Brasilitherium on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Brasilodon'' ("tooth from Brazil") is an extinct
 The first three specimens referred to ''Brasilodon quadrangularis'' were found at the Linha São Luiz site, a quarry near the town of Faxinal do Soturno in the state of
The first three specimens referred to ''Brasilodon quadrangularis'' were found at the Linha São Luiz site, a quarry near the town of Faxinal do Soturno in the state of

 Different specimens of ''Brasilodon'' had widely varying skull lengths, ranging from , owing mainly to differences in age. The skull had a low, elongated shape when seen from the side. The top of the
Different specimens of ''Brasilodon'' had widely varying skull lengths, ranging from , owing mainly to differences in age. The skull had a low, elongated shape when seen from the side. The top of the
 Like most cynodonts, ''Brasilodon'' possessed a
Like most cynodonts, ''Brasilodon'' possessed a
 The
The
 The specimen UFRGS-PV-1043-T preserves a complete left humerus (upper arm bone), with a length of . The shaft of the humerus was slender. It was somewhat twisted, with an angulation of 15 degrees between the opposite ends of the bone. A twisted humerus is found in most cynodonts outside
The specimen UFRGS-PV-1043-T preserves a complete left humerus (upper arm bone), with a length of . The shaft of the humerus was slender. It was somewhat twisted, with an angulation of 15 degrees between the opposite ends of the bone. A twisted humerus is found in most cynodonts outside  The left radius of UFRGS-PV-1043-T is long. The radius was slender, with a circular cross-section near the proximal end (closer to the elbow). The head of the radius (where it articulated with the humerus) was approximately circular, with a cup-shaped depression in the middle surrounded by a bulbous rim. The head was angled somewhat towards the anteromedial (front right) side. On the posteromedial (back right) side of the head, there was a small articular facet where it would have articulated with the radial notch of the ulna. There was no radial tuberosity for the attachment of the
The left radius of UFRGS-PV-1043-T is long. The radius was slender, with a circular cross-section near the proximal end (closer to the elbow). The head of the radius (where it articulated with the humerus) was approximately circular, with a cup-shaped depression in the middle surrounded by a bulbous rim. The head was angled somewhat towards the anteromedial (front right) side. On the posteromedial (back right) side of the head, there was a small articular facet where it would have articulated with the radial notch of the ulna. There was no radial tuberosity for the attachment of the  The
The  The right femur (thigh bone) of UFRGS-PV-1043-T is long. The shaft of the femur was mostly straight, but with a prominent forward bend close to the hip joint, as in other non-mammalian cynodonts; in modern mammals, this bend is less well-developed. The proximal part of the shaft (closer to the hip) was mostly square-shaped, but it became more compressed from front to back more distally (towards the knee), while simultaneously becoming wider from side to side. The proximal and distal ends of the bone had the same width. On the proximal end of the bone, the
The right femur (thigh bone) of UFRGS-PV-1043-T is long. The shaft of the femur was mostly straight, but with a prominent forward bend close to the hip joint, as in other non-mammalian cynodonts; in modern mammals, this bend is less well-developed. The proximal part of the shaft (closer to the hip) was mostly square-shaped, but it became more compressed from front to back more distally (towards the knee), while simultaneously becoming wider from side to side. The proximal and distal ends of the bone had the same width. On the proximal end of the bone, the  UFRGS-PV-1043-T preserves a nearly complete left tibia (shin bone). It was a slender bone, with the preserved parts having a length of . The shaft was mostly straight, but with a slight medial (rightwards) curve in the proximal part (towards the knee); more basal cynodonts generally had a stronger medial curve of the tibia. The shaft became progressively more flattened towards the distal end (towards the ankle). On the proximal part, there were two articular facets, the medial and
UFRGS-PV-1043-T preserves a nearly complete left tibia (shin bone). It was a slender bone, with the preserved parts having a length of . The shaft was mostly straight, but with a slight medial (rightwards) curve in the proximal part (towards the knee); more basal cynodonts generally had a stronger medial curve of the tibia. The shaft became progressively more flattened towards the distal end (towards the ankle). On the proximal part, there were two articular facets, the medial and


genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
of small, mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
-like cynodont
Cynodontia () is a clade of eutheriodont therapsids that first appeared in the Late Permian (approximately 260 Megaannum, mya), and extensively diversified after the Permian–Triassic extinction event. Mammals are cynodonts, as are their extin ...
s that lived in what is now Brazil during the Norian
The Norian is a division of the Triassic geological period, Period. It has the rank of an age (geology), age (geochronology) or stage (stratigraphy), stage (chronostratigraphy). It lasted from ~227.3 to Mya (unit), million years ago. It was prec ...
age of the Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch a ...
epoch, about 225.42 million years ago. While no complete skeletons have been found, the length of ''Brasilodon'' has been estimated at . Its dentition shows that it was most likely an insectivore
file:Common brown robberfly with prey.jpg, A Asilidae, robber fly eating a hoverfly
An insectivore is a carnivore, carnivorous animal or plant which eats insects. An alternative term is entomophage, which can also refer to the Entomophagy ...
. The genus is monotypic
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unisp ...
, containing only the species ''B. quadrangularis''. ''Brasilodon'' belongs to the family Brasilodontidae, whose members were some of the closest relatives of mammals, the only cynodonts alive today. Two other brasilodontid genera, ''Brasilitherium'' and ''Minicynodon'', are now considered to be junior synonym
In taxonomy, the scientific classification of living organisms, a synonym is an alternative scientific name for the accepted scientific name of a taxon. The botanical and zoological codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently.
...
s of ''Brasilodon''.
Discovery and naming
 The first three specimens referred to ''Brasilodon quadrangularis'' were found at the Linha São Luiz site, a quarry near the town of Faxinal do Soturno in the state of
The first three specimens referred to ''Brasilodon quadrangularis'' were found at the Linha São Luiz site, a quarry near the town of Faxinal do Soturno in the state of Rio Grande do Sul
Rio Grande do Sul (, ; ; "Great River of the South") is a Federative units of Brazil, state in the South Region, Brazil, southern region of Brazil. It is the Federative units of Brazil#List, fifth-most populous state and the List of Brazilian s ...
. The rocks where ''Brasilodon'' was found belong to the upper part of the Candelária Sequence of the Santa Maria Supersequence, corresponding to the traditional Caturrita Formation, which has been dated to the early Norian
The Norian is a division of the Triassic geological period, Period. It has the rank of an age (geology), age (geochronology) or stage (stratigraphy), stage (chronostratigraphy). It lasted from ~227.3 to Mya (unit), million years ago. It was prec ...
age of the Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch a ...
. The holotype
A holotype (Latin: ''holotypus'') is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of s ...
(UFRGS-PV-0611-T) consists of a well-preserved skull retaining both the left and right upper postcanine teeth, but missing the lower jaw. The referred specimen UFRGS-PV-0716-T consists of the left front part of the skull, preserving 6 postcanines. The specimen UFRGS-PV-0628-T consists of a partial skull including the lower jaw, with most of the upper and lower dentition preserved. Many other specimens of ''Brasilodon'' have since been discovered, both in Faxinal do Soturno and in Candelária, and comprising both cranial and postcranial material.
The genus ''Brasilodon'' was named in a 2003 paper by José F. Bonaparte, Agustín G. Martinelli, Cesar L. Schultz and Rogerio Rubert. The generic name ''Brasilodon'' is derived from the country of Brazil where it was found, and from the Greek word , meaning "tooth". The intended meaning is "tooth from Brazil". The specific epithet ''quadrangularis'' refers to the rectangular shape of the upper postcanine teeth.
In the same 2003 article, the species ''Brasilitherium riograndensis'' was named, based on six specimens. Specimens attributed to ''Brasilitherium'' have been found at the same localities as ''Brasilodon'', and have been distinguished from this taxon largely by their smaller size, different skull proportions, and by the presence of a cusp d in the lower postcanines of ''Brasilitherium'', but not in ''Brasilodon''. A 2005 paper erected the family Brasilodontidae for the two genera. In 2010 a third brasilodontid species, ''Minicynodon maieri'', was named by Bonaparte ''et al.'', based on a single well-preserved skull from Faxinal do Soturno. This species was differentiated from ''Brasilodon'' by the firm attachment of the bones of the skull roof
The skull roof or the roofing bones of the skull are a set of bones covering the brain, eyes and nostrils in bony fishes, including land-living vertebrates. The bones are derived from dermal bone and are part of the dermatocranium.
In com ...
, and from ''Brasilitherium'' by the lack of a cusp b in the lower postcanines. ''Minicynodon'' was also interpreted as possessing a double jaw joint, unlike the other two species. Later studies have cast doubt on the validity of ''Brasilitherium'' and ''Minicynodon'', proposing instead that they, along with ''Brasilodon'', merely represent individual variation within a single species. In that case, ''Brasilodon'' is the valid taxon, whereas ''Brasilitherium'' and ''Minicynodon'' are invalid junior synonym
In taxonomy, the scientific classification of living organisms, a synonym is an alternative scientific name for the accepted scientific name of a taxon. The botanical and zoological codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently.
...
s.
Description
''Brasilodon'' was a small, derived cynodont, with an estimated total length of around . It exhibited many mammal-like features, including a well-developedsecondary palate
The secondary palate is an anatomical structure that divides the nasal cavity from the oral cavity in many vertebrates.
In human embryology, it refers to that portion of the hard palate that is formed by the growth of the two palatine shelves med ...
, symmetrical tooth development, and a more derived ear anatomy than in earlier cynodonts.
Skull

 Different specimens of ''Brasilodon'' had widely varying skull lengths, ranging from , owing mainly to differences in age. The skull had a low, elongated shape when seen from the side. The top of the
Different specimens of ''Brasilodon'' had widely varying skull lengths, ranging from , owing mainly to differences in age. The skull had a low, elongated shape when seen from the side. The top of the braincase
In human anatomy, the neurocranium, also known as the braincase, brainpan, brain-pan, or brainbox, is the upper and back part of the skull, which forms a protective case around the brain. In the human skull, the neurocranium includes the calv ...
was fairly wide, with a short and low parietal crest. ''Brasilodon'' lacked prefrontal and postorbital
The ''postorbital'' is one of the bones in vertebrate skulls which forms a portion of the dermal skull roof and, sometimes, a ring about the orbit. Generally, it is located behind the postfrontal and posteriorly to the orbital fenestra. In some ve ...
bones, which were found in more basal probainognathians like ''Prozostrodon
''Prozostrodon'' is an extinct genus of probainognathian cynodonts that was closely related to mammals. The remains were found in Brazil and are dated to the Carnian age of the Late Triassic. The holotype has an estimated skull length of , indica ...
''. There was no postorbital bar
The postorbital bar (or postorbital bone) is a bony arched structure that connects the frontal bone of the skull to the zygomatic arch, which runs laterally around the eye socket. It is a trait that only occurs in mammalian taxa, such as most strep ...
behind the eye socket
In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket/hole of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents. In the adult human, the volume of the orbit is ...
. The zygomatic arch
In anatomy, the zygomatic arch (colloquially known as the cheek bone), is a part of the skull formed by the zygomatic process of temporal bone, zygomatic process of the temporal bone (a bone extending forward from the side of the skull, over the ...
(cheek bone) was quite low and slender.
The lower jaw consisted mainly of the dentary bone, which bore the teeth. The tip of the lower jaw was bent upwards. The symphysis
A symphysis (, : symphyses) is a fibrocartilaginous fusion between two bones. It is a type of cartilaginous joint, specifically a secondary cartilaginous joint.
# A symphysis is an amphiarthrosis, a slightly movable joint.
# A growing together o ...
, the joint between the two halves of the dentary, was unfused, with a rough surface where ligament
A ligament is a type of fibrous connective tissue in the body that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes (land animals with internal bones) have liga ...
s would have been attached. The meckelian groove was located near the lower edge of the dentary. The postdentary bones, a set of bones in the lower jaw located behind the dentary, were highly reduced compared to the condition in more primitive cynodonts. Like in most non-mammalian cynodonts, the jaw joint in ''Brasilodon'' involved the quadrate bone
The quadrate bone is a skull bone in most tetrapods, including amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, birds), and early synapsids.
In most tetrapods, the quadrate bone connects to the quadratojugal and squamosal bones in the skull, and forms up ...
(a bone of the cranium, homologous to the incus
The ''incus'' (: incudes) or anvil in the ear is one of three small bones (ossicles) in the middle ear. The incus receives vibrations from the malleus, to which it is connected laterally, and transmits these to the stapes medially. The incus i ...
of modern mammals) and the articular bone
The articular bone is part of the lower jaw of most vertebrates, including most jawed fish, amphibians, birds and various kinds of reptiles, as well as ancestral mammals.
Anatomy
In most vertebrates, the articular bone is connected to two othe ...
(one of the postdentary bones, homologous to the malleus
The ''malleus'', or hammer, is a hammer-shaped small bone or ossicle of the middle ear. It connects with the incus, and is attached to the inner surface of the eardrum. The word is Latin for 'hammer' or 'mallet'. It transmits the sound vibra ...
). There may also have been a contact between the dentary and the squamosal bone
The squamosal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians, and birds. In fishes, it is also called the pterotic bone.
In most tetrapods, the squamosal and quadratojugal bones form the cheek series of the skull. The bone forms an ancestral ...
, with the articular process of the dentary having a thickened end, apparently a precursor condition to the fully developed dentary condyle of more derived mammaliamorph
Mammaliamorpha is a clade of cynodonts. It contains the clades Tritylodontidae and Mammaliaformes, as well as a few genera that do not belong to either of these groups. The family Tritheledontidae has also been placed in Mammaliamorpha by some ...
s. The quadrate bone had a well-developed stapedial process, similar to that of the basal mammaliaform
Mammaliaformes ("mammalian forms") is a clade of synapsid tetrapods that includes the crown group mammals and their closest extinct relatives; the group radiated from earlier probainognathian cynodonts during the Late Triassic. It is defined a ...
''Morganucodon
''Morganucodon'' ("Glamorgan tooth") is an early mammaliaform genus that lived from the Late Triassic to the Middle Jurassic. It first appeared about 205 million years ago. Unlike many other early mammaliaforms, ''Morganucodon'' is well represent ...
''.
The front part of the roof of the mouth consisted of a well-developed secondary palate
The secondary palate is an anatomical structure that divides the nasal cavity from the oral cavity in many vertebrates.
In human embryology, it refers to that portion of the hard palate that is formed by the growth of the two palatine shelves med ...
, formed by the maxillae and the palatine bone
In anatomy, the palatine bones (; derived from the Latin ''palatum'') are two irregular bones of the facial skeleton in many animal species, located above the uvula in the throat. Together with the maxilla, they comprise the hard palate.
Stru ...
s, which extended about as far back as the last postcanine. The secondary palate had a groove that the lower postcanines would have fit into when the mouth was closed. Behind the secondary palate was the primary palate
Around the 5th week, the intermaxillary segment arises as a result of fusion of the two medial nasal processes and the frontonasal process within the embryo. The intermaxillary segment gives rise to the primary palate. The primary palate will form ...
, formed by the vomer
The vomer (; ) is one of the unpaired facial bones of the skull. It is located in the midsagittal line, and articulates with the sphenoid, the ethmoid, the left and right palatine bones, and the left and right maxillary bones. The vomer forms ...
and the pterygoid bones. There was a pair of gaps between the pterygoids called the interpterygoid vacuities. Well-developed interpterygoid vacuities are known in basal cynodonts like '' Procynosuchus'', but the vacuities are generally reduced or absent in more advanced groups, so their presence in ''Brasilodon'' is likely a derived condition. The pterygoids had a transverse contact with the basipterygoid process of the basisphenoid bone. The basicranium was wide when seen from below. The prootic and opisthotic bones were fused into a petrosal bone, which had a well-defined promontorium. There were separate foramina
In anatomy and osteology, a foramen (; : foramina, or foramens ; ) is an opening or enclosed gap within the dense connective tissue (bones and deep fasciae) of extant and extinct amniote animals, typically to allow passage of nerves, arter ...
(holes) for the maxillary and mandibular nerves. Next to the crista interfenestralis there was a large depression called the "stapedial recess", which bore several foramina. The occipital condyle
The occipital condyles are undersurface protuberances of the occipital bone in vertebrates, which function in articulation with the superior facets of the Atlas (anatomy), atlas vertebra.
The condyles are oval or reniform (kidney-shaped) in shape ...
s were located further back than the lambdoid crest.
The cranial endocast, the interior surface of the braincase, is an important source of information about the brains of prehistoric animals, as the brains themselves are very rarely preserved in fossils. A 2013 study by Rodrigues ''et al.'' described the endocast of the specimen UFRGS-PV-1043-T, which was originally assigned to the genus ''Brasilitherium''. The endocast had a length of , which is 46.5% of the total length of this skull. The maximum width of the endocast was . The shape of the endocast indicates that the animal possessed well-developed olfactory bulb
The olfactory bulb (Latin: ''bulbus olfactorius'') is a neural structure of the vertebrate forebrain involved in olfaction, the sense of smell. It sends olfactory information to be further processed in the amygdala, the orbitofrontal cortex (OF ...
s, the parts of the brain associated with the sense of smell. On the other hand, the cerebral hemisphere
The vertebrate cerebrum (brain) is formed by two cerebral hemispheres that are separated by a groove, the longitudinal fissure. The brain can thus be described as being divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each of these hemispheres ...
s were smaller than in basal mammaliaforms like ''Morganucodon''. It is unclear if ''Brasilodon'' possessed a neocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, ...
, a part of the brain found in modern mammals. The encephalisation quotient (relative brain size) was interpreted to likely be higher than in more basal cynodonts, such as the traversodontid '' Massetognathus'', but lower than in basal mammaliaforms and modern mammals. Like other non-mammalian cynodonts, ''Brasilodon'' likely had a lissencephalic (smooth) brain surface.
Dentition
 Like most cynodonts, ''Brasilodon'' possessed a
Like most cynodonts, ''Brasilodon'' possessed a heterodont
In anatomy, a heterodont (from Greek, meaning 'different teeth') is an animal which possesses more than a single tooth morphology.
Human dentition is heterodont and diphyodont as an example.
In vertebrates, heterodont pertains to animals wher ...
dentition, divided into incisor
Incisors (from Latin ''incidere'', "to cut") are the front teeth present in most mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and on the mandible below. Humans have a total of eight (two on each side, top and bottom). Opossums have 18, wher ...
s, canines and postcanines. The specimens originally assigned to ''Brasilodon'' do not preserve any of the upper incisors, but some specimens attributed to ''Brasilitherium'' bore 4 pairs of incisors in the upper jaw. There were 3 pairs of lower incisors; the first lower incisor was procumbent (forwards-pointing). In adult specimens, the canines were large and flattened from side to side, but had no serration
Serration is a saw-like appearance or a row of sharp or tooth-like projections. A serrated cutting edge has many small points of contact with the material being cut. By having less contact area than a smooth blade or other edge, the applied pr ...
s. In small individuals attributed to ''Brasilitherium'', there were two pairs of functional canines, which were only slightly bigger than the incisors.
There were up to 8 pairs of postcanines in both jaws. The postcanines had a rectangular shape when looking towards the crown
A crown is a traditional form of head adornment, or hat, worn by monarchs as a symbol of their power and dignity. A crown is often, by extension, a symbol of the monarch's government or items endorsed by it. The word itself is used, parti ...
. There was little variation in shape in the upper postcanines, while the lower ones exhibited more variation. The upper postcanines were considerably smaller than the lower ones, a condition observed in many other probainognathians. The postcanines were "triconodont-like", with three main cusps arranged in a roughly straight line. There was a large central cusp, termed cusp A in the upper teeth and cusp a in the lower ones, a smaller cusp in front of the central cusp (cusp B/b), and another small cusp behind the central cusp (cusp C/c). In the lower postcanines of some specimens, there was an additional cusp (cusp d) behind cusp c; the absence or presence of this cusp has been used to distinguish ''Brasilodon'' from ''Brasilitherium'', but it is likely that the lack of a cusp d in some specimens is caused by tooth wear
Tooth wear refers to loss of tooth substance by means other than dental caries. Tooth wear is a very common condition that occurs in approximately 97% of the population. This is a normal physiological process occurring throughout life; but with i ...
in older individuals. The postcanines bore varying numbers of accessory cusps as well, sometimes forming a cingulum. In older specimens, there was a large gap (diastema
A diastema (: diastemata, from Greek , 'space') is a space or gap between two teeth. Many species of mammals have diastemata as a normal feature, most commonly between the incisors and molars. More colloquially, the condition may be referred to ...
) between the canines and postcanines, which was created by the first postcanine being shed but not replaced. There was a tongue-and-groove system in the middle lower postcanines for the interlocking between neighbouring teeth, with cusp d fitting between cusp b and the accessory cusp e, but this system was apparently not functional due to the distance between the teeth. The roots of the postcanines were not fully divided as they are in modern mammals, but they had a noticeable constriction in the middle, giving them an 8-shaped cross-section. The nutritious canals of the roots were divided too. The postcanine roots were secured to the jaw by a ring of ossified periodontal ligament
The periodontal ligament, commonly abbreviated as the PDL, are a group of specialized connective tissue fibers that essentially attach a tooth to the alveolar bone within which they sit. It inserts into root cementum on one side and onto alveo ...
.
Vertebrae and ribs
 The
The vertebra
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spina ...
e of ''Brasilodon'' are poorly known. One specimen (UFRGS-PV-1043-T) preserves 4 isolated presacral vertebrae, all of which are badly preserved. The vertebral centra were ''platycoelous'', having a flat front end and a concave back end. Such a shape is also seen in some tritylodontids and basal mammaliaforms, but not in more basal cynodonts, which generally had ''amphicoelous'' vertebrae that were concave on both sides. The neural canal was fairly large, while the lateral walls were thin. The neural arches were fused to the centra in this specimen, showing that it was an adult. One of the vertebrae preserves a small and cylindrical diapophysis (transverse process). The zygapophyses (articular processes, four extensions of each vertebra which connect neighbouring vertebrae together) are poorly preserved, but the postzygapophyses apparently were nearly horizontal and located rather high on the vertebrae. The shape of the base of the neural spine (a pointed extension on the top surface of the vertebra) indicates that it was elongated anteroposteriorly (in a front-to-back direction).
The specimen UFRGS-PV-1043-T also preserves 4 isolated rib
In vertebrate anatomy, ribs () are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the thoracic cavity, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the ...
fragments. The ribs were flattened anteroposteriorly. Many non-probainognathian cynodonts, including most cynognathia
Cynognathia ("dog jaw") is one of two major clades of cynodonts, the other being Probainognathia. Cynognathians included the large carnivorous genus '' Cynognathus'' and the herbivorous or omnivorous gomphodonts such as traversodontids. Cynogn ...
ns, had wide extensions known as ''costal plates'' on their ribs; these plates are absent in most probainognathians, including ''Brasilodon''.
Limbs and limb girdles
The lower part of a rightscapula
The scapula (: scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side ...
(shoulder blade) is preserved in the specimen UFRGS-PV-1043-T, with two other associated bone fragments likely representing the middle part of the dorsal (upper) margin, and the anterior (front) margin, respectively. The scapula was a thin bone, with a constricted base as in other epicynodonts. The upper margin was somewhat convex, while the posterodorsal (upper back) angle was pointed. The front and back margins had sideways-projecting flanges, as seen in other non-mammaliaform epicynodonts. There was a well-developed acromion
In human anatomy, the acromion (from Greek: ''akros'', "highest", ''ōmos'', "shoulder", : acromia) or summit of the shoulder is a bony process on the scapula (shoulder blade). Together with the coracoid process, it extends laterally over the sh ...
process at the end of the front margin. The acromion was forwards-pointing as in many other cynodonts. There was a deep infraspinous fossa on the side of the scapula, but a supraspinous fossa
The supraspinous fossa (supraspinatus fossa, supraspinatous fossa) of the posterior aspect of the scapula (the shoulder blade) is smaller than the infraspinous fossa, concave, smooth, and broader at its vertebral than at its humeral end. Its m ...
was seemingly absent. The glenoid facet of the scapula (the area where it connected to the humerus
The humerus (; : humeri) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius (bone), radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extrem ...
) was concave and had a somewhat ovoid
An oval () is a closed curve in a plane which resembles the outline of an egg. The term is not very specific, but in some areas of mathematics (projective geometry, technical drawing, etc.), it is given a more precise definition, which may inc ...
shape. The glenoid appears to have been downwards-pointing, unlike the more sideways-facing glenoids of certain early-diverging cynodonts. The coracoid
A coracoid is a paired bone which is part of the shoulder assembly in all vertebrates except therian mammals (marsupials and placentals). In therian mammals (including humans), a coracoid process is present as part of the scapula, but this is n ...
and procoracoid bones have not been preserved, but there were articular surfaces for these bones on the scapula.
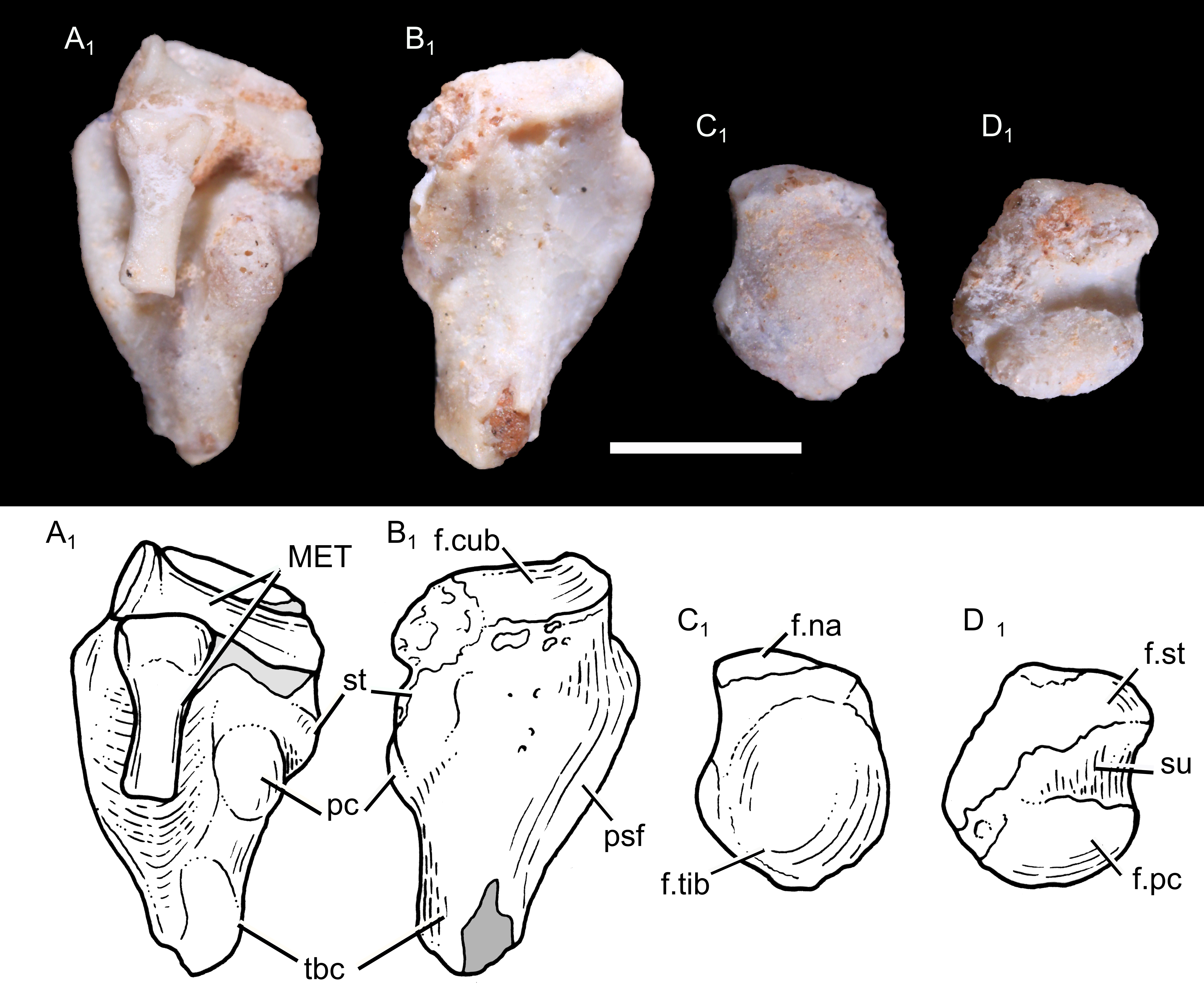
 The specimen UFRGS-PV-1043-T preserves a complete left humerus (upper arm bone), with a length of . The shaft of the humerus was slender. It was somewhat twisted, with an angulation of 15 degrees between the opposite ends of the bone. A twisted humerus is found in most cynodonts outside
The specimen UFRGS-PV-1043-T preserves a complete left humerus (upper arm bone), with a length of . The shaft of the humerus was slender. It was somewhat twisted, with an angulation of 15 degrees between the opposite ends of the bone. A twisted humerus is found in most cynodonts outside Theria
Theria ( or ; ) is a scientific classification, subclass of mammals amongst the Theriiformes. Theria includes the eutherians (including the Placentalia, placental mammals) and the metatherians (including the marsupials) but excludes the egg-lay ...
(the clade containing modern marsupial
Marsupials are a diverse group of mammals belonging to the infraclass Marsupialia. They are natively found in Australasia, Wallacea, and the Americas. One of marsupials' unique features is their reproductive strategy: the young are born in a r ...
s and placental
Placental mammals (infraclass Placentalia ) are one of the three extant subdivisions of the class Mammalia, the other two being Monotremata and Marsupialia. Placentalia contains the vast majority of extant mammals, which are partly distinguished ...
s), including in modern monotreme
Monotremes () are mammals of the order Monotremata. They are the only group of living mammals that lay eggs, rather than bearing live young. The extant monotreme species are the platypus and the four species of echidnas. Monotremes are typified ...
s. However, the twisting of the humerus was relatively low in ''Brasilodon'' when compared to that of many other non-therian cynodonts. On the proximal side (the side connecting to the shoulder), the humeral head had a hemispherical shape typical of mammaliaforms, but unlike that of more basal cynodonts, where the humeral head was generally more ovoid. Unlike in most therians, the humeral head faced posterolaterally (backwards and to the side). There was a ridge extending from the humeral head to the ectepicondylar crest on the other end of the bone. Unlike more basal cynodonts, ''Brasilodon'' had a distinct greater tubercle
The greater tubercle of the humerus is the outward part the upper end of that bone, adjacent to the large rounded prominence of the humerus head. It provides attachment points for the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and teres minor muscles, th ...
, though it was quite small. The lesser tubercle
The lesser tubercle of the humerus
The humerus (; : humeri) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius (bone), radius and ulna, and consists of thre ...
had a thick and bulbous shape. It was larger than the greater tubercle, as in basal mammaliaforms and monotremes, but unlike in multituberculate
Multituberculata (commonly known as multituberculates, named for the multiple tubercles of their teeth) is an extinct order of rodent-like mammals with a fossil record spanning over 130 million years. They first appeared in the Middle Jurassic, a ...
s, spalacotheriid
Spalacotheriidae is a family of extinct mammals belonging to the paraphyletic group 'Symmetrodonta'. They lasted from the Early Cretaceous to the Campanian in North America, Europe, Asia and North Africa.
Spalacotheriids are characterised by hav ...
s and therians. The deltopectoral crest was confluent with the greater tubercle, and extended across 48% of the length of the humerus. The crest was quite large and robust, like in other non-mammalian cynodonts, monotremes and fossorial
A fossorial animal () is one that is adapted to digging and which lives primarily (but not solely) underground. Examples of fossorial vertebrates are Mole (animal), moles, badgers, naked mole-rats, meerkats, armadillos, wombats, and mole salamand ...
(burrowing) therians such as moles. On the other side of the bone, there was another crest known as the teres crest. This crest was found in most Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era is the Era (geology), era of Earth's Geologic time scale, geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Period (geology), Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian r ...
cynodonts, but missing in '' Vincelestes'' and therians. The teres crest was about as long as the deltopectoral crest, and extended from the lesser tubercle to a large and ovoid protrusion near the middle of the bone. This protrusion may have served as an anchor for the teres major muscle
The teres major muscle is a muscle of the upper limb. It attaches to the scapula and the humerus and is one of the seven scapulohumeral muscles. It is a thick but somewhat flattened muscle.
The teres major muscle (from Latin ''teres'', meanin ...
. A similar structure existed in many other Mesozoic cynodonts, but not in multituberculates, spalacotheriids or therians. On the front surface of the humerus, there was a wide bicipital groove, bordered by the deltopectoral and teres crests, similar to that of many other Mesozoic cynodonts. The bicipital groove likely served as an attachment point for the coracobrachialis muscle
The coracobrachialis muscle muscle in the upper medial part of the arm. It is located within the anterior compartment of the arm. It originates from the coracoid process of the scapula; it inserts onto the middle of the medial aspect of the body ...
. The distal side of the humerus (the side connected to the radius
In classical geometry, a radius (: radii or radiuses) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its Centre (geometry), center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The radius of a regular polygon is th ...
and ulna
The ulna or ulnar bone (: ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone in the forearm stretching from the elbow to the wrist. It is on the same side of the forearm as the little finger, running parallel to the Radius (bone), radius, the forearm's other long ...
of the forearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, techn ...
) had a width of 43% the length of the humerus. This was narrower than in many other non-mammalian cynodonts, as well as in monotremes, but wider than in the basal mammaliaform ''Morganucodon'' and the therian ''Didelphis''. The entepicondyle was quite robust, and had a protrusion that pointed towards the proximal end of the bone. The ectepicondyle was more narrow and less protruding than the entepicondyle. The entepicondylar foramen
The entepicondylar foramen is an opening in the distal (far) end of the humerus (upper arm bone) present in some mammals. It is often present in primitive placentals, such as the enigmatic Madagascan '' Plesiorycteropus''. In most Neotominae and a ...
was a large and elongated hole. Conversely, there was no ectepicondylar foramen; this hole was found in most cynodonts more basal than ''Brasilodon'', but missing in tritylodontids and most mammaliaforms. The ulnar and radial
Radial is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
Mathematics and Direction
* Vector (geometric), a line
* Radius, adjective form of
* Radial distance (geometry), a directional coordinate in a polar coordinate system
* Radial set
* A ...
condyles (the parts connecting to the ulna and radius, respectively) had a bulbous shape, as seen in other non-mammalian cynodonts. The condyles were separated by a narrow groove, and lacked the trochlear (pulley-like) shape seen in many crown-group mammals, like therians or the stem-monotreme ''Kryoryctes
''Kryoryctes'' is a genus of prehistoric monotreme mammal from the Early Cretaceous (Albian) Eumeralla Formation of Victoria (Australia), Victoria, Australia from the Otway Group of Dinosaur Cove. It is known only from a partial right humerus, es ...
''. The ulnar condyle was visible both on the front and back sides of the humerus. Its front side was somewhat transversely compressed. The radial condyle was larger than the ulnar condyle, but was not visible at the back side of the bone. The olecranon fossa
The olecranon fossa is a deep triangular depression on the posterior side of the humerus, superior to the trochlea. It provides space for the olecranon of the ulna during extension of the forearm.
Structure
The olecranon fossa is located ...
(a depression on the back side of the humerus) was quite shallow, unlike the deeper fossa seen in multituberculates, ''Vincelestes'' and therians.
 The left radius of UFRGS-PV-1043-T is long. The radius was slender, with a circular cross-section near the proximal end (closer to the elbow). The head of the radius (where it articulated with the humerus) was approximately circular, with a cup-shaped depression in the middle surrounded by a bulbous rim. The head was angled somewhat towards the anteromedial (front right) side. On the posteromedial (back right) side of the head, there was a small articular facet where it would have articulated with the radial notch of the ulna. There was no radial tuberosity for the attachment of the
The left radius of UFRGS-PV-1043-T is long. The radius was slender, with a circular cross-section near the proximal end (closer to the elbow). The head of the radius (where it articulated with the humerus) was approximately circular, with a cup-shaped depression in the middle surrounded by a bulbous rim. The head was angled somewhat towards the anteromedial (front right) side. On the posteromedial (back right) side of the head, there was a small articular facet where it would have articulated with the radial notch of the ulna. There was no radial tuberosity for the attachment of the biceps
The biceps or biceps brachii (, "two-headed muscle of the arm") is a large muscle that lies on the front of the upper arm between the shoulder and the elbow. Both heads of the muscle arise on the scapula and join to form a single muscle bel ...
muscle. The distal end of the bone (closer to the wrist) was shaped like a flattened rectangle. The distal end was somewhat curved posteromedially, which would have allowed the bone to cross over the front of the ulna, as in tritylodontids, ''Morganucodon'' and opossums. The distal articular surface (where it connected to the wrist) also had a rectangular shape.
The right ulna of UFRGS-PV-1043-T has a length of . As in most cynodonts, the ulna was narrow mediolaterally (from side to side), and had a sigmoid (s-like) shape. On the sides of the bone, there were two grooves running from one end of the bone to the other, enclosed by thickened edges on the front and back sides. The grooves are thought to have served as attachment points for extensor and flexor muscles. On the proximal end of the bone, there was a well-developed and ossified olecranon
The olecranon (, ), is a large, thick, curved bony process on the proximal, posterior end of the ulna. It forms the protruding part of the elbow and is opposite to the cubital fossa or elbow pit (trochlear notch). The olecranon serves as a lever ...
process. With the exception of ''Trucidocynodon
''Trucidocynodon'' is an extinct genus of ecteniniid cynodonts from the Upper Triassic (Carnian) of Brazil. It contains a single species, ''Trucidocynodon riograndensis''. Fossils of ''Trucidocynodon'' were discovered in outcrops of the Upper Sa ...
'' and tritylodontids, no cynodonts more basal than ''Brasilodon'' are known to have had an ossified olecranon, and it is thought to have been cartilaginous
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. Semi-transparent and non-porous, it is usually covered by a tough and fibrous membrane called perichondrium. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints ...
in those taxa. The olecranon of ''Brasilodon'' made up a bit less than 20% of the length of the ulna, and was directed forwards relative to the rest of the bone. The olecranon was somewhat thicker from side to side than the rest of the bone. The semilunar notch
The trochlear notch (), also known as semilunar notch and greater sigmoid cavity, is a large depression in the upper extremity of the ulna that fits the trochlea of the humerus (the bone directly above the ulna in the arm) as part of the elbow ...
, where the ulna articulated with the ulnar condyle of the humerus, was large and semicircular. The anconeal process was quite small, like in more basal cynodonts and the docodont
Docodonta is an Order (biology), order of extinct Mesozoic Mammaliaformes, mammaliaforms (advanced cynodonts closely related to true Crown group, crown-group mammals). They were among the most common mammaliaforms of their time, persisting from t ...
mammaliaform ''Haldanodon
''Haldanodon'' is an extinct docodont mammaliaform which lived in the Upper Jurassic (Kimmeridgian, about 145 million years ago). Its fossil remains have been found in Portugal, in the well-known fossil locality of Guimarota, which is in the Alco ...
'', but unlike in many other mammaliaforms, where the anconeal process forms a prominent crest.
 The
The pelvis
The pelvis (: pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of an Anatomy, anatomical Trunk (anatomy), trunk, between the human abdomen, abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also c ...
(hip bone) of UFRGS-PV-1043-T preserves a complete left acetabulum
The acetabulum (; : acetabula), also called the cotyloid cavity, is a wikt:concave, concave surface of the pelvis. The femur head, head of the femur meets with the pelvis at the acetabulum, forming the Hip#Articulation, hip joint.
Structure
The ...
and pubis, and an incomplete left ilium and ischium
The ischium (; : is ...
. The acetabulum is where the femur
The femur (; : femurs or femora ), or thigh bone is the only long bone, bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many quadrupeds, four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg.
The Femo ...
of the hindlimb articulates with the pelvis. The acetabulum of ''Brasilodon'' was a deep, spherical and sideways-facing depression. The three bones making up the acetabulum (pubis, ilium and ischium) were fused together, with no sutures being visible; this is a feature that ''Brasilodon'' shared with mammaliaforms, while the bones were more distinct in some more basal cynodonts such as traversodontids. The bones formed three distinct crests known as ''supraacetabular buttresses'' around the acetabulum. The buttresses were separated by gaps of , unlike in modern therians, where there is a fully ossified rim around the acetabulum. The gaps would likely have been filled by fibrocartilage
Fibrocartilage consists of a mixture of white fibrous tissue and cartilaginous tissue in various proportions. It owes its inflexibility and toughness to the former of these constituents, and its elasticity to the latter. It is the only type of ...
in the living animal. The blade of the ilium is badly preserved, but the shape of the base indicates that the postacebular (backwards-pointing) part of the blade was either reduced or absent in ''Brasilodon'', much like in other prozostrodontia
Prozostrodontia is a clade of cynodonts including mammaliaforms and their closest relatives such as Tritheledontidae and Tritylodontidae. It was erected as a node-based taxon by Liu and Olsen (2010) and defined as the least inclusive clade contai ...
ns. The pubic tuberosity was located below the acetabulum as in most probainognathians, including modern therians. In basal epicynodonts, monotremes and the spalacotheriid ''Akidolestes
''Akidolestes'' is an extinct genus of mammals of the family Spalacotheriidae, a group of mammals related to therians (the subclass containing marsupials and placentals).
The genus name, ''Akidolestes'', is derived from ''akido'', Greek for p ...
'', the pubic tuberosity was located in front of the acetabulum instead. The pubis and ischium formed a large and ovoid obturator foramen
The obturator foramen is the large, Bilateral symmetry, bilaterally paired opening of the bony pelvis. It is formed by the pubis and ischium. It is mostly closed by the obturator membrane except for a small opening, the obturator canal, through wh ...
.
 The right femur (thigh bone) of UFRGS-PV-1043-T is long. The shaft of the femur was mostly straight, but with a prominent forward bend close to the hip joint, as in other non-mammalian cynodonts; in modern mammals, this bend is less well-developed. The proximal part of the shaft (closer to the hip) was mostly square-shaped, but it became more compressed from front to back more distally (towards the knee), while simultaneously becoming wider from side to side. The proximal and distal ends of the bone had the same width. On the proximal end of the bone, the
The right femur (thigh bone) of UFRGS-PV-1043-T is long. The shaft of the femur was mostly straight, but with a prominent forward bend close to the hip joint, as in other non-mammalian cynodonts; in modern mammals, this bend is less well-developed. The proximal part of the shaft (closer to the hip) was mostly square-shaped, but it became more compressed from front to back more distally (towards the knee), while simultaneously becoming wider from side to side. The proximal and distal ends of the bone had the same width. On the proximal end of the bone, the femoral head
The femoral head (femur head or head of the femur) is the highest part of the thigh bone (femur
The femur (; : femurs or femora ), or thigh bone is the only long bone, bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and the ...
(which articulated with the acetabulum of the hip) had a hemispherical shape. The head was separated from the rest of the bone by a short femoral neck, as in tritylodontids and mammaliaforms; more primitive cynodonts lacked a femoral neck. The head was angled around 60 degrees medially (to the right) compared to the longitudinal axis of the femur, resembling the condition in multituberculates and spalacotheriids. Unlike in mammaliaforms, there was no fovea capitis on the femoral head. Slightly distally to the femoral head, there was a well-developed projection known as the greater trochanter on the left side of the bone. A distinct greater trochanter is also found in tritylodontids and mammaliaforms, but the greater trochanter was confluent with the femoral head in more basal cynodonts. On the right side of the bone, there was a short crest called the lesser trochanter
In human anatomy, the lesser trochanter is a conical, posteromedial, bony projection from the shaft of the femur. It serves as the principal insertion site of the iliopsoas muscle.
Structure
The lesser trochanter is a conical posteromedial p ...
. The lesser trochanter pointed to the right, and was visible on the front side of the bone, as in many other probainognathians. In more basal cynodonts, it generally was more backwards-pointing, and not visible on the front side. The lesser trochanter did not extend as far towards the proximal end of the bone as in basal mammaliaforms. There was no third trochanter
In human anatomy, the third trochanter is a bony projection occasionally present on the proximal femur near the superior border of the gluteal tuberosity. When present, it is oblong, rounded, or conical in shape and sometimes continuous with the ...
. On the back side of the femur, between the greater and lesser trochanters, there was a deep and narrow depression called the intertrochanteric fossa. On the distal edge of this fossa, there was an intertrochanteric crest
The intertrochanteric crest is a prominent bony ridge upon the posterior surface of the femur at the junction of the neck and the shaft of the femur. It extends between the greater trochanter superiorly, and the lesser trochanter inferiorly.
An ...
which connected the two trochanters. This crest is also found in most therians, but was missing in most Mesozoic cynodont groups. There was a relatively shallow, triangular depression located distally to the intertrochanteric crest; this probably served as an attachment point for the hip adductor muscles. On the back side of the distal end of the femur, there were two condyles that would have connected to the tibia
The tibia (; : tibiae or tibias), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two Leg bones, bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outsi ...
, the medial and lateral
Lateral is a geometric term of location which may also refer to:
Biology and healthcare
* Lateral (anatomy), a term of location meaning "towards the side"
* Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle, an intrinsic muscle of the larynx
* Lateral release ( ...
condyles. The medial condyle was compressed from side to side. The popliteal fossa
The popliteal fossa (also referred to as hough or kneepit in analogy to the cubital fossa) is a shallow depression located at the back of the knee joint. The bones of the popliteal fossa are the femur and the tibia. Like other flexion surfaces ...
had a triangular shape and was located close to the condyles.
 UFRGS-PV-1043-T preserves a nearly complete left tibia (shin bone). It was a slender bone, with the preserved parts having a length of . The shaft was mostly straight, but with a slight medial (rightwards) curve in the proximal part (towards the knee); more basal cynodonts generally had a stronger medial curve of the tibia. The shaft became progressively more flattened towards the distal end (towards the ankle). On the proximal part, there were two articular facets, the medial and
UFRGS-PV-1043-T preserves a nearly complete left tibia (shin bone). It was a slender bone, with the preserved parts having a length of . The shaft was mostly straight, but with a slight medial (rightwards) curve in the proximal part (towards the knee); more basal cynodonts generally had a stronger medial curve of the tibia. The shaft became progressively more flattened towards the distal end (towards the ankle). On the proximal part, there were two articular facets, the medial and lateral
Lateral is a geometric term of location which may also refer to:
Biology and healthcare
* Lateral (anatomy), a term of location meaning "towards the side"
* Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle, an intrinsic muscle of the larynx
* Lateral release ( ...
facets, which articulated with the condyles of the femur. The lateral facet was wider than the medial one. The distal end of the tibia has not been preserved.
UFRGS-PV-1043-T preserves two left tarsal bones, the calcaneum
In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus (; from the Latin ''calcaneus'' or ''calcaneum'', meaning heel; : calcanei or calcanea) or heel bone is a bone of the tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is t ...
and astragalus
Astragalus may refer to:
* ''Astragalus'' (plant), a large genus of herbs and small shrubs
*Astragalus (bone)
The talus (; Latin for ankle or ankle bone; : tali), talus bone, astragalus (), or ankle bone is one of the group of foot bones known ...
. The calcaneum (heel bone) of ''Brasilodon'' had a low and broad shape, unlike the narrow calcaneum found in multituberculates, the "symmetrodont
Symmetrodonta is a group of Mesozoic mammals and mammal-like synapsids characterized by the triangular aspect of the molars when viewed from above, and the absence of a well-developed talonid. The traditional group of 'symmetrodonts' ranges in ...
" '' Zhangheotherium'' and therians. It had a convex upper surface and a concave lower surface. There was a well-developed tuber calcis on the back end of the bone; this feature is found in most eucynodonts, but is missing in more basal taxa like '' Thrinaxodon''. There was a peroneal shelf on the lateral (left) side of the calcaneum. On the medial (right) side, there was a projection known as the sustentaculum tali, which would have connected to the underside of the astragalus (ankle bone). In basal cynodonts like ''Thrinaxodon'', no sustentaculum tali has been found, suggesting that it was cartilaginous, if it even existed in those taxa. The left astragalus was smaller than the calcaneum. It had a hemispherical dorsomedial (top right) surface and a flat lateroplantar (bottom left) surface. The front end of the astragalus had a small head. The neck that separated the head from the rest of the bone was shorter than in modern therians.
UFRGS-PV-1043-T also preserves two incomplete metatarsal
The metatarsal bones or metatarsus (: metatarsi) are a group of five long bones in the midfoot, located between the tarsal bones (which form the heel and the ankle) and the phalanges ( toes). Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are ...
s, comprising a proximal and a distal end, which would have connected to the tarsals and to the phalanges, respectively. The proximal end bore a circular depression, while distal end had two symmetrical condyles. A possible metapod (metatarsal or metacarpal
In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus, also known as the "palm bones", are the appendicular bones that form the intermediate part of the hand between the phalanges (fingers) and the carpal bones ( wrist bones), which articulate ...
) fragment is also known from the specimen UFRGS-PV-0765-T, which had a broad proximal part and a more narrow shaft. Both of these specimens also preserve some phalanges (finger bones), with UFRGS-PV-0765-T preserving a nearly complete middle phalange. This phalange was rather short, with a concave proximal end and two small condyles on the distal end.
Classification
The genus ''Brasilodon'' belongs to Brasilodontidae, a family of advanced probainognathian cynodonts. Along with ''Brasilodon'', two contemporary genera (''Brasilitherium'' and ''Minicynodon'') have been assigned to the family, both of which are likely to be synonyms of ''Brasilodon''. ''Protheriodon
''Protheriodon'' is an extinct genus of probainognathian cynodonts which existed in the Santa Maria Formation of the Paraná Basin in southeastern Brazil during the middle Triassic period. It contains the species ''Protheriodon estudianti''. It ...
'', a genus from the Middle Triassic
In the geologic timescale, the Middle Triassic is the second of three epoch (geology), epochs of the Triassic period (geology), period or the middle of three series (stratigraphy), series in which the Triassic system (stratigraphy), system is di ...
( Ladinian) of Brazil, and '' Panchetocynodon'', a poorly known cynodont from the Early Triassic
The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between 251.9 Ma and Ma (million years ago). Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which ...
(Induan
The Induan is the first age of the Early Triassic epoch in the geologic timescale, or the lowest stage of the Lower Triassic series in chronostratigraphy. It spans the time between 251.9 Ma and 249.9 Ma (million years ago). The Induan is so ...
) of India, were also placed in Brasilodontidae in a 2013 paper by José Bonaparte. However, ''Protheriodon'' has more recently been found to be an early-diverging probainognathian unrelated to brasilodontids, while ''Panchetocynodon'' is otherwise treated as an ''incertae sedis
or is a term used for a taxonomy (biology), taxonomic group where its broader relationships are unknown or undefined. Alternatively, such groups are frequently referred to as "enigmatic taxa". In the system of open nomenclature, uncertainty ...
'' taxon, whose relationships to other taxa are unclear, due to its incompleteness.
Features of the skull and dentition of ''Brasilodon'' indicate that it was a derived cynodont closely related to mammals, the only extant cynodonts. Phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical dat ...
analyses have commonly recovered it as a member of the clade Mammaliamorpha, lying closer to mammals than the tritylodontids, but outside Mammaliaformes, a more exclusive clade containing mammals and their closest relatives, such as morganucodonts, docodonts and haramiyida
Haramiyida is a possibly Paraphyly, paraphyletic order of Mammaliaformes, mammaliaform cynodonts or mammals of controversial taxonomic affinites. Their teeth, which are by far the most common remains, resemble those of the multituberculates. Howe ...
ns. The cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not s ...
below is adapted from a 2019 analysis by Wallace ''et al.'':


Palaeobiology

Locomotion
Features of the postcranium indicate that ''Brasilodon'' was a generalised animal capable of diverse modes of locomotion, including digging and climbing. The large tuberosity near the deltopectoral crest of the humerus implies that the teres major muscle (an important retractor muscle of the forelimb) was quite large, as seen in modern fossorialrodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the Order (biology), order Rodentia ( ), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and Mandible, lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal specie ...
s. The digging adaptations of ''Brasilodon'' were however less pronounced than in modern fossorial mammals, as well as many other non-mammalian cynodonts. Evidence for scansorial (climbing) abilities includes the hemispherical humeral and femoral heads, which would have allowed a wide range of rotation of the shoulder and hip joints, the well-developed ectepicondylar crest, the hemispherical capitulum and nearly circular radial head, which would have conferred high mobility to the elbow, and the small anconeal process of the ulna. Several features of the humerus, including the twisted shaft, indicate that ''Brasilodon'' had sprawling or semi-sprawling forelimbs. On the other hand, features of the pelvis and hindlimbs, such as the poorly developed postacetabular portion of the iliac blade, indicate a more erect ( parasagittal) posture of the hindlimbs.
Tooth replacement
According to one theory, outlined in detail in a 2010 paper by Martinelli ''et al.'', ''Brasilodon'' had apolyphyodont
A polyphyodont is any animal whose tooth (animal), teeth are continually replaced. In contrast, diphyodonts are characterized by having only two successive sets of teeth.
Polyphyodonts include most toothed fishes (most notably sharks), many repti ...
tooth replacement, where the teeth were replaced more than once throughout the animal's lifetime, though it is unclear how many successive postcanine replacements there were in ''Brasilodon''. The postcanine replacement ceased long before the death of an individual, allowing extremely strong wear to develop in the teeth in older individuals. In some cases, the individual's teeth wore down over time to less than half the height of the crown still remaining. The size of the postcanine diastema indicates that the front postcanines may have been lost faster than in the primitive cynodont ''Thrinaxodon''.
According to Martinelli ''et al.'' (2010), the postcanines were replaced in an alternating manner. The postcanine replacement would have occurred from the back to the front, like in several other non-mammaliaform probainognathians, and would thus have differed from that of early mammaliaforms, where the postcanines were replaced from the front towards the back. This may have been due to the unlimited skull growth of early probainognathians. Tooth replacement variation can perhaps also be attributed to diet, with the herbivorous/omnivorous traversodontids having widened postcanines and a sequential tooth replacement, and carnivorous and insectivorous non-mammaliaform probainognathians like ''Brasilodon'' having an alternating tooth replacement instead.
A 2022 study by Cabreira ''et al.'' suggests that ''Brasilodon'' actually was diphyodont
A diphyodont is any animal with two sets of teeth, initially the ''deciduous'' set and consecutively the '' permanent'' set. Most mammals are diphyodonts—as to chew their food they need a strong, durable and complete set of teeth.
Diphyodonts ...
, replacing its teeth only once, like most modern mammals. According to this theory, the postcanines in ''Brasilodon'' consisted of a set of deciduous teeth
Deciduous teeth or primary teeth, also informally known as baby teeth, milk teeth, or temporary teeth,Fehrenbach, MJ and Popowics, T. (2026). ''Illustrated Dental Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy'', 6th edition, Elsevier, page 287–296. are ...
, which were replaced, and a set of permanent teeth
Permanent teeth or adult teeth are the second set of teeth formed in diphyodont mammals. In humans and old world simians, there are thirty-two permanent teeth, consisting of six maxillary and six mandibular molars, four maxillary and four mandib ...
divided into premolar
The premolars, also called premolar Tooth (human), teeth, or bicuspids, are transitional teeth located between the Canine tooth, canine and Molar (tooth), molar teeth. In humans, there are two premolars per dental terminology#Quadrant, quadrant in ...
s and molars
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat tooth, teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammal, mammals. They are used primarily to comminution, grind food during mastication, chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, '' ...
. The study suggests that the deciduous postcanines in ''Brasilodon'' erupted sequentially in a back-to-front direction, while the molars were added in the opposite direction, from the front to the back.
Palaeoecology
Specimens of ''Brasilodon'' have been found in two localities. The holotype was found at the Linha São Luiz locality, within the municipality of Faxinal do Soturno. Other specimens have been found at the Sesmaria do Pinhal locality in the municipality of Candelária; both of these locations lie within the Brazilian part of theParaná Basin
The Paraná Basin (, ) is a large cratonic sedimentary basin situated in the central-eastern part of South America. About 75% of its areal distribution occurs in Brazil, from Mato Grosso to Rio Grande do Sul states. The remainder area is distribu ...
. The rocks where ''Brasilodon'' was found belong to the upper part of the Candelária Sequence, which corresponds to a biostratigraphic unit known as the ''Riograndia'' Assemblage Zone. The ''Riograndia'' AZ has been dated to the early Norian age of the Late Triassic epoch, around 225.42 million years ago. Cynodonts are one of the most common and taxonomically diverse elements in this Assemblage Zone, and are represented by many well-preserved specimens. In addition to ''Brasilodon'', cynodonts are represented by the tritheledontids ''Irajatherium
''Irajatherium'' is an extinct genus of cynodonts, known only of the type species ''Irajatherium hernandezi''.Martinelli et al., 2005 It is named in honor of Irajá Damiani Pinto.
Species
''Irajatherium hernandezi'' is a species known only by ...
'' and ''Riograndia
''Riograndia'' is an extinct genus of prozostrodontian cynodonts from the Late Triassic of Brazil. The type species, type and only species is ''Riograndia guaibensis'', named after the State of Rio Grande do Sul and Guaíba Basin, where it was di ...
'', the basal mammaliamorph '' Botucaraitherium'', and indeterminate traversodontids. Other animals include the dicynodont
Dicynodontia is an extinct clade of anomodonts, an extinct type of non-mammalian therapsid. Dicynodonts were herbivores that typically bore a pair of tusks, hence their name, which means 'two dog tooth'. Members of the group possessed a horny, t ...
'' Jachaleria'', the procolophonid '' Soturnia'', the lepidosauromorphs '' Cargninia'', '' Clevosaurus'' and '' Lanceirosphenodon'', and the avemetatarsalia
Avemetatarsalia (meaning "bird metatarsals") is a clade of diapsid Reptile, reptiles containing all archosaurs more closely related to birds than to crocodilians. The two most successful groups of avemetatarsalians were the dinosaurs and pterosau ...
ns '' Faxinalipterus'', '' Guaibasaurus'', ''Macrocollum
''Macrocollum'' is a genus of unaysauridae, unaysaurid sauropodomorph dinosaur that lived during the Late Triassic period (geology), period (early Norian) in what is now Brazil. It is one of the oldest dinosaurs known.
Discovery and naming
''Mac ...
'', ''Maehary
''Maehary'' (meaning "one who looks to the sky" in Guarani language, Guaraní) is an extinct genus of probable gracilisuchid pseudosuchian archosaurs from the Late Triassic (Norian) Caturrita Formation of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. The genus con ...
'', '' Sacisaurus'' and '' Unaysaurus''. Indeterminate remains of temnospondyl
Temnospondyli (from Greek language, Greek τέμνειν, ''temnein'' 'to cut' and σπόνδυλος, ''spondylos'' 'vertebra') or temnospondyls is a diverse ancient order (biology), order of small to giant tetrapods—often considered Labyrinth ...
s, phytosaurs and other groups have also been found.
The location where these fossils were found is a fluvial system, characterized by large quantities of fine sandstone forming sandy beds, resulting from sedimentation in the basin during peak flow events.
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q1064317 Mammaliamorpha Norian genera Late Triassic synapsids of South America Triassic Brazil Fossils of Brazil Paraná Basin Transitional fossils Fossil taxa described in 2003 Taxa named by José Bonaparte