|
Myeloid Leukemia
Myeloid leukemia is a type of leukemia affecting myeloid tissue. Types include: * Acute myeloid leukemia: A cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of myeloblasts that build up in the bone marrow and blood and interfere with normal blood cell production. * Chronic myelogenous leukemia: A cancer of the white blood cells. * Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia: A life-threatening leukemia in which malignant megakaryoblasts proliferate abnormally and injure various tissues. * Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: A rare hematologic malignancy which is a malignancy of plasmacytoid dendritic cells. See also * Hematological malignancies * Myeloblast The myeloblast is a unipotent white blood cell which differentiates into the effectors of the granulocyte series. It is found in the bone marrow. Stimulation of myeloblasts by G-CSF and other cytokines triggers maturation, differentiation, prolife ... * transient myeloproliferative disease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oncology
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the study, treatment, diagnosis, and prevention of cancer. A medical professional who practices oncology is an ''oncologist''. The name's Etymology, etymological origin is the Greek word ὄγκος (''ónkos''), meaning "tumor", "volume" or "mass". Oncology is focused on the diagnosis of cancer in a person, therapy (e.g., surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and other modalities), monitoring of patients after treatment, palliative care of people with advanced-stage cancers, Ethics, ethical questions surrounding cancer care, Screening (medicine), screening of patients, and the study of cancer treatments through clinical research. An oncologist typically focuses on a specialty area in cancer treatment, such as surgery, Radiation therapy, radiation, gynecology, gynecologic oncology, geriatrics, geriatric oncology, pediatrics, pediatric oncology, and various organ-specific disciplines (breast, brain, liver, among others). The exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
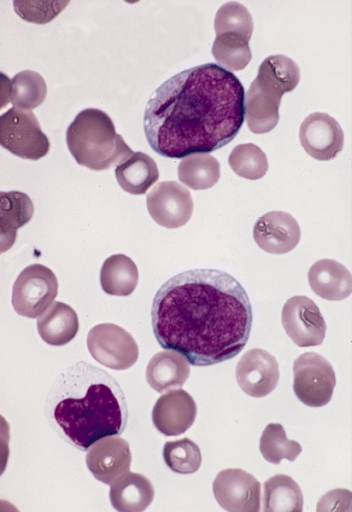
Acute Megakaryoblastic Leukemia
Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (AMKL) is life-threatening leukemia in which malignant megakaryoblasts proliferate abnormally and injure various tissues. Megakaryoblasts are the most immature precursor cells in a platelet-forming lineage; they mature to promegakaryocytes and, ultimately, megakaryocytes which cells shed membrane-enclosed particles, i.e. platelets, into the circulation. Platelets are critical for the normal clotting of blood. While malignant megakaryoblasts usually are the predominant proliferating and tissue-damaging cells, their similarly malignant descendants, promegakaryocytes and megakaryocytes, are variable contributors to the malignancy. AMKL is commonly regarded as a subtype of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). More formally, it is classified under the AML- M7 category of the French-American-British classification and by the World Health Organization of 2016 in the AML-Not Otherwise Specified subcategory. Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia falls into three dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myeloid Leukemia
Myeloid leukemia is a type of leukemia affecting myeloid tissue. Types include: * Acute myeloid leukemia: A cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of myeloblasts that build up in the bone marrow and blood and interfere with normal blood cell production. * Chronic myelogenous leukemia: A cancer of the white blood cells. * Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia: A life-threatening leukemia in which malignant megakaryoblasts proliferate abnormally and injure various tissues. * Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: A rare hematologic malignancy which is a malignancy of plasmacytoid dendritic cells. See also * Hematological malignancies * Myeloblast The myeloblast is a unipotent white blood cell which differentiates into the effectors of the granulocyte series. It is found in the bone marrow. Stimulation of myeloblasts by G-CSF and other cytokines triggers maturation, differentiation, prolife ... * transient myeloproliferative disease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transient Myeloproliferative Disease
Transient myeloproliferative disease (TMD) occurs in a significant percentage of individuals born with the congenital genetic disorder, Down syndrome. It may occur in individuals who are not diagnosed with the syndrome but have some hematological cells containing genetic abnormalities that are similar to those found in Down syndrome. TMD usually develops in utero, is diagnosed prenatally or within ~3 months of birth, and thereafter resolves rapidly and spontaneously. However, during the prenatal-to-postnatal period, the disease may cause irreparable damage to various organs and in ~20% of individuals death. Moreover, ~10% of individuals diagnosed with TMD develop acute megakaryoblastic leukemia at some time during the 5 years following its resolution. TMD is a life-threatening, precancerous condition in fetuses as well as infants in their first few months of life. Transient myeloproliferative disease involves the excessive proliferation of non-malignant megakaryoblasts. Megakaryobl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myeloblast
The myeloblast is a unipotent white blood cell which differentiates into the effectors of the granulocyte series. It is found in the bone marrow. Stimulation of myeloblasts by G-CSF and other cytokines triggers maturation, differentiation, proliferation and cell survival. Structure Myeloblasts reside extravascularly in the bone marrow. Hematopoiesis takes place in the extravascular cavities between the sinuses of the marrow. The wall of the sinuses is composed of two different types of cells, endothelial cells and adventitial reticular cells. The hemopoietic cells are aligned in cords or wedges between these sinuses, with myeloblasts and other granular progenitors concentrated in the subcortical regions of these hemopoietic cords. Myeloblasts are rather small cells with a diameter between 14 and 18μm. The major part is occupied by a large oval nucleus composed of very fine nonaggregated chromatin and possessing 3 or more nucleoli. The cytoplasm has a basophilic character an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematological Malignancies
Tumors of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues (American English) or tumours of the haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues (British English) are tumors that affect the blood, bone marrow, lymph, and lymphatic system. Because these tissues are all intimately connected through both the circulatory system and the immune system, a disease affecting one will often affect the others as well, making aplasia, myeloproliferation and lymphoproliferation (and thus the leukemias, myelomas, and the lymphomas) closely related and often overlapping problems. While uncommon in solid tumors, chromosomal translocations are a common cause of these diseases. This commonly leads to a different approach in diagnosis and treatment of hematological malignancies. Hematological malignancies are malignant neoplasms ("cancer"), and they are generally treated by specialists in hematology and/or oncology. In some centers "hematology/oncology" is a single subspecialty of internal medicine while in others they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) are a rare type of immune cell that are known to secrete large quantities of type 1 interferon (IFNs) in response to a viral infection. They circulate in the blood and are found in peripheral lymphoid organs. They develop from bone marrow hematopoietic stem cells and constitute 2% of nucleated cells) and bone marrow and evidence (i.e. cytopenias) of bone marrow failure. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm has a high rate of recurrence following initial treatments with various chemotherapy regimens. In consequence, the disease has a poor overall prognosis and newer chemotherapeutic and novel non-chemotherapeutic drug regimens to improve the situation are under study. Role in immunity Upon stimulation and subsequent activation of TLR7 and TLR9, these cells produce large amounts (up to 1,000 times more than other cell type) of type I interferon (mainly IFN-α and IFN-β), which are critical anti-viral compounds mediating a wide range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematologic Disease
Hematologic diseases are disorders which primarily affect the blood and blood-forming organs. Hematologic diseases include rare genetic disorders, anemia, HIV, sickle cell disease and complications from chemotherapy or transfusions. Myeloid * Hemoglobinopathies (congenital abnormality of the hemoglobin molecule or of the rate of hemoglobin synthesis) ** Sickle cell disease ** Thalassemia ** Methemoglobinemia * Anemias (lack of red blood cells or hemoglobin) ** Iron-deficiency anemia ** Megaloblastic anemia *** Vitamin B12 deficiency **** Pernicious anemia *** Folate deficiency ** Hemolytic anemias (destruction of red blood cells) *** Genetic disorders of RBC membrane **** Hereditary spherocytosis **** Hereditary elliptocytosis **** Congenital dyserythropoietic anemia *** Genetic disorders of RBC metabolism **** Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PD) **** Pyruvate kinase deficiency *** Immune mediated hemolytic anemia ( direct Coombs test is positive) **** Autoim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blastic Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Neoplasm
Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN) is a rare hematologic malignancy. It was initially regarded as a form of lymphocyte-derived cutaneous lymphoma and alternatively named CD4+CD56+ hematodermic tumor, blastic NK cell lymphoma, and agranular CD4+ NK cell leukemia. Later, however, the disease was determined to be a malignancy of plasmacytoid dendritic cells rather than lymphocytes and therefore termed blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm. In 2016, the World Health Organization designated BPDCN to be in its own separate category within the myeloid class of neoplasms. It is estimated that BPDCN constitutes 0.44% of all hematological malignancies. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm is an aggressive malignancy with features of cutaneous lymphoma (e.g. malignant plasmacytoid dendritic cell infiltrations into the skin to form single or multiple lesions) and/or leukemia (i.e. malignant plasmacytoid dendritic cells in blood and bone marrow). While common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megakaryoblast
A megakaryoblast () is a precursor cell to a promegakaryocyte. During thrombopoiesis, the promegakaryocyte matures into the form of a megakaryocyte. From the megakaryocyte, platelets are formed. The megakaryoblast is the beginning of the thrombocytic series or platelet forming series. Megakaryoblasts typically have a large oval-shaped nucleus or a nucleus that is lobed with many nuclei. The megakaryoblast resembles the myeloblast or lymphoblast morphologically; however the megakaryoblast varies in phenotype and the structure viewed with electron microscopy. Increased amounts of megakaryoblasts in the bone marrow may indicate a disease state. An example of this is acute megakaryoblastic leukemia, which occurs when the level of megakaryoblasts in the bone marrow exceeds 20%. Development The megakaryocyte develops through the following lineage: : CFU-Meg (hematopoietic stem cell/hemocytoblast) → megakaryoblast → promegakaryocyte → megakaryocyte The megakaryoblast is deri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malignant
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous benign tumor, ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not self-limited in its growth, is capable of invading into adjacent tissues, and may be capable of spreading to distant tissues. A benign tumor has none of those properties, but may still be harmful to health. The term benign in more general medical use characterizes a condition or growth that is not cancerous, i.e. does not spread to other parts of the body or invade nearby tissue. Sometimes the term is used to suggest that a condition is not dangerous or serious. Malignancy in cancers is characterized by anaplasia, invasiveness, and metastasis. Malignant tumors are also characterized by genome instability, so that cancers, as assessed by whole genome sequencing, frequently have between 10,000 and 100,000 mutations in their ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Blood Cell
White blood cells (scientific name leukocytes), also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign entities. White blood cells are generally larger than red blood cells. They include three main subtypes: granulocytes, lymphocytes and monocytes. All white blood cells are produced and derived from multipotent cells in the bone marrow known as hematopoietic stem cells. Leukocytes are found throughout the body, including the blood and lymphatic system. All white blood cells have nuclei, which distinguishes them from the other blood cells, the anucleated red blood cells (RBCs) and platelets. The different white blood cells are usually classified by cell lineage ( myeloid cells or lymphoid cells). White blood cells are part of the body's immune system. They help the body fight infection and other diseases. Types of white blood cells are granulocytes (neutrophils, eosino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |