Babur on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Babur (; 14 February 148326 December 1530; born Zahīr ud-Dīn Muhammad) was the founder of the
 He thus assumed the title of '' Padshah'' (emperor) among the Timurids—though this title was insignificant since most of his ancestral lands were taken, Kabul itself was in danger and Shaybani continued to be a threat. Babur prevailed during a potential rebellion in Kabul, but two years later a revolt among some of his leading generals drove him out of Kabul. Escaping with very few companions, Babur soon returned to the city, capturing Kabul again and regaining the allegiance of the rebels. Meanwhile, Shaybani was defeated and killed by Ismail I, Shah of Shia Safavid Persia, in 1510.
Babur and the remaining Timurids used this opportunity to reconquer their ancestral territories. Over the following few years, Babur and Shah Ismail formed a partnership in an attempt to take over parts of Central Asia. In return for Ismail's assistance, Babur permitted the Safavids to act as a suzerain over him and his followers. Thus, in 1513, after leaving his brother Nasir Mirza to rule Kabul, he managed to take Samarkand for the third time; he also took Bokhara but lost both again to the Uzbeks. Shah Ismail reunited Babur with his sister Khānzāda, who had been imprisoned by and forced to marry the recently deceased Shaybani. Babur returned to Kabul after three years in 1514. The following 11 years of his rule mainly involved dealing with relatively insignificant rebellions from Afghan tribes, his nobles and relatives, in addition to conducting raids across the eastern mountains. Babur began to modernise and train his army despite it being, for him, relatively peaceful times.
He thus assumed the title of '' Padshah'' (emperor) among the Timurids—though this title was insignificant since most of his ancestral lands were taken, Kabul itself was in danger and Shaybani continued to be a threat. Babur prevailed during a potential rebellion in Kabul, but two years later a revolt among some of his leading generals drove him out of Kabul. Escaping with very few companions, Babur soon returned to the city, capturing Kabul again and regaining the allegiance of the rebels. Meanwhile, Shaybani was defeated and killed by Ismail I, Shah of Shia Safavid Persia, in 1510.
Babur and the remaining Timurids used this opportunity to reconquer their ancestral territories. Over the following few years, Babur and Shah Ismail formed a partnership in an attempt to take over parts of Central Asia. In return for Ismail's assistance, Babur permitted the Safavids to act as a suzerain over him and his followers. Thus, in 1513, after leaving his brother Nasir Mirza to rule Kabul, he managed to take Samarkand for the third time; he also took Bokhara but lost both again to the Uzbeks. Shah Ismail reunited Babur with his sister Khānzāda, who had been imprisoned by and forced to marry the recently deceased Shaybani. Babur returned to Kabul after three years in 1514. The following 11 years of his rule mainly involved dealing with relatively insignificant rebellions from Afghan tribes, his nobles and relatives, in addition to conducting raids across the eastern mountains. Babur began to modernise and train his army despite it being, for him, relatively peaceful times.
 Babur still wanted to escape from the Uzbeks, and he chose India as a refuge instead of Badakhshan, which was to the north of Kabul. He wrote, "In the presence of such power and potency, we had to think of some place for ourselves and, at this crisis and in the crack of time there was, put a wider space between us and the strong foeman." After his third loss of Samarkand, Babur gave full attention to the conquest of North India, launching a campaign; he reached the Chenab River, now in
Babur still wanted to escape from the Uzbeks, and he chose India as a refuge instead of Badakhshan, which was to the north of Kabul. He wrote, "In the presence of such power and potency, we had to think of some place for ourselves and, at this crisis and in the crack of time there was, put a wider space between us and the strong foeman." After his third loss of Samarkand, Babur gave full attention to the conquest of North India, launching a campaign; he reached the Chenab River, now in
 In November 1525, Babur got news at
In November 1525, Babur got news at
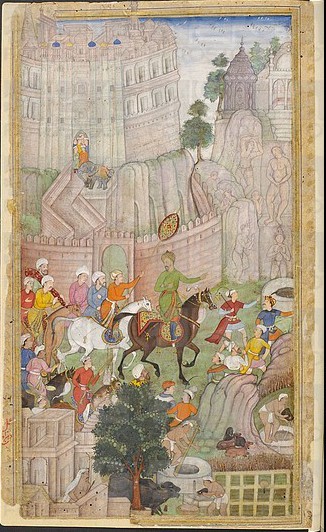 The Battle of Khanwa was fought between Babur and the Rajput ruler of Mewar,
The Battle of Khanwa was fought between Babur and the Rajput ruler of Mewar,
 Babur was an acclaimed writer, who had a profound love for literature. His library was one of his most beloved possessions that he always carried around with him, and books were one of the treasures he searched for in new conquered lands. In his memoirs, when he listed sovereigns and nobles of a conquered land, he also mentioned poets, musicians and other educated people.
Even though he died aged 47, Babur left a rich literary and scientific heritage. He authored his famous memoir the Bāburnāma, as well as beautiful lyrical works or ''ghazals'', treatises on Muslim jurisprudence (Mubayyin), poetics (Aruz risolasi), music, and a special
Babur was an acclaimed writer, who had a profound love for literature. His library was one of his most beloved possessions that he always carried around with him, and books were one of the treasures he searched for in new conquered lands. In his memoirs, when he listed sovereigns and nobles of a conquered land, he also mentioned poets, musicians and other educated people.
Even though he died aged 47, Babur left a rich literary and scientific heritage. He authored his famous memoir the Bāburnāma, as well as beautiful lyrical works or ''ghazals'', treatises on Muslim jurisprudence (Mubayyin), poetics (Aruz risolasi), music, and a special
I am become a desert wanderer for Islam,
Having joined battle with infidels and Hindus
I readied myself to become a martyr,
God be thanked I am become a ghazi.
 It is generally agreed that, as a Timurid, Babur was not only significantly influenced by the Persian culture, but also that his empire gave rise to the expansion of the Persianate ethos in the Indian subcontinent. He emerged in his own telling as a
It is generally agreed that, as a Timurid, Babur was not only significantly influenced by the Persian culture, but also that his empire gave rise to the expansion of the Persianate ethos in the Indian subcontinent. He emerged in his own telling as a
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an Early modern period, early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to ...
in the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; August 1227), also known as Chinggis Khan, was the founder and first khan (title), khan of the Mongol Empire. After spending most of his life uniting the Mongols, Mongol tribes, he launched Mongol invasions and ...
through his father and mother respectively. He was also given the posthumous name
A posthumous name is an honorary Personal name, name given mainly to revered dead people in East Asian cultural sphere, East Asian culture. It is predominantly used in Asian countries such as China, Korea, Vietnam, Japan, Malaysia and Thailand. ...
of ''Firdaws Makani'' ('Dwelling in Paradise').
Born in Andijan
Andijan ( ), also spelt Andijon () and formerly romanized as Andizhan ( ), is a city in Uzbekistan. It is the administrative, economic, and cultural center of Andijan Region. Andijan is a district-level city with an area of . Andijan is the most ...
in the Fergana Valley (now in Uzbekistan
, image_flag = Flag of Uzbekistan.svg
, image_coat = Emblem of Uzbekistan.svg
, symbol_type = Emblem of Uzbekistan, Emblem
, national_anthem = "State Anthem of Uzbekistan, State Anthem of the Republ ...
), Babur was the eldest son of Umar Shaikh Mirza II (1456–1494, Timurid governor of Fergana
Fergana ( uz-Latn-Cyrl, Fargʻona, Фарғона, ), () or Ferghana, also Farghana is a district-level city and the capital of Fergana Region in eastern Uzbekistan. Fergana is about 320 km east of Tashkent, about 75 km southwest of A ...
from 1469 to 1494) and a great-great-great-grandson of Timur (1336–1405). Babur ascended the throne of Fergana in its capital Akhsikath in 1494 at the age of twelve and faced rebellion. He conquered Samarkand
Samarkand ( ; Uzbek language, Uzbek and Tajik language, Tajik: Самарқанд / Samarqand, ) is a city in southeastern Uzbekistan and among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in Central As ...
two years later, only to lose Fergana soon after. In his attempt to reconquer Fergana, he lost control of Samarkand. In 1501, his attempt to recapture both the regions failed when the Uzbek prince Muhammad Shaybani defeated him and founded the Khanate of Bukhara.
In 1504, he conquered Kabul
Kabul is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province. The city is divided for administration into #Districts, 22 municipal districts. A ...
, which was under the putative rule of Abdur Razaq Mirza, the infant heir of Ulugh Beg II. Babur formed a partnership with the Safavid emperor Ismail I and reconquered parts of Turkestan, including Samarkand, only to again lose it and the other newly conquered lands to the Shaybanids
The Shibanids or Shaybanids, more accurately known as the Abul-Khayrid-Shibanids, were a dynasty of Uzbek ( Turko-Mongol) origin who ruled over the Khanate of Bukhara (from 1505 to 1598), the Khanate of Khwarezm (Khiva) (from 1511 to 1695), a ...
.
After losing Samarkand for the third time, Babur turned his attention to India and employed aid from the neighbouring Safavid and Ottoman empires. Quote: "Babur then adroitly gave the Ottomans his promise not to attack them in return for their military aid, which he received in the form of the newest of battlefield inventions, the matchlock gun and cast cannons, as well as instructors to train his men to use them." He defeated Ibrahim Lodi, the Sultan of Delhi, at the First Battle of Panipat
The First Battle of Panipat, on 21 April 1526 was fought between the invading forces of Babur against Ibrahim Khan Lodi, the List of sultans of Delhi, Sultan of Delhi, in North India. Babur's forces, em ...
in 1526 and founded the Mughal Empire. Before the defeat of Lodi at Delhi, the Sultanate of Delhi had been a spent force, long in a state of decline.
The rival adjacent Kingdom of Mewar under the rule of Rana Sanga
Sangram Singh I (12 April 1482 – 30 January 1528), most commonly known as Rana Sanga, was the Rana of Mewar, Maharana of Mewar from 1509 to 1528. A member of the List of Ranas of Mewar, Sisodia dynasty, he controlled parts of present-day Ra ...
had become one of the most powerful states in North India. Sanga unified several Rajput clans for the first time since Prithviraj Chauhan and advanced on Babur with a grand coalition of 80,000-100,000 Rajputs, engaging Babur in the Battle of Khanwa. Babur arrived at Khanwa with 40,000-50,000 soldiers. Nonetheless, Sanga suffered a major defeat due to Babur's skillful troop positioning and use of gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, charcoal (which is mostly carbon), and potassium nitrate, potassium ni ...
, specifically matchlock
A matchlock or firelock is a historical type of firearm wherein the gunpowder is ignited by a burning piece of flammable cord or twine that is in contact with the gunpowder through a mechanism that the musketeer activates by pulling a lever or Tri ...
s and small cannon
A cannon is a large-caliber gun classified as a type of artillery, which usually launches a projectile using explosive chemical propellant. Gunpowder ("black powder") was the primary propellant before the invention of smokeless powder during th ...
s. The battle was one of the most decisive events in Indian history, more so than the First Battle of Panipat, as the defeat of Rana Sanga was a watershed event in the Mughal conquest of North India.
Religiously, Babur started his life as a staunch Sunni Muslim, but he underwent significant evolution. Babur became more tolerant as he conquered new territories and grew older, allowing other religions to peacefully coexist in his empire and at his court. He also displayed a certain attraction to theology, poetry, geography
Geography (from Ancient Greek ; combining 'Earth' and 'write', literally 'Earth writing') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding o ...
, history, and biology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and ...
—disciplines he promoted at his court—earning him a frequent association with representatives of the Timurid Renaissance
The Timurid Renaissance was a historical period in Asian history, Asian and Islamic history spanning the late 14th, the 15th, and the early 16th centuries. Following the Islamic Golden Age, the Timurid Empire, based in Central Asia and ruled by ...
. His religious and philosophical stances are characterized as humanistic
Humanism is a philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential, and agency of human beings, whom it considers the starting point for serious moral and philosophical inquiry.
The meaning of the term "humanism" ha ...
.
Babur married several times. Notable among his children were Humayun, Kamran Mirza, Hindal Mirza, Masuma Sultan Begum, and the author Gulbadan Begum. Babur died in 1530 in Agra
Agra ( ) is a city on the banks of the Yamuna river in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, about south-east of the national capital Delhi and 330 km west of the state capital Lucknow. With a population of roughly 1.6 million, Agra is the ...
and Humayun succeeded him. Babur was first buried in Agra but, as per his wishes, his remains were moved to Kabul and reburied. He ranks as a national hero in Uzbekistan
, image_flag = Flag of Uzbekistan.svg
, image_coat = Emblem of Uzbekistan.svg
, symbol_type = Emblem of Uzbekistan, Emblem
, national_anthem = "State Anthem of Uzbekistan, State Anthem of the Republ ...
and Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan, officially the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia lying in the Tian Shan and Pamir Mountains, Pamir mountain ranges. Bishkek is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Kyrgyzstan, largest city. Kyrgyz ...
. Many of his poems have become popular folk songs. He wrote the ''Baburnama
The ''Bāburnāma'' (; ) is the memoirs of Babur, Ẓahīr-ud-Dīn Muhammad Bābur (1483–1530), founder of the Mughal Empire and a great-great-great-grandson of Timur. It is written in the Chagatai language, known to Babur as ''Türki'' "Turkic ...
'' in Chaghatai Turkic; it was translated into Persian during the reign (1556–1605) of his grandson, the emperor Akbar.
Name
''Ẓahīr-ud-Dīn'' is Arabic for "Defender of the Faith" (ofIslam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
), and ''Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of A ...
'' honours the Islamic prophet
Prophets in Islam () are individuals in Islam who are believed to spread God's message on Earth and serve as models of ideal human behaviour. Some prophets are categorized as messengers (; sing. , ), those who transmit divine revelation, mos ...
. The name was chosen for Babur by the Sufi
Sufism ( or ) is a mysticism, mystic body of religious practice found within Islam which is characterized by a focus on Islamic Tazkiyah, purification, spirituality, ritualism, and Asceticism#Islam, asceticism.
Practitioners of Sufism are r ...
saint Khwaja Ahrar, who was the spiritual master of his father. The difficulty of pronouncing the name for his Central Asian Turco-Mongol army may have been responsible for the greater popularity of his nickname Babur, also variously spelled Baber, Babar, and Bābor. The name is generally taken in reference to the Persian word ''babur'' (), meaning "tiger" or "panther". The word repeatedly appears in Ferdowsi
Abu'l-Qâsem Ferdowsi Tusi (also Firdawsi, ; 940 – 1019/1025) was a Persians, Persian poet and the author of ''Shahnameh'' ("Book of Kings"), which is one of the world's longest epic poetry, epic poems created by a single poet, and the gre ...
's ''Shahnameh
The ''Shahnameh'' (, ), also transliterated ''Shahnama'', is a long epic poem written by the Persian literature, Persian poet Ferdowsi between and 1010 CE and is the national epic of Greater Iran. Consisting of some 50,000 distichs or couple ...
'' and was borrowed into the Turkic languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of more than 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and West Asia. The Turkic langua ...
of Central Asia.
Background
Babur's memoirs form the main source for details of his life. They are known as the ''Baburnama
The ''Bāburnāma'' (; ) is the memoirs of Babur, Ẓahīr-ud-Dīn Muhammad Bābur (1483–1530), founder of the Mughal Empire and a great-great-great-grandson of Timur. It is written in the Chagatai language, known to Babur as ''Türki'' "Turkic ...
'' and were written in Chagatai, his first language
A first language (L1), native language, native tongue, or mother tongue is the first language a person has been exposed to from birth or within the critical period hypothesis, critical period. In some countries, the term ''native language'' ...
, though, according to Dale, "his Turkic prose is highly Persianized in its sentence structure, morphology or word formation and vocabulary." ''Baburnama'' was translated into Persian during the rule of Babur's grandson Akbar.
Babur was born on 14 February 1483 in the city of Andijan
Andijan ( ), also spelt Andijon () and formerly romanized as Andizhan ( ), is a city in Uzbekistan. It is the administrative, economic, and cultural center of Andijan Region. Andijan is a district-level city with an area of . Andijan is the most ...
, Fergana Valley, contemporary Uzbekistan. He was the eldest son of Umar Shaikh Mirza II, ruler of the Fergana Valley, the son of Abū Saʿīd Mirza (and grandson of Miran Shah
Mirza Jalal-ud-din Miran Shah Beg (1366 – 20 April 1408), commonly known as Miran Shah (), was a son of the Central Asian conqueror Timur, founder of the Timurid Empire.
During his father's reign, Miran Shah was initially a powerful regio ...
, who was himself son of Timur) and his wife Qutlugh Nigar Khanum, daughter of Yunus Khan, the ruler of Moghulistan (a descendant of Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; August 1227), also known as Chinggis Khan, was the founder and first khan (title), khan of the Mongol Empire. After spending most of his life uniting the Mongols, Mongol tribes, he launched Mongol invasions and ...
).
Babur hailed from the Turkic Barlas
The Barlas (;Grupper, S. M. 'A Barulas Family Narrative in the Yuan Shih: Some Neglected Prosopographical and Institutional Sources on Timurid Origins'. Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi 8 (1992–94): 11–97 Chagatay language, Chagatay/ ''Barlās'' ...
tribe, which was of Mongol origin and had embraced the Turco-Persian tradition
The composite Turko-Persian, Turco-Persian,
''Turko-Persia in historical perspective'', Cambridge University Press, ...
They had also converted to Islam centuries earlier and resided in Turkestan and Khorasan.
Aside from the Chaghatai Turkic, Babur was equally fluent in ''Turko-Persia in historical perspective'', Cambridge University Press, ...
Classical Persian
Persian ( ), also known by its endonym Farsi (, Fārsī ), is a Western Iranian language belonging to the Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian subdivision of the Indo-European languages. Persian is a pluricentric language predominantly spoke ...
, the lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, link language or language of wider communication (LWC), is a Natural language, language systematically used to make co ...
of the Timurid elite.
Some of Babur's relatives, such as his uncles Mahmud Khan (Moghul Khan)
Sultan Mahmud Khan (Chagatai language, Chagatai and Persian language, Persian: سلطان محمود خان; b. 1464 – d. 1508), was Khan of Tashkent (1487–1502 or 1503) and of the Moghuls of western Moghulistan (1487–1508). He was the eldes ...
and Ahmad Khan, continued to identify as Mongols, and allowed him to use their Mongol troops to help recover his fortunes in the turbulent years that followed.
Hence, Babur, though nominally a Mongol (or ''Moghul'' in Persian language), drew much of his support from the local Turkic and Iranian people of Central Asia, and his army was diverse in its ethnic makeup. It included Sarts, Tajiks
Tajiks (; ; also spelled ''Tadzhiks'' or ''Tadjiks'') is the name of various Persian-speaking Eastern Iranian groups of people native to Central Asia, living primarily in Afghanistan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. Even though the term ''Tajik'' ...
, ethnic Afghans, Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of yea ...
, as well as Barlas and Chaghatayid Turko-Mongols from Central Asia.
Ruler of Central Asia
As Timurid ruler of Fergana
In 1494, eleven-year-old Babur became the Timurid ruler of Fergana, in present-day Uzbekistan, after his father Umar Sheikh Mirza died "while tending pigeons in an ill-constructeddovecote
A dovecote or dovecot , doocot (Scots Language, Scots) or columbarium is a structure intended to house Domestic pigeon, pigeons or doves. Dovecotes may be free-standing structures in a variety of shapes, or built into the end of a house or b ...
that toppled into the ravine
A ravine is a landform that is narrower than a canyon and is often the product of streambank erosion. Ravines are typically classified as larger in scale than gullies, although smaller than valleys. Ravines may also be called a cleuch, dell, ...
below the palace". During this time, two of his uncles from the neighbouring kingdoms, who were hostile to his father, and a group of nobles who wanted his younger brother Jahangir to be the ruler, threatened his succession to the throne. His uncles were relentless in their attempts to dislodge him from this position as well as from many of his other territorial possessions to come. Babur was able to secure his throne mainly because of help from his maternal grandmother, Aisan Daulat Begum, although there was also some luck involved.
Most territories around his kingdom were ruled by his relatives, who were descendants of either Timur or Genghis Khan, and were constantly in conflict. At that time, rival princes were fighting over the city of Samarkand to the west, which was ruled by his paternal cousin. Babur had a great ambition to capture the city. In 1497, he besieged Samarkand for seven months before eventually gaining control over it. He was fifteen years old and for him the campaign was a huge achievement. Babur was able to hold the city despite desertions in his army, but he later fell seriously ill. Meanwhile, a rebellion back home, approximately away, amongst nobles who favoured his brother, robbed him of Fergana. As he was marching to recover it, he left Samarkand to Sultan Mahmud Mirza, leaving him with neither territory in his possession. He had held Samarkand for 100 days, and he considered this defeat as his biggest loss, obsessing over it even later in his life after his conquests in India.
For three years, Babur concentrated on building a strong army, recruiting widely amongst the Tajiks of Badakhshan in particular. In 1500–1501, he again laid siege to Samarkand, and indeed he took the city briefly, but he was in turn besieged by his most formidable rival, Muhammad Shaybani, Khan of the Uzbeks. The situation became such that Babar was compelled to give his sister, Khanzada, to Shaybani in marriage as part of the peace settlement. Only after this were Babur and his troops allowed to depart the city in safety. Samarkand, his lifelong obsession, was thus lost again. He then tried to reclaim Fergana, but lost the battle there also and, escaping with a small band of followers, he wandered the mountains of central Asia and took refuge with hill tribes. By 1502, he had resigned all hopes of recovering Fergana; he was left with nothing and was forced to try his luck elsewhere. He finally went to Tashkent
Tashkent (), also known as Toshkent, is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Uzbekistan, largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of more than 3 million people as of April 1, 2024. I ...
, which was ruled by his maternal uncle, but he found himself less than welcome there. Babur wrote, "During my stay in Tashkent, I endured much poverty and humiliation. No country, or hope of one!" Thus, during the ten years since becoming the ruler of Fergana, Babur suffered many short-lived victories and was without shelter and in exile, aided by friends and peasants.
At Kabul
Kabul was ruled by Babur's paternal uncle Ulugh Beg II, who died leaving only an infant as heir. The city was then claimed by Mukin Begh, who was considered to be a usurper and was opposed by the local populace. In 1504, Babur was able to cross the snowyHindu Kush
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range in Central Asia, Central and South Asia to the west of the Himalayas. It stretches from central and eastern Afghanistan into northwestern Pakistan and far southeastern Tajikistan. The range forms the wester ...
mountains and capture Kabul from the remaining Arghunids, who were forced to retreat to Kandahar. With this move, he gained a new kingdom, re-established his fortunes and would remain its ruler until 1526. In 1505, because of the low revenue generated by his new mountain kingdom, Babur began his first expedition to India; in his memoirs, he wrote, "My desire for Hindustan had been constant. It was in the month of Shaban, the Sun being in Aquarius, that we rode out of Kabul for Hindustan". It was a brief raid across the Khyber Pass
The Khyber Pass (Urdu: درۂ خیبر; ) is a mountain pass in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan, on the border with the Nangarhar Province of Afghanistan. It connects the town of Landi Kotal to the Valley of Peshawar at Jamrud by tr ...
.
In the same year, Babur united with Sultan Husayn Mirza Bayqarah of Herat
Herāt (; Dari/Pashto: هرات) is an oasis city and the third-largest city in Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Se ...
, a fellow Timurid and distant relative, against their common enemy, the Uzbek Shaybani. However, this venture did not take place because Husayn Mirza died in 1506 and his two sons were reluctant to go to war. Babur instead stayed at Herat after being invited by the two Mirza brothers. It was then the cultural capital of the eastern Muslim world. Though he was disgusted by the vices and luxuries of the city, he marvelled at the intellectual abundance there, which he stated was "filled with learned and matched men". He became acquainted with the work of the Chagatai poet Mir Ali Shir Nava'i, who encouraged the use of Chagatai as a literary language
Literary language is the Register (sociolinguistics), register of a language used when writing in a formal, academic writing, academic, or particularly polite tone; when speaking or writing in such a tone, it can also be known as formal language. ...
. Nava'i's proficiency with the language, which he is credited with founding, may have influenced Babur in his decision to use it for his memoirs. He spent two months there before being forced to leave because of diminishing resources; it later was overrun by Shaybani and the Mirzas fled.
Babur became the only reigning ruler of the Timurid dynasty after the loss of Herat, and many princes sought refuge with him at Kabul because of Shaybani's invasion in the west.
 He thus assumed the title of '' Padshah'' (emperor) among the Timurids—though this title was insignificant since most of his ancestral lands were taken, Kabul itself was in danger and Shaybani continued to be a threat. Babur prevailed during a potential rebellion in Kabul, but two years later a revolt among some of his leading generals drove him out of Kabul. Escaping with very few companions, Babur soon returned to the city, capturing Kabul again and regaining the allegiance of the rebels. Meanwhile, Shaybani was defeated and killed by Ismail I, Shah of Shia Safavid Persia, in 1510.
Babur and the remaining Timurids used this opportunity to reconquer their ancestral territories. Over the following few years, Babur and Shah Ismail formed a partnership in an attempt to take over parts of Central Asia. In return for Ismail's assistance, Babur permitted the Safavids to act as a suzerain over him and his followers. Thus, in 1513, after leaving his brother Nasir Mirza to rule Kabul, he managed to take Samarkand for the third time; he also took Bokhara but lost both again to the Uzbeks. Shah Ismail reunited Babur with his sister Khānzāda, who had been imprisoned by and forced to marry the recently deceased Shaybani. Babur returned to Kabul after three years in 1514. The following 11 years of his rule mainly involved dealing with relatively insignificant rebellions from Afghan tribes, his nobles and relatives, in addition to conducting raids across the eastern mountains. Babur began to modernise and train his army despite it being, for him, relatively peaceful times.
He thus assumed the title of '' Padshah'' (emperor) among the Timurids—though this title was insignificant since most of his ancestral lands were taken, Kabul itself was in danger and Shaybani continued to be a threat. Babur prevailed during a potential rebellion in Kabul, but two years later a revolt among some of his leading generals drove him out of Kabul. Escaping with very few companions, Babur soon returned to the city, capturing Kabul again and regaining the allegiance of the rebels. Meanwhile, Shaybani was defeated and killed by Ismail I, Shah of Shia Safavid Persia, in 1510.
Babur and the remaining Timurids used this opportunity to reconquer their ancestral territories. Over the following few years, Babur and Shah Ismail formed a partnership in an attempt to take over parts of Central Asia. In return for Ismail's assistance, Babur permitted the Safavids to act as a suzerain over him and his followers. Thus, in 1513, after leaving his brother Nasir Mirza to rule Kabul, he managed to take Samarkand for the third time; he also took Bokhara but lost both again to the Uzbeks. Shah Ismail reunited Babur with his sister Khānzāda, who had been imprisoned by and forced to marry the recently deceased Shaybani. Babur returned to Kabul after three years in 1514. The following 11 years of his rule mainly involved dealing with relatively insignificant rebellions from Afghan tribes, his nobles and relatives, in addition to conducting raids across the eastern mountains. Babur began to modernise and train his army despite it being, for him, relatively peaceful times.
Foreign relations
Determined to conquer the Uzbeks and recapture his ancestral homeland, Babur was wary of their allies theOttomans
Ottoman may refer to:
* Osman I, historically known in English as "Ottoman I", founder of the Ottoman Empire
* Osman II, historically known in English as "Ottoman II"
* Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empir ...
, and made no attempt to establish formal diplomatic relations with them. He did, however, employ the matchlock
A matchlock or firelock is a historical type of firearm wherein the gunpowder is ignited by a burning piece of flammable cord or twine that is in contact with the gunpowder through a mechanism that the musketeer activates by pulling a lever or Tri ...
commander Mustafa Rumi and several other Ottomans. From them, he adopted the tactic of using matchlocks and cannons in the field (rather than only in siege
A siege () . is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or by well-prepared assault. Siege warfare (also called siegecrafts or poliorcetics) is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict charact ...
s), which gave him an important advantage in India.
Formation of the Mughal Empire
 Babur still wanted to escape from the Uzbeks, and he chose India as a refuge instead of Badakhshan, which was to the north of Kabul. He wrote, "In the presence of such power and potency, we had to think of some place for ourselves and, at this crisis and in the crack of time there was, put a wider space between us and the strong foeman." After his third loss of Samarkand, Babur gave full attention to the conquest of North India, launching a campaign; he reached the Chenab River, now in
Babur still wanted to escape from the Uzbeks, and he chose India as a refuge instead of Badakhshan, which was to the north of Kabul. He wrote, "In the presence of such power and potency, we had to think of some place for ourselves and, at this crisis and in the crack of time there was, put a wider space between us and the strong foeman." After his third loss of Samarkand, Babur gave full attention to the conquest of North India, launching a campaign; he reached the Chenab River, now in Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
, in 1519. Until 1524, his aim was to only expand his rule to Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
, mainly to fulfill the legacy of his ancestor Timur, since it used to be part of his empire. At the time parts of North India were part of the Delhi Sultanate, ruled by Ibrahim Lodi of the Lodi dynasty, but the sultanate was crumbling and there were many defectors. Babur received invitations from Daulat Khan Lodi, Governor of Punjab and Ala-ud-Din, uncle of Ibrahim. He sent an ambassador to Ibrahim, claiming himself the rightful heir to the throne, but the ambassador was detained at Lahore
Lahore ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, second-largest city in Pakistan, after Karachi, and ...
, Punjab, and released months later.
Babur started for Lahore in 1524 but found that Daulat Khan Lodi had been driven out by forces sent by Ibrahim Lodi. When Babur arrived at Lahore, the Lodi army marched out and his army was routed. In response, Babur burned Lahore for two days, then marched to Dibalpur, placing Alam Khan, another rebel uncle of Lodi, as governor. Alam Khan was quickly overthrown and fled to Kabul. In response, Babur supplied Alam Khan with troops who later joined up with Daulat Khan Lodi, and together with about 30,000 troops, they besieged Ibrahim Lodi at Delhi. The sultan easily defeated and drove off Alam's army, and Babur realised that he would not allow him to occupy the Punjab.
First Battle of Panipat
 In November 1525, Babur got news at
In November 1525, Babur got news at Peshawar
Peshawar is the capital and List of cities in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa by population, largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. It is the sixth most populous city of Pakistan, with a district p ...
that Daulat Khan Lodi had switched sides, and Babur drove out Ala-ud-Din. Babur then marched onto Lahore to confront Daulat Khan Lodi, only to see Daulat's army melt away at their approach. Daulat surrendered and was pardoned. Thus within three weeks of crossing the Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayas, Himalayan river of South Asia, South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northw ...
Babur had become the master of Punjab.
Babur marched on to Delhi via Sirhind. He reached Panipat on 20 April 1526 and there met Ibrahim Lodi's numerically superior army of about 100,000 soldiers and 100 elephants. In the battle that began on the following day, Babur used the tactic of ''Tulugma'', encircling Ibrahim Lodi's army and forcing it to face artillery fire directly, as well as frightening its war elephants. Ibrahim Lodi died during the battle, thus ending the Lodi dynasty.
Babur wrote in his memoirs about his victory:
After the battle, Babur occupied Delhi, Gwalior and Agra, took the throne of Lodi, and laid the foundation for the eventual rise of Mughal rule in India. However, before he became North India's ruler, he had to fend off challengers, such as Rana Sanga.
Many of Babur's men allegedly wanted to leave India due to its warm climate, but Babur motivated them to stay and expand his empire.
Battle of Khanwa
 The Battle of Khanwa was fought between Babur and the Rajput ruler of Mewar,
The Battle of Khanwa was fought between Babur and the Rajput ruler of Mewar, Rana Sanga
Sangram Singh I (12 April 1482 – 30 January 1528), most commonly known as Rana Sanga, was the Rana of Mewar, Maharana of Mewar from 1509 to 1528. A member of the List of Ranas of Mewar, Sisodia dynasty, he controlled parts of present-day Ra ...
on 16 March 1527. Rana Sanga wanted to overthrow Babur, whom he considered to be a foreigner ruling in India, and also to extend the Rajput territories by annexing Delhi and Agra
Agra ( ) is a city on the banks of the Yamuna river in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, about south-east of the national capital Delhi and 330 km west of the state capital Lucknow. With a population of roughly 1.6 million, Agra is the ...
. He was supported by Afghan chiefs who felt Babur had been deceptive by refusing to fulfil promises made to them. Upon receiving news of Rana Sangha's advance towards Agra, Babur after annexing Gwalior and Bayana took a defensive position at Khanwa (currently in the Indian state of Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; Literal translation, lit. 'Land of Kings') is a States and union territories of India, state in northwestern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the List of states and union territories of ...
), from where he hoped to launch a counterattack later. According to K.V. Krishna Rao, Babur won the battle because of his "superior generalship" and modern tactics; the battle was one of the first in India that featured cannons and muskets. Rao also notes that Rana Sanga faced "treachery" when the Hindu chief Silhadi joined Babur's army with a garrison of 6,000 soldiers.
Battle of Chanderi
The Battle of Chanderi took place the year after the Battle of Khanwa. On receiving news that Rana Sanga had made preparations to renew the conflict with him, Babur decided to isolate the Rana by defeating one of his staunchest allies, Medini Rai, who was the ruler of Malwa. Upon reaching Chanderi, on 20 January 1528, Babur offered Shamsabad to Medini Rao in exchange for Chanderi as a peace overture, but the offer was rejected. The outer fortress of Chanderi was taken by Babur's army at night, and the next morning the upper fort was captured. Babur himself expressed surprise that the upper fort had fallen within an hour of the final assault. Seeing no hope of victory, Medini Rai organized a '' jauhar'', during which women and children within the fortress immolated themselves. A small number of soldiers also collected in Medini Rao's house and killed each other in collective suicide. This sacrifice does not seem to have impressed Babur, who did not express a word of admiration for the enemy in his autobiography.Religious policy
Babur defeated and killed Ibrahim Lodi, the last Sultan of the Lodi dynasty, in 1526. Babur ruled for 4 years and was succeeded by his son Humayun whose reign was temporarily usurped by the Suri dynasty. During their 30-year rule, religious violence continued in India. Records of the violence and trauma, from Sikh-Muslim perspective, include those recorded inSikh
Sikhs (singular Sikh: or ; , ) are an ethnoreligious group who adhere to Sikhism, a religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ''Si ...
literature of the 16th century. The violence of Babur in the 1520s was witnessed by Guru Nanak
Gurū Nānak (15 April 1469 – 22 September 1539; Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਨਾਨਕ; pronunciation: , ), also known as ('Father Nanak'), was an Indian spiritual teacher, mystic and poet, who is regarded as the founder of Sikhism and is t ...
, who commented upon it in four hymns. Historians suggest the early Mughal period of religious violence contributed to introspection and then the transformation in Sikhism from pacifism to militancy for self-defense. According to Babur's autobiography, ''Baburnama
The ''Bāburnāma'' (; ) is the memoirs of Babur, Ẓahīr-ud-Dīn Muhammad Bābur (1483–1530), founder of the Mughal Empire and a great-great-great-grandson of Timur. It is written in the Chagatai language, known to Babur as ''Türki'' "Turkic ...
'', his campaign in northwest India targeted Hindus and Sikhs as well as apostates (non-Sunni sects of Islam), and an immense number were killed, with Muslim camps building "towers of skulls of the infidels" on hillocks. In Babur's secret will, in the year 935AH, 1529 AD, to Humayun, Babur advises Humayun to administer justice according to the ways of every religion, avoid sacrifice of the cow, not to ruin the temples and shrines of any law obeying community, overlook the dissensions of the Shias and the Sunnis.
Personal life and relationships
There are no descriptions about Babur's physical appearance, except from the paintings in the translation of the ''Baburnama'' prepared during the reign of Akbar. In his autobiography, Babur claimed to be strong and physically fit, and that he had swum across every major river he encountered, including twice across theGanges River
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
in North India.
Babur did not initially know Old Hindi
Old Hindi, also known as Khariboli, was the earliest stage of the Hindustani language, and so the ancestor of today's Hindi and Urdu. It developed from Shauraseni, and was spoken by the peoples of the region around Delhi, in roughly the 10th–1 ...
; however, his Turkic poetry indicates that he picked up some of its vocabulary later in life.
Unlike his father, he had ascetic tendencies and did not have any great interest in women. In his first marriage, he was "bashful" towards Aisha Sultan Begum, later losing his affection for her. Babur showed similar shyness in his interactions with Baburi, a boy in his camp with whom he had an infatuation around this time, recounting that:
However, Babur acquired several more wives and concubines over the years, and as required for a prince, he was able to ensure the continuity of his line.
Babur's first wife, Aisha Sultan Begum, was his paternal cousin, the daughter of Sultan Ahmad Mirza, his father's brother. She was an infant when betrothed to Babur, who was himself five years old. They married eleven years later, . The couple had one daughter, Fakhr-un-Nissa, who died within a year in 1500. Three years later, after Babur's first defeat at Fergana, Aisha left him and returned to her father's household. In 1504, Babur married Zaynab Sultan Begum, who died childless within two years. In the period 1506–08, Babur married four women, Maham Begum (in 1506), Masuma Sultan Begum, Gulrukh Begum and Dildar Begum. Babur had four children by Maham Begum, of whom only one survived infancy. This was his eldest son and heir, Humayun. Masuma Sultan Begum died during childbirth; the year of her death is disputed (either 1508 or 1519). Gulrukh bore Babur two sons, Kamran and Askari, and Dildar Begum was the mother of Babur's youngest son, Hindal. Babur later married Mubaraka Yusufzai, a Pashtun woman of the Yusufzai tribe. Gulnar Aghacha and Nargul Aghacha were two Circassian slaves given to Babur as gifts by Tahmasp Shah Safavi, the Shah of Persia. They became "recognized ladies of the royal household."
During his rule in Kabul, when there was a time of relative peace, Babur pursued his interests in literature, art, music and gardening. Previously, he never drank alcohol and avoided it when he was in Herat. In Kabul, he first tasted it at the age of thirty. He then began to drink regularly, host wine parties and consume preparations made from opium
Opium (also known as poppy tears, or Lachryma papaveris) is the dried latex obtained from the seed Capsule (fruit), capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid mor ...
. Though religion had a central place in his life, Babur also approvingly quoted a line of poetry by one of his contemporaries: "I am drunk, officer. Punish me when I am sober". He quit drinking for health reasons before the Battle of Khanwa, just two years before his death, and demanded that his court do the same. But he did not stop chewing narcotic preparations, and did not lose his sense of irony. He wrote, "Everyone regrets drinking and swears an oath (of abstinence
Abstinence is the practice of self-enforced restraint from indulging in bodily activities that are widely experienced as giving pleasure. Most frequently, the term refers to sexual abstinence, but it can also mean abstinence from alcohol (drug), ...
); I swore the oath and regret that."
Babur was opposed to the blind obedience towards the Chinggisid laws and customs that were influential in Turco-Mongol society:"Previously our ancestors had shown unusual respect for the Chingizid code (). They did not violate this code sitting and rising at councils and court, at feasts and dinners. oweverChingez Khan's code is not a ''nass qati'' (categorical text) that a person must follow. Whenever one leaves a good custom, it should be followed. If ancestors leave a bad custom, however it is necessary to substitute a good one."Making clear that to him, the categorical text (i.e. the
Quran
The Quran, also Romanization, romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a Waḥy, revelation directly from God in Islam, God (''Allah, Allāh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which ...
) had displaced Genghis Khan's ''Yassa
The Yassa (alternatively ''Yasa'', ''Yasaq'', ''Jazag'' or ''Zasag''; ) was the oral law code of the Mongols, gradually built up through the reign of Genghis Khan. It was the '' de facto'' law of the Mongol Empire, even though the "law" was kep ...
'' in moral and legal matters.
Poetry
 Babur was an acclaimed writer, who had a profound love for literature. His library was one of his most beloved possessions that he always carried around with him, and books were one of the treasures he searched for in new conquered lands. In his memoirs, when he listed sovereigns and nobles of a conquered land, he also mentioned poets, musicians and other educated people.
Even though he died aged 47, Babur left a rich literary and scientific heritage. He authored his famous memoir the Bāburnāma, as well as beautiful lyrical works or ''ghazals'', treatises on Muslim jurisprudence (Mubayyin), poetics (Aruz risolasi), music, and a special
Babur was an acclaimed writer, who had a profound love for literature. His library was one of his most beloved possessions that he always carried around with him, and books were one of the treasures he searched for in new conquered lands. In his memoirs, when he listed sovereigns and nobles of a conquered land, he also mentioned poets, musicians and other educated people.
Even though he died aged 47, Babur left a rich literary and scientific heritage. He authored his famous memoir the Bāburnāma, as well as beautiful lyrical works or ''ghazals'', treatises on Muslim jurisprudence (Mubayyin), poetics (Aruz risolasi), music, and a special calligraphy
Calligraphy () is a visual art related to writing. It is the design and execution of lettering with a pen, ink brush, or other writing instruments. Contemporary calligraphic practice can be defined as "the art of giving form to signs in an e ...
, known as ''khatt-i Baburi''.
Babur's Bāburnāma is a collection of memoirs, written in the Chagatai language
Chagatai (, ), also known as Turki, Eastern Turkic, or Chagatai Turkic (), is an Extinct language, extinct Turkic languages, Turkic language that was once widely spoken across Central Asia. It remained the shared literary language in the region u ...
and later translated into Persian, the usual literary language of the Mughal court, during the rule of emperor Akbar. However, Babur's Turkic prose in Bāburnāma is already highly Persianized in its sentence structure, vocabulary, and morphology, and also consists of several phrases and minor poems in Persian.
Babur wrote most of his poems in Chagatai Turkic, known to him as ''Türki'', but he also composed in Persian. However, he was mostly praised for his literary works written in Turkic, which drew comparison with the poetry of Ali-Shir Nava'i.
The following ruba'i is an example of Babur's poetry written in Turkic, composed in the aftermath of his famous victory in North India to celebrate his ghazi status.
Family
Consorts
* Aisha Sultan Begum ( 1499; 1503), daughter of Sultan Ahmed Mirza — First wife of Babur * Zainab Sultan Begum ( 1504; 1506–07), daughter of Sultan Mahmud Mirza * Maham Begum ( 1506) — Babur's chief and favourite consort * Masuma Sultan Begum ( 1507; 1508), daughter of Sultan Ahmed Mirza and half-sister of Aisha Sultan Begum * Bibi Mubarika ( 1519), Pashtun of the Yusufzai tribe *Gulrukh Begum (not to be confused with Babur's daughter Gulrukh Begum, who was also known as Gulbarg Begum) *Dildar Begum *Gulnar Aghacha, Circassian concubine *Nargul Aghacha, Circassian concubine The identity of the mother of one of Babur's daughters, Gulrukh Begum is disputed. Gulrukh's mother may have been the daughter of Sultan Mahmud Mirza by his wife Pasha Begum who is referred to as Saliha Sultan Begum in certain secondary sources, however this name is not mentioned in theBaburnama
The ''Bāburnāma'' (; ) is the memoirs of Babur, Ẓahīr-ud-Dīn Muhammad Bābur (1483–1530), founder of the Mughal Empire and a great-great-great-grandson of Timur. It is written in the Chagatai language, known to Babur as ''Türki'' "Turkic ...
or the works of Gulbadan Begum, which casts doubt on her existence. This woman may never have existed at all or she may even be the same woman as Dildar Begum.
Issue
The sons of Babur were: * Humayun ( 1508; 1556) — with Maham Begum — succeeded Babur as the secondMughal Emperor
The emperors of the Mughal Empire, who were all members of the Timurid dynasty (House of Babur), ruled the empire from its inception on 21 April 1526 to its dissolution on 21 September 1857. They were supreme monarchs of the Mughal Empire in ...
* Kamran Mirza ( 1512; 1557) — with Gulrukh Begum
* Askari Mirza ( 1518; 1557) — with Gulrukh Begum
* Hindal Mirza ( 1519; 1551) — with Dildar Begum
*Ahmad Mirza ( young) — with Gulrukh Begum
*Shahrukh Mirza ( young) — with Gulrukh Begum
*Barbul Mirza ( infancy) — with Maham Begum
*Alwar Mirza ( young) — with Dildar Begum
*Faruq Mirza ( infancy) — with Maham Begum
The daughters of Babur were:
* Fakhr-un-Nissa Begum ( & 1501) — with Aisha Sultan Begum
*Aisan Daulat Begum ( infancy) — with Maham Begum
*Mehr Jahan Begum ( infancy) — with Maham Begum
* Masuma Sultan Begum ( 1508) — with Masuma Sultan Begum — Married to Muhammad Zaman Mirza.
*Gulzar Begum ( infancy) — with Gulrukh Begum
* Gulrukh Begum (Gulbarg Begum) — Identity of mother is disputed, may have been Dildar Begum or Saliha Sultan Begum — Married to Nuruddin Muhammad Mirza, son of Khwaja Hasan Naqshbandi, with whom she had Salima Sultan Begum, wife of Bairam Khan and later the Mughal Emperor Akbar.
* Gulbadan Begum ( – 1603) — with Dildar Begum — Married Khizr Khwaja Khan, son of her father's cousin Aiman Khwajah Sultan of Moghulistan, son of Ahmad Alaq of Moghulistan, the maternal uncle of Emperor Babur.
* Gulchehra Begum ( – 1557) — with Dildar Begum — Married firstly in 1530 to Sultan Tukhta Bugha Khan, son of Ahmad Alaq of Moghulistan, the maternal uncle of Emperor Babur. Married secondly to Abbas Sultan Uzbeg.
*Gulrang Begum — with Dildar Begum — Married in 1530 to Isan Timur Sultan, ninth son of Ahmad Alaq of Moghulistan, the maternal uncle of Emperor Babur.
Death and legacy
Babur died in Agra on and was succeeded by his eldest son, Humayun. He was first buried in Chauburji,Agra
Agra ( ) is a city on the banks of the Yamuna river in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, about south-east of the national capital Delhi and 330 km west of the state capital Lucknow. With a population of roughly 1.6 million, Agra is the ...
. Later, as per his wishes, his mortal remains were moved to Kabul and reburied in Bagh-e Babur in Kabul sometime between 1539 and 1544.
 It is generally agreed that, as a Timurid, Babur was not only significantly influenced by the Persian culture, but also that his empire gave rise to the expansion of the Persianate ethos in the Indian subcontinent. He emerged in his own telling as a
It is generally agreed that, as a Timurid, Babur was not only significantly influenced by the Persian culture, but also that his empire gave rise to the expansion of the Persianate ethos in the Indian subcontinent. He emerged in his own telling as a Timurid Renaissance
The Timurid Renaissance was a historical period in Asian history, Asian and Islamic history spanning the late 14th, the 15th, and the early 16th centuries. Following the Islamic Golden Age, the Timurid Empire, based in Central Asia and ruled by ...
inheritor, leaving signs of Islamic, artistic literary, and social aspects in India.
F. Lehmann states in the ''Encyclopædia Iranica
''Encyclopædia Iranica'' is a project whose goal is to create a comprehensive and authoritative English-language encyclopedia about the history, culture, and civilization of Iranian peoples from prehistory to modern times.
Scope
The ''Encyc ...
'':
Although all applications of modern Central Asian ethnicities to people of Babur's time are anachronistic, Soviet and Uzbek sources regard Babur as an ethnic Uzbek. At the same time, during the Soviet Union Uzbek scholars were censored for idealising and praising Babur and other historical figures such as Ali-Shir Nava'i.
Babur is considered a national hero in Uzbekistan. On 14 February 2008, stamps in his name were issued in the country to commemorate his 525th birth anniversary. Many of Babur's poems have become popular Uzbek folk songs, especially by Sherali Joʻrayev. Some sources claim that Babur is a national hero in Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan, officially the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia lying in the Tian Shan and Pamir Mountains, Pamir mountain ranges. Bishkek is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Kyrgyzstan, largest city. Kyrgyz ...
too. In October 2005, Pakistan developed the Babur Cruise Missile, named in his honour.
'' Shahenshah Babar'', an Indian film about the emperor directed by Wajahat Mirza was released in 1944. The 1960 Indian biographical film ''Babar'' by Hemen Gupta covered the emperor's life with Gajanan Jagirdar in the lead role.
One of the enduring features of Babur's life was that he left behind the lively and well-written autobiography known as ''Baburnama''. Quoting Henry Beveridge, Stanley Lane-Poole writes:
In his own words, "The cream of my testimony is this, do nothing against your brothers even though they may deserve it." Also, "The new year, the spring, the wine and the beloved are joyful. Babur make merry, for the world will not be there for you a second time."
Citations
References
* * * * * *Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* * {{Authority control 1483 births 1530 deaths People from Andijan 1530 in India Timurid dynasty 16th-century Indian monarchs Indian Sunni Muslims Emperors of the Mughal Empire 16th-century Indian Muslims Turkic culture Founding monarchs in Asia 16th-century Mughal Empire people Chagatai-language writers