Ansa Cervicalis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The ansa cervicalis (or ansa hypoglossi in older literature) is a loop formed by muscular branches of the
 The superior root of the ansa cervicalis (formerly known as descendens hypoglossi) is by fibres of the cervical spinal nerve 1 (and, according to some sources, of
The superior root of the ansa cervicalis (formerly known as descendens hypoglossi) is by fibres of the cervical spinal nerve 1 (and, according to some sources, of
Image:Gray784.png, Cervical plexus shown in purple
Image:Gray804.png, Plan of the cervical plexus.
Image:Gray808.png, The right brachial plexus with its short branches, viewed from in front.
Image:Cervical plexus.gif, Cervical plexus
File:Slide1EBA.JPG, Muscles, arteries and nerves of neck. Newborn dissection.
Photo and description
at
cervical plexus
The cervical plexus is a nerve plexus of the anterior rami of the first (i.e. upper-most) four cervical spinal nerves C1-C4. The cervical plexus provides motor innervation to some muscles of the neck, and the diaphragm; it provides sensory inne ...
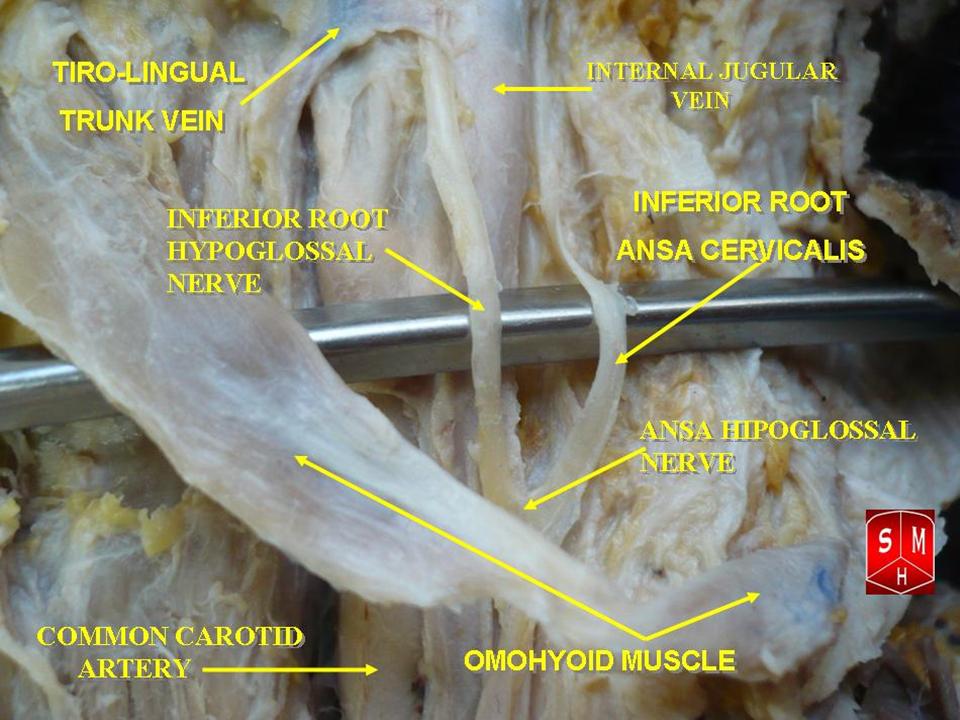
formed by branches of cervical spinal nerves C1-C3. The ansa cervicalis has two roots - a superior root (formed by branch of C1) and an inferior root (formed by union of branches of C2 and C3) - that unite distally, forming a loop. It is situated anterior to the carotid sheath
The carotid sheath is a condensation of the deep cervical fascia enveloping multiple vital neurovascular structures of the neck, including the common and internal carotid arteries, the internal jugular vein, the vagus nerve (CN X), and ansa c ...
.
Branches of the ansa cervicalis innervate three of the four infrahyoid muscles: the sternothyroid, sternohyoid, and omohyoid muscles (note that the thyrohyoid muscle
The thyrohyoid muscle is a small skeletal muscle of the neck. Above, it attaches onto the greater cornu of the hyoid bone; below, it attaches onto the oblique line of the thyroid cartilage. It is innervated by fibres derived from the cervical spin ...
is the one infrahyoid muscle not innervated by the ansa cervicalis - it is instead innervated by cervical spinal nerve 1 via a separate thyrohyoid branch).
Its name means "handle of the neck" in Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
.
Anatomy
The ansa cervicalis is typically embedded within the anterior wall of thecarotid sheath
The carotid sheath is a condensation of the deep cervical fascia enveloping multiple vital neurovascular structures of the neck, including the common and internal carotid arteries, the internal jugular vein, the vagus nerve (CN X), and ansa c ...
anterior to the internal jugular vein
The internal jugular vein is a paired jugular vein that collects blood from the brain and the superficial parts of the face and neck. This vein runs in the carotid sheath with the common carotid artery and vagus nerve.
It begins in the posteri ...
.
Superior root
 The superior root of the ansa cervicalis (formerly known as descendens hypoglossi) is by fibres of the cervical spinal nerve 1 (and, according to some sources, of
The superior root of the ansa cervicalis (formerly known as descendens hypoglossi) is by fibres of the cervical spinal nerve 1 (and, according to some sources, of cervical spinal nerve 2
The cervical spinal nerve 2 (C2) is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment.American Medical Association
as well) that have joined and run with the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) for some distance before progressively branching off the CN XII in the carotid triangle to form the superior root.
The superior root is situated within the carotid triangle. It passes anterior-ward between the internal carotid artery
The internal carotid artery is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior cerebral artery, anterior and middle cerebral artery, middle cerebral circulation.
In human anatomy, the internal and external carotid artery, external carotid ari ...
and the common carotid artery
In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) () are artery, arteries that supply the head and neck with oxygenated blood; they divide in the neck to form the external carotid artery, external and internal carotid artery, inte ...
. It curves around the occipital artery
The occipital artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that provides arterial supply to the back of the scalp, sternocleidomastoid muscles, and deep muscles of the back and neck.
Structure
Origin
The occipital artery arises from (the ...
before descending upon the anterior aspect of the internal carotid artery
The internal carotid artery is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior cerebral artery, anterior and middle cerebral artery, middle cerebral circulation.
In human anatomy, the internal and external carotid artery, external carotid ari ...
and the common carotid artery
In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) () are artery, arteries that supply the head and neck with oxygenated blood; they divide in the neck to form the external carotid artery, external and internal carotid artery, inte ...
. on the carotid sheath
The carotid sheath is a condensation of the deep cervical fascia enveloping multiple vital neurovascular structures of the neck, including the common and internal carotid arteries, the internal jugular vein, the vagus nerve (CN X), and ansa c ...
. It issues a branch to the superior belly of the omohyoid muscle, and the upper parts of the sternothyroid and sternohyoid muscles before uniting with the inferior root.
Inferior root
The inferior root of the ansa cervicalis (formerly known as descendens cervicalis) is formed by the union of fibers of theanterior rami
The ventral ramus (: rami) (Latin for 'branch') is the anterior division of a spinal nerve. The ventral rami supply the antero-lateral parts of the trunk and the limbs. They are mainly larger than the dorsal rami.
Shortly after a spinal nerve e ...
spinal cervical nerves C2- C3 that unite as part of the cervical plexus
The cervical plexus is a nerve plexus of the anterior rami of the first (i.e. upper-most) four cervical spinal nerves C1-C4. The cervical plexus provides motor innervation to some muscles of the neck, and the diaphragm; it provides sensory inne ...
.
The inferior root curves posteroanteriorly around the lateral side of the internal jugular vein
The internal jugular vein is a paired jugular vein that collects blood from the brain and the superficial parts of the face and neck. This vein runs in the carotid sheath with the common carotid artery and vagus nerve.
It begins in the posteri ...
before descending to unite with the superior root upon the (inferior portion of) the internal jugular vein. It may occasionally pass anterior in between the internal jugular vein and the internal carotid artery
The internal carotid artery is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior cerebral artery, anterior and middle cerebral artery, middle cerebral circulation.
In human anatomy, the internal and external carotid artery, external carotid ari ...
.
Branches
Branches to the sternothyroid muscle, sternohyoid muscle, and inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle issue from the loop of the ansa cervicalis, whereas the branch for the superior belly of the omohyoid muscle arises from the superior root.Additional images
References
* "Ansa cervicalis." ''Stedman's Medical Dictionary, 27th ed.'' (2000). * ''Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice.'' (2005).External links
*Photo and description
at
Tufts University
Tufts University is a private research university in Medford and Somerville, Massachusetts, United States, with additional facilities in Boston and Grafton, as well as Talloires, France. Tufts also has several Doctor of Physical Therapy p ...
*
* https://web.archive.org/web/20080304085514/http://www.med.mun.ca/anatomyts/nerve/cerplex.htm
{{Authority control
Nerves of the head and neck