Aural Imbalance on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory science.
Sound may be heard through solid,
 There are three main components of the human
There are three main components of the human
 The inner ear consists of the cochlea, which is a spiral-shaped, fluid-filled tube. It is divided lengthwise by the organ of Corti, which is the main organ of mechanical to neural transduction. Inside the organ of Corti is the basilar membrane, a structure that vibrates when waves from the middle ear propagate through the cochlear fluid – endolymph. The basilar membrane is tonotopic, so that each frequency has a characteristic place of resonance along it. Characteristic frequencies are high at the basal entrance to the cochlea, and low at the apex. Basilar membrane motion causes depolarization of the hair cells, specialized auditory receptors located within the organ of Corti. While the hair cells do not produce action potentials themselves, they release neurotransmitter at synapses with the fibers of the auditory nerve, which does produce action potentials. In this way, the patterns of oscillations on the basilar membrane are converted to
The inner ear consists of the cochlea, which is a spiral-shaped, fluid-filled tube. It is divided lengthwise by the organ of Corti, which is the main organ of mechanical to neural transduction. Inside the organ of Corti is the basilar membrane, a structure that vibrates when waves from the middle ear propagate through the cochlear fluid – endolymph. The basilar membrane is tonotopic, so that each frequency has a characteristic place of resonance along it. Characteristic frequencies are high at the basal entrance to the cochlea, and low at the apex. Basilar membrane motion causes depolarization of the hair cells, specialized auditory receptors located within the organ of Corti. While the hair cells do not produce action potentials themselves, they release neurotransmitter at synapses with the fibers of the auditory nerve, which does produce action potentials. In this way, the patterns of oscillations on the basilar membrane are converted to
 The sound information from the cochlea travels via the auditory nerve to the cochlear nucleus in the
The sound information from the cochlea travels via the auditory nerve to the cochlear nucleus in the
 Not all sounds are normally audible to all animals. Each species has a range of normal hearing for both amplitude and
Not all sounds are normally audible to all animals. Each species has a range of normal hearing for both amplitude and
World Health Organization, Deafness and Hearing Loss
* * *
Open University - OpenLearn - Article about hearing
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hearing (Sense) Sound Audiology Auditory system
liquid
A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. As such, it is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, gas, a ...
, or gaseous matter. It is one of the traditional five senses. Partial or total inability to hear is called hearing loss.
In humans and other vertebrates, hearing is performed primarily by the auditory system
The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs (the ears) and the auditory parts of the sensory system.
System overview
The outer ear funnels sound vibrations to the eardrum, increasin ...
: mechanical waves, known as vibrations, are detected by the ear and transduced into nerve impulses that are perceived by the brain (primarily in the temporal lobe). Like touch, audition requires sensitivity to the movement of molecules in the world outside the organism. Both hearing and touch are types of mechanosensation.
Hearing mechanism
 There are three main components of the human
There are three main components of the human auditory system
The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs (the ears) and the auditory parts of the sensory system.
System overview
The outer ear funnels sound vibrations to the eardrum, increasin ...
: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear.
Outer ear
The outer ear includes the pinna, the visible part of the ear, as well as theear canal
The ear canal (external acoustic meatus, external auditory meatus, EAM) is a pathway running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The adult human ear canal extends from the pinna to the eardrum and is about in length and in diameter.
Struc ...
, which terminates at the eardrum
In the anatomy of humans and various other tetrapods, the eardrum, also called the tympanic membrane or myringa, is a thin, cone-shaped membrane that separates the external ear
The outer ear, external ear, or auris externa is the extern ...
, also called the tympanic membrane. The pinna serves to focus sound waves through the ear canal toward the eardrum. Because of the asymmetrical character of the outer ear of most mammals, sound is filtered differently on its way into the ear depending on the location of its origin. This gives these animals the ability to localize sound vertically. The eardrum is an airtight membrane, and when sound waves arrive there, they cause it to vibrate following the waveform of the sound. Cerumen (ear wax) is produced by ceruminous and sebaceous glands in the skin of the human ear canal, protecting the ear canal and tympanic membrane from physical damage and microbial invasion.
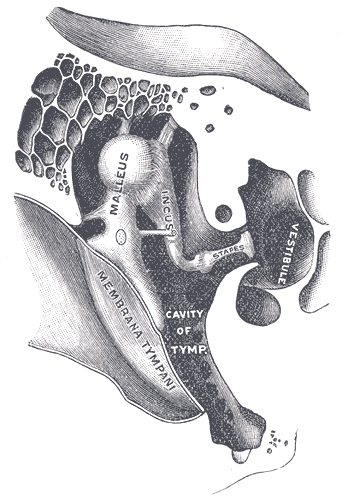
Middle ear
The middle ear consists of a small air-filled chamber that is located medial to the eardrum. Within this chamber are the three smallest bones in the body, known collectively as theossicles
The ossicles (also called auditory ossicles) are three bones in either middle ear that are among the smallest bones in the human body. They serve to transmit sounds from the air to the fluid-filled labyrinth (cochlea). The absence of the auditory ...
which include the malleus, incus, and stapes (also known as the hammer, anvil, and stirrup, respectively). They aid in the transmission of the vibrations from the eardrum into the inner ear, the cochlea. The purpose of the middle ear ossicles is to overcome the impedance mismatch between air waves and cochlear waves, by providing impedance matching.
Also located in the middle ear are the stapedius muscle and tensor tympani muscle, which protect the hearing mechanism through a stiffening reflex. The stapes transmits sound waves to the inner ear through the oval window, a flexible membrane separating the air-filled middle ear from the fluid-filled inner ear. The round window, another flexible membrane, allows for the smooth displacement of the inner ear fluid caused by the entering sound waves.
Inner ear
 The inner ear consists of the cochlea, which is a spiral-shaped, fluid-filled tube. It is divided lengthwise by the organ of Corti, which is the main organ of mechanical to neural transduction. Inside the organ of Corti is the basilar membrane, a structure that vibrates when waves from the middle ear propagate through the cochlear fluid – endolymph. The basilar membrane is tonotopic, so that each frequency has a characteristic place of resonance along it. Characteristic frequencies are high at the basal entrance to the cochlea, and low at the apex. Basilar membrane motion causes depolarization of the hair cells, specialized auditory receptors located within the organ of Corti. While the hair cells do not produce action potentials themselves, they release neurotransmitter at synapses with the fibers of the auditory nerve, which does produce action potentials. In this way, the patterns of oscillations on the basilar membrane are converted to
The inner ear consists of the cochlea, which is a spiral-shaped, fluid-filled tube. It is divided lengthwise by the organ of Corti, which is the main organ of mechanical to neural transduction. Inside the organ of Corti is the basilar membrane, a structure that vibrates when waves from the middle ear propagate through the cochlear fluid – endolymph. The basilar membrane is tonotopic, so that each frequency has a characteristic place of resonance along it. Characteristic frequencies are high at the basal entrance to the cochlea, and low at the apex. Basilar membrane motion causes depolarization of the hair cells, specialized auditory receptors located within the organ of Corti. While the hair cells do not produce action potentials themselves, they release neurotransmitter at synapses with the fibers of the auditory nerve, which does produce action potentials. In this way, the patterns of oscillations on the basilar membrane are converted to spatiotemporal pattern
Spatiotemporal patterns are patterns that occur in a wide range of natural phenoma and are characterized by a spatial and a temporal patterning. The general rules of pattern formation hold. In contrast to "static", pure spatial patterns, the ...
s of firings which transmit information about the sound to the brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is cont ...
.
Neuronal
brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is cont ...
. From there, the signals are projected to the inferior colliculus in the midbrain tectum. The inferior colliculus integrates auditory input with limited input from other parts of the brain and is involved in subconscious reflexes such as the auditory startle response
In animals, including humans, the startle response is a largely unconscious defensive response to sudden or threatening stimuli, such as sudden noise or sharp movement, and is associated with negative Affect (psychology), affect.Rammirez-Moreno, D ...
.
The inferior colliculus in turn projects to the medial geniculate nucleus, a part of the thalamus where sound information is relayed to the primary auditory cortex in the temporal lobe. Sound is believed to first become consciously experienced at the primary auditory cortex. Around the primary auditory cortex lies Wernickes area
Wernicke's area (; ), also called Wernicke's speech area, is one of the two parts of the cerebral cortex that are linked to speech, the other being Broca's area. It is involved in the comprehension of written and spoken language, in contrast to B ...
, a cortical area involved in interpreting sounds that is necessary to understand spoken words.
Disturbances (such as stroke
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functionin ...
or trauma) at any of these levels can cause hearing problems, especially if the disturbance is bilateral. In some instances it can also lead to auditory hallucinations or more complex difficulties in perceiving sound.
Hearing tests
Hearing can be measured by behavioral tests using an audiometer. Electrophysiological tests of hearing can provide accurate measurements of hearing thresholds even in unconscious subjects. Such tests include auditory brainstem evoked potentials (ABR), otoacoustic emissions (OAE) and electrocochleography (ECochG). Technical advances in these tests have allowed hearing screening for infants to become widespread. Hearing can be measured by mobile applications which includes audiological hearing test function orhearing aid application
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory ...
. These applications allow the user to measure hearing thresholds at different frequencies ( audiogram). Despite possible errors in measurements, hearing loss can be detected.
Hearing loss
There are several different types of hearing loss: conductive hearing loss,sensorineural hearing loss
Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is a type of hearing loss in which the root cause lies in the inner ear or sensory organ (cochlea and associated structures) or the vestibulocochlear nerve (cranial nerve VIII). SNHL accounts for about 90% of rep ...
and mixed types.
There are defined degrees of hearing loss:
* Mild hearing loss - People with mild hearing loss have difficulties keeping up with conversations, especially in noisy surroundings. The most quiet sounds that people with mild hearing loss can hear with their better ear are between 25 and 40 dB HL.
* Moderate hearing loss - People with moderate hearing loss have difficulty keeping up with conversations when they are not using a hearing aid. On average, the most quiet sounds heard by people with moderate hearing loss with their better ear are between 40 and 70 dB HL.
* Severe hearing loss - People with severe hearing loss depend on powerful hearing aid. However, they often rely on lip-reading even when they are using hearing aids. The most quiet sounds heard by people with severe hearing loss with their better ear are between 70 and 95 dB HL.
* Profound hearing loss - People with profound hearing loss are very hard of hearing and they mostly rely on lip-reading and sign language. The most quiet sounds heard by people with profound hearing loss with their better ear are from 95 dB HL or more.
Causes
*Heredity *Congenital conditions *Presbycusis *Acquired **Noise-induced hearing loss **Ototoxic drugs and chemicals **InfectionPrevention
Hearing protection is the use of devices designed to preventnoise-induced hearing loss
Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) is a hearing impairment resulting from exposure to loud sound. People may have a loss of perception of a narrow range of frequencies or impaired perception of sound including sensitivity to sound or ringing ...
(NIHL), a type of post-lingual hearing impairment Post-lingual deafness is a deafness which develops after the acquisition of speech and language, usually after the age of six.
Post-lingual hearing impairments are far more common than prelingual deafness. Typically, hearing loss is gradual, and o ...
. The various means used to prevent hearing loss generally focus on reducing the levels of noise to which people are exposed. One way this is done is through environmental modifications such as acoustic quieting Acoustic quieting is the process of making machinery quieter by damping vibrations to prevent them from reaching the observer. Machinery vibrates, causing sound waves in air, hydroacoustic waves in water, and mechanical stresses in solid matter. ...
, which may be achieved with as basic a measure as lining a room with curtain
A curtain is a piece of cloth or other material intended to block or obscure light, air drafts, or (in the case of a shower curtain), water. A curtain is also the movable screen or theater curtain, drape in a theatre that separates the stage fro ...
s, or as complex a measure as employing an anechoic chamber
An anechoic chamber (''an-echoic'' meaning "non-reflective") is a room designed to stop reflections of either sound or electromagnetic waves. They are also often isolated from energy entering from their surroundings. This combination means t ...
, which absorbs nearly all sound. Another means is the use of devices such as earplug
An earplug is a device that is inserted in the ear canal to protect the user's ears from loud noises, intrusion of water, foreign bodies, dust or excessive wind. Since they reduce the sound volume, earplugs are often used to help prevent hearing ...
s, which are inserted into the ear canal to block noise, or earmuffs
Earmuffs are clothing accessories or personal protective equipment designed to cover a person's ears for hearing protection or warmth. They consist of a thermoplastic or metal head-band that fits over the top or back of the head, and a cushion ...
, objects designed to cover a person's ears entirely.
Management
The loss of hearing, when it is caused by neural loss, cannot presently be cured. Instead, its effects can be mitigated by the use of audioprosthetic devices, i.e. hearing assistive devices such ashearing aid
A hearing aid is a device designed to improve hearing by making sound audible to a person with hearing loss. Hearing aids are classified as medical devices in most countries, and regulated by the respective regulations. Small audio amplifiers su ...
s and cochlear implants
A cochlear implant (CI) is a surgically implanted neuroprosthesis that provides a person who has moderate-to-profound sensorineural hearing loss with sound perception. With the help of therapy, cochlear implants may allow for improved speech unde ...
. In a clinical setting, this management is offered by otologists and audiologists
Audiology (from Latin , "to hear"; and from Greek , ''-logia'') is a branch of science that studies hearing, balance, and related disorders. Audiologists treat those with hearing loss and proactively prevent related damage. By employing various ...
.
Relation to health
Hearing loss
Hearing loss is a partial or total inability to hear. Hearing loss may be present at birth or acquired at any time afterwards. Hearing loss may occur in one or both ears. In children, hearing problems can affect the ability to acquire spoken la ...
is associated with Alzheimer's disease and dementia
Dementia is a disorder which manifests as a set of related symptoms, which usually surfaces when the brain is damaged by injury or disease. The symptoms involve progressive impairments in memory, thinking, and behavior, which negatively affe ...
with a greater degree of hearing loss tied to a higher risk. There is also an association between type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes, formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urinati ...
and hearing loss.
Hearing underwater
Hearing threshold and the ability to localize sound sources are reduced underwater in humans, but not in aquatic animals, including whales, seals, and fish which have ears adapted to process water-borne sound.In vertebrates
frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from '' angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is ...
. Many animals use sound to communicate with each other, and hearing in these species is particularly important for survival and reproduction. In species that use sound as a primary means of communication, hearing is typically most acute for the range of pitches produced in calls and speech.
Frequency range
Frequencies capable of being heard by humans are calledaudio
Audio most commonly refers to sound, as it is transmitted in signal form. It may also refer to:
Sound
*Audio signal, an electrical representation of sound
*Audio frequency, a frequency in the audio spectrum
* Digital audio, representation of soun ...
or sonic. The range is typically considered to be between 20 Hz and 20,000 Hz. Frequencies higher than audio are referred to as ultrasonic
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies f ...
, while frequencies below audio are referred to as infrasonic
Infrasound, sometimes referred to as low status sound, describes sound waves with a frequency below the lower limit of human audibility (generally 20 Hz). Hearing becomes gradually less sensitive as frequency decreases, so for humans to perce ...
. Some bats
Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera.''cheir'', "hand" and πτερόν''pteron'', "wing". With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most bi ...
use ultrasound for echolocation while in flight. Dog
The dog (''Canis familiaris'' or ''Canis lupus familiaris'') is a domesticated descendant of the wolf. Also called the domestic dog, it is derived from the extinct Pleistocene wolf, and the modern wolf is the dog's nearest living relativ ...
s are able to hear ultrasound, which is the principle of 'silent' dog whistle
A dog whistle (also known as silent whistle or Galton's whistle) is a type of whistle that emits sound in the ultrasonic range, which humans cannot hear but some other animals can, including dogs and domestic cats, and is used in their traini ...
s. Snake
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more j ...
s sense infrasound through their jaws, and baleen whale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully aquatic placental marine mammals. As an informal and colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea, i.e. all cetaceans apart from dolphins and ...
s, giraffe
The giraffe is a large African hoofed mammal belonging to the genus ''Giraffa''. It is the tallest living terrestrial animal and the largest ruminant on Earth. Traditionally, giraffes were thought to be one species, '' Giraffa cameloparda ...
s, dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal within the infraorder Cetacea. Dolphin species belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontoporiidae (t ...
s and elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae ...
s use it for communication. Some fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% ...
have the ability to hear more sensitively due to a well-developed, bony connection between the ear and their swim bladder. This "aid to the deaf" for fishes appears in some species such as carp
Carp are various species of oily freshwater fish from the family Cyprinidae, a very large group of fish native to Europe and Asia. While carp is consumed in many parts of the world, they are generally considered an invasive species in parts of ...
and herring
Herring are forage fish, mostly belonging to the family of Clupeidae.
Herring often move in large schools around fishing banks and near the coast, found particularly in shallow, temperate waters of the North Pacific and North Atlantic Ocea ...
.
In invertebrates
Even though they don’t have ears, invertebrates have developed other structures and systems to decode vibrations traveling through the air, or “sound.” Charles Henry Turner was the first scientist to formally show this phenomenon through rigorously controlled experiments in ants. Turner ruled out the detection of ground vibration and suggested that other insects likely have auditory systems as well. Many insects detect sound through the way air vibrations deflect hairs along their body. Some insects have even developed specialized hairs tuned to detecting particular frequencies, such as certain caterpillar species that have evolved hair with properties such that it resonates most with the sound of buzzing wasps, thus warning them of the presence of natural enemies. Tautz, Jürgen, and Michael Rostás. "Honeybee buzz attenuates plant damage by caterpillars." Current Biology 18, no. 24 (2008): R1125-R1126. Some insects possess atympanal organ
A tympanal organ (or tympanic organ) is a hearing organ in insects, consisting of a membrane ( tympanum) stretched across a frame backed by an air sac and associated sensory neurons. Sounds vibrate the membrane, and the vibrations are sensed by ...
. These are "eardrums", that cover air filled chambers on the legs. Similar to the hearing process with vertebrates, the eardrums react to sonar waves. Receptors that are placed on the inside translate the oscillation into electric signals and send them to the brain. Several groups of flying insects that are preyed upon by echolocating bat
Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera.''cheir'', "hand" and πτερόν''pteron'', "wing". With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most bi ...
s can perceive the ultrasound emissions this way and reflexively practice ultrasound avoidance Ultrasound avoidance is an escape or avoidance reflex displayed by certain animal species that are preyed upon by echolocating predators. Ultrasound avoidance is known for several groups of insects that have independently evolved mechanisms for ult ...
.
See also
Physiological
*Ear
An ear is the organ that enables hearing and, in mammals, body balance using the vestibular system. In mammals, the ear is usually described as having three parts—the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The outer ear consists ...
* Hearing loss
Hearing loss is a partial or total inability to hear. Hearing loss may be present at birth or acquired at any time afterwards. Hearing loss may occur in one or both ears. In children, hearing problems can affect the ability to acquire spoken la ...
* Hearing test
A hearing test provides an evaluation of the sensitivity of a person's sense of hearing and is most often performed by an audiologist using an audiometer. An audiometer is used to determine a person's hearing sensitivity at different frequencie ...
General
*Auditory scene analysis
In perception and psychophysics, auditory scene analysis (ASA) is a proposed model for the basis of auditory perception. This is understood as the process by which the human auditory system organizes sound into perceptually meaningful elements. T ...
* Auditory science Auditory science or hearing science is a field of research and education concerning the perception of sounds by humans, animals, or machines. It is a heavily interdisciplinary field at the crossroad between acoustics, neuroscience, and psychology. ...
* Auditory system
The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs (the ears) and the auditory parts of the sensory system.
System overview
The outer ear funnels sound vibrations to the eardrum, increasin ...
* Bone conduction
Bone conduction is the conduction of sound to the inner ear primarily through the bones of the skull, allowing the hearer to perceive audio content without blocking the ear canal. Bone conduction transmission occurs constantly as sound waves vib ...
* Hearing range
Hearing range describes the range of frequencies that can be heard by humans or other animals, though it can also refer to the range of levels. The human range is commonly given as 20 to 20,000 Hz, although there is considerable variatio ...
* Human echolocation
Human echolocation is the ability of humans to detect objects in their environment by sensing echoes from those objects, by actively creating sounds: for example, by tapping their canes, lightly stomping their foot, snapping their fingers, or maki ...
* Listening
Listening is giving attention to a sound or action. When listening, a person hears what others are saying and tries to understand what it means. The act of listening involves complex affective, cognitive and behavioral processes. Affective p ...
* Neuronal encoding of sound
The neural encoding of sound is the representation of auditory sensation and perception in the nervous system.
This article explores the basic physiological principles of sound perception, and traces hearing mechanisms from sound as pressure ...
* Temporal envelope and fine structure Temporal envelope (ENV) and temporal fine structure (TFS) are changes in the amplitude and frequency of sound perceived by humans over time. These temporal changes are responsible for several aspects of auditory perception, including loudness, pitc ...
*World Hearing Day
World Hearing Day is a campaign held each year by Office of Prevention of Blindness and Deafness of the World Health Organization (WHO). Activities take place across the globe and an event is hosted at the World Health Organization on March 3. The ...
*Safe listening
Safe listening is a framework for health promotion actions to ensure that sound-related recreational activities (such as concerts, nightclubs, and listening to music, broadcasts, or podcasts) do not pose a risk to hearing.
While research shows ...
Test and measurement
*Audiogram
An audiogram is a graph that shows the audible threshold for standardized frequencies as measured by an audiometer. The Y axis represents intensity measured in decibels and the X axis represents frequency measured in hertz. The threshold of hea ...
* Audiometry
Audiometry () is a branch of audiology and the science of measuring hearing acuity for variations in sound intensity and pitch and for tonal purity, involving thresholds and differing frequencies. Typically, audiometric tests determine a subj ...
* Dichotic listening
Dichotic listening is a psychological test commonly used to investigate selective attention and the lateralization of brain function within the auditory system. It is used within the fields of cognitive psychology and neuroscience.
In a standard ...
(test)
* Auditory brainstem response
The auditory brainstem response (ABR), also called brainstem evoked response audiometry (BERA), is an auditory evoked potential extracted from ongoing electrical activity in the brain and recorded via electrodes placed on the scalp. The measured ...
(test)
Disorders
*Auditory processing disorder
Auditory processing disorder (APD), rarely known as King-Kopetzky syndrome or auditory disability with normal hearing (ADN), is a neurodevelopmental disorder affecting the way the brain processes auditory information. Individuals with APD usually ...
* Endaural phenomena
Endaural phenomena are sounds that are heard without any external acoustic stimulation. Endaural means "in the ear". Phenomena include transient ringing in the ears (that sound like sine tones), white noise-like sounds, and subjective tinnitus. En ...
* Hearing loss
Hearing loss is a partial or total inability to hear. Hearing loss may be present at birth or acquired at any time afterwards. Hearing loss may occur in one or both ears. In children, hearing problems can affect the ability to acquire spoken la ...
* Hyperacusis
Hyperacusis is the increased sensitivity to sound and a low tolerance for environmental noise. Definitions of hyperacusis can vary significantly; it can refer to normal noises being perceived as: loud, annoying, painful, fear-inducing, or a combina ...
* Presbycusis
Presbycusis (also spelled presbyacusis, from Greek πρέσβυς ''presbys'' "old" + ἄκουσις ''akousis'' "hearing"), or age-related hearing loss, is the cumulative effect of aging on hearing. It is a progressive and irreversible bilateral ...
* Tinnitus
Tinnitus is the perception of sound when no corresponding external sound is present. Nearly everyone experiences a faint "normal tinnitus" in a completely quiet room; but it is of concern only if it is bothersome, interferes with normal hearin ...
References
Further reading
*External links
World Health Organization, Deafness and Hearing Loss
* * *
Open University - OpenLearn - Article about hearing
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hearing (Sense) Sound Audiology Auditory system