Bacterial Vaginitis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is an
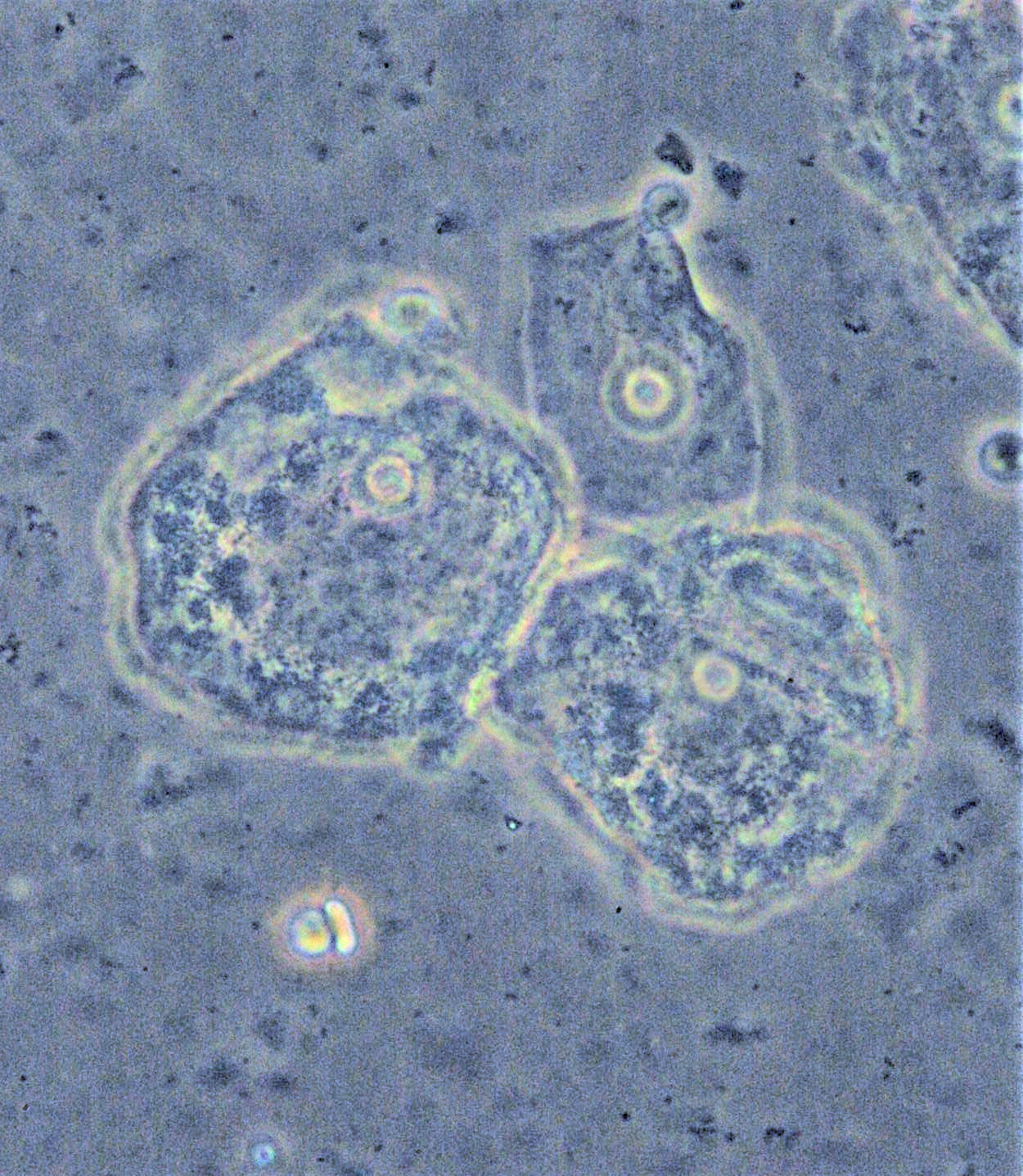

 To make a diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis, a swab from inside the vagina should be obtained. These swabs can be tested for:
*
To make a diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis, a swab from inside the vagina should be obtained. These swabs can be tested for:
*
WHO fact sheet on bacterial vaginosis
{{DEFAULTSORT:Bacterial Vaginosis Inflammatory diseases of female pelvic organs Mycoplasma Probiotics Sexually transmitted diseases and infections Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate
infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
of the vagina
In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular sex organ, reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The #Vag ...
caused by excessive growth of bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
. Common symptoms include increased vaginal discharge that often smells like fish. The discharge is usually white or gray in color. Burning with urination may occur. Itching is uncommon. Occasionally, there may be no symptoms. Having BV approximately doubles the risk of infection by a number of sexually transmitted infections, including HIV/AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, pr ...
. It also increases the risk of early delivery among pregnant women.
BV is caused by an imbalance of the naturally occurring bacteria in the vagina. There is a change in the most common type of bacteria and a hundred to thousandfold increase in total numbers of bacteria present. Typically, bacteria other than ''Lactobacilli'' become more common. Risk factors include douching, new or multiple sex partners, antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
s, and using an intrauterine device, among others. However, it is not considered a sexually transmitted infection and, unlike gonorrhoea and chlamydia, sexual partners are not treated. Diagnosis is suspected based on the symptoms, and may be verified by testing the vaginal discharge and finding a higher than normal vaginal pH, and large numbers of bacteria. BV is often confused with a vaginal yeast infection or infection with ''Trichomonas''.
Usually treatment is with an antibiotic, such as clindamycin or metronidazole
Metronidazole, sold under the brand name Flagyl and Metrogyl among others, is an antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication. It is used either alone or with other antibiotics to treat pelvic inflammatory disease, endocarditis, and bacterial vagino ...
. These medications may also be used in the second or third trimesters of pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
. The antiseptic
An antiseptic ( and ) is an antimicrobial substance or compound that is applied to living tissue to reduce the possibility of sepsis, infection, or putrefaction. Antiseptics are generally distinguished from ''antibiotics'' by the latter's abil ...
boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen orthoborate, trihydroxidoboron or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white ...
can also be effective. BV often recurs following treatment. Probiotics may help prevent re-occurrence. It is unclear if the use of probiotics or antibiotics affects pregnancy outcomes.
BV is the most common vaginal infection in women of reproductive age. The percentage of women affected at any given time varies between 5% and 70%. BV is most common in parts of Africa and least common in Asia and Europe. In the United States about 30% of women between the ages of 14 and 49 are affected. Rates vary considerably between ethnic group
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, traditions, society, re ...
s within a country. While BV-like symptoms have been described for much of recorded history
Recorded history or written history describes the historical events that have been recorded in a written form or other documented communication which are subsequently evaluated by historians using the historical method. For broader world h ...
, the first clearly documented case occurred in 1894.
Signs and symptoms
Although about 50% of women with BV are asymptomatic, common symptoms include increased vaginal discharge that usually smells like fish. The discharge is often white or gray in color. There may be burning with urination. The discharge coats the walls of the vagina, and is usually without significant irritation, pain, or erythema (redness), although mild itching can sometimes occur. By contrast, the normal vaginal discharge will vary in consistency and amount throughout themenstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is a series of natural changes in hormone production and the structures of the uterus and ovaries of the female reproductive system that makes pregnancy possible. The ovarian cycle controls the production and release of eg ...
and is at its clearest at ovulation
Ovulation is an important part of the menstrual cycle in female vertebrates where the egg cells are released from the ovaries as part of the ovarian cycle. In female humans ovulation typically occurs near the midpoint in the menstrual cycle and ...
—about two weeks before the period starts. Some practitioners claim that BV can be asymptomatic in almost half of affected women, though others argue that this is often a misdiagnosis.
Complications
Although previously considered a mere nuisance infection, untreated bacterial vaginosis may cause increased susceptibility to sexually transmitted infections, including HIV, and pregnancy complications. It has been shown that HIV-infected women with bacterial vaginosis (BV) are more likely to transmit HIV to their sexual partners than those without BV. There is evidence of an association between BV and increased rates of sexually transmitted infections such as HIV/AIDS. BV is associated with up to a six-fold increase in HIV shedding. BV is a risk factor for viral shedding andherpes simplex virus
Herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2) are two members of the Herpesviridae#Human herpesvirus types, human ''Herpesviridae'' family, a set of viruses that produce Viral disease, viral infections in the majority of humans. Both HSV-1 a ...
type 2 infection. BV may increase the risk of infection with or reactivation of human papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and r ...
(HPV).
In addition, bacterial vaginosis as either pre-existing, or acquired, may increase the risk of pregnancy complications, most notably premature birth
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 weeks, very early preterm birth is betwee ...
or miscarriage
Miscarriage, also known in medical terms as a spontaneous abortion, is an end to pregnancy resulting in the loss and expulsion of an embryo or fetus from the womb before it can fetal viability, survive independently. Miscarriage before 6 weeks ...
.
Pregnant women with BV have a higher risk of chorioamnionitis, miscarriage, preterm birth, premature rupture of membranes, and postpartum endometritis. Women with BV who are treated with in vitro fertilization
In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a process of fertilisation in which an egg is combined with sperm in vitro ("in glass"). The process involves monitoring and stimulating the ovulatory process, then removing an ovum or ova (egg or eggs) from ...
have a lower implantation rate and higher rates of early pregnancy loss.
Causes
Healthy vaginal microbiota consists of species that neither cause symptoms or infections, nor negatively affect pregnancy. It is dominated mainly by Lactobacillus species. BV is defined by the disequilibrium in the vaginal microbiota, with decline in the number of lactobacilli. While the infection involves a number of bacteria, it is believed that most infections start with '' Gardnerella vaginalis'' creating abiofilm
A biofilm is a Syntrophy, syntrophic Microbial consortium, community of microorganisms in which cell (biology), cells cell adhesion, stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy ext ...
, which allows other opportunistic bacteria, such as '' Prevotella'' and '' Bacteroides'', to thrive.
One of the main risks for developing BV is douching, which alters the vaginal microbiota and predisposes women to developing BV. Douching is strongly discouraged by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and various medical authorities, for this and other reasons.
BV is a risk factor for pelvic inflammatory disease, HIV, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), endometriosis, and reproductive and obstetric disorders or negative outcomes. Although BV can be associated with sexual activity, there is no clear evidence of sexual transmission. It is possible for sexually inactive persons to develop bacterial vaginosis.
Also, subclinical iron deficiency may correlate with bacterial vaginosis in early pregnancy. A longitudinal study published in February 2006, in the ''American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology'', showed a link between psychosocial stress and bacterial vaginosis persisted even when other risk factors were taken into account. Exposure to the spermicide nonoxynol-9
Nonoxynol-9, sometimes abbreviated as N-9, is an organic compound that is used as a surfactant. It is a member of the Nonoxynols, nonoxynol family of nonionic surfactants. N-9 and related compounds are ingredients in various cleaning and cosmet ...
does not affect the risk of developing bacterial vaginosis.
The cause of the fishy smell of BV is mainly due to reduction of trimethylamine oxide (TMAO) to trimethylamine (TMA) by bacteria in vaginal secretion. TMA is the same compound that is predominantly responsible for the smell of decomposing fish. The diamines putrescine
Putrescine is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4(NH2)2. It is a colorless solid that melts near room temperature. It is classified as a diamine. Together with cadaverine, it is largely responsible for the foul odor of Putrefaction, putref ...
and cadaverine
Cadaverine is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)5(NH2)2. Classified as a diamine, it is a colorless liquid with an unpleasant odor. It is present in small quantities in living organisms but is often associated with the putrefaction of Tiss ...
, which are the decarboxylation products of arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidinium, guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) a ...
and lysine amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
, respectively, are also present in BV and may contribute to the fishy smell of the condition as well.
Diagnosis


 To make a diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis, a swab from inside the vagina should be obtained. These swabs can be tested for:
*
To make a diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis, a swab from inside the vagina should be obtained. These swabs can be tested for:
* Gram stain
Gram stain (Gram staining or Gram's method), is a method of staining used to classify bacterial species into two large groups: gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria. It may also be used to diagnose a fungal infection. The name comes ...
which shows the depletion of lactobacilli and overgrowth of '' Gardnerella vaginalis'' bacteria. Bacterial vaginosis is usually confirmed by a Gram stain of vaginal secretions.
* A characteristic "fishy" odor on wet mount. This test, called the ''whiff test'', is performed by adding a small amount of potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which utili ...
to a microscope slide containing the vaginal discharge. A characteristic fishy odor is considered a positive whiff test and is suggestive of bacterial vaginosis. Addition of a base to vaginal secretion with the diamines putrescine
Putrescine is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4(NH2)2. It is a colorless solid that melts near room temperature. It is classified as a diamine. Together with cadaverine, it is largely responsible for the foul odor of Putrefaction, putref ...
and cadaverine
Cadaverine is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)5(NH2)2. Classified as a diamine, it is a colorless liquid with an unpleasant odor. It is present in small quantities in living organisms but is often associated with the putrefaction of Tiss ...
causes them to become volatile and thereby produce a more intense fishy smell.
* Loss of acidity. To control bacterial growth, the vagina is normally slightly acidic with a pH of 3.8–4.2. A swab of the discharge is put onto litmus paper to check its acidity. A pH greater than 4.5 is considered alkaline and is suggestive of bacterial vaginosis.
* The presence of '' clue cells'' on wet mount. Similar to the whiff test, the test for clue cells is performed by placing a drop of sodium chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as Salt#Edible salt, edible salt, is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. It is transparent or translucent, brittle, hygroscopic, and occurs a ...
solution on a slide containing vaginal discharge. If present, clue cells can be visualized under a microscope. They are so-named because they give a clue to the reason behind the discharge. These are epithelial cells that are coated with bacteria.
Differential diagnosis for bacterial vaginosis includes the following:
* Normal vaginal discharge.
* Candidiasis (thrush, or a yeast infection).
* Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis (trich) is an infectious disease caused by the parasite ''Trichomonas vaginalis''. About 70% of affected people do not have symptoms when infected. When symptoms occur, they typically begin 5 to 28 days after exposure. Symptoms ca ...
, an infection caused by ''Trichomonas vaginalis
''Trichomonas vaginalis'' is an Anaerobic organism, anaerobic, flagellated protozoan parasite and the causative agent of a Sexually transmitted infection, sexually transmitted disease called trichomoniasis. It is the most common pathogenic protoz ...
''.
* Aerobic vaginitis
The Center for Disease Control (CDC) defines STIs as "a variety of clinical syndromes and infections caused by pathogens that can be acquired and transmitted through sexual activity." But the CDC does not specifically identify BV as sexually transmitted infection.
Amsel criteria
In clinical practice BV can be diagnosed using the Amsel criteria: # Thin, white, yellow, homogeneous discharge # Clue cells onmicroscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view subjects too small to be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical mic ...
# pH of vaginal fluid >4.5
# Release of a fishy odor on adding alkali—10% potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which utili ...
(KOH) solution.
At least three of the four criteria should be present for a confirmed diagnosis.
A modification of the Amsel criteria accepts the presence of two instead of three factors and is considered equally diagnostic.
Gram stain
An alternative is to use a Gram-stained vaginal smear, with the Hay/Ison criteria or the Nugent criteria. The Hay/Ison criteria are defined as follows: * Grade 1 (Normal): Lactobacillus morphotypes predominate. * Grade 2 (Intermediate): Some lactobacilli present, but ''Gardnerella'' or ''Mobiluncus'' morphotypes also present. * Grade 3 (Bacterial Vaginosis): Predominantly ''Gardnerella'' and/or ''Mobiluncus'' morphotypes. Few or absent lactobacilli. (Hay et al., 1994) ''Gardnerella vaginalis'' is the main culprit in BV. ''Gardnerella vaginalis'' is a short, Gram-variable rod (coccobacillus). Hence, the presence of clue cells and gram variable coccobacilli are indicative or diagnostic of bacterial vaginosis.Nugent score
The Nugent score is now rarely used by physicians due to the time it takes to read the slides and requires the use of a trained microscopist. A score of 0–10 is generated from combining three other scores. The scores are as follows: * 0–3 is considered negative for BV * 4–6 is considered intermediate * 7+ is considered indicative of BV. At least 10–20 high power (1000× oil immersion) fields are counted and an average determined. DNA hybridization testing with Affirm VPIII was compared to the Gram stain using the Nugent criteria. The Affirm VPIII test may be used for the rapid diagnosis of BV in symptomatic women but uses expensive proprietary equipment to read results, and does not detect other pathogens that cause BV, including ''Prevotella'' spp, ''Bacteroides'' spp, and ''Mobiluncus'' spp. The cervicovaginal microbiome measured using 16S rRNA sequencing has the capacity to increase throughput of the Nugent Score and has demonstrate to be directly comparable to clinical Nugent Score measurement.Screening
Screening during pregnancy is not recommended in the United States as of 2020 because " the US Preventive Services Task Force concludes that the current evidence is insufficient to assess the balance of benefits and harms of screening for bacterial vaginosis in pregnant persons at increased risk for preterm delivery".Prevention
Some steps suggested to lower the risk include: not douching, avoiding sex, or limiting the number of sex partners.Systematic review
A systematic review is a scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from published studies on ...
s and meta-analyses
Meta-analysis is a method of synthesis of quantitative data from multiple independent studies addressing a common research question. An important part of this method involves computing a combined effect size across all of the studies. As such, th ...
from 2022 to 2023 have concluded that probiotics may help prevent re-occurrence.
Early evidence suggested that antibiotic treatment of male partners could re-establish the normal microbiota of the male urogenital tract and prevent the recurrence of infection. However, a 2016 Cochrane review found high-quality evidence that treating the sexual partners of women with bacterial vaginosis had no effect on symptoms, clinical outcomes, or recurrence in the affected women. It also found that such treatment may lead treated sexual partners to report increased adverse events.
Treatment
Antibiotics
Treatment is typically with theantibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
s metronidazole
Metronidazole, sold under the brand name Flagyl and Metrogyl among others, is an antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication. It is used either alone or with other antibiotics to treat pelvic inflammatory disease, endocarditis, and bacterial vagino ...
or clindamycin. They can be either given by mouth
Oral administration is a route of administration whereby a substance is taken through the Human mouth, mouth, swallowed, and then processed via the digestive system. This is a common route of administration for many medications.
Oral administ ...
or applied inside the vagina with similar efficacy. Other antibiotics related to metronidazole, including tinidazole and the newer secnidazole, are also approved and used to treat BV. When clindamycin is given to pregnant women symptomatic with BV before 22 weeks of gestation the risk of pre-term birth before 37 weeks of gestation is lower. Additional antibiotics that are not approved for treatment of BV but might work include macrolides, lincosamides, and penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of beta-lactam antibiotic, β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' Mold (fungus), moulds, principally ''Penicillium chrysogenum, P. chrysogenum'' and ''Penicillium rubens, P. ru ...
s.
Although antibiotics are effective, about 10% to 15% of people do not improve with the first course of antibiotics and recurrence rates of up to 80% have been documented. Recurrence rates are increased with sexual activity with the same pre-/post-treatment partner and inconsistent condom use.
BV is not considered a sexually transmitted infection
A sexually transmitted infection (STI), also referred to as a sexually transmitted disease (STD) and the older term venereal disease (VD), is an infection that is Transmission (medicine), spread by Human sexual activity, sexual activity, e ...
, and antibiotic treatment of a male sexual partner of a woman with BV is not recommended.
Antiseptics
Topicalantiseptic
An antiseptic ( and ) is an antimicrobial substance or compound that is applied to living tissue to reduce the possibility of sepsis, infection, or putrefaction. Antiseptics are generally distinguished from ''antibiotics'' by the latter's abil ...
s, for example dequalinium chloride, policresulen, hexetidine, povidone-iodine, or boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen orthoborate, trihydroxidoboron or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white ...
vaginal suppositories may be applied, if the risk of ascending infections is low (outside of pregnancy and in immunocompetent people without histories of upper genital tract infections).
Dequalinium chloride is available as a prescription vaginal tablet, for instance in Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
and Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
, is given as a 6-day course, and is non-inferior to metronidazole in the treatment of bacterial vaginosis. Povidone-iodine is approved as a vaginal gel to treat bacterial vaginosis under the brand name Astrodimer, among others. One study found that vaginal irrigations with hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscosity, viscous than Properties of water, water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usua ...
(3%) resulted in a slight improvement, but this was much less than with the use of oral metronidazole. Dequalinium chloride and povidone-iodine (as Astrodimer) have the best evidence of effectiveness. Neither of these are available in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, though they are available in other countries. Intravaginal boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen orthoborate, trihydroxidoboron or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white ...
, alone or in conjunction with other medications, may be helpful in the treatment of recurrent BV.
TOL-463, an experimental
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs whe ...
formulation of boric acid enhanced with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), is under development as an intravaginal medication for the treatment of BV and has shown preliminary effectiveness in clinical trials.
Probiotics
A 2009 Cochrane review found tentative but insufficient evidence for probiotics as a treatment for BV. A 2014 review reached the same conclusion. A 2013 review found some evidence supporting the use of probiotics during pregnancy. The preferred probiotics for BV are those containing high doses of lactobacilli (around 109 ) given in the vagina. Intravaginal administration is preferred to taking them by mouth. Prolonged repetitive courses of treatment appear to be more promising than short courses. The lack of effectiveness of commercially available ''Lactobacillus'' probiotics may be because most do not actually contain vaginal lactobacilli strains. LACTIN-V is a live biopharmaceutical medication containing the vaginally important '' Lactobacillus crispatus'' which is under development for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis and recurrent urinary tract infections. It has shown initial effectiveness in considerably reducing recurrence of bacterial vaginosis following antibiotic treatment. LACTIN-V is not yetFood and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respo ...
(FDA)-approved or commercially available.
Miscellaneous
Estrogen-containing contraceptives have been found to decrease recurrence of BV.Epidemiology
BV is the most common infection of the vagina in women of reproductive age. The percentage of women affected at any given time varies between 5% and 70%. BV is most common in parts of Africa, and least common in Asia and Europe. In the United States, about 30% of those between the ages of 14 and 49 are affected. Rates vary considerably between ethnic groups within a country.References
External links
WHO fact sheet on bacterial vaginosis
{{DEFAULTSORT:Bacterial Vaginosis Inflammatory diseases of female pelvic organs Mycoplasma Probiotics Sexually transmitted diseases and infections Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate