thelarche on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Thelarche, also known as
Thelarche, also known as
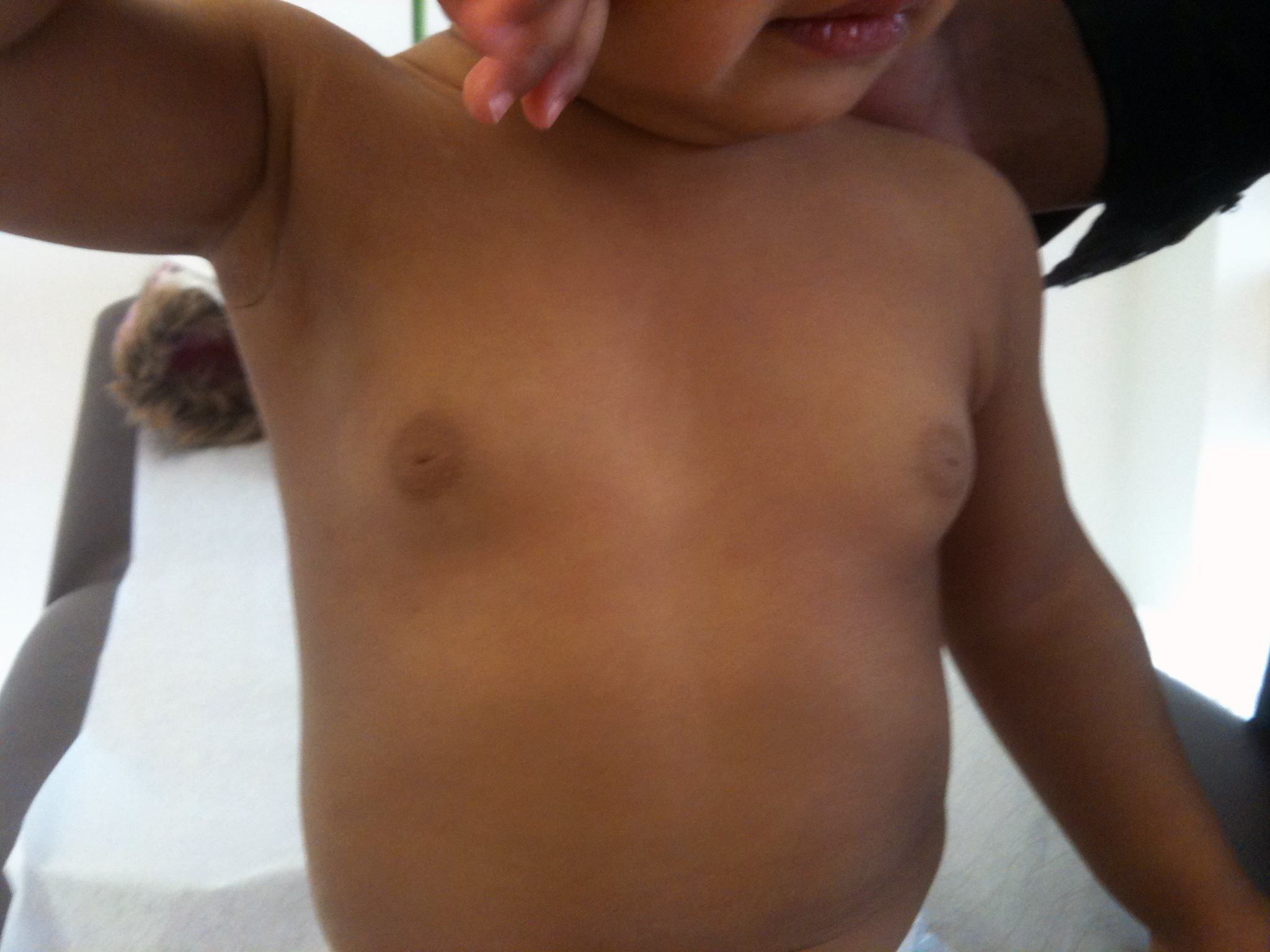
 Thelarche, also known as
Thelarche, also known as breast
The breasts are two prominences located on the upper ventral region of the torso among humans and other primates. Both sexes develop breasts from the same embryology, embryological tissues. The relative size and development of the breasts is ...
budding, is the onset of secondary breast development
Breast development, also known as mammogenesis, is a complex biological process in primates that takes place throughout a female's life.
It occurs across several phases, including prenatal development, puberty, and pregnancy. At menopause, breas ...
, often representing the beginning of pubertal development. It is the stage at which male and female breasts differentiate due to variance in hormone levels; however, some males have a condition in which they develop breasts, termed gynecomastia
Gynecomastia (also spelled gynaecomastia) is the non-cancerous enlargement of one or both breasts in men due to the growth of breast tissue as a result of a hormone imbalance between estrogens and androgens. Updated by Brent Wisse (10 Novemb ...
. Thelarche typically occurs between the ages of 8 and 13 years with significant variation between individuals. However, the initial growth of breast tissue occurs during fetal development. It is usually the first sign of puberty in females (less commonly, it can be the second sign, after pubarche
Pubarche () refers to the first appearance of pubic hair at puberty. It is one of the earliest physical changes of puberty and can occur independently of complete puberty. It is usually the second sign of puberty, after thelarche in females and gon ...
).
Usually, females experience menarche about two years after thelarche has begun, with complete breast development from thelarche to adult breasts, taking between 2 and 4 years but can last up to age 18. Moreover, puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles i ...
is considered delayed if breast development does not start at age 13 or if a female has not had her first period (menarche
Menarche ( ; ) is the first menstrual cycle, or first menstruation, menstrual bleeding, in female humans. From both social and medical perspectives, it is often considered the central event of female puberty, as it signals the possibility of fe ...
) within three years of thelarche. Additionally, secondary breast development occurring before the age of 7 years could be a sign of premature thelarche
Premature thelarche (PT) is a medical condition, characterised by isolated breast development in female infants. It occurs in females younger than 8 years, with the highest occurrence before the age of 2. PT is rare, occurring in 2.2-4.7% of female ...
or precocious puberty
In medicine, precocious puberty is puberty occurring at an unusually early age. In most cases, the process is normal in every aspect except the unusually early age and simply represents a variation of normal development. There is early developm ...
. Of note, for some girls, thelarche will occur, with subsequent regression of breast development, and then months or years later, normal breast growth will commence again accompanied by normal pubertal changes; this is termed transient thelarche.
Pubertal changes, including breast development, are assessed using the Tanner Scale
The Tanner scale (also known as the Tanner stages or sexual maturity rating (SMR)) is a scale of physical development as pre-pubescent children transition into adolescence, and then adulthood. The scale defines physical measurements of devel ...
(Sexual Maturity Rating Scale) where stage 1 is before, stage 2 is the breast budding or thelarche stage, stages 3 and 4 are continual breast growth and areola
The human areola (''areola mammae'', or ) is the pigmented area on the breast around the nipple. More generally, an areola is a small circular area on the Human body, body with a different histology from the surrounding Tissue (biology), tissue ...
r development, and stage 5 signifies completion of development. This system does not use breast size but instead examines the shape of breasts, nipples, and areolae to determine the progression of growth.
Various hormones interact and result in the changes seen during thelarche. The growth and accumulation of adipose tissue
Adipose tissue (also known as body fat or simply fat) is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. It also contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, Blood vessel, vascular endothel ...
in the breasts are induced by estrogen
Estrogen (also spelled oestrogen in British English; see spelling differences) is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three ...
, while the development of mammary gland
A mammary gland is an exocrine gland that produces milk in humans and other mammals. Mammals get their name from the Latin word ''mamma'', "breast". The mammary glands are arranged in organs such as the breasts in primates (for example, human ...
s and areolae are caused by progesterone
Progesterone (; P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the ma ...
; both estrogen and progesterone are produced by ovaries
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocr ...
. Due to change in hormone levels, young breasts are likely to develop asymmetrically, and in many cases, adult breasts will remain unequal in size or shape.
Epidemiology and trends
The age of thelarche has been decreasing in the past few decades. Between 1973 and 2013, the age of thelarche decreased at a rate of 0.24 years per decade. Other contemporary trends that may be contributing to this change in the onset of thelarche include increasing BMI, changes in pubertal timing, and environmental exposures. Studies also indicate associations between the average age of thelarche and race. The average age of thelarche for African American females in the United States is between 8.9 and 9.5 years, the average for Caucasians is 10–10.4 years, and the average age of thelarche for Hispanic females is approximately 9.8 years. Additionally, in African American and Mexican American girls, breast development may occur earlier than in other ethnic cohorts and can be normal in the 7th year of age. Due to the decreasing age of thelarche over time, there is discussion of adjusting the cutoff for early thelarche to 7 years old for white females and six years old for black females. Furthermore, there have been associations between obesity, chemical contaminants, and the earlier average age of thelarche. Studies have shown that obesity is associated with an earlier average age of thelarche. Moreover, the prevalence of premature thelarche has been increasing over the past several years which many attribute to pesticides. Experimental data indicate the impact of chemical contaminants in gestation and puberty, with the chemical such as phthalates having a high association with premature thelarche frequency.Premature thelarche
Premature thelarche
Premature thelarche (PT) is a medical condition, characterised by isolated breast development in female infants. It occurs in females younger than 8 years, with the highest occurrence before the age of 2. PT is rare, occurring in 2.2-4.7% of female ...
is a benign condition in which a young female has breast development before age eight without any accompanied pubertal changes. Individuals undergoing isolated premature thelarche do not experience menstruation
Menstruation (also known as a period, among other colloquial terms) is the regular discharge of blood and Mucous membrane, mucosal tissue from the endometrium, inner lining of the uterus through the vagina. The menstrual cycle is characterized ...
, pubic hair growth (pubarche
Pubarche () refers to the first appearance of pubic hair at puberty. It is one of the earliest physical changes of puberty and can occur independently of complete puberty. It is usually the second sign of puberty, after thelarche in females and gon ...
), or the bone growth characteristic of puberty. Initial breast development can be bilateral or unilateral and usually begins with a firm, disc-like area of tissue under the areola, which can be mistaken for a mass but is almost always a normal physiologic process. The breast is often tender, and palpation is sometimes painful, but breast discharge is absent. Usually, the breasts do not develop past stage 3 on the Tanner Scale, hence maintaining adolescent nipples. Moreover, in 90% of patients with isolated premature thelarche, breast enlargement will resolve six months to 6 years after diagnosis.
The most common age for females to develop isolated premature thelarche is between 0 and 2 years, with a prevalence rate between 2.2 and 4.7 percent of all female infants. The breasts of these females typically exhibit alternating progression and regression patterns of growth in 6-week intervals, often completely decreasing in size within 1.5 years. Due to the benign nature of the condition and the tendency to self-resolve, premature thelarche does not require treatment. However, premature thelarche should be evaluated to rule out additional causes, such as hypothyroidism or precocious puberty, especially if other symptoms are present. Such evaluations will typically involve serial examinations and radiographs.
Precocious puberty
Precocious puberty
In medicine, precocious puberty is puberty occurring at an unusually early age. In most cases, the process is normal in every aspect except the unusually early age and simply represents a variation of normal development. There is early developm ...
is a condition where children undergo puberty before seven or eight years. Precocious puberty differs from premature thelarche in that the individual experiences additional aspects of puberty, including menarche
Menarche ( ; ) is the first menstrual cycle, or first menstruation, menstrual bleeding, in female humans. From both social and medical perspectives, it is often considered the central event of female puberty, as it signals the possibility of fe ...
, adrenarche
Adrenarche is an early stage in sexual maturation that happens in some higher primates (including humans), typically peaks at around 20 years of age, and is involved in the development of pubic hair, body odor, skin oiliness#Oily skin, skin oiline ...
, pubarche
Pubarche () refers to the first appearance of pubic hair at puberty. It is one of the earliest physical changes of puberty and can occur independently of complete puberty. It is usually the second sign of puberty, after thelarche in females and gon ...
, vaginal discharge
Vaginal discharge is a mixture of liquid, cells, and bacteria that lubricate and protect the vagina. This mixture is constantly produced by the cells of the vagina and cervix, and it exits the body through the vaginal opening. The composition, ...
, and bone growth, while the sole presence of early thelarche identifies premature thelarche. Though premature thelarche and precocious puberty are distinct conditions, there is some overlap; an estimated 14 to 18 percent of females who exhibit premature thelarche will additionally develop precocious puberty. Precocious puberty can be identified using a pelvic ultrasound to assess the size of ovaries and uterus relative to the individual's age. Other methods of diagnosis consist of blood tests to determine hormone levels and simple physician assessments with follow-up appointments to track the progression of development.
Thelarche variant
The thelarche variant, also named exaggerated thelarche, is an intermediate condition between premature thelarche and precocious puberty. This condition resembles premature thelarche without the cyclic waxing and waning of breast growth. Pubic hair growth (pubarche
Pubarche () refers to the first appearance of pubic hair at puberty. It is one of the earliest physical changes of puberty and can occur independently of complete puberty. It is usually the second sign of puberty, after thelarche in females and gon ...
) and advanced bone growth are often present in the thelarche variant. Yet, this growth does not result in complete sexual maturity as occurs with precocious puberty.
See also
*Puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles i ...
* Adrenarche
Adrenarche is an early stage in sexual maturation that happens in some higher primates (including humans), typically peaks at around 20 years of age, and is involved in the development of pubic hair, body odor, skin oiliness#Oily skin, skin oiline ...
* Gonadarche
* Pubarche
Pubarche () refers to the first appearance of pubic hair at puberty. It is one of the earliest physical changes of puberty and can occur independently of complete puberty. It is usually the second sign of puberty, after thelarche in females and gon ...
* Menarche
Menarche ( ; ) is the first menstrual cycle, or first menstruation, menstrual bleeding, in female humans. From both social and medical perspectives, it is often considered the central event of female puberty, as it signals the possibility of fe ...
* Spermarche
Spermarche, also known as semenarche, is the time at which a male experiences his first ejaculation. It is considered to be the counterpart of menarche in females. Depending on upbringing, cultural differences, and prior sexual knowledge, males may ...
* Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia (also spelled gynaecomastia) is the non-cancerous enlargement of one or both breasts in men due to the growth of breast tissue as a result of a hormone imbalance between estrogens and androgens. Updated by Brent Wisse (10 Novemb ...
References
{{Reproductive physiology Gynaecological endocrinology Animal developmental biology Pediatrics Sexuality and age Endocrinology Developmental stages