Annelid Genera on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The annelids (), also known as the segmented worms, are animals that comprise the
 Annelids' cuticles are made of
Annelids' cuticles are made of
 Feeding structures in the mouth region vary widely, and have little correlation with the animals' diets. Many polychaetes have a muscular
Feeding structures in the mouth region vary widely, and have little correlation with the animals' diets. Many polychaetes have a muscular

 Since annelids are soft-bodied, their fossils are rare.
Since annelids are soft-bodied, their fossils are rare.
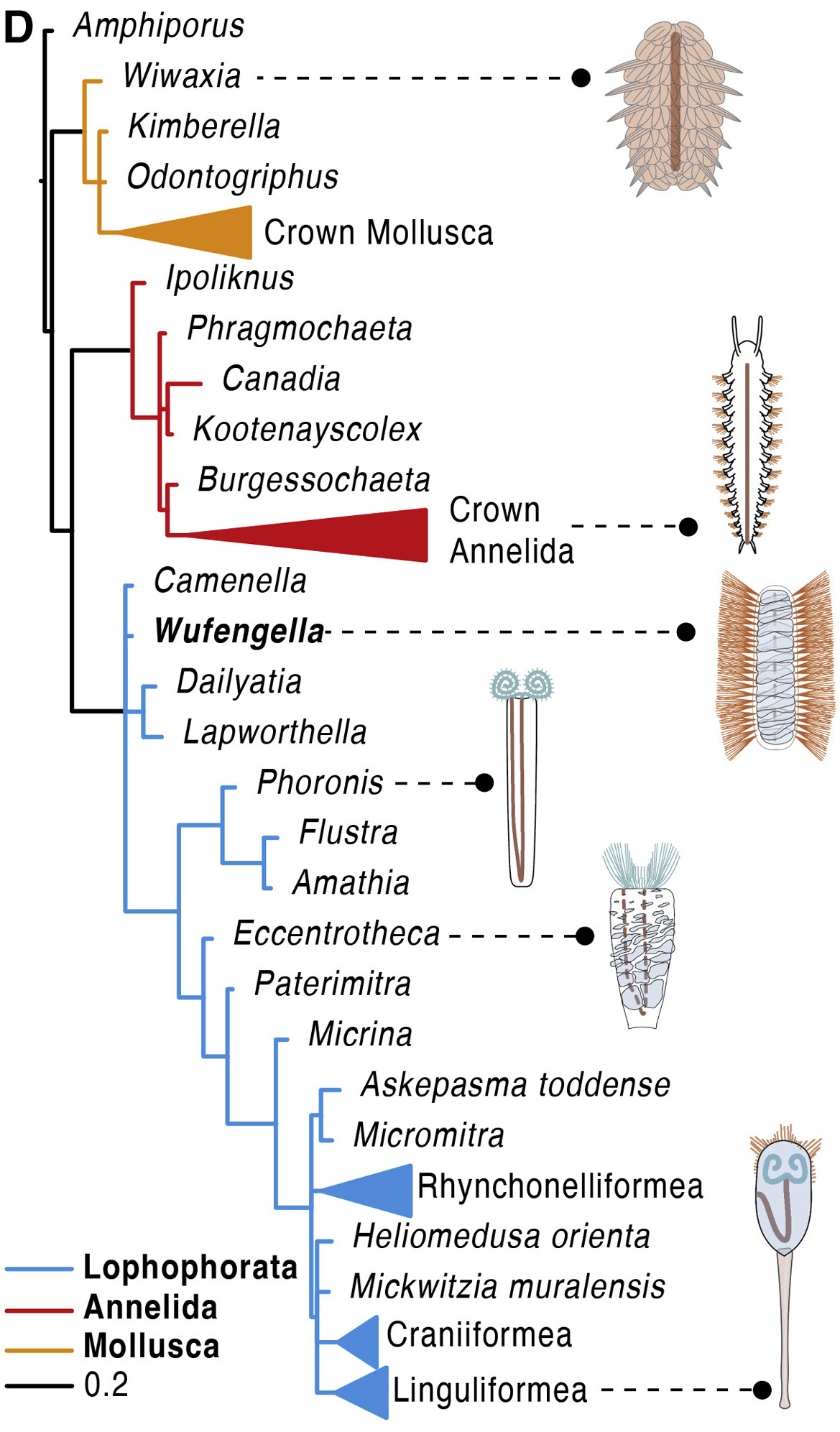 Fossil discoveries lead to the hypothesis that Annelida and the lophophorates are more closely related to each other than any other
Fossil discoveries lead to the hypothesis that Annelida and the lophophorates are more closely related to each other than any other
phylum
In biology, a phylum (; : phyla) is a level of classification, or taxonomic rank, that is below Kingdom (biology), kingdom and above Class (biology), class. Traditionally, in botany the term division (taxonomy), division has been used instead ...
Annelida (; ). The phylum contains over 22,000 extant species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
, including ragworms, earthworm
An earthworm is a soil-dwelling terrestrial invertebrate that belongs to the phylum Annelida. The term is the common name for the largest members of the class (or subclass, depending on the author) Oligochaeta. In classical systems, they we ...
s, and leech
Leeches are segmented parasitism, parasitic or Predation, predatory worms that comprise the Class (biology), subclass Hirudinea within the phylum Annelida. They are closely related to the Oligochaeta, oligochaetes, which include the earthwor ...
es. The species exist in and have adapted to various ecologies – some in marine environments as distinct as tidal zones and hydrothermal vent
Hydrothermal vents are fissures on the seabed from which geothermally heated water discharges. They are commonly found near volcanically active places, areas where tectonic plates are moving apart at mid-ocean ridges, ocean basins, and hot ...
s, others in fresh water, and yet others in moist terrestrial environments.
The annelids are bilaterally symmetrical
Symmetry in biology refers to the symmetry observed in organisms, including plants, animals, fungi, and bacteria. External symmetry can be easily seen by just looking at an organism. For example, the face of a human being has a plane of symme ...
, triploblastic, coelom
The coelom (or celom) is the main body cavity in many animals and is positioned inside the body to surround and contain the digestive tract and other organs. In some animals, it is lined with mesothelium. In other animals, such as molluscs, i ...
ate, invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
organisms. They also have parapodia
In invertebrates, the term parapodium ( Gr. ''para'', beyond or beside + ''podia'', feet; : parapodia) refers to lateral outgrowths or protrusions from the body. Parapodia are predominantly found in annelids, where they are paired, unjointed late ...
for locomotion. Most textbooks still use the traditional division into polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine Annelid, annelid worms, common name, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called c ...
s (almost all marine), oligochaetes (which include earthworms) and leech
Leeches are segmented parasitism, parasitic or Predation, predatory worms that comprise the Class (biology), subclass Hirudinea within the phylum Annelida. They are closely related to the Oligochaeta, oligochaetes, which include the earthwor ...
-like species. Cladistic
Cladistics ( ; from Ancient Greek 'branch') is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups ("clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is ...
research since 1997 has radically changed this scheme, viewing leeches as a sub-group of oligochaetes and oligochaetes as a sub-group of polychaetes. In addition, the Pogonophora, Echiura
The Echiura, or spoon worms, are a small group of ocean, marine animals. Once treated as a separate phylum, they are now considered to belong to Annelida. Annelids typically have their bodies divided into Segmentation (biology), segments, but e ...
and Sipuncula
The Sipuncula or Sipunculida (common names sipunculid worms or peanut worms) is a class containing about 162 species of marine annelid worms, that have secondarily lost their segmentation. Sipuncula was once considered a phylum of unsegmented ...
, previously regarded as separate phyla, are now regarded as sub-groups of polychaetes. Annelids are considered members of the Lophotrochozoa, a "super-phylum" of protostome
Protostomia () is the clade of animals once thought to be characterized by the formation of the organism's mouth before its anus during embryonic development. This nature has since been discovered to be extremely variable among Protostomia's memb ...
s that also includes mollusc
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
s, brachiopod
Brachiopods (), phylum (biology), phylum Brachiopoda, are a phylum of animals that have hard "valves" (shells) on the upper and lower surfaces, unlike the left and right arrangement in bivalve molluscs. Brachiopod valves are hinged at the rear e ...
s, and nemerteans.
The basic annelid form consists of multiple segments. Each segment has the same sets of organs and, in most polychaetes, has a pair of parapodia
In invertebrates, the term parapodium ( Gr. ''para'', beyond or beside + ''podia'', feet; : parapodia) refers to lateral outgrowths or protrusions from the body. Parapodia are predominantly found in annelids, where they are paired, unjointed late ...
that many species use for locomotion. Septa
SEPTA, the Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority, is a regional public transportation authority that operates bus, rapid transit, commuter rail, light rail, and electric trolleybus services for nearly four million people througho ...
separate the segments of many species, but are poorly defined or absent in others, and Echiura
The Echiura, or spoon worms, are a small group of ocean, marine animals. Once treated as a separate phylum, they are now considered to belong to Annelida. Annelids typically have their bodies divided into Segmentation (biology), segments, but e ...
and Sipuncula
The Sipuncula or Sipunculida (common names sipunculid worms or peanut worms) is a class containing about 162 species of marine annelid worms, that have secondarily lost their segmentation. Sipuncula was once considered a phylum of unsegmented ...
show no obvious signs of segmentation. In species with well-developed septa, the blood circulates entirely within blood vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (bi ...
s, and the vessels in segments near the front ends of these species are often built up with muscles that act as hearts. The septa of such species also enable them to change the shapes of individual segments, which facilitates movement by peristalsis
Peristalsis ( , ) is a type of intestinal motility, characterized by symmetry in biology#Radial symmetry, radially symmetrical contraction and relaxation of muscles that propagate in a wave down a tube, in an wikt:anterograde, anterograde dir ...
("ripples" that pass along the body) or by undulations that improve the effectiveness of the parapodia. In species with incomplete septa or none, the blood circulates through the main body cavity without any kind of pump, and there is a wide range of locomotory techniques – some burrowing species turn their pharynges inside out to drag themselves through the sediment
Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently sediment transport, transported by the action of ...
.
Earthworms are oligochaetes that support terrestrial food chain
A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web, often starting with an autotroph (such as grass or algae), also called a producer, and typically ending at an apex predator (such as grizzly bears or killer whales), detritivore (such as ...
s both as prey and predators, and in some regions are important in aeration and enriching of soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, water, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms. Some scientific definitions distinguish dirt from ''soil'' by re ...
. The burrowing of marine polychaetes, which may constitute up to a third of all species in near-shore environments, encourages the development of ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
s by enabling water and oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
to penetrate the sea floor. In addition to improving soil fertility
Soil fertility refers to the ability of soil to sustain agricultural plant growth, i.e. to provide plant habitat and result in sustained and consistent yields of high quality.
, annelids serve humans as food and as bait. Scientists observe annelids to monitor the quality of marine and fresh water. Although blood-letting is used less frequently by doctors than it once was, some leech species are regarded as endangered because they have been over-harvested for this purpose in the last few centuries. Ragworms' jaws are studied by engineers as they offer an exceptional combination of lightness and strength.
Since annelids are soft-bodied, their fossils are rare – mostly jaws and the mineralized tubes that some of the species secreted. Although some late Ediacaran
The Ediacaran ( ) is a geological period of the Neoproterozoic geologic era, Era that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period at 635 Million years ago, Mya to the beginning of the Cambrian Period at 538.8 Mya. It is the last ...
fossils may represent annelids, the oldest known fossil that is identified with confidence comes from about in the early Cambrian
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordov ...
period. Fossils of most modern mobile polychaete groups appeared by the end of the Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ...
, about . Palaeontologists disagree about whether some body fossils from the mid Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and System (geology), system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era (geology), Era, and the second of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon (geology), Eon. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years f ...
, about , are the remains of oligochaetes, and the earliest indisputable fossils of the group appear in the Paleogene
The Paleogene Period ( ; also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene) is a geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Neogene Period Ma. It is the fir ...
period, which began 66 million years ago.
Classification and diversity
There are over 22,000 living annelid species, ranging in size from microscopic to the Australian giant Gippsland earthworm and ''Amynthas mekongianus
''Amynthas mekongianus'', the Mekong worm or Mekong giant earthworm, previously known as ''Megascolex mekongianus'', is a species of earthworm in the family Megascolecidae. It is native to the vicinity of the Mekong, River Mekong in southeastern ...
'', which can both grow up to long to the largest annelid, '' Microchaetus rappi'' which can grow up to 6.7 m (22 ft). Although research since 1997 has radically changed scientists' views about the evolutionary family tree of the annelids, most textbooks use the traditional classification into the following sub-groups:
*Polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine Annelid, annelid worms, common name, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called c ...
s (about 12,000 species). As their name suggests, they have multiple chetae ("hairs") per segment. Polychaetes have parapodia
In invertebrates, the term parapodium ( Gr. ''para'', beyond or beside + ''podia'', feet; : parapodia) refers to lateral outgrowths or protrusions from the body. Parapodia are predominantly found in annelids, where they are paired, unjointed late ...
that function as limbs, and nuchal organs that are thought to be chemosensors. Most are marine animals, although a few species live in fresh water and even fewer on land.
* Clitellates (about 10,000 species ). These have few or no chetae per segment, and no nuchal organs or parapodia. However, they have a unique reproductive organ, the ring-shaped clitellum
The clitellum is a thickened glandular and non-segmented section of the body wall near the head in earthworms and leeches that secretes a viscid sac in which eggs are stored. It is located near the anterior end of the body, between the fourteenth ...
("pack saddle
]
A pack saddle is any device designed to be secured on the back of a horse, mule, or other working animal so it can carry heavy loads such as luggage, firewood, small cannons, or other things too heavy to be carried by humans.
Description
Ide ...
") around their bodies, which produces a Pupa, cocoon that stores and nourishes fertilized eggs until they hatch or, in moniligastrids, yolky eggs that provide nutrition for the embryos. The clitellates are sub-divided into:
** Oligochaetes ("with few hairs"), which includes earthworms
An earthworm is a soil-dwelling terrestrial animal, terrestrial invertebrate that belongs to the phylum Annelida. The term is the common name for the largest members of the class (biology), class (or subclass (biology), subclass, depending on ...
. Oligochaetes have a sticky pad in the roof of the mouth. Most are burrowers that feed on wholly or partly decomposed organic materials.
**Hirudinea
Leeches are segmented parasitic or predatory worms that comprise the subclass Hirudinea within the phylum Annelida. They are closely related to the oligochaetes, which include the earthworm, and like them have soft, muscular segmented bo ...
, whose name means "leech
Leeches are segmented parasitism, parasitic or Predation, predatory worms that comprise the Class (biology), subclass Hirudinea within the phylum Annelida. They are closely related to the Oligochaeta, oligochaetes, which include the earthwor ...
-shaped" and whose best known members are leeches. Marine species are mostly blood-sucking parasite
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted str ...
s, mainly on fish, while most freshwater species are predators. They have suckers at both ends of their bodies, and use these to move rather like inchworms.
The Archiannelida, minute annelids that live in the spaces between grains of marine sediment
Marine sediment, or ocean sediment, or seafloor sediment, are deposits of insoluble particles that have accumulated on the seafloor. These particles either have their origins in soil and Rock (geology), rocks and have been Sediment transport, ...
, were treated as a separate class
Class, Classes, or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used d ...
because of their simple body structure, but are now regarded as polychaetes. Some other groups of animals have been classified in various ways, but are now widely regarded as annelids:
*Pogonophora / Siboglinidae
Siboglinidae is a family (biology), family of polychaete Annelida, annelid worms whose members made up the former phylum, phyla Pogonophora and Vestimentifera (the giant tube worms). The family is composed of around 100 species of vermiform creatu ...
were first discovered in 1914, and their lack of a recognizable gut made it difficult to classify them. They have been classified as a separate phylum
In biology, a phylum (; : phyla) is a level of classification, or taxonomic rank, that is below Kingdom (biology), kingdom and above Class (biology), class. Traditionally, in botany the term division (taxonomy), division has been used instead ...
, Pogonophora, or as two phyla, Pogonophora and Vestimentifera. More recently they have been re-classified as a family
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictabili ...
, Siboglinidae, within the polychaetes.
*The Echiura
The Echiura, or spoon worms, are a small group of ocean, marine animals. Once treated as a separate phylum, they are now considered to belong to Annelida. Annelids typically have their bodies divided into Segmentation (biology), segments, but e ...
have a checkered taxonomic history: in the 19th century they were assigned to the phylum "Gephyrea", which is now empty as its members have been assigned to other phyla; the Echiura were next regarded as annelids until the 1940s, when they were classified as a phylum in their own right; but a molecular phylogenetics
Molecular phylogenetics () is the branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences, predominantly in DNA sequences, to gain information on an organism's evolutionary relationships. From these analyses, it is possible to ...
analysis in 1997 concluded that echiurans are annelids.
*Myzostomida
The Myzostomida or Myzostomatida are an order of small marine (ocean), marine worms, which are Parasitism, parasitic on echinoderms, mostly crinoids. These highly unusual and diverse annelids were first discovered by Friedrich Sigismund Leuckart ...
live on crinoid
Crinoids are marine invertebrates that make up the class Crinoidea. Crinoids that remain attached to the sea floor by a stalk in their adult form are commonly called sea lilies, while the unstalked forms, called feather stars or comatulids, are ...
s and other echinoderm
An echinoderm () is any animal of the phylum Echinodermata (), which includes starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars and sea cucumbers, as well as the sessile sea lilies or "stone lilies". While bilaterally symmetrical as ...
s, mainly as parasites. In the past they have been regarded as close relatives of the trematode
Trematoda is a Class (biology), class of flatworms known as trematodes, and commonly as flukes. They are obligate parasite, obligate Endoparasites, internal parasites with a complex biological life cycle, life cycle requiring at least two Host ( ...
flatworm
Platyhelminthes (from the Greek language, Greek πλατύ, ''platy'', meaning "flat" and ἕλμινς (root: ἑλμινθ-), ''helminth-'', meaning "worm") is a Phylum (biology), phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, Segmentation (biology), ...
s or of the tardigrade
Tardigrades (), known colloquially as water bears or moss piglets, are a phylum of eight-legged segmented micro-animals. They were first described by the German zoologist Johann August Ephraim Goeze in 1773, who called them . In 1776, th ...
s, but in 1998 it was suggested that they are a sub-group of polychaetes. However, another analysis in 2002 suggested that myzostomids are more closely related to flatworms or to rotifer
The rotifers (, from Latin 'wheel' and 'bearing'), sometimes called wheel animals or wheel animalcules, make up a phylum (Rotifera ) of microscopic and near-microscopic Coelom#Pseudocoelomates, pseudocoelomate animals.
They were first describ ...
s and acanthocephales.
*Sipuncula
The Sipuncula or Sipunculida (common names sipunculid worms or peanut worms) is a class containing about 162 species of marine annelid worms, that have secondarily lost their segmentation. Sipuncula was once considered a phylum of unsegmented ...
was originally classified as annelids, despite the complete lack of segmentation, bristle
A bristle is a stiff hair or feather (natural or artificial), either on an animal, such as a pig, a plant, or on a tool such as a brush or broom.
Synthetic types
Synthetic materials such as nylon are also used to make bristles in items such as b ...
s and other annelid characters. The phylum Sipuncula was later allied with the Mollusca
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
, mostly on the basis of development
Development or developing may refer to:
Arts
*Development (music), the process by which thematic material is reshaped
* Photographic development
*Filmmaking, development phase, including finance and budgeting
* Development hell, when a proje ...
al and larva
A larva (; : larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into their next life stage. Animals with indirect development such as insects, some arachnids, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase ...
l characters. Phylogenetic analyses based on 79 ribosomal proteins indicated a position of Sipuncula within Annelida. Subsequent analysis of the mitochondrion
A mitochondrion () is an organelle found in the cell (biology), cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double lipid bilayer, membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine tri ...
's DNA has confirmed their close relationship to the Myzostomida
The Myzostomida or Myzostomatida are an order of small marine (ocean), marine worms, which are Parasitism, parasitic on echinoderms, mostly crinoids. These highly unusual and diverse annelids were first discovered by Friedrich Sigismund Leuckart ...
and Annelida (including echiura
The Echiura, or spoon worms, are a small group of ocean, marine animals. Once treated as a separate phylum, they are now considered to belong to Annelida. Annelids typically have their bodies divided into Segmentation (biology), segments, but e ...
ns and pogonophorans). It has also been shown that a rudimentary neural segmentation similar to that of annelids occurs in the early larval stage, even if these traits are absent in the adults.
Mitogenomic and phylogenomic analysis also implies that Orthonectida
Orthonectida () is a small phylum (biology), phylum of poorly known parasites of marine invertebrates that are among the simplest of multi-cellular organisms. Members of this phylum are known as orthonectids.
Biology
The adults, which are the se ...
, a group of extremely simplified parasites traditionally placed in Mesozoa, are actually reduced annelids. Research suggest that also nemertea
Nemertea is a phylum of animals also known as ribbon worms or proboscis worms, consisting of about 1300 known species. Most ribbon worms are very slim, usually only a few millimeters wide, although a few have relatively short but wide bodies. ...
ns are annelids, with Oweniidae and Magelonidae as their closest relatives.
Distinguishing features
No single feature distinguishes annelids from otherinvertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
phyla, but they have a distinctive combination of features. Their bodies are long, with segments that are divided externally by shallow ring-like constrictions called annuli and internally by septa ("partitions") at the same points, although in some species the septa are incomplete and in a few cases missing. Most of the segments contain the same sets of organs, although sharing a common gut, circulatory system
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart ...
and nervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the complex system, highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its behavior, actions and sense, sensory information by transmitting action potential, signals to and from different parts of its body. Th ...
makes them inter-dependent. Their bodies are covered by a cuticle
A cuticle (), or cuticula, is any of a variety of tough but flexible, non-mineral outer coverings of an organism, or parts of an organism, that provide protection. Various types of "cuticle" are non- homologous, differing in their origin, structu ...
(outer covering) that does not contain cells but is secreted by cells in the skin underneath, is made of tough but flexible collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix of the connective tissues of many animals. It is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up 25% to 35% of protein content. Amino acids are bound together to form a trip ...
and does not molt – on the other hand arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
s' cuticles are made of the more rigid α-chitin
Chitin (carbon, C8hydrogen, H13oxygen, O5nitrogen, N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of N-Acetylglucosamine, ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cell ...
, and molt until the arthropods reach their full size. Most annelids have closed circulatory systems, where the blood makes its entire circuit via blood vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (bi ...
s.
Description
Segmentation
In addition to Sipuncula and Echiura, also lineages like Lobatocerebrum, Diurodrilus and Polygordius have lost their segmentation, but these are the exceptions from the rule. Most of an annelid's body consists of segments that are practically identical, having the same sets of internal organs and externalchaeta
A chaeta or cheta (; ) is a chitinous bristle or seta found on annelid worms, although the term is also frequently used to describe similar structures in other invertebrates such as arthropods. Polychaete annelids (''polychaeta'' literally me ...
e (Greek χαιτη, meaning "hair") and, in some species, appendages. The frontmost and rearmost sections are not regarded as true segments as they do not contain the standard sets of organs and do not develop in the same way as the true segments. The frontmost section, called the prostomium
The prostomium (From Ancient Greek, meaning "before the mouth"; : prostomia; sometimes also called the "acron") is the Cephalization, cephalized first body segment in an annelid worm's body at the anterior end. It is in front of (but does not in ...
(Greek προ- meaning "in front of" and στομα meaning "mouth") contains the brain and sense organs, while the rearmost, called the pygidium (Greek πυγιδιον, meaning "little tail") or periproct contains the anus
In mammals, invertebrates and most fish, the anus (: anuses or ani; from Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is the external body orifice at the ''exit'' end of the digestive tract (bowel), i.e. the opposite end from the mouth. Its function is to facil ...
, generally on the underside. The first section behind the prostomium, called the peristomium (Greek περι- meaning "around" and στομα meaning "mouth"), is regarded by some zoologists as not a true segment, but in some polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine Annelid, annelid worms, common name, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called c ...
s the peristomium has chetae and appendages like those of other segments.
The segments develop one at a time from a growth zone just ahead of the pygidium, so that an annelid's youngest segment is just in front of the growth zone while the peristomium is the oldest. This pattern is called teloblastic growth. Some groups of annelids, including all leech
Leeches are segmented parasitism, parasitic or Predation, predatory worms that comprise the Class (biology), subclass Hirudinea within the phylum Annelida. They are closely related to the Oligochaeta, oligochaetes, which include the earthwor ...
es, have fixed maximum numbers of segments, while others add segments throughout their lives.
The phylum's name is derived from the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
word ''annelus'', meaning "little ring".
Body wall, chaetae and parapodia
collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix of the connective tissues of many animals. It is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up 25% to 35% of protein content. Amino acids are bound together to form a trip ...
fibers, usually in layers that spiral in alternating directions so that the fibers cross each other. These are secreted by the one-cell deep epidermis (outermost skin layer). A few marine annelids that live in tubes lack cuticles, but their tubes have a similar structure, and mucus
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both Serous fluid, serous and muc ...
-secreting gland
A gland is a Cell (biology), cell or an Organ (biology), organ in an animal's body that produces and secretes different substances that the organism needs, either into the bloodstream or into a body cavity or outer surface. A gland may also funct ...
s in the epidermis protect their skins. Under the epidermis is the dermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (skin), epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis (anatomy), cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from s ...
, which is made of connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, a group of cells that are similar in structure, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops mostly from the mesenchyme, derived from the mesod ...
, in other words a combination of cells and non-cellular materials such as collagen. Below this are two layers of muscles, which develop from the lining of the coelom
The coelom (or celom) is the main body cavity in many animals and is positioned inside the body to surround and contain the digestive tract and other organs. In some animals, it is lined with mesothelium. In other animals, such as molluscs, i ...
(body cavity): circular muscles make a segment longer and slimmer when they contract, while under them are longitudinal muscles, usually four distinct strips, whose contractions make the segment shorter and fatter. But several families have lost the circular muscles, and it has been suggested that the lack of circular muscles is a plesiomorphic
In phylogenetics, a plesiomorphy ("near form") and symplesiomorphy are synonyms for an ancestral character shared by all members of a clade, which does not distinguish the clade from other clades.
Plesiomorphy, symplesiomorphy, apomorphy, an ...
character in Annelida. Some annelids also have oblique internal muscles that connect the underside of the body to each side.
The seta
In biology, setae (; seta ; ) are any of a number of different bristle- or hair-like structures on living organisms.
Animal setae
Protostomes
Depending partly on their form and function, protostome setae may be called macrotrichia, chaetae, ...
e ("hairs") of annelids project out from the epidermis to provide traction and other capabilities. The simplest are unjointed and form paired bundles near the top and bottom of each side of each segment. The parapodia
In invertebrates, the term parapodium ( Gr. ''para'', beyond or beside + ''podia'', feet; : parapodia) refers to lateral outgrowths or protrusions from the body. Parapodia are predominantly found in annelids, where they are paired, unjointed late ...
("limbs") of annelids that have them often bear more complex chetae at their tips – for example jointed, comb-like or hooked. Chetae are made of moderately flexible β-chitin
Chitin (carbon, C8hydrogen, H13oxygen, O5nitrogen, N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of N-Acetylglucosamine, ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cell ...
and are formed by follicles, each of which has a chetoblast ("hair-forming") cell at the bottom and muscles that can extend or retract the cheta. The chetoblasts produce chetae by forming microvilli, fine hair-like extensions that increase the area available for secreting the cheta. When the cheta is complete, the microvilli withdraw into the chetoblast, leaving parallel tunnels that run almost the full length of the cheta. Hence annelids' chetae are structurally different from the seta
In biology, setae (; seta ; ) are any of a number of different bristle- or hair-like structures on living organisms.
Animal setae
Protostomes
Depending partly on their form and function, protostome setae may be called macrotrichia, chaetae, ...
e ("bristles") of arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
s, which are made of the more rigid α-chitin, have a single internal cavity, and are mounted on flexible joints in shallow pits in the cuticle.
Nearly all polychaetes have parapodia that function as limbs, while other major annelid groups lack them. Parapodia are unjointed paired extensions of the body wall, and their muscles are derived from the circular muscles of the body. They are often supported internally by one or more large, thick chetae. The parapodia of burrowing and tube-dwelling polychaetes are often just ridges whose tips bear hooked chetae. In active crawlers and swimmers the parapodia are often divided into large upper and lower paddles on a very short trunk, and the paddles are generally fringed with chetae and sometimes with cirri (fused bundles of cilia
The cilium (: cilia; ; in Medieval Latin and in anatomy, ''cilium'') is a short hair-like membrane protrusion from many types of eukaryotic cell. (Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea.) The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike proj ...
) and gill
A gill () is a respiration organ, respiratory organ that many aquatic ecosystem, aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow r ...
s.
Nervous system and senses
Thebrain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
generally forms a ring round the pharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the human mouth, mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates ...
(throat), consisting of a pair of ganglia
A ganglion (: ganglia) is a group of neuron cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. In the somatic nervous system, this includes dorsal root ganglia and trigeminal ganglia among a few others. In the autonomic nervous system, there a ...
(local control centers) above and in front of the pharynx, linked by nerve cords either side of the pharynx to another pair of ganglia just below and behind it. The brains of polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine Annelid, annelid worms, common name, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called c ...
s are generally in the prostomium, while those of clitellates are in the peristomium or sometimes the first segment behind the prostomium. In some very mobile and active polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine Annelid, annelid worms, common name, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called c ...
s the brain is enlarged and more complex, with visible hindbrain, midbrain and forebrain sections. The rest of the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
, the ventral nerve cord
The ventral nerve cord is a major structure of the invertebrate central nervous system. It is the functional equivalent of the vertebrate spinal cord. The ventral nerve cord coordinates neural signaling from the brain to the body and vice ve ...
, is generally "ladder-like", consisting of a pair of nerve cords that run through the bottom part of the body and have in each segment paired ganglia linked by a transverse connection. From each segmental ganglion a branching system of local nerves runs into the body wall and then encircles the body. However, in most polychaetes the two main nerve cords are fused, and in the tube-dwelling genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
''Owenia'' the single nerve chord has no ganglia and is located in the epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and Subcutaneous tissue, hypodermis. The epidermal layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the ...
.
As in arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
s, each muscle fiber (cell) is controlled by more than one neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
, and the speed and power of the fiber's contractions depends on the combined effects of all its neurons. Vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s have a different system, in which one neuron controls a group of muscle fibers. Most annelids' longitudinal nerve trunks include giant axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis) or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, spelling differences) is a long, slender cellular extensions, projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, ...
s (the output signal lines of nerve cells). Their large diameter decreases their resistance, which allows them to transmit signals exceptionally fast. This enables these worms to withdraw rapidly from danger by shortening their bodies. Experiments have shown that cutting the giant axons prevents this escape response but does not affect normal movement.
The sensors are primarily single cells that detect light, chemicals, pressure waves and contact, and are present on the head, appendages (if any) and other parts of the body. Nuchal ("on the neck") organs are paired, cilia
The cilium (: cilia; ; in Medieval Latin and in anatomy, ''cilium'') is a short hair-like membrane protrusion from many types of eukaryotic cell. (Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea.) The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike proj ...
ted structures found only in polychaetes, and are thought to be chemosensors. Some polychaetes also have various combinations of ocelli
A simple eye or ocellus (sometimes called a pigment pit) is a form of eye or an optical arrangement which has a single lens without the sort of elaborate retina that occurs in most vertebrates. These eyes are called "simple" to distinguish the ...
("little eyes") that detect the direction from which light is coming and camera eyes or compound eye
A compound eye is a Eye, visual organ found in arthropods such as insects and crustaceans. It may consist of thousands of ommatidium, ommatidia, which are tiny independent photoreception units that consist of a cornea, lens (anatomy), lens, and p ...
s that can probably form images. The compound eyes probably evolved independently of arthropods' eyes. Some tube-worms use ocelli widely spread over their bodies to detect the shadows of fish, so that they can quickly withdraw into their tubes. Some burrowing and tube-dwelling polychaetes have statocyst
The statocyst is a balance sensory receptor present in some aquatic invertebrates, including bivalves, cnidarians, ctenophorans, echinoderms, cephalopods, crustaceans, and gastropods, A similar structure is also found in '' Xenoturbella''. T ...
s (tilt and balance sensors) that indicate which way is down. A few polychaete genera
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial s ...
have on the undersides of their heads palps that are used both in feeding and as "feelers", and some of these also have antennae that are structurally similar but probably are used mainly as "feelers".
Coelom, locomotion and circulatory system
Most annelids have a pair ofcoelom
The coelom (or celom) is the main body cavity in many animals and is positioned inside the body to surround and contain the digestive tract and other organs. In some animals, it is lined with mesothelium. In other animals, such as molluscs, i ...
ata (body cavities) in each segment, separated from other segments by septa
SEPTA, the Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority, is a regional public transportation authority that operates bus, rapid transit, commuter rail, light rail, and electric trolleybus services for nearly four million people througho ...
and from each other by vertical mesenteries. Each septum forms a sandwich with connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, a group of cells that are similar in structure, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops mostly from the mesenchyme, derived from the mesod ...
in the middle and mesothelium
The mesothelium is a membrane composed of simple squamous epithelium, simple squamous epithelial cells of mesodermal origin, which forms the lining of several body cavities: the pleura (pleural cavity around the lungs), peritoneum (abdominopelvic ...
(membrane
A membrane is a selective barrier; it allows some things to pass through but stops others. Such things may be molecules, ions, or other small particles. Membranes can be generally classified into synthetic membranes and biological membranes. Bi ...
that serves as a lining) from the preceding and following segments on either side. Each mesentery is similar except that the mesothelium is the lining of each of the pair of coelomata, and the blood vessels and, in polychaetes, the main nerve cords are embedded in it. The mesothelium is made of modified epitheliomuscular cells; in other words, their bodies form part of the epithelium but their bases extend to form muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
fibers in the body wall. The mesothelium may also form radial and circular muscles on the septa, and circular muscles around the blood vessels and gut. Parts of the mesothelium, especially on the outside of the gut, may also form chloragogen cells that perform similar functions to the liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
s of vertebrates: producing and storing glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. It is the main storage form of glucose in the human body.
Glycogen functions as one of three regularly used forms ...
and fat
In nutrition science, nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such chemical compound, compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers specif ...
; producing the oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
-carrier hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin, Hb or Hgb) is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transportation of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrates contain hemoglobin, with the sole exception of the fish family Channichthyidae. Hemoglobin ...
; breaking down protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s; and turning nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
ous waste products into ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pu ...
and urea
Urea, also called carbamide (because it is a diamide of carbonic acid), is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two Amine, amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest am ...
to be excreted.
Many annelids move by peristalsis
Peristalsis ( , ) is a type of intestinal motility, characterized by symmetry in biology#Radial symmetry, radially symmetrical contraction and relaxation of muscles that propagate in a wave down a tube, in an wikt:anterograde, anterograde dir ...
(waves of contraction and expansion that sweep along the body), or flex the body while using parapodia
In invertebrates, the term parapodium ( Gr. ''para'', beyond or beside + ''podia'', feet; : parapodia) refers to lateral outgrowths or protrusions from the body. Parapodia are predominantly found in annelids, where they are paired, unjointed late ...
to crawl or swim. In these animals the septa enable the circular and longitudinal muscles to change the shape of individual segments, by making each segment a separate fluid-filled "balloon". However, the septa are often incomplete in annelids that are semi- sessile or that do not move by peristalsis or by movements of parapodia – for example some move by whipping movements of the body, some small marine species move by means of cilia
The cilium (: cilia; ; in Medieval Latin and in anatomy, ''cilium'') is a short hair-like membrane protrusion from many types of eukaryotic cell. (Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea.) The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike proj ...
(fine muscle-powered hairs) and some burrowers turn their pharynges (throats) inside out to penetrate the sea-floor and drag themselves into it.
The fluid in the coelomata contains coelomocyte cells that defend the animals against parasites and infections. In some species coelomocytes may also contain a respiratory pigment – red hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin, Hb or Hgb) is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transportation of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrates contain hemoglobin, with the sole exception of the fish family Channichthyidae. Hemoglobin ...
in some species, green chlorocruorin in others (dissolved in the plasma) – and provide oxygen transport within their segments. Respiratory pigment is also dissolved in the blood plasma
Blood plasma is a light Amber (color), amber-colored liquid component of blood in which blood cells are absent, but which contains Blood protein, proteins and other constituents of whole blood in Suspension (chemistry), suspension. It makes up ...
. Species with well-developed septa generally also have blood vessels running all long their bodies above and below the gut, the upper one carrying blood forwards while the lower one carries it backwards. Networks of capillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the in ...
in the body wall and around the gut transfer blood between the main blood vessels and to parts of the segment that need oxygen and nutrients. Both of the major vessels, especially the upper one, can pump blood by contracting. In some annelids the forward end of the upper blood vessel is enlarged with muscles to form a heart, while in the forward ends of many earthworm
An earthworm is a soil-dwelling terrestrial invertebrate that belongs to the phylum Annelida. The term is the common name for the largest members of the class (or subclass, depending on the author) Oligochaeta. In classical systems, they we ...
s some of the vessels that connect the upper and lower main vessels function as hearts. Species with poorly developed or no septa generally have no blood vessels and rely on the circulation within the coelom for delivering nutrients and oxygen.
However, leech
Leeches are segmented parasitism, parasitic or Predation, predatory worms that comprise the Class (biology), subclass Hirudinea within the phylum Annelida. They are closely related to the Oligochaeta, oligochaetes, which include the earthwor ...
es and their closest relatives have a body structure that is very uniform within the group but significantly different from that of other annelids, including other members of the Clitellata. In leeches there are no septa, the connective tissue layer of the body wall is so thick that it occupies much of the body, and the two coelomata are widely separated and run the length of the body. They function as the main blood vessels, although they are side-by-side rather than upper and lower. However, they are lined with mesothelium, like the coelomata and unlike the blood vessels of other annelids. Leeches generally use suckers at their front and rear ends to move like inchworms. The anus is on the upper surface of the pygidium.
Respiration
In some annelids, includingearthworm
An earthworm is a soil-dwelling terrestrial invertebrate that belongs to the phylum Annelida. The term is the common name for the largest members of the class (or subclass, depending on the author) Oligochaeta. In classical systems, they we ...
s, all respiration is via the skin. However, many polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine Annelid, annelid worms, common name, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called c ...
s and some clitellates (the group to which earthworms belong) have gill
A gill () is a respiration organ, respiratory organ that many aquatic ecosystem, aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow r ...
s associated with most segments, often as extensions of the parapodia
In invertebrates, the term parapodium ( Gr. ''para'', beyond or beside + ''podia'', feet; : parapodia) refers to lateral outgrowths or protrusions from the body. Parapodia are predominantly found in annelids, where they are paired, unjointed late ...
in polychaetes. The gills of tube-dwellers and burrowers usually cluster around whichever end has the stronger water flow.
Feeding and excretion
 Feeding structures in the mouth region vary widely, and have little correlation with the animals' diets. Many polychaetes have a muscular
Feeding structures in the mouth region vary widely, and have little correlation with the animals' diets. Many polychaetes have a muscular pharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the human mouth, mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates ...
that can be everted (turned inside out to extend it). In these animals the foremost few segments often lack septa so that, when the muscles in these segments contract, the sharp increase in fluid pressure from all these segments everts the pharynx very quickly. Two families
Family (from ) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictability, structure, and safety as ...
, the Eunicidae and Phyllodocidae, have evolved jaws, which can be used for seizing prey, biting off pieces of vegetation, or grasping dead and decaying matter. On the other hand, some predatory polychaetes have neither jaws nor eversible pharynges. Selective deposit feeders generally live in tubes on the sea-floor and use palps to find food particles in the sediment and then wipe them into their mouths. Filter feeders use "crowns" of palps covered in cilia
The cilium (: cilia; ; in Medieval Latin and in anatomy, ''cilium'') is a short hair-like membrane protrusion from many types of eukaryotic cell. (Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea.) The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike proj ...
that wash food particles towards their mouths. Non-selective deposit feeders ingest soil or marine sediment
Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently sediment transport, transported by the action of ...
s via mouths that are generally unspecialized. Some clitellates have sticky pads in the roofs of their mouths, and some of these can evert the pads to capture prey. Leeches often have an eversible proboscis, or a muscular pharynx with two or three teeth.
The gut is generally an almost straight tube supported by the mesenteries (vertical partitions within segments), and ends with the anus
In mammals, invertebrates and most fish, the anus (: anuses or ani; from Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is the external body orifice at the ''exit'' end of the digestive tract (bowel), i.e. the opposite end from the mouth. Its function is to facil ...
on the underside of the pygidium. However, in members of the tube-dwelling family Siboglinidae
Siboglinidae is a family (biology), family of polychaete Annelida, annelid worms whose members made up the former phylum, phyla Pogonophora and Vestimentifera (the giant tube worms). The family is composed of around 100 species of vermiform creatu ...
the gut is blocked by a swollen lining that houses symbiotic
Symbiosis (Ancient Greek : living with, companionship < : together; and ''bíōsis'': living) is any type of a close and long-term biolo ...
bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
, which can make up 15% of the worms' total weight. The bacteria convert inorganic
An inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bondsthat is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemistry''.
Inor ...
matter – such as hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is toxic, corrosive, and flammable. Trace amounts in ambient atmosphere have a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. Swedish chemist ...
and carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
from hydrothermal vents, or methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
from seeps – to organic matter that feeds themselves and their hosts, while the worms extend their palps into the gas flows to absorb the gases needed by the bacteria.
Annelids with blood vessels use metanephridia
The nephridium (: nephridia) is an invertebrate organ, found in pairs and performing a function similar to the vertebrate kidneys (which originated from the chordate nephridia). Nephridia remove metabolic wastes from an animal's body. Nephridia co ...
to remove soluble waste products, while those without use protonephridia. Both of these systems use a two-stage filtration process, in which fluid and waste products are first extracted and these are filtered again to re-absorb any re-usable materials while dumping toxic and spent materials as urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and many other animals. In placental mammals, urine flows from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder and exits the urethra through the penile meatus (mal ...
. The difference is that protonephridia combine both filtration stages in the same organ, while metanephridia perform only the second filtration and rely on other mechanisms for the first – in annelids special filter cells in the walls of the blood vessels let fluids and other small molecules pass into the coelomic fluid, where it circulates to the metanephridia. In annelids the points at which fluid enters the protonephridia or metanephridia are on the forward side of a septum while the second-stage filter and the nephridiopore (exit opening in the body wall) are in the following segment. As a result, the hindmost segment (before the growth zone and pygidium) has no structure that extracts its wastes, as there is no following segment to filter and discharge them, while the first segment contains an extraction structure that passes wastes to the second, but does not contain the structures that re-filter and discharge urine.
Reproduction and life cycle
Asexual reproduction

Polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine Annelid, annelid worms, common name, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called c ...
s can reproduce asexually, by dividing into two or more pieces or by budding
Budding or blastogenesis is a type of asexual reproduction in which a new organism develops from an outgrowth or bud due to cell division at one particular site. For example, the small bulb-like projection coming out from the yeast cell is kno ...
off a new individual while the parent remains a complete organism. Some oligochaetes, such as '' Aulophorus furcatus'', seem to reproduce entirely asexually, while others reproduce asexually in summer and sexually in autumn. Asexual reproduction in oligochaetes is always by dividing into two or more pieces, rather than by budding. However, leech
Leeches are segmented parasitism, parasitic or Predation, predatory worms that comprise the Class (biology), subclass Hirudinea within the phylum Annelida. They are closely related to the Oligochaeta, oligochaetes, which include the earthwor ...
es have never been seen reproducing asexually.
Most polychaetes and oligochaetes also use similar mechanisms to regenerate after suffering damage. Two polychaete genera
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial s ...
, '' Chaetopterus'' and '' Dodecaceria'', can regenerate from a single segment, and others can regenerate even if their heads are removed. Annelids are the most complex animals that can regenerate after such severe damage. On the other hand, leeches cannot regenerate.
Sexual reproduction
It is thought that annelids were originally animals with two separate sexes, which released ova andsperm
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm ...
into the water via their nephridia
The nephridium (: nephridia) is an invertebrate organ, found in pairs and performing a function similar to the vertebrate kidneys (which originated from the chordate nephridia). Nephridia remove metabolic wastes from an animal's body. Nephridia co ...
. The fertilized eggs develop into trochophore
A trochophore () is a type of free-swimming planktonic marine larva with several bands of cilia.
By moving their cilia rapidly, they make a water eddy to control their movement, and to bring their food closer in order to capture it more easily.
...
larva
A larva (; : larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into their next life stage. Animals with indirect development such as insects, some arachnids, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase ...
e, which live as plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms that drift in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) but are unable to actively propel themselves against ocean current, currents (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are ca ...
. Later they sink to the sea-floor and metamorphose into miniature adults: the part of the trochophore between the apical tuft and the prototroch becomes the prostomium (head); a small area round the trochophore's anus
In mammals, invertebrates and most fish, the anus (: anuses or ani; from Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is the external body orifice at the ''exit'' end of the digestive tract (bowel), i.e. the opposite end from the mouth. Its function is to facil ...
becomes the pygidium (tail-piece); a narrow band immediately in front of that becomes the growth zone that produces new segments; and the rest of the trochophore becomes the peristomium (the segment that contains the mouth).
However, the lifecycles of most living polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine Annelid, annelid worms, common name, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called c ...
s, which are almost all marine animals, are unknown, and only about 25% of the 300+ species whose lifecycles are known follow this pattern. About 14% use a similar external fertilization but produce yolk
Among animals which produce eggs, the yolk (; also known as the vitellus) is the nutrient-bearing portion of the egg whose primary function is to supply food for the development of the embryo. Some types of egg contain no yolk, for example bec ...
-rich eggs, which reduce the time the larva needs to spend among the plankton, or eggs from which miniature adults emerge rather than larvae. The rest care for the fertilized eggs until they hatch – some by producing jelly-covered masses of eggs which they tend, some by attaching the eggs to their bodies and a few species by keeping the eggs within their bodies until they hatch. These species use a variety of methods for sperm transfer; for example, in some the females collect sperm released into the water, while in others the males have a penis
A penis (; : penises or penes) is a sex organ through which male and hermaphrodite animals expel semen during copulation (zoology), copulation, and through which male placental mammals and marsupials also Urination, urinate.
The term ''pen ...
that inject sperm into the female. There is no guarantee that this is a representative sample of polychaetes' reproductive patterns, and it simply reflects scientists' current knowledge.
Some polychaetes breed only once in their lives, while others breed almost continuously or through several breeding seasons. While most polychaetes remain of one sex all their lives, a significant percentage of species are full hermaphrodite
A hermaphrodite () is a sexually reproducing organism that produces both male and female gametes. Animal species in which individuals are either male or female are gonochoric, which is the opposite of hermaphroditic.
The individuals of many ...
s or change sex during their lives. Most polychaetes whose reproduction has been studied lack permanent gonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a Heterocrine gland, mixed gland and sex organ that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gon ...
s, and it is uncertain how they produce ova and sperm. In a few species the rear of the body splits off and becomes a separate individual that lives just long enough to swim to a suitable environment, usually near the surface, and spawn.
Most mature clitellates (the group that includes earthworm
An earthworm is a soil-dwelling terrestrial invertebrate that belongs to the phylum Annelida. The term is the common name for the largest members of the class (or subclass, depending on the author) Oligochaeta. In classical systems, they we ...
s and leeches
Leeches are segmented parasitic or predatory worms that comprise the subclass Hirudinea within the phylum Annelida. They are closely related to the oligochaetes, which include the earthworm, and like them have soft, muscular segmented bod ...
) are full hermaphrodites, although in a few leech species younger adults function as males and become female at maturity. All have well-developed gonads, and all copulate. Earthworms store their partners' sperm in spermatheca
The spermatheca (pronounced : spermathecae ), also called ''receptaculum seminis'' (: ''receptacula seminis''), is an organ of the female reproductive tract in insects, e.g. ants, bees, some molluscs, Oligochaeta worms and certain other in ...
e ("sperm stores") and then the clitellum
The clitellum is a thickened glandular and non-segmented section of the body wall near the head in earthworms and leeches that secretes a viscid sac in which eggs are stored. It is located near the anterior end of the body, between the fourteenth ...
produces a Pupa, cocoon that collects ova from the ovaries
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocr ...
and then sperm from the spermathecae. Fertilization and development of earthworm eggs takes place in the cocoon. Leeches' eggs are fertilized in the ovaries, and then transferred to the cocoon. In all clitellates the cocoon also either produces yolk when the eggs are fertilized or nutrients while they are developing. All clitellates hatch as miniature adults rather than larvae.
Ecological significance
Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English Natural history#Before 1900, naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all speci ...
's book '' The Formation of Vegetable Mould Through the Action of Worms'' (1881) presented the first scientific analysis of earthworms' contributions to soil fertility
Soil fertility refers to the ability of soil to sustain agricultural plant growth, i.e. to provide plant habitat and result in sustained and consistent yields of high quality.
. Some burrow while others live entirely on the surface, generally in moist leaf litter
Plant litter (also leaf litter, tree litter, soil litter, litterfall, or duff) is dead plant material (such as leaves, bark, needles, twigs, and cladodes) that has fallen to the ground. This detritus or dead organic material and its constituen ...
. The burrowers loosen the soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, water, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms. Some scientific definitions distinguish dirt from ''soil'' by re ...
so that oxygen and water can penetrate it, and both surface and burrowing worms help to produce soil by mixing organic and mineral matter, by accelerating the decomposition
Decomposition is the process by which dead organic substances are broken down into simpler organic or inorganic matter such as carbon dioxide, water, simple sugars and mineral salts. The process is a part of the nutrient cycle and is ess ...
of organic matter and thus making it more quickly available to other organisms, and by concentrating minerals and converting them to forms that plants can use more easily. Earthworms are also important prey for birds ranging in size from robins to stork
Storks are large, long-legged, long-necked wading birds with long, stout bills. They belong to the family Ciconiidae, and make up the order Ciconiiformes . Ciconiiformes previously included a number of other families, such as herons and ibise ...
s, and for mammals ranging from shrew
Shrews ( family Soricidae) are small mole-like mammals classified in the order Eulipotyphla. True shrews are not to be confused with treeshrews, otter shrews, elephant shrews, West Indies shrews, or marsupial shrews, which belong to dif ...
s to badger
Badgers are medium-sized short-legged omnivores in the superfamily Musteloidea. Badgers are a polyphyletic rather than a natural taxonomic grouping, being united by their squat bodies and adaptions for fossorial activity rather than by the ...
s, and in some cases conserving earthworms may be essential for conserving endangered birds.
Terrestrial annelids can be invasive in some situations. In the glaciated areas of North America, for example, almost all native earthworms are thought to have been killed by the glaciers and the worms currently found in those areas are all introduced from other areas, primarily from Europe, and, more recently, from Asia. Northern hardwood forests are especially negatively impacted by invasive worms through the loss of leaf duff, soil fertility, changes in soil chemistry and the loss of ecological diversity. Especially of concern is '' Amynthas agrestis'' and at least one state (Wisconsin) has listed it as a prohibited species.
Earthworms migrate only a limited distance annually on their own, and the spread of invasive worms is increased rapidly by anglers and from worms or their cocoons in the dirt on vehicle tires or footwear.
Marine annelids may account for over one-third of bottom-dwelling animal species around coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in group ...
s and in tidal zones. Burrowing species increase the penetration of water and oxygen into the sea-floor sediment
Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently sediment transport, transported by the action of ...
, which encourages the growth of populations of aerobic bacteria and small animals alongside their burrows.
Although blood-sucking leech
Leeches are segmented parasitism, parasitic or Predation, predatory worms that comprise the Class (biology), subclass Hirudinea within the phylum Annelida. They are closely related to the Oligochaeta, oligochaetes, which include the earthwor ...
es do little direct harm to their victims, some transmit flagellate
A flagellate is a cell or organism with one or more whip-like appendages called flagella. The word ''flagellate'' also describes a particular construction (or level of organization) characteristic of many prokaryotes and eukaryotes and the ...
s that can be very dangerous to their hosts. Some small tube-dwelling oligochaetes transmit myxosporean parasite
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted str ...
s that cause whirling disease in fish.
Interaction with humans
Earthworms make a significant contribution tosoil fertility
Soil fertility refers to the ability of soil to sustain agricultural plant growth, i.e. to provide plant habitat and result in sustained and consistent yields of high quality.
. The rear end of the Palolo worm, a marine polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine Annelid, annelid worms, common name, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called c ...
that tunnels through coral, detaches in order to spawn at the surface, and the people of Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa and known until 1997 as Western Samoa, is an island country in Polynesia, part of Oceania, in the South Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main islands (Savai'i and Upolu), two smaller, inhabited ...
regard these spawning modules as a delicacy. Anglers sometimes find that worms are more effective bait than artificial flies, and worms can be kept for several days in a tin lined with damp moss. Ragworms are commercially important as bait and as food sources for aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. Nelu ...
, and there have been proposals to farm them in order to reduce over-fishing of their natural populations. Some marine polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine Annelid, annelid worms, common name, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called c ...
s' predation on molluscs causes serious losses to fishery and aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. Nelu ...
operations.
Scientists study aquatic annelids to monitor the oxygen content, salinity and pollution levels in fresh and marine water.
Accounts of the use of leech
Leeches are segmented parasitism, parasitic or Predation, predatory worms that comprise the Class (biology), subclass Hirudinea within the phylum Annelida. They are closely related to the Oligochaeta, oligochaetes, which include the earthwor ...
es for the medically dubious practice of blood-letting have come from China around 30 AD, India around 200 AD, ancient Rome around 50 AD and later throughout Europe. In the 19th century medical demand for leeches was so high that some areas' stocks were exhausted and other regions imposed restrictions or bans on exports, and ''Hirudo medicinalis
''Hirudo medicinalis'', or the European medicinal leech, is one of several species of leeches used as medicinal leeches.
Other species of ''Hirudo'' sometimes also used as medicinal leeches include ''Hirudo orientalis, H. orientalis'', ''Hirudo ...
'' is treated as an endangered species by both IUCN
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the status ...
and CITES
CITES (shorter acronym for the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora, also known as the Washington Convention) is a multilateral treaty to protect endangered plants and animals from the threats of inte ...
. More recently leeches have been used to assist in microsurgery, and their saliva
Saliva (commonly referred as spit or drool) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which ...
has provided anti-inflammatory
Anti-inflammatory is the property of a substance or treatment that reduces inflammation, fever or swelling. Anti-inflammatory drugs, also called anti-inflammatories, make up about half of analgesics. These drugs reduce pain by inhibiting mechan ...
compounds and several important anticoagulant
An anticoagulant, commonly known as a blood thinner, is a chemical substance that prevents or reduces the coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some occur naturally in blood-eating animals, such as leeches and mosquitoes, which ...
s, one of which also prevents tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s from spreading.
Ragworms' jaws are strong but much lighter than the hard parts of many other organisms, which are biomineralized with calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
salts. These advantages have attracted the attention of engineers. Investigations showed that ragworm jaws are made of unusual protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s that bind strongly to zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
.
Evolutionary history
Fossil record
 Since annelids are soft-bodied, their fossils are rare.
Since annelids are soft-bodied, their fossils are rare. Polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine Annelid, annelid worms, common name, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called c ...
s' fossil record consists mainly of the jaws that some species had and the mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid substance with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Mi ...
ized tubes that some secreted. Some Ediacaran
The Ediacaran ( ) is a geological period of the Neoproterozoic geologic era, Era that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period at 635 Million years ago, Mya to the beginning of the Cambrian Period at 538.8 Mya. It is the last ...
fossils such as '' Dickinsonia'' in some ways resemble polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine Annelid, annelid worms, common name, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called c ...
s, but the similarities are too vague for these fossils to be classified with confidence. The small shelly fossil
The small shelly fauna, small shelly fossils (SSF), or early skeletal fossils (ESF) are biomineralization, mineralized fossils, many only a few millimetres long, with a nearly continuous record from the latest stages of the Ediacaran to the end o ...
'' Cloudina'', from , has been classified by some authors as an annelid, but by others as a cnidarian
Cnidaria ( ) is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic invertebrates found both in fresh water, freshwater and marine environments (predominantly the latter), including jellyfish, hydroid (zoology), hydroids, ...
(i.e. in the phylum to which jellyfish
Jellyfish, also known as sea jellies or simply jellies, are the #Life cycle, medusa-phase of certain gelatinous members of the subphylum Medusozoa, which is a major part of the phylum Cnidaria. Jellyfish are mainly free-swimming marine animal ...
and sea anemone
Sea anemones ( ) are a group of predation, predatory marine invertebrates constituting the order (biology), order Actiniaria. Because of their colourful appearance, they are named after the ''Anemone'', a terrestrial flowering plant. Sea anemone ...
s belong). Until 2008 the earliest fossils widely accepted as annelids were the polychaetes '' Canadia'' and '' Burgessochaeta'', both from Canada's Burgess Shale
The Burgess Shale is a fossil-bearing deposit exposed in the Canadian Rockies of British Columbia, Canada. It is famous for the exceptional preservation of the soft parts of its fossils. At old (middle Cambrian), it is one of the earliest fos ...
, formed about in the Middle Cambrian
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordov ...
. '' Myoscolex'', found in Australia and a little older than the Burgess Shale, was possibly an annelid. However, it lacks some typical annelid features and has features which are not usually found in annelids and some of which are associated with other phyla. Then Simon Conway Morris and John Peel reported '' Phragmochaeta'' from Sirius Passet, about , and concluded that it was the oldest annelid known to date. There has been vigorous debate about whether the Burgess Shale fossil '' Wiwaxia'' was a mollusc
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
or an annelid. Polychaetes diversified in the early Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and System (geology), system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era (geology), Era, and the second of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon (geology), Eon. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years f ...
, about . It is not until the early Ordovician that the first annelid jaws are found, thus the crown-group cannot have appeared before this date and probably appeared somewhat later. By the end of the Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ...
, about , fossils of most of the modern mobile polychaete groups had appeared. Many fossil tubes look like those made by modern sessile polychaetes, but the first tubes clearly produced by polychaetes date from the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
, less than . In 2012, a 508 million year old species of annelid found near the Burgess shale
The Burgess Shale is a fossil-bearing deposit exposed in the Canadian Rockies of British Columbia, Canada. It is famous for the exceptional preservation of the soft parts of its fossils. At old (middle Cambrian), it is one of the earliest fos ...
beds in British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that ...
, '' Kootenayscolex'', was found that changed the hypotheses about how the annelid head developed. It appears to have bristles on its head segment akin to those along its body, as if the head simply developed as a specialized version of a previously generic segment.
The earliest good evidence for oligochaetes occurs in the Tertiary period
The Tertiary ( ) is an obsolete Period (geology), geologic period spanning 66 million to 2.6 or 1.8 million years ago. The period began with the extinction of the non-bird, avian dinosaurs in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, at t ...
, which began , and it has been suggested that these animals evolved around the same time as flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (). The term angiosperm is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek words (; 'container, vessel') and (; 'seed'), meaning that the seeds are enclosed with ...
s in the early Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
, from . A trace fossil
A trace fossil, also called an ichnofossil (; ), is a fossil record of biological activity by lifeforms, but not the preserved remains of the organism itself. Trace fossils contrast with body fossils, which are the fossilized remains of part ...
consisting of a convoluted burrow
file:Chipmunk-burrow (exits).jpg, An eastern chipmunk at the entrance of its burrow
A burrow is a hole or tunnel excavated into the ground by an animal to construct a space suitable for habitation or temporary refuge, or as a byproduct of Animal lo ...
partly filled with small fecal pellets may be evidence that earthworms were present in the early Triassic
The Triassic ( ; sometimes symbolized 🝈) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.5 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.4 Mya. The Triassic is t ...
period from . Body fossils going back to the mid Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and System (geology), system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era (geology), Era, and the second of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon (geology), Eon. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years f ...
, from , have been tentatively classified as oligochaetes, but these identifications are uncertain and some have been disputed.
Internal relationships
Traditionally the annelids have been divided into two major groups, thepolychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine Annelid, annelid worms, common name, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called c ...
s and clitellates. In turn the clitellates were divided into oligochaetes, which include earthworm
An earthworm is a soil-dwelling terrestrial invertebrate that belongs to the phylum Annelida. The term is the common name for the largest members of the class (or subclass, depending on the author) Oligochaeta. In classical systems, they we ...
s, and hirudinomorphs, whose best-known members are leech
Leeches are segmented parasitism, parasitic or Predation, predatory worms that comprise the Class (biology), subclass Hirudinea within the phylum Annelida. They are closely related to the Oligochaeta, oligochaetes, which include the earthwor ...
es. For many years there was no clear arrangement of the approximately 80 polychaete families
Family (from ) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictability, structure, and safety as ...
into higher-level groups. In 1997 Greg Rouse and Kristian Fauchald attempted a "first heuristic step in terms of bringing polychaete systematics to an acceptable level of rigour", based on anatomical structures, and divided polychaetes into:
* Scolecida, less than 1,000 burrowing species that look rather like earthworms.
* Palpata, the great majority of polychaetes, divided into:
**Canalipalpata
Canalipalpata, also known as bristle-footed annelids or fan-head worms, is an order of polychaete worms, with 31 families in it including the suborder Sabellida (families Serpulidae (tubeworms) and Sabellidae (fanworms and feather duster worm ...
, which are distinguished by having long grooved palps that they use for feeding, and most of which live in tubes.
**Aciculata
Errantia is a diverse group of marine life, marine polychaete worms in the phylum Annelida. Traditionally a subclass (biology), subclass of the paraphyletic class Polychaeta, it is currently regarded as a monophyletic group within the larger Pleis ...
, the most active polychaetes, which have parapodia reinforced by internal spines (aciculae).
Also in 1997 Damhnait McHugh, using molecular phylogenetics
Molecular phylogenetics () is the branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences, predominantly in DNA sequences, to gain information on an organism's evolutionary relationships. From these analyses, it is possible to ...
to compare similarities and differences in one gene, presented a very different view, in which: the clitellates were an offshoot of one branch of the polychaete family tree; the pogonophorans and echiurans, which for a few decades had been regarded as a separate phyla
Phyla, the plural of ''phylum'', may refer to:
* Phylum, a biological taxon between Kingdom and Class
* by analogy, in linguistics, a large division of possibly related languages, or a major language family which is not subordinate to another
Phy ...
, were placed on other branches of the polychaete tree. Subsequent molecular phylogenetics analyses on a similar scale presented similar conclusions.
In 2007 Torsten Struck and colleagues compared three genes in 81 taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and ...
, of which nine were outgroups, in other words not considered closely related to annelids but included to give an indication of where the organisms under study are placed on the larger tree of life. For a cross-check the study used an analysis of 11 genes (including the original 3) in ten taxa. This analysis agreed that clitellates, pogonophorans and echiurans were on various branches of the polychaete family tree. It also concluded that the classification of polychaetes into Scolecida, Canalipalpata and Aciculata was useless, as the members of these alleged groups were scattered all over the family tree derived from comparing the 81 taxa. It also placed sipuncula
The Sipuncula or Sipunculida (common names sipunculid worms or peanut worms) is a class containing about 162 species of marine annelid worms, that have secondarily lost their segmentation. Sipuncula was once considered a phylum of unsegmented ...
ns, generally regarded at the time as a separate phylum, on another branch of the polychaete tree, and concluded that leeches were a sub-group of oligochaetes rather than their sister-group among the clitellates. Rouse accepted the analyses based on molecular phylogenetics, and their main conclusions are now the scientific consensus, although the details of the annelid family tree remain uncertain.
In addition to re-writing the classification of annelids and three previously independent phyla, the molecular phylogenetics analyses undermine the emphasis that decades of previous writings placed on the importance of segmentation in the classification of invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
s. Polychaetes, which these analyses found to be the parent group, have completely segmented bodies, while polychaetes' echiurans and sipunculan offshoots are not segmented and pogonophores are segmented only in the rear parts of their bodies. It now seems that segmentation can appear and disappear much more easily in the course of evolution than was previously thought. The 2007 study also noted that the ladder-like nervous system, which is associated with segmentation, is less universal than previously thought in both annelids and arthropods.
The updated phylogenetic tree
A phylogenetic tree or phylogeny is a graphical representation which shows the evolutionary history between a set of species or taxa during a specific time.Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA. In ...
of the annelid phylum is comprised by a grade of basal groups of polychaetes: Palaeoannelida, Chaetopteriformia and the Amphinomida/Sipuncula
The Sipuncula or Sipunculida (common names sipunculid worms or peanut worms) is a class containing about 162 species of marine annelid worms, that have secondarily lost their segmentation. Sipuncula was once considered a phylum of unsegmented ...
/'' Lobatocerebrum'' clade. This grade is followed by Pleistoannelida
Pleistoannelida is a group of annelid worms that comprises the vast majority of the diversity in phylum Annelida. Discovered through phylogenetic analyses, it is the largest clade of annelids, comprised by the last common ancestor of the highly di ...
, the clade containing nearly all of annelid diversity, divided into two highly diverse groups: Sedentaria
Sedentaria is a diverse clade of annelid worms. It is traditionally treated as a subclass of the paraphyletic class Polychaeta, but it is also a monophyletic group uniting several polychaetes and the monophyletic class Clitellata. It is the sis ...
and Errantia
Errantia is a diverse group of marine life, marine polychaete worms in the phylum Annelida. Traditionally a subclass (biology), subclass of the paraphyletic class Polychaeta, it is currently regarded as a monophyletic group within the larger Pleis ...
. Sedentaria
Sedentaria is a diverse clade of annelid worms. It is traditionally treated as a subclass of the paraphyletic class Polychaeta, but it is also a monophyletic group uniting several polychaetes and the monophyletic class Clitellata. It is the sis ...
contains the clitellates, pogonophorans, echiurans and some archiannelids, as well as several polychaete groups. Errantia
Errantia is a diverse group of marine life, marine polychaete worms in the phylum Annelida. Traditionally a subclass (biology), subclass of the paraphyletic class Polychaeta, it is currently regarded as a monophyletic group within the larger Pleis ...
contains the eunicid and phyllodocid polychaetes, and several archiannelids. Some small groups, such as the Myzostomida
The Myzostomida or Myzostomatida are an order of small marine (ocean), marine worms, which are Parasitism, parasitic on echinoderms, mostly crinoids. These highly unusual and diverse annelids were first discovered by Friedrich Sigismund Leuckart ...
, are more difficult to place due to long branching, but belong to either one of these large groups.
External relationships
Annelids are members of the protostomes, one of the two major superphyla ofbilaterian
Bilateria () is a large clade of animals characterised by bilateral symmetry during embryonic development. This means their body plans are laid around a longitudinal axis with a front (or "head") and a rear (or "tail") end, as well as a left–r ...
animals – the other is the deuterostomes, which includes vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s. Within the protostomes, annelids used to be grouped with arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
s under the super-group Articulata ("jointed animals"), as segmentation is obvious in most members of both phyla. However, the genes that drive segmentation in arthropods do not appear to do the same in annelids. Arthropods and annelids both have close relatives that are unsegmented. It is at least as easy to assume that they evolved segmented bodies independently as it is to assume that the ancestral protostome or bilaterian was segmented and that segmentation disappeared in many descendant phyla. The current view is that annelids are grouped with mollusc
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
s, brachiopod
Brachiopods (), phylum (biology), phylum Brachiopoda, are a phylum of animals that have hard "valves" (shells) on the upper and lower surfaces, unlike the left and right arrangement in bivalve molluscs. Brachiopod valves are hinged at the rear e ...
s and several other phyla that have lophophores (fan-like feeding structures) and/or trochophore
A trochophore () is a type of free-swimming planktonic marine larva with several bands of cilia.
By moving their cilia rapidly, they make a water eddy to control their movement, and to bring their food closer in order to capture it more easily.
...
larvae as members of Lophotrochozoa. Meanwhile, arthropods are now regarded as members of the Ecdysozoa
Ecdysozoa () is a group of protostome animals, including Arthropoda (insects, chelicerates (including arachnids), crustaceans, and myriapods), Nematoda, and several smaller phylum (biology), phyla. The grouping of these animal phyla into a single ...
("animals that molt"), along with some phyla that are unsegmented.
The "Lophotrochozoa" hypothesis is also supported by the fact that many phyla within this group, including annelids, mollusc
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
s, nemerteans and flatworm
Platyhelminthes (from the Greek language, Greek πλατύ, ''platy'', meaning "flat" and ἕλμινς (root: ἑλμινθ-), ''helminth-'', meaning "worm") is a Phylum (biology), phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, Segmentation (biology), ...
s, follow a similar pattern in the fertilized egg's development. When their cells divide after the 4-cell stage, descendants of these four cells form a spiral pattern. In these phyla the "fates" of the embryo's cells, in other words the roles their descendants will play in the adult animal, are the same and can be predicted from a very early stage. Hence this development pattern is often described as "spiral determinate cleavage
Cleavage may refer to:
Science
* Cleavage (crystal), the way in which a crystal or mineral tends to split
* Cleavage (embryo), the division of cells in an early embryo
* Cleavage (geology), foliation of rock perpendicular to stress, a result of ...
".
 Fossil discoveries lead to the hypothesis that Annelida and the lophophorates are more closely related to each other than any other
Fossil discoveries lead to the hypothesis that Annelida and the lophophorates are more closely related to each other than any other phyla
Phyla, the plural of ''phylum'', may refer to:
* Phylum, a biological taxon between Kingdom and Class
* by analogy, in linguistics, a large division of possibly related languages, or a major language family which is not subordinate to another
Phy ...
. Because of the body plan of lophotrochozoan fossils, a phylogenetic analysis
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical data ...
found the lophophorates as the sister group
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and ...
of annelids. Both groups share in common: the presence of chaeta
A chaeta or cheta (; ) is a chitinous bristle or seta found on annelid worms, although the term is also frequently used to describe similar structures in other invertebrates such as arthropods. Polychaete annelids (''polychaeta'' literally me ...
e secreted by microvilli; paired, metameric coelom
The coelom (or celom) is the main body cavity in many animals and is positioned inside the body to surround and contain the digestive tract and other organs. In some animals, it is lined with mesothelium. In other animals, such as molluscs, i ...
ic compartments; and a similar metanephridial structure.
Notes
References
External links
* * {{Authority control Articles containing video clips Cambrian first appearances Extant Cambrian first appearances