|
Avibirnavirus
''Avibirnavirus'' is a genus of viruses in family ''Birnaviridae''. There is a single species in this genus: ''Infectious bursal disease virus'', which infects chickens and other fowl. It causes severe inflammation of the bursa of Fabricius, and causes considerable morbidity and mortality. History Initially, the virus was discovered in 1957 in Gumboro, Delaware, United States. Later, the disease was termed Gumboro disease. Since its discovery, the virus has been found to have a worldwide distribution. Structure Avibirnaviruses are non-enveloped, and their single shelled icosahedral capsid exhibits a T=13 symmetry. The diameter of the capsid is around 70 nm. Genome The double-stranded RNA genome of Avibirnaviruses is linear and segmented into two segments (A and B). The combined lengths of the two segments is around 6,000 nucleotides, almost entirely composed of reading-frames. The genome codes for 4-5 proteins depending on the strain. The high degree of antigenic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birnaviridae
''Birnaviridae'' is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses. Salmonid fish, birds and insects serve as natural hosts. There are currently 11 species in this family, divided among seven genera. Diseases associated with this family include infectious pancreatic necrosis in salmonid fish, which causes significant losses to the aquaculture industry, with chronic infection in adult salmonid fish and acute viral disease in young salmonid fish. Structure Viruses in family ''Birnaviridae'' are non-enveloped, with icosahedral single-shelled geometries, and T=13 symmetry. The diameter is around 70 nm. Genome The genome is composed of linear, bi-segmented, double-stranded RNA. It is around 5.9–6.9 kbp in length and codes for five to six proteins. Birnaviruses encode the following proteins: RNA-directed RNA polymerase (VP1), which lacks the highly conserved Gly-Asp-Asp (GDD) sequence, a component of the proposed catalytic site of this enzyme family that exists in the conserve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation Rate
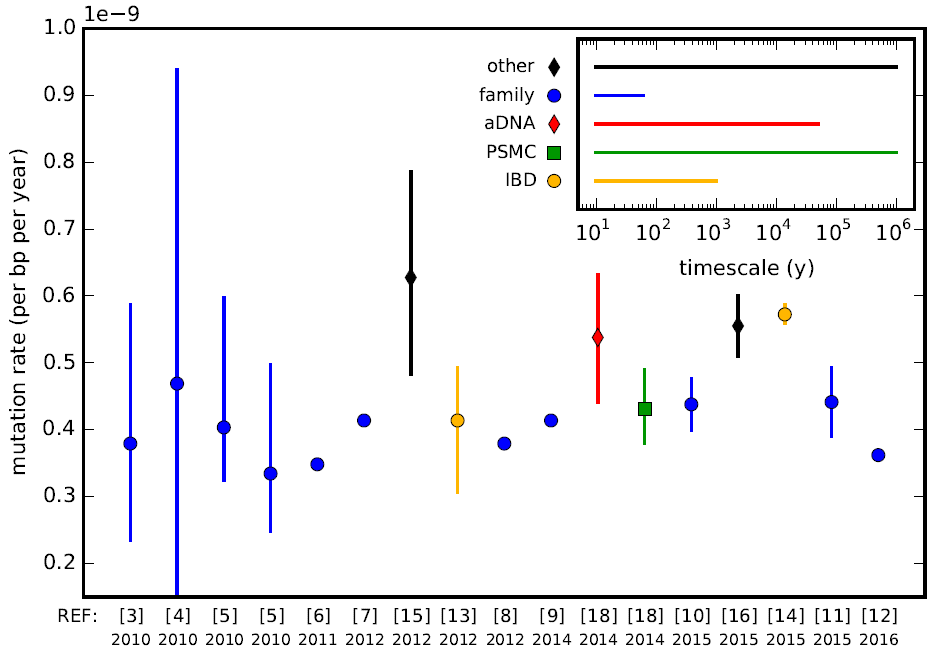
In genetics, the mutation rate is the frequency of new mutations in a single gene or organism over time. Mutation rates are not constant and are not limited to a single type of mutation; there are many different types of mutations. Mutation rates are given for specific classes of mutations. Point mutations are a class of mutations which are changes to a single base. Missense mutation, Missense and Nonsense mutations are two subtypes of point mutations. The rate of these types of substitutions can be further subdivided into a mutation spectrum which describes the influence of the genetic context on the mutation rate. There are several natural units of time for each of these rates, with rates being characterized either as mutations per base pair per cell division, per gene per generation, or per genome per generation. The mutation rate of an organism is an evolved characteristic and is strongly influenced by the genetics of each organism, in addition to strong influence from the envi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leucine Zipper
A leucine zipper (or leucine scissors) is a common three-dimensional structural motif in proteins. They were first described by Landschulz and collaborators in 1988 when they found that an enhancer binding protein had a very characteristic 30-amino acid segment and the display of these amino acid sequences on an idealized alpha helix revealed a periodic repetition of leucine residues at every seventh position over a distance covering eight helical turns. The polypeptide segments containing these periodic arrays of leucine residues were proposed to exist in an alpha-helical conformation and the leucine side chains from one alpha helix interdigitate with those from the alpha helix of a second polypeptide, facilitating dimerization. Leucine zippers are a dimerization motif of the bZIP (Basic-region leucine zipper) class of eukaryotic transcription factors. The bZIP domain is 60 to 80 amino acids in length with a highly conserved DNA binding basic region and a more diversified leu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reactive Oxygen Species
In chemistry, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly reactive chemicals formed from diatomic oxygen (). Examples of ROS include peroxides, superoxide, hydroxyl radical, singlet oxygen, and alpha-oxygen. The reduction of molecular oxygen () produces superoxide (), which is the precursor to most other reactive oxygen species: :O2 + e^- -> \ ^\bullet O2- Dismutation of superoxide produces hydrogen peroxide (): :2 H+ + \ ^\bullet O2^- + \ ^\bullet O2^- -> H2O2 + O2 Hydrogen peroxide in turn may be partially reduced, thus forming hydroxide ions and hydroxyl radicals (), or fully reduced to water: :H2O2 + e^- -> HO^- + \ ^\bullet OH :2 H+ + 2 e- + H2O2 -> 2 H2O In a biological context, ROS are byproducts of the normal metabolism of oxygen. ROS have roles in cell signaling and homeostasis. ROS are intrinsic to cellular functioning, and are present at low and stationary levels in normal cells. In plants, ROS are involved in metabolic processes related to photoprotection a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) or RNA replicase is an enzyme that catalyzes the replication of RNA from an RNA template. Specifically, it catalyzes synthesis of the RNA strand complementary to a given RNA template. This is in contrast to typical DNA-dependent RNA polymerases, which all organisms use to catalyze the transcription of RNA from a DNA template. RdRp is an essential protein encoded in the genomes of most RNA-containing viruses with no DNA stage including SARS-CoV-2. Some eukaryotes also contain RdRps, which are involved in RNA interference and differ structurally from viral RdRps. History Viral RdRps were discovered in the early 1960s from studies on mengovirus and polio virus when it was observed that these viruses were not sensitive to actinomycin D, a drug that inhibits cellular DNA-directed RNA synthesis. This lack of sensitivity suggested that there is a virus-specific enzyme that could copy RNA from an RNA template and not from a DNA template. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyprotein
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes including apoptosis, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or misfolded proteins in cells. Consequently, abnormality in the regulation of proteolysis can cause disease. Proteolysis can also be used as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, and it may also be used in industry, for example in food p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Reading Frames
In molecular biology, open reading frames (ORFs) are defined as spans of DNA sequence between the start and stop codons. Usually, this is considered within a studied region of a prokaryotic DNA sequence, where only one of the six possible reading frames will be "open" (the "reading", however, refers to the RNA produced by transcription of the DNA and its subsequent interaction with the ribosome in translation). Such an ORF may contain a start codon (usually AUG in terms of RNA) and by definition cannot extend beyond a stop codon (usually UAA, UAG or UGA in RNA). That start codon (not necessarily the first) indicates where translation may start. The transcription termination site is located after the ORF, beyond the translation stop codon. If transcription were to cease before the stop codon, an incomplete protein would be made during translation. In eukaryotic genes with multiple exons, introns are removed and exons are then joined together after transcription to yield the fin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homologous Recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which genetic information is exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of double-stranded or single-stranded nucleic acids (usually DNA as in cellular organisms but may be also RNA in viruses). Homologous recombination is widely used by cells to accurately DNA repair harmful breaks that occur on both strands of DNA, known as double-strand breaks (DSB), in a process called homologous recombinational repair (HRR). Homologous recombination also produces new combinations of DNA sequences during meiosis, the process by which eukaryotes make gamete cells, like sperm and egg cells in animals. These new combinations of DNA represent genetic variation in offspring, which in turn enables populations to adapt during the course of evolution. Homologous recombination is also used in horizontal gene transfer to exchange genetic material between different strains and species of bacteria and viruses. Horizontal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigenic Variation
Antigenic variation or antigenic alteration refers to the mechanism by which an infectious agent such as a protozoan, bacterium or virus alters the proteins or carbohydrates on its surface and thus avoids a host immune response, making it one of the mechanisms of antigenic escape. It is related to phase variation. Antigenic variation not only enables the pathogen to avoid the immune response in its current host, but also allows re-infection of previously infected hosts. Immunity to re-infection is based on recognition of the antigens carried by the pathogen, which are "remembered" by the acquired immune response. If the pathogen's dominant antigen can be altered, the pathogen can then evade the host's acquired immune system. Antigenic variation can occur by altering a variety of surface molecules including proteins and carbohydrates. Antigenic variation can result from gene conversion, site-specific DNA inversions, hypermutation, or recombination of sequence cassettes. The re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virion
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898,Dimmock p. 4 more than 9,000 virus species have been described in detail of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) the genetic materia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)