|
Lck
Tyrosin-protein kinase Lck (or lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase) is a 56 kDa protein that is found inside lymphocytes and encoded in the human by the ''LCK'' gene. The Lck is a member of Src kinase family (SKF) and is important for the activation of T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling in both naive T cells and effector T cells. The role of Lck is less prominent in the activation or in the maintenance of memory CD8 T cells in comparison to CD4 T cells. In addition, the constitutive activity of the mouse Lck homolog varies among memory T cell subsets. It seems that in mice, in the effector memory T cell (TEM) population, more than 50% of Lck is present in a constitutively active conformation, whereas less than 20% of Lck is present as active form in central memory T cells. These differences are due to differential regulation by SH2 domain–containing phosphatase-1 (Shp-1) and C-terminal Src kinase. Lck is responsible for the initiation of the TCR signaling cascade insi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Cell Receptor
The T-cell receptor (TCR) is a protein complex, located on the surface of T cells (also called T lymphocytes). They are responsible for recognizing fragments of antigen as peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. The binding between TCR and antigen peptides is of relatively low affinity and is biologically degenerate (that is, many TCRs recognize the same antigen peptide, and many antigen peptides are recognized by the same TCR). The TCR is composed of two different protein chains (that is, it is a hetero dimer). In humans, in 95% of T cells the TCR consists of an alpha (α) chain and a beta (β) chain (encoded by ''TRA'' and ''TRB'', respectively), whereas in 5% of T cells the TCR consists of gamma and delta (γ/δ) chains (encoded by '' TRG'' and '' TRD'', respectively). This ratio changes during ontogeny and in diseased states (such as leukemia). It also differs between species. Orthologues of the 4 loci have been mapped in various species. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
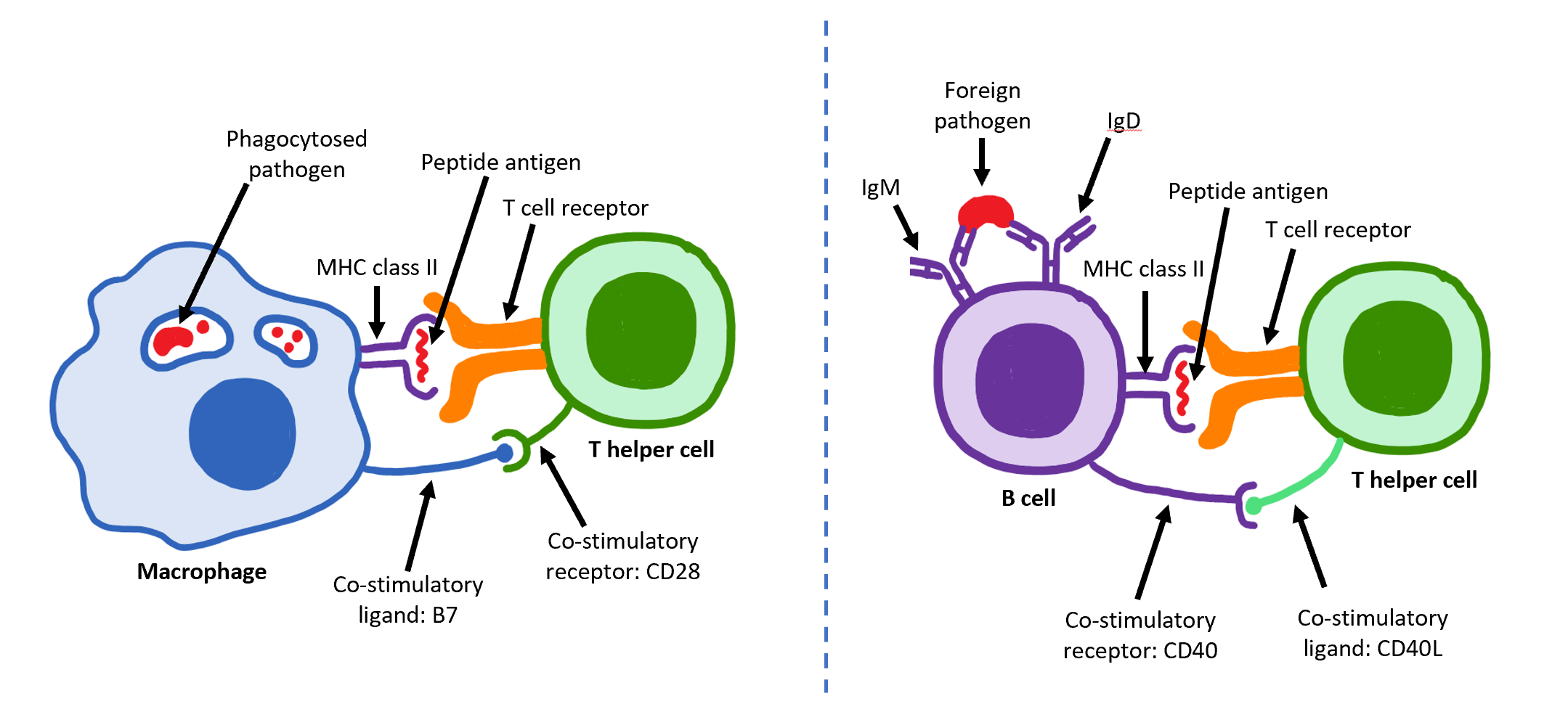
T Helper Cell
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are considered essential in B cell Immunoglobulin class switching, antibody class switching, breaking Cross-presentation, cross-tolerance in dendritic cells, in the activation and growth of cytotoxic T cells, and in maximizing bactericidal activity of phagocytes such as macrophages and neutrophils. CD4+ cells are mature Th cells that express the surface protein CD4. Genetic variation in regulatory elements expressed by CD4+ cells determines susceptibility to a broad class of autoimmune diseases. Structure and function Th cells contain and release cytokines to aid other immune cells. Cytokines are small protein mediators that alter the behavior of target cells that express Receptor (biochemistry), receptors for those cytokines. These cells help polar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ZAP-70
ZAP-70 (Zeta-chain-associated protein kinase 70) is a protein normally expressed near the surface membrane of Lymphocyte, lymphocytes (T cells, natural killer cells, and a subset of B cell, B cells). It is most prominently known to be recruited upon antigen binding to the T cell receptor (TCR), and it plays a critical role in T cell signaling. ZAP-70 was initially discovered in TCR-stimulated Jurkat cells, an immortal line of human T lymphocytes, in 1991. Its molecular weight is 70 kDa, and it is a member of the protein-tyrosine kinase family and is a paralog, close homolog of Tyrosine-protein kinase SYK, SYK. SYK and ZAP70 share a common evolution, evolutionary origin and split from a Most recent common ancestor, common ancestor in the jawed vertebrates. The importance of ZAP-70 in T cell activation was determined when comparing ZAP-70 expression in patients with SCID (severe combined immunodeficiency). ZAP-70 deficient individuals were found to have no functioning T cells in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid Raft
The cell membrane, plasma membranes of cells contain combinations of glycosphingolipids, cholesterol and protein Receptor (biochemistry), receptors organized in glycolipoprotein lipid microdomains termed lipid rafts. Their existence in cellular membranes remains controversial. Indeed, Kervin and Overduin imply that lipid rafts are misconstrued protein islands, which they propose form through a proteolipid code. Nonetheless, it has been proposed that they are specialized membrane microdomains which compartmentalize cellular processes by serving as organising centers for the assembly of signaling molecules, allowing a closer interaction of protein receptors and their effectors to promote kinetically favorable interactions necessary for the signal transduction. Lipid rafts influence membrane fluidity and membrane protein Protein targeting, trafficking, thereby regulating neurotransmission and receptor trafficking. Lipid rafts are more ordered and tightly packed than the surrounding bil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Cell
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface receptor, cell surface. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response. One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes: Cytotoxic T cell, CD8+ "killer" (cytotoxic) and T helper cell, CD4+ "helper" T cells. (These are named for the presen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linker For Activation Of T Cells
The Linker for activation of T cells, also known as linker of activated T cells or LAT, is a protein involved in the T-cell receptor, T-cell antigen receptor signal transduction pathway which in humans is encoded by the ''LAT'' gene. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Function The LAT protein encoded by the gene of the same name, plays a key role in the diversification of T cell signaling pathways following activation of the T-cell antigen receptor (T-cell receptor, TCR) signal transduction pathway, which is first catalyzed by TCR binding to MHC class II. LAT is a transmembrane protein localizes to lipid rafts (also known as glycosphingolipid-enriched microdomains or GEMs) and acts as a docking site for SH2 domain-containing proteins. Upon phosphorylation, this protein recruits multiple Signal transducing adaptor protein, adaptor proteins and downstream signaling molecules into multimolecular signaling complexes located nea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD247
T-cell surface glycoprotein CD3 zeta chain also known as T-cell receptor T3 zeta chain or CD247 (Cluster of Differentiation 247) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CD247'' gene. Some older literature mention a similar protein called "CD3 eta" in mice. It is now understood to be an isoform differing in the last exon. Genomics The gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 1 at location 1q22-q25 on the Crick (negative) strand. The encoded protein is 164 amino acids long with a predicted weight of 18.696 kilo Daltons. Function T-cell receptor zeta (ζ), together with T-cell receptor alpha/beta and gamma/delta heterodimers and CD3-gamma, -delta, and -epsilon, forms the T-cell receptor-CD3 complex. The zeta chain plays an important role in coupling antigen recognition to several intracellular signal-transduction pathways. Low expression of the antigen results in impaired immune response. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Src Family Kinase
Src kinase family is a family of non-receptor tyrosine kinases that includes nine members: Src (gene), Src, YES1, Yes, FYN, Fyn, and FGR (gene), Fgr, forming the SrcA subfamily, Lck, HCK, Hck, Tyrosine-protein kinase BLK, Blk, and Lyn (Src family Kinase), Lyn in the SrcB subfamily, and FRK (gene), Frk in its own subfamily. Frk has homologs in invertebrates such as flies and worms, and Src homologs exist in organisms as diverse as unicellular choanoflagellates, but the SrcA and SrcB subfamilies are specific to vertebrates. Src family kinases contain six conserved domains: a N-terminal Myristoylation, myristoylated segment, a SH2 domain, a SH3 domain, a linker region, a tyrosine kinase domain, and C-terminal tail. Src family kinases interact with many cellular cytosolic, nuclear and membrane proteins, modifying these proteins by phosphorylation of tyrosine residues. A number of substrates have been discovered for these enzymes. Deregulation, including constitutive activation or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SH2 Domain
The SH2 (Src Homology 2) domain is a structurally conserved protein domain contained within the Src oncoprotein and in many other intracellular signal-transducing proteins. SH2 domains bind to phosphorylated tyrosine residues on other proteins, modifying the function or activity of the SH2-containing protein. The SH2 domain may be considered the prototypical modular protein-protein interaction domain, allowing the transmission of signals controlling a variety of cellular functions. SH2 domains are especially common in adaptor proteins that aid in the signal transduction of receptor tyrosine kinase pathways. Structure and interactions SH2 domains contain about 100 amino acid residues and exhibit a central antiparallel β-sheet centered between two α-helices. Binding to phosphotyrosine-containing peptides involves a strictly-conserved Arg residue that pairs with the negatively-charged phosphate on the phosphotyrosine, and a surrounding pocket that recognizes flanking seque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a conditionally essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Greek ''tyrós'', meaning ''cheese'', as it was first discovered in 1846 by German chemist Justus von Liebig in the protein casein from cheese. It is called tyrosyl when referred to as a functional group or side chain. While tyrosine is generally classified as a hydrophobic amino acid, it is more hydrophilic than phenylalanine. It is encoded by the codons UAC and UAU in messenger RNA. The one-letter symbol Y was assigned to tyrosine for being alphabetically nearest of those letters available. Note that T was assigned to the structurally simpler threonine, U was avoided for its similarity with V for valine, W was assigned to tryptophan, while X was reserved for undetermined or atypical amino acids. The mnemonic t''Y''rosine was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |