|
Potassium Cyanate
Potassium cyanate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula, formula KOCN (sometimes denoted KCNO). It is a colourless solid. It is used to prepare many other compounds including useful herbicide. Worldwide production of the potassium and sodium salts was 20,000 tons in 2006.Peter M. Schalke1, "Cyanates, Inorganic Salts" Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry2006, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. . Article Online Posting Date: July 15, 2006 Structure and bonding The cyanate anion is isoelectronic with carbon dioxide and with the azide anion, being linear. The C-N distance is 121 pm, about 5 pm longer than for cyanide. Potassium cyanate is isostructural with potassium azide. Uses The potassium and sodium salts can be used interchangeably for the majority of applications. Potassium cyanate is often preferred to the sodium salt, which is less soluble in water and less readily available in pure form. Potassium cyanate is used as a basic raw material for various org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Compound
An inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bondsthat is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as ''inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep Mantle (geology), mantle remain active areas of investigation. All allotropes (structurally different pure forms of an element) and some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon (graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, graphene, etc.), carbon monoxide , carbon dioxide , carbides, and salt (chemistry), salts of inorganic anions such as carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, thiocyanates, isothiocyanates, etc. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it cannot occur within life, living things. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
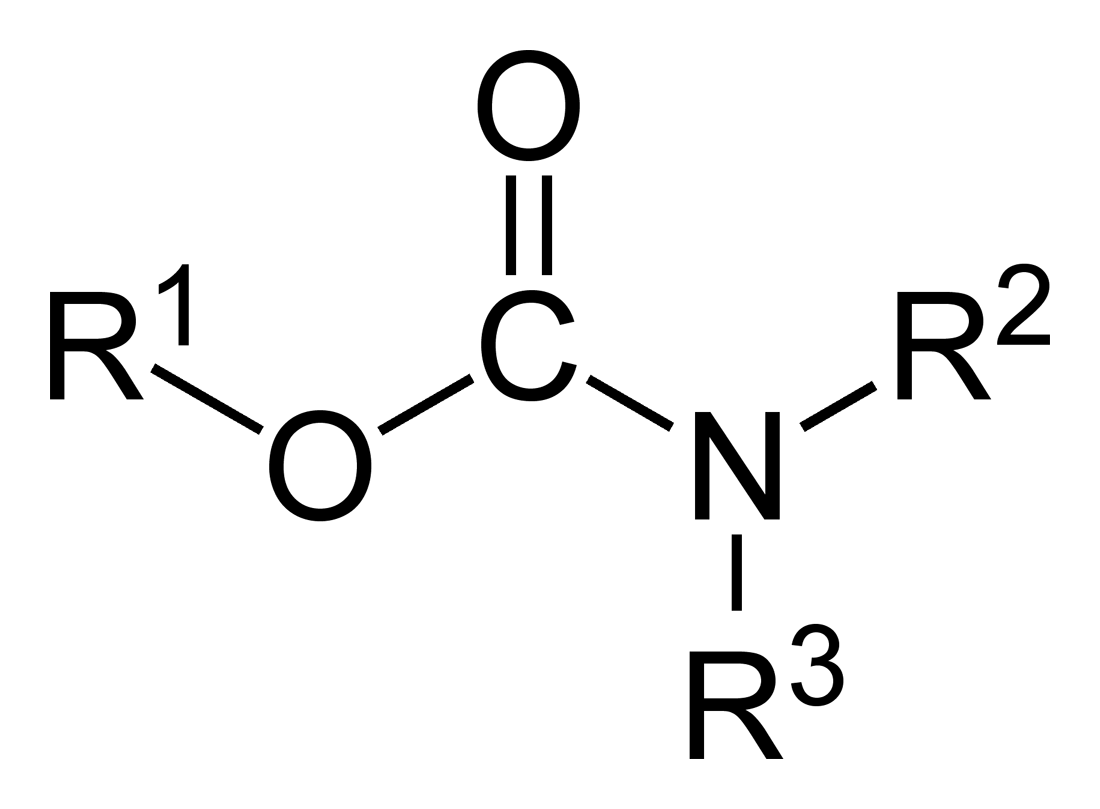
Carbamate
In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general Chemical formula, formula and Chemical structure, structure , which are formally Derivative (chemistry), derived from carbamic acid (). The term includes organic compounds (e.g., the ester ethyl carbamate), formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salt (chemistry), salts with the carbamate anion (e.g. ammonium carbamate). Polymers whose repeat units are joined by carbamate like groups are an important family of plastics, the polyurethanes. See for clarification. Properties While carbamic acids are unstable, many carbamate esters and salt (chemistry), salts are stable and well known. Equilibrium with carbonate and bicarbonate In water solutions, the carbamate anion slowly equilibrates with the ammonium cation and the carbonate or bicarbonate anions: : : Calcium carbamate is soluble in water, whereas calcium carbona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isocyanic Acid
Isocyanic acid is a chemical compound with the structural formula HNCO, which is often written as . It is a colourless, volatile and poisonous gas, condensing at 23.5 °C. It is the predominant tautomer and an isomer of cyanic acid ''(aka. cyanol)'' (), and the monomer of cyanuric acid. The derived anion of isocyanic acid is the same as the derived anion of cyanic acid, and that anion is , which is called cyanate. The related functional group is isocyanate; it is distinct from cyanate (), fulminate (), and nitrile oxide (). Isocyanic acid was discovered in 1830 by Justus von Liebig and Friedrich Wöhler. Isocyanic acid is the simplest stable chemical compound that contains carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen, the four most commonly found elements in organic chemistry and biology. It is the only fairly stable one of the four linear isomers with molecular formula HOCN that have been synthesized, the others being cyanic acid (cyanol, ) and the elusive fulminic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tautomer
In chemistry, tautomers () are structural isomers (constitutional isomers) of chemical compounds that readily interconvert. The chemical reaction interconverting the two is called tautomerization. This conversion commonly results from the relocation of a hydrogen atom within the compound. The phenomenon of tautomerization is called tautomerism, also called desmotropism. Tautomerism is for example relevant to the behavior of amino acids and nucleic acids, two of the fundamental building blocks of life. Care should be taken not to confuse tautomers with depictions of "contributing structures" in chemical resonance. Tautomers are distinct chemical species that can be distinguished by their differing atomic connectivities, molecular geometries, and physicochemical and spectroscopic properties, whereas resonance forms are merely alternative Lewis structure (valence bond theory) depictions of a single chemical species, whose true structure is a quantum superposition, essentially the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanuric Acid
Cyanuric acid or 1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triol is a chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula (CNOH)3. Like many industrially useful chemicals, this triazine has many synonyms. This white, odorless solid finds use as a precursor or a component of bleaches, disinfectants, and herbicides. In 1997, worldwide production was 160 000 tonnes.Klaus Huthmacher, Dieter Most "Cyanuric Acid and Cyanuric Chloride" Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry" 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi 10.1002/14356007.a08 191 Properties and synthesis Properties Cyanuric acid can be viewed as the cyclic trimer (chemistry), trimer of the elusive chemical species Isocyanic acid#cyanicacid2025-03-05, cyanic acid, HOCN. The ring can readily interconvert between several chemical structure, structures via Lactam#Lactam–lactim tautomerism, lactam–lactim tautomerism. Although the triol tautomer may have aromatic character, the keto form predominates in solution. The hydroxyl (-OH) groups ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biuret
Biuret ( ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is a white solid that is soluble in hot water. A variety of organic derivatives are known. The term "biuret" also describes a family of organic compounds with the chemical formula , where are hydrogen, organyl or other groups. Also known as carbamylurea, it results from the condensation of two equivalents of urea. It is a common undesirable impurity in urea-based fertilizers, as biuret is toxic to plants. Preparation and structure The parent compound can be prepared by heating urea at 150 °C for ~6 hours until it gets slightly cloudy, then recrystallizing from water. After that, it can be recrystallized repeatedly from 2% sodium hydroxide solution and water to finally get base-free crystalline needles of the monohydrate which are free of cyanuric acid. While heating, a lot of ammonia is expelled: : Under related conditions, pyrolysis of urea affords triuret . In general, organic biurets (those with alkyl or aryl gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Carbonate
Potassium carbonate is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a white salt, which is soluble in water and forms a strongly alkaline solution. It is deliquescent, often appearing as a damp or wet solid. Potassium carbonate is mainly used in the production of soap and glass. Commonly, it can be found as the result of leakage of alkaline batteries. Potassium carbonate is a potassium salt of carbonic acid. This salt consists of potassium cations and carbonate anions , and is therefore an alkali metal carbonate. History Potassium carbonate is the primary component of potash and the more refined pearl ash or salt of tartar. Historically, pearl ash was created by baking potash in a kiln to remove impurities. The fine, white powder remaining was the pearl ash. The first patent issued by the US Patent Office was awarded to Samuel Hopkins in 1790 for an improved method of making potash and pearl ash. In late 18th-century North America, before the development of baking pow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferritic Nitrocarburizing
Ferritic nitrocarburizing or FNC, also known by the proprietary names "Tenifer", "Tufftride", Melonite, and "Arcor",Other trade names include Tuffride/ Tuffrider, QPQ, Sulfinuz, Sursulf, Meli 1, and Nitride, among others is a range of proprietary case hardening processes that diffuse nitrogen and carbon into ferrous metals at sub-critical temperatures during a salt bath. Other methods of ferritic nitrocarburizing include gaseous processes such as Nitrotec and ion (plasma) ones. The processing temperature ranges from to , but usually occurs at . Steel and other ferrous alloys remain in the ferritic phase region at this temperature. This allows for better control of the dimensional stability that would not be present in case hardening processes that occur when the alloy is transitioned into the austenitic phase.. There are four main classes of ferritic nitrocarburizing: ''gaseous'', ''salt bath'', ''ion'' or ''plasma'', and ''fluidized-bed''.. The process improves three main s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Treatment
Heat treating (or heat treatment) is a group of industrial, thermal and metalworking processes used to alter the physical, and sometimes chemical, properties of a material. The most common application is metallurgical. Heat treatments are also used in the manufacture of many other materials, such as glass. Heat treatment involves the use of heating or chilling, normally to extreme temperatures, to achieve the desired result such as hardening or softening of a material. Heat treatment techniques include annealing, case hardening, precipitation strengthening, tempering, carburizing, normalizing and quenching. Although the term ''heat treatment'' applies only to processes where the heating and cooling are done for the specific purpose of altering properties intentionally, heating and cooling often occur incidentally during other manufacturing processes such as hot forming or welding. Physical processes Photomicrographs of steel. Top: In annealed (slowly cooled) steel, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxycarbamide
Hydroxycarbamide, also known as hydroxyurea, is an antimetabolite medication used in sickle-cell disease, essential thrombocythemia, chronic myelogenous leukemia, polycythemia vera, and cervical cancer. In sickle-cell disease it increases fetal hemoglobin and decreases the number of attacks. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include bone marrow suppression, fevers, loss of appetite, psychiatric problems, shortness of breath, and headaches. There is also concern that it increases the risk of later cancers. Use during pregnancy is typically harmful to the fetus. Hydroxycarbamide is in the antineoplastic family of medications. It is believed to work by blocking the making of DNA. Hydroxycarbamide was approved for medical use in the United States in 1967. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Hydroxycarbamide is available as a generic medication. Medical uses Hydroxycarbamide is used for the following indications: * Myeloprolifera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isocyanate
In organic chemistry, isocyanate is the functional group with the formula . Organic compounds that contain an isocyanate group are referred to as isocyanates. An organic compound with two isocyanate groups is known as a diisocyanate. Diisocyanates are manufactured for the production of polyurethanes, a class of polymers. Isocyanates should not be confused with cyanate esters and isocyanides, very different families of compounds. The cyanate (cyanate ester) functional group () is arranged differently from the isocyanate group (). Isocyanides have the connectivity , lacking the oxygen of the cyanate groups. Structure and bonding In terms of bonding, isocyanates are closely related to carbon dioxide (CO2) and carbodiimides (C(NR)2). The C−N=C=O unit that defines isocyanates is planar, and the N=C=O linkage is nearly linear. In phenyl isocyanate, the C=N and C=O distances are respectively 1.195 and 1.173 Å. The C−N=C angle is 134.9° and the N=C=O angle is 173.1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semicarbazide
Semicarbazide is the chemical compound with the formula OC(NH2)(N2H3). It is a water-soluble white solid. It is a derivative of urea. Synthesis The compound prepared by treating urea with hydrazine:Jean-Pierre Schirmann, Paul Bourdauducq "Hydrazine" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2002. . :OC(NH2)2 + N2H4 → OC(NH2)(N2H3) + NH3 A further reaction can occur to give carbohydrazide: :OC(NH2)(N2H3) + N2H4 → OC(N2H3)2 + NH3 Derivatives Semicarbazide is frequently reacted with aldehydes and ketones to produce semicarbazones via a condensation reaction. This is an example of imine formation resulting from the reaction of a primary amine with a carbonyl group. The reaction is useful because semicarbazones, like oximes and 2,4-DNPs, typically have high melting points and crystallize, facilitating purification or identification of reaction products. Properties Semicarbazide products (semicarbazones and thiosemicarbazones) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |