes hardened skin that forms as a response to repeated friction, pressure, or other irritation. Since repeated contact is required, calluses are most often found on the feet and hands, but they may occur anywhere on the skin. Some degree of callus, such as on the bottom of the foot, is normal.
Calluses are generally not harmful and help prevent
 Calluses and corns may heal by themselves eventually, once the irritation is consistently avoided. They may also be dissolved with
Calluses and corns may heal by themselves eventually, once the irritation is consistently avoided. They may also be dissolved with
 A callus (: calluses) is an area of thickened and sometimes hardened skin that forms as a response to repeated friction, pressure, or other irritation. Since repeated contact is required, calluses are most often found on the feet and hands, but they may occur anywhere on the skin. Some degree of callus, such as on the bottom of the foot, is normal.
Calluses are generally not harmful and help prevent
A callus (: calluses) is an area of thickened and sometimes hardened skin that forms as a response to repeated friction, pressure, or other irritation. Since repeated contact is required, calluses are most often found on the feet and hands, but they may occur anywhere on the skin. Some degree of callus, such as on the bottom of the foot, is normal.
Calluses are generally not harmful and help prevent blister
A blister is a small pocket of body fluid (lymph, serum, plasma, blood, or pus) within the upper layers of the skin, usually caused by forceful rubbing (friction), burning, freezing, chemical exposure or infection. Most blisters are filled ...
s, as well as offering protection. However, excessive formation may sometimes lead to other problems, such as a skin ulceration or infection, or cause the affected person to try to offload the affected painful area, which can place excessive stress on the asymptomatic side.
Rubbing that is too frequent or forceful will cause blister
A blister is a small pocket of body fluid (lymph, serum, plasma, blood, or pus) within the upper layers of the skin, usually caused by forceful rubbing (friction), burning, freezing, chemical exposure or infection. Most blisters are filled ...
s, as opposed to calluses, to form.
Cause
Normally, a callus will form on any part of the skin exposed to excess friction over a long period of time. Activities that are known for causing calluses include construction work and craftwork,the arts
The arts or creative arts are a vast range of human practices involving creative expression, storytelling, and cultural participation. The arts encompass diverse and plural modes of thought, deeds, and existence in an extensive range of m ...
, food preparation
{{catexp, articles about specific foodstuffs. See :Food and drink for more general topics relating to food.
Food watchlist articles ...
, many sports
Sport is a physical activity or game, often competitive and organized, that maintains or improves physical ability and skills. Sport may provide enjoyment to participants and entertainment to spectators. The number of participants in ...
and physical activities, and fashion choices like wearing high heels
High-heeled shoes, also known as high heels (colloquially shortened to heels), are a type of shoe with an upward-angled sole. The heel in such shoes is raised above the ball of the foot. High heels cause the legs to appear longer, make the we ...
.
Although calluses can occur anywhere on the body as a reaction to moderate, constant "grinding" pressure, they are most often found on the foot
The foot (: feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is an organ at the terminal part of the leg made up o ...
(where the most pressure and friction are applied). On the feet (arguably the source of the most problematic calluses), they typically form on the metatarsal-phalangeal joint area ("balls of the foot"), heels and small toes due to the compression applied by tightly fitting shoes.
Biologically, calluses are formed by the accumulation of terminally differentiated keratinocyte
Keratinocytes are the primary type of cell found in the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. In humans, they constitute 90% of epidermal skin cells. Basal cells in the basal layer (''stratum basale'') of the skin are sometimes referre ...
s in the outermost layer of skin. Though the cells of calluses are dead, they are quite resistant to mechanical and chemical damage due to extensive networks of cross-linked proteins and hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the chemical property of a molecule (called a hydrophobe) that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water. In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, thu ...
keratin intermediate filaments
Intermediate filaments (IFs) are cytoskeletal structural components found in the cells of vertebrates, and many invertebrates. Homologues of the IF protein have been noted in an invertebrate, the cephalochordate ''Branchiostoma''.
Intermedi ...
containing many disulfide bonds
In chemistry, a disulfide (or disulphide in British English) is a compound containing a functional group or the anion. The linkage is also called an SS-bond or sometimes a disulfide bridge and usually derived from two thiol groups.
In in ...
. It is the natural reaction of the palmar or plantar
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provi ...
skin. Too much friction occurring too fast for the skin to develop a protective callus will cause a blister
A blister is a small pocket of body fluid (lymph, serum, plasma, blood, or pus) within the upper layers of the skin, usually caused by forceful rubbing (friction), burning, freezing, chemical exposure or infection. Most blisters are filled ...
or abrasion instead.
Sometimes a callus occurs where there is no rubbing or pressure. These hyperkeratoses can have a variety of causes. Some toxic materials, such as arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is not ...
, can cause thick palms and soles. Some diseases, such as syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms depend on the stage it presents: primary, secondary, latent syphilis, latent or tertiary. The prim ...
, can cause thickening of the palms and soles as well as pinpoint hyperkeratoses. There is a benign condition called ''keratosis palmaris et plantaris'', which produces corns in the creases of the fingers and non-weight bearing spaces of the feet. Some of this may be caused by actinic keratosis, which occurs due to overexposure to sun or with age and hormonal shifts.
Corns
Acorn
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout Poaceae, grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples of Mexico, indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago ...
(or ''clavus'', plural ''clavi'') is a cone-shaped callus that penetrates into the dermis, usually on the feet or hands. Corns may form due to chronic pressure or rubbing at a pressure point (in this skin over a bone), or due to scar tissue from a healing wound creating pressure in a weight-bearing area such as the sole of the foot. If there is constant stimulation of the tissue producing the corns, even after the corn is surgically removed, the skin may continue to grow as a corn.
The hard part at the center of the corn resembles a funnel with a broad raised top and a pointed bottom. Because of their shape, corns intensify the pressure at the tip and can cause deep tissue damage and ulceration
An ulcer is a discontinuity or break in a bodily membrane that impedes normal function of the affected Organ (biology), organ. According to Robbins's pathology, "ulcer is the breach of the continuity of skin, epithelium or mucous membrane caus ...
. The scientific name for a corn is ''heloma'' (plural ''helomata''). A hard corn is called a ''heloma durum'', while a soft corn is called a ''heloma molle''.
The location of the soft corns tends to differ from that of hard corns. Hard corns occur on dry, flat surfaces of skin. Soft corns (frequently found between adjacent toes) stay moist, keeping the surrounding skin soft. The corn's center is not soft however, but indurated
In materials science, friability ( ), the condition of being friable, describes the tendency of a solid substance to break into smaller pieces under stress or contact, especially by rubbing. The opposite of friable is indurate.
Substances tha ...
.
The specific diagnostic workup and treatments for corns may differ substantially from other forms of calluses.
Prevention
Corns and calluses are easier to prevent than to treat. When it is undesirable to form a callus, minimizing rubbing and pressure will prevent callus formation. Footwear should be properly fitted, gloves may be worn, and protective pads, rings or skin dressings may be used. People with poor circulation or sensation should check their skin often for signs of rubbing and irritation so they can minimize any damage.Treatment
 Calluses and corns may heal by themselves eventually, once the irritation is consistently avoided. They may also be dissolved with
Calluses and corns may heal by themselves eventually, once the irritation is consistently avoided. They may also be dissolved with keratolytic
Keratolytic () therapy is a type of medical treatment to remove warts, calluses and other lesions in which the epidermis produces excess skin. In this therapy, acidic topical medicines, such as Whitfield's ointment or Jessner's solution, are a ...
agents containing salicylic acid
Salicylic acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H4COOH. A colorless (or white), bitter-tasting solid, it is a precursor to and a active metabolite, metabolite of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin). It is a plant hormone, and has been lis ...
, sanded down with a pumice
Pumice (), called pumicite in its powdered or dust form, is a volcanic rock that consists of extremely vesicular rough-textured volcanic glass, which may or may not contain crystals. It is typically light-colored. Scoria is another vesicula ...
stone or silicon carbide
Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum (), is a hard chemical compound containing silicon and carbon. A wide bandgap semiconductor, it occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite, but has been mass-produced as a powder a ...
sandpaper or filed down with a callus shaver, or pared down by a professional such as a podiatrist
A podiatrist ( ) is a medical professional devoted to the treatment of disorders of the foot, ankle, and related structures of the leg. The term originated in North America but has now become the accepted term in the English-speaking world for ...
.
Diabetes
People withdiabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
face special skin challenges. Because diabetes affects the capillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the in ...
, the small blood vessels which feed the skin, thickening of the skin with callus increases the difficulty of supplying nutrients to the skin. Callus formation is seen in high numbers of patients with diabetes, and together with absent foot pulses and formation of hammer toe, -12% having callus formation -56% having callus present this may be an early sign of individuals at an increased risk for foot ulcers.
The stiffness of a callus or corn, coupled with the shear and pressure that caused it, may tear the capillaries or adjoining tissue, causing bleeding within the callus or corn. This can often be result of trying to pick, cut, or shave off the callus by yourself at home. Although the bleeding can be small, sometimes small pools of blood or hematoma
A hematoma, also spelled haematoma, or blood suffusion is a localized bleeding outside of blood vessels, due to either disease or trauma including injury or surgery and may involve blood continuing to seep from broken capillaries. A hematoma is ...
are formed. The blood itself is an irritant, a foreign body within the callus that makes the area burn or itch. If the pool of blood is exposed to the outside, infection may follow. Infection may also lead to ulceration
An ulcer is a discontinuity or break in a bodily membrane that impedes normal function of the affected Organ (biology), organ. According to Robbins's pathology, "ulcer is the breach of the continuity of skin, epithelium or mucous membrane caus ...
. This process can be prevented at several places. Diabetic foot infections are the leading cause of diabetic limb amputation
Amputation is the removal of a Limb (anatomy), limb or other body part by Physical trauma, trauma, medical illness, or surgery. As a surgical measure, it is used to control pain or a disease process in the affected limb, such as cancer, malign ...
.
Society and culture
Calluses in the hands are frequently associated withmanual labor
Manual labour (in Commonwealth English, manual labor in American English) or manual work is physical work done by humans, in contrast to labour by machines and working animals. It is most literally work done with the hands (the word ''manual'' ...
and blue-collar worker
A blue-collar worker is a person who performs manual labour, manual labor or Tradesman, skilled trades. Blue-collar work may involve skilled or unskilled labor. The type of work may involve manufacturing, retail, Warehouse, warehousing, mining, ...
s. During the Gads Hill Train Robbery in 1874, the James–Younger Gang purportedly refrained from robbing men with calloused hands, assuming them to be working class laborers. A similar notion is also present in Māori culture
Māori culture () is the customs, cultural practices, and beliefs of the Māori people of New Zealand. It originated from, and is still part of, Polynesians, Eastern Polynesian culture. Māori culture forms a distinctive part of Culture of New ...
, where the words ''raupā'' and ''raupo'' refer to hands left cracked and chapped due to manual work, and are used as simile
A simile () is a type of figure of speech that directly ''compares'' two things. Similes are often contrasted with metaphors, where similes necessarily compare two things using words such as "like", "as", while metaphors often create an implicit c ...
s for someone deemed a hard worker.
Calluses have also been known to develop on the forehead from the frequent prostrations required in Muslim prayer; known as a prayer bump or ''zebiba'', such calluses are considered marks of piety in some Muslim countries, and people have been known to take special steps, such as praying on straw mats, to encourage the callus to develop.
Calluses may also form on the finger
A finger is a prominent digit (anatomy), digit on the forelimbs of most tetrapod vertebrate animals, especially those with prehensile extremities (i.e. hands) such as humans and other primates. Most tetrapods have five digits (dactyly, pentadact ...
tips from the repeated pressure and friction of playing stringed instruments. This formation of calluses allows the player to repeatedly depress the strings without causing pain. Because of this, callus formation is viewed as something of a rite of passage for beginner string players.
Calluses also commonly form on the palms of the hands in certain athletic sports such as weightlifting
Weightlifting or weight lifting generally refers to physical exercises and sports in which people lift weights, often in the form of dumbbells, barbells or machines. People engage in weightlifting for a variety of different reasons. These can ...
and gymnastics
Gymnastics is a group of sport that includes physical exercises requiring Balance (ability), balance, Strength training, strength, Flexibility (anatomy), flexibility, agility, Motor coordination, coordination, artistry and endurance. The movem ...
due to the repeated gripping of bars.
See also
*Callosity
A callosity is a type of callus, a piece of skin that has become thickened as a result of repeated contact and friction.
Primates
All Old World monkeys, gibbons, and some chimpanzees have pads on their rears known as ''ischium, ischial callos ...
* Hyperkeratosis
Hyperkeratosis is thickening of the stratum corneum (the outermost layer of the epidermis, or skin), often associated with the presence of an abnormal quantity of keratin,Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelso; Abbas, Abul (2004) ''Robbins & Cotran Pathol ...
References
Further reading
* ''Taber's Cyclopedic Medical Dictionary'', 15th Edition, CL Thomas, M.D., M.P.H., editor, F.A. Davis Company, Philadelphia, PA, 1985. * ''The Merck Manual of Medical Information, Home Edition'', R Berkow, M.D., et al., editors, Merck Research Laboratories, Whitehouse Station, NJ, 1997. {{Cutaneous ketatosis, ulcer, atrophy, necrobiosis, and vasculitis Foot diseases Skin conditions resulting from physical factors es:Callo fr:Cal (médecine) io:Kalo it:Callo pl:Modzel pt:Calo tr:Nasır