B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a
 The cancerous cell in ALL is the lymphoblast. Normal lymphoblasts develop into mature, infection-fighting B-cells or T-cells, also called
The cancerous cell in ALL is the lymphoblast. Normal lymphoblasts develop into mature, infection-fighting B-cells or T-cells, also called
File:ALL - Peripherial Blood - Diagnosis - 01.jpg, Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), peripheral blood of a child, Pappenheim stain, magnification x100
File:ALL-KM-2.jpg, Bone marrow smear (large magnification) from a person with ALL
File:ALL-KM-3.jpg, Bone marrow smear from a person with ALL
 The aim of treatment is to induce a lasting remission, defined as the absence of detectable cancer cells in the body (usually less than 5% blast cells in the bone marrow) or the absence of
The aim of treatment is to induce a lasting remission, defined as the absence of detectable cancer cells in the body (usually less than 5% blast cells in the bone marrow) or the absence of
 However, there are differing prognoses for ALL among individuals depending on a variety of factors:
* Gender: Females tend to fare better than males.
* Ethnicity: Caucasians are more likely to develop acute leukemia than
However, there are differing prognoses for ALL among individuals depending on a variety of factors:
* Gender: Females tend to fare better than males.
* Ethnicity: Caucasians are more likely to develop acute leukemia than
cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
of the lymphoid line of blood cell
A blood cell (also called a hematopoietic cell, hemocyte, or hematocyte) is a cell produced through hematopoiesis and found mainly in the blood. Major types of blood cells include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), ...
s characterized by the development of large numbers of immature lymphocytes. Symptoms may include feeling tired, pale skin color, fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
, easy bleeding or bruising, enlarged lymph nodes, or bone pain. As an acute leukemia
Acute leukemia or acute leukaemia is a family of serious medical conditions relating to an original diagnosis of leukemia. In most cases, these can be classified according to the lineage, myeloid or lymphoid, of the malignant cells that grow uncont ...
, ALL progresses rapidly and is typically fatal within weeks or months if left untreated.
In most cases, the cause is unknown. Genetic risk factors may include Down syndrome, Li–Fraumeni syndrome
Li–Fraumeni syndrome (LFS) is a rare, autosomal dominant, hereditary disorder that predisposes carriers to cancer development. It was named after two American physicians, Frederick Pei Li and Joseph F. Fraumeni Jr., who first recognized the ...
, or neurofibromatosis type 1
Neurofibromatosis (NF) refers to a group of three distinct genetic conditions in which tumors grow in the nervous system. The tumors are non-cancerous (benign) and often involve the skin or surrounding bone. Although symptoms are often mild, e ...
. Environmental risk factors may include significant radiation exposure
Radiation exposure is a measure of the ionization of air due to ionizing radiation from photons. It is defined as the electric charge freed by such radiation in a specified volume of air divided by the mass of that air. As of 2007, "medical radia ...
or prior chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
. Evidence regarding electromagnetic field
An electromagnetic field (also EM field) is a physical field, varying in space and time, that represents the electric and magnetic influences generated by and acting upon electric charges. The field at any point in space and time can be regarde ...
s or pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all p ...
s is unclear. Some hypothesize that an abnormal immune response to a common infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
may be a trigger. The underlying mechanism involves multiple genetic mutations
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosi ...
that results in rapid cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell (biology), cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukar ...
. The excessive immature lymphocytes in the bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It i ...
interfere with the production of new red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), referred to as erythrocytes (, with -''cyte'' translated as 'cell' in modern usage) in academia and medical publishing, also known as red cells, erythroid cells, and rarely haematids, are the most common type of blood cel ...
s, white blood cell
White blood cells (scientific name leukocytes), also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign entities. White blood cells are genera ...
s, and platelet
Platelets or thrombocytes () are a part of blood whose function (along with the coagulation#Coagulation factors, coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping to form a thrombus, blood clot. Platelets have no ...
s. Diagnosis is typically based on blood tests
A blood test is a laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose test or a cho ...
and bone marrow examination
Bone marrow examination refers to the pathologic analysis of samples of bone marrow obtained by bone marrow biopsy (often called trephine biopsy) and bone marrow aspiration. Bone marrow examination is used in the diagnosis of a number of conditi ...
.
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia is typically treated initially with chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
aimed at bringing about remission. This is then followed by further chemotherapy typically over a number of years. Treatment usually also includes intrathecal chemotherapy since systemic chemotherapy can have limited penetration into the central nervous system and the central nervous system is a common site for relapse of acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Treatment can also include radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a therapy, treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of treatment of cancer, cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignancy, malignant cell (biology), ...
if spread to the brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
has occurred. Stem cell transplantation
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood, in order to replicate inside a patient and produce a ...
may be used if the disease recurs following standard treatment. Additional treatments such as Chimeric antigen receptor T cell immunotherapy
Immunotherapy or biological therapy is the treatment of disease by activating or suppressing the immune system. Immunotherapies designed to elicit or amplify an immune response are classified as ''activation immunotherapies,'' while immunotherap ...
are being used and further studied.
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia affected about 876,000 people globally in 2015 and resulted in about 111,000 deaths. It occurs most commonly in children, particularly those between the ages of two and five. In the United States it is the most common cause of cancer and death from cancer among children. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia is notable for being the first disseminated cancer to be cured. Survival for children increased from under 10% in the 1960s to 90% in 2015. Survival rates remain lower for babies (50%) and adults (35%).
Signs and symptoms
Initialsymptoms
Signs and symptoms are diagnostic indications of an illness, injury, or condition.
Signs are objective and externally observable; symptoms are a person's reported subjective experiences.
A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature ...
can be nonspecific, particularly in children. Over 50% of children with leukemia had one or more of five features: a liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
one can feel (64%), a spleen
The spleen (, from Ancient Greek '' σπλήν'', splḗn) is an organ (biology), organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter.
The spleen plays important roles in reg ...
one can feel (61%), pale complexion (54%), fever (53%), and bruising (52%). Additionally, recurrent infections, feeling tired, arm or leg pain, and enlarged lymph nodes can be prominent features. The B symptoms
B symptoms are a set of symptoms, namely fever, night sweats, and unintentional weight loss, that can be associated with both Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. These symptoms are not specific to lymphomas, especially each one considered ...
, such as fever, night sweats, and weight loss, are often present as well.
Central nervous system (CNS) symptoms such as cranial neuropathies due to meningeal infiltration are identified in less than 10% of adults and less than 5% of children, particularly mature B-cell ALL (Burkitt leukemia) at presentation.
The signs and symptoms of acute lymphoblastic leukemia are variable and include:
* Generalized weakness and feeling tired
* Anemia
* Dizziness
* Headache, vomiting, lethargy, neck stiffness, or cranial nerve palsies (CNS involvement)
* Frequent or unexplained fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
and infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
* Weight loss and/or loss of appetite
* Excessive and unexplained bruising
* Bone pain, joint pain (caused by the spread of "blast" cells to the surface of the bone or into the joint from the marrow cavity)
* Breathlessness
* Enlarged lymph nodes, liver, and/or spleen
* Pitting edema (swelling) in the lower limbs and/or abdomen
* Petechiae, which are tiny red spots or lines in the skin due to low platelet
Platelets or thrombocytes () are a part of blood whose function (along with the coagulation#Coagulation factors, coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping to form a thrombus, blood clot. Platelets have no ...
levels
* Testicular enlargement
* Mediastinal mass
Cause
lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells (for cell-mediated and cytotoxic adaptive immunity), B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity), an ...
s. Signals in the body control the number of lymphocytes so neither too few nor too many are made. In ALL, the normal development of some lymphocytes and the control over the number of lymphoid cells become defective.
ALL emerges when a single lymphoblast gains many mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, ...
s to gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
s that affect blood cell
A blood cell (also called a hematopoietic cell, hemocyte, or hematocyte) is a cell produced through hematopoiesis and found mainly in the blood. Major types of blood cells include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), ...
development and proliferation. In childhood ALL, this process begins at conception with the inheritance of some of these genes. These genes, in turn, increase the risk that more mutations will occur in developing lymphoid cells. Certain genetic syndromes, like Down Syndrome, have the same effect. Environmental risk factors are also needed to help create enough genetic mutations to cause disease. Evidence for the role of the environment is seen in childhood ALL among twins, where only 10–15% of both genetically identical twins get ALL. Since they have the same genes, different environmental exposures explain why one twin gets ALL and the other does not.
Infant ALL is a rare variant that occurs in babies less than one-year-old. ''KMT2A
Histone-lysine ''N''-methyltransferase 2A, also known as acute lymphoblastic leukemia 1 (ALL-1), myeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia 1 (MLL1), or zinc finger protein HRX (HRX), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''KMT2A'' gene.
...
'' (formerly ''MLL'') gene rearrangements are most common and happen in the embryo or fetus before birth. These rearrangements result in increased expression of blood cell development genes by promoting gene transcription and through epigenetic
In biology, epigenetics is the study of changes in gene expression that happen without changes to the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix ''epi-'' (ἐπι- "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are "on top of" or "in ...
changes. In contrast to childhood ALL, environmental factors are not thought to play a significant role. Aside from the ''KMT2A'' rearrangement, only one extra mutation is typically found. Environmental exposures are not needed to help create more mutations.
Risk factors
Genetics
Common inherited risk factors include mutations in '' ARID5B'', ''CDKN2A
''CDKN2A'', also known as cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A, is a gene which in humans is located at chromosome 9, band p21.3. It is ubiquitously expressed in many tissues and cell types. The gene codes for two proteins, including the INK4 f ...
/ 2B'', '' CEBPE'', '' IKZF1'', ''GATA3
GATA3 is a transcription factor that in humans is encoded by the ''GATA3'' gene. Studies in animal models and humans indicate that it controls the expression of a wide range of biologically and clinically important genes.
The GATA3 transcription ...
'', '' PIP4K2A'' and, more rarely, ''TP53
p53, also known as tumor protein p53, cellular tumor antigen p53 (UniProt name), or transformation-related protein 53 (TRP53) is a regulatory transcription factor protein that is often mutated in human cancers. The p53 proteins (originally thou ...
''. These genes play important roles in cellular development, proliferation, and differentiation. Individually, most of these mutations are low risk for ALL. A significant risk of disease occurs when a person inherits several of these mutations together.
The uneven distribution of genetic risk factors may help explain differences in disease rates among ethnic groups. For instance, the ''ARID5B'' mutation is less common in ethnic African populations.
Several genetic syndromes also carry an increased risk of ALL. These include: Down syndrome, Fanconi anemia
Fanconi anemia (FA) is a rare, autosomal recessive genetic disease characterized by aplastic anemia, congenital defects, endocrinological abnormalities, and an increased incidence of developing cancer. The study of Fanconi anemia has improve ...
, Bloom syndrome
Bloom syndrome (often abbreviated as BS in literature) is a rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder characterized by short stature, predisposition to the development of cancer, and genomic instability. BS is caused by mutations in the '' BLM'' g ...
, X-linked agammaglobulinemia, severe combined immunodeficiency
Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), also known as Swiss-type agammaglobulinemia, is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the disturbed development of functional T cells and B cells caused by numerous genetic mutations that result in diff ...
, Shwachman–Diamond syndrome
Shwachman–Diamond syndrome (SDS), or Shwachman–Bodian–Diamond syndrome, is a rare congenital disorder characterized by exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, bone marrow dysfunction, skeletal and cardiac abnormalities and short stature. After c ...
, Kostmann syndrome
Severe congenital neutropenia (SCN), also often known as Kostmann syndrome or disease, is a group of rare disorders that affect myelopoiesis, causing a congenital form of neutropenia, usually without other physical malformations. SCN manifests in ...
, neurofibromatosis type 1
Neurofibromatosis (NF) refers to a group of three distinct genetic conditions in which tumors grow in the nervous system. The tumors are non-cancerous (benign) and often involve the skin or surrounding bone. Although symptoms are often mild, e ...
, ataxia-telangiectasia, paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) is a rare, acquired, life-threatening disease of the blood characterized by destruction of red blood cells by the complement system, a part of the body's innate immune system. This destructive process ...
, and Li–Fraumeni syndrome
Li–Fraumeni syndrome (LFS) is a rare, autosomal dominant, hereditary disorder that predisposes carriers to cancer development. It was named after two American physicians, Frederick Pei Li and Joseph F. Fraumeni Jr., who first recognized the ...
. Fewer than 5% of cases are associated with a known genetic syndrome.
Rare mutations in ''ETV6'' and ''PAX5
Paired box protein Pax-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PAX5'' gene.
Function
The PAX5 gene is a member of the paired box (PAX) family of transcription factors. The central feature of this gene family is a novel, highly con ...
'' are associated with a familial form of ALL with autosomal
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosome ...
dominant patterns of inheritance
Inheritance is the practice of receiving private property, titles, debts, entitlements, privileges, rights, and obligations upon the death of an individual. The rules of inheritance differ among societies and have changed over time. Offi ...
.
Environmental
The environmental exposures that contribute to the emergence of ALL are contentious and a subject of ongoing debate. High levels of radiation exposure from nuclear fallout is a known risk factor for developing leukemia. Evidence whether lesser radiation, as fromx-ray imaging
Radiography is an imaging technology, imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical ("diagnostic" radiog ...
during pregnancy, increases the risk of disease remains inconclusive. Studies that have identified an association between x-ray imaging during pregnancy and ALL found only a slightly increased risk. Exposure to strong electromagnetic radiation from power lines has also been associated with a slightly increased ALL risk. This result is questioned as no causal mechanism linking electromagnetic radiation with cancer is known.
High birth weight (greater than 4000 g or 8.8 lbs) is also associated with a small increased risk. The mechanism connecting high birth weight to ALL is also not known.
Evidence suggests that secondary leukemia can develop in individuals treated with certain types of chemotherapy, such as epipodophyllotoxins and cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian cancer, breast cancer ...
.
Infections
There is some evidence that a common infection, such asinfluenza
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These sympto ...
, may indirectly promote the emergence of ALL. The delayed-infection hypothesis states that ALL results from an abnormal immune response to infection in a person with genetic risk factors. Delayed development of the immune system due to limited disease exposure may result in excessive production of lymphocytes and increased mutation rate during an illness. Several studies have identified lower ALL rates among children with greater exposure to illness early in life. Very young children who attend daycare have lower rates of ALL. Evidence from many other studies looking at disease exposure and ALL is inconclusive. Some researchers have linked the hygiene hypothesis
In medicine, the hygiene hypothesis states that early childhood exposure to particular microorganisms (such as the gut flora and helminth parasites) protects against allergies by properly tuning the immune system. In particular, a lack of such e ...
.
Mechanism
Several characteristic genetic changes lead to the creation of a leukemic lymphoblast. These changes includechromosomal translocation
In genetics, chromosome translocation is a phenomenon that results in unusual rearrangement of chromosomes. This includes "balanced" and "unbalanced" translocation, with three main types: "reciprocal", "nonreciprocal" and "Robertsonian" transloc ...
s, intrachromosomal rearrangements, changes in the number of chromosomes in leukemic cells, and additional mutations in individual genes. Chromosomal translocations involve moving a large region of DNA from one chromosome to another. This move can result in placing a gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
from one chromosome that promotes cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell (biology), cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukar ...
to a more actively transcribed area on another chromosome. The result is a cell that divides more often. An example of this includes the translocation of ''C-MYC
''Myc'' is a family of regulator genes and proto-oncogenes that code for transcription factors. The ''Myc'' family consists of three related human genes: ''c-myc'' ( MYC), ''l-myc'' ( MYCL), and ''n-myc'' ( MYCN). ''c-myc'' (also sometimes ...
'', a gene that encodes a transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding t ...
that leads to increased cell division, next to the immunoglobulin heavy- or light-chain gene enhancers
In genetics, an enhancer is a short (50–1500 bp) region of DNA that can be bound by proteins ( activators) to increase the likelihood that transcription of a particular gene will occur. These proteins are usually referred to as transcriptio ...
, leading to increased ''C-MYC'' expression and increased cell division. Other large changes in chromosomal structure can result in the placement of two genes directly next to each other. The result is the combination of two usually separate proteins into a new fusion protein
Fusion proteins or chimeric (kī-ˈmir-ik) proteins (literally, made of parts from different sources) are proteins created through the joining of two or more genes that originally coded for separate proteins. Translation of this '' fusion gene'' ...
. This protein can have a new function that promotes the development of cancer. Examples of this include the ''ETV6
ETV6 (i.e. translocation-Ets-leukemia virus) protein is a transcription factor that in humans is encoded by the ''ETV6'' (previously known as ''TEL'') gene. The ETV6 protein regulates the development and growth of diverse cell types, particularly ...
''–''RUNX1
Runt-related transcription factor 1 (RUNX1) also known as acute myeloid leukemia 1 protein (AML1) or core-binding factor subunit alpha-2 (CBFA2) and it is a protein that is encoded by the ''RUNX1'' gene, in humans.
RUNX1 is a transcription facto ...
'' fusion gene that combines two factors that promote blood cell development and the ''BCR''- ''ABL1'' fusion gene of the Philadelphia chromosome
The Philadelphia chromosome or Philadelphia translocation (Ph) is an abnormal version of chromosome 22 where a part of the ''ABL (gene), Abelson murine leukemia'' 1 (''ABL1'') gene on chromosome 9 breaks off and attaches to the ''BCR (gene), break ...
. ''BCR''–''ABL1'' encodes an always-activated tyrosine kinase
A tyrosine kinase is an enzyme that can transfer a phosphate group from ATP to the tyrosine residues of specific proteins inside a cell. It functions as an "on" or "off" switch in many cellular functions.
Tyrosine kinases belong to a larger cla ...
that causes frequent cell division. These mutations produce a cell that divides more often, even in the absence of growth factor
A growth factor is a naturally occurring substance capable of stimulating cell proliferation, wound healing, and occasionally cellular differentiation. Usually it is a secreted protein or a steroid hormone. Growth factors are important for ...
s.
Other genetic changes in B-cell ALL include changes to the number of chromosomes within the leukemic cells. Gaining at least five additional chromosomes, called high hyperdiploidy, occurs more commonly. Less often, chromosomes are lost, called hypodiploidy, which is associated with a poorer prognosis. Additional common genetic changes in B-cell ALL involve non-inherited mutations to ''PAX5'' and ''IKZF1''. In T-cell ALL, ''LYL1
Protein lyl-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LYL1'' gene.
Interactions
LYL1 has been shown to interact with TCF3
Transcription factor 3 (E2A immunoglobulin enhancer-binding factors E12/E47), also known as TCF3, is a protei ...
'', ''TAL1
__NOTOC__
T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia protein 1 (i.e. TAL1 but also termed stem cell leukemia/T-cell acute leukemia 1 .e. SCL/TAL1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TAL1'' gene.
The protein encoded by TAL1 is a basic helix-l ...
'', ''TLX1
T-cell leukemia homeobox protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TLX1'' gene, which was initially named ''HOX11''.
Interactions
TLX1 has been shown to Protein-protein interaction, interact with PPP1CC, PPP2CB and PPP2CA.
...
'', and '' TLX3'' rearrangements can occur.
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia results when enough of these genetic changes are present in a single lymphoblast. In childhood ALL, for example, one fusion gene translocation is often found along with six to eight other ALL-related genetic changes. The initial leukemic lymphoblast copies itself into an excessive number of new lymphoblasts, none of which can develop into functioning lymphocytes. These lymphoblasts build up in the bone marrow and may spread to other sites in the body, such as lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that includ ...
s, the mediastinum
The mediastinum (from ;: mediastina) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is a region that contains vital organs and structures within the thorax, mainly the heart and its vessels, the eso ...
, the spleen
The spleen (, from Ancient Greek '' σπλήν'', splḗn) is an organ (biology), organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter.
The spleen plays important roles in reg ...
, the testicle
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is Homology (biology), homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of Androgen, androgens, p ...
s, and the brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
, leading to the common symptoms of the disease.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing ALL begins with a thorough medical history,physical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a Disease, medical condition. It generally consists of a series of ...
, complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC) or full haemogram (FHG), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide cytometry, information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blo ...
, and blood smears. While many symptoms of ALL can be found in common illnesses, persistent or unexplained symptoms raise suspicion of cancer. Because many features on the medical history and examination are not specific to ALL, further testing is often needed. A large number of white blood cells and lymphoblasts in the circulating blood can be suspicious for ALL because they indicate a rapid production of lymphoid cells in the marrow. The higher these numbers typically point to a worse prognosis. While white blood cell counts at initial presentation can vary significantly, circulating lymphoblast cells are seen on peripheral blood smears in the majority of cases.
A bone marrow biopsy
Bone marrow examination refers to the pathologic analysis of samples of bone marrow obtained by bone marrow biopsy (often called trephine biopsy) and bone marrow aspiration. Bone marrow examination is used in the diagnosis of a number of condit ...
provides conclusive proof of ALL, typically with >20% of all cells being leukemic lymphoblasts. A lumbar puncture (also known as a spinal tap) can determine whether the spinal column and brain have been invaded. Brain and spinal column involvement can be diagnosed either through confirmation of leukemic cells in the lumbar puncture or through clinical signs of CNS leukemia as described above. Laboratory tests that might show abnormalities include blood count, kidney function, electrolyte, and liver enzyme tests.
Pathological
Pathology is the study of disease. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatme ...
examination, cytogenetics
Cytogenetics is essentially a branch of genetics, but is also a part of cell biology/cytology (a subdivision of human anatomy), that is concerned with how the chromosomes relate to cell behaviour, particularly to their behaviour during mitosis an ...
(in particular the presence of Philadelphia chromosome
The Philadelphia chromosome or Philadelphia translocation (Ph) is an abnormal version of chromosome 22 where a part of the ''ABL (gene), Abelson murine leukemia'' 1 (''ABL1'') gene on chromosome 9 breaks off and attaches to the ''BCR (gene), break ...
), and immunophenotyping
Immunophenotyping is a technique used to study the protein expressed by cells. This technique is commonly used in basic science research and laboratory diagnostic purpose. This can be done on tissue section (fresh or fixed tissue), cell suspensio ...
establish whether the leukemic cells are myeloblast
The myeloblast is a unipotent white blood cell which differentiates into the effectors of the granulocyte series. It is found in the bone marrow. Stimulation of myeloblasts by G-CSF and other cytokines triggers maturation, differentiation, prolife ...
ic (neutrophils, eosinophils, or basophils) or lymphoblastic ( B lymphocytes or T lymphocyte
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell ...
s). Cytogenetic testing on the marrow samples can help classify disease and predict how aggressive the disease course will be. Different mutations have been associated with shorter or longer survival. Immunohistochemical
Immunohistochemistry is a form of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens in cells and tissue, by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. Albert Hewett ...
testing may reveal TdT or CALLA
''Calla'' is a genus of flowering plant in the family Araceae, containing the single species ''Calla palustris'' (bog arum, marsh calla, wild calla, squaw claw, and water-arumDickinson, T.; Metsger, D.; Bull, J.; & Dickinson, R. (2004) ROM Field ...
antigens on the surface of leukemic cells. TdT is a protein expressed early in the development of pre-T and pre-B cells, whereas CALLA
''Calla'' is a genus of flowering plant in the family Araceae, containing the single species ''Calla palustris'' (bog arum, marsh calla, wild calla, squaw claw, and water-arumDickinson, T.; Metsger, D.; Bull, J.; & Dickinson, R. (2004) ROM Field ...
is an antigen found in 80% of ALL cases and also in the "blast crisis" of CML.
Medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to revea ...
(such as ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply ...
or CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
ning) can find invasion of other organs
In a multicellular organism, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to a ...
, commonly the lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
s, liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
, spleen
The spleen (, from Ancient Greek '' σπλήν'', splḗn) is an organ (biology), organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter.
The spleen plays important roles in reg ...
, lymph nodes
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped Organ (anatomy), organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphoc ...
, brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
, kidneys
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and right in the retro ...
, and reproductive organs
A sex organ, also known as a reproductive organ, is a part of an organism that is involved in sexual reproduction. Sex organs constitute the primary sex characteristics of an organism. Sex organs are responsible for producing and transporting ...
.
Immunophenotyping
In addition to cell morphology and cytogenetics,immunophenotyping
Immunophenotyping is a technique used to study the protein expressed by cells. This technique is commonly used in basic science research and laboratory diagnostic purpose. This can be done on tissue section (fresh or fixed tissue), cell suspensio ...
, a laboratory technique used to identify proteins that are expressed on their cell surface, is a key component in the diagnosis of ALL. The preferred method of immunophenotyping is through flow cytometry
Flow cytometry (FC) is a technique used to detect and measure the physical and chemical characteristics of a population of cells or particles.
In this process, a sample containing cells or particles is suspended in a fluid and injected into the ...
. In the malignant lymphoblasts of ALL, expression of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT), also known as DNA nucleotidylexotransferase (DNTT) or terminal transferase, is a specialized DNA polymerase expressed in immature, pre-B, pre-T lymphoid cells, and acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphom ...
(TdT) on the cell surface can help differentiate malignant lymphocyte cells from reactive lymphocytes, white blood cells that are reacting normally to an infection in the body. On the other hand, myeloperoxidase
Myeloperoxidase (MPO) is a peroxidase enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MPO'' gene on chromosome 17. MPO is most abundantly expressed in neutrophils (a subtype of white blood cells), and produces hypohalous acids to carry out their anti ...
(MPO), a marker for the myeloid
Myeloid tissue, in the bone marrow sense of the word '' myeloid'' ('' myelo-'' + '' -oid''), is tissue of bone marrow, of bone marrow cell lineage, or resembling bone marrow, and myelogenous tissue (''myelo-'' + '' -genous'') is any tissue ...
lineage, is typically not expressed. Because precursor B cells and precursor T cells look the same, immunophenotyping can help differentiate the subtype of ALL and the level of maturity of the malignant white blood cells. The subtypes of ALL as determined by immunophenotype and according to the stages of maturation.
An extensive panel of monoclonal antibodies to cell surface markers, particularly CD or cluster of differentiation markers, are used to classify cells by lineage. Below are immunological markers associated with B cell and T cell ALL.
Cytogenetics
Cytogenetic analysis has shown different proportions and frequencies of genetic abnormalities in cases of ALL from different age groups. This information is particularly valuable for classification and can in part explain the different prognoses of these groups. In regards to genetic analysis, cases can be stratified according toploidy
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, ...
, a number of sets of chromosomes in the cell, and specific genetic abnormalities, such as translocations
In genetics, chromosome translocation is a phenomenon that results in unusual rearrangement of chromosomes. This includes "balanced" and "unbalanced" translocation, with three main types: "reciprocal", "nonreciprocal" and "Robertsonian" transloc ...
. Hyperdiploid cells are defined as cells with more than 50 chromosomes, while hypodiploid are defined as cells with less than 44 chromosomes. Hyperdiploid cases tend to carry a good prognosis while hypodiploid cases do not. For example, the most common specific abnormality in childhood B-ALL is the t(12;21) ''ETV6
ETV6 (i.e. translocation-Ets-leukemia virus) protein is a transcription factor that in humans is encoded by the ''ETV6'' (previously known as ''TEL'') gene. The ETV6 protein regulates the development and growth of diverse cell types, particularly ...
''–''RUNX1'' translocation, in which the ''RUNX1
Runt-related transcription factor 1 (RUNX1) also known as acute myeloid leukemia 1 protein (AML1) or core-binding factor subunit alpha-2 (CBFA2) and it is a protein that is encoded by the ''RUNX1'' gene, in humans.
RUNX1 is a transcription facto ...
'' gene, encoding a protein involved in transcriptional control of hemopoiesis, has been translocated and repressed by the ''ETV6''–''RUNX1'' fusion protein.
Below is a table with the frequencies of some cytogenetic translocations
In genetics, chromosome translocation is a phenomenon that results in unusual rearrangement of chromosomes. This includes "balanced" and "unbalanced" translocation, with three main types: "reciprocal", "nonreciprocal" and "Robertsonian" transloc ...
and molecular genetic abnormalities in ALL.
Classification
French-American-British Historically, before 2008, ALL was classified morphologically using the French-American-British (FAB) system that heavily relied on morphological assessment. The FAB system takes into account information on size,cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell a ...
, nucleoli
The nucleolus (; : nucleoli ) is the largest structure in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is best known as the site of ribosome biogenesis. The nucleolus also participates in the formation of signal recognition particles and plays a ro ...
, basophilia (color of cytoplasm), and vacuolation
A vacuole () is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in plant and fungal cells and some protist, animal, and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic mo ...
(bubble-like properties).
While some clinicians still use the FAB scheme to describe tumor cell appearance, much of this classification has been abandoned because of its limited impact on treatment choice and prognostic value.
World Health Organization
In 2008, the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
(WHO) classification of ALL was developed in an attempt to create a classification system that was more clinically relevant and could produce meaningful prognostic and treatment decisions. This system recognized differences in genetic, immunophenotype
Immunophenotyping is a technique used to study the protein expressed by cells. This technique is commonly used in basic science research and laboratory diagnostic purpose. This can be done on tissue section (fresh or fixed tissue), cell suspensio ...
, molecular, and morphological features found through cytogenetic
Cytogenetics is essentially a branch of genetics, but is also a part of cell biology/cytology (a subdivision of human anatomy), that is concerned with how the chromosomes relate to cell behaviour, particularly to their behaviour during mitosis an ...
and molecular diagnostics
Molecular diagnostics is a collection of techniques used to analyze biological markers in the genome and proteome, and how their cells express their genes as proteins, applying molecular biology to medical tests, medical testing. In medicine th ...
tests. This subtyping helps determine the prognosis and the most appropriate treatment for each specific case of ALL.
The WHO subtypes related to ALL are:
* B-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma
** Not otherwise specified (NOS)
** with recurrent genetic abnormalities
** with t(9;22)(q34.1;q11.2);''BCR-ABL1''
** with t(v;11q23.3);''KMT2A'' rearranged
** with t(12;21)(p13.2;q22.1); ''ETV6-RUNX1''
** with t(5;14)(q31.1;q32.3) ''IL3-IGH''
** with t(1;19)(q23;p13.3);''TCF3-PBX1''
** with hyperdiploidy
** with hypodiploidy
* T-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma
* Acute leukemias of ambiguous lineage
** Acute undifferentiated leukemia
** Mixed phenotype acute leukemia Mixed-phenotype acute leukemia (MPAL) is a group of blood cancers (leukemia) which have combined features of myeloid and lymphoid cancers. It is a rare disease, constituting about 2–5% of all leukemia cases. It mostly involve myeloid with either ...
(MPAL) with t(9;22)(q34.1;q11.2); ''BCR–ABL1''
** MPAL with t(v;11q23.3); ''KMT2A'' rearranged
** MPAL, B/myeloid, NOS
** MPAL, T/myeloid, NOS
Treatment
 The aim of treatment is to induce a lasting remission, defined as the absence of detectable cancer cells in the body (usually less than 5% blast cells in the bone marrow) or the absence of
The aim of treatment is to induce a lasting remission, defined as the absence of detectable cancer cells in the body (usually less than 5% blast cells in the bone marrow) or the absence of minimal residual disease
Minimal residual disease (MRD), also known as molecular residual disease, is the medical condition in which small number of cancer cells persist in a patient either during or after treatment when the patient is in Remission (medicine), remission ...
.
Over the past several decades, there have been strides to increase the efficacy of treatment regimens, resulting in increased survival rates. Possible treatments for acute leukemia include chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
, steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration.
Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes t ...
s, radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a therapy, treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of treatment of cancer, cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignancy, malignant cell (biology), ...
, intensive combined treatments (including bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It i ...
or stem cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can change into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of cell ...
transplants), targeted therapy, and/or growth factors.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
is the initial treatment of choice, and most people with ALL receive a combination of medications. There are no surgical options because of the body-wide distribution of the malignant cells. In general, cytotoxic chemotherapy for ALL combines multiple antileukemic drugs tailored to each person. Chemotherapy for ALL consists of three phases: remission induction, intensification, and maintenance therapy.
Adult chemotherapy regimens mimic those of childhood ALL; however, are linked with a higher risk of disease relapse with chemotherapy alone. Two subtypes of ALL (B-cell ALL and T-cell ALL) require special considerations when it comes to selecting an appropriate treatment regimen in adults with ALL. B-cell ALL is often associated with cytogenetic abnormalities (specifically, t(8;14), t (2;8), and t(8;22)), which require aggressive therapy consisting of brief, high-intensity regimens. T-cell ALL responds to cyclophosphamide-containing agents the most.
Recent updates on the treatment of adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) include advancements in immunotherapy, particularly the use of monoclonal antibodies like blinatumomab and inotuzumab ozogamicin, which target specific cancer cells and are used alongside stem cell transplantation. Additionally, tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) such as imatinib and dasatinib are incorporated for Philadelphia chromosome-positive ALL, improving treatment outcomes.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy (or radiotherapy) is used on painful bony areas, in high disease burdens, or as part of the preparations for abone marrow transplant
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood, in order to replicate inside a patient and produce a ...
(total body irradiation). In the past, physicians commonly utilized radiation in the form of whole-brain radiation for central nervous system prophylaxis, to prevent the occurrence and/or recurrence of leukemia in the brain. Recent studies showed that CNS chemotherapy provided results as favorable but with fewer developmental side effects. As a result, the use of whole-brain radiation has been more limited. Most specialists in adult leukemia have abandoned the use of radiation therapy for CNS prophylaxis, instead using intrathecal chemotherapy.
Biological therapy
Selection of biological targets based on their combinatorial effects on the leukemic lymphoblasts can lead to clinical trials for improvement in the effects of ALL treatment. Tyrosine-kinase inhibitors (TKIs), such asimatinib
Imatinib, sold under the brand names Gleevec and Glivec (both marketed worldwide by Novartis) among others, is an oral targeted therapy medication used to treat cancer. Imatinib is a small molecule inhibitor targeting multiple tyrosine kinases ...
, are often incorporated into the treatment plan for people with ''Bcr-Abl1+ (Ph+)'' ALL. However, this subtype of ALL is frequently resistant to the combination of chemotherapy and TKIs, and allogeneic stem cell transplantation is often recommended upon relapse.
Blinatumomab is not only a promising add-on to chemotherapy in infant ALL, it is also a promising standalone therapy in children.
Immunotherapy
Chimeric antigen receptor
In biology, chimeric antigen receptors (CARs)—also known as chimeric immunoreceptors, chimeric T cell receptors or artificial T cell receptors—are receptor proteins that have been engineered to give T cells the new ability to target a specific ...
s (CARs) have been developed as a promising immunotherapy
Immunotherapy or biological therapy is the treatment of disease by activating or suppressing the immune system. Immunotherapies designed to elicit or amplify an immune response are classified as ''activation immunotherapies,'' while immunotherap ...
for ALL. This technology uses a single chain variable fragment
A single-chain variable fragment (scFv) is not actually a fragment of an antibody, but instead is a fusion protein of the variable regions of the heavy (VH) and light chains (VL) of immunoglobulins, connected with a short linker peptide of t ...
(scFv) designed to recognize the cell surface marker CD19
B-lymphocyte antigen CD19, also known as CD19 molecule ( Cluster of Differentiation 19), B-Lymphocyte Surface Antigen B4, T-Cell Surface Antigen Leu-12 and CVID3 is a transmembrane protein that in humans is encoded by the gene ''CD19''. In human ...
as a method of treating ALL.
CD19 is a molecule found on all B-cells and can be used as a means of distinguishing the potentially malignant B-cell population. In this therapy, mice are immunized with the CD19 antigen and produce anti-CD19 antibodies. Hybridomas
Hybridoma technology is a method for producing large quantities of monoclonal antibodies by fusing antibody producing B cells with myeloma cells (cancerous B cells). This creates hybrid cells, ''hybridomas,'' that produce the antibody from thei ...
developed from mouse spleen cells fused to a myeloma cell line can be developed as a source for the cDNA encoding the CD19-specific antibody. The cDNA is sequenced and the sequence encoding the variable heavy and variable light chains of these antibodies are cloned together using a small peptide
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty am ...
linker. This resulting sequence encodes the scFv. This can be cloned into a transgene
A transgene is a gene that has been transferred naturally, or by any of a number of genetic engineering techniques, from one organism to another. The introduction of a transgene, in a process known as transgenesis, has the potential to change the ...
, encoding what will become the endodomain of the CAR. Varying arrangements of subunits serve as the endodomain, but they generally consist of the hinge region that attaches to the scFv, a transmembrane region, the intracellular region of a costimulatory molecule such as CD28
CD28 (Cluster of Differentiation 28) is a protein expressed on T cells that provides essential co-stimulation, co-stimulatory signals required for T cell activation and survival. When T cells are stimulated through CD28 in conjunction with the T- ...
, and the intracellular domain of CD3-zeta containing ITAM repeats. Other sequences frequently included are: 4-1bb and OX40. The final transgene sequence, containing the scFv and endodomain sequences is then inserted into immune effector cells that are obtained from the person and expanded ''in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning ''in glass'', or ''in the glass'') Research, studies are performed with Cell (biology), cells or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in ...
''. In trials these have been a type of T-cell
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their ce ...
capable of cytotoxicity
Cytotoxicity is the quality of being toxic to cells. Examples of toxic agents are toxic metals, toxic chemicals, microbe neurotoxins, radiation particles and even specific neurotransmitters when the system is out of balance. Also some types of d ...
.
Inserting the DNA into the effector cell can be accomplished by several methods. Most commonly, this is done using a lentivirus
''Lentivirus'' is a genus of retroviruses that cause chronic and deadly diseases characterized by long incubation periods, in humans and other mammalian species. The genus includes the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), which causes AIDS. Lent ...
that encodes the transgene. Pseudotyped, self-inactivating lentiviruses are an effective method for the stable insertion of a desired transgene into the target cell. Other methods include electroporation
Electroporation, also known as electropermeabilization, is a microbiological and biotechnological technique in which an electric field is applied to cells to briefly increase the permeability of the cell membrane. The application of a high-vo ...
and transfection
Transfection is the process of deliberately introducing naked or purified nucleic acids into eukaryotic cells. It may also refer to other methods and cell types, although other terms are often preferred: " transformation" is typically used to des ...
, but these are limited in their efficacy as transgene expression diminishes over time.
The gene-modified effector cells are then transplanted back into the person. Typically this process is done in conjunction with a conditioning regimen such as cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian cancer, breast cancer ...
, which has been shown to potentiate the effects of infused T-cells. This effect has been attributed to making an immunologic space within which the cells populate. The process as a whole results in an effector cell
In cell biology, an effector cell is any of various types of cell that actively responds to a stimulus and effects some change (brings it about).
Examples of effector cells include:
* The muscle, gland or organ cell capable of responding to ...
, typically a T-cell, that can recognize a tumor cell antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule, moiety, foreign particulate matter, or an allergen, such as pollen, that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response.
...
in a manner that is independent of the major histocompatibility complex
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a large Locus (genetics), locus on vertebrate DNA containing a set of closely linked polymorphic genes that code for Cell (biology), cell surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system. The ...
and which can initiate a cytotoxic response.
In 2017, tisagenlecleucel
Tisagenlecleucel, sold under the brand name Kymriah, is a CAR T cells medication for the treatment of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) which uses the body's own T cells to fight cancer (adoptive cell transfer).
The most common serious ...
was approved by the FDA
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
as a CAR-T
In biology, chimeric antigen receptors (CARs)—also known as chimeric immunoreceptors, chimeric T cell receptors or artificial T cell receptors—are receptor proteins that have been engineered to give T cells the new ability to target a specific ...
therapy for people with acute B-cell lymphoblastic leukaemia who did not respond adequately to other treatments or have relapsed. In a 22-day process, the "drug" is customized for each person. T cells purified from each person are modified by a virus that inserts genes that encode a chimaeric antigen receptor into their DNA, one that recognizes leukemia cells.
Obecabtagene autoleucel (Aucatzyl) was approved for medical use in the United States in November 2024.
Relapsed ALL
Typically, people who experience a relapse in their ALL after initial treatment have a poorer prognosis than those who remain in complete remission after induction therapy. It is unlikely that recurrent leukemia will respond favorably to the standard chemotherapy regimen that was initially implemented, and instead, these people should be trialed on reinduction chemotherapy followed by allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. These people in relapse may also receive blinatumomab, as it has shown to increase remission rates and overall survival rates, without increased toxic effects. Low-dosepalliative
Palliative care (from Latin root "to cloak") is an interdisciplinary medical care-giving approach aimed at optimizing quality of life and mitigating or reducing suffering among people with serious, complex, and often terminal illnesses. Man ...
radiation may also help reduce the burden of tumors inside or outside the central nervous system and alleviate some symptoms.
There has also been evidence and approval of use for dasatinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor
A tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) is a pharmaceutical drug that inhibits tyrosine kinases. Tyrosine kinases are enzymes responsible for the activation of many proteins by signal transduction cascades. The proteins are activated by adding a phosph ...
. It has shown efficacy in cases of people with Ph1-positive and imatinib
Imatinib, sold under the brand names Gleevec and Glivec (both marketed worldwide by Novartis) among others, is an oral targeted therapy medication used to treat cancer. Imatinib is a small molecule inhibitor targeting multiple tyrosine kinases ...
-resistant ALL, but more research needs to be done on long-term survival and time to relapse.
Side effects
Chemotherapies or stem cell transplantations may require aplatelet transfusion
Platelet transfusion, is the process of infusing platelet concentrate into the body via vein, to prevent or treat the bleeding in people with either a thrombocytopenia, low platelet count or poor platelet function. Often this occurs in people ...
to prevent bleeding. Moreover, patients undergoing a stem cell transplantation can develop a graft-versus-host disease
Graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) is a syndrome, characterized by inflammation in different organs. GvHD is commonly associated with bone marrow transplants and stem cell transplants.
White blood cells of the donor's immune system which rema ...
(GvHD). It was evaluated whether mesenchymal stromal cells can be used to prevent a GvHD. The evidence is very uncertain about the therapeutic effect of mesenchymal stromal cells to treat graft-versus-host diseases after a stem cell transplantation on the all-cause mortality and complete disappearance of chronic acute graft-versus-host diseases. Mesenchymal stromal cells may result in little to no difference in the all-cause mortality, relapse of malignant disease, and incidence of acute and chronic graft-versus-host diseases if they are used for prophylactic reasons.
Supportive therapy
Adding physical exercises to the standard treatment for adult patients with haematological malignancies like ALL may result in little to no difference in mortality, quality of life, and physical functioning. These exercises may result in a slight reduction in depression. Furthermore, aerobic physical exercises probably reduce fatigue. The evidence is very uncertain about the effect on anxiety and serious adverse events.Cell therapy
Brexucabtagene autoleucel (Tecartus) was approved by the FDA in October 2021 for the treatment of adults with relapsed or refractory B-cell precursor ALL, and later by the EMA in December 2021. Each dose of brexucabtagene autoleucel is a customized treatment created using the recipient's immune system to help fight the leukaeamia. The recipient'sT cell
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell ...
s, a type of white blood cell, are collected and genetically modified to include a new gene that facilitates the targeting and killing of the lymphoma cells. These modified T cells are then infused back into the recipient.
Prognosis
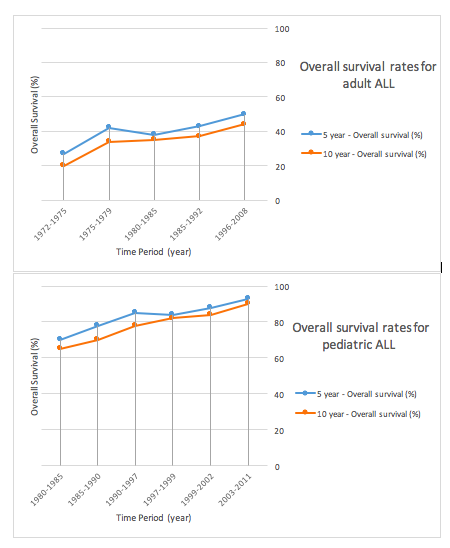
Before the development of chemotherapy regimens and hematopoietic stem cell transplants, children were surviving a median length of 3 months, largely due to either infection or bleeding. Since the advent of chemotherapy, the prognosis for childhood leukemia has improved greatly and children with ALL are estimated to have a 95% probability of achieving a successful remission after 4 weeks of initiating treatment. People in pediatric care with ALL in developed countries have a greater than 80% five-year survival rate. It is estimated that 60–80% of adults undergoing induction chemotherapy achieve complete remission after 4 weeks, and those over the age of 70 have a cure rate of 5%. However, there are differing prognoses for ALL among individuals depending on a variety of factors:
* Gender: Females tend to fare better than males.
* Ethnicity: Caucasians are more likely to develop acute leukemia than
However, there are differing prognoses for ALL among individuals depending on a variety of factors:
* Gender: Females tend to fare better than males.
* Ethnicity: Caucasians are more likely to develop acute leukemia than African-Americans
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from any of the Black racial groups of Africa. ...
, Asians
"Asian people" (sometimes "Asiatic people")United States National Library of Medicine. Medical Subject Headings. 2004. November 17, 200Nlm.nih.gov: ''Asian Continental Ancestry Group'' is also used for categorical purposes. is an umbrella term ...
, or Hispanics
The term Hispanic () are people, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or broadly. In some contexts, especially within the United States, "Hispanic" is used as an ethnic or meta-ethnic term.
The term commonly appli ...
. However, they also tend to have a better prognosis than non-Caucasians.
* Age at diagnosis: children 1–10 years of age are most likely to develop ALL and to be cured of it. Cases in older people are more likely to result from chromosomal abnormalities (e.g., the Philadelphia chromosome) that make treatment more difficult and prognoses poorer. Older people are also likely to have co-morbid medical conditions that make it even more difficult to tolerate ALL treatment.
* White blood cell count at diagnosis of greater than 30,000 (B-ALL) or 100,000 (T-ALL) is associated with worse outcomes
* Cancer spreading into the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
(brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
or spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
) has worse outcomes.
* Morphological, immunological, and genetic subtypes
* Person's response to initial treatment and longer length of time required (greater than 4 weeks) to reach complete remission
* Early relapse of ALL
* Minimal residual disease
Minimal residual disease (MRD), also known as molecular residual disease, is the medical condition in which small number of cancer cells persist in a patient either during or after treatment when the patient is in Remission (medicine), remission ...
* Genetic disorder
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosome abnormality. Although polygenic disorders ...
s, such as Down syndrome, and other chromosomal abnormalities (aneuploidy and translocations)
Cytogenetics, the study of characteristic large changes in the chromosomes
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most importa ...
of cancer cell
Cancer cells are cells that divide continually, forming solid tumors or flooding the blood or lymph with abnormal cells. Cell division is a normal process used by the body for growth and repair. A parent cell divides to form two daughter cells, an ...
s, is an important predictor of outcome. Some cytogenetic subtypes have a worse prognosis than others. These include:
* Person with t(9,22) positive-ALL (30% of adult ALL cases) and other ''Bcr-abl-''rearranged leukemias are more likely to have a poor prognosis, but survival rates may rise with treatment consisting of chemotherapy and ''Bcr-abl'' tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
* A translocation between chromosomes 4 and 11 occurs in about 4% of cases and is most common in infants under 12 months.
* Hyperdiploidy (>50 chromosomes) and t(12;21) are good prognostic factors and also makeup 50% of pediatric ALL cases.
Unclassified ALL is considered to have an intermediate prognosis risk, somewhere in-between the good and poor risk categories.
Epidemiology
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia affected about 876,000 people and resulted in 111,000 deaths globally in 2015. It occurs in both children and adults with the highest rates seen between the ages three and seven years. Around 75% of cases occur before the age of 6 with a secondary rise after the age of 40. It is estimated to affect 1 in 1500 children. Accounting for the broad age profiles of those affected, ALL newly occurs in about 1.7 per 100,000 people annually. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia represents approximately 20% of adults and 80% of childhood leukemias, making it the most common childhood cancer. Although 80 to 90% of children will have a long-term complete response with treatment, it remains the leading cause of cancer-related deaths among children. 85% of cases are of B-cell lineage and have an equal number of cases in both males and females. The remaining 15% of T-cell lineage have a male predominance. Globally, ALL typically occurs more often in Caucasians, Hispanics, and Latin Americans than in Africans. In the US, ALL is more common in children from Caucasian (36 cases/million) and Hispanic (41 cases/million) descent when compared to those from African (15 cases/million) descent.Pregnancy
Leukemia is rarely associated with pregnancy, affecting only about 1 in 10,000 pregnant women. The management of leukemia in a pregnant woman depends primarily on the type of leukemia. Acute leukemias normally require prompt, aggressive treatment, despite significant risks ofpregnancy loss Pregnancy loss is the loss of an embryo or fetus. The terms early pregnancy loss and late pregnancy loss are often used but there is no consensus over their definitions.
Unintentional pregnancy loss
* Miscarriage
** Toxic abortion, caused by poll ...
and birth defect
A birth defect is an abnormal condition that is present at birth, regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth de ...
s, especially if chemotherapy is given during the developmentally sensitive first trimester
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception usually occurs following vaginal intercourse, but can also ...
.
References
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Acute lymphocytic leukemia Articles containing video clips Pediatric cancers Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate