Birnaviridae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Birnaviridae'' is a family of
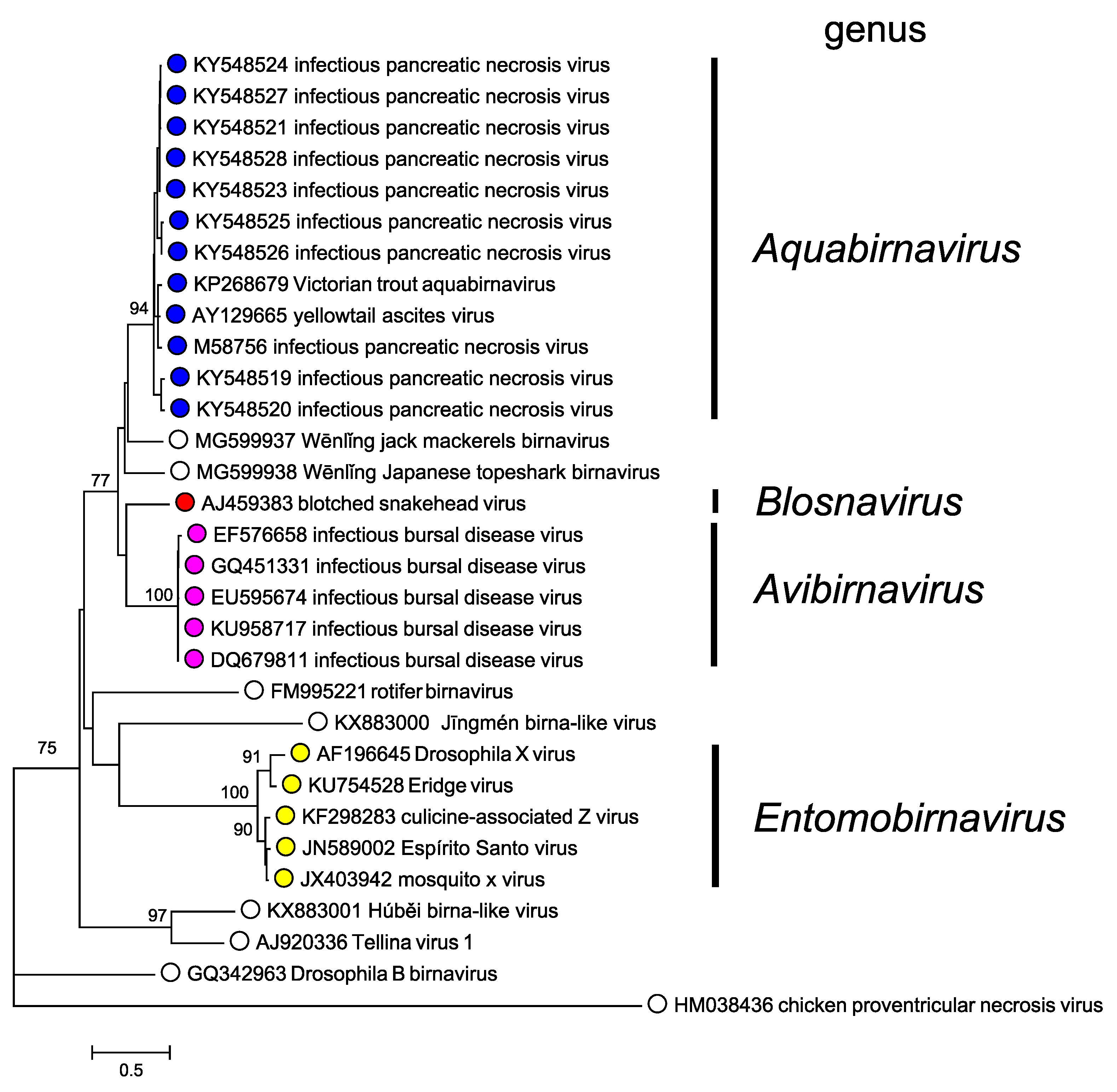 The following genera are recognized:
* '' Aquabirnavirus''
* '' Avibirnavirus''
* '' Blosnavirus''
* '' Dronavirus''
* '' Entomobirnavirus''
* '' Ronavirus''
* '' Telnavirus''
The following genera are recognized:
* '' Aquabirnavirus''
* '' Avibirnavirus''
* '' Blosnavirus''
* '' Dronavirus''
* '' Entomobirnavirus''
* '' Ronavirus''
* '' Telnavirus''
ICTV Report: ''Birnaviridae''
{{Taxonbar, from=Q733661 Protein families Virus families Riboviria
double-stranded RNA viruses
Double-stranded RNA viruses (dsRNA viruses) are a polyphyletic group of viruses that have double-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid. The double-stranded genome is used as a template by the viral RNA dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) to ...
. Salmonid fish, birds and insects serve as natural hosts. There are currently 11 species in this family, divided among seven genera. Diseases associated with this family include infectious pancreatic necrosis in salmonid fish, which causes significant losses to the aquaculture industry, with chronic infection in adult salmonid fish and acute viral disease in young salmonid fish.
Structure
Viruses in family ''Birnaviridae'' are non-enveloped, with icosahedral single-shelled geometries, and T=13 symmetry. The diameter is around 70 nm.Genome
The genome is composed of linear, bi-segmented, double-stranded RNA. It is around 5.9–6.9 kbp in length and codes for five to six proteins. Birnaviruses encode the following proteins: RNA-directed RNA polymerase (VP1), which lacks the highly conserved Gly-Asp-Asp (GDD) sequence, a component of the proposedcatalytic
Catalysis () is the increase in reaction rate, rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst ...
site of this enzyme family that exists in the conserved motif VI of the palm domain of other RNA-directed RNA polymerases.
The large RNA segment, segment A, of birnaviruses code
In communications and information processing, code is a system of rules to convert information—such as a letter, word, sound, image, or gesture—into another form, sometimes shortened or secret, for communication through a communicati ...
s for a polyprotein (N-VP2-VP4-VP3-C) that is processed into the major structural protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s of the virion: VP2, VP3 (a minor structural component of the virus), and into the putative protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyzes proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the formation of new protein products ...
VP4. VP4 protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
is involved in generating VP2 and VP3. recombinant VP3 is more immunogenic than recombinant VP2.
Infectious pancreatic necrosis virus (IPNV), a birnavirus, is an important pathogen
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a Germ theory of d ...
in fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
farms. Analyses of viral protein
The term viral protein refers to both the products of the genome of a virus and any host proteins incorporated into the viral particle. Viral proteins are grouped according to their functions, and groups of viral proteins include structural protei ...
s showed that VP2 is the major structural
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
and immunogenic polypeptide
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty ...
of the virus. All neutralizing monoclonal antibodies
A monoclonal antibody (mAb, more rarely called moAb) is an antibody produced from a Lineage (evolution), cell lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell.
Mon ...
are specific to VP2 and bind
BIND () is a suite of software for interacting with the Domain Name System (DNS). Its most prominent component, named (pronounced ''name-dee'': , short for ''name Daemon (computing), daemon''), performs both of the main DNS server roles, acting ...
to continuous or discontinuous epitopes
An epitope, also known as antigenic determinant, is the part of an antigen that is recognized by the immune system, specifically by antibodies, B cells, or T cells. The part of an antibody that binds to the epitope is called a paratope. Although ep ...
. The variable domain of VP2 and the 20 adjacent amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s of the conserved C-terminal
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, carboxy tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When t ...
are probably the most important in inducing an immune response
An immune response is a physiological reaction which occurs within an organism in the context of inflammation for the purpose of defending against exogenous factors. These include a wide variety of different toxins, viruses, intra- and extracellula ...
for the protection of animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
s.
Non structural
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
VP5 is found in RNA segment A. The function of this small viral protein is unknown. It is believed to be involved in influencing apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biol ...
, but studies are not completely concurring. The protein can not be found in the virion.
Viral Replication
Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by cell receptorendocytosis
Endocytosis is a cellular process in which Chemical substance, substances are brought into the cell. The material to be internalized is surrounded by an area of cell membrane, which then buds off inside the cell to form a Vesicle (biology and chem ...
. Replication follows the double-stranded RNA virus replication model in the cytoplasm. Double-stranded RNA virus transcription is the method of transcription in cytoplasm. The virus is released by budding. Salmonid fish (''Aquabirnavirus''), young sexually immature chickens (''Avibirnavirus''), insects (''Entomobirnavirus''), and blotched snakehead fish (''Blosnavirus'') are the natural hosts. Transmission routes are contact.
Taxonomy
 The following genera are recognized:
* '' Aquabirnavirus''
* '' Avibirnavirus''
* '' Blosnavirus''
* '' Dronavirus''
* '' Entomobirnavirus''
* '' Ronavirus''
* '' Telnavirus''
The following genera are recognized:
* '' Aquabirnavirus''
* '' Avibirnavirus''
* '' Blosnavirus''
* '' Dronavirus''
* '' Entomobirnavirus''
* '' Ronavirus''
* '' Telnavirus''
References
External links
ICTV Report: ''Birnaviridae''
{{Taxonbar, from=Q733661 Protein families Virus families Riboviria