|
Vaginal Discharge
Vaginal discharge is a mixture of liquid, cells, and bacteria that lubricate and protect the vagina. This mixture is constantly produced by the cells of the vagina and cervix, and it exits the body through the vaginal opening. The composition, quality, and amount of discharge varies between individuals, and can vary throughout the menstrual cycle and throughout the stages of sexual and reproductive development. Normal vaginal discharge may have a thin, watery consistency or a thick, sticky consistency, and it may be clear or white in color. Normal vaginal discharge may be large in volume but typically does not have a strong odor, nor is it typically associated with itching or pain. While most discharge is considered physiologic (represents normal functioning of the body), some changes in discharge can reflect infection or other pathological processes. Infections that may cause changes in vaginal discharge include vaginal yeast infections, bacterial vaginosis, and sexually trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervix
The cervix (: cervices) or cervix uteri is a dynamic fibromuscular sexual organ of the female reproductive system that connects the vagina with the uterine cavity. The human female cervix has been documented anatomically since at least the time of Hippocrates, over 2,000 years ago. The cervix is approximately 4 cm long with a diameter of approximately 3 cm and tends to be described as a cylindrical shape, although the front and back walls of the cervix are contiguous. The size of the cervix changes throughout a woman's life cycle. For example, women in the fertile years of their reproductive cycle tend to have larger cervixes than postmenopausal women; likewise, women who have produced offspring have a larger cervix than those who have not. In relation to the vagina, the part of the cervix that opens to the uterus is called the ''internal os'' and the opening of the cervix in the vagina is called the ''external os''. Between them is a conduit commonly called the cervic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
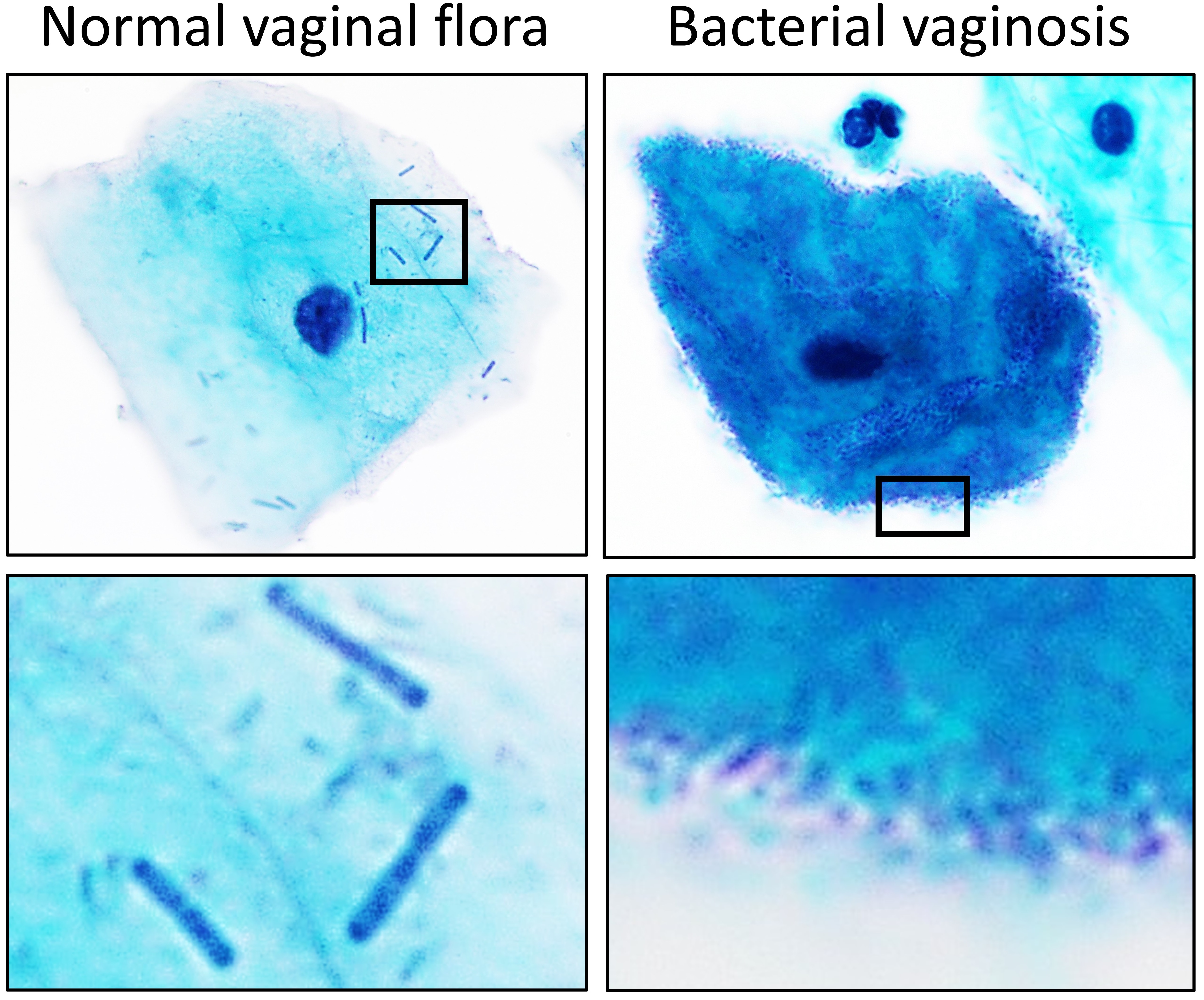
Vaginal Flora
Vaginal flora, vaginal microbiota or vaginal microbiome are the microorganisms that colonize the vagina. They were discovered by the German gynecologist Albert Döderlein in 1892 and are part of the overall human flora. The amount and type of bacteria present have significant implications for an individual's overall health. The primary colonizing bacteria of a healthy individual are of the genus ''Lactobacillus'', such as ''Lactobacillus crispatus, L. crispatus'', and the lactic acid they produce is thought to protect against infection by pathogenic species. Lactobacilli The primary colonizing bacteria of a healthy individual are of the genus ''Lactobacillus'' (90–95%), the most common being ''Lactobacillus crispatus, L. crispatus'', ''Lactobacillus iners, L. iners'', ''Lactobacillus jensenii, L. jensenii'', and ''Lactobacillus gasseri, L. gasseri''. Since the first description of lactobacilli by Döderlein, lactobacilli have been generally considered the gatekeepers of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progesterone
Progesterone (; P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the major progestogen in the body. Progesterone has a variety of important functions in the body. It is also a crucial metabolic intermediate in the production of other endogenous steroids, including the sex hormones and the corticosteroids, and plays an important role in brain function as a neurosteroid. In addition to its role as a natural hormone, progesterone is also used as a medication, such as in combination with estrogen for contraception, to reduce the risk of Uterine cancer, uterine or cervical cancer, in hormone replacement therapy, and in feminizing hormone therapy. It was first prescribed in 1934. Biological activity Progesterone is the most important progestogen in the body. As a potent agonist of the progesterone receptor, nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovulation
Ovulation is an important part of the menstrual cycle in female vertebrates where the egg cells are released from the ovaries as part of the ovarian cycle. In female humans ovulation typically occurs near the midpoint in the menstrual cycle and after the follicular phase. Ovulation is stimulated by an increase in luteinizing hormone (LH). The ovarian follicles rupture and release the secondary oocyte ovarian cells. After ovulation, during the luteal phase, the egg will be available to be fertilized by sperm. If it is not, it will break down in less than a day. Meanwhile, the uterine lining ( endometrium) continues to thicken to be able to receive a fertilized egg. If no conception occurs, the uterine lining will eventually break down and be shed from the body via the vagina during menstruation. Some people choose to track ovulation in order to improve or aid becoming pregnant by timing intercourse with their ovulation. The signs of ovulation may include cervical muc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. It is the main storage form of glucose in the human body. Glycogen functions as one of three regularly used forms of energy reserves, creatine phosphate being for very short-term, glycogen being for short-term and the triglyceride stores in adipose tissue (i.e., body fat) being for long-term storage. Protein, broken down into amino acids, is seldom used as a main energy source except during starvation and glycolytic crisis ''(see bioenergetic systems)''. In humans, glycogen is made and stored primarily in the cells of the liver and skeletal muscle. In the liver, glycogen can make up 5–6% of the organ's fresh weight: the liver of an adult, weighing 1.5 kg, can store roughly 100–120 grams of glycogen. In skeletal muscle, glycogen is found in a low concentration (1–2% of the muscle mass): the skeletal muscle of an adult weighing 70 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
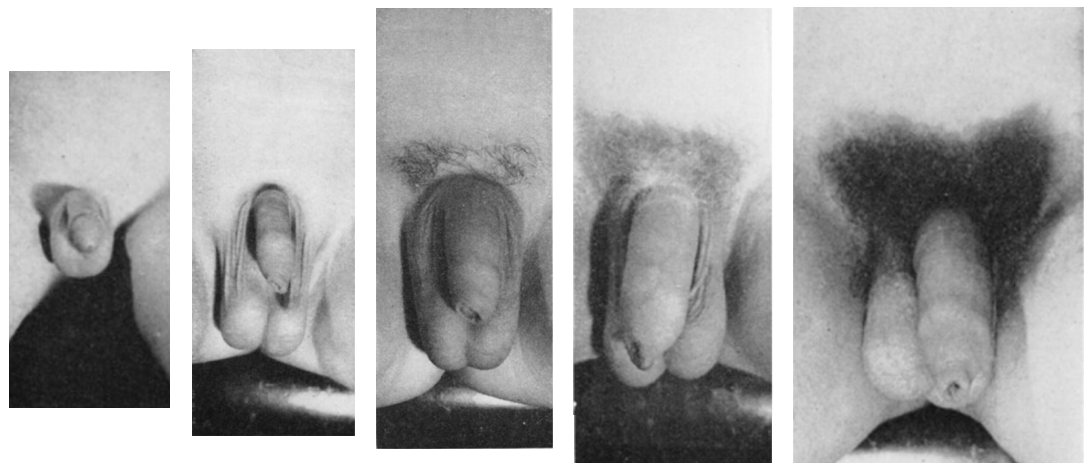
Thelarche
Thelarche, also known as breast budding, is the onset of secondary breast development, often representing the beginning of pubertal development. It is the stage at which male and female breasts differentiate due to variance in hormone levels; however, some males have a condition in which they develop breasts, termed gynecomastia. Thelarche typically occurs between the ages of 8 and 13 years with significant variation between individuals. However, the initial growth of breast tissue occurs during fetal development. It is usually the first sign of puberty in females (less commonly, it can be the second sign, after pubarche). Usually, females experience menarche about two years after thelarche has begun, with complete breast development from thelarche to adult breasts, taking between 2 and 4 years but can last up to age 18. Moreover, puberty is considered delayed if breast development does not start at age 13 or if a female has not had her first period (menarche) within three years of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
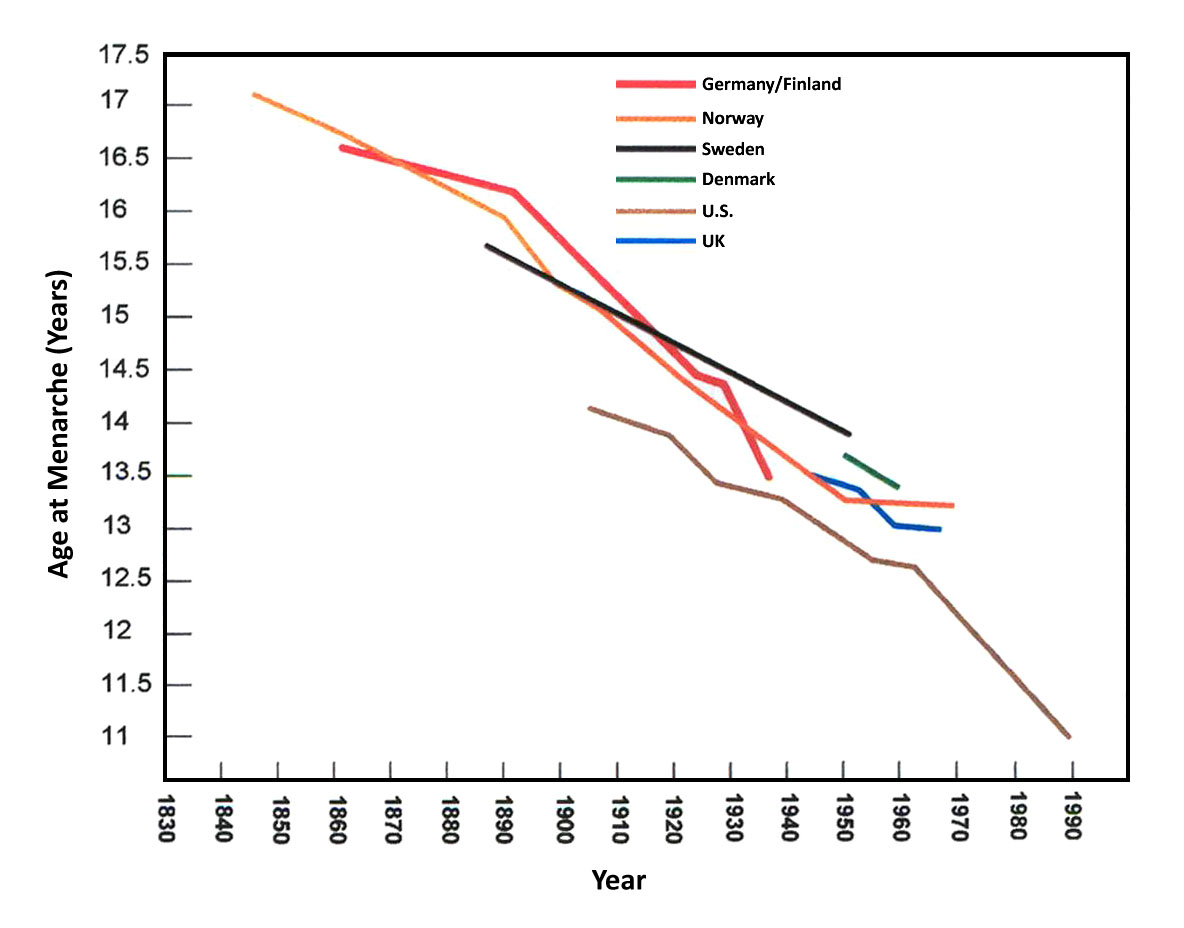
Menarche
Menarche ( ; ) is the first menstrual cycle, or first menstruation, menstrual bleeding, in female humans. From both social and medical perspectives, it is often considered the central event of female puberty, as it signals the possibility of fertility. Girls experience menarche at different ages, but the most common age is 12. Having menarche occur between the ages of 9–14 in the West is considered normal.US National Health Statistics Report September 2020 The timing of menarche is influenced by female biology, as well as Genetics, genetic, environmental factors, and nutritional factors. The mean age of menarche has declined over the last century, but the magnitude of the decline and the factors responsible remain subjects of contention. The worldwide average age of menarche is very difficult to estimate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles in a male. In response to the signals, the gonads produce hormones that stimulate libido and the growth, function, and transformation of the brain, bones, muscle, blood, skin, hair, breasts, and sex organs. Physical growth—height and weight—accelerates in the first half of puberty and is completed when an adult body has been developed. Before puberty, the external sex organs, known as primary sexual characteristics, are sex characteristics that distinguish males and females. Puberty leads to sexual dimorphism through the development of the secondary sex characteristics, which further distinguish the sexes. On average, females begin puberty at age 10½ and complete puberty at ages 15-17; males begin at ages 11½-12 and complete pube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus
''Staphylococcus'', from Ancient Greek σταφυλή (''staphulḗ''), meaning "bunch of grapes", and (''kókkos''), meaning "kernel" or " Kermes", is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical ( cocci), and form in grape-like clusters. ''Staphylococcus'' species are facultative anaerobic organisms (capable of growth both aerobically and anaerobically). The name was coined in 1880 by Scottish surgeon and bacteriologist Alexander Ogston (1844–1929), following the pattern established five years earlier with the naming of '' Streptococcus''. It combines the prefix "staphylo-" (from ), and suffixed by the (from ). Staphylococcus was one of the leading infections in hospitals and many strains of this bacterium have become antibiotic resistant. Despite strong attempts to get rid of them, staphylococcus bacteria stay present in hospitals, where they can infect people who are most at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
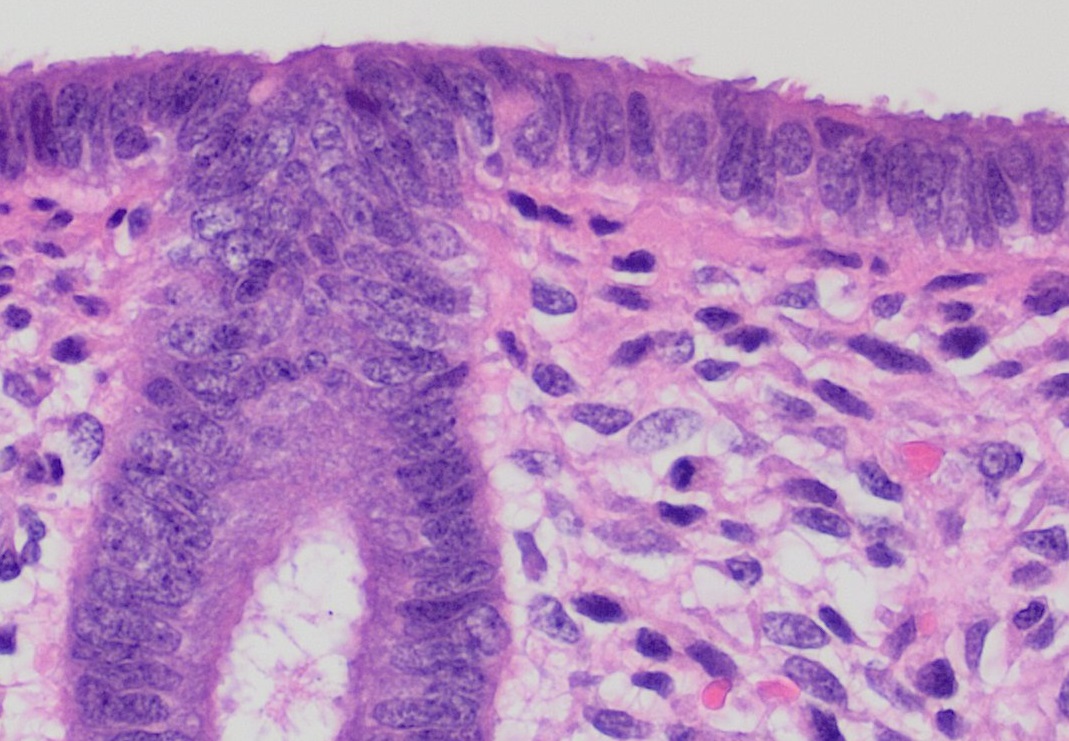
Endometrium
The endometrium is the inner epithelium, epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The functional layer thickens and then is shed during menstruation in humans and some other mammals, including other apes, Old World monkeys, some species of bat, the elephant shrew and the Cairo spiny mouse. In most other mammals, the endometrium is reabsorbed in the estrous cycle. During pregnancy, the glands and blood vessels in the endometrium further increase in size and number. Vascular spaces fuse and become interconnected, forming the placenta, which supplies oxygen and nutrition to the embryo and fetus.Blue Histology - Female Reproductive System ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estrogen
Estrogen (also spelled oestrogen in British English; see spelling differences) is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal activity: estrone (E1), estradiol (E2), and estriol (E3). Estradiol, an estrane, is the most potent and prevalent. Another estrogen called estetrol (E4) is produced only during pregnancy. Estrogens are synthesized in all vertebrates and some insects. Quantitatively, estrogens circulate at lower levels than androgens in both men and women. While estrogen levels are significantly lower in males than in females, estrogens nevertheless have important physiological roles in males. Like all steroid hormones, estrogens readily diffuse across the cell membrane. Once inside the cell, they bind to and activate estrogen receptors (ERs) which in turn modulate the expression of many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infant
In common terminology, a baby is the very young offspring of adult human beings, while infant (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'baby' or 'child') is a formal or specialised synonym. The terms may also be used to refer to juveniles of other organisms. A newborn is, in colloquial use, a baby who is only hours, days, or weeks old; while in medical contexts, a newborn or neonate (from Latin, ''neonatus'', newborn) is an infant in the first 28 days after birth (the term applies to premature, full term, and postmature infants). Infants born prior to 37 weeks of gestation are called "premature", those born between 39 and 40 weeks are "full term", those born through 41 weeks are "late term", and anything beyond 42 weeks is considered "post term". Before birth, the offspring is called a fetus. The term ''infant'' is typically applied to very young children under one year of age; however, definitions may vary and may include children up to two years of age. When a human chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |