Bolos on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Volos (; ) is a coastal
 Modern Volos is built on the area of the ancient cities of
Modern Volos is built on the area of the ancient cities of
 Ottoman rule was not yet firm. The first period of Ottoman control lasted from 1393 to 1397, followed by another , but it was not until 1423 that Volos was definitively incorporated into the Ottoman Empire. The Ottoman name of the city was . The Ottomans strengthened the town's fortifications against a possible
Ottoman rule was not yet firm. The first period of Ottoman control lasted from 1393 to 1397, followed by another , but it was not until 1423 that Volos was definitively incorporated into the Ottoman Empire. The Ottoman name of the city was . The Ottomans strengthened the town's fortifications against a possible
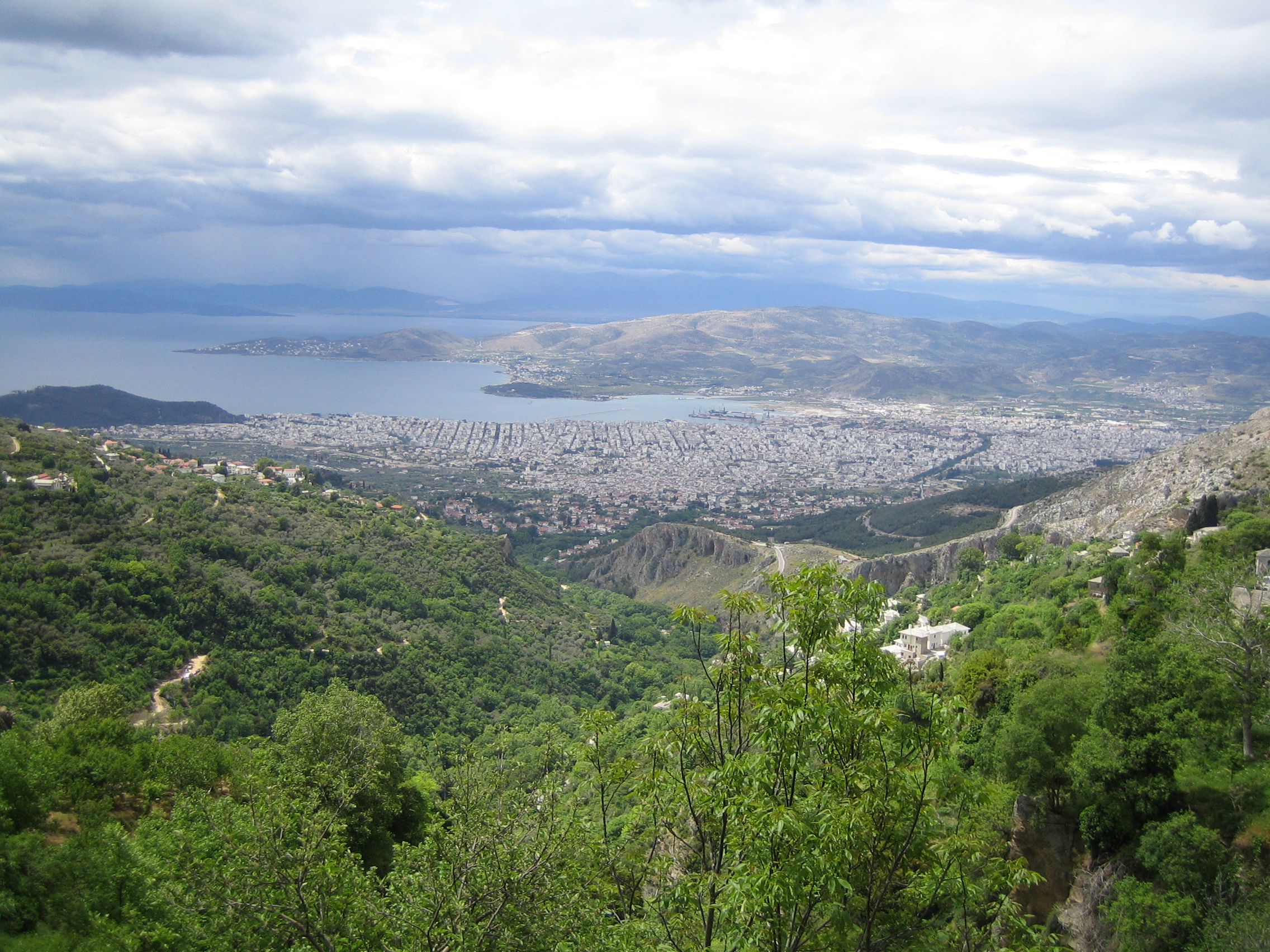 Volos is the administrative centre of the Magnesia regional unit. Many of the city domains are separated through natural barricades, such as rivers.
Three main rivers/mountain torrents all rise from mount
Volos is the administrative centre of the Magnesia regional unit. Many of the city domains are separated through natural barricades, such as rivers.
Three main rivers/mountain torrents all rise from mount
Σιδηροδρομικός σταθμός Βόλου 3601.jpg, The railway station, designed by Evaristo De Chirico.
Καπναποθήκες Σπίρερ 3653.jpg, The old Spierer tobacco warehouse
Archaeological Museum of Volos.jpg, Archaeological Museum of Volos
The development of the new city coincided with the flourishing of

 The city of Volos consists of the administrative and academic centre of
The city of Volos consists of the administrative and academic centre of
Volos 2w.jpg, View of the port.
Ikarous Volos 20110707 b.jpg, Cargo ship at the harbour.
Volos1.JPG, The promenade
Volos
The Official website of the Greek National Tourism Organisation
Port of Volos
{{Authority control Greek prefectural capitals Municipalities of Thessaly Mediterranean port cities and towns in Greece Provinces of Greece Port cities of the Aegean Sea Populated places in Magnesia (regional unit)
port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Hamburg, Manch ...
city
A city is a human settlement of a substantial size. The term "city" has different meanings around the world and in some places the settlement can be very small. Even where the term is limited to larger settlements, there is no universally agree ...
in Thessaly
Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, a ...
situated midway on the Greek mainland, about north of Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
and south of Thessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its Thessaloniki metropolitan area, metropolitan area) and the capital cit ...
. It is the capital of the Magnesia regional unit of the Thessaly Region. Volos is also the only outlet to the sea from Thessaly, the country's largest agricultural region. With a population of 85,803 (2021), the city is an important industrial centre, and its port provides a bridge between Europe and Asia.
Volos is the newest of the Greek port cities, with a large proportion of modern buildings erected following catastrophic earthquakes in 1955. It includes the municipal units of Volos, Nea Ionia
Nea Ionia (, meaning New Ionia) is a town and a northern suburb of the Athens agglomeration, Greece, and a municipality of the Attica region. It was named after Ionia, the region in Anatolia from which many Greeks migrated in the 1920s as a part ...
and Iolkos
Iolcus (; also rendered ''Iolkos'' ; and Ἰαωλκός; ; ) is an ancient city, a modern village and a former municipality in Magnesia, Thessaly, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of Volos, of which it is a municipal un ...
, as well as smaller suburban
A suburb (more broadly suburban area) is an area within a metropolitan area. They are oftentimes where most of a metropolitan areas jobs are located with some being predominantly residential. They can either be denser or less densely populated ...
communities. The economy of the city is based on manufacturing, trade, services and tourism. Home to the University of Thessaly
The University of Thessaly (UTh; Greek: ) is a public university in Thessaly, Greece, founded in 1984. The university includes the main campus in the city of Volos and regional campuses located in Karditsa, Larissa, Trikala, and the city of Lamia ...
, the city also offers facilities for conferences, exhibitions and major sporting, cultural and scientific events. Volos participated in the 2004 Olympic Games
The 2004 Summer Olympics (), officially the Games of the XXVIII Olympiad (), and officially branded as Athens 2004 (), were an international multi-sport event held from 13 to 29 August 2004 in Athens, Greece.
The Games saw 10,625 athletes ...
, and the city has since played host to other athletic events, such as the European Athletic Championships
The European Athletics Championships is a biennial (from 2010) athletics event organised by the European Athletic Association and is recognised as the elite continental outdoor athletics championships for Europe.
Editions
First held, for me ...
. Volos hosted the 7th International Olympiad on Astronomy and Astrophysics
The International Olympiad on Astronomy and Astrophysics (IOAA) is an annual astronomy and astrophysics competition for high school students. It is one of the international science olympiads.
The Olympiad was founded from a dissidence inside ...
from 27 July to 5 August 2013.
Location
Built at the innermost point of thePagasetic Gulf
The Pagasetic Gulf () is a rounded gulf (max. depth 102 metres) in the Magnesia regional unit (east central Greece) that is formed by the Mount Pelion peninsula. It is connected with the Euboic Sea. The passage into the Euboic Sea is narrow an ...
and at the foot of Mount Pilio (Pelion
Pelion or Pelium (Modern , ''Pílio''; Ancient Greek/Katharevousa: Πήλιον, ''Pēlion'') is a mountain at the southeastern part of Thessaly in northern Greece, forming a hook-like peninsula between the Pagasetic Gulf and the Aegean Sea. Its ...
, the land of the Centaurs
A centaur ( ; ; ), occasionally hippocentaur, also called Ixionidae (), is a creature from Greek mythology with the upper body of a human and the lower body and legs of a horse that was said to live in the mountains of Thessaly. In one version o ...
). The city spreads in the plain on the foothills of Mount Pelion, bordering the town of Agria
Agria () is a town and a former municipality in Magnesia, Thessaly, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Volos, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 25.227 km2. It lies ...
to the east and Nea Anchialos
Nea Anchialos () is a town and a former municipality in Magnesia, Thessaly, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Volos, of which it is a municipal unit. It is situated southwest of Volos and north of Almyr ...
to the southwest. Volos' municipality includes both towns, along with many nearby villages, including Makrinitsa
Makrinitsa (), nicknamed "balcony of Mt. Pelion," is a village and a former community in Magnesia, Thessaly, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Volos, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit ...
and Portaria
Portaria (Greek language, Greek: Πορταριά) is a village and a former Communities and Municipalities of Greece, municipality in Magnesia (regional unit), Magnesia, Thessaly, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the m ...
.
Volos is a major commercial port of mainland Greece in the Aegean sea (after Piraeus and Thessaloniki), with connection by ferry and hydrofoil to the nearby Sporades
The (Northern) Sporades are an archipelago along the east coast of Greece, northeast of the island of Euboea,"Skyros - Britannica Concise" (description), Britannica Concise, 2006, webpageEB-Skyrosnotes "including Skiathos, Skopelos, Skyros, and Al ...
Islands, which include Skiathos
Skiathos (, ; , ; and ) is a small Greece, Greek Islands of Greece, island in the northwest Aegean Sea. Skiathos is the westernmost island in the Northern Sporades archipelago, east of the Pelion peninsula in Magnesia (regional unit), Magnesia ...
, Skopelos
Skopelos (, ) is a Greek island in the western Aegean Sea. Skopelos is one of several islands that comprise the Northern Sporades island group, which lies east of the Pelion peninsula on the mainland and north of the island of Euboea. It is par ...
and Alonissos
Alonnisos ( ), also transliterated as Alonissos, is a Greek island in the Aegean Sea. After Skiathos and Skopelos it is the third member of the Northern Sporades. It is (2 nm) east of the island of Skopelos. Alonnisos is also the name of a ...
. There are also connections to Lemnos
Lemnos ( ) or Limnos ( ) is a Greek island in the northern Aegean Sea. Administratively the island forms a separate municipality within the Lemnos (regional unit), Lemnos regional unit, which is part of the North Aegean modern regions of Greece ...
, Lesbos
Lesbos or Lesvos ( ) is a Greek island located in the northeastern Aegean Sea. It has an area of , with approximately of coastline, making it the third largest island in Greece and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, eighth largest ...
, Chios
Chios (; , traditionally known as Scio in English) is the fifth largest Greece, Greek list of islands of Greece, island, situated in the northern Aegean Sea, and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, tenth largest island in the Medi ...
and Skyros
Skyros (, ), in some historical contexts Romanization of Greek, Latinized Scyros (, ), is an island in Greece. It is the southernmost island of the Sporades, an archipelago in the Aegean Sea. Around the 2nd millennium BC, the island was known as ...
.
History
Antiquity
 Modern Volos is built on the area of the ancient cities of
Modern Volos is built on the area of the ancient cities of Demetrias
Demetrias () was a Greek city in Magnesia in ancient Thessaly (east central Greece), situated at the head of the Pagasaean Gulf, near the modern city of Volos.
History
It was founded in 294 BCE by Demetrius Poliorcetes, who removed th ...
, Pagasae
Pagasae or Pagases (), also Pagasa, was a town and polis (city-state) of Magnesia in ancient Thessaly, currently a suburb of Volos. It is situated at the northern extremity of the bay named after it (Παγασητικὸς κόλπος, or ).
...
and Iolcos
Iolcus (; also rendered ''Iolkos'' ; and Ἰαωλκός; ; ) is an ancient city, a modern village and a former municipality in Magnesia, Thessaly, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of Volos, of which it is a municipal un ...
. Demetrias was established in 293 BC by Demetrius Poliorcetes
Demetrius I Poliorcetes (; , , ; ) was a Macedonian Greek nobleman and military leader who became king of Asia between 306 and 301 BC, and king of Macedon between 294 and 288 BC. A member of the Antigonid dynasty, he was the son of its founder, ...
, King of Macedon
Macedonia ( ; , ), also called Macedon ( ), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, which later became the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal ...
. Iolcus
Iolcus (; also rendered ''Iolkos'' ; and Ἰαωλκός; ; ) is an ancient city, a modern village and a former municipality in Magnesia, Thessaly, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of Volos, of which it is a municipal un ...
, or Iolkos, was known in mythology as the homeland of the hero Jason
Jason ( ; ) was an ancient Greek mythological hero and leader of the Argonauts, whose quest for the Golden Fleece is featured in Greek literature. He was the son of Aeson, the rightful king of Iolcos. He was married to the sorceress Med ...
, who boarded the ship Argo
In Greek mythology, the ''Argo'' ( ; ) was the ship of Jason and the Argonauts. The ship was built with divine aid, and some ancient sources describe her as the first ship to sail the seas. The ''Argo'' carried the Argonauts on their quest fo ...
accompanied by the Argonauts
The Argonauts ( ; ) were a band of heroes in Greek mythology, who in the years before the Trojan War (around 1300 BC) accompanied Jason to Colchis in his quest to find the Golden Fleece. Their name comes from their ship, ''Argo'', named after it ...
and sailed in quest of the Golden Fleece to Colchis
In classical antiquity and Greco-Roman geography, Colchis (; ) was an exonym for the Georgian polity of Egrisi ( ka, ეგრისი) located on the eastern coast of the Black Sea, centered in present-day western Georgia.
Its population, the ...
. To the west of Volos lie the Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
settlements of Dimini
Dimini (; older form: ''Diminion'') is a village near the city of Volos, in Thessaly (central Greece), in Magnesia. It was the seat of the municipality of Aisonia. The name Aisonia dates back to ancient times. Currently, Dimini is the weste ...
, with a ruined acropolis
An acropolis was the settlement of an upper part of an ancient Greek city, especially a citadel, and frequently a hill with precipitous sides, mainly chosen for purposes of defense. The term is typically used to refer to the Acropolis of Athens ...
, walls, and two beehive tombs dating to between 4000 and 1200 BC, and Sesklo
Sesklo (; ) is a village in Greece that is located near Volos, a city located within the municipality of Aisonia. The municipality is located within the regional unit of Magnesia that is located within the administrative region of Thessaly. ...
, with the remains of the oldest acropolis in Greece (6000 BC). The mound of Kastro/Palaia in western Volos is the site of a Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
settlement, including a Mycenaean palace complex where a couple of preserved Linear B
Linear B is a syllabary, syllabic script that was used for writing in Mycenaean Greek, the earliest Attested language, attested form of the Greek language. The script predates the Greek alphabet by several centuries, the earliest known examp ...
tablets have been found.
Byzantine era
Iolcus is still attested in the early Byzantine period but was eclipsed for most of theMiddle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
by Demetrias. The Slavic
Slavic, Slav or Slavonic may refer to:
Peoples
* Slavic peoples, an ethno-linguistic group living in Europe and Asia
** East Slavic peoples, eastern group of Slavic peoples
** South Slavic peoples, southern group of Slavic peoples
** West Slav ...
tribe of the Belegezites settled in the area during the 7th century.
Volos first appears again in 1333, as one of the cities captured by the Byzantine general John Monomachos
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Second Ep ...
in Thessaly, under the name "Golos" (Γόλος). The name is of Slavic origin, from ''golo'', ''golъ'', "barren". Another theory derives the name from Slavic ''golosh'', "seat of administration". Two alternative theories allude to a Greek origin through the words βολή (throw), as fishermen threw their nets into the sea from that area, and βώλος (piece of land) but the Greek scholar G. Hatzidakis considers them to be paretymologies at best. The modern form of the name is first attested in 1540.
The walls of medieval Golos follow the traces of the fortifications of ancient Iolcus, and many remnants of the ancient city have been found in the medieval citadel.
Along with the rest of Thessaly, Volos fell under Serbian
Serbian may refer to:
* Pertaining to Serbia in Southeast Europe; in particular
**Serbs, a South Slavic ethnic group native to the Balkans
** Serbian language
** Serbian culture
**Demographics of Serbia, includes other ethnic groups within the co ...
rule in 1348, governed by Gregory Preljub
Preljub ( sr-Cyrl, Прељуб; c. 1312–1356) was a Serbian magnate who served Emperor Stefan Dušan (r. 1331–55) as '' vojvoda'' (general). He participated in the southern conquests and held Thessaly with the rank of ''caesar'' (''kesar'') ...
. After Preljub's death Thessaly passed under the brief rule of Nikephoros II Orsini
Nikephoros II Orsini Doukas (Greek: Νικηφόρος Β΄ Δούκας, ''Nikēphoros II Doukas''), was the ruler of Epirus from 1335 to 1338 and from 1356 until his death in 1359.
Life
Nikephoros was the son of John Orsini of Epirus and An ...
, followed by the Serbian rulers Simeon Uroš
Simeon Uroš ( sr-Cyrl, Симеон Урош, ; 1326–1370), nicknamed Siniša (), was a self-proclaimed Emperor of Serbs and Greeks, from 1356 to 1370. He was son of Serbian King Stephen Uroš III and Byzantine Princess Maria Palaiologina. ...
and John Uroš
Jovan Uroš Nemanjić ( sr-Cyrl, Јован Урош Немањић) or John Ouresis Doukas Palaiologos or Joasaph of Meteora (), was the ruler of Thessaly from c. 1370 to c. 1373, retiring as a monk for the next half century thereafter. He died i ...
. After the latter's death in 1373, Thessaly returned under Byzantine rule for twenty years, until its conquest by the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
under Sultan Bayezid I
Bayezid I (; ), also known as Bayezid the Thunderbolt (; ; – 8 March 1403), was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1389 to 1402. He adopted the title of ''Sultan-i Rûm'', ''Rûm'' being the Arabic name for the Eastern Roman Empire. In 139 ...
.
Ottoman era
 Ottoman rule was not yet firm. The first period of Ottoman control lasted from 1393 to 1397, followed by another , but it was not until 1423 that Volos was definitively incorporated into the Ottoman Empire. The Ottoman name of the city was . The Ottomans strengthened the town's fortifications against a possible
Ottoman rule was not yet firm. The first period of Ottoman control lasted from 1393 to 1397, followed by another , but it was not until 1423 that Volos was definitively incorporated into the Ottoman Empire. The Ottoman name of the city was . The Ottomans strengthened the town's fortifications against a possible Venetian
Venetian often means from or related to:
* Venice, a city in Italy
* Veneto, a region of Italy
* Republic of Venice (697–1797), a historical nation in that area
Venetians might refer to:
* Masters of Venetian painting in 15th-16th centuries
* ...
attack, and installed not only a garrison, but also Muslim settlers from Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
. The local Christian population in turn moved to the slopes of Pelion. From this time on, Volos became the chief settlement on the Pagasetic Gulf.
The city began to spread outside its walls in the late 16th/early 17th centuries, coinciding with a growth in commerce, helped by the city's famed twice-weekly local fair and the first works at the waterfront harbour. The fortress was captured by the Venetians under Francesco Morosini
Francesco Morosini (26 February 1619 – 16 January 1694) was the Doge of Venice from 1688 to 1694, at the height of the Great Turkish War. He was one of the many Doges and generals produced by the Venetian noble Morosini family.Encyclopæd ...
in 1665, during the Cretan War, but recovered and refortified by the Ottomans.
In May 1821, at the beginning of the Greek Revolution
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. In 1826, the Greeks were assisted ...
, the Greek rebels of Mount Pelion tried to capture the fortress but failed. On 8 April 1827, the Greek fleet, under the command of the British philhellene
Philhellenism ("the love of Greek culture") was an intellectual movement prominent mostly at the turn of the 19th century. It contributed to the sentiments that led Europeans such as Lord Byron, Charles Nicolas Fabvier and Richard Church to a ...
Frank Abney Hastings
Frank Abney Hastings () (14 February 1794 – 1 June 1828) was a British naval officer and Philhellene. Born to a noble British family, he served in the Royal Navy, seeing action at the Battle of Trafalgar and the Battle of New Orleans. In 18 ...
, captured five Ottoman ships in the city's harbour and forced the local garrison to evacuate the fortress. The provisional government of Greece claimed Volos as part of Greek national territory, but the Treaty of Constantinople (1832)
The Great Powers ratified the terms of the Constantinople Arrangement in connection with the border between Greece and the Ottoman Empire in the London Protocol of 30 August 1832, which marked the end of the Greek War of Independence and establi ...
, which established a Greek independent state, set its northern boundary along a line running south from Arta to Volos. Volos was incorporated into the Greek Kingdom in November 1881 with the rest of Thessaly.
Modern Volos
After its incorporation into theGreek Kingdom
The Kingdom of Greece (, Romanization, romanized: ''Vasíleion tis Elládos'', pronounced ) was the Greece, Greek Nation state, nation-state established in 1832 and was the successor state to the First Hellenic Republic. It was internationally ...
, the town had a population of only 4,900, but grew rapidly in the next four decades as merchants, businessmen, craftsmen and sailors gravitated toward it from the surrounding area. In the 1920s a large influx of refugees to the settlement took place, especially from Ionia
Ionia ( ) was an ancient region encompassing the central part of the western coast of Anatolia. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionians who ...
, but also from Pontus
Pontus or Pontos may refer to:
* Short Latin name for the Pontus Euxinus, the Greek name for the Black Sea (aka the Euxine sea)
* Pontus (mythology), a sea god in Greek mythology
* Pontus (region), on the southern coast of the Black Sea, in modern ...
, Cappadocia
Cappadocia (; , from ) is a historical region in Central Anatolia region, Turkey. It is largely in the provinces of Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde. Today, the touristic Cappadocia Region is located in Nevşehir ...
and Eastern Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Se ...
. In 1882, Andreas Syngros
Andreas Syggros (; 12 October 1830 – 13 February 1899) was a Greek banker from Istanbul, at the time known internationally as Constantinople, and a philanthropist.
Born in Istanbul to Chiot parents who left the island due to the Massacre o ...
established the Privileged Bank of Epirothessaly
The Privileged Bank of Epirothessaly (, ), sometimes referred to in English as Privileged Bank of Epirus and Thessaly, was one of Greece's four banks of issue before the 1928 establishment of the Bank of Greece, together with the National Bank of ...
, which the National Bank of Greece
The National Bank of Greece (NBG; ) is a banking and financial services company with its headquarters in Athens, Greece. Founded in 1841 as the newly independent country's first financial institution, it has long been the largest Greek bank, a ...
acquired in 1899 after its founder's death. Volos was occupied by Ottomans on 8 May 1897, during the Greco Turkish War.
The city had a vibrant Jewish community in the early 20th century: from ≈500 in 1896, it rose to ≈2,000 in 1930, before falling drastically to 882 members in 1940, because of emigration to the great cities of Thessaloniki and Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
or abroad. During the Axis occupation of Greece
The occupation of Greece by the Axis Powers () began in April 1941 after Nazi Germany Battle of Greece, invaded the Kingdom of Greece in order to assist its ally, Fascist Italy (1922–1943), Italy, in their Greco-Italian War, ongoing war that w ...
, the prompt actions of the local rabbi, Moshe Pesach, and the Greek authorities saved about 700 of the local Jewish community from deportation to the Nazi death camps.
After an aerial attack by Italian troops in November 1940 and another by the Germans in 1941, many of the city's inhabitants took refuge in the villages of Pelion
Pelion or Pelium (Modern , ''Pílio''; Ancient Greek/Katharevousa: Πήλιον, ''Pēlion'') is a mountain at the southeastern part of Thessaly in northern Greece, forming a hook-like peninsula between the Pagasetic Gulf and the Aegean Sea. Its ...
. Abandoning Volos after Italy's capitulation in September 1943, the Italians left storerooms full of food, arms and ammunition. Large quantities of this material was transported with the Pelion railway
Pelion railway is a narrow gauge railway line of Thessaly Railways private-owned company in Greece, connecting the city of Volos with the town of Mileai on Pelion.
History
After Thessaly Railways completed the construction of the lines from ...
to the mountain village Milies
Milies () is a village and a former Communities and Municipalities of Greece, municipality in Magnesia (regional unit), Magnesia, Thessaly, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality South Pelion, of which it is ...
and under the supervision of ELAS
The Greek People's Liberation Army (, ''Ellinikós Laïkós Apeleftherotikós Stratós''; ELAS) was the military arm of the left-wing National Liberation Front (EAM) during the period of the Greek resistance until February 1945, when, followi ...
loaded onto mule
The mule is a domestic equine hybrid between a donkey, and a horse. It is the offspring of a male donkey (a jack) and a female horse (a mare). The horse and the donkey are different species, with different numbers of chromosomes; of the two ...
s and taken to secure hideaways. When the Germans set off a column to Milies an officer and a soldier were killed by resistance fighters. In reprisal nearly the whole village was burnt down by German occupation troops on 4 October 1943. According to the official report of the municipality the Germans executed 25 men, and three inhabitants died in their houses from the flames.
Volos is also well known for its assortment of mezedes and a clear alcoholic beverage known as ''tsipouro
Tsipouro () is an un-aged brandy from Greece and in particular Thessaly, Epirus, Macedonia. Tsipouro is a strong distilled spirit containing 40–45% alcohol by volume and is traditionally produced from grape pomace (the residue of the winepress ...
''.
A street in a sister city, Rostov-on-Don
Rostov-on-Don is a port city and the administrative centre of Rostov Oblast and the Southern Federal District of Russia. It lies in the southeastern part of the East European Plain on the Don River, from the Sea of Azov, directly north of t ...
, bears the name ''Улица Греческого Города Волос'' (Street of the Greek City of Volos), weaving through a mix of early 20th-century buildings with characteristic inner yards, tiered balconies and open iron stairs that lend the old Rostov its characteristic Mediterranean look.
In September 2023 the city of Volos was flooded by massive rain.
Administration
The municipality Volos was formed at the 2011 local government reform by the merger of the following nine former municipalities, that became municipal units: *Agria
Agria () is a town and a former municipality in Magnesia, Thessaly, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Volos, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 25.227 km2. It lies ...
* Aisonia
Aisonia () is a former municipality in Magnesia, Thessaly, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Volos, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 75.504 km2. Population 3,249 ( ...
* Artemida
* Iolcos
Iolcus (; also rendered ''Iolkos'' ; and Ἰαωλκός; ; ) is an ancient city, a modern village and a former municipality in Magnesia, Thessaly, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of Volos, of which it is a municipal un ...
* Makrinitsa
Makrinitsa (), nicknamed "balcony of Mt. Pelion," is a village and a former community in Magnesia, Thessaly, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Volos, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit ...
* Nea Anchialos
Nea Anchialos () is a town and a former municipality in Magnesia, Thessaly, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Volos, of which it is a municipal unit. It is situated southwest of Volos and north of Almyr ...
* Nea Ionia
Nea Ionia (, meaning New Ionia) is a town and a northern suburb of the Athens agglomeration, Greece, and a municipality of the Attica region. It was named after Ionia, the region in Anatolia from which many Greeks migrated in the 1920s as a part ...
* Portaria
Portaria (Greek language, Greek: Πορταριά) is a village and a former Communities and Municipalities of Greece, municipality in Magnesia (regional unit), Magnesia, Thessaly, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the m ...
* Volos
The municipality has an area of 385.614 km2, the municipal unit 108.6 km2.
Province
The province of Volos () was one of theprovinces
A province is an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman , which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outside Italy. The term ''provi ...
of the Magnesia Prefecture. Its territory corresponded with that of the current municipalities Volos, Rigas Feraios
Rigas Feraios ( , sometimes ''Rhegas Pheraeos''; ) or Velestinlis (Βελεστινλής , also transliterated ''Velestinles''); 1757 – 24 June 1798), born as Antonios Rigas Velestinlis (), was a Greek writer, political thinker and revo ...
, South Pelion
South Pelion (, ''Notio Pilio'') is a municipality in the Magnesia regional unit, Thessaly, Greece. The seat of the municipality is the town Argalasti. The municipality has an area of 368.539 km2. It comprises the southern part of Mount Pelion. ...
and Zagora-Mouresi
Zagora–Mouresi (, ) is a municipality in the Magnesia regional unit, Thessaly, Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders ...
. It was abolished in 2006.
Geography
Pelion
Pelion or Pelium (Modern , ''Pílio''; Ancient Greek/Katharevousa: Πήλιον, ''Pēlion'') is a mountain at the southeastern part of Thessaly in northern Greece, forming a hook-like peninsula between the Pagasetic Gulf and the Aegean Sea. Its ...
(with its peak at ), crossing the city to create a unique urban geography, before ending in the Pagasetic Gulf
The Pagasetic Gulf () is a rounded gulf (max. depth 102 metres) in the Magnesia regional unit (east central Greece) that is formed by the Mount Pelion peninsula. It is connected with the Euboic Sea. The passage into the Euboic Sea is narrow an ...
flowing west. The Anavros
The river Anavros and Anaurus (, , ) is a torrent near the ancient city of Iolkos (modern-day Volos), flowing from Mount Pelion into the Pagasetic Gulf.
The hero Jason was said to have lost a sandal in its waters, as he ferried the disguised go ...
river, famous for Jason
Jason ( ; ) was an ancient Greek mythological hero and leader of the Argonauts, whose quest for the Golden Fleece is featured in Greek literature. He was the son of Aeson, the rightful king of Iolcos. He was married to the sorceress Med ...
's pass, divides the Nea Demetriada district from the rest of the urban area. Krafsidonas
The Krafsidonas () is, with a length of , the longest torrent that runs solely within the interior of Volos, Greece. It has its origin in the central Pelion Mountains, flowing southwest to the Pagasetic Gulf.
The places that the river flows thr ...
is the major river passing through the city and constitutes the natural lung of the urbanized area of Volos, as well as the boundary between the major municipalities of the metropolitan city, the municipalities of Volos and Nea Ionia
Nea Ionia (, meaning New Ionia) is a town and a northern suburb of the Athens agglomeration, Greece, and a municipality of the Attica region. It was named after Ionia, the region in Anatolia from which many Greeks migrated in the 1920s as a part ...
. Xirias (Ξηριάς), is the largest torrent in the metropolitan urban area of Volos and passes through the Nea Ionia municipal area.
Climate
Volos experiences a ''Csa'' hot-summerMediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate ( ), also called a dry summer climate, described by Köppen and Trewartha as ''Cs'', is a temperate climate type that occurs in the lower mid-latitudes (normally 30 to 44 north and south latitude). Such climates typic ...
, with neither particularly high nor extremely low temperatures throughout the year. Its climate is one of fairly low humidity, favorable for all kinds of activities. Measurable rainfall occurs on average around 89 days per year. Thunderstorms occur sparsely throughout the year, more often during the warmer months. Snow occurs more or less every year on a few occasions, though it usually doesn't cause disruption to daily life. The Pelion
Pelion or Pelium (Modern , ''Pílio''; Ancient Greek/Katharevousa: Πήλιον, ''Pēlion'') is a mountain at the southeastern part of Thessaly in northern Greece, forming a hook-like peninsula between the Pagasetic Gulf and the Aegean Sea. Its ...
mountain, with its own microclimate, affects the city's weather, acting as a rain shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.
Evaporated moisture from body of water, bodies of water (such as oceans and larg ...
to the north-easterly winds thus limiting the amount of precipitation the city receives in comparison to the eastern side of the mountain. Average temperature values, like in most regions, have slightly increased in more recent periods.
Architecture
Two of the most known churches of Volos, St Nicholas and St Constantine and Helen on the promenade, were designed by architect Aristotelis Zachos. Volos was once also characterised by a number of old mansions, the majority of which were destroyed after the earthquakes in 1955. Nowadays, only some of them have been saved, restored and have a new, mainly public, use.neoclassicism
Neoclassicism, also spelled Neo-classicism, emerged as a Western cultural movement in the decorative arts, decorative and visual arts, literature, theatre, music, and architecture that drew inspiration from the art and culture of classical antiq ...
. Public buildings conformed to this style and private buildings belonging to prosperous merchants were particularly sophisticated. Typical examples include:
* The 3-story Hotel de France, with its impressive decorative murals (1894, Iasonos and K. Kartali Street)
* Old Tobacco Factory of Matsaggos (1890)
* Yellow Tobacco Warehouse (1926)
* The National Bank, formerly the Privileged Bank of Epirothessaly
The Privileged Bank of Epirothessaly (, ), sometimes referred to in English as Privileged Bank of Epirus and Thessaly, was one of Greece's four banks of issue before the 1928 establishment of the Bank of Greece, together with the National Bank of ...
(1895)
* The Bank of Athens
The Bank of Athens (, ), colloquially known as ''Athinaiki'', was a Greek bank based in Athens, Greece, from where it took its name. Founded in 1893 and long affiliated with France's Banque de l'Union Parisienne (BUP), it was Greece's second-large ...
(1903, today the library of University of Thessaly
The University of Thessaly (UTh; Greek: ) is a public university in Thessaly, Greece, founded in 1984. The university includes the main campus in the city of Volos and regional campuses located in Karditsa, Larissa, Trikala, and the city of Lamia ...
)
* The Achillopouleion Hospital (1901)
* The Archaeological Museum of Volos
The Archaeological Museum of Volos, also known as Athanasakeion Archaeological Museum of Volos, is an archaeology museum in Volos, Greece, that houses many exquisite finds from early 20th-century and modern archaeological excavations in Thessa ...
, Athanasakeio (1909)
* The Agricultural Bank (1909, formerly the Kosmadopoulos Bank)
* The Cine-theater Achilleion (1925)
* The Aegli Hotel, (1927), designed by Kassiopoulos
* The Building of the Air-force High officials Club near Agios Konstantinos Park, believed to have been designed by Le Corbusier
Charles-Édouard Jeanneret (6 October 188727 August 1965), known as Le Corbusier ( , ; ), was a Swiss-French architectural designer, painter, urban planner and writer, who was one of the pioneers of what is now regarded as modern architecture ...
* The Bank of Greece
The Bank of Greece ( , ) is the national central bank for Greece within the Eurosystem. It was the Greek central bank from 1927 to 2000, issuing the drachma. Since 2014, it has also been Greece's national competent authority within European ...
building (1935)
* Municipal conservatory of Volos
* The old factory of Tsalapatas
* Tsikrikis Mansion
* Kitsos Makris' house (today Kitsos Makris Folklore Centre)
* Volos City Hall
* The Railway Station of Volos, designed by Evaristo De Chirico
* The Averofeian Courthouse
* The family houses of Kartalis, Glavanis, Kastemis, Saratsis
* The Sarafopoulos Mansion (1927), today the Volos Club
* The well-preserved Regas house and its singular decorative murals, today the Lyceum of Greek women
Districts

Education
 The city of Volos consists of the administrative and academic centre of
The city of Volos consists of the administrative and academic centre of University of Thessaly
The University of Thessaly (UTh; Greek: ) is a public university in Thessaly, Greece, founded in 1984. The university includes the main campus in the city of Volos and regional campuses located in Karditsa, Larissa, Trikala, and the city of Lamia ...
, which was founded in 1984, and is the most important centre of education in central Greece. The faculties of Engineering, Humanities and Social Sciences and Agricultural Sciences, with their twelve departments, are based in Volos, emphasising the academic, economic and cultural development of the city. The faculties are located in different areas of the city ; “Pedion Areos” Campus is used by the Departments of the School of Engineering, while the School of Humanities and Social Sciences is located in the centre of Volos. The School of Agricultural Sciences is based in a renovated building in Fytoko. In addition to Greek students, the city and the university attract many foreign students via Erasmus and other programmes.
In addition, in the city, there are 56 kindergartens, 51 primary schools, 18 junior high schools and 13 senior high schools.
Economy
Volos is one of the most industrialized provincial cities of Greece, because of its strategic location between the largest population centers of the country (Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
– Thessaloníki
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its Thessaloniki metropolitan area, metropolitan area) and the capital cit ...
) and its port. Industry is intensely specialized in steel production and manufacturing. Three major steel producers (METKA
METKA ATE is the business unit of the Greek company Mytilineos S.A., undertaking the construction of large-scale projects in the sectors of energy, infrastructure and defence.
Metka’s main business activity is in construction of large power ...
, SIDENOR and Hellenic Steel Industry (Ελληνική Χαλυβουργία)) have production facilities in the industrial areas of Volos and nearby Almyros
Almyros or Halmyros (, ) is a town and a municipality of the regional units of Greece, regional unit of Magnesia (regional unit), Magnesia, modern regions of Greece, region of Thessaly, Greece. It lies in the center of prosperous fertile plain know ...
.
AGET Heracles, a member of the Lafarge
La Farge, LaFarge or Lafarge can refer to:
People
* Antoinette LaFarge (1966–), American artist and writer
* Christopher Grant LaFarge (1862–1938), American architect and partner in the firm Heins & LaFarge
* Christopher Grant La Farge ( ...
group, operates one of the largest cement facilities in the world (with capacity exceeding 7,000,000 tn) with its own private port, next to the city. Volos is also active in the research sector, hosting the Institute of Bio-Economy and Agri-Technology (iBO), one of the five Institutes of the Center for Research and Technology – Hellas (CERTH).
Port
The port lies upon the ancient Thessalian settlement of Iolkos. According to Greek mythology, this was where the hero Jason built his trireme, Argo, and along with his oarsmen set course for Colchis, bringing back and marrying priestess Medea. The new port was founded in 1893 and was the most significant element in the industrial development of the area. Today, Volos has the third-largest cargo port in Greece (afterPiraeus
Piraeus ( ; ; , Ancient: , Katharevousa: ) is a port city within the Athens urban area ("Greater Athens"), in the Attica region of Greece. It is located southwest of Athens city centre along the east coast of the Saronic Gulf in the Ath ...
and Thessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its Thessaloniki metropolitan area, metropolitan area) and the capital cit ...
), carrying agricultural and industrial products. In the past, it was home to a maritime link with Tartus
Tartus ( / ALA-LC: ''Ṭarṭūs''; known in the County of Tripoli as Tortosa and also transliterated from French language, French Tartous) is a major port city on the Mediterranean coast of Syria. It is the second largest port city in Syria (af ...
, Syria.
Ferries and flying dolphins operate daily, connecting Volos to the Magnesia islands of the Sporades
The (Northern) Sporades are an archipelago along the east coast of Greece, northeast of the island of Euboea,"Skyros - Britannica Concise" (description), Britannica Concise, 2006, webpageEB-Skyrosnotes "including Skiathos, Skopelos, Skyros, and Al ...
, (Skiathos
Skiathos (, ; , ; and ) is a small Greece, Greek Islands of Greece, island in the northwest Aegean Sea. Skiathos is the westernmost island in the Northern Sporades archipelago, east of the Pelion peninsula in Magnesia (regional unit), Magnesia ...
, Skopelos
Skopelos (, ) is a Greek island in the western Aegean Sea. Skopelos is one of several islands that comprise the Northern Sporades island group, which lies east of the Pelion peninsula on the mainland and north of the island of Euboea. It is par ...
, Alonissos
Alonnisos ( ), also transliterated as Alonissos, is a Greek island in the Aegean Sea. After Skiathos and Skopelos it is the third member of the Northern Sporades. It is (2 nm) east of the island of Skopelos. Alonnisos is also the name of a ...
). In addition, many cruise ships use the port of Volos as a destination. During the summers of 2015 and 2016, more than 100 cruises arrived in Volos, carrying more than 100,000 visitors.
International relations
The city of Volos has always had a major role in the financial, economic, commercial and administrative matters of the region ofThessaly
Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, a ...
and Central Greece, due to the strategic position of the city's port, unique between Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
and Thessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its Thessaloniki metropolitan area, metropolitan area) and the capital cit ...
.
International consulates
Several European countries have established consulates in Volos including: * Belgium * Denmark * France * Germany * Italy * NetherlandsTwin towns — sister cities
Volos is twinned with: *Antofagasta
Antofagasta () is a port city in northern Chile, about north of Santiago. It is the capital of Antofagasta Province and Antofagasta Region. According to the 2015 census, the city has a population of 402,669.
Once claimed by Bolivia follo ...
, Chile
* Batumi
Batumi (; ka, ბათუმი ), historically Batum or Batoum, is the List of cities and towns in Georgia (country), second-largest city of Georgia (country), Georgia and the capital of the Autonomous Republic of Adjara, located on the coast ...
, Georgia
* Le Mans
Le Mans (; ) is a Communes of France, city in Northwestern France on the Sarthe (river), Sarthe River where it meets the Huisne. Traditionally the capital of the Provinces of France, province of Maine (province), Maine, it is now the capital of ...
, France
* Pleven
Pleven ( ) is the seventh most populous city in Bulgaria. Located in the northern part of the country, it is the administrative centre of Pleven Province, as well as of the subordinate Pleven municipality. It is the biggest economic center in ...
, Bulgaria
* Rostov-on-Don
Rostov-on-Don is a port city and the administrative centre of Rostov Oblast and the Southern Federal District of Russia. It lies in the southeastern part of the East European Plain on the Don River, from the Sea of Azov, directly north of t ...
, Russia
* Smederevo
Smederevo ( sr-Cyrl, Смедерево, ) is a list of cities in Serbia, city and the administrative center of the Podunavlje District in eastern Serbia. It is situated on the right bank of the Danube, about downstream of the Serbian capital, ...
, Serbia
* Sochi
Sochi ( rus, Сочи, p=ˈsotɕɪ, a=Ru-Сочи.ogg, from – ''seaside'') is the largest Resort town, resort city in Russia. The city is situated on the Sochi (river), Sochi River, along the Black Sea in the North Caucasus of Souther ...
, Russia
Culture
The wider region of Volos is a place rich with history, finding the first signals of culture in theNeolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
period. In the villages of Sesklo
Sesklo (; ) is a village in Greece that is located near Volos, a city located within the municipality of Aisonia. The municipality is located within the regional unit of Magnesia that is located within the administrative region of Thessaly. ...
and Dimini
Dimini (; older form: ''Diminion'') is a village near the city of Volos, in Thessaly (central Greece), in Magnesia. It was the seat of the municipality of Aisonia. The name Aisonia dates back to ancient times. Currently, Dimini is the weste ...
, the first traces of Neolithic culture in Europe have been discovered.
Moreover, close by Volos, there are the ancient Dimitrias, a town built by Dimitrios Poliorkitis in 294-2 AC. Today, the ancient theatre of Dimitrias
Theatre or theater is a collaborative form of performing art that uses live performers, usually actors to present experiences of a real or imagined event before a live audience in a specific place, often a stage. The performers may communicat ...
remains preserved. Also present are the archaeological areas of Goritsa hill, archaeological findings dating from the early Christian period in Nea Anchialos
Nea Anchialos () is a town and a former municipality in Magnesia, Thessaly, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Volos, of which it is a municipal unit. It is situated southwest of Volos and north of Almyr ...
, and the wall of Volos's old castle, which is open to visitors.
Volos consists of a city with diverse Greek trades, as its industrial development encouraged many people to move to the city. The city's industrial and financial evolution also gradually resulted in cultural and social evolution, too; in 1894, Volos acquired its Municipal Theater and later its Gymnastics Club. In 1908, Volos became home to the first Labour Union in Greece.
After 1922, following the Asia Minor Catastrophe
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
, Volos received a large number of people from the destroyed regions. This coexistence with the locals deeply influenced the culture of the city, leaving a mark still visible in the food, music, sports, entertainment and social life of the city today.
In modern times, there are plentiful museums and galleries to be visited throughout the city, but also in the wider region. Above all, Volos forms one of the most attractive and tourist-friendly cities in Greece because of its physical setting, combining the Pagasetic Gulf
The Pagasetic Gulf () is a rounded gulf (max. depth 102 metres) in the Magnesia regional unit (east central Greece) that is formed by the Mount Pelion peninsula. It is connected with the Euboic Sea. The passage into the Euboic Sea is narrow an ...
with Mount Pelion
Pelion or Pelium (Modern , ''Pílio''; Ancient Greek/Katharevousa: Πήλιον, ''Pēlion'') is a mountain at the southeastern part of Thessaly in northern Greece, forming a hook-like peninsula between the Pagasetic Gulf and the Aegean Sea. Its ...
.
Volos was a candidate city for the European Capital of Culture
A European Capital of Culture is a city designated by the European Union (EU) for a period of one calendar year during which it organises a series of cultural events with a strong pan-European dimension. Being a European Capital of Culture can ...
, 2021.
Museums and galleries
*Archaeological Museum of Volos
The Archaeological Museum of Volos, also known as Athanasakeion Archaeological Museum of Volos, is an archaeology museum in Volos, Greece, that houses many exquisite finds from early 20th-century and modern archaeological excavations in Thessa ...
* Volos Natural History Museum
* Modern History Museum of Volos City
* Giorgio de Chirico Art Centre
The Giorgio de Chirico Art Centre () is an art centre/museum in a three-story building in Volos, Magnesia, Greece. It is named for internationally famous Italian artist Giorgio de Chirico, who was born to Italian parents in Volos on July 10, 188 ...
* Thessaly Railway Museum, Railway Station of Volos
* The Rooftile and Brickworks Museum N. & S. Tsalapatas, National Museum of Industrial History
* Entomological Museum of Volos
* Theofilos Museum, Anakasia (works of the artist Theofilos Hatzimikhail)
Cuisine
One of the main characteristics and most widely known specialities of Volos is its traditional drink,tsipouro
Tsipouro () is an un-aged brandy from Greece and in particular Thessaly, Epirus, Macedonia. Tsipouro is a strong distilled spirit containing 40–45% alcohol by volume and is traditionally produced from grape pomace (the residue of the winepress ...
, and the seafood that is served accompanying the drink.
Local specialities include:
* ''Boubari''
* ''Spetzofai''
* ''Melachrini'' (dessert)
* Spoon sweets
Spoon sweets are sweet preserves, served in a spoon as a gesture of hospitality in Bosnia, Serbia, Albania, Greece, Turkey, Kosovo, Cyprus, the Balkans, parts of the Middle East, and Russia. They can be made from almost any fruit, though sour a ...
* Tsipouro
Tsipouro () is an un-aged brandy from Greece and in particular Thessaly, Epirus, Macedonia. Tsipouro is a strong distilled spirit containing 40–45% alcohol by volume and is traditionally produced from grape pomace (the residue of the winepress ...
(drink)
Sports
Volos, taking advantage of its physical setting by the sea, has a significant presence in Greek sporting history in the areas ofrowing
Rowing is the act of propelling a human-powered watercraft using the sweeping motions of oars to displace water and generate reactional propulsion. Rowing is functionally similar to paddling, but rowing requires oars to be mechanically a ...
and sailing
Sailing employs the wind—acting on sails, wingsails or kites—to propel a craft on the surface of the ''water'' (sailing ship, sailboat, raft, Windsurfing, windsurfer, or Kitesurfing, kitesurfer), on ''ice'' (iceboat) or on ''land'' (Land sa ...
. The city also has two covered and one open sporting swimming pools, with a long history in swimming and water polo. Additionally, Volos has clubs and facilities in several sports, including football, basketball, volleyball, tennis and horseriding. The most popular clubs, with significant contributions to the sporting and cultural history of the city and significant successes in football, are Olympiakos Volou
Olympiacos Volos Football Club () is a Greek football club based in the city of Volos.
History
In 1938 Olympiacos achieves the biggest distinction made from a provincial team at the time, succeeding to enter the final eight in Greek Football Cup. ...
and Niki Volou. The main clubs of Volos are shown below :
With its sporting traditions, Volos was one of the five cities that played host to the 2004 Summer Olympics
The 2004 Summer Olympics (), officially the Games of the XXVIII Olympiad (), and officially branded as Athens 2004 (), were an international multi-sport event held from 13 to 29 August 2004 in Athens, Greece.
The Games saw 10,625 athletes ...
.
Since 2004, Volos's facilities have hosted significant sports events, such as the 27th European Championship of Artistic Gymnastics in 2006, the FIBA European Youth Championship (2015), when Greece won the gold medal, and the Finals of Greek Football Cup
The Greek Football Cup (), commonly known as the Greek Cup or Betsson Greek Cup for sponsorship reasons is a Greek football competition, run by the Hellenic Football Federation.
The Greek Cup is the second-most important domestic men's footba ...
, in 2007 and 2017.
Transport
All land transport reaches Volos, while the International Airport of Central Greece inNea Anchialos
Nea Anchialos () is a town and a former municipality in Magnesia, Thessaly, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Volos, of which it is a municipal unit. It is situated southwest of Volos and north of Almyr ...
links the city to international destinations, and the Port of Volos provides links to the islands, mostly the Sporades
The (Northern) Sporades are an archipelago along the east coast of Greece, northeast of the island of Euboea,"Skyros - Britannica Concise" (description), Britannica Concise, 2006, webpageEB-Skyrosnotes "including Skiathos, Skopelos, Skyros, and Al ...
, as well as to some destinations in Pilio
Pelion or Pelium (Modern , ''Pílio''; Ancient Greek/Katharevousa: Πήλιον, ''Pēlion'') is a mountain at the southeastern part of Thessaly in northern Greece, forming a hook-like peninsula between the Pagasetic Gulf and the Aegean Sea. It ...
.
Motorways
Volos is linked through Greece's E75 Highway Axis (most often known asPATHE
Pathe or Pathé may refer to:
* Pathé, a French company established in 1896
* Pathé Exchange, U.S. division of the French film company that was spun off into an independent entity
* Pathé News, a French and British distributor of cinema newsr ...
) with Northern and Southern Greece. Beyond this, the Axis E65 will be the gateway to Western Greece and the port of Igoumenitsa
Igoumenitsa () is a coastal city in northwestern Greece. It is the capital of the regional unit of Thesprotia.
Igoumenitsa is the chief port of Thesprotia and Epirus, and one of the largest passenger ports of Greece, connecting northwestern Main ...
, through the plains of inner Thessaly
Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, a ...
, when this part of the E65 link is completed.
Airport
The city of Volos, along with the rest of Central Greece, is linked to the rest of Greece and Europe by theNea Anchialos National Airport
Nea Anchialos National Airport () is an airport located near the town of Nea Anchialos in Greece. It serves the regional unit of Magnesia and is also known as ''Central Greece Airport''.
Overview
The airport is at an elevation of above mean ...
. The airport has the second longest commercial runway in Greece after Eleftherios Venizelos
Eleftherios Kyriakou Venizelos (, ; – 18 March 1936) was a Cretan State, Cretan Greeks, Greek statesman and prominent leader of the Greek national liberation movement. As the leader of the Liberal Party (Greece), Liberal Party, Venizelos ser ...
.
Volos is the first city in Europe to feature Seaplane Services through Argo Airways, which is based in Volos. The seaplanes connect Volos with Skiathos, Skopelos, Allonisos, Athens and Thessaloniki.
Railway
Today, the city is served by direct lines to the rest of Greece, and the railway complex houses facilities for train maintenance. Volos is directly linked with Athens once per day, withThessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its Thessaloniki metropolitan area, metropolitan area) and the capital cit ...
twice per day, and with Larissa
Larissa (; , , ) is the capital and largest city of the Thessaly region in Greece. It is the fifth-most populous city in Greece with a population of 148,562 in the city proper, according to the 2021 census. It is also the capital of the Larissa ...
15 times a day. In the past, Volos was served by railway lines of three different gauges, the metre gauge
Metre-gauge railways ( US: meter-gauge railways) are narrow-gauge railways with track gauge of or 1 metre.
Metre gauge is used in around of tracks around the world. It was used by several European colonial powers including France, Britain and ...
line of Thessaly Railways
Thessaly Railways () was a private railway company in Greece, which owned and operated the metre gauge railway network of Thessaly and Pelion railway from 1884 to 1955, when the private company was absorbed by the Hellenic State Railways state-ow ...
to Kalampaka
Kalabaka (, ''Kalabáka'', alternative transliterations are ''Kalambaka'' and ''Kalampaka'') is a town and seat of the municipality of Meteora in the Trikala regional unit, part of Thessaly in Greece. The population was 11,492 at the 2021 cens ...
, the standard gauge line to Larissa and the gauge line to Pelion
Pelion or Pelium (Modern , ''Pílio''; Ancient Greek/Katharevousa: Πήλιον, ''Pēlion'') is a mountain at the southeastern part of Thessaly in northern Greece, forming a hook-like peninsula between the Pagasetic Gulf and the Aegean Sea. Its ...
. Remnants of triple gauge lines still exist near the station. Currently, the Pelion railway line operates for tourist reasons every Saturday, Sunday and public holiday from mid-April to the end of October. The train runs every day during July and August.
Notable people
Mythology
*Iason
Jason ( ; ) was an ancient Greek mythological hero and leader of the Argonauts, whose quest for the Golden Fleece is featured in Greek literature. He was the son of Aeson, the rightful king of Iolcos. He was married to the sorceress Medea, t ...
, mythological hero
* Peleus
In Greek mythology, Peleus (; Ancient Greek: Πηλεύς ''Pēleus'') was a hero, king of Phthia, husband of Thetis and the father of their son Achilles. This myth was already known to the hearers of Homer in the late 8th century BC.
Biogra ...
, mythological hero
* Chiron
In Greek mythology, Chiron ( ; also Cheiron or Kheiron; ) was held to be the superlative centaur amongst his brethren since he was called the "wisest and justest of all the centaurs".
Biography
Chiron was notable throughout Greek mythology for ...
, centaur
Modern
*Giorgio de Chirico
Giuseppe Maria Alberto Giorgio de Chirico ( ; ; 10 July 1888 – 20 November 1978) was an Italian artist and writer born in Greece. In the years before World War I, he founded the art movement, which profoundly influenced the surrealists. His ...
, painter (1888–1978)
* Vangelis
Evangelos Odysseas Papathanassiou (, ; 29 March 1943 – 17 May 2022), known professionally as Vangelis ( ; , ), was a Greek musician, composer, and producer of electronic, progressive, ambient, and classical orchestral music. He composed ...
, composer (1943–2022)
* John Argyris
Johann Hadji Argyris FRS (Greek: Ιωάννης Χατζι Αργύρης; 19 August 1913 – 2 April 2004) was a Greek pioneer of computer applications in science and engineering,Hughes TJR, Oden JT, and Papadrakakis M (2011) ''John H Argyris' ...
, pioneer in engineering, Professor of Imperial College London
Imperial College London, also known as Imperial, is a Public university, public research university in London, England. Its history began with Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, Prince Albert, husband of Queen Victoria, who envisioned a Al ...
and University of Stuttgart
The University of Stuttgart () is a research university located in Stuttgart, Germany. It was founded in 1829 and is organized into 10 faculties. It is one of the oldest technical universities in Germany with programs in civil, mechanical, ind ...
(1913–2004)
* Fotis Kouvelis
Fotis-Fanourios Kouvelis (; born 3 September 1948) is a Greek lawyer and leftist politician.
Biography
Kouvelis was born in Volos. He studied law and political science at the University of Athens.
A member of Lambrakis Youth, he was a founding ...
, politician, leader of the Democratic Left
* Dimitrios Trichopoulos, medical doctor, Professor of Harvard School of Public Health
The Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health is the public health school at Harvard University, located in the Longwood Medical Area of Boston, Massachusetts. It was named after Hong Kong entrepreneur Chan Tseng-hsi in 2014 following a US$350 ...
* Georgios Kartalis
Georgios Kartalis (; 1908–1957) was a Greek politician.
Early life and political career
Kartalis was born in Athens to a distinguished family from Volos. He went to school in Geneva and enrolled in the ETH Zürich, only to change after the fi ...
, politician (1908–1957)
* Yorgos Foudoulis
Yorgos Foudoulis (born 1964) is a Greek classical guitarist and composer. His professional activities include performing, master classes, editing, and recording.
He is the director of the Examination Center of Trinity College London in Volos, Gr ...
, musician and composer (1964)
* Moshe Pesach, rabbi of Volos and Chief Rabbi of Greece
* Lavrentis Mahairitsas
Lavrentis Machairitsas (; 5 November 1956 – 9 September 2019) was a Greek rock musician from Volos, Thessaly, Greece.
Biography
Early years
Machairitsas was born in Volos and began taking piano lessons at the age of six. These lessons las ...
, musician and songwriter (1956-2019)
* Artemis Alexiadou, linguist (1969)
* Apostolia Zoi
Apostolia Zoi (, ) is a Greek singer who was born in Elassona, Greece, and she grew up in Volos. She has released four studio albums.
Biography Early life
At the age of 14, Apostolia moved to Thessaloniki to pursue her interest in diving and swi ...
, singer (1980)
* Andromache (Mary) Mavroyeni Papanicolaou, (1890-1982), wife of George N. Papanicolaou, MD, PhD and first cytotechnologist
Athletes
*Vasileios Polymeros
Vasileios Polymeros (, born 20 February 1976 in Volos) is a Greek rower. He won the bronze medal in men's lightweight double sculls with Nikolaos Skiathitis at the 2004 Summer Olympics in Athens, Greece and the silver in men's lightweight doubl ...
, rower, olympic medalist (1976)
* Nikolaos Skiathitis, rower, olympic medalist (1981)
* Olga Vasdeki
Olga Vasdeki (, , born 26 September 1973 in Volos) is a Greek triple jumper.
She was the most successful Greek triple jumper and Greek record holder until 1998, when she won the gold medal at the European Championships in Budapest, being at the ...
, triple jumper (1973)
* Spyridon Vasdekis
Spyridon "Spyros" Vasdekis (, born 23 January 1970) is a retired Greek long jumper.
He was born in Volos.
He won the gold medal at the 1993 Mediterranean Games, finished tenth at the 1993 World Championships, third at the 1996 European Indoo ...
, long jumper (1970)
* Paraskevi Tsiamita
Paraskevi "Voula" Tsiamita (, , born 10 March 1972) is a Greek former track and field athlete who competed in long jump and triple jump.
She was born in Volos, on 10 March 1972. Her origins come from the nearby village of Sesklo, and she is of ...
, triple, long jumper (1972)
* Nikos Boudouris
Nikolaos "Nikos" Boudouris (alternate spellings: Bountouris, Mpoudouris, Mpountouris, ; born 25 September 1971 in Volos, Greece) is a former Greek professional basketball player and coach. During his pro playing career, Boudouris won what were at ...
, basketball player (1971)
* Panagiotis Liadelis
Panagiotis Liadelis (born December 7, 1974, in Volos, Greece) is a retired Greek professional basketball player. At a height of 1.94 m (6 ft 4 in) tall, he played as a point guard-shooting guard.
Professional career
Liadelis played for many ...
, basketball player (1974)
* Athanasios Kostoulas, football player (1976)
* Efthalia Koutroumanidou, beach volleyball player (1982)
* Evanthia Makrygianni
Evanthia Makrygianni (born 30 August 1986) is a Greek former synchronized swimmer who competed in the 2008 Summer Olympics
The 2008 Summer Olympics (), officially the Games of the XXIX Olympiad () and officially branded as Beijing 2008 ( ...
, synchronized swimmer (1986)
* Christos Volikakis
Christos Volikakis (; born 25 March 1988, in Volos
Volos (; ) is a coastal port city in Thessaly situated midway on the Greek mainland, about north of Athens and south of Thessaloniki. It is the capital of the Magnesia (regional unit ...
, track cyclist (1988)
* Adam Tzanetopoulos, football player (1995)
See also
*Thessaly
Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, a ...
* Magnesia
* Pelion
Pelion or Pelium (Modern , ''Pílio''; Ancient Greek/Katharevousa: Πήλιον, ''Pēlion'') is a mountain at the southeastern part of Thessaly in northern Greece, forming a hook-like peninsula between the Pagasetic Gulf and the Aegean Sea. Its ...
* Sporades
The (Northern) Sporades are an archipelago along the east coast of Greece, northeast of the island of Euboea,"Skyros - Britannica Concise" (description), Britannica Concise, 2006, webpageEB-Skyrosnotes "including Skiathos, Skopelos, Skyros, and Al ...
* University of Thessaly
The University of Thessaly (UTh; Greek: ) is a public university in Thessaly, Greece, founded in 1984. The university includes the main campus in the city of Volos and regional campuses located in Karditsa, Larissa, Trikala, and the city of Lamia ...
Footnotes
References
*External links
*Volos
The Official website of the Greek National Tourism Organisation
Port of Volos
{{Authority control Greek prefectural capitals Municipalities of Thessaly Mediterranean port cities and towns in Greece Provinces of Greece Port cities of the Aegean Sea Populated places in Magnesia (regional unit)