CD4 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 Like many cell surface receptors/markers, CD4 is a member of the
Like many cell surface receptors/markers, CD4 is a member of the
 CD4 is closely related to LAG-3, and together they form an evolutionary conserved system from the level of sharks competing for binding Lck by conserved motifs in their cytoplasmic tails: CD4 through a Cys-X-Cys/His motif and LAG-3 through an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motif like (ITIM-like) motif. LAG-3, which is an inhibitory receptor, is upregulated in activated T cells as a kind of
CD4 is closely related to LAG-3, and together they form an evolutionary conserved system from the level of sharks competing for binding Lck by conserved motifs in their cytoplasmic tails: CD4 through a Cys-X-Cys/His motif and LAG-3 through an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motif like (ITIM-like) motif. LAG-3, which is an inhibitory receptor, is upregulated in activated T cells as a kind of
Mouse CD Antigen Chart
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Cd4 Clusters of differentiation Glycoproteins Immunology Protein domains T cells
 In
In molecular biology
Molecular biology is a branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecule, molecular basis of biological activity in and between Cell (biology), cells, including biomolecule, biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactio ...
, CD4 (cluster of differentiation
The cluster of differentiation (also known as cluster of designation or classification determinant and often abbreviated as CD) is a protocol used for the identification and investigation of cell surface molecules providing targets for immunophe ...
4) is a glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide (sugar) chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known a ...
that serves as a co-receptor
A co-receptor is a cell surface receptor that binds a signalling molecule in addition to a primary receptor in order to facilitate Ligand (biochemistry), ligand recognition and initiate biological processes, such as entry of a pathogen into a host ...
for the T-cell receptor
The T-cell receptor (TCR) is a protein complex, located on the surface of T cells (also called T lymphocytes). They are responsible for recognizing fragments of antigen as peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. ...
(TCR). CD4 is found on the surface of immune cells such as helper T cell
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are considere ...
s, monocytes
Monocytes are a type of leukocyte or white blood cell. They are the largest type of leukocyte in blood and can differentiate into macrophages and monocyte-derived dendritic cells. As a part of the vertebrate innate immune system monocytes also i ...
, macrophages
Macrophages (; abbreviated MPhi, φ, MΦ or MP) are a type of white blood cell of the innate immune system that engulf and digest pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that ...
, and dendritic cells
A dendritic cell (DC) is an antigen-presenting cell (also known as an ''accessory cell'') of the mammalian immune system. A DC's main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system ...
. It was discovered in the late 1970s and was originally known as leu-3 and T4 (after the OKT4 monoclonal antibody
A monoclonal antibody (mAb, more rarely called moAb) is an antibody produced from a cell lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell.
Monoclonal antibodie ...
that reacted with it) before being named CD4 in 1984. In humans, the CD4 protein is encoded by the ''CD4'' gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
.
CD4+ T helper cells are white blood cells
White blood cells (scientific name leukocytes), also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign entities. White blood cells are genera ...
that are an essential part of the human immune system. They are often referred to as CD4 cells, T helper cells or T4 cells. They are called helper cells because one of their main roles is to send signals to other types of immune cells, including CD8
CD8 (cluster of differentiation 8) is a transmembrane protein, transmembrane glycoprotein that serves as a co-receptor for the T-cell receptor (TCR). Along with the TCR, the CD8 co-receptor plays a role in T cell Cell signaling, signaling and aid ...
killer cells, which then destroy the infectious particle. If CD4 cells become depleted, for example in untreated HIV infection, or following immune suppression prior to a transplant, the body is left vulnerable to a wide range of infections that it would otherwise have been able to fight.
Structure
 Like many cell surface receptors/markers, CD4 is a member of the
Like many cell surface receptors/markers, CD4 is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily
The immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF) is a large protein superfamily of cell surface and soluble proteins that are involved in the recognition, binding, or adhesion processes of cells. Molecules are categorized as members of this superfamily ...
.
It has four immunoglobulin domains (D1 to D4) that are exposed on the extracellular surface of the cell:
* D1 and D3 resemble immunoglobulin
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as pathogenic bacteria, bacteria and viruses, includin ...
variable (IgV) domains.
* D2 and D4 resemble immunoglobulin
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as pathogenic bacteria, bacteria and viruses, includin ...
constant (IgC) domains.
The immunoglobulin
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as pathogenic bacteria, bacteria and viruses, includin ...
variable (IgV) domain of D1 adopts an immunoglobulin-like β-sandwich fold with seven β-strands in two β-sheets, in a Greek key topology.
CD4 interacts with the β2-domain of MHC class II
MHC Class II molecules are a class of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules normally found only on professional antigen-presenting cells such as dendritic cells, macrophages, some endothelial cells, thymic epithelial cells, and B cell ...
molecules through its D1 domain. T cells displaying CD4 molecules (and not CD8
CD8 (cluster of differentiation 8) is a transmembrane protein, transmembrane glycoprotein that serves as a co-receptor for the T-cell receptor (TCR). Along with the TCR, the CD8 co-receptor plays a role in T cell Cell signaling, signaling and aid ...
) on their surface, therefore, are specific for antigens presented by MHC II and not by MHC class I
MHC class I molecules are one of two primary classes of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules (the other being MHC class II) and are found on the cell surface of all nucleated cells in the bodies of vertebrates. They also occur on ...
(they are ''MHC class II-restricted''). MHC class I contains Beta-2 microglobulin
β2 microglobulin (B2M) is a component of MHC class I molecules. MHC class I molecules have α1, α2, and α3 proteins which are present on all nucleated cells (excluding red blood cells). In humans, the β2 microglobulin protein is encoded by t ...
.
The short cytoplasmic
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell and ...
/intracellular
This glossary of biology terms is a list of definitions of fundamental terms and concepts used in biology, the study of life and of living organisms. It is intended as introductory material for novices; for more specific and technical definitions ...
tail (C) of CD4 contains a special sequence of amino acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the Proteinogenic amino acid, 22 α-amino acids incorporated into p ...
that allow it to recruit and interact with the tyrosine kinase
A tyrosine kinase is an enzyme that can transfer a phosphate group from ATP to the tyrosine residues of specific proteins inside a cell. It functions as an "on" or "off" switch in many cellular functions.
Tyrosine kinases belong to a larger cla ...
Lck.
Function
CD4 is aco-receptor
A co-receptor is a cell surface receptor that binds a signalling molecule in addition to a primary receptor in order to facilitate Ligand (biochemistry), ligand recognition and initiate biological processes, such as entry of a pathogen into a host ...
of the T cell receptor
The T-cell receptor (TCR) is a protein complex, located on the surface of T cells (also called T lymphocytes). They are responsible for recognizing fragments of antigen as peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. ...
(TCR) and assists the latter in communicating with antigen-presenting cell
An antigen-presenting cell (APC) or accessory cell is a Cell (biology), cell that displays an antigen bound by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins on its surface; this process is known as antigen presentation. T cells may recognize the ...
s. The TCR complex and CD4 bind to distinct regions of the antigen-presenting MHC class II
MHC Class II molecules are a class of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules normally found only on professional antigen-presenting cells such as dendritic cells, macrophages, some endothelial cells, thymic epithelial cells, and B cell ...
molecule. The extracellular
This glossary of biology terms is a list of definitions of fundamental terms and concepts used in biology, the study of life and of living organisms. It is intended as introductory material for novices; for more specific and technical definitions ...
D1 domain of CD4 binds to the β2 region of MHC class II. The resulting close proximity between the TCR complex and CD4 allows the tyrosine kinase Lck bound to the cytoplasmic tail of CD4 to phosphorylate tyrosine residues of immunoreceptor tyrosine activation motif An immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) is a conserved sequence of four amino acids that is repeated twice in the cytoplasmic tails of non-catalytic tyrosine-phosphorylated receptors, cell-surface proteins found mainly on immune cel ...
s (ITAMs) on the cytoplasmic domains of CD3 to amplify the signal generated by the TCR. Phosphorylated ITAMs on CD3 recruit and activate SH2 domain-containing protein tyrosine kinases (PTK), such as ZAP70, to further mediate downstream signalling through tyrosine phosphorylation. These signals lead to the activation of transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding t ...
s, including NF-κB
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) is a family of transcription factor protein complexes that controls transcription (genetics), transcription of DNA, cytokine production and cell survival. NF-κB is found i ...
, NFAT
Nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) is a family of transcription factors shown to be important in immune response. One or more members of the NFAT family is expressed in most cells of the immune system. NFAT is also involved in the developme ...
, AP-1, to promote T cell activation.
 CD4 is closely related to LAG-3, and together they form an evolutionary conserved system from the level of sharks competing for binding Lck by conserved motifs in their cytoplasmic tails: CD4 through a Cys-X-Cys/His motif and LAG-3 through an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motif like (ITIM-like) motif. LAG-3, which is an inhibitory receptor, is upregulated in activated T cells as a kind of
CD4 is closely related to LAG-3, and together they form an evolutionary conserved system from the level of sharks competing for binding Lck by conserved motifs in their cytoplasmic tails: CD4 through a Cys-X-Cys/His motif and LAG-3 through an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motif like (ITIM-like) motif. LAG-3, which is an inhibitory receptor, is upregulated in activated T cells as a kind of negative feedback
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function (Mathematics), function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is feedback, fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused ...
loop.
Other interactions
CD4 has also been shown to interact with SPG21, and Uncoordinated-119 (Unc-119).Disease
HIV infection
HIV-1 uses CD4 to gain entry into host T-cells and achieves this through itsviral envelope
A viral envelope is the outermost layer of many types of viruses. It protects the genetic material in their life cycle when traveling between host cells. Not all viruses have envelopes. A viral envelope protein or E protein is a protein in the en ...
protein known as gp120. The binding to CD4 creates a shift in the conformation of gp120 allowing HIV-1 to bind to a co-receptor expressed on the host cell. These co-receptors are chemokine receptors CCR5
C-C chemokine receptor type 5, also known as CCR5 or CD195, is a protein on the surface of white blood cells that is involved in the immune system as it acts as a receptor for chemokines.
In humans, the ''CCR5'' gene that encodes the CCR5 p ...
or CXCR4. Following a structural change in another viral protein ( gp41), HIV inserts a fusion peptide into the host cell that allows the outer membrane of the virus to fuse with the cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extr ...
.
HIV pathology
HIV infection leads to a progressive reduction in the number of T cells expressing CD4. Medical professionals refer to the CD4 count to decide when to begin treatment during HIV infection, although recent medical guidelines have changed to recommend treatment at all CD4 counts as soon as HIV is diagnosed. A CD4 count measures the number of T cells expressing CD4. While CD4 counts are not a direct HIV test—e.g. they do not check the presence of viral DNA, or specific antibodies against HIV—they are used to assess the immune system of a patient.National Institutes of Health
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in 1887 and is part of the United States Department of Health and Human Service ...
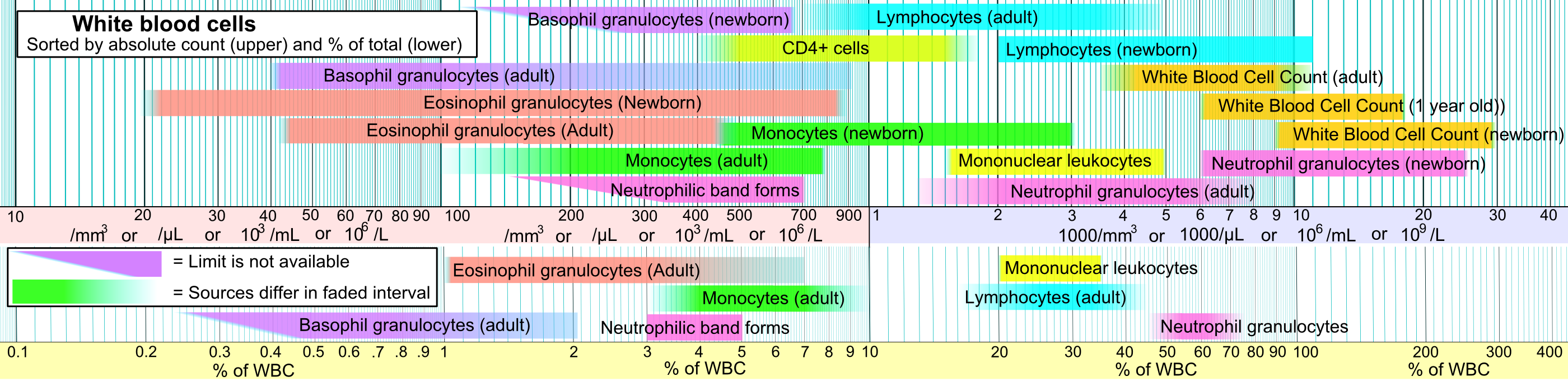
guidelines recommend treatment of any HIV-positive individuals, regardless of CD4 count Normal blood values are usually expressed as the number of cells per microliter (μL, or equivalently, cubic millimeter, mm3) of blood, with normal values for CD4 cells being 500–1200 cells/mm3. Patients often undergo treatments when the CD4 counts reach a level of 350 cells per microliter in Europe but usually around 500/μL in the US; people with less than 200 cells per microliter are at high risk of contracting AIDS defined illnesses. Medical professionals also refer to CD4 tests to determine efficacy of treatment.
Viral load testing provides more information about the efficacy for therapy than CD4 counts. For the first 2 years of HIV therapy, CD4 counts may be done every 3–6 months. If a patient's viral load becomes undetectable after 2 years then CD4 counts might not be needed if they are consistently above 500/mm3. If the count remains at 300–500/mm3, then the tests can be done annually. It is not necessary to schedule CD4 counts with viral load tests and the two should be done independently when each is indicated.

Other diseases
CD4 continues to be expressed in mostneoplasm
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s derived from T helper cells
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are considere ...
. It is therefore possible to use CD4 immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry is a form of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens in cells and tissue, by exploiting the principle of Antibody, antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. Alber ...
on tissue biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, an interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiology, interventional cardiologist. The process involves the extraction of sampling (medicine), sample ...
samples to identify most forms of peripheral T cell lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). The name typically refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enlarged lymph node ...
and related malignant conditions. The antigen has also been associated with a number of autoimmune diseases
An autoimmune disease is a condition that results from an anomalous response of the adaptive immune system, wherein it mistakenly targets and attacks healthy, functioning parts of the body as if they were foreign organisms. It is estimated that ...
such as vitiligo
Vitiligo (, ) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that causes patches of skin to lose pigment or color. The cause of vitiligo is unknown, but it may be related to immune system changes, genetic factors, stress, or sun exposure, and susceptibili ...
and type I diabetes mellitus.
T-cells play a large part in autoinflammatory diseases. When testing a drug's efficacy or studying diseases, it is helpful to quantify the amount of T-cells
on fresh-frozen tissue with CD4+, CD8+, and CD3+ T-cell markers (which stain different markers on a T-cell – giving different results).
See also
*CD4+ T cells and antitumor immunity
In molecular biology, CD4 ( cluster of differentiation 4) is a glycoprotein that serves as a co-receptor for the T-cell receptor (TCR). CD4 is found on the surface of immune cells such as helper T cells, monocytes, macrophages, and dendrit ...
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * *External links
*Mouse CD Antigen Chart
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Cd4 Clusters of differentiation Glycoproteins Immunology Protein domains T cells