|
Aiman Khwajah Sultan
Aiman Khwajah Sultan was a Prince of Eastern Moghulistan and the son of Ahmad Alaq, who ruled as the khan of Eastern Moghulistan from 1487 to 1503. As a grandson of Yunus Khan, Aiman Khwajah Sultan was the first cousin of the Mughal Emperor Babur, and his children married into the Mughal dynasty. Aiman Khwajah Sultan was a direct male-line descendant of Genghis Khan, through his son Chagatai Khan. Issue Aiman's son, Khizr Khwaja Khan was married to Gulbadan Begum, daughter of Emperor Babur and his consort Dildar Begum. Another of Aiman's sons, Aq Sultan, was married to Habiba Begum, daughter of Kamran Mirza, son of Babur Babur (; 14 February 148326 December 1530; born Zahīr ud-Dīn Muhammad) was the founder of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan through his father and mother respectively. He was also .... References Chagatai khans Uyghur people {{Mongol-royal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moghulistan
Moghulistan, also called the Moghul Khanate or the Eastern Chagatai Khanate, was a Muslims, Muslim, Mongol, and later Turkic peoples, Turkic breakaway khanate of the Chagatai Khanate and a historical geographic area north of the Tian Shan, Tengri Tagh mountain range, on the border of Central Asia and East Asia. That area today includes parts of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and northwest Xinjiang, China. The khanate nominally ruled over the area from the mid-14th century until the late 17th century. Beginning in the mid-14th century a new khanate, in the form of a nomadic tribal confederacy headed by a member of the family of Chagatai, arose in the region of the Ili River. It is therefore considered to be a continuation of the Chagatai Khanate, but it is also referred to as the ''Moghul Khanate''. In actuality, local control rested with local Mongol Dughlats or Naqshbandi Sufis in their respective oases. Although the rulers enjoyed great wealth from trade with the Ming dynasty, it wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borjigin
A Borjigin is a member of the Mongol sub-clan that started with Bodonchar Munkhag of the Kiyat clan. Yesugei's descendants were thus said to be Kiyat-Borjigin. The senior Borjigids provided ruling princes for Mongolia and Inner Mongolia until the 20th century.Humphrey & Sneath, p. 27. The clan formed the ruling class among the Mongols and some other peoples of Central Asia and Eastern Europe. Today, the Borjigid are found in most of Mongolia, Inner Mongolia and Xinjiang, and genetic research has shown that descent from Genghis Khan and Timur is common throughout Central Asia and other regions. Origin and name The patrilineage began with Blue-grey Wolf (Börte Chino) and Fallow Doe (Gua Maral). According to '' The Secret History of the Mongols'', their 11th generation descendant Dobu Mergen's widow Alan Gua the Fair was impregnated by a ray of light. Her youngest son became the ancestor of the later Borjigid. He was Bodonchar Munkhag, who along with his brothers s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahmad Alaq
Sultan Ahmad Khan ( Chagatai and Persian: سلطان احمد خان; b. 1465 – 1504), better known as Ahmad Alaq was the Khan of Eastern Moghulistan ( Turpan Khanate) from 1487 to 1504. He was the second son of Yunus Khan. His mother was Shah Begum, fourth daughter of Badakhshan prince Lali. Ahmad Alaq was a direct male-line descendant of Genghis Khan, through his son Chagatai Khan. Life During his father's lifetime Ahmad was behind several rebellions against him. When Yunus Khan took up residence in Tashkent in 1484, Ahmad and a large body of Moghuls fled to the steppes. In 1487, Ahmad's father died and was succeeded in the territory he still controlled by another son, Mahmud Khan. Ahmad's reign was marked by conflicts with several of his neighbors. Conflict in the Ming Turpan Border Wars over Hami with the Ming Dynasty China resulted in an economic blockade of the region, which allowed the Chinese to eventually emerge victorious. A campaign against the Mirza Abu B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunni Islam
Sunni Islam is the largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any Succession to Muhammad, successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr () rightfully succeeded him as the caliph of the Muslim community, being appointed at the meeting of Saqifa. This contrasts with the Succession of ʿAlī (Shia Islam), Shia view, which holds that Muhammad appointed Ali, Ali ibn Abi Talib () as his successor. Nevertheless, Sunnis revere Ali, along with Abu Bakr, Umar () and Uthman () as 'Rashidun, rightly-guided caliphs'. The term means those who observe the , the practices of Muhammad. The Quran, together with hadith (especially the Six Books) and (scholarly consensus), form the basis of all Fiqh, traditional jurisprudence within Sunni Islam. Sharia legal rulings are derived from these basic sources, in conjunction with Istislah, consideration of Maslaha, public welfare and Istihsan, jur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khan (title)
Khan (, , ) is a historic Turkic peoples, Turkic and Proto-Mongols, Mongolic title originating among nomadic tribes in the Eurasian Steppe#Divisions, Central and Eastern Eurasian Steppe to refer to a king. It first appears among the Rouran and then the Göktürks as a variant of khagan (sovereign, emperor) and implied a subordinate ruler. In the Seljuk Empire, Seljük Empire, it was the highest noble title, ranking above malik (king) and emir (prince). In the Mongol Empire it signified the ruler of a Orda (organization), horde (''ulus''), while the ruler of all the Mongols was the khagan or great khan. It is a title commonly used to signify the head of a Pashtun Pashtun tribes, tribe or clan. The title subsequently declined in importance. During the Safavid Iran, Safavid and Qajar Iran, Qajar dynasty it was the title of an army general high noble rank who was ruling a province, and in Mughal Empire, Mughal India it was a high noble rank restricted to courtiers. After the downfal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yunus Khan
Yunus Khan (b. 1416 – d. 1487) ( Chagatai and Persian: یونس خان), was Khan of Moghulistan from 1462 until his death in 1487. He is identified by many historians with Ḥājjī `Ali (, Pinyin: ''Hazhi Ali''; Chagatai and Persian: حاجی علی), of the contemporary Chinese records. He was the maternal grandfather of Babur, founder of the Mughal Empire. Yunus Khan was a direct male-line descendant of Genghis Khan, through his son Chagatai Khan. Background and family Yunus Ali was the eldest son of Uwais Khan (or Vais Khan) of Moghulistan. When Vais Khan was killed in 1428 AD, the Moghuls were split as to who should succeed him. Although 12-year-old Yunus Khan was his eldest son, the majority favored Yunus' younger brother, Esen Buqa. As a result, Yunus and his supporters fled to Ulugh Beg, the Timurid ruler of Transoxiana, who however imprisoned the group. Ulugh Beg's father, Shah Rukh, took charge of the young Yunus and treated him well. He sent Yunus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
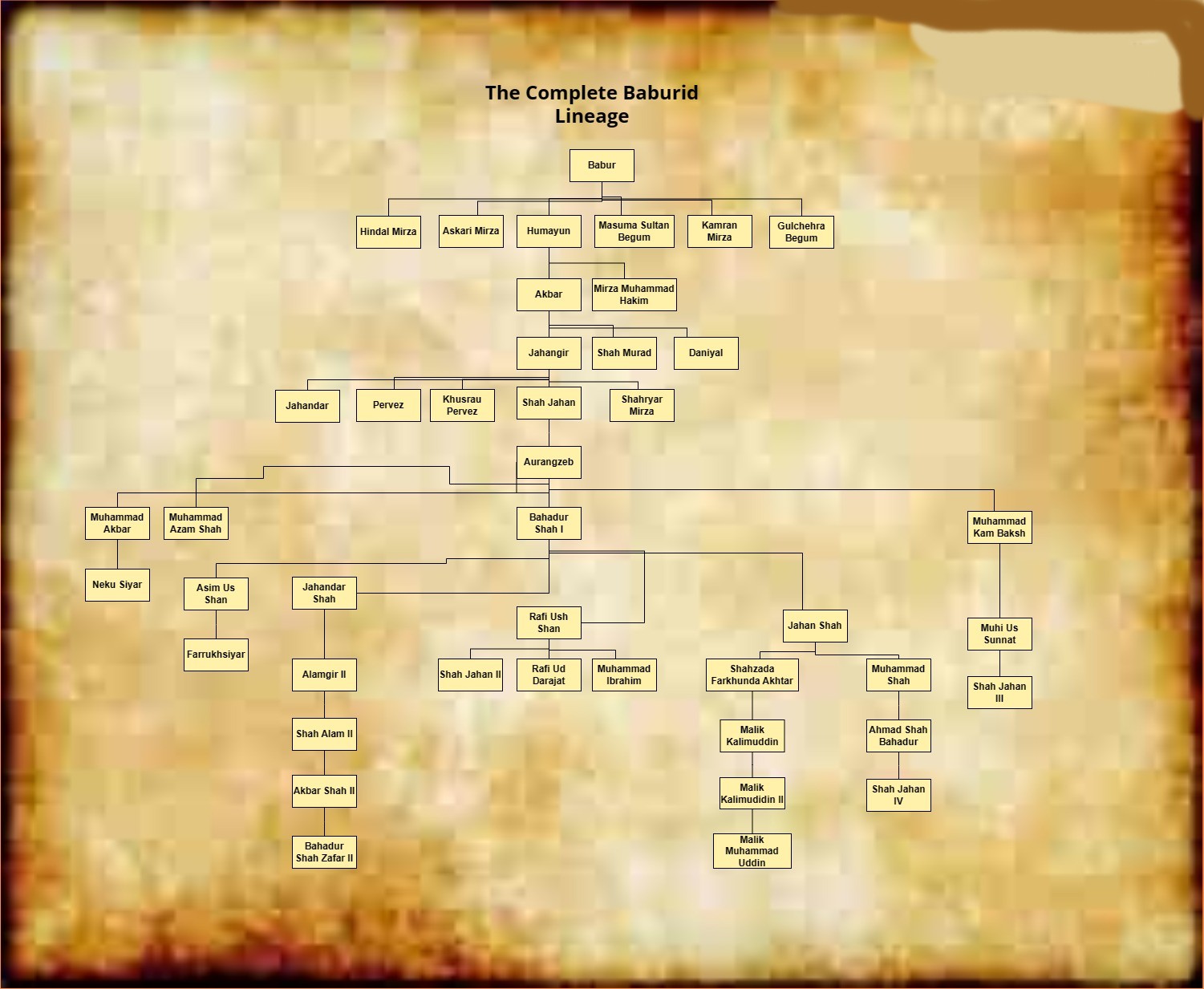
Babur
Babur (; 14 February 148326 December 1530; born Zahīr ud-Dīn Muhammad) was the founder of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan through his father and mother respectively. He was also given the posthumous name of ''Firdaws Makani'' ('Dwelling in Paradise'). Born in Andijan in the Fergana Valley (now in Uzbekistan), Babur was the eldest son of Umar Shaikh Mirza II (1456–1494, Timurid governor of Fergana from 1469 to 1494) and a great-great-great-grandson of Timur (1336–1405). Babur ascended the throne of Fergana in its capital Akhsikath in 1494 at the age of twelve and faced rebellion. He conquered Samarkand two years later, only to lose Fergana soon after. In his attempt to reconquer Fergana, he lost control of Samarkand. In 1501, his attempt to recapture both the regions failed when the Uzbek prince Muhammad Shaybani defeated him and founded the Khanate of Bukhara. In 1504, he conquered Kabul, which was un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mughal Dynasty
The Mughal dynasty () or the House of Babur (), was a Central Asian dynasty of Turco-Mongol tradition, Turco-Mongol origin that ruled large parts of the Indian subcontinent from the early 16th to the 19th century. The dynasty was a cadet branch of the Timurid dynasty, which had ruled in parts of Central Asia and Iran in the 14th and 15th centuries. The Mughals originated as a branch of the Central Asian Timurid dynasty, Timurid Dynasty which belonged to the Barlas, Barlas tribe, which was a branch of the Borjigin Clan. Babur (1483–1530), the founder of the Mughal dynasty, was a direct descendant of the Asian conqueror Timur, Timur (Tamerlane) through his father and Mongol emperor Genghis Khan through his mother. Many of the later Mughal emperors had significant Indian and Persian ancestry through marriage alliances. During much of the Empire's history, the emperor functioned as the absolute Head of State, Head of government and Head of the military, while during its declinin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; August 1227), also known as Chinggis Khan, was the founder and first khan (title), khan of the Mongol Empire. After spending most of his life uniting the Mongols, Mongol tribes, he launched Mongol invasions and conquests, a series of military campaigns, conquering large parts of Mongol conquest of China, China and Mongol invasion of Central Asia, Central Asia. Born between 1155 and 1167 and given the name Temüjin, he was the eldest child of Yesugei, a Mongol chieftain of the Borjigin, Borjigin clan, and his wife Hö'elün. When Temüjin was eight, his father died and his family was abandoned by its tribe. Reduced to near-poverty, Temüjin killed Behter, his older half-brother to secure his familial position. His charismatic personality helped to attract his first followers and to form alliances with two prominent Eurasian Steppe, steppe leaders named Jamukha and Toghrul; they worked together to retrieve Temüjin's newlywed wife Börte, who had b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chagatai Khan
Chagatai Khan (; – 1242) was a son of Genghis Khan and a prominent figure in the early Mongol Empire. The second son of Genghis's wife Börte, Chagatai was renowned for his masterful knowledge of Mongol custom and law, which he scrupulously obeyed, and his harsh temperament. Because Genghis felt that he was too inflexible in character, most notably never accepting the legitimacy of his elder brother Jochi, he excluded Chagatai from succession to the Mongol throne. He was nevertheless a key figure in ensuring the stability of the empire after Genghis's death and during the reign of his younger brother Ögedei Khan. Chagatai held military commands alongside his brothers during the Mongol conquest of the Jin dynasty in 1211 and the invasion of the Khwarazmian Empire in 1219. During the latter, he was appointed to a key role in organising logistics in addition to battlefield responsibilities, but was censured after feuding with Jochi during the Siege of Gurganj. After the ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulbadan Begum
Gulbadan Begum ( 1523 – 7 February 1603) was a Mughal princess and the daughter of Emperor Babur, the founder of the Mughal Empire. She is best known as the author of '' Humayun-Nama'', the account of the life of her half-brother and Babar's successor, Emperor Humayun, which she wrote on the request of her nephew and Humayun's son, Emperor Akbar. Gulbadan's recollection of Babur is brief, but she gives a refreshing account of Humayun's household and provides rare material regarding his confrontation with her half-brother, Kamran Mirza. She records the fratricidal conflict among her brothers with a sense of grief. Gulbadan Begum was about eight years old at the time of her father's death in 1530 and was brought up by her older half-brother, Humayun. She was married to a Chagatai noble, her cousin, Khizr Khwaja Khan, the son of Aiman Khwajah Sultan, son of Khan Ahmad Alaq of the Turpan Khanate in Moghulistan at the age of seventeen. She spent most of her life in Kab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamran Mirza
Kamran Mirza () (1512 – 5 October 1557) was the second son of Babur, the founder of the Mughal Empire and the first Mughal Emperor. Kamran Mirza was born in Kabul to Babur's wife Gulrukh Begum. He was half-brother to Babur's eldest son Humayun, who would go on and inherit the Mughal throne, but he was full-brother to Babur's third son, Askari. A divan written in Persian and Chagatai is attributed to him. During the Reign of Babur While his father, Babur Mirza, was conquering northern India from 1525 onwards, Kamran remained in Kandahar in order to secure his northern flank. He was still in charge of the northern part of the newly formed empire, when his father died in 1530. According to the Mughal historian Abul Fazl, Babur's last words to Humayun were "do nothing against your brothers, even though they may deserve it". In India In 1538, Kamran first crossed into India, bringing with him 12,000 soldiers, while Humayun was away fighting in Bengal. He appeared to have co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |