Backbone-dependent Rotamer Library on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 Many modeling programs, such as
Many modeling programs, such as
 The effect of backbone conformation on side-chain rotamer frequencies is primarily due to
The effect of backbone conformation on side-chain rotamer frequencies is primarily due to 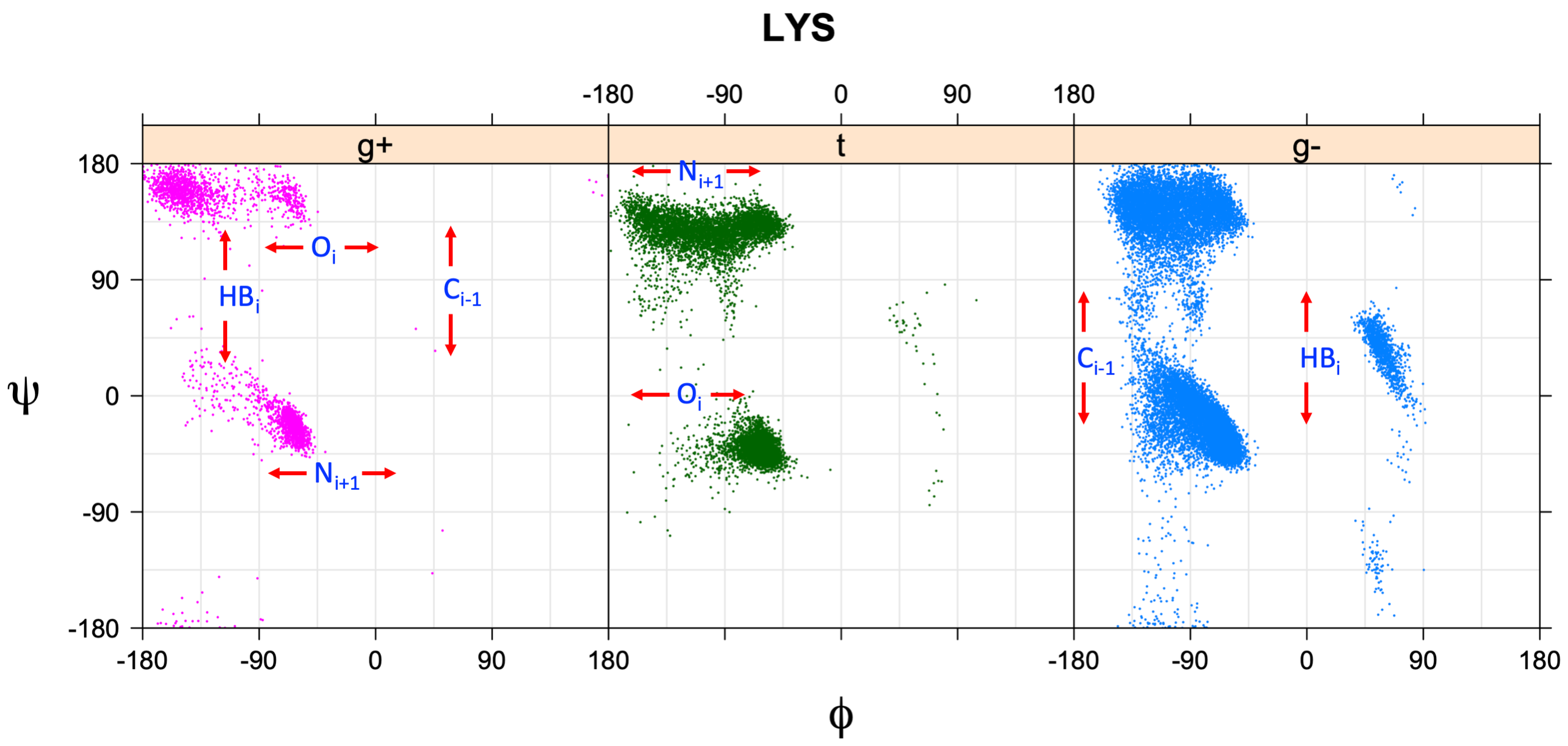 The φ,ψ-dependent interactions of backbone atoms and side-chain Cγ atoms can be observed in the distribution of observations in the
The φ,ψ-dependent interactions of backbone atoms and side-chain Cγ atoms can be observed in the distribution of observations in the  Side-chain types with two heavy atoms (Val, Ile, Thr) have backbone-dependent interactions with both heavy atoms. Val has CG1 at χ1 and CG2 at χ1+120°. Because Val g+ and g- conformations have steric interactions with the backbone near ψ=120° and -60° (the most populated ψ ranges), Val is the only amino acid where the t rotamer (χ1~180°) is the most common. At most values of φ and ψ, only one rotamer of Val is allowed (shown in figure). Ile has CG1 at χ1 and CG2 at χ1-120°. Thr has OG1 at χ1 and CG2 at χ1-120°.
Side-chain types with two heavy atoms (Val, Ile, Thr) have backbone-dependent interactions with both heavy atoms. Val has CG1 at χ1 and CG2 at χ1+120°. Because Val g+ and g- conformations have steric interactions with the backbone near ψ=120° and -60° (the most populated ψ ranges), Val is the only amino acid where the t rotamer (χ1~180°) is the most common. At most values of φ and ψ, only one rotamer of Val is allowed (shown in figure). Ile has CG1 at χ1 and CG2 at χ1-120°. Thr has OG1 at χ1 and CG2 at χ1-120°.
GalaxyRefine
ref name="HPS2013"/> *
SCWRL4
ref name="KSD2009"/> * Protein Design **
EvoEF2
ref name="HZ2020"/> * Visualization of Protein Mutations **
Dunbrack 2010 Backbone-Dependent Rotamer Library
Protein Side-chain Conformational Analysis
Richardson Backbone-Independent Rotamer Libraries
Dynameomics Backbone-Independent and Backbone-Dependent Rotamer Libraries
Protein structure Bioinformatics Molecular modelling
 In
In biochemistry
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology ...
, a backbone-dependent rotamer library provides the frequencies, mean dihedral angles
A dihedral angle is the angle between two intersecting planes or half-planes. In chemistry, it is the clockwise angle between half-planes through two sets of three atoms, having two atoms in common. In solid geometry, it is defined as the un ...
, and standard deviations of the discrete conformations (known as rotamer
In chemistry, conformational isomerism is a form of stereoisomerism in which the isomers can be interconverted just by rotations about formally single bonds (refer to figure on single bond rotation). While any two arrangements of atoms in a mole ...
s) of the amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha ...
side chains in protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
s as a function of the backbone dihedral angle
A dihedral angle is the angle between two intersecting planes or half-planes. In chemistry, it is the clockwise angle between half-planes through two sets of three atoms, having two atoms in common. In solid geometry, it is defined as the un ...
s φ and ψ of the Ramachandran map. By contrast, backbone-independent rotamer libraries express the frequencies and mean dihedral angles for all side chains in proteins, regardless of the backbone conformation of each residue type. Backbone-dependent rotamer libraries have been shown to have significant advantages over backbone-independent rotamer libraries, principally when used as an energy term, by speeding up search times of side-chain packing algorithms used in protein structure prediction
Protein structure prediction is the inference of the three-dimensional structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence—that is, the prediction of its secondary and tertiary structure from primary structure. Structure prediction is differen ...
and protein design
Protein design is the rational design of new protein molecules to design novel activity, behavior, or purpose, and to advance basic understanding of protein function. Proteins can be designed from scratch (''de novo'' design) or by making calcul ...
.
History
The first backbone-dependent rotamer library was developed in 1993 by Roland Dunbrack andMartin Karplus
Martin Karplus (born March 15, 1930) is an Austrian and American theoretical chemist. He is the Director of the Biophysical Chemistry Laboratory, a joint laboratory between the French National Center for Scientific Research and the University of ...
to assist the prediction of the Cartesian coordinates of a protein's side chains given the experimentally determined or predicted Cartesian coordinates of its main chain. The library was derived from the structures of 132 proteins from the Protein Data Bank
The Protein Data Bank (PDB) is a database for the three-dimensional structural data of large biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids. The data, typically obtained by X-ray crystallography, NMR spectroscopy, or, increasingly, c ...
with resolution
Resolution(s) may refer to:
Common meanings
* Resolution (debate), the statement which is debated in policy debate
* Resolution (law), a written motion adopted by a deliberative body
* New Year's resolution, a commitment that an individual ma ...
of 2.0 Å or better. The library provided the counts and frequencies of χ1 or χ1+χ2 rotamers of 18 amino acids (excluding glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid ( carbamic acid is unstable), with the chemical formula NH2‐ CH2‐ COOH. Glycine is one of the proteinog ...
and alanine
Alanine (symbol Ala or A), or α-alanine, is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an amine group and a carboxylic acid group, both attached to the central carbon atom which also carries a methyl group side ...
residue types, since they do not have a χ1 dihedral) for each 20° x 20° bin of the Ramachandran map (φ,ψ = -180° to -160°, -160° to -140° etc.).
In 1997, Dunbrack and Fred E. Cohen
Fred may refer to:
People
* Fred (name), including a list of people and characters with the name
Mononym
* Fred (cartoonist) (1931–2013), pen name of Fred Othon Aristidès, French
* Fred (footballer, born 1949) (1949–2022), Frederico Rodr ...
at the University of California, San Francisco
The University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) is a public land-grant research university in San Francisco, California. It is part of the University of California system and is dedicated entirely to health science and life science. It co ...
presented a backbone-dependent rotamer library derived from Bayesian statistics
Bayesian statistics is a theory in the field of statistics based on the Bayesian interpretation of probability where probability expresses a ''degree of belief'' in an event. The degree of belief may be based on prior knowledge about the event, ...
. The Bayesian approach provided the opportunity for the definition of a Bayesian prior for the frequencies of rotamers in each 10° x 10° bin derived by assuming that the steric and electrostatic effects of the φ and ψ dihedral angles are independent. In addition, a periodic kernel with 180° periodicity was used to count side chains 180° away in each direction from the bin of interest. As an exponent of a sin2 function, it behaved much like a von Mises distribution
In probability theory and directional statistics, the von Mises distribution (also known as the circular normal distribution or Tikhonov distribution) is a continuous probability distribution on the circle. It is a close approximation to the w ...
commonly used in directional statistics Directional statistics (also circular statistics or spherical statistics) is the subdiscipline of statistics that deals with directions (unit vectors in Euclidean space, R''n''), axes ( lines through the origin in R''n'') or rotations in R''n''. M ...
. The 1997 library was made publicly available via the World Wide Web in 1997, and found early use in protein structure prediction
Protein structure prediction is the inference of the three-dimensional structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence—that is, the prediction of its secondary and tertiary structure from primary structure. Structure prediction is differen ...
and protein design
Protein design is the rational design of new protein molecules to design novel activity, behavior, or purpose, and to advance basic understanding of protein function. Proteins can be designed from scratch (''de novo'' design) or by making calcul ...
. The library derived from Bayesian statistics was updated in 2002
 Many modeling programs, such as
Many modeling programs, such as Rosetta
Rosetta or Rashid (; ar, رشيد ' ; french: Rosette ; cop, ϯⲣⲁϣⲓⲧ ''ti-Rashit'', Ancient Greek: Βολβιτίνη ''Bolbitinē'') is a port city of the Nile Delta, east of Alexandria, in Egypt's Beheira governorate. The ...
, use a backbone-dependent rotamer library as a scoring function (usually in the form E=-ln(p(rotamer(''i'') , φ,ψ)) for the ''i''th rotamer, and optimize the backbone conformation of proteins by minimizing the rotamer energy with derivatives of the log probabilities with respect to φ,ψ. This requires smooth probability functions with smooth derivatives, because most mathematical optimization
Mathematical optimization (alternatively spelled ''optimisation'') or mathematical programming is the selection of a best element, with regard to some criterion, from some set of available alternatives. It is generally divided into two subfi ...
algorithms use first and sometimes second derivatives and will get stuck in local minima on rough surfaces. In 2011, Shapovalov and Dunbrack published a smoothed backbone-dependent rotamer library derived from kernel density estimates and kernel regressions with von Mises distribution
In probability theory and directional statistics, the von Mises distribution (also known as the circular normal distribution or Tikhonov distribution) is a continuous probability distribution on the circle. It is a close approximation to the w ...
kernels on the φ,ψ variables. The treatment of the non-rotameric degrees of freedom (those dihedral angles not about sp3-sp3 bonds, such as asparagine
Asparagine (symbol Asn or N) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the depro ...
and aspartate
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Like all other amino acids, it contains an amino group and a carboxylic acid. Its α-amino group is in the pro ...
χ2, phenylalanine
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F) is an essential α-amino acid with the formula . It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of alanine. This essential amino a ...
, tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Gr ...
, histidine
Histidine (symbol His or H) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated –NH3+ form under biological conditions), a carboxylic acid group (which is in the ...
, tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W)
is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromati ...
χ2, and glutamine
Glutamine (symbol Gln or Q) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Its side chain is similar to that of glutamic acid, except the carboxylic acid group is replaced by an amide. It is classified as a charge-neutral ...
and glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can syn ...
χ3) was improved by modeling the dihedral angle probability density of each of these dihedral angles as a function of χ1 rotamer (or χ1 and χ2 for Gln and Glu) and φ,ψ. The functions are essentially regressions of a periodic probability density on a torus
In geometry, a torus (plural tori, colloquially donut or doughnut) is a surface of revolution generated by revolving a circle in three-dimensional space about an axis that is coplanar with the circle.
If the axis of revolution does not ...
.
In addition to statistical analysis of structures in the Protein Data Bank
The Protein Data Bank (PDB) is a database for the three-dimensional structural data of large biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids. The data, typically obtained by X-ray crystallography, NMR spectroscopy, or, increasingly, c ...
, backbone-dependent rotamer libraries can also be derived from molecular dynamics
Molecular dynamics (MD) is a computer simulation method for analyzing the physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a fixed period of time, giving a view of the dynamic "evolution" of th ...
simulations of proteins, as demonstrated by the Dynameomics Library from Valerie Daggett
Valerie Daggett is a professor of bioengineering at the University of Washington in Seattle, Washington, United States.
Education and career
Daggett has a B.S. from Reed College. She received her Ph.D. from the University of California, San ...
's research group. Because these libraries are based on sampling from simulations, they can generate far larger numbers of data points across regions of the Ramachandran map that are sparsely populated in experimental structures, leading to higher statistical significance in these regions. Rotamer libraries derived from simulations are dependent on the force field used in the simulations. The Dynameomics Library is built on simulations using the ENCAD force field of Levitt et al. from 1995.
Backbone-dependence of rotamer populations
 The effect of backbone conformation on side-chain rotamer frequencies is primarily due to
The effect of backbone conformation on side-chain rotamer frequencies is primarily due to steric repulsion
Steric effects arise from the spatial arrangement of atoms. When atoms come close together there is a rise in the energy of the molecule. Steric effects are nonbonding interactions that influence the shape ( conformation) and reactivity of ions ...
s between backbone atoms whose position is dependent on φ and ψ and the side-chain γ heavy atoms (carbon, oxygen, or sulfur) of each residue type (PDB atom types CG, CG1, CG2, OG, OG1, SG). These occur in predictable combinations that depend on the dihedrals connecting the backbone atoms to the side-chain atoms. These steric interactions occur when the connecting dihedral angles form a pair of dihedral angles with values or , in a manner related to the phenomenon of pentane interference. For example, the nitrogen atom of residue i+1 is connected to the γ heavy atom of any side chain by a connected set of 5 atoms: N(i+1)-C(i)-Cα(i)-Cβ(i)-Cγ(i). The dihedral angle N(i+1)-C(i)-Cα(i)-Cβ(i) is equal to ψ+120°, and C(i)-Cα(i)-Cβ(i)-Cγ(i) is equal to χ1-120°. When ψ is -60° and χ1 is +60° (the g+ rotamer of a side chain), there is a steric interaction between N(i+1) and Cγ because the dihedral angles connecting them are N(i+1)-C(i)-Cα(i)-Cβ(i) = ψ+120° = +60°, and C(i)-Cα(i)-Cβ(i)-Cγ(i) = χ1-120° = -60°. The same interaction occurs when ψ is 0° and χ1 is 180° (the trans rotamer of a side chain). The carbonyl oxygen of residue i plays the same role when ψ=-60° for the g+ rotamer and when ψ=180° for the trans rotamer. Finally, φ-dependent interactions occur between the side-chain γ heavy atoms in g- and g+ rotamers on the one hand, and the carbonyl carbon of residue i-1 and a γ heavy atom, and between the backbone NH of residue i and its hydrogen-bonding partner on the other.
 The φ,ψ-dependent interactions of backbone atoms and side-chain Cγ atoms can be observed in the distribution of observations in the
The φ,ψ-dependent interactions of backbone atoms and side-chain Cγ atoms can be observed in the distribution of observations in the Ramachandran plot
In biochemistry, a Ramachandran plot (also known as a Rama plot, a Ramachandran diagram or a �,ψplot), originally developed in 1963 by G. N. Ramachandran, C. Ramakrishnan, and V. Sasisekharan, is a way to visualize energetically allowed region ...
of each χ1 rotamer (marked in the figure). At these positions, the Ramachandran populations of the rotamers are significantly reduced. They can be summarized as follows:
 Side-chain types with two heavy atoms (Val, Ile, Thr) have backbone-dependent interactions with both heavy atoms. Val has CG1 at χ1 and CG2 at χ1+120°. Because Val g+ and g- conformations have steric interactions with the backbone near ψ=120° and -60° (the most populated ψ ranges), Val is the only amino acid where the t rotamer (χ1~180°) is the most common. At most values of φ and ψ, only one rotamer of Val is allowed (shown in figure). Ile has CG1 at χ1 and CG2 at χ1-120°. Thr has OG1 at χ1 and CG2 at χ1-120°.
Side-chain types with two heavy atoms (Val, Ile, Thr) have backbone-dependent interactions with both heavy atoms. Val has CG1 at χ1 and CG2 at χ1+120°. Because Val g+ and g- conformations have steric interactions with the backbone near ψ=120° and -60° (the most populated ψ ranges), Val is the only amino acid where the t rotamer (χ1~180°) is the most common. At most values of φ and ψ, only one rotamer of Val is allowed (shown in figure). Ile has CG1 at χ1 and CG2 at χ1-120°. Thr has OG1 at χ1 and CG2 at χ1-120°.
Uses
The Dunbrack backbone-dependent rotamer library is used in a number of programs for protein structure prediction and computational design, including: * Side-chain conformation prediction in protein structure modeling ** Swiss-model and its software, ProMod3 **Rosetta
Rosetta or Rashid (; ar, رشيد ' ; french: Rosette ; cop, ϯⲣⲁϣⲓⲧ ''ti-Rashit'', Ancient Greek: Βολβιτίνη ''Bolbitinē'') is a port city of the Nile Delta, east of Alexandria, in Egypt's Beheira governorate. The ...
** I-TASSER
I-TASSER (Iterative Threading ASSEmbly Refinement) is a bioinformatics method for predicting three-dimensional structure model of protein molecules from amino acid sequences. It detects structure templates from the Protein Data Bank by a technique ...
** Phyre
Phyre and Phyre2 (Protein Homology/AnalogY Recognition Engine; pronounced as 'fire') are free web-based services for protein structure prediction. Phyre is among the most popular methods for protein structure prediction having been cited over 15 ...
** OEChem TK
** YASARA
*GalaxyRefine
ref name="HPS2013"/> *
SCWRL4
ref name="KSD2009"/> * Protein Design **
Rosetta
Rosetta or Rashid (; ar, رشيد ' ; french: Rosette ; cop, ϯⲣⲁϣⲓⲧ ''ti-Rashit'', Ancient Greek: Βολβιτίνη ''Bolbitinē'') is a port city of the Nile Delta, east of Alexandria, in Egypt's Beheira governorate. The ...
*EvoEF2
ref name="HZ2020"/> * Visualization of Protein Mutations **
PyMol
PyMOL is an open source but proprietary molecular visualization system created by Warren Lyford DeLano. It was commercialized initially by DeLano Scientific LLC, which was a private software company dedicated to creating useful tools that beco ...
** UCSF Chimera
UCSF Chimera (or simply Chimera) is an extensible program for interactive visualization and analysis of molecular structures and related data, including density maps, supramolecular assemblies, sequence alignments, docking results, trajectories, a ...
References
{{Reflist, refs= {{cite journal , last1=Huang , first1=X , last2=Pearce , first2=R , last3=Zhang , first3=Y , title=Toward the Accuracy and Speed of Protein Side-Chain Packing: A Systematic Study on Rotamer Libraries. , journal=Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling , date=2020 , volume=60 , issue=1 , pages=410–420 , doi=10.1021/acs.jcim.9b00812 , pmid=31851497 , pmc=7938712 , url=https://par.nsf.gov/servlets/purl/10167312 , access-date=18 February 2021 {{cite journal , last1=Alford , first1=RF , last2=Leaver-Fay , first2=A , last3=Jeliazkov , first3=JR , last4=O'Meara , first4=MJ , last5=DiMaio , first5=FP , last6=Park , first6=H , last7=Shapovalov , first7=MV , last8=Renfrew , first8=PD , last9=Mulligan , first9=VK , last10=Kappel , first10=K , last11=Labonte , first11=JW , last12=Pacella , first12=MS , last13=Bonneau , first13=R , last14=Bradley , first14=P , last15=Dunbrack , first15=RL , last16=Das , first16=R , last17=Baker , first17=D , last18=Kuhlman , first18=B , last19=Kortemme , first19=T , last20=Gray , first20=JJ , title=The Rosetta All-Atom Energy Function for Macromolecular Modeling and Design. , journal=Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation , date=13 June 2017 , volume=13 , issue=6 , pages=3031–3048 , doi=10.1021/acs.jctc.7b00125 , pmid=28430426, pmc=5717763 {{cite journal , last1=Dunbrack , first1=RL, Jr. , last2=Karplus , first2=M , title=Backbone-dependent rotamer library for proteins. Application to side-chain prediction. , journal=Journal of Molecular Biology , date=1993 , volume=230 , issue=2 , pages=543–74 , doi=10.1006/jmbi.1993.1170 , pmid=8464064 {{cite journal , last1=Dunbrack , first1=RL, Jr. , last2=Karplus , first2=M , title=Conformational analysis of the backbone-dependent rotamer preferences of protein sidechains , journal=Nature Structural Biology , date=1994 , volume=1 , issue=5 , pages=334–340 , doi=10.1038/nsb0594-334 , pmid=7664040 , s2cid=9157373 , url=https://www.nature.com/articles/nsb0594-334 , issn=1545-9985 {{cite journal , last1=Dunbrack , first1=RL, Jr. , last2=Cohen , first2=FE , title=Bayesian statistical analysis of protein side-chain rotamer preferences. , journal=Protein Science , date=1997 , volume=6 , issue=8 , pages=1661–81 , doi=10.1002/pro.5560060807 , pmid=9260279, pmc=2143774 {{cite journal , last1=Bower , first1=MJ , last2=Cohen , first2=FE , last3=Dunbrack , first3=RL, Jr , title=Prediction of protein side-chain rotamers from a backbone-dependent rotamer library: a new homology modeling tool. , journal=Journal of Molecular Biology , date=1997 , volume=267 , issue=5 , pages=1268–82 , doi=10.1006/jmbi.1997.0926 , pmid=9150411 {{cite journal , last1=Dunbrack , first1=RL, Jr , title=Rotamer libraries in the 21st century. , journal=Current Opinion in Structural Biology , date=2002 , volume=12 , issue=4 , pages=431–40 , doi=10.1016/s0959-440x(02)00344-5 , pmid=12163064 {{cite journal , last1=Shapovalov , first1=MV , last2=Dunbrack , first2=RL, Jr , title=A smoothed backbone-dependent rotamer library for proteins derived from adaptive kernel density estimates and regressions. , journal=Structure (Cell Press) , date=2011 , volume=19 , issue=6 , pages=844–58 , doi=10.1016/j.str.2011.03.019 , pmid=21645855, pmc=3118414 {{cite journal , last1=Kuhlman , first1=B , last2=Baker , first2=D , title=Native protein sequences are close to optimal for their structures. , journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America , date=2000 , volume=97 , issue=19 , pages=10383–8 , doi=10.1073/pnas.97.19.10383 , pmid=10984534, pmc=27033 , bibcode=2000PNAS...9710383K , doi-access=free {{cite journal , last1=Waterhouse , first1=A , last2=Bertoni , first2=M , last3=Bienert , first3=S , last4=Studer , first4=G , last5=Tauriello , first5=G , last6=Gumienny , first6=R , last7=Heer , first7=FT , last8=de Beer , first8=TAP , last9=Rempfer , first9=C , last10=Bordoli , first10=L , last11=Lepore , first11=R , last12=Schwede , first12=T , title=SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. , journal=Nucleic Acids Research , date=2018 , volume=46 , issue=W1 , pages=W296–W303 , doi=10.1093/nar/gky427 , pmid=29788355 , pmc=6030848 , url= {{cite web , last1=Pettersen , first1=EF , last2=Goddard , first2=TD , last3=Huang , first3=CC , last4=Meng , first4=EC , last5=Couch , first5=GS , last6=Croll , first6=TI , last7=Morris , first7=JH , last8=Ferrin , first8=TE , title=Rotamer Tools (ChimeraX) , url=https://www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimerax/docs/user/tools/rotamers.html , website=The ChimeraX User Guide , publisher=Regents of the University of California , access-date=9 February 2021 {{cite journal , last1=Heo , first1=L , last2=Park , first2=H , last3=Seok , first3=C , title=GalaxyRefine: Protein structure refinement driven by side-chain repacking. , journal=Nucleic Acids Research , date=2013 , volume=41 , issue=Web Server issue , pages=W384-8 , doi=10.1093/nar/gkt458 , pmid=23737448 , pmc=3692086 , url= {{cite journal , last1=Kelley , first1=LA , last2=Mezulis , first2=S , last3=Yates , first3=CM , last4=Wass , first4=MN , last5=Sternberg , first5=MJ , title=The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. , journal=Nature Protocols , date=2015 , volume=10 , issue=6 , pages=845–58 , doi=10.1038/nprot.2015.053 , pmid=25950237 , pmc=5298202 , url= {{cite web , last1=Kulp , first1=Daniel W. , title=Rotamer Toggle - PyMOLWiki , url=https://pymolwiki.org/index.php/Rotamer_Toggle , website=pymolwiki.org , publisher=SBGrid Consortium , access-date=10 February 2021 {{cite journal , last1=Huang , first1=X , last2=Pearce , first2=R , last3=Zhang , first3=Y , title=EvoEF2: accurate and fast energy function for computational protein design. , journal=Bioinformatics , date=2020 , volume=36 , issue=4 , pages=1135–1142 , doi=10.1093/bioinformatics/btz740 , pmid=31588495, pmc=7144094 {{cite web , last1=OpenEye Scientific Software , title=Macromolecule Conformations — Toolkits -- Java , url=https://docs.eyesopen.com/toolkits/java/oechemtk/mmolconformations.html , website=OEChem Toolkit 3.1.0.0 , access-date=10 February 2021 {{cite web , last1=Krieger , first1=E , title=Protein side-chain modeling in YASARA , url=http://www.yasara.org/sidechains.htm , website=www.yasara.org , publisher=Yasara Biosciences , access-date=10 February 2021 {{cite journal , last1=Krivov , first1=Georgii G. , last2=Shapovalov , first2=Maxim V. , last3=Dunbrack , first3=Roland L. , title=Improved prediction of protein side-chain conformations with SCWRL4 , journal=Proteins: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics , date=2009 , volume=77 , issue=4 , pages=778–795 , doi=10.1002/prot.22488 , pmid=19603484 , pmc=2885146 , url=, issn=1097-0134 {{cite journal , last1=Studer , first1=G , last2=Tauriello , first2=G , last3=Bienert , first3=S , last4=Biasini , first4=M , last5=Johner , first5=N , last6=Schwede , first6=T , title=ProMod3-A versatile homology modelling toolbox. , journal=PLOS Computational Biology , date=2021 , volume=17 , issue=1 , pages=e1008667 , doi=10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008667 , pmid=33507980 , pmc=7872268 , bibcode=2021PLSCB..17E8667S {{cite journal , last1=Towse , first1=Clare-Louise , last2=Rysavy , first2=Steven J. , last3=Vulovic , first3=Ivan M. , last4=Daggett , first4=Valerie , title=New Dynamic Rotamer Libraries: Data-Driven Analysis of Side-Chain Conformational Propensities , journal=Structure , date=5 January 2016 , volume=24 , issue=1 , pages=187–199 , doi=10.1016/j.str.2015.10.017 , pmid=26745530 , pmc=4715459 , issn=0969-2126 {{cite journal , last1=Levitt , first1=Michael , last2=Hirshberg , first2=Miriam , last3=Sharon , first3=Ruth , last4=Daggett , first4=Valerie , title=Potential energy function and parameters for simulations of the molecular dynamics of proteins and nucleic acids in solution , journal=Computer Physics Communications , date=1995 , volume=91 , issue=1 , pages=215–231 , doi=10.1016/0010-4655(95)00049-L , bibcode=1995CoPhC..91..215LExternal Links
Dunbrack 2010 Backbone-Dependent Rotamer Library
Protein Side-chain Conformational Analysis
Richardson Backbone-Independent Rotamer Libraries
Dynameomics Backbone-Independent and Backbone-Dependent Rotamer Libraries
Protein structure Bioinformatics Molecular modelling