|
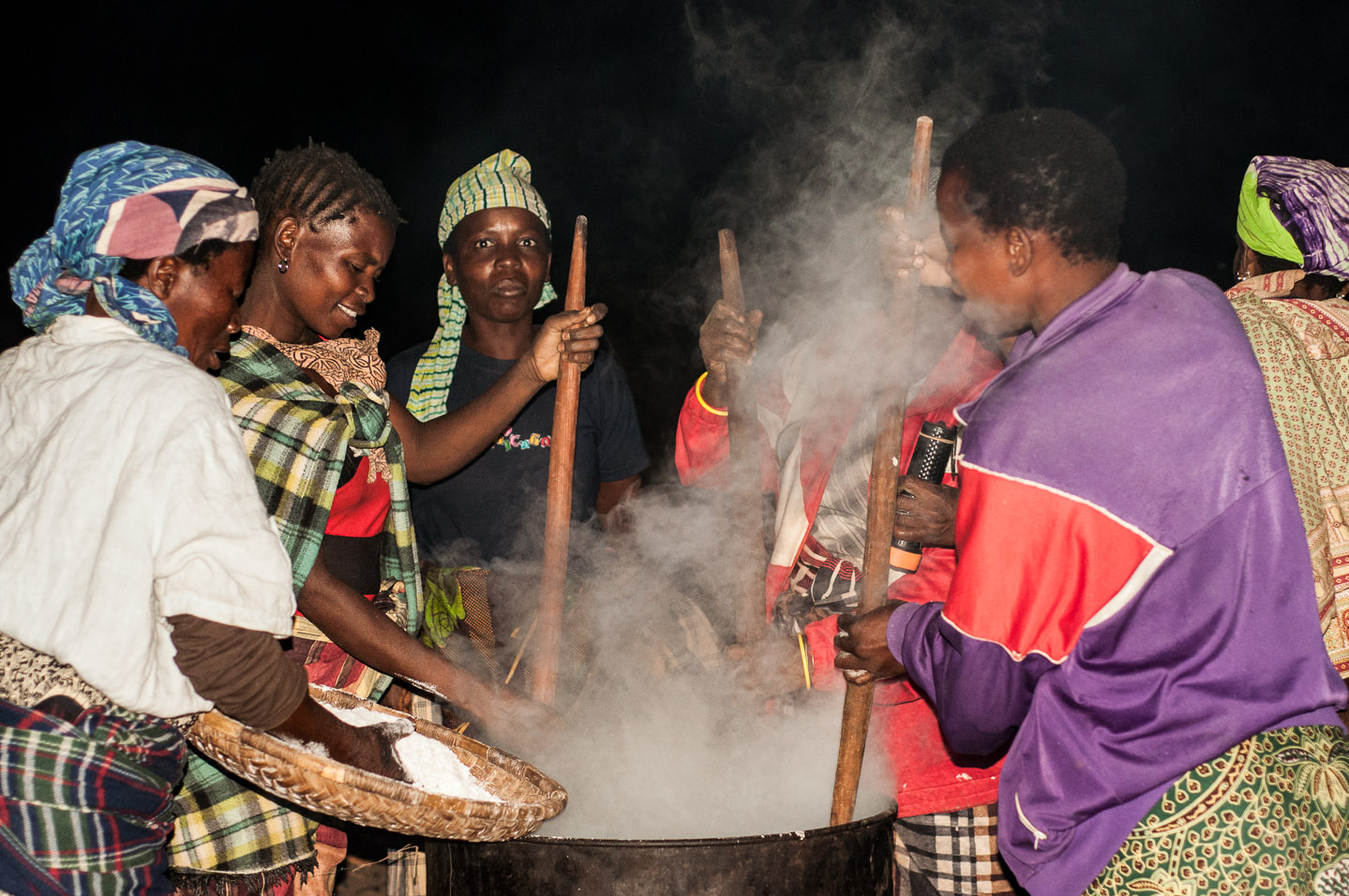
Fufu
Fufu (or fufuo, foofoo, foufou ) is a pounded meal found in West African cuisine. It is a Twi word that originates from the Akans in Ghana. The word has been expanded to include several variations of the pounded meal found in other African countries including Sierra Leone, Liberia, Cote D'Ivoire, Burkina Faso, Benin, Togo, Nigeria, Cameroon, the Democratic Republic of Congo, the Central African Republic, the Republic of Congo, Angola and Gabon. It also includes variations in the Greater Antilles and Central America, where African culinary influence is high. Although the original ingredients for fufu are boiled cassava, plantains, and cocoyam, it is also made in different ways in other West African countries. In Ghana, Ivory Coast, and Liberia, they use the method of separately mixing and pounding equal portions of boiled cassava with green plantain or cocoyam, or by mixing cassava/plantains or cocoyam flour with water and stirring it on a stove. Its thickness is then adj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
West African Cuisine
West African cuisine encompasses a diverse range of foods that are split between its 16 countries. In West Africa, many families grow and raise their own food, and within each there is a division of labor. Indigenous foods consist of a number of plant species and animals, and are important to those whose lifestyle depends on farming and hunting. The history of West Africa also plays a large role in their cuisine and recipes, as interactions with different cultures (particularly the Arab world and later Europeans) over the centuries have introduced many ingredients that went on to become key components of the various national cuisines today. History During the early modern period, European explorers and slave traders influenced regional cuisines in West Africa, but only to a limited extent. However, it was European merchant and slave ships which brought chili peppers, maize and tomatoes from the New World, which have become ubiquitous components of West African cuisines, along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cooking Banana
Cooking bananas are a group of banana cultivars in the genus ''Musa (genus), Musa'' whose fruits are generally used in cooking. They are not eaten raw and are generally starchy. Many cooking bananas are referred to as plantains or 'green bananas'. In botanical usage, the term "plantain" is used only for true plantains, while other starchy cultivars used for cooking are called "cooking bananas". True plantains are cooking cultivars belonging to the AAB group, while cooking bananas are any cooking cultivar belonging to the List of banana cultivars, AAB, AAA, ABB, or BBB groups. The currently accepted scientific name for all such cultivars in these groups is Musa × paradisiaca, ''Musa'' × ''paradisiaca''. Fe'i bananas (''Musa'' × ''troglodytarum'') from the Pacific Islands are often eaten roasted or boiled, and are thus informally referred to as "mountain plantains", but they do not belong to any of the species from which all modern banana cultivars are descended. Cooking bananas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nsima
Ugali, also known as posho, nsima, papa, pap, sadza, isitshwala, akume, amawe, ewokple, akple, and #Names, other names, is a type of maize, corn meal made from maize flour, maize or corn or ''mahindi'' flour in several African countries: Kenya, Uganda, Tanzania, Zimbabwe, Zambia, Lesotho, Eswatini, Angola, Mozambique, Namibia, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Malawi, Botswana and South Africa, and in West Africa by the Ewe people, Ewes of Togo, Ghana, Benin, Nigeria and Côte d'Ivoire. It is cooked in boiling water or milk until it reaches a stiff or firm dough-like consistency. In 2017, the dish was added to the UNESCO UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage Lists, Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity, one of a few foods on the list. Names This dish is eaten widely across Africa, where it has different local names: Etymology The word ''ugali'' is an African languages, African term derived from Swahili language, Swahili; it is also widely known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pap (food)
Ugali, also known as posho, nsima, papa, pap, sadza, isitshwala, akume, amawe, ewokple, akple, and other names, is a type of corn meal made from maize or corn or ''mahindi'' flour in several African countries: Kenya, Uganda, Tanzania, Zimbabwe, Zambia, Lesotho, Eswatini, Angola, Mozambique, Namibia, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Malawi, Botswana and South Africa, and in West Africa by the Ewes of Togo, Ghana, Benin, Nigeria and Côte d'Ivoire. It is cooked in boiling water or milk until it reaches a stiff or firm dough-like consistency. In 2017, the dish was added to the UNESCO Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity, one of a few foods on the list. Names This dish is eaten widely across Africa, where it has different local names: Etymology The word ''ugali'' is an African term derived from Swahili; it is also widely known as ''nsima'' in Malawian languages such as Chichewa and Chitumbuka. In parts of Kenya, the dish also goes by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Egusi Soup
Egusi, also spelled egushi ( Yoruba: Ẹ̀gúṣí), are the protein-rich seeds of certain cucurbitaceous plants ( squash, melon, gourd), which, after being dried and ground, are used as a major ingredient in West African cuisine. Egusi is a Yoruba word, and the popular method of cooking it is deeply rooted in Yoruba culinary traditions. Egusi melon seeds are large and white in appearance; sometimes they look brownish or off-white in color but the main egusi color is primarily white. Scholars disagree whether the word is used more properly for the seeds of the colocynth, those of a particular large-seeded variety of the watermelon, or generically for those of ''any'' cucurbitaceous plant. Egusi seeds are in a class of their own and should never be mistaken for pumpkin or watermelon seeds. In particular the name "egusi" may refer to either or both plants (or more generically to other cucurbits) in their capacity as seed crops, or to a soup made from these seeds and popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a country in Central Africa. It shares boundaries with Nigeria to the west and north, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Its coastline lies on the Bight of Biafra, part of the Gulf of Guinea, and the Atlantic Ocean. Due to its strategic position at the crossroads between West Africa and Central Africa, it has been categorized as being in both camps. Cameroon's population of nearly 31 million people speak 250 native languages, in addition to the national tongues of English and French, or both. Early inhabitants of the territory included the Sao civilisation around Lake Chad and the Baka people (Cameroon and Gabon), Baka hunter-gatherers in the southeastern rainforest. Portuguese discoveries, Portuguese explorers reached the coast in the 15th century and named the area ''Rio dos Camarões'' (''Shrimp River''), which became ''C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Liberia
Liberia, officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to Guinea–Liberia border, its north, Ivory Coast to Ivory Coast–Liberia border, its east, and the Atlantic Ocean to its south and southwest. It has a population of around 5.5million and covers an area of . The official language is English. Languages of Liberia, Over 20 indigenous languages are spoken, reflecting the country's ethnic and cultural diversity. The capital and largest List of cities in Liberia, city is Monrovia. Liberia began in the early 19th century as a project of the American Colonization Society (ACS), which believed that black people would face better chances for freedom and prosperity in Africa than in the United States. Between 1822 and the outbreak of the American Civil War in 1861, more than 15,000 freed and free-born African Americans, along with 3,198 Afro-Caribbeans, relocated to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso is a landlocked country in West Africa, bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the south, and Ivory Coast to the southwest. It covers an area of 274,223 km2 (105,878 sq mi). In 2024, the country had an estimated population of approximately 23,286,000. Previously called the Republic of Upper Volta (1958–1984), it was Geographical renaming, renamed Burkina Faso by then-List of heads of state of Burkina Faso, president Thomas Sankara. Its citizens are known as Burkinabes, and its Capital city, capital and largest city is Ouagadougou. The largest ethnic group in Burkina Faso is the Mossi people, who settled the area in the 11th and 13th centuries. They established powerful Mossi Kingdoms, kingdoms such as Ouagadougou, Tenkodogo, and Yatenga. In 1896, it was Colonization, colonized by the French colonial empire, French as part of French West Africa; in 1958, Upper Volta became a self-governing colony wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chikwangue
Chikwangue, also known in Cameroon as and in the Congo River basin language of Lingala as , is a starchy, fermented-cassava product that is a staple food across Central Africa: the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), the Republic of Congo (RotC), Gabon, Cameroon and Equatorial Guinea. Chikwangue is made by fermenting cassava in water for up to fourteen days, then turning it into a paste and wrapping it in marantaceae leaves for steaming. Preparation and use The cassava is first peeled, cut into small chunks, and placed in water to ferment (). The fermented cassava is then pounded into a paste and par-cooked, before being wrapped in ''Megaphrynium macrostachyum'' (a plant of the marantaceae or arrowroot family), or banana leaves and steamed or boiled for up to two hours. The several stages and long processing time are necessary for foods produced from cassava to render them safe to eat. Cassava contains cyanogenic and antinutritional compounds which are dissipated or inactivate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Akan People
The Akan () people are a kwa languages, Kwa group living primarily in present-day Ghana and in parts of Ivory Coast and Togo in West Africa. The Akan speak languages within the Central Tano languages, Central Tano branch of the Potou–Tano languages, Potou–Tano subfamily of the Niger–Congo languages, Niger–Congo family.''Languages of the Akan Area: Papers in Western Kwa Linguistics and on the Linguistic Geography of the Area of Ancient''. Isaac K. Chinebuah, H. Max J. Trutenau, Linguistic Circle of Accra, Basler Afrika Bibliographien, 1976, pp. 168. Subgroups of the Akan people include: the Adansi, Agona, Akuapem people, Akuapem, Akwamu, Akyem, Anyi people, Anyi, Ashanti people, Asante, Baoulé people, Baoulé, Bono people, Bono, Chakosi people, Chakosi, Fante people, Fante, Kwahu, Sefwi people, Sefwi, Wassa, Ahanta people, Ahanta, Denkyira and Nzema people, Nzema, among others. The Akan subgroups all have cultural attributes in common; most notably the tracing of royal m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |