Biochemistry Profile on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of
 It was once generally believed that life and its materials had some essential property or substance (often referred to as the " vital principle") distinct from any found in non-living matter, and it was thought that only living beings could produce the molecules of life. In 1828,
It was once generally believed that life and its materials had some essential property or substance (often referred to as the " vital principle") distinct from any found in non-living matter, and it was thought that only living beings could produce the molecules of life. In 1828,
 Lipid, Lipids comprise a diverse range of molecules and to some extent is a catchall for relatively water-insoluble or nonpolar compounds of biological origin, including waxes, fatty acids, fatty-acid derived phospholipids, sphingolipids, glycolipids, and terpenoids (e.g., retinoids and steroids). Some lipids are linear, open-chain aliphatic molecules, while others have ring structures. Some are aromatic (with a cyclic [ring] and planar [flat] structure) while others are not. Some are flexible, while others are rigid.
Lipids are usually made from one molecule of glycerol combined with other molecules. In triglycerides, the main group of bulk lipids, there is one molecule of glycerol and three fatty acids. Fatty acids are considered the monomer in that case, and may be Saturated and unsaturated compounds, saturated (no double bonds in the carbon chain) or unsaturated (one or more double bonds in the carbon chain).
Most lipids have some Polar molecule, polar character and are largely nonpolar. In general, the bulk of their structure is nonpolar or hydrophobic ("water-fearing"), meaning that it does not interact well with polar solvents like
Lipid, Lipids comprise a diverse range of molecules and to some extent is a catchall for relatively water-insoluble or nonpolar compounds of biological origin, including waxes, fatty acids, fatty-acid derived phospholipids, sphingolipids, glycolipids, and terpenoids (e.g., retinoids and steroids). Some lipids are linear, open-chain aliphatic molecules, while others have ring structures. Some are aromatic (with a cyclic [ring] and planar [flat] structure) while others are not. Some are flexible, while others are rigid.
Lipids are usually made from one molecule of glycerol combined with other molecules. In triglycerides, the main group of bulk lipids, there is one molecule of glycerol and three fatty acids. Fatty acids are considered the monomer in that case, and may be Saturated and unsaturated compounds, saturated (no double bonds in the carbon chain) or unsaturated (one or more double bonds in the carbon chain).
Most lipids have some Polar molecule, polar character and are largely nonpolar. In general, the bulk of their structure is nonpolar or hydrophobic ("water-fearing"), meaning that it does not interact well with polar solvents like
 Proteins are very large molecules—macro-biopolymers—made from monomers called
Proteins are very large molecules—macro-biopolymers—made from monomers called 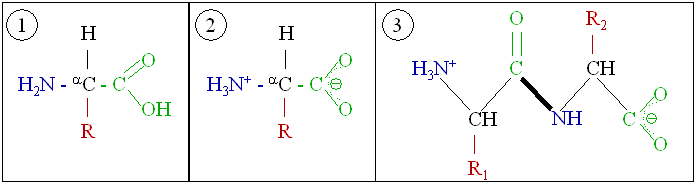
 Proteins can have structural and/or functional roles. For instance, movements of the proteins actin and myosin ultimately are responsible for the contraction of skeletal muscle. One property many proteins have is that they specifically bind to a certain molecule or class of molecules—they may be ''extremely'' selective in what they bind. Antibody, Antibodies are an example of proteins that attach to one specific type of molecule. Antibodies are composed of heavy and light chains. Two heavy chains would be linked to two light chains through disulfide linkages between their amino acids. Antibodies are specific through variation based on differences in the N-terminal domain.
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), which uses antibodies, is one of the most sensitive tests modern medicine uses to detect various biomolecules. Probably the most important proteins, however, are the
Proteins can have structural and/or functional roles. For instance, movements of the proteins actin and myosin ultimately are responsible for the contraction of skeletal muscle. One property many proteins have is that they specifically bind to a certain molecule or class of molecules—they may be ''extremely'' selective in what they bind. Antibody, Antibodies are an example of proteins that attach to one specific type of molecule. Antibodies are composed of heavy and light chains. Two heavy chains would be linked to two light chains through disulfide linkages between their amino acids. Antibodies are specific through variation based on differences in the N-terminal domain.
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), which uses antibodies, is one of the most sensitive tests modern medicine uses to detect various biomolecules. Probably the most important proteins, however, are the 
 Ingested proteins are usually broken up into single amino acids or dipeptides in the small intestine and then absorbed. They can then be joined to form new proteins. Intermediate products of glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the pentose phosphate pathway can be used to form all twenty amino acids, and most bacteria and plants possess all the necessary enzymes to synthesize them. Humans and other mammals, however, can synthesize only half of them. They cannot synthesize isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine. Because they must be ingested, these are the essential amino acids. Mammals do possess the enzymes to synthesize alanine, asparagine, aspartate, cysteine, glutamate, glutamine, glycine, proline, serine, and tyrosine, the nonessential amino acids. While they can synthesize arginine and histidine, they cannot produce it in sufficient amounts for young, growing animals, and so these are often considered essential amino acids.
If the amino group is removed from an amino acid, it leaves behind a carbon skeleton called an α-keto acid. Enzymes called transaminases can easily transfer the amino group from one amino acid (making it an α-keto acid) to another α-keto acid (making it an amino acid). This is important in the biosynthesis of amino acids, as for many of the pathways, intermediates from other biochemical pathways are converted to the α-keto acid skeleton, and then an amino group is added, often via transamination. The amino acids may then be linked together to form a protein.
A similar process is used to break down proteins. It is first hydrolyzed into its component amino acids. Free ammonia (NH3), existing as the ammonium ion (NH4+) in blood, is toxic to life forms. A suitable method for excreting it must therefore exist. Different tactics have evolved in different animals, depending on the animals' needs. Unicellular organisms release the ammonia into the environment. Likewise, Osteichthyes, bony fish can release ammonia into the water where it is quickly diluted. In general, mammals convert ammonia into urea, via the urea cycle.
In order to determine whether two proteins are related, or in other words to decide whether they are homologous or not, scientists use sequence-comparison methods. Methods like sequence alignments and structural alignments are powerful tools that help scientists identify Sequence homology, homologies between related molecules. The relevance of finding homologies among proteins goes beyond forming an evolutionary pattern of Protein family, protein families. By finding how similar two protein sequences are, we acquire knowledge about their structure and therefore their function.
Ingested proteins are usually broken up into single amino acids or dipeptides in the small intestine and then absorbed. They can then be joined to form new proteins. Intermediate products of glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the pentose phosphate pathway can be used to form all twenty amino acids, and most bacteria and plants possess all the necessary enzymes to synthesize them. Humans and other mammals, however, can synthesize only half of them. They cannot synthesize isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine. Because they must be ingested, these are the essential amino acids. Mammals do possess the enzymes to synthesize alanine, asparagine, aspartate, cysteine, glutamate, glutamine, glycine, proline, serine, and tyrosine, the nonessential amino acids. While they can synthesize arginine and histidine, they cannot produce it in sufficient amounts for young, growing animals, and so these are often considered essential amino acids.
If the amino group is removed from an amino acid, it leaves behind a carbon skeleton called an α-keto acid. Enzymes called transaminases can easily transfer the amino group from one amino acid (making it an α-keto acid) to another α-keto acid (making it an amino acid). This is important in the biosynthesis of amino acids, as for many of the pathways, intermediates from other biochemical pathways are converted to the α-keto acid skeleton, and then an amino group is added, often via transamination. The amino acids may then be linked together to form a protein.
A similar process is used to break down proteins. It is first hydrolyzed into its component amino acids. Free ammonia (NH3), existing as the ammonium ion (NH4+) in blood, is toxic to life forms. A suitable method for excreting it must therefore exist. Different tactics have evolved in different animals, depending on the animals' needs. Unicellular organisms release the ammonia into the environment. Likewise, Osteichthyes, bony fish can release ammonia into the water where it is quickly diluted. In general, mammals convert ammonia into urea, via the urea cycle.
In order to determine whether two proteins are related, or in other words to decide whether they are homologous or not, scientists use sequence-comparison methods. Methods like sequence alignments and structural alignments are powerful tools that help scientists identify Sequence homology, homologies between related molecules. The relevance of finding homologies among proteins goes beyond forming an evolutionary pattern of Protein family, protein families. By finding how similar two protein sequences are, we acquire knowledge about their structure and therefore their function.
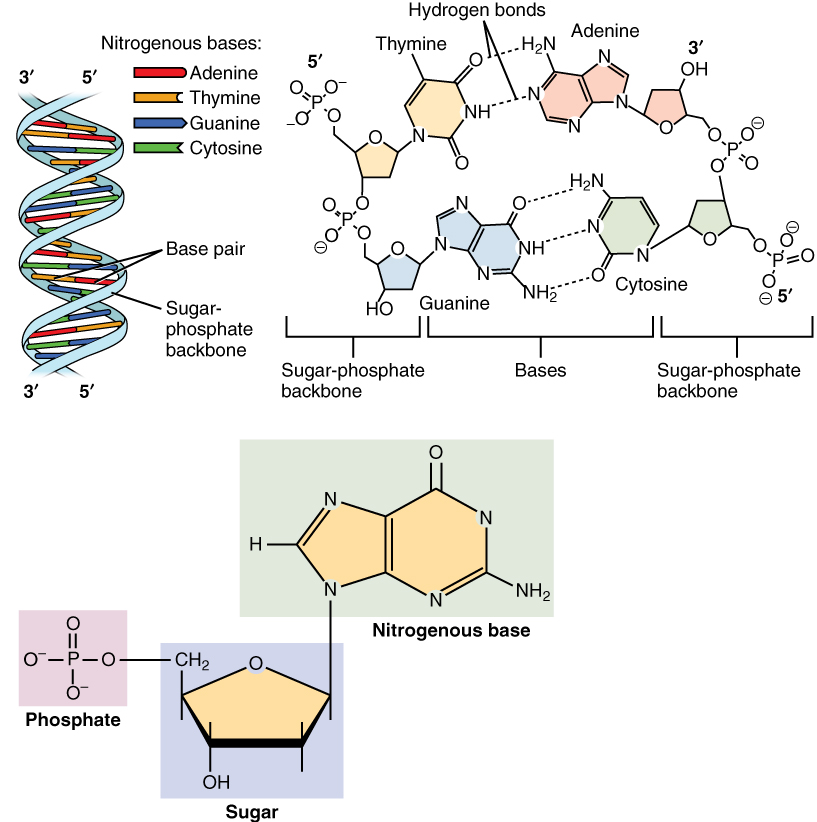 Nucleic acids, so-called because of their prevalence in cellular cell nucleus, nuclei, is the generic name of the family of biopolymers. They are complex, high-molecular-weight biochemical macromolecules that can convey genetic information in all living cells and viruses. The monomers are called nucleotides, and each consists of three components: a nitrogenous heterocyclic base (chemistry), base (either a purine or a pyrimidine), a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group.
Nucleic acids, so-called because of their prevalence in cellular cell nucleus, nuclei, is the generic name of the family of biopolymers. They are complex, high-molecular-weight biochemical macromolecules that can convey genetic information in all living cells and viruses. The monomers are called nucleotides, and each consists of three components: a nitrogenous heterocyclic base (chemistry), base (either a purine or a pyrimidine), a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group.
 The most common nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). The phosphate group and the sugar of each nucleotide bond with each other to form the backbone of the nucleic acid, while the sequence of nitrogenous bases stores the information. The most common nitrogenous bases are adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine, and uracil. The nitrogenous bases of each strand of a nucleic acid will form hydrogen bonds with certain other nitrogenous bases in a complementary strand of nucleic acid. Adenine binds with thymine and uracil, thymine binds only with adenine, and cytosine and guanine can bind only with one another. Adenine, thymine, and uracil contain two hydrogen bonds, while hydrogen bonds formed between cytosine and guanine are three.
Aside from the genetic material of the cell, nucleic acids often play a role as second messengers, as well as forming the base molecule for adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy-carrier molecule found in all living organisms. Also, the nitrogenous bases possible in the two nucleic acids are different: adenine, cytosine, and guanine occur in both RNA and DNA, while thymine occurs only in DNA and uracil occurs in RNA.
The most common nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). The phosphate group and the sugar of each nucleotide bond with each other to form the backbone of the nucleic acid, while the sequence of nitrogenous bases stores the information. The most common nitrogenous bases are adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine, and uracil. The nitrogenous bases of each strand of a nucleic acid will form hydrogen bonds with certain other nitrogenous bases in a complementary strand of nucleic acid. Adenine binds with thymine and uracil, thymine binds only with adenine, and cytosine and guanine can bind only with one another. Adenine, thymine, and uracil contain two hydrogen bonds, while hydrogen bonds formed between cytosine and guanine are three.
Aside from the genetic material of the cell, nucleic acids often play a role as second messengers, as well as forming the base molecule for adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy-carrier molecule found in all living organisms. Also, the nitrogenous bases possible in the two nucleic acids are different: adenine, cytosine, and guanine occur in both RNA and DNA, while thymine occurs only in DNA and uracil occurs in RNA.
The Virtual Library of Biochemistry, Molecular Biology and Cell Biology
Biochemistry, 5th ed.
Full text of Berg, Tymoczko, and Stryer, courtesy of National Center for Biotechnology Information, NCBI.
SystemsX.ch – The Swiss Initiative in Systems Biology
Full text of Biochemistry
by Kevin and Indira, an introductory biochemistry textbook. {{Authority control Biochemistry, Biotechnology Molecular biology Genomics,
chemical process
In a scientific sense, a chemical process is a method or means of somehow changing one or more chemicals or chemical compounds. Such a chemical process can occur by itself or be caused by an outside force, and involves a chemical reaction of som ...
es within and relating to living organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
s. A sub-discipline of both chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules a ...
and biology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and ...
, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology
Structural biology deals with structural analysis of living material (formed, composed of, and/or maintained and refined by living cells) at every level of organization.
Early structural biologists throughout the 19th and early 20th centuries we ...
, enzymology
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
, and metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become successful at explaining living processes through these three disciplines. Almost all areas of the life sciences are being uncovered and developed through biochemical methodology and research. Voet (2005), p. 3. Biochemistry focuses on understanding the chemical basis that allows biological molecules to give rise to the processes that occur within living cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
* Cellphone, a phone connected to a cellular network
* Clandestine cell, a penetration-resistant form of a secret or outlawed organization
* Electrochemical cell, a d ...
and between cells,Karp
Karp may refer to:
Places
* Karp, Podlaskie Voivodeship, in north-east Poland
* Karp, Lublin Voivodeship, in east Poland
People
* Karp (surname)
* Karp Khachvankyan (1923–1998), Armenian actor and director
Other uses
* KARP-FM, a radio statio ...
(2009), p. 2. in turn relating greatly to the understanding of tissues and organs
In a multicellular organism, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to a ...
as well as organism structure and function.Miller
A miller is a person who operates a mill, a machine to grind a grain (for example corn or wheat) to make flour. Milling is among the oldest of human occupations. "Miller", "Milne" and other variants are common surnames, as are their equivalents ...
(2012). p. 62. Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology
Molecular biology is a branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecule, molecular basis of biological activity in and between Cell (biology), cells, including biomolecule, biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactio ...
, the study of the molecular
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, ...
mechanisms of biological phenomena.Astbury Astbury is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Andrew Astbury, English swimmer
* Ian Astbury, English rock singer
* Jill Astbury, Australian researcher into violence against women
*William Astbury
William Thomas Astbury FRS ( ...
(1961), p. 1124.
Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions, and interactions of biological macromolecule
A macromolecule is a "molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass." Polymers are physi ...
s such as protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s, nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that are crucial in all cells and viruses. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomer components: a pentose, 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nuclei ...
s, carbohydrate
A carbohydrate () is a biomolecule composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. The typical hydrogen-to-oxygen atomic ratio is 2:1, analogous to that of water, and is represented by the empirical formula (where ''m'' and ''n'' ...
s, and lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing ...
s. They provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life.Eldra
''Eldra'' is a 2003 British drama film
In film and television, drama is a category or genre of narrative fiction (or semi-fiction) intended to be more serious than humorous in tone. The drama of this kind is usually qualified with ad ...
(2007), p. 45. The chemistry of the cell also depends upon the reactions of small molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ...
s and ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
s. These can be inorganic
An inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bondsthat is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemistry''.
Inor ...
(for example, water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
and metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated wit ...
ions) or organic
Organic may refer to:
* Organic, of or relating to an organism, a living entity
* Organic, of or relating to an anatomical organ
Chemistry
* Organic matter, matter that has come from a once-living organism, is capable of decay or is the product ...
(for example, the amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s, which are used to synthesize proteins).Marks
Marks may refer to:
Business
* Mark's, a Canadian retail chain
* Marks & Spencer, a British retail chain
* Collective trade marks
A collective trademark, collective trade mark, or collective mark is a trademark owned by an organization (such ...
(2012), Chapter 14. The mechanisms used by cells to harness energy from their environment via chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemistry, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. When chemical reactions occur, the atoms are rearranged and the reaction is accompanied by an Gibbs free energy, ...
s are known as metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
, nutrition
Nutrition is the biochemistry, biochemical and physiology, physiological process by which an organism uses food and water to support its life. The intake of these substances provides organisms with nutrients (divided into Macronutrient, macro- ...
, and agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
. In medicine, biochemist
Biochemists are scientists who are trained in biochemistry. They study chemical processes and chemical transformations in living organisms. Biochemists study DNA, proteins and Cell (biology), cell parts. The word "biochemist" is a portmanteau of ...
s investigate the causes and cures of disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function (biology), function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical condi ...
s. Nutrition studies how to maintain health and wellness and also the effects of nutritional deficiencies
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a Deficiency (medicine), deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and Vitamin deficiency, other nutrients whic ...
.UNICEF
UNICEF ( ), originally the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund, officially United Nations Children's Fund since 1953, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing Humanitarianism, humanitarian and Development a ...
(2010), pp. 61, 75. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, water, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms. Some scientific definitions distinguish dirt from ''soil'' by re ...
and fertilizer
A fertilizer or fertiliser is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from liming materials or other non-nutrient soil amendments. Man ...
s with the goal of improving crop cultivation, crop storage, and pest control
Pest control is the regulation or management of a species defined as a pest (organism), pest; such as any animal, plant or fungus that impacts adversely on human activities or environment. The human response depends on the importance of the da ...
. In recent decades, biochemical principles and methods have been combined with problem-solving approaches from engineering
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, s ...
to manipulate living systems in order to produce useful tools for research, industrial processes, and diagnosis and control of diseasethe discipline of biotechnology
Biotechnology is a multidisciplinary field that involves the integration of natural sciences and Engineering Science, engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms and parts thereof for products and services. Specialists ...
.
History
At its most comprehensive definition, biochemistry can be seen as a study of the components and composition of living things and how they come together to become life. In this sense, the history of biochemistry may therefore go back as far as theancient Greeks
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically re ...
. Helvoort (2000), p. 81. However, biochemistry as a specific scientific discipline
The branches of science, also referred to as sciences, scientific fields or scientific disciplines, are commonly divided into three major groups:
* Formal sciences: the study of formal systems, such as those under the branches of logic and mat ...
began sometime in the 19th century, or a little earlier, depending on which aspect of biochemistry is being focused on. Some argued that the beginning of biochemistry may have been the discovery of the first enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
, diastase
A diastase (; from Greek διάστασις, "separation") is any one of a group of enzymes that catalyses the breakdown of starch into maltose. For example, the diastase α-amylase degrades starch to a mixture of the disaccharide maltose; the ...
(now called amylase
An amylase () is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyses the hydrolysis of starch (Latin ') into sugars. Amylase is present in the saliva of humans and some other mammals, where it begins the chemical process of digestion. Foods that contain large ...
), in 1833 by Anselme Payen
Anselme Payen (; 6 January 1795 – 12 May 1871) was a French chemist known for discovering the enzyme diastase, and the carbohydrate cellulose.
Biography
Payen was born in Paris. He began studying science with his father when he was a 13-yea ...
, while others considered Eduard Buchner
Eduard Buchner (; 20 May 1860 – 13 August 1917) was a German chemist and Zymurgy, zymologist, awarded the 1907 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his work on fermentation (biochemistry), fermentation.
Biography
Early years
Buchner was born in Mun ...
's first demonstration of a complex biochemical process alcoholic fermentation
Ethanol fermentation, also called alcoholic fermentation, is a biological process which converts sugars such as glucose, fructose, and sucrose into cellular energy, producing ethanol and carbon dioxide as by-products. Because yeasts perform this ...
in cell-free extracts in 1897 to be the birth of biochemistry. Some might also point as its beginning to the influential 1842 work by Justus von Liebig
Justus ''Freiherr'' von Liebig (12 May 1803 – 18 April 1873) was a Germans, German scientist who made major contributions to the theory, practice, and pedagogy of chemistry, as well as to agricultural and biology, biological chemistry; he is ...
, ''Animal chemistry, or, Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic matter, organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain ...
in its applications to physiology
Physiology (; ) is the science, scientific study of function (biology), functions and mechanism (biology), mechanisms in a life, living system. As a branches of science, subdiscipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ syst ...
and pathology
Pathology is the study of disease. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatme ...
'', which presented a chemical theory of metabolism, or even earlier to the 18th century studies on fermentation
Fermentation is a type of anaerobic metabolism which harnesses the redox potential of the reactants to make adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and organic end products. Organic molecules, such as glucose or other sugars, are catabolized and reduce ...
and respiration
Respiration may refer to:
Biology
* Cellular respiration, the process in which nutrients are converted into useful energy in a cell
** Anaerobic respiration, cellular respiration without oxygen
** Maintenance respiration, the amount of cellul ...
by Antoine Lavoisier
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier ( ; ; 26 August 17438 May 1794), When reduced without charcoal, it gave off an air which supported respiration and combustion in an enhanced way. He concluded that this was just a pure form of common air and that i ...
. Many other pioneers in the field who helped to uncover the layers of complexity of biochemistry have been proclaimed founders of modern biochemistry. Emil Fischer
Hermann Emil Louis Fischer (; 9 October 1852 – 15 July 1919) was a German chemist and List of Nobel laureates in Chemistry, 1902 recipient of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. He discovered the Fischer esterification. He also developed the Fisch ...
, who studied the chemistry of proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, re ...
, and F. Gowland Hopkins, who studied enzymes
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as pro ...
and the dynamic nature of biochemistry, represent two examples of early biochemists.
The term "biochemistry" was first used when Vinzenz Kletzinsky (1826–1882) had his "Compendium der Biochemie" printed in Vienna in 1858; it derived from a combination of biology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and ...
and chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules a ...
. In 1877, Felix Hoppe-Seyler
Ernst Felix Immanuel Hoppe-Seyler (''né'' Felix Hoppe; 26 December 1825 – 10 August 1895) was a German physiologist and chemist, and the principal founder of the disciplines of biochemistry and molecular biology. He had discovered Yeast nuclei ...
used the term ( in German) as a synonym for physiological chemistry
Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, a ...
in the foreword to the first issue of '' Zeitschrift für Physiologische Chemie'' (Journal of Physiological Chemistry) where he argued for the setting up of institutes dedicated to this field of study. The German chemist
A chemist (from Greek ''chēm(ía)'' alchemy; replacing ''chymist'' from Medieval Latin ''alchemist'') is a graduated scientist trained in the study of chemistry, or an officially enrolled student in the field. Chemists study the composition of ...
Carl Neuberg
Carl Alexander Neuberg (29 July 1877 – 30 May 1956) was an early pioneer in biochemistry, and he has sometimes been referred to as the "father of modern biochemistry". His notable contribution to science includes the discovery of the carboxyl ...
however is often cited to have coined the word in 1903, Ben-Menahem (2009), p. 2982. while some credited it to Franz Hofmeister
Franz Hofmeister (30 August 1850, in Prague – 26 July 1922, in Würzburg) was an early protein scientist, and is famous for his studies of salts that influence the solubility and conformational stability of proteins. In 1902, Hofmeister became t ...
.
 It was once generally believed that life and its materials had some essential property or substance (often referred to as the " vital principle") distinct from any found in non-living matter, and it was thought that only living beings could produce the molecules of life. In 1828,
It was once generally believed that life and its materials had some essential property or substance (often referred to as the " vital principle") distinct from any found in non-living matter, and it was thought that only living beings could produce the molecules of life. In 1828, Friedrich Wöhler
Friedrich Wöhler Royal Society of London, FRS(For) HonFRSE (; 31 July 180023 September 1882) was a German chemist known for his work in both organic chemistry, organic and inorganic chemistry, being the first to isolate the chemical elements be ...
published a paper on his serendipitous
Serendipity is an unplanned fortunate discovery. The term was coined by Horace Walpole in 1754.
The concept is often associated with scientific and technological breakthroughs, where accidental discoveries led to new insights or inventions. Man ...
urea
Urea, also called carbamide (because it is a diamide of carbonic acid), is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two Amine, amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest am ...
synthesis
Synthesis or synthesize may refer to:
Science Chemistry and biochemistry
*Chemical synthesis, the execution of chemical reactions to form a more complex molecule from chemical precursors
**Organic synthesis, the chemical synthesis of organi ...
from potassium cyanate
Potassium cyanate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula, formula KOCN (sometimes denoted KCNO). It is a colourless solid. It is used to prepare many other compounds including useful herbicide. Worldwide production of the potassium an ...
and ammonium sulfate
Ammonium sulfate (American English and international scientific usage; ammonium sulphate in British English); (NH4)2SO4, is an inorganic salt with a number of commercial uses. The most common use is as a soil fertilizer. It contains 21% nitrogen a ...
; some regarded that as a direct overthrow of vitalism and the establishment of organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic matter, organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain ...
. Kauffman (2001), pp. 121–133. However, the Wöhler synthesis has sparked controversy as some reject the death of vitalism at his hands. Since then, biochemistry has advanced, especially since the mid-20th century, with the development of new techniques such as chromatography
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the Separation process, separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it ...
, X-ray diffraction
X-ray diffraction is a generic term for phenomena associated with changes in the direction of X-ray beams due to interactions with the electrons around atoms. It occurs due to elastic scattering, when there is no change in the energy of the waves. ...
, dual polarisation interferometry
Dual-polarization interferometry (DPI) is an analytical technique that probes molecular layers adsorbed to the surface of a waveguide using the evanescent wave of a laser beam. It is used to measure the conformational change in proteins, or o ...
, NMR spectroscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy or magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), is a spectroscopic technique based on re-orientation of atomic nuclei with non-zero nuclear spins in an external magnetic f ...
, radioisotopic labeling
Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope (an atom with a detectable variation in neutron count) through chemical reaction, metabolic pathway, or a biological cell. The reactant is 'labeled' ...
, electron microscopy
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of electrons as a source of illumination. It uses electron optics that are analogous to the glass lenses of an optical light microscope to control the electron beam, for instance focusing i ...
and molecular dynamics
Molecular dynamics (MD) is a computer simulation method for analyzing the Motion (physics), physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a fixed period of time, giving a view of the dynamics ( ...
simulations. These techniques allowed for the discovery and detailed analysis of many molecules and metabolic pathway
In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell (biology), cell. The reactants, products, and Metabolic intermediate, intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are ...
s of the cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
* Cellphone, a phone connected to a cellular network
* Clandestine cell, a penetration-resistant form of a secret or outlawed organization
* Electrochemical cell, a de ...
, such as glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvic acid, pyruvate and, in most organisms, occurs in the liquid part of cells (the cytosol). The Thermodynamic free energy, free energy released in this process is used to form ...
and the Krebs cycle
The citric acid cycle—also known as the Krebs cycle, Szent–Györgyi–Krebs cycle, or TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of biochemical reactions that release the energy stored in nutrients through acetyl-CoA oxidation. The e ...
(citric acid cycle), and led to an understanding of biochemistry on a molecular level.
Another significant historic event in biochemistry is the discovery of the gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
, and its role in the transfer of information in the cell. In the 1950s, James D. Watson
James Dewey Watson (born April 6, 1928) is an American molecular biologist, geneticist, and zoologist. In 1953, he co-authored with Francis Crick the academic paper in ''Nature'' proposing the double helix structure of the DNA molecule. Wats ...
, Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick (8 June 1916 – 28 July 2004) was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and Maurice Wilkins played crucial roles in deciphering the Nucleic acid doub ...
, Rosalind Franklin
Rosalind Elsie Franklin (25 July 192016 April 1958) was a British chemist and X-ray crystallographer. Her work was central to the understanding of the molecular structures of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), RNA (ribonucleic acid), viruses, coal ...
and Maurice Wilkins
Maurice Hugh Frederick Wilkins (15 December 1916 – 5 October 2004) was a New Zealand-born British biophysicist and Nobel laureate whose research spanned multiple areas of physics and biophysics, contributing to the scientific understanding ...
were instrumental in solving DNA structure
Nucleic acid structure refers to the structure of nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA. Chemically speaking, DNA and RNA are very similar. Nucleic acid structure is often divided into four different levels: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaterna ...
and suggesting its relationship with the genetic transfer of information. In 1958, George Beadle
George Wells Beadle (October 22, 1903 – June 9, 1989) was an American geneticist. In 1958 he shared one-half of the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine with Edward Tatum for their discovery of the role of genes in regulating biochemical eve ...
and Edward Tatum
Edward Lawrie Tatum (December 14, 1909 – November 5, 1975) was an American geneticist. He shared half of the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1958 with George Beadle for showing that genes control individual steps in metabolism. The o ...
received the Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; ; ) are awards administered by the Nobel Foundation and granted in accordance with the principle of "for the greatest benefit to humankind". The prizes were first awarded in 1901, marking the fifth anniversary of Alfred N ...
for work in fungi showing that one gene produces one enzyme. Krebs (2012), p. 32. In 1988, Colin Pitchfork
Colin Pitchfork (born 23 March 1960) is an English child-murderer and child-rapist. He was the first person convicted of rape and murder using DNA profiling after he murdered two girls in neighbouring Leicestershire villages: Lynda Mann in Nar ...
was the first person convicted of murder with DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
evidence, which led to the growth of forensic science
Forensic science combines principles of law and science to investigate criminal activity. Through crime scene investigations and laboratory analysis, forensic scientists are able to link suspects to evidence. An example is determining the time and ...
.Butler
A butler is a person who works in a house serving and is a domestic worker in a large household. In great houses, the household is sometimes divided into departments, with the butler in charge of the dining room, wine cellar, and pantries, pantr ...
(2009), p. 5. More recently, Andrew Z. Fire
Andrew Zachary Fire (born April 27, 1959) is an American biologist and professor of pathology and of genetics at the Stanford University School of Medicine. He was awarded the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, along with Craig C. Mell ...
and Craig C. Mello
Craig Cameron Mello (born October 18, 1960) is an American biologist and professor of molecular medicine at the University of Massachusetts Medical School in Worcester, Massachusetts. He was awarded the 2006 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicin ...
received the 2006 Nobel Prize for discovering the role of RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules are involved in sequence-specific suppression of gene expression by double-stranded RNA, through translational or transcriptional repression. Historically, RNAi was known by ...
(RNAi) in the silencing of gene expression
Gene expression is the process (including its Regulation of gene expression, regulation) by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, proteins or non-coding RNA, ...
. Chandan (2007), pp. 193–194.
Starting materials: the chemical elements of life
Around two dozenchemical elements
A chemical element is a chemical substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons. The number of protons is called the atomic number of that element. For example, oxygen has an atomic number of 8: each oxygen atom has 8 protons in i ...
are essential to various kinds of biological life
Life, also known as biota, refers to matter that has biological processes, such as signaling and self-sustaining processes. It is defined descriptively by the capacity for homeostasis, organisation, metabolism, growth, adaptation, res ...
. Most rare elements on Earth are not needed by life (exceptions being selenium and iodine), while a few common ones (aluminium and titanium) are not used. Most organisms share element needs, but there are a few differences between plants and animals. For example, ocean algae use bromine, but land plants and animals do not seem to need any. All animals require sodium, but is not an essential element for plants. Plants need boron and silicon, but animals may not (or may need ultra-small amounts).
Just six elements—carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, calcium and phosphorus—make up almost 99% of the mass of living cells, including those in the human body (see composition of the human body for a complete list). In addition to the six major elements that compose most of the human body, humans require smaller amounts of possibly 18 more.
Biomolecules
The 4 main classes of molecules in biochemistry (often called biomolecules) arecarbohydrate
A carbohydrate () is a biomolecule composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. The typical hydrogen-to-oxygen atomic ratio is 2:1, analogous to that of water, and is represented by the empirical formula (where ''m'' and ''n'' ...
s, lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing ...
s, protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s, and nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that are crucial in all cells and viruses. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomer components: a pentose, 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nuclei ...
s.#Slabaugh, Slabaugh (2007), pp. 3–6. Many biological molecules are polymers: in this terminology, monomers are relatively small macromolecules that are linked together to create large macromolecule
A macromolecule is a "molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass." Polymers are physi ...
s known as polymers. When monomers are linked together to synthesize a Biopolymer, biological polymer, they undergo a process called Dehydration reaction, dehydration synthesis. Different macromolecules can assemble in larger complexes, often needed for biological activity.
Carbohydrates
Two of the main functions of carbohydrates are energy storage and providing structure. One of the common sugars known as glucose is a carbohydrate, but not all carbohydrates are sugars. There are more carbohydrates on Earth than any other known type of biomolecule; they are used to store energy and Deoxyribose, genetic information, as well as play important roles in cell to Cell–cell interaction, cell interactions and Cell signaling, communications. The simplest type of carbohydrate is a monosaccharide, which among other properties contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, mostly in a ratio of 1:2:1 (generalized formula C''n''H2''n''O''n'', where ''n'' is at least 3). Glucose (C6H12O6) is one of the most important carbohydrates; others include fructose (C6H12O6), the sugar commonly associated with the sweet taste of fruits,#Whiting, Whiting (1970), pp. 1–31. and deoxyribose (C5H10O4), a component ofDNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
. A monosaccharide can switch between Open-chain compound, acyclic (open-chain) form and a cyclic compound, cyclic form. The open-chain form can be turned into a ring of carbon atoms bridged by an oxygen atom created from the carbonyl group of one end and the hydroxyl group of another. The cyclic molecule has a hemiacetal or hemiketal group, depending on whether the linear form was an aldose or a ketose.
In these cyclic forms, the ring usually has 5 or 6 atoms. These forms are called furanoses and pyranoses, respectively—by analogy with furan and pyran, the simplest compounds with the same carbon-oxygen ring (although they lack the carbon-carbon double bonds of these two molecules). For example, the aldohexose glucose may form a hemiacetal linkage between the hydroxyl on carbon 1 and the oxygen on carbon 4, yielding a molecule with a 5-membered ring, called glucofuranose. The same reaction can take place between carbons 1 and 5 to form a molecule with a 6-membered ring, called glucopyranose. Cyclic forms with a 7-atom ring called heptoses are rare.
Two monosaccharides can be joined by a Glycosidic bond, glycosidic or ester bond into a ''disaccharide'' through a dehydration reaction during which a molecule of water is released. The reverse reaction in which the glycosidic bond of a disaccharide is broken into two monosaccharides is termed ''hydrolysis''. The best-known disaccharide is sucrose or ordinary sugar, which consists of a glucose molecule and a fructose molecule joined. Another important disaccharide is lactose found in milk, consisting of a glucose molecule and a galactose molecule. Lactose may be hydrolysed by lactase, and deficiency in this enzyme results in lactose intolerance.
When a few (around three to six) monosaccharides are joined, it is called an ''oligosaccharide'' (''oligo-'' meaning "few"). These molecules tend to be used as markers and Cell signaling, signals, as well as having some other uses.#Varki, Varki (1999), p. 17. Many monosaccharides joined form a polysaccharide. They can be joined in one long linear chain, or they may be Branching (polymer chemistry), branched. Two of the most common polysaccharides are cellulose and glycogen, both consisting of repeating glucose monomers. ''Cellulose'' is an important structural component of plant's cell walls and ''glycogen'' is used as a form of energy storage in animals.
Sugar can be characterized by having Reducing sugar, reducing or non-reducing ends. A reducing end of a carbohydrate is a carbon atom that can be in equilibrium with the open-chain aldehyde (aldose) or keto form (ketose). If the joining of monomers takes place at such a carbon atom, the free hydroxy group of the pyranose or furanose form is exchanged with an OH-side-chain of another sugar, yielding a full acetal. This prevents opening of the chain to the aldehyde or keto form and renders the modified residue non-reducing. Lactose contains a reducing end at its glucose moiety, whereas the galactose moiety forms a full acetal with the C4-OH group of glucose. Saccharose does not have a reducing end because of full acetal formation between the aldehyde carbon of glucose (C1) and the keto carbon of fructose (C2).
Lipids
water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
. Another part of their structure is polar or hydrophilic ("water-loving") and will tend to associate with polar solvents like water. This makes them amphiphilic molecules (having both hydrophobic and hydrophilic portions). In the case of cholesterol, the polar group is a mere –OH (hydroxyl or alcohol).
In the case of phospholipids, the polar groups are considerably larger and more polar, as described below.
Lipids are an integral part of our daily diet. Most oils and milk products that we use for cooking and eating like butter, cheese, ghee etc. are composed of fats. Vegetable oils are rich in various polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA). Lipid-containing foods undergo digestion within the body and are broken into fatty acids and glycerol, the final degradation products of fats and lipids. Lipids, especially phospholipids, are also used in various pharmaceutical products, either as co-solubilizers (e.g. in parenteral infusions) or else as drug carrier components (e.g. in a liposome or transfersome).
Proteins
amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s. An amino acid consists of an alpha carbon atom attached to an amino group, –NH2, a carboxylic acid group, –COOH (although these exist as –NH3+ and –COO− under physiologic conditions), a simple hydrogen atom, and a side chain commonly denoted as "–R". The side chain "R" is different for each amino acid of which there are 20 proteinogenic amino acid, standard ones. It is this "R" group that makes each amino acid different, and the properties of the side chains greatly influence the overall Protein tertiary structure, three-dimensional conformation of a protein. Some amino acids have functions by themselves or in a modified form; for instance, glutamate functions as an important neurotransmitter. Amino acids can be joined via a peptide bond. In this Dehydration reaction, dehydration synthesis, a water molecule is removed and the peptide bond connects the nitrogen of one amino acid's amino group to the carbon of the other's carboxylic acid group. The resulting molecule is called a ''dipeptide'', and short stretches of amino acids (usually, fewer than thirty) are called ''peptides'' or polypeptides. Longer stretches merit the title ''proteins''. As an example, the important blood blood plasma, serum protein human serum albumin, albumin contains 585 Protein structure, amino acid residues.#Metzler, Metzler (2001), p. 58.

 Proteins can have structural and/or functional roles. For instance, movements of the proteins actin and myosin ultimately are responsible for the contraction of skeletal muscle. One property many proteins have is that they specifically bind to a certain molecule or class of molecules—they may be ''extremely'' selective in what they bind. Antibody, Antibodies are an example of proteins that attach to one specific type of molecule. Antibodies are composed of heavy and light chains. Two heavy chains would be linked to two light chains through disulfide linkages between their amino acids. Antibodies are specific through variation based on differences in the N-terminal domain.
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), which uses antibodies, is one of the most sensitive tests modern medicine uses to detect various biomolecules. Probably the most important proteins, however, are the
Proteins can have structural and/or functional roles. For instance, movements of the proteins actin and myosin ultimately are responsible for the contraction of skeletal muscle. One property many proteins have is that they specifically bind to a certain molecule or class of molecules—they may be ''extremely'' selective in what they bind. Antibody, Antibodies are an example of proteins that attach to one specific type of molecule. Antibodies are composed of heavy and light chains. Two heavy chains would be linked to two light chains through disulfide linkages between their amino acids. Antibodies are specific through variation based on differences in the N-terminal domain.
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), which uses antibodies, is one of the most sensitive tests modern medicine uses to detect various biomolecules. Probably the most important proteins, however, are the enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
s. Virtually every reaction in a living cell requires an enzyme to lower the activation energy of the reaction. These molecules recognize specific reactant molecules called ''substrate (biochemistry), substrates''; they then Catalysis, catalyze the reaction between them. By lowering the activation energy, the enzyme speeds up that reaction by a rate of 1011 or more; a reaction that would normally take over 3,000 years to complete spontaneously might take less than a second with an enzyme. The enzyme itself is not used up in the process and is free to catalyze the same reaction with a new set of substrates. Using various modifiers, the activity of the enzyme can be regulated, enabling control of the biochemistry of the cell as a whole.
The structure of proteins is traditionally described in a hierarchy of four levels. The primary structure of a protein consists of its linear sequence of amino acids; for instance, "alanine-glycine-tryptophan-serine-glutamate-asparagine-glycine-lysine-...". Secondary structure is concerned with local morphology (morphology being the study of structure). Some combinations of amino acids will tend to curl up in a coil called an alpha helix, α-helix or into a sheet called a Beta sheet, β-sheet; some α-helixes can be seen in the hemoglobin schematic above. Tertiary structure is the entire three-dimensional shape of the protein. This shape is determined by the sequence of amino acids. In fact, a single change can change the entire structure. The alpha chain of hemoglobin contains 146 amino acid residues; substitution of the glutamate residue at position 6 with a valine residue changes the behavior of hemoglobin so much that it results in sickle-cell disease. Finally, quaternary structure is concerned with the structure of a protein with multiple peptide subunits, like hemoglobin with its four subunits. Not all proteins have more than one subunit.

 Ingested proteins are usually broken up into single amino acids or dipeptides in the small intestine and then absorbed. They can then be joined to form new proteins. Intermediate products of glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the pentose phosphate pathway can be used to form all twenty amino acids, and most bacteria and plants possess all the necessary enzymes to synthesize them. Humans and other mammals, however, can synthesize only half of them. They cannot synthesize isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine. Because they must be ingested, these are the essential amino acids. Mammals do possess the enzymes to synthesize alanine, asparagine, aspartate, cysteine, glutamate, glutamine, glycine, proline, serine, and tyrosine, the nonessential amino acids. While they can synthesize arginine and histidine, they cannot produce it in sufficient amounts for young, growing animals, and so these are often considered essential amino acids.
If the amino group is removed from an amino acid, it leaves behind a carbon skeleton called an α-keto acid. Enzymes called transaminases can easily transfer the amino group from one amino acid (making it an α-keto acid) to another α-keto acid (making it an amino acid). This is important in the biosynthesis of amino acids, as for many of the pathways, intermediates from other biochemical pathways are converted to the α-keto acid skeleton, and then an amino group is added, often via transamination. The amino acids may then be linked together to form a protein.
A similar process is used to break down proteins. It is first hydrolyzed into its component amino acids. Free ammonia (NH3), existing as the ammonium ion (NH4+) in blood, is toxic to life forms. A suitable method for excreting it must therefore exist. Different tactics have evolved in different animals, depending on the animals' needs. Unicellular organisms release the ammonia into the environment. Likewise, Osteichthyes, bony fish can release ammonia into the water where it is quickly diluted. In general, mammals convert ammonia into urea, via the urea cycle.
In order to determine whether two proteins are related, or in other words to decide whether they are homologous or not, scientists use sequence-comparison methods. Methods like sequence alignments and structural alignments are powerful tools that help scientists identify Sequence homology, homologies between related molecules. The relevance of finding homologies among proteins goes beyond forming an evolutionary pattern of Protein family, protein families. By finding how similar two protein sequences are, we acquire knowledge about their structure and therefore their function.
Ingested proteins are usually broken up into single amino acids or dipeptides in the small intestine and then absorbed. They can then be joined to form new proteins. Intermediate products of glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the pentose phosphate pathway can be used to form all twenty amino acids, and most bacteria and plants possess all the necessary enzymes to synthesize them. Humans and other mammals, however, can synthesize only half of them. They cannot synthesize isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine. Because they must be ingested, these are the essential amino acids. Mammals do possess the enzymes to synthesize alanine, asparagine, aspartate, cysteine, glutamate, glutamine, glycine, proline, serine, and tyrosine, the nonessential amino acids. While they can synthesize arginine and histidine, they cannot produce it in sufficient amounts for young, growing animals, and so these are often considered essential amino acids.
If the amino group is removed from an amino acid, it leaves behind a carbon skeleton called an α-keto acid. Enzymes called transaminases can easily transfer the amino group from one amino acid (making it an α-keto acid) to another α-keto acid (making it an amino acid). This is important in the biosynthesis of amino acids, as for many of the pathways, intermediates from other biochemical pathways are converted to the α-keto acid skeleton, and then an amino group is added, often via transamination. The amino acids may then be linked together to form a protein.
A similar process is used to break down proteins. It is first hydrolyzed into its component amino acids. Free ammonia (NH3), existing as the ammonium ion (NH4+) in blood, is toxic to life forms. A suitable method for excreting it must therefore exist. Different tactics have evolved in different animals, depending on the animals' needs. Unicellular organisms release the ammonia into the environment. Likewise, Osteichthyes, bony fish can release ammonia into the water where it is quickly diluted. In general, mammals convert ammonia into urea, via the urea cycle.
In order to determine whether two proteins are related, or in other words to decide whether they are homologous or not, scientists use sequence-comparison methods. Methods like sequence alignments and structural alignments are powerful tools that help scientists identify Sequence homology, homologies between related molecules. The relevance of finding homologies among proteins goes beyond forming an evolutionary pattern of Protein family, protein families. By finding how similar two protein sequences are, we acquire knowledge about their structure and therefore their function.
Nucleic acids
 Nucleic acids, so-called because of their prevalence in cellular cell nucleus, nuclei, is the generic name of the family of biopolymers. They are complex, high-molecular-weight biochemical macromolecules that can convey genetic information in all living cells and viruses. The monomers are called nucleotides, and each consists of three components: a nitrogenous heterocyclic base (chemistry), base (either a purine or a pyrimidine), a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group.
Nucleic acids, so-called because of their prevalence in cellular cell nucleus, nuclei, is the generic name of the family of biopolymers. They are complex, high-molecular-weight biochemical macromolecules that can convey genetic information in all living cells and viruses. The monomers are called nucleotides, and each consists of three components: a nitrogenous heterocyclic base (chemistry), base (either a purine or a pyrimidine), a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group.
Metabolism
Carbohydrates as energy source
Glucose is an energy source in most life forms. For instance, polysaccharides are broken down into their monomers byenzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
s (glycogen phosphorylase removes glucose residues from glycogen, a polysaccharide). Disaccharides like lactose or sucrose are cleaved into their two component monosaccharides.
Glycolysis (anaerobic)
Glucose is mainly metabolized by a very important ten-step Metabolic pathway, pathway calledglycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvic acid, pyruvate and, in most organisms, occurs in the liquid part of cells (the cytosol). The Thermodynamic free energy, free energy released in this process is used to form ...
, the net result of which is to break down one molecule of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate. This also produces a net two molecules of Adenosine triphosphate, ATP, the energy currency of cells, along with two reducing equivalents of converting Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide: oxidized form) to NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide: reduced form). This does not require oxygen; if no oxygen is available (or the cell cannot use oxygen), the NAD is restored by converting the pyruvate to lactic acid, lactate (lactic acid) (e.g. in humans) or to ethanol plus carbon dioxide (e.g. in yeast). Other monosaccharides like galactose and fructose can be converted into intermediates of the glycolytic pathway.
Aerobic
In aerobic glycolysis, aerobic cells with sufficient oxygen, as in most human cells, the pyruvate is further metabolized. It is irreversibly converted to acetyl-CoA, giving off one carbon atom as the waste product carbon dioxide, generating another reducing equivalent as NADH. The two molecules acetyl-CoA (from one molecule of glucose) then enter the citric acid cycle, producing two molecules of ATP, six more NADH molecules and two reduced (ubi)quinones (via FADH2, FADH2 as enzyme-bound cofactor), and releasing the remaining carbon atoms as carbon dioxide. The produced NADH and quinol molecules then feed into the enzyme complexes of the respiratory chain, an electron transport system transferring the electrons ultimately to oxygen and conserving the released energy in the form of a proton gradient over a membrane (inner mitochondrial membrane in eukaryotes). Thus, oxygen is reduced to water and the original electron acceptors NAD+ and quinone are regenerated. This is why humans breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide. The energy released from transferring the electrons from high-energy states in NADH and quinol is conserved first as proton gradient and converted to ATP via ATP synthase. This generates an additional ''28'' molecules of ATP (24 from the 8 NADH + 4 from the 2 quinols), totaling to 32 molecules of ATP conserved per degraded glucose (two from glycolysis + two from the citrate cycle). It is clear that using oxygen to completely oxidize glucose provides an organism with far more energy than any oxygen-independent metabolic feature, and this is thought to be the reason why complex life appeared only after Earth's atmosphere accumulated large amounts of oxygen.Gluconeogenesis
In vertebrates, vigorously contracting skeletal muscles (during weightlifting or sprinting, for example) do not receive enough oxygen to meet the energy demand, and so they shift to Fermentation (biochemistry), anaerobic metabolism, converting glucose to lactate. The combination of glucose from noncarbohydrates origin, such as fat and proteins. This only happens when glycogen supplies in the liver are worn out. The pathway is a crucial reversal ofglycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvic acid, pyruvate and, in most organisms, occurs in the liquid part of cells (the cytosol). The Thermodynamic free energy, free energy released in this process is used to form ...
from pyruvate to glucose and can use many sources like amino acids, glycerol and Krebs Cycle. Large scale protein and fat catabolism usually occur when those suffer from starvation or certain endocrine disorders. The liver regenerates the glucose, using a process called gluconeogenesis. This process is not quite the opposite of glycolysis, and actually requires three times the amount of energy gained from glycolysis (six molecules of ATP are used, compared to the two gained in glycolysis). Analogous to the above reactions, the glucose produced can then undergo glycolysis in tissues that need energy, be stored as glycogen (or starch in plants), or be converted to other monosaccharides or joined into di- or oligosaccharides. The combined pathways of glycolysis during exercise, lactate's crossing via the bloodstream to the liver, subsequent gluconeogenesis and release of glucose into the bloodstream is called the Cori cycle.#Fromm, Fromm and Hargrove (2012), pp. 183–194.
Relationship to other "molecular-scale" biological sciences
Researchers in biochemistry use specific techniques native to biochemistry, but increasingly combine these with techniques and ideas developed in the fields of genetics,molecular biology
Molecular biology is a branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecule, molecular basis of biological activity in and between Cell (biology), cells, including biomolecule, biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactio ...
, and biophysics. There is not a defined line between these disciplines. Biochemistry studies the chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules a ...
required for biological activity of molecules, molecular biology studies their biological activity, genetics studies their heredity, which happens to be carried by their genome. This is shown in the following schematic that depicts one possible view of the relationships between the fields:
* ''Biochemistry'' is the study of the chemical substances and vital processes occurring in live organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
s. Biochemists focus heavily on the role, function, and structure of biomolecules. The study of the chemistry behind biological processes and the synthesis of biologically active molecules are applications of biochemistry. Biochemistry studies life at the atomic and molecular level.
* ''Genetics'' is the study of the effect of genetic differences in organisms. This can often be inferred by the absence of a normal component (e.g. one gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
). The study of "mutants" – organisms that lack one or more functional components with respect to the so-called "wild type" or normal phenotype. Genetic interactions (epistasis) can often confound simple interpretations of such "Gene knockout, knockout" studies.
* ''Molecular biology'' is the study of molecular underpinnings of the biological phenomena, focusing on molecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms and interactions. The central dogma of molecular biology, where genetic material is transcribed into RNA and then translated into protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
, despite being oversimplified, still provides a good starting point for understanding the field. This concept has been revised in light of emerging novel roles for RNA.
* ''Chemical biology'' seeks to develop new tools based on small molecules that allow minimal perturbation of biological systems while providing detailed information about their function. Further, chemical biology employs biological systems to create non-natural hybrids between biomolecules and synthetic devices (for example emptied viral capsids that can deliver gene therapy or Pharmaceutical drug, drug molecules).
See also
Lists
* List of important publications in chemistry#Biochemistry, Important publications in biochemistry (chemistry) * List of biochemistry topics * List of biochemists * List of biomoleculesSee also
* Astrobiology * Biochemistry (journal) * Biological Chemistry (journal) * Biophysics * Chemical ecology * Computational biomodeling * Dedicated bio-based chemical * Enzyme Commission number, EC number * Hypothetical types of biochemistry * International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology * Metabolome * Metabolomics * Molecular biology * Molecular medicine * Plant biochemistry * Proteolysis * Small molecule * Structural biology * TCA cycleNotes
References
Cited literature
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* Fruton, Joseph S. ''iarchive:proteinsenzymesg0000frut, Proteins, Enzymes, Genes: The Interplay of Chemistry and Biology''. Yale University Press: New Haven, 1999. * Keith Roberts, Martin Raff, Bruce Alberts, Peter Walter, Julian Lewis and Alexander Johnson, ''Molecular Biology of the Cell'' ** 4th Edition, Routledge, March, 2002, hardcover, 1616 pp. ** 3rd Edition, Garland, 1994, ** 2nd Edition, Garland, 1989, * Kohler, Robert. ''From Medical Chemistry to Biochemistry: The Making of a Biomedical Discipline''. Cambridge University Press, 1982. *External links
*The Virtual Library of Biochemistry, Molecular Biology and Cell Biology
Biochemistry, 5th ed.
Full text of Berg, Tymoczko, and Stryer, courtesy of National Center for Biotechnology Information, NCBI.
SystemsX.ch – The Swiss Initiative in Systems Biology
Full text of Biochemistry
by Kevin and Indira, an introductory biochemistry textbook. {{Authority control Biochemistry, Biotechnology Molecular biology Genomics,