Bangui on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bangui (; or Bangî in Sango, formerly written Bangi in English) is the capital and largest city of the
 The modern settlement of Bangui was founded by Michel Dolisie and Alfred Uzac on 26 June 1889 on the direction of
The modern settlement of Bangui was founded by Michel Dolisie and Alfred Uzac on 26 June 1889 on the direction of
 In late 2012, the
In late 2012, the
 Close to the river, the city centre features a large
Close to the river, the city centre features a large
 Bangui serves as an administrative, trade, and commercial centre. During the Second World War the country became wealthier as exports of rubber, cotton, coffee, uranium and diamonds increased. After the war, the employment of local people in mainstream administration led to the development of the country's infrastructure, which increased trade while slowing the national movement for independence.
During David Dacko's presidency from 1960 to 1966, there was a significant increase in the production of
Bangui serves as an administrative, trade, and commercial centre. During the Second World War the country became wealthier as exports of rubber, cotton, coffee, uranium and diamonds increased. After the war, the employment of local people in mainstream administration led to the development of the country's infrastructure, which increased trade while slowing the national movement for independence.
During David Dacko's presidency from 1960 to 1966, there was a significant increase in the production of
 The old town of Bangui has retained its colonial town planning, with wide boulevards leading towards a central market square. Attractions in Bangui include Boganda Museum, Bangui Zoo, and the Presidential Palace, formerly the Bokassa Palace. Notre-Dame Cathedral is the seat of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Bangui. Boganda Museum (''Musée de Boganda'') has displays of traditional musical instruments, weapons, rural architectural features, ancient hunting tools, pottery, and also many religious antiques. It has a collection of bark cloth, the material used to cover Bokassa's bed.
There are several hotels up to international standards. The Ledger Plaza Bangui on the outskirts has an outdoor swimming pool, tennis court, and comfortable amenities. The National Hotel was established in 1970 with 30 rooms. Also of note are the Golf Palace Hotel, the Hotel du Centre with 72 rooms, JM Residence, the Oubangui Hotel, established in 1985, and Hotel Somba with 23 rooms.
The old town of Bangui has retained its colonial town planning, with wide boulevards leading towards a central market square. Attractions in Bangui include Boganda Museum, Bangui Zoo, and the Presidential Palace, formerly the Bokassa Palace. Notre-Dame Cathedral is the seat of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Bangui. Boganda Museum (''Musée de Boganda'') has displays of traditional musical instruments, weapons, rural architectural features, ancient hunting tools, pottery, and also many religious antiques. It has a collection of bark cloth, the material used to cover Bokassa's bed.
There are several hotels up to international standards. The Ledger Plaza Bangui on the outskirts has an outdoor swimming pool, tennis court, and comfortable amenities. The National Hotel was established in 1970 with 30 rooms. Also of note are the Golf Palace Hotel, the Hotel du Centre with 72 rooms, JM Residence, the Oubangui Hotel, established in 1985, and Hotel Somba with 23 rooms.
 The cuisine of CAR is referred to as Centrafrican and the staple diet in Bangui includes
The cuisine of CAR is referred to as Centrafrican and the staple diet in Bangui includes
 Bangui has a rich music tradition and showcases the country's music. Its musicians also perform in many countries abroad. The Bangui band groups were influenced by Zokela in the 1980s. The innovative music is based on dance bands who have adopted the Congolese music with electronic support. The music is rhythmic and blends with the Congolese rumba ( soukous), which was influenced by son cubano, cha-cha-cha, and merengue. Popular Central African music groups or dance bands who perform in the city are Musiki, Zokela, Makembe, Cool Stars, Cannon Stars, and Super Stars. Bokassa, during his tenure as president, established a music recording studio in Bangui and employed musicians to sing his praise with songs extolling his qualities as an emperor and to develop his cult image among his people.
Bangui has a rich music tradition and showcases the country's music. Its musicians also perform in many countries abroad. The Bangui band groups were influenced by Zokela in the 1980s. The innovative music is based on dance bands who have adopted the Congolese music with electronic support. The music is rhythmic and blends with the Congolese rumba ( soukous), which was influenced by son cubano, cha-cha-cha, and merengue. Popular Central African music groups or dance bands who perform in the city are Musiki, Zokela, Makembe, Cool Stars, Cannon Stars, and Super Stars. Bokassa, during his tenure as president, established a music recording studio in Bangui and employed musicians to sing his praise with songs extolling his qualities as an emperor and to develop his cult image among his people.
 The most popular sport is basketball. Bangui hosted the FIBA Africa Championship 1974, where the Central African Republic's national basketball team won one of its two continental titles.
The most popular sport is basketball. Bangui hosted the FIBA Africa Championship 1974, where the Central African Republic's national basketball team won one of its two continental titles.
 The French system of education is the norm and French is the language of teaching, although the Sango language is promoted in schools. A substantial percentage of the population is literate. Schooling is compulsory for children ages 6 to 14.
Bangui is home to the University of Bangui, founded in 1969 by President Jean-Bédel Bokassa who named it after himself; it started functioning in 1970. A public institution, the university provides non-agricultural education in the Central African Republic. Since 1981, the University Library has been in a separate building that houses its science, literature, and law collections. The medical school of the university has its own library.
The other educational institutions are the National School of Arts and the Central School of Agriculture, in addition to many religious and technical schools.
A school in the eastern part of the city, Lycée Charles de Gaulle, was established by the French and is named after
The French system of education is the norm and French is the language of teaching, although the Sango language is promoted in schools. A substantial percentage of the population is literate. Schooling is compulsory for children ages 6 to 14.
Bangui is home to the University of Bangui, founded in 1969 by President Jean-Bédel Bokassa who named it after himself; it started functioning in 1970. A public institution, the university provides non-agricultural education in the Central African Republic. Since 1981, the University Library has been in a separate building that houses its science, literature, and law collections. The medical school of the university has its own library.
The other educational institutions are the National School of Arts and the Central School of Agriculture, in addition to many religious and technical schools.
A school in the eastern part of the city, Lycée Charles de Gaulle, was established by the French and is named after
Central African Republic
The Central African Republic (CAR) is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It is bordered by Chad to Central African Republic–Chad border, the north, Sudan to Central African Republic–Sudan border, the northeast, South Sudan to Central ...
. It was established as a French outpost in 1889 and named after its location on the northern bank of the Ubangi River (); the Ubangi itself was named from the Bobangi word for the "rapids" located beside the settlement, which marked the end of navigable water north from Brazzaville
Brazzaville () is the capital (political), capital and largest city of the Republic of the Congo. Administratively, it is a Departments of the Republic of the Congo, department and a Communes of the Republic of the Congo, commune. Constituting t ...
. The majority of the population of the Central African Republic lives in the western parts of the country, in Bangui and the surrounding area.
The city has been part of Bangui Prefecture since December 2020. it had an estimated population of 889,231.
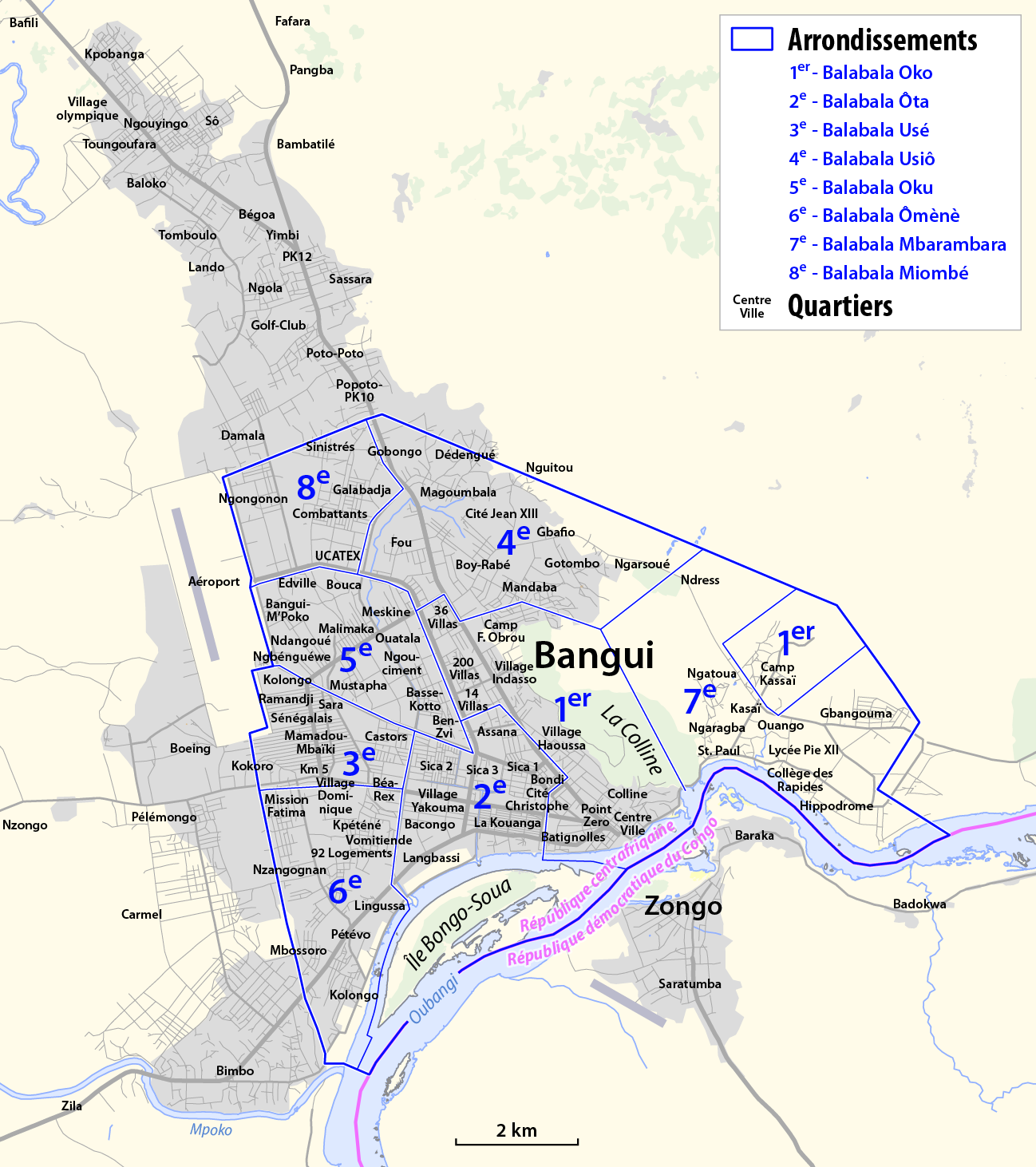
The city consists of eight urban districts ('' arrondissements''), 16 groups (''groupements'') and 205 neighbourhoods (''quartiers''). As the capital of the Central African Republic
The Central African Republic (CAR) is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It is bordered by Chad to Central African Republic–Chad border, the north, Sudan to Central African Republic–Sudan border, the northeast, South Sudan to Central ...
, Bangui acts as an administrative, trade, and commercial centre. The National Assembly, government buildings, banks, foreign enterprises and embassies, hospitals, hotels, main markets and the Ngaragba Central Prison are all located here. Bangui manufactures textiles
Textile is an Hyponymy and hypernymy, umbrella term that includes various Fiber, fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, Staple (textiles)#Filament fiber, filaments, Thread (yarn), threads, and different types of #Fabric, fabric. ...
, food products, beer
Beer is an alcoholic beverage produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches from cereal grain—most commonly malted barley, although wheat, maize (corn), rice, and oats are also used. The grain is mashed to convert starch in the ...
, shoes
A shoe is an item of footwear intended to protect and comfort the human foot. Though the human foot can adapt to varied terrains and climate conditions, it is vulnerable, and shoes provide protection. Form was originally tied to function, but ...
and soap
Soap is a salt (chemistry), salt of a fatty acid (sometimes other carboxylic acids) used for cleaning and lubricating products as well as other applications. In a domestic setting, soaps, specifically "toilet soaps", are surfactants usually u ...
. Its Notre-Dame Cathedral is the seat of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Bangui. The city is also home to the University of Bangui, inaugurated in 1970. It is served by the Bangui M'Poko International Airport.
History
Archaeological studies in and around Bangui have yielded at least 26 ancientIron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
sites that contain many metallurgical tools and objects, illuminating the pre-European history of the city and surrounding area. The archaeological sites were added to the UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
World Heritage
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
Tentative List on 11 April 2006 in the Cultural category. The site closest to Bangui is Pendere-Sengue, from Independence Avenue, where archaeologists and conservation agencies have carried out studies. It is a paleo-metallurgical site where several thousand shards of ceramics, iron tools, pottery, and an iron spatula weighing have been unearthed. Its dating, compared with similar sites in Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
and Sudan
Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa. It borders the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Libya to the northwest, Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the east, Eritrea and Ethiopi ...
, could be close to the ninth century BC.
 The modern settlement of Bangui was founded by Michel Dolisie and Alfred Uzac on 26 June 1889 on the direction of
The modern settlement of Bangui was founded by Michel Dolisie and Alfred Uzac on 26 June 1889 on the direction of Brazzaville
Brazzaville () is the capital (political), capital and largest city of the Republic of the Congo. Administratively, it is a Departments of the Republic of the Congo, department and a Communes of the Republic of the Congo, commune. Constituting t ...
administrator Albert Dolisie. It was located in what was then the upper reaches of the French Congo, the present-day Congo. The original site was south of the Ubangi rapids. Its territory was organized first into the territory of the Upper Ubangi (') and then as the separate colony of Ubangi-Shari
Ubangi-Shari () was a French colonial empire, French colony in central Africa, a part of French Equatorial Africa. It was named after the Ubangi River, Ubangi and Chari River, Chari rivers of the Central African Republic, rivers along which it w ...
. The initial capitals of these areas were at les Abiras and Fort de Possel further upstream, but the rapids at Bangui blocked them from direct communication along the river and caused the settlement there to grow in importance until, in 1906, it was chosen as the new headquarters for the French administration. Bangui retained its importance as a military and administrative centre when the colony was folded into French Equatorial Africa
French Equatorial Africa (, or AEF) was a federation of French colonial territories in Equatorial Africa which consisted of Gabon, French Congo, Ubangi-Shari, and Chad. It existed from 1910 to 1958 and its administration was based in Brazzav ...
and under both Vichy and Free French
Free France () was a resistance government
claiming to be the legitimate government of France following the dissolution of the Third French Republic, Third Republic during World War II. Led by General , Free France was established as a gover ...
control during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. The French operated a radio transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter (often abbreviated as XMTR or TX in technical documents) is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna with the purpose of signal transmissio ...
in Bangui, which was described in 1932 as "the most remote radio station in Africa".
The colony of Ubangi-Shari
Ubangi-Shari () was a French colonial empire, French colony in central Africa, a part of French Equatorial Africa. It was named after the Ubangi River, Ubangi and Chari River, Chari rivers of the Central African Republic, rivers along which it w ...
received its autonomy in 1958 as the Central African Republic and became independent from France in 1960. In 1970, President Jean-Bédel Bokassa inaugurated the University of Bangui. He established the national airline Air Centrafrique the following year and ordered the construction of two new luxury hotel
A hotel is an establishment that provides paid lodging on a short-term basis. Facilities provided inside a hotel room may range from a modest-quality mattress in a small room to large suites with bigger, higher-quality beds, a dresser, a re ...
s in Bangui. With tensions mounting between Bangui and Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
as a result of Bokassa's uncontrollable expenditures, western bank
A bank is a financial institution that accepts Deposit account, deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital m ...
s refused to lend him any more money. Relations with the French worsened still further in April 1974, when the body of Brigette Miroux was discovered in a hotel room in Bangui. Miroux was a native of northern France who in 1973 came to the Central African Republic to become a "hostess" in Bokassa's Caravelle aircraft. It was reported in the French media that she had been Bokassa's mistress and that he was responsible for her murder. As a result, Bokassa banned import of French newspaper
A newspaper is a Periodical literature, periodical publication containing written News, information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background. Newspapers can cover a wide variety of fields such as poli ...
s and assumed control of the Agence France-Presse
Agence France-Presse (; AFP) is a French international news agency headquartered in Paris, France. Founded in 1835 as Havas, it is the world's oldest news agency.
With 2,400 employees of 100 nationalities, AFP has an editorial presence in 260 c ...
office in Bangui. By 1975, Bangui had a population of 300,723.
In March 1981, widespread violence took place in Bangui following elections, after Operation Caban
Operation Caban was a bloodless military operation by the France, French intelligence service Service de documentation extérieure et de contre-espionnage, SDECE in September 1979 to depose Emperor of Central Africa, Emperor Jean-Bédel Bokassa, ...
led the French to drop Bokassa (who had begun to call himself Emperor Bokassa I) and to replace him with David Dacko. Opponents of the President met in Bangui and were forced to flee the country. After returning voluntarily to Bangui in the autumn of 1986, Bokassa went on trial. Initially faced with the death penalty, in February 1988 he was instead sentenced to life imprisonment. His successor was General André Kolingba, army chief of staff of Dacko's army, who took over control from the local French military on 1 September 1981 under the pretext that the country was heading towards civil war. Although he attempted to combat corruption and control the national economy, he was unable to achieve his reforms. By the middle of the 1980s the country's economic situation had deteriorated as 80% of the revenue went towards meeting the salaries of the staff.
Under pressure from a donor group called GIBAFOR (France, USA, Japan, Germany, EU, World Bank and the UN) Kolingba made moves to restore a degree of democracy in the country in 1991 with a multiparty government. Elections were held in 1993 and 1994. The first round was sabotaged by the government when it was clear they would lose. Under continued donor pressure elections were held again in 1994 as before with help from the UN Electoral Assistance Division. During these elections, Ange-Félix Patassé was elected to the post of president. Since he was from northern CAR, the southern group of Kolingba started a rebellion during 1996.
In May 1996, about 200 soldiers of the Central African Republic mutinied in Bangui, demanding salary increases and the abdication of Ange-Félix Patassé. In the aftermath, the renegades plundered and killed more than 50 people. Following this, the French troops stationed in the country suppressed the rebellion and restored the dictatorial power. After being elected, President Patassé announced a national unity government in early 1997. The Patassé government, the opposition parties, and religious groups signed the Bangui Agreements in January 1997 which were a series of measures designed to reconcile competing political factions, reform and strengthen the economy. The same year, the rebel troops refused a military base in Bangui and in June a new revolt broke out.
In view of frequent political unrest the city was named in 1996 as one of the most dangerous cities in the world. On 25 October 2002, several towns in the country and later Bangui itself were attacked by the forces of General François Bozizé
François Bozizé Yangouvonda (born 14 October 1946) is a Central African Republic, Central African politician who was List of heads of state of the Central African Republic, President of the Central African Republic from 2003 to 2013. He was th ...
, backed with international support. Bozizé refused to accept an arrest warrant and "defected with about a hundred troops, engaged in street battles in the northern neighborhoods of Bangui (traditionally supporting Patassé)" and went north. Bozizé went into exile in Chad
Chad, officially the Republic of Chad, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North Africa, North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to Chad–Libya border, the north, Sudan to Chad–Sudan border, the east, the Central Afric ...
but his troops returned to Bangui and fighting continued. Peace-keeping forces were ineffective, leaving Patassé isolated, and with support from Chad, Bozizé's troops were successful in removing Patassé's government. Patassé, who was returning from Niger after attending a conference, was not permitted to land in Bangui and he took asylum in Togo
Togo, officially the Togolese Republic, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Ghana to Ghana–Togo border, the west, Benin to Benin–Togo border, the east and Burkina Faso to Burkina Faso–Togo border, the north. It is one of the le ...
, and Bozizé seized power and suspended the constitution. An all-party National Transitional Government was set up which functioned as an interim legislative body. However, the "climate of distrust continued".
2013 rebellion
 In late 2012, the
In late 2012, the Séléka
Séléka CPSK-CPJP-UFDR was an alliance of rebel militia groups that subjugated the Central African Republic (CAR) on 24 March 2013. After its official dissolution in September 2013, the remaining rebel groups became known as Ex-Séléka. Sél� ...
coalition rebelled against the autocratic rule of François Bozizé
François Bozizé Yangouvonda (born 14 October 1946) is a Central African Republic, Central African politician who was List of heads of state of the Central African Republic, President of the Central African Republic from 2003 to 2013. He was th ...
and entered the city. After capturing Bria, Sibut
Sibut (), formerly Fort Sibut () is the capital of Kémo, one of the 16 prefectures of the Central African Republic. An important transport hub, it is situated north of the capital Bangui and is known for its market.
Sibut is located at t ...
, and other important towns, they were on the verge of capturing Damara, the last strategic town before Bangui. France and the US refused to support the president and neighbouring countries reinforced the Central African Multinational Force (Fomac).
In January 2013, the rebels terminated their operations, hoping for a negotiated settlement. Following a ceasefire
A ceasefire (also known as a truce), also spelled cease-fire (the antonym of 'open fire'), is a stoppage of a war in which each side agrees with the other to suspend aggressive actions often due to mediation by a third party. Ceasefires may b ...
and a power-sharing agreement, Séléka and Bozizé agreed to honour the rebel's demands for the release of rebel prisoners and the expulsion of foreign troops from the country. The agreement allowed Bozizé to complete his term in office and to include members of Séléka in a new government. It was also agreed that fresh elections would be held in 2016. The agreement was not honoured and the rebels captured Bangui on 23 March 2013, forcing Bozizé to flee the capital.
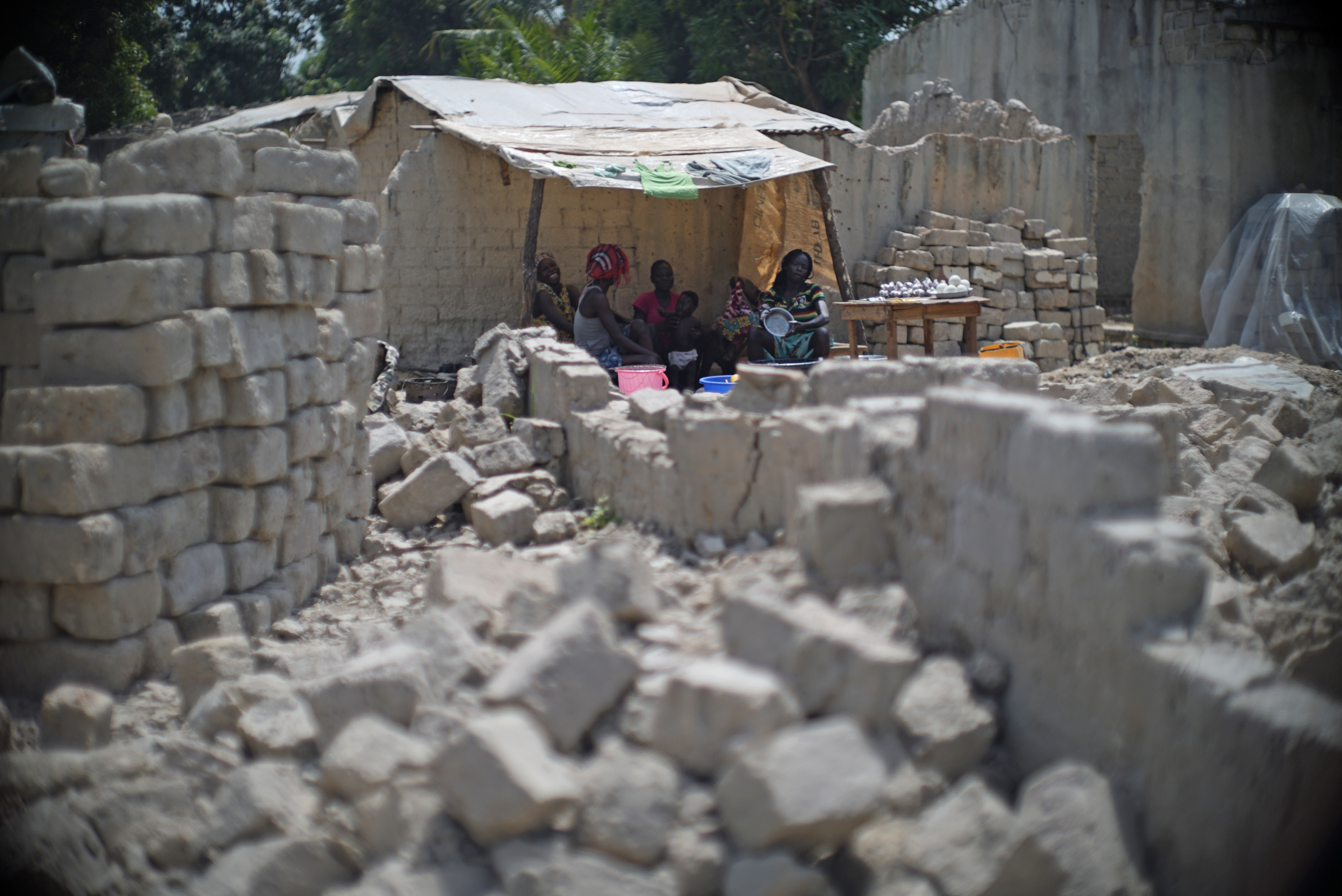
As of early January 2014, "around 500,000 have fled their homes" in Bangui, "almost half the city's population."
On 13 January 2021 around 200 rebels attacked Bangui, killing one peacekeeper before being repelled.
Geography and climate
Bangui, close to the country's southern border, lies on the northern banks of the Ubangi River just below a series of rapids that limit major commercial shipping upriver. The only major city located on the river, it covers an area of . The navigable Ubangi River, with the backdrop of lush green hills, turns sharply south below Bangui and connects to theCongo River
The Congo River, formerly also known as the Zaire River, is the second-longest river in Africa, shorter only than the Nile, as well as the third-largest river in the world list of rivers by discharge, by discharge volume, following the Amazon Ri ...
just south of the equator near Brazzaville as its chief northern tributary. The Ubangi river marks the border between the Central African Republic and the Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), also known as the DR Congo, Congo-Kinshasa, or simply the Congo (the last ambiguously also referring to the neighbouring Republic of the Congo), is a country in Central Africa. By land area, it is t ...
. The Congolese town of Zongo is situated across the river from Bangui. The river flows to the east of downtown Bangui. During the rainy season the discharge in the river is three times higher than during the rest of the year. The city was also known as ''La Coquette'' (the beautiful city) in the 1970s.
 Close to the river, the city centre features a large
Close to the river, the city centre features a large arch
An arch is a curved vertical structure spanning an open space underneath it. Arches may support the load above them, or they may perform a purely decorative role. As a decorative element, the arch dates back to the 4th millennium BC, but stru ...
dedicated to Bokassa as well as the presidential palace and the central market. Lying further north, the heart of the residential area has the largest market and most of the nightlife
Nightlife is a collective term for entertainment that is available and generally more popular from the late evening into the early hours of the morning. It includes pubs, bars, nightclubs, parties, live music, concerts, cabarets, theatre, ...
. Many of those in the suburbs live in houses known as Kodros, built of mud bricks with a thatched roof.
The Bangui Magnetic Anomaly, one of the earth's largest crustal anomalies and the largest in Africa, has its centre in Bangui." It takes the form of a huge ellipse of x , with its central point at 6 degrees north and 18 degrees east. It consists of three parts or segments, which comprise the northern, the southern and the central anomalies. The magnetic equator passes through the feature's centre. Although it is well documented, the feature's origins are not fully understood.
The Central African Republic is situated just north of the Equator with daily temperatures normally reaching at least 30 °C. Bangui, close to the Equator in the south of the country, it is slightly hotter and wetter than the northern regions. It has a tropical savanna climate
Tropical savanna climate or tropical wet and dry climate is a tropical climate sub-type that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification categories ''Aw'' (for a dry "winter") and ''As'' (for a dry "summer"). The driest month has less than ...
(Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (1951–2014), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author ...
: Aw) with dry winters. While the warm season is from 23 January to 18 March, the cold season lasts from 20 June to 27 August, when rainfall is frequently accompanied by thunderstorms. The city is bordered by thick tropical rainforests along the river banks. Several of its neighbourhoods are in low-lying areas prone to recurrent flooding with severe rains in June and July 2009 leaving 11,000 people homeless.
Demographics
After the Central African Republic attained independence in 1960, developmental activities began, and the urbanization of Bangui ensued. This is evidenced by the population growth from 279,800 in 1975 to 427,435 in 1988 to 524,000 by 1994, and to 652,000 in 2001. Apart from the ethnic people of the country, the city is also home for a minority group of Greek, Portuguese and Yemeni traders, and also has a small community ofFrench people
French people () are a nation primarily located in Western Europe that share a common Culture of France, French culture, History of France, history, and French language, language, identified with the country of France.
The French people, esp ...
. The Bangui resident community includes diamond traders from western Africa and Chad, traders from many African countries, and refugees from the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Nigeria.
The official languages of the country are French and Sango; the latter (originally a language from the Ubangi River region) is spoken by 90% of the population. Some of the other languages spoken are Baya (Gbaya), Banda, Ngbaka, Sara, Mbum, Kare, and Mandjia. Sango was simplified by Christian missionaries and is widely used to this day.
Economy
 Bangui serves as an administrative, trade, and commercial centre. During the Second World War the country became wealthier as exports of rubber, cotton, coffee, uranium and diamonds increased. After the war, the employment of local people in mainstream administration led to the development of the country's infrastructure, which increased trade while slowing the national movement for independence.
During David Dacko's presidency from 1960 to 1966, there was a significant increase in the production of
Bangui serves as an administrative, trade, and commercial centre. During the Second World War the country became wealthier as exports of rubber, cotton, coffee, uranium and diamonds increased. After the war, the employment of local people in mainstream administration led to the development of the country's infrastructure, which increased trade while slowing the national movement for independence.
During David Dacko's presidency from 1960 to 1966, there was a significant increase in the production of diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Diamond is tasteless, odourless, strong, brittle solid, colourless in pure form, a poor conductor of e ...
s. This occurred when the monopoly of the French concessionary companies was ended with a law allowing local citizens to dig for diamonds. After Dacko set up a diamond cutting
Diamond cutting is the practice of shaping a Diamond (gemstone), diamond from a rough stone into a faceted gem. Cutting diamonds requires specialized knowledge, tools, equipment, and techniques because of its extreme difficulty.
The first guild ...
factory at Bangui, diamonds became the country's leading export. But by the end of his five-year tenure, rampant corruption and financial indiscipline had resulted in workers being left unpaid and civil unrest ensued. Bokassa then seized power in a military coup in 1966.
Concurrently, Bangui also became the key centre for social and cultural activity in the region, when new institutions were established in the city. However, political turmoil in the country, rampant corruption, and the dictatorial rule of President Bokassa centred in the city, brought in economic recession in the 1970s exacerbated by a fall in international prices for its major exports. This caused impoverishment of the people and severe conflict, further compounded by refugees migrating from troubled neighbouring countries.
Bangui received its first bank in 1946 when a branch of the Paris-based Banque de l'Afrique Occidentale was established there. Arab sellers dominated the city, and it was historically an important centre for ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and Tooth, teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mamm ...
trading. Bangui manufactures include textiles
Textile is an Hyponymy and hypernymy, umbrella term that includes various Fiber, fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, Staple (textiles)#Filament fiber, filaments, Thread (yarn), threads, and different types of #Fabric, fabric. ...
, food products, beer, shoes
A shoe is an item of footwear intended to protect and comfort the human foot. Though the human foot can adapt to varied terrains and climate conditions, it is vulnerable, and shoes provide protection. Form was originally tied to function, but ...
, and soap
Soap is a salt (chemistry), salt of a fatty acid (sometimes other carboxylic acids) used for cleaning and lubricating products as well as other applications. In a domestic setting, soaps, specifically "toilet soaps", are surfactants usually u ...
. The main exports are cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
, rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds.
Types of polyisoprene ...
, timber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into uniform and useful sizes (dimensional lumber), including beams and planks or boards. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, window frames). ...
, coffee
Coffee is a beverage brewed from roasted, ground coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content, but decaffeinated coffee is also commercially a ...
, and sisal
Sisal (, ; ''Agave sisalana'') is a species of flowering plant native to southern Mexico, but widely cultivated and naturalized in many other countries. It yields a stiff fibre used in making rope and various other products. The sisal fiber is ...
. Because of the ongoing strife, unemployment hovered near 23% in the city . Ngaragba Central Prison, the national prison for men, is located in Bangui. , it had 476 inmates; prison conditions are reported to be poor.
Landmarks
 The old town of Bangui has retained its colonial town planning, with wide boulevards leading towards a central market square. Attractions in Bangui include Boganda Museum, Bangui Zoo, and the Presidential Palace, formerly the Bokassa Palace. Notre-Dame Cathedral is the seat of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Bangui. Boganda Museum (''Musée de Boganda'') has displays of traditional musical instruments, weapons, rural architectural features, ancient hunting tools, pottery, and also many religious antiques. It has a collection of bark cloth, the material used to cover Bokassa's bed.
There are several hotels up to international standards. The Ledger Plaza Bangui on the outskirts has an outdoor swimming pool, tennis court, and comfortable amenities. The National Hotel was established in 1970 with 30 rooms. Also of note are the Golf Palace Hotel, the Hotel du Centre with 72 rooms, JM Residence, the Oubangui Hotel, established in 1985, and Hotel Somba with 23 rooms.
The old town of Bangui has retained its colonial town planning, with wide boulevards leading towards a central market square. Attractions in Bangui include Boganda Museum, Bangui Zoo, and the Presidential Palace, formerly the Bokassa Palace. Notre-Dame Cathedral is the seat of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Bangui. Boganda Museum (''Musée de Boganda'') has displays of traditional musical instruments, weapons, rural architectural features, ancient hunting tools, pottery, and also many religious antiques. It has a collection of bark cloth, the material used to cover Bokassa's bed.
There are several hotels up to international standards. The Ledger Plaza Bangui on the outskirts has an outdoor swimming pool, tennis court, and comfortable amenities. The National Hotel was established in 1970 with 30 rooms. Also of note are the Golf Palace Hotel, the Hotel du Centre with 72 rooms, JM Residence, the Oubangui Hotel, established in 1985, and Hotel Somba with 23 rooms.
Culture
Customs
Polygamy
Polygamy (from Late Greek , "state of marriage to many spouses") is the practice of marriage, marrying multiple spouses. When a man is married to more than one wife at the same time, it is called polygyny. When a woman is married to more tha ...
is an accepted practice among men.
When someone dies in Bangui a representative from his or her village attends the funeral. "This person is charged with indicating to the deceased the way back home so that the deceased may avenge himself and herself and demonstrate the power of the family". The representative who attends the funeral also carries a little dust from the grave to the village, and gives it to the village's medicine man so that he can ascertain the reasons for his death.
Most of the holidays in Bangui are festivals related to the Christian and Muslim faiths and are the same as those observed in other parts of the world. National holidays include Independence Day and the birthdays of Boganda and several other national heroes.
Cuisine
 The cuisine of CAR is referred to as Centrafrican and the staple diet in Bangui includes
The cuisine of CAR is referred to as Centrafrican and the staple diet in Bangui includes cassava
''Manihot esculenta'', common name, commonly called cassava, manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America, from Brazil, Paraguay and parts of the Andes. Although ...
, rice
Rice is a cereal grain and in its Domestication, domesticated form is the staple food of over half of the world's population, particularly in Asia and Africa. Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice)—or, much l ...
, squash, pumpkin
A pumpkin is a cultivar, cultivated winter squash in the genus ''Cucurbita''. The term is most commonly applied to round, orange-colored squash varieties, but does not possess a scientific definition. It may be used in reference to many dif ...
s and plantains served with a sauce
In cooking, a sauce is a liquid, cream, or semi- solid food, served on or used in preparing other foods. Most sauces are not normally consumed by themselves; they add flavour, texture, and visual appeal to a dish. ''Sauce'' is a French wor ...
and grilled meat. Okra
Okra (, ), ''Abelmoschus esculentus'', known in some English-speaking countries as lady's fingers, is a flowering plant in the Malvaceae, mallow family native to East Africa. Cultivated in tropical, subtropical, and warm temperate regions aro ...
or ''gombo'' is a popular vegetable. Peanut
The peanut (''Arachis hypogaea''), also known as the groundnut, goober (US), goober pea, pindar (US) or monkey nut (UK), is a legume crop grown mainly for its edible seeds. It is widely grown in the tropics and subtropics by small and large ...
s and peanut butter
Peanut butter is a food Paste (food), paste or Spread (food), spread made from Grinding (abrasive cutting), ground, dry roasting, dry-roasted peanuts. It commonly contains additional ingredients that modify the taste or texture, such as salt, ...
are widely used. Game
A game is a structured type of play usually undertaken for entertainment or fun, and sometimes used as an educational tool. Many games are also considered to be work (such as professional players of spectator sports or video games) or art ...
is popular, as are the fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
-based dishes ''maboké'' and ''soussou''. Manioc flour is used for preparing fufu.
Alcoholic beverage
Drinks containing alcohol (drug), alcohol are typically divided into three classes—beers, wines, and Distilled beverage, spirits—with alcohol content typically between 3% and 50%. Drinks with less than 0.5% are sometimes considered Non-al ...
s served are locally brewed beer, palm wine
Palm wine, known by several #Names, local names, is an alcoholic beverage created from the sap of various species of palm trees such as the Borassus, palmyra, date palms, and coconut palms. It is known by various names in different regions and ...
and banana wine. Non-alcoholic beverage
An alcohol-free or non-alcoholic drink, also known as a temperance drink, is a version of an alcoholic drink made without Alcohol (drug), alcohol, or with the alcohol removed or reduced to almost zero. These may take the form of a non-alcoholic mi ...
s include ginger beer.
Art
Bangui's artisans' market has traditional wares representing the art products from different regions of the country. Handicrafts include woven mats and baskets, wooden utensils of simple design, carved stools, pottery, musical instruments, tanned skins, and wood products. Thebalafon
The balafon (pronounced , or, by analogy with ''xylophone'' etc., ) is a gourd-resonated xylophone, a type of struck idiophone. It is closely associated with the neighbouring Mandé peoples, Mandé, Bwaba Bobo people, Bobo, Senufo people, Seno ...
, similar to a xylophone, is made out of the horns of animals. Innovative designs include butterfly wings stuck with gum on paper, and ebony and hardwood carvings of wood from the tropical region. Artwork also covers carved animals and human figures. The crafts center in Bangui provides training to about 100 students in artistic crafting in leather
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning (leather), tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffal ...
, ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and Tooth, teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mamm ...
and ebony wares.
Music
 Bangui has a rich music tradition and showcases the country's music. Its musicians also perform in many countries abroad. The Bangui band groups were influenced by Zokela in the 1980s. The innovative music is based on dance bands who have adopted the Congolese music with electronic support. The music is rhythmic and blends with the Congolese rumba ( soukous), which was influenced by son cubano, cha-cha-cha, and merengue. Popular Central African music groups or dance bands who perform in the city are Musiki, Zokela, Makembe, Cool Stars, Cannon Stars, and Super Stars. Bokassa, during his tenure as president, established a music recording studio in Bangui and employed musicians to sing his praise with songs extolling his qualities as an emperor and to develop his cult image among his people.
Bangui has a rich music tradition and showcases the country's music. Its musicians also perform in many countries abroad. The Bangui band groups were influenced by Zokela in the 1980s. The innovative music is based on dance bands who have adopted the Congolese music with electronic support. The music is rhythmic and blends with the Congolese rumba ( soukous), which was influenced by son cubano, cha-cha-cha, and merengue. Popular Central African music groups or dance bands who perform in the city are Musiki, Zokela, Makembe, Cool Stars, Cannon Stars, and Super Stars. Bokassa, during his tenure as president, established a music recording studio in Bangui and employed musicians to sing his praise with songs extolling his qualities as an emperor and to develop his cult image among his people.
Sports
 The most popular sport is basketball. Bangui hosted the FIBA Africa Championship 1974, where the Central African Republic's national basketball team won one of its two continental titles.
The most popular sport is basketball. Bangui hosted the FIBA Africa Championship 1974, where the Central African Republic's national basketball team won one of its two continental titles.
Football (soccer)
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 Football player, players who almost exclusively use their feet to propel a Ball (association football), ball around a rectangular f ...
is also popular. Both men and women from Bangui and throughout the country have participated in the Olympic Games
The modern Olympic Games (Olympics; ) are the world's preeminent international Olympic sports, sporting events. They feature summer and winter sports competitions in which thousands of athletes from around the world participate in a Multi-s ...
since 1968 as well as in many international events. The locals also organize boat races with hundreds of participants on the Ubangi River, which is a significant attraction.
Education
 The French system of education is the norm and French is the language of teaching, although the Sango language is promoted in schools. A substantial percentage of the population is literate. Schooling is compulsory for children ages 6 to 14.
Bangui is home to the University of Bangui, founded in 1969 by President Jean-Bédel Bokassa who named it after himself; it started functioning in 1970. A public institution, the university provides non-agricultural education in the Central African Republic. Since 1981, the University Library has been in a separate building that houses its science, literature, and law collections. The medical school of the university has its own library.
The other educational institutions are the National School of Arts and the Central School of Agriculture, in addition to many religious and technical schools.
A school in the eastern part of the city, Lycée Charles de Gaulle, was established by the French and is named after
The French system of education is the norm and French is the language of teaching, although the Sango language is promoted in schools. A substantial percentage of the population is literate. Schooling is compulsory for children ages 6 to 14.
Bangui is home to the University of Bangui, founded in 1969 by President Jean-Bédel Bokassa who named it after himself; it started functioning in 1970. A public institution, the university provides non-agricultural education in the Central African Republic. Since 1981, the University Library has been in a separate building that houses its science, literature, and law collections. The medical school of the university has its own library.
The other educational institutions are the National School of Arts and the Central School of Agriculture, in addition to many religious and technical schools.
A school in the eastern part of the city, Lycée Charles de Gaulle, was established by the French and is named after President of France
The president of France, officially the president of the French Republic (), is the executive head of state of France, and the commander-in-chief of the French Armed Forces. As the presidency is the supreme magistracy of the country, the po ...
Charles de Gaulle
Charles André Joseph Marie de Gaulle (22 November 18909 November 1970) was a French general and statesman who led the Free France, Free French Forces against Nazi Germany in World War II and chaired the Provisional Government of the French Re ...
. Several notable Africans, including writers such as Calixthe Beyala, have studied in the city. Beyala studied at the Lycée des Rapides.
Places of worship
Among the places of worship, they are predominantlyChristian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
churches and temples: Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Bangui (Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
), Evangelical Lutheran Church of the Central African Republic (Lutheran World Federation
The Lutheran World Federation (LWF; ) is a global Communion (religion), communion of national and regional Lutheran denominations headquartered in the Ecumenical Centre in Geneva, Switzerland. The federation was founded in the Swedish city of L ...
), Evangelical Baptist Church of the Central African Republic (Baptist World Alliance
The Baptist World Alliance (BWA) is an international communion of Baptists, with an estimated 51 million people from 266 member bodies in 134 countries and territories as of 2024. A voluntary association of Baptist churches, the BWA accounts f ...
). There are also Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
mosques.
Transport
Bangui is the transport hub of the Central African Republic. As of 1999, eight roads connected the city to other main towns in the country, Cameroon, Chad andSouth Sudan
South Sudan (), officially the Republic of South Sudan, is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered on the north by Sudan; on the east by Ethiopia; on the south by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda and Kenya; and on the ...
; of these, only the toll roads are paved. During the rainy season from March to November, some roads are impassable. The road network in the city emanates from the Palace de la Republique.
River ferries
A ferry is a boat or ship that transports passengers, and occasionally vehicles and cargo, across a body of water. A small passenger ferry with multiple stops, like those in Venice, Italy, is sometimes referred to as a water taxi or water bus.
...
sail from the river port at Bangui to Brazzaville and Zongo. The river can be navigated most of the year between Bangui and Brazzaville. From Brazzaville, goods are transported by rail to Pointe-Noire, Congo's Atlantic port. The river port handles the overwhelming majority of the country's international trade and has a cargo handling capacity of 350,000 tons; it has length of wharfs and of warehousing space.
The first airstrip in Bangui was built between 1920 and 1925. Bangui M'Poko International Airport is located on of deforested land off the Avenue of Martyrs to the north of the old town, between the Koudoukou Avenue and the University of Bangui.
Healthcare
A general hospital is located in the eastern side of the city. Modern healthcare facilities exist in Bangui (unlike the rest of the country) but are poor, providing only minimal care. Wealthier citizens make use of private clinics. The prevalence of HIV in Bangui is twice the national average. In late 2019, MSF started providing free medical care to HIV patients in the city; in the first year of the project, 1851 patients were admitted for HIV treatment, 558 of whom were newly diagnosed. The risk of catchingmalaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
in Bangui and pygmy
In anthropology, pygmy peoples are ethnic groups whose average height is unusually short. The term pygmyism is used to describe the phenotype of endemic short stature (as opposed to disproportionate dwarfism occurring in isolated cases in a po ...
camps is also much higher than in the rest of the country.
A conference of public health officials including representatives of the Centers for Disease Control
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency under the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and is headquartered in Atlanta, ...
and the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
was held in Bangui in October 1985. The conference evolved a diagnostic definition of AIDS which came to be known as the Bangui definition for AIDS. The conference defined symptoms of AIDS in Africa as "prolonged fever for a month or more, weight loss of over 10% and prolonged diarrhea". The Bangui definition proved problematic as immune suppression can also be caused by malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
.
Media
Severalperiodicals
Periodical literature (singularly called a periodical publication or simply a periodical) consists of Publication, published works that appear in new releases on a regular schedule (''issues'' or ''numbers'', often numerically divided into annu ...
and three daily newspaper
A newspaper is a Periodical literature, periodical publication containing written News, information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background. Newspapers can cover a wide variety of fields such as poli ...
s are published in Bangui: ''E le Songo'', the country's first newspaper, began publication in 1982. The other main newspapers are ''Le Novateur'', ''Le Citoyen'' and ''L'Echo de Centrafrique''. Most of the country's institutions have offices in Bangui, including French ones such as Électricité de France
Électricité de France SA (; ), commonly known as EDF, is a French multinational corporation, multinational electric utility company owned by the government of France. Headquartered in Paris, with €139.7 billion in sales in 2023, EDF ope ...
(EDF).
Radio stations operating in Bangui include '' Radio Centrafrique'', Radio Nehemie, Radio Notre-Dame, Radio Voix de la paix, Radio Ndeke Luka, RFI, Radio Voik de la grace, Radio Linga FM, Africa no.1, and Tropic FM. BBC World Service
The BBC World Service is a British Public broadcasting, public service broadcaster owned and operated by the BBC. It is the world's largest external broadcaster in terms of reception area, language selection and audience reach. It broadcas ...
is the only English broadcasting station that is heard in the city on 90.2 FM, as all other local channels broadcast in either French and/or Sango. For reliable news, the UN runs channel Radio Ndeke Luka is on 100.8 FM.
Notable people
* Élie Doté, politician and prime minister * Eloge Enza Yamissi, football player * Manassé Enza-Yamissi, football player * André Kolingba, president *Anicet Lavodrama
Anicet-Richard Lavodrama y Ondoma (born 4 July 1963 in Bangui) is a retired professional basketball player from the Central African Republic.
Professional career
Lavodrama played for Houston Baptist Huskies men's basketball, the Houston Baptist H ...
, basketball player
* Joachim N'Dayen, archbishop of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Bangui
* Nathalie Tauziat, French tennis player
* Romain Sato, basketball player
Twin towns/Sister cities
Bangui
Bangui (; or Bangî in Sango language, Sango, formerly written Bangi in English) is the Capital (political), capital and List of cities in the Central African Republic, largest city of the Central African Republic. It was established as a Fren ...
is twinned with:
Dodoma, Tanzania
Tanzania, officially the United Republic of Tanzania, is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It is bordered by Uganda to the northwest; Kenya to the northeast; the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to t ...
Linz
Linz (Pronunciation: , ; ) is the capital of Upper Austria and List of cities and towns in Austria, third-largest city in Austria. Located on the river Danube, the city is in the far north of Austria, south of the border with the Czech Repub ...
, Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
See also
* Jojo (chimpanzee)References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * *External links
* * {{Authority control Capitals in Africa Central African Republic–Democratic Republic of the Congo border crossings Populated places in the Central African Republic Populated places established in 1889 Prefectures of the Central African Republic Sub-prefectures of the Central African Republic Ubangi River 1889 establishments in Africa