Ancient Greek civilization on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern
 In 499 BC, the
In 499 BC, the 
 Ten years later, a second invasion was launched by Darius' son Xerxes. The city-states of northern and central Greece submitted to the Persian forces without resistance, but a coalition of 31 Greek city states, including Athens and Sparta, determined to resist the Persian invaders. At the same time, Greek Sicily was invaded by a Carthaginian force. In 480 BC, the first major battle of the invasion was fought at
Ten years later, a second invasion was launched by Darius' son Xerxes. The city-states of northern and central Greece submitted to the Persian forces without resistance, but a coalition of 31 Greek city states, including Athens and Sparta, determined to resist the Persian invaders. At the same time, Greek Sicily was invaded by a Carthaginian force. In 480 BC, the first major battle of the invasion was fought at
 The period from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC until the death of
The period from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC until the death of  In the early part of the Hellenistic period, the exact borders of the Hellenistic kingdoms were not settled. Antigonus attempted to expand his territory by attacking the other successor kingdoms until they joined against him, and he was killed at the Battle of Ipsus in 301 BC. His son Demetrius spent many years in Seleucid captivity, and his son, Antigonus II, only reclaimed the Macedonian throne around 276. Meanwhile, the Seleucid kingdom gave up territory in the east to the Indian king
In the early part of the Hellenistic period, the exact borders of the Hellenistic kingdoms were not settled. Antigonus attempted to expand his territory by attacking the other successor kingdoms until they joined against him, and he was killed at the Battle of Ipsus in 301 BC. His son Demetrius spent many years in Seleucid captivity, and his son, Antigonus II, only reclaimed the Macedonian throne around 276. Meanwhile, the Seleucid kingdom gave up territory in the east to the Indian king
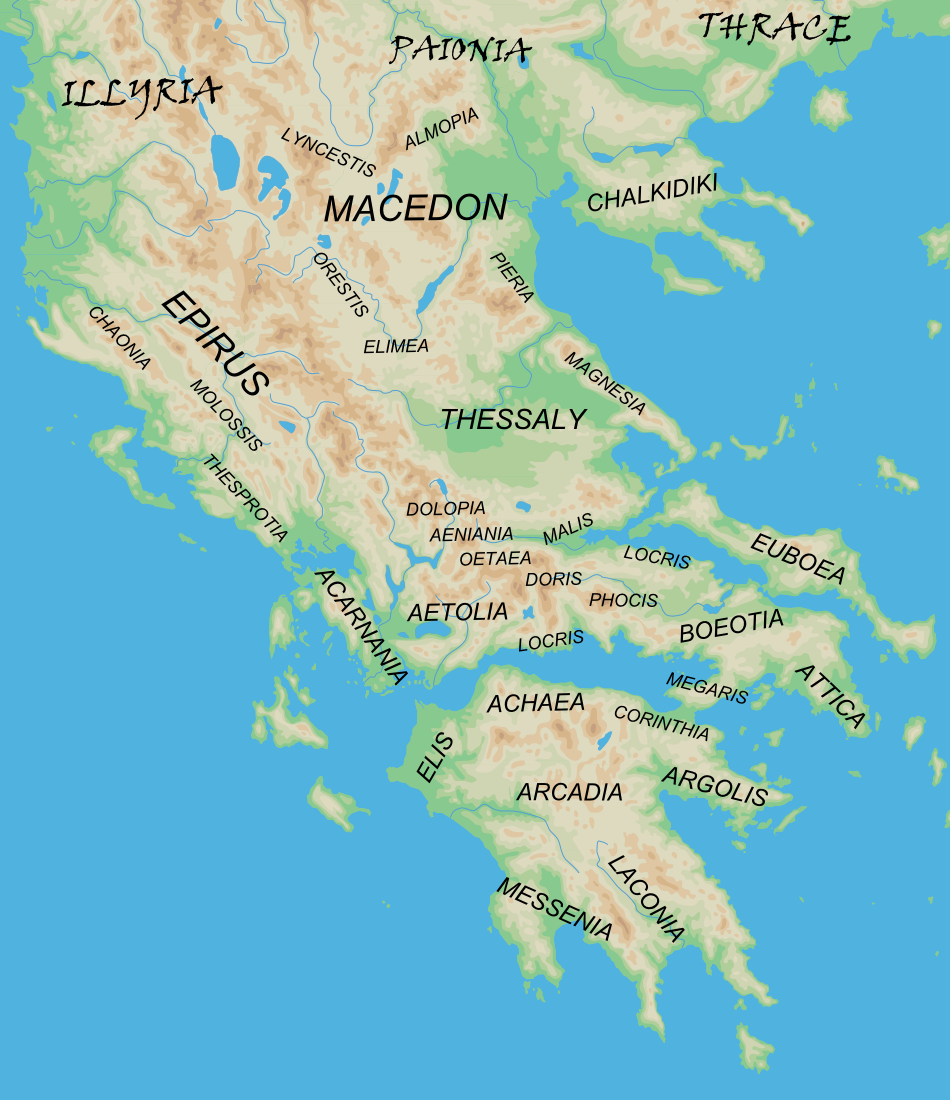 The territory of Greece is mountainous, and as a result, ancient Greece consisted of many smaller regions, each with its own dialect, cultural peculiarities, and identity. Regionalism and regional conflicts were prominent features of ancient Greece. Cities tended to be located in valleys between mountains, or on coastal plains, and dominated a certain area around them.
In the south lay the
The territory of Greece is mountainous, and as a result, ancient Greece consisted of many smaller regions, each with its own dialect, cultural peculiarities, and identity. Regionalism and regional conflicts were prominent features of ancient Greece. Cities tended to be located in valleys between mountains, or on coastal plains, and dominated a certain area around them.
In the south lay the

 During the Archaic period, the Greek Classical demography#Ancient Greece and Greek colonies, population grew beyond the capacity of the limited arable land of Greece proper, Greek colonisation, resulting in the large-scale establishment of colonies elsewhere: according to one estimate, the population of the widening area of Greek settlement increased roughly ten-fold from 800 to 400 BC, from 800,000 to as many as –10 million. This was not simply for trade, but also to found settlements. These Greek colonies were not, as Roman colonies were, dependent on their mother-city, but were independent city-states in their own right.
Greeks settled outside of Greece in two distinct ways. The first was in permanent settlements founded by Greeks, which formed as independent poleis. The second form was in what historians refer to as ''emporium (antiquity), emporia''; trading posts which were occupied by both Greeks and non-Greeks and which were primarily concerned with the manufacture and sale of goods. Examples of this latter type of settlement are found at Al Mina in the east and Pithekoussai in the west. From around 750 to 500 BC, Greeks settled colonies in all directions. To the east, the Aegean Sea, Aegean coast of Asia Minor was colonized first, followed by Ancient history of Cyprus, Cyprus and the coasts of Thrace, the Sea of Marmara and south coast of the Black Sea.
Eventually, Greek colonization reached as far northeast as present-day Ukraine and Russia (Taganrog). To the west the coasts of Illyria, Southern Italy (called "Magna Graecia") were settled, followed by Southern France, Corsica, and even eastern Spain. Greek colonies were also founded in Ancient Egypt, Egypt and Ancient Libya, Libya. Modern Syracuse, Italy, Syracuse, Naples, Marseille and Istanbul had their beginnings as the Greek colonies Syracusae (), Neapolis (), Massalia () and Byzantion (). These colonies played an important role in the spread of Greek influence throughout Europe and also aided in the establishment of long-distance trading networks between the Greek city-states, boosting the economy of ancient Greece.
During the Archaic period, the Greek Classical demography#Ancient Greece and Greek colonies, population grew beyond the capacity of the limited arable land of Greece proper, Greek colonisation, resulting in the large-scale establishment of colonies elsewhere: according to one estimate, the population of the widening area of Greek settlement increased roughly ten-fold from 800 to 400 BC, from 800,000 to as many as –10 million. This was not simply for trade, but also to found settlements. These Greek colonies were not, as Roman colonies were, dependent on their mother-city, but were independent city-states in their own right.
Greeks settled outside of Greece in two distinct ways. The first was in permanent settlements founded by Greeks, which formed as independent poleis. The second form was in what historians refer to as ''emporium (antiquity), emporia''; trading posts which were occupied by both Greeks and non-Greeks and which were primarily concerned with the manufacture and sale of goods. Examples of this latter type of settlement are found at Al Mina in the east and Pithekoussai in the west. From around 750 to 500 BC, Greeks settled colonies in all directions. To the east, the Aegean Sea, Aegean coast of Asia Minor was colonized first, followed by Ancient history of Cyprus, Cyprus and the coasts of Thrace, the Sea of Marmara and south coast of the Black Sea.
Eventually, Greek colonization reached as far northeast as present-day Ukraine and Russia (Taganrog). To the west the coasts of Illyria, Southern Italy (called "Magna Graecia") were settled, followed by Southern France, Corsica, and even eastern Spain. Greek colonies were also founded in Ancient Egypt, Egypt and Ancient Libya, Libya. Modern Syracuse, Italy, Syracuse, Naples, Marseille and Istanbul had their beginnings as the Greek colonies Syracusae (), Neapolis (), Massalia () and Byzantion (). These colonies played an important role in the spread of Greek influence throughout Europe and also aided in the establishment of long-distance trading networks between the Greek city-states, boosting the economy of ancient Greece.
 Ancient Greece consisted of several hundred relatively independent city-states ('' poleis''). This was a situation unlike that in most other contemporary societies, which were either tribal or Realm, kingdoms ruling over relatively large territories. Undoubtedly, the geography of Greece—divided and sub-divided by hills, mountains, and rivers—contributed to the fragmentary nature of ancient Greece. On the one hand, the ancient Greeks had no doubt that they were "one people"; they had the same State religion, religion, same basic culture, and same language. Furthermore, the Greeks were very aware of their tribal origins;
Ancient Greece consisted of several hundred relatively independent city-states ('' poleis''). This was a situation unlike that in most other contemporary societies, which were either tribal or Realm, kingdoms ruling over relatively large territories. Undoubtedly, the geography of Greece—divided and sub-divided by hills, mountains, and rivers—contributed to the fragmentary nature of ancient Greece. On the one hand, the ancient Greeks had no doubt that they were "one people"; they had the same State religion, religion, same basic culture, and same language. Furthermore, the Greeks were very aware of their tribal origins;
 Initially many Greek city-states seem to have been petty kingdoms; there was often a city official carrying some residual, ceremonial functions of the king (''basileus''), e.g., the ''archon basileus'' in Athens. However, by the Archaic period and the first historical consciousness, most had already become aristocratic oligarchies. It is unclear exactly how this change occurred. For instance, in Athens, the kingship had been reduced to a hereditary, lifelong chief magistracy (''Archon of Athens, archon'') by ; by 753 BC this had become a decennial, elected archonship, and finally an annually elected archonship by 683 BC. Through each stage, more power would have been transferred to the aristocracy as a whole, and away from a single individual.
Inevitably, the domination of politics and concomitant aggregation of wealth by small groups of families was apt to cause social unrest in many ''poleis''. In many cities a tyrant (not in the modern sense of repressive autocracies), would at some point seize control and govern according to their own will; often a populist agenda would help sustain them in power. In a system wracked with class conflict, government by a 'strongman' was often the best solution.
Athens fell under a tyranny in the second half of the 6th century BC. When this tyranny was ended, the Athenians founded Athenian democracy, the world's first democracy as a radical solution to prevent the aristocracy regaining power. A Popular assembly, citizens' assembly (the ''Ecclesia (ancient Athens), Ecclesia''), for the discussion of city policy, had existed since the reforms of Draco in 621 BC; all citizens were permitted to attend after the reforms of
Initially many Greek city-states seem to have been petty kingdoms; there was often a city official carrying some residual, ceremonial functions of the king (''basileus''), e.g., the ''archon basileus'' in Athens. However, by the Archaic period and the first historical consciousness, most had already become aristocratic oligarchies. It is unclear exactly how this change occurred. For instance, in Athens, the kingship had been reduced to a hereditary, lifelong chief magistracy (''Archon of Athens, archon'') by ; by 753 BC this had become a decennial, elected archonship, and finally an annually elected archonship by 683 BC. Through each stage, more power would have been transferred to the aristocracy as a whole, and away from a single individual.
Inevitably, the domination of politics and concomitant aggregation of wealth by small groups of families was apt to cause social unrest in many ''poleis''. In many cities a tyrant (not in the modern sense of repressive autocracies), would at some point seize control and govern according to their own will; often a populist agenda would help sustain them in power. In a system wracked with class conflict, government by a 'strongman' was often the best solution.
Athens fell under a tyranny in the second half of the 6th century BC. When this tyranny was ended, the Athenians founded Athenian democracy, the world's first democracy as a radical solution to prevent the aristocracy regaining power. A Popular assembly, citizens' assembly (the ''Ecclesia (ancient Athens), Ecclesia''), for the discussion of city policy, had existed since the reforms of Draco in 621 BC; all citizens were permitted to attend after the reforms of
 Slaves had no power or status. Slaves had the right to have a family and own property, subject to their master's goodwill and permission, but they had no political rights. By 600 BC, chattel slavery had spread in Greece. By the 5th century BC, slaves made up one-third of the total population in some city-states. Between 40 and 80% of the population of Classical Athens were slaves. Slaves outside of Sparta almost never revolted because they were made up of too many nationalities and were too scattered to organize. However, unlike later Western culture, the ancient Greeks did not think in terms of race (human categorization), race.
Most families owned slaves as household servants and laborers, and even poor families might have owned a few slaves. Owners were not allowed to beat or kill their slaves. Owners often promised to free slaves in the future to encourage slaves to work hard. Unlike in Rome, freedmen did not become citizens. Instead, they were mixed into the population of ''metics'', which included people from foreign countries or other city-states who were officially allowed to live in the state.
City-states legally owned slaves. These public slaves had a larger measure of independence than slaves owned by families, living on their own and performing specialized tasks. In Athens, public slaves were trained to look out for counterfeit coinage, while temple slaves acted as servants of the temple's Lists of Greek mythological figures, deity and Scythian slaves were employed in Athens as a police force corralling citizens to political functions.
Sparta had a special type of slaves called ''helots''. Helots were Messenians enslaved en masse during the First Messenian War, Messenian Wars by the state and assigned to families where they were forced to stay. Helots raised food and did household chores so that women could concentrate on raising strong children while men could devote their time to training as hoplites. Their masters treated them harshly, and helots slave rebellion, revolted against their masters several times. In 370/369 BC, as a result of Epaminondas' liberation of Messenia from Spartan rule, the helot system there came to an end and the helots won their freedom. However, it persisted in Laconia until the 2nd century BC.
Slaves had no power or status. Slaves had the right to have a family and own property, subject to their master's goodwill and permission, but they had no political rights. By 600 BC, chattel slavery had spread in Greece. By the 5th century BC, slaves made up one-third of the total population in some city-states. Between 40 and 80% of the population of Classical Athens were slaves. Slaves outside of Sparta almost never revolted because they were made up of too many nationalities and were too scattered to organize. However, unlike later Western culture, the ancient Greeks did not think in terms of race (human categorization), race.
Most families owned slaves as household servants and laborers, and even poor families might have owned a few slaves. Owners were not allowed to beat or kill their slaves. Owners often promised to free slaves in the future to encourage slaves to work hard. Unlike in Rome, freedmen did not become citizens. Instead, they were mixed into the population of ''metics'', which included people from foreign countries or other city-states who were officially allowed to live in the state.
City-states legally owned slaves. These public slaves had a larger measure of independence than slaves owned by families, living on their own and performing specialized tasks. In Athens, public slaves were trained to look out for counterfeit coinage, while temple slaves acted as servants of the temple's Lists of Greek mythological figures, deity and Scythian slaves were employed in Athens as a police force corralling citizens to political functions.
Sparta had a special type of slaves called ''helots''. Helots were Messenians enslaved en masse during the First Messenian War, Messenian Wars by the state and assigned to families where they were forced to stay. Helots raised food and did household chores so that women could concentrate on raising strong children while men could devote their time to training as hoplites. Their masters treated them harshly, and helots slave rebellion, revolted against their masters several times. In 370/369 BC, as a result of Epaminondas' liberation of Messenia from Spartan rule, the helot system there came to an end and the helots won their freedom. However, it persisted in Laconia until the 2nd century BC.
 At least in the Archaic period, the fragmentary nature of ancient Greece, with many competing city-states, increased the frequency of conflict but conversely limited the scale of warfare. Unable to maintain professional armies, the city-states relied on their own citizens to fight. This inevitably reduced the potential duration of campaigns, as citizens would need to return to their own professions (especially in the case of, for example, farmers). Campaigns would therefore often be restricted to summer. When battles occurred, they were usually set piece and intended to be decisive. Casualties were slight compared to later battles, rarely amounting to more than five percent of the losing side, but the slain often included the most prominent citizens and generals who led from the front.
The scale and scope of warfare in ancient Greece changed dramatically as a result of the
At least in the Archaic period, the fragmentary nature of ancient Greece, with many competing city-states, increased the frequency of conflict but conversely limited the scale of warfare. Unable to maintain professional armies, the city-states relied on their own citizens to fight. This inevitably reduced the potential duration of campaigns, as citizens would need to return to their own professions (especially in the case of, for example, farmers). Campaigns would therefore often be restricted to summer. When battles occurred, they were usually set piece and intended to be decisive. Casualties were slight compared to later battles, rarely amounting to more than five percent of the losing side, but the slain often included the most prominent citizens and generals who led from the front.
The scale and scope of warfare in ancient Greece changed dramatically as a result of the
 Ancient Greek philosophy focused on the role of reason and inquiry. In many ways, it had an important influence on modern philosophy, as well as modern science. Clear unbroken lines of influence lead from ancient Greek and Hellenistic philosophers, to medieval Early Islamic philosophy, Muslim philosophers and Islamic science, Islamic scientists, to the European Renaissance and Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment, to the secular sciences of the modern day.
Neither reason nor inquiry began with the ancient Greeks. Defining the difference between the Greek quest for knowledge and the quests of the elder civilizations, such as the ancient Egyptians and Babylonians, has long been a topic of study by theorists of civilization.
The first known philosophers of Greece were the pre-Socratics, who attempted to provide naturalistic, non-mythical descriptions of the world. They were followed by Socrates, one of the first philosophers based in Athens during fifth-century Athens, its golden age whose ideas, despite being known by second-hand accounts instead of writings of his own, laid the basis of Western philosophy. Socrates' disciple
Ancient Greek philosophy focused on the role of reason and inquiry. In many ways, it had an important influence on modern philosophy, as well as modern science. Clear unbroken lines of influence lead from ancient Greek and Hellenistic philosophers, to medieval Early Islamic philosophy, Muslim philosophers and Islamic science, Islamic scientists, to the European Renaissance and Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment, to the secular sciences of the modern day.
Neither reason nor inquiry began with the ancient Greeks. Defining the difference between the Greek quest for knowledge and the quests of the elder civilizations, such as the ancient Egyptians and Babylonians, has long been a topic of study by theorists of civilization.
The first known philosophers of Greece were the pre-Socratics, who attempted to provide naturalistic, non-mythical descriptions of the world. They were followed by Socrates, one of the first philosophers based in Athens during fifth-century Athens, its golden age whose ideas, despite being known by second-hand accounts instead of writings of his own, laid the basis of Western philosophy. Socrates' disciple
 Like poetry, Greek prose had its origins in the archaic period, and the earliest writers of Greek philosophy, history, and medical literature all date to the 6th century BC. Prose first emerged as the writing style adopted by the presocratic philosophers Anaximander and Anaximenes of Miletus, Anaximenes—though Thales of Miletus, considered the first Greek philosopher, apparently wrote nothing. Prose as a genre reached maturity in the classical era, and the major Greek prose genres—philosophy, history, rhetoric, and dialogue—developed in this period.
The Hellenistic period saw the literary centre of the Greek world move from Athens, where it had been in the classical period, to Alexandria. At the same time, other Hellenistic kings such as the Antigonids and the Attalids were patrons of scholarship and literature, turning Pella and Pergamon respectively into cultural centres. It was thanks to this cultural patronage by Hellenistic kings, and especially the Museum at Alexandria, that so much ancient Greek literature has survived. The Library of Alexandria, part of the Museum, had the previously unenvisaged aim of collecting together copies of all known authors in Greek. Almost all of the surviving non-technical Hellenistic literature is poetry, and Hellenistic poetry tended to be highly intellectual, blending different genres and traditions, and avoiding linear narratives. The Hellenistic period also saw a shift in the ways literature was consumed—while in the archaic and classical periods literature had typically been experienced in public performance, in the Hellenistic period it was more commonly read privately. At the same time, Hellenistic poets began to write for private, rather than public, consumption.
With Octavian's victory at Actium in 31 BC, Rome began to become a major centre of Greek literature, as important Greek authors such as Strabo and Dionysius of Halicarnassus came to Rome. The period of greatest innovation in Greek literature under Rome was the "long second century" from approximately 80 AD to around 230 AD. This innovation was especially marked in prose, with the development of the novel and a revival of prominence for display oratory both dating to this period.
Like poetry, Greek prose had its origins in the archaic period, and the earliest writers of Greek philosophy, history, and medical literature all date to the 6th century BC. Prose first emerged as the writing style adopted by the presocratic philosophers Anaximander and Anaximenes of Miletus, Anaximenes—though Thales of Miletus, considered the first Greek philosopher, apparently wrote nothing. Prose as a genre reached maturity in the classical era, and the major Greek prose genres—philosophy, history, rhetoric, and dialogue—developed in this period.
The Hellenistic period saw the literary centre of the Greek world move from Athens, where it had been in the classical period, to Alexandria. At the same time, other Hellenistic kings such as the Antigonids and the Attalids were patrons of scholarship and literature, turning Pella and Pergamon respectively into cultural centres. It was thanks to this cultural patronage by Hellenistic kings, and especially the Museum at Alexandria, that so much ancient Greek literature has survived. The Library of Alexandria, part of the Museum, had the previously unenvisaged aim of collecting together copies of all known authors in Greek. Almost all of the surviving non-technical Hellenistic literature is poetry, and Hellenistic poetry tended to be highly intellectual, blending different genres and traditions, and avoiding linear narratives. The Hellenistic period also saw a shift in the ways literature was consumed—while in the archaic and classical periods literature had typically been experienced in public performance, in the Hellenistic period it was more commonly read privately. At the same time, Hellenistic poets began to write for private, rather than public, consumption.
With Octavian's victory at Actium in 31 BC, Rome began to become a major centre of Greek literature, as important Greek authors such as Strabo and Dionysius of Halicarnassus came to Rome. The period of greatest innovation in Greek literature under Rome was the "long second century" from approximately 80 AD to around 230 AD. This innovation was especially marked in prose, with the development of the novel and a revival of prominence for display oratory both dating to this period.
Hippocrates
Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2006. Microsoft Corporation
31 October 2009. in recognition of his lasting contributions to the field as the founder of the Hippocratic school of medicine. This intellectual school revolutionized medicine in ancient Greece, establishing it as a discipline distinct from other fields that it had traditionally been associated with (notably theurgy and philosophy), thus making medicine a profession.
The Canadian Museum of Civilization—Greece Secrets of the Past
Ancient Greece
website from the British Museum
Economic history of ancient Greece
(archived 2 May 2006)
The Greek currency history
Limenoscope
an ancient Greek ports database (archived 11 May 2011)
Greek and Roman theatre architecture
Illustrated Greek History
Janice Siegel, Department of Classics, Hampden–Sydney College, Virginia {{Authority control Ancient Greece, Articles which contain graphical timelines
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages
The Greek Dark Ages ( 1180–800 BC) were earlier regarded as two continuous periods of Greek history: the Postpalatial Bronze Age (c. 1180–1050 BC) and the Prehistoric Iron Age or Early Iron Age (c. 1050–800 BC). The last included all the ...
of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity
Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural History of Europe, European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the inter ...
(), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically related city-states and communities. Prior to the Roman period, most of these regions were officially unified only once under the Kingdom of Macedon from 338 to 323 BC. In Western history, the era of classical antiquity was immediately followed by the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages (historiography), Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th to the 10th century. They marked the start o ...
and the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
period.
Three centuries after the decline of Mycenaean Greece
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age in ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1750 to 1050 BC.. It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainla ...
during the Bronze Age collapse, Greek urban poleis began to form in the 8th century BC, ushering in the Archaic period and the colonization of the Mediterranean Basin. This was followed by the age of Classical Greece
Classical Greece was a period of around 200 years (the 5th and 4th centuries BC) in ancient Greece,The "Classical Age" is "the modern designation of the period from about 500 B.C. to the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C." ( Thomas R. Mar ...
, from the Greco-Persian Wars
The Greco-Persian Wars (also often called the Persian Wars) were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Polis, Greek city-states that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world ...
to the death of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
in 323 BC, and which included the Golden Age of Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
and the Peloponnesian War
The Second Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), often called simply the Peloponnesian War (), was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek war fought between Classical Athens, Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Ancien ...
. The unification of Greece by Macedon under Philip II and subsequent conquest of the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, i ...
by Alexander the Great spread Hellenistic civilization across the Middle East. The Hellenistic period
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
is considered to have ended in 30 BC, when the last Hellenistic kingdom, Ptolemaic Egypt Ptolemaic is the adjective formed from the name Ptolemy, and may refer to:
Pertaining to the Ptolemaic dynasty
* Ptolemaic dynasty, the Macedonian Greek dynasty that ruled Egypt founded in 305 BC by Ptolemy I Soter
*Ptolemaic Kingdom
Pertaining ...
, was annexed by the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
.
Classical Greek culture, especially philosophy, had a powerful influence on ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Em ...
, which carried a version of it throughout the Mediterranean and much of Europe. For this reason, Classical Greece is generally considered the cradle of Western civilization, the seminal culture from which the modern West derives many of its founding archetypes and ideas in politics, philosophy, science, and art.
Chronology
Classical antiquity
Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural History of Europe, European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the inter ...
in the Mediterranean region is commonly considered to have begun in the 8th century BC (around the time of the earliest recorded poetry of Homer) and ended in the 6th century AD.
Classical antiquity in Greece was preceded by the Greek Dark Ages
The Greek Dark Ages ( 1180–800 BC) were earlier regarded as two continuous periods of Greek history: the Postpalatial Bronze Age (c. 1180–1050 BC) and the Prehistoric Iron Age or Early Iron Age (c. 1050–800 BC). The last included all the ...
(), archaeologically characterised by the protogeometric and geometric styles of designs on pottery. Following the Dark Ages was the Archaic period, beginning around the 8th century BC, which saw early developments in Greek culture and society leading to the Classical period from the Persian invasion of Greece in 480 BC until the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC. The Classical period is characterized by a "classical" style, i.e. one which was considered exemplary by later observers, most famously in the Parthenon
The Parthenon (; ; ) is a former Ancient Greek temple, temple on the Acropolis of Athens, Athenian Acropolis, Greece, that was dedicated to the Greek gods, goddess Athena. Its decorative sculptures are considered some of the high points of c ...
of Athens. Politically, the Classical period was dominated by Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
and the Delian League
The Delian League was a confederacy of Polis, Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, founded in 478 BC under the leadership (hegemony) of Classical Athens, Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Achaemenid Empire, Persian ...
during the 5th century, but displaced by Spartan hegemony
Spartan hegemony refers to the period of dominance by Sparta in Greek affairs from 404 to 371 BC. Even before this period the polis of Sparta was the greatest Spartan army, military land power of classical Ancient Greece, Greek antiquity and govern ...
during the early 4th century BC, before power shifted to Thebes and the Boeotian League and finally to the League of Corinth
The League of Corinth, also referred to as the Hellenic League (, ''koinòn tõn Hellḗnōn''; or simply , ''the Héllēnes''), was a federation of Greek states created by Philip IIDiodorus Siculus, Book 16, 89. «διόπερ ἐν Κορί� ...
led by Macedon. This period was shaped by the Greco-Persian Wars
The Greco-Persian Wars (also often called the Persian Wars) were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Polis, Greek city-states that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world ...
, the Peloponnesian War
The Second Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), often called simply the Peloponnesian War (), was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek war fought between Classical Athens, Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Ancien ...
, and the Rise of Macedon.
Following the Classical period was the Hellenistic period (323–146 BC), during which Greek culture and power expanded into the Near East
The Near East () is a transcontinental region around the Eastern Mediterranean encompassing the historical Fertile Crescent, the Levant, Anatolia, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and coastal areas of the Arabian Peninsula. The term was invented in the 20th ...
from the death of Alexander until the Roman conquest. Roman Greece is usually counted from the Roman victory over the Corinth
Corinth ( ; , ) is a municipality in Corinthia in Greece. The successor to the ancient Corinth, ancient city of Corinth, it is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Sin ...
ians at the Battle of Corinth in 146 BC to the establishment of Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion () was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' continued to be used as a n ...
by Constantine as the capital of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
in 330 AD. Finally, Late Antiquity
Late antiquity marks the period that comes after the end of classical antiquity and stretches into the onset of the Early Middle Ages. Late antiquity as a period was popularized by Peter Brown (historian), Peter Brown in 1971, and this periodiza ...
refers to the period of Christianization
Christianization (or Christianisation) is a term for the specific type of change that occurs when someone or something has been or is being converted to Christianity. Christianization has, for the most part, spread through missions by individu ...
during the later 4th to early 6th centuries AD, consummated by the closure of the Academy of Athens by Justinian I
Justinian I (, ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign was marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovatio imperii'', or "restoration of the Empire". This ambition was ...
in 529.
Historiography
The historical period of ancient Greece is unique in world history as the first period attested directly in comprehensive, narrativehistoriography
Historiography is the study of the methods used by historians in developing history as an academic discipline. By extension, the term ":wikt:historiography, historiography" is any body of historical work on a particular subject. The historiog ...
, while earlier ancient history or protohistory
Protohistory is the period between prehistory and written history, during which a culture or civilization has not yet developed writing, but other cultures that have developed writing have noted the existence of those pre-literate groups in the ...
is known from much more fragmentary documents such as annals, king lists, and pragmatic epigraphy
Epigraphy () is the study of inscriptions, or epigraphs, as writing; it is the science of identifying graphemes, clarifying their meanings, classifying their uses according to dates and cultural contexts, and drawing conclusions about the wr ...
.
Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
is widely known as the "father of history": his '' Histories'' are eponymous of the entire field. Written between the 450s and 420s BC, Herodotus' work reaches about a century into the past, discussing 6th-century BC historical figures such as Darius I of Persia, Cambyses II and Psamtik III, and alluding to some 8th-century BC persons such as Candaules. The accuracy of Herodotus' works is debated.
Herodotus was succeeded by authors such as Thucydides
Thucydides ( ; ; BC) was an Classical Athens, Athenian historian and general. His ''History of the Peloponnesian War'' recounts Peloponnesian War, the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been d ...
, Xenophon
Xenophon of Athens (; ; 355/354 BC) was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian. At the age of 30, he was elected as one of the leaders of the retreating Ancient Greek mercenaries, Greek mercenaries, the Ten Thousand, who had been ...
, Demosthenes
Demosthenes (; ; ; 384 – 12 October 322 BC) was a Greek statesman and orator in ancient Athens. His orations constitute a significant expression of contemporary Athenian intellectual prowess and provide insight into the politics and cu ...
, Plato
Plato ( ; Greek language, Greek: , ; born BC, died 348/347 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher of the Classical Greece, Classical period who is considered a foundational thinker in Western philosophy and an innovator of the writte ...
and Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
. Most were either Athenian or pro-Athenian, which is why far more is known about the history and politics of Athens than of many other cities.
Their scope is further limited by a focus on political, military and diplomatic history, ignoring economic and social history.
History
Archaic period
The archaic period, lasting approximately from 800 to 500 BC, saw the culmination of political and social developments which had begun in the Greek Dark Age, with the ''polis'' (city-state) becoming the most important unit of political organisation in Greece. The absence of powerful states in Greece after the collapse of Mycenaean power, and the geography of Greece, where many settlements were separated from their neighbours by mountainous terrain, encouraged the development of small independent city-states. Several Greek states saw tyrants rise to power in this period, most famously atCorinth
Corinth ( ; , ) is a municipality in Corinthia in Greece. The successor to the ancient Corinth, ancient city of Corinth, it is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Sin ...
from 657 BC. The period also saw the founding of Greek colonies around the Mediterranean, with Euboean settlements at Al-Mina
Al-Mina (Arabic: "the port") is the modern name given by Leonard Woolley to an ancient trading post on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast of northern Syria (region), Syria, at the mouth of the Orontes River. It is now located in Hatay pr ...
in the east as early as 800 BC, and Ischia in the west by 775. Increasing contact with non-Greek peoples in this period, especially in the Near East, inspired developments in art and architecture, the adoption of coinage, and the development of the Greek alphabet.
Athens developed its democratic system over the course of the archaic period. Already in the 7th century, the right of all citizen men to attend the assembly appears to have been established. After a failed coup led by Cylon of Athens around 636 BC, Draco was appointed to establish a code of laws in 621. This failed to reduce the political tension between the poor and the elites, and in 594 Solon
Solon (; ; BC) was an Archaic Greece#Athens, archaic History of Athens, Athenian statesman, lawmaker, political philosopher, and poet. He is one of the Seven Sages of Greece and credited with laying the foundations for Athenian democracy. ...
was given the authority to enact another set of reforms, which attempted to balance the power of the rich and the poor. In the middle of the 6th century, Pisistratus established himself as a tyrant, and after his death in 527 his son Hippias inherited his position; by the end of the 6th century he had been overthrown, and Cleisthenes
Cleisthenes ( ; ), or Clisthenes (), was an ancient Athenian lawgiver credited with reforming the constitution of ancient Athens and setting it on a democratic footing in 508 BC. For these accomplishments, historians refer to him as "the fath ...
carried out further democratising reforms.
In Sparta, a political system with two kings, a council of elders, and five ephors
The ephors were a board of five magistrates in ancient Sparta. They had an extensive range of judicial, religious, legislative, and military powers, and could shape Sparta's home and foreign affairs.
The word "''ephors''" (Ancient Greek ''éph ...
developed over the course of the 8th and 7th centuries. According to Spartan tradition, this constitution was established by the legendary lawgiver Lycurgus. Over the course of the first and second Messenian wars, Sparta subjugated the neighbouring region of Messenia
Messenia or Messinia ( ; ) is a regional unit (''perifereiaki enotita'') in the southwestern part of the Peloponnese region, in Greece. Until the implementation of the Kallikratis plan on 1 January 2011, Messenia was a prefecture (''nomos' ...
, enserfing the population.
In the 6th century, Greek city-states began to develop formal relationships with one another, where previously individual rulers had relied on personal relationships with the elites of other cities. Towards the end of the Archaic period, Sparta began to build a series of alliances, the Peloponnesian League, with cities including Corinth
Corinth ( ; , ) is a municipality in Corinthia in Greece. The successor to the ancient Corinth, ancient city of Corinth, it is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Sin ...
, Elis, and Megara
Megara (; , ) is a historic town and a municipality in West Attica, Greece. It lies in the northern section of the Isthmus of Corinth opposite the island of Salamis Island, Salamis, which belonged to Megara in archaic times, before being taken ...
, isolating Messenia and reinforcing Sparta's position against Argos, the other major power in the Peloponnese. Other alliances in the 6th century included those between Elis and Heraea in the Peloponnese; and between the Greek colony Sybaris in southern Italy, its allies, and the Serdaioi.
Classical Greece
 In 499 BC, the
In 499 BC, the Ionia
Ionia ( ) was an ancient region encompassing the central part of the western coast of Anatolia. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionians who ...
n city states under Persian rule rebelled against their Persian-supported tyrant rulers. Supported by troops sent from Athens and Eretria, they advanced as far as Sardis and burnt the city before being driven back by a Persian counterattack. The revolt continued until 494, when the rebelling Ionians were defeated. Darius did not forget that Athens had assisted the Ionian revolt, and in 490 he assembled an armada to retaliate. Though heavily outnumbered, the Athenians—supported by their Plataean allies—defeated the Persian hordes at the Battle of Marathon, and the Persian fleet turned tail.
Thermopylae
Thermopylae (; ; Ancient: , Katharevousa: ; ; "hot gates") is a narrow pass and modern town in Lamia (city), Lamia, Phthiotis, Greece. It derives its name from its Mineral spring, hot sulphur springs."Thermopylae" in: S. Hornblower & A. Spaw ...
, where a small rearguard of Greeks, led by three hundred Spartans, held a crucial pass guarding the heart of Greece for several days; at the same time Gelon, tyrant of Syracuse, defeated the Carthaginian invasion at the Battle of Himera.
The Persians were decisively defeated at sea by a primarily Athenian naval force at the Battle of Salamis, and on land in 479 BC at the Battle of Plataea. The alliance against Persia continued, initially led by the Spartan Pausanias but from 477 by Athens, and by 460 Persia had been driven out of the Aegean. During this long campaign, the Delian League
The Delian League was a confederacy of Polis, Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, founded in 478 BC under the leadership (hegemony) of Classical Athens, Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Achaemenid Empire, Persian ...
gradually transformed from a defensive alliance of Greek states into an Athenian empire, as Athens' growing naval power intimidated the other league states. Athens ended its campaigns against Persia in 450, after a disastrous defeat in Egypt in 454, and the death of Cimon
Cimon or Kimon (; – 450BC) was an Athenian '' strategos'' (general and admiral) and politician.
He was the son of Miltiades, also an Athenian ''strategos''. Cimon rose to prominence for his bravery fighting in the naval Battle of Salamis ...
in action against the Persians on Cyprus in 450.
As the Athenian fight against the Persian empire waned, conflict grew between Athens and Sparta. Suspicious of the increasing Athenian power funded by the Delian League, Sparta offered aid to reluctant members of the League to rebel against Athenian domination. These tensions were exacerbated in 462 BC when Athens sent a force to aid Sparta in overcoming a helot revolt, but this aid was rejected by the Spartans. In the 450s, Athens took control of Boeotia, and won victories over Aegina
Aegina (; ; ) is one of the Saronic Islands of Greece in the Saronic Gulf, from Athens. Tradition derives the name from Aegina (mythology), Aegina, the mother of the mythological hero Aeacus, who was born on the island and became its king.
...
and Corinth. However, Athens failed to win a decisive victory, and in 447 lost Boeotia again. Athens and Sparta signed the Thirty Years' Peace in the winter of 446/445, ending the conflict.
Despite the treaty, Athenian relations with Sparta declined again in the 430s, and in 431 BC the Peloponnesian War
The Second Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), often called simply the Peloponnesian War (), was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek war fought between Classical Athens, Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Ancien ...
began. The first phase of the war saw a series of fruitless annual invasions of Attica by Sparta, while Athens successfully fought the Corinthian empire in northwest Greece and defended its own empire, despite a plague which killed the leading Athenian statesman Pericles
Pericles (; ; –429 BC) was a Greek statesman and general during the Golden Age of Athens. He was prominent and influential in Ancient Athenian politics, particularly between the Greco-Persian Wars and the Peloponnesian War, and was acclaimed ...
. The war turned after Athenian victories led by Cleon at Pylos
Pylos (, ; ), historically also known as Navarino, is a town and a former Communities and Municipalities of Greece, municipality in Messenia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part of ...
and Sphakteria, and Sparta sued for peace, but the Athenians rejected the proposal. The Athenian failure to regain control of Boeotia at Delium and Brasidas' successes in northern Greece in 424 improved Sparta's position after Sphakteria. After the deaths of Cleon and Brasidas, the strongest proponents of war on each side, a peace treaty was negotiated in 421 by the Athenian general Nicias.
The peace did not last, however. In 418 BC allied forces of Athens and Argos were defeated by Sparta at Mantinea. In 415 Athens launched an ambitious naval expedition to dominate Sicily; the expedition ended in disaster at the harbor of Syracuse, with almost the entire army killed, and the ships destroyed. Soon after the Athenian defeat in Syracuse, Athens' Ionian allies began to rebel against the Delian league, while Persia began to once again involve itself in Greek affairs on the Spartan side. Initially the Athenian position continued relatively strong, with important victories at Cyzicus
Cyzicus ( ; ; ) was an ancient Greek town in Mysia in Anatolia in the current Balıkesir Province of Turkey. It was located on the shoreward side of the present Kapıdağ Peninsula (the classical Arctonnesus), a tombolo which is said to have or ...
in 410 and Arginusae in 406. However, in 405 the Spartan Lysander
Lysander (; ; 454 BC – 395 BC) was a Spartan military and political leader. He destroyed the Athenian fleet at the Battle of Aegospotami in 405 BC, forcing Athens to capitulate and bringing the Peloponnesian War to an end. He then played ...
defeated Athens in the Battle of Aegospotami, and began to blockade Athens' harbour; driven by hunger, Athens sued for peace, agreeing to surrender their fleet and join the Spartan-led Peloponnesian League. Following the Athenian surrender, Sparta installed an oligarchic regime, the Thirty Tyrants The Thirty Tyrants (, ''hoi triákonta týrannoi'') were an oligarchy that briefly ruled Classical Athens, Athens from 404 BC, 404 BCE to 403 BC, 403 BCE. Installed into power by the Sparta, Spartans after the Athenian surrender in the Peloponnesian ...
, in Athens, one of a number of Spartan-backed oligarchies which rose to power after the Peloponnesian war. Spartan predominance did not last: after only a year, the Thirty had been overthrown.
The first half of the 4th century saw the major Greek states attempt to dominate the mainland; none were successful, and their resulting weakness led to a power vacuum which was eventually filled by Macedon under Philip II and then Alexander the Great. In the immediate aftermath of the Peloponnesian war, Sparta attempted to extend their own power, leading Argos, Athens, Corinth, and Thebes to join against them. Aiming to prevent any single Greek state gaining the dominance that would allow it to challenge Persia, the Persian king initially joined the alliance against Sparta, before imposing the Peace of Antalcidas
The King's Peace (387 BC) was a peace treaty guaranteed by the Persian King Artaxerxes II that ended the Corinthian War in ancient Greece. The treaty is also known as the Peace of Antalcidas, after Antalcidas, the Spartan diplomat who traveled to ...
("King's Peace") which restored Persia's control over the Anatolian Greeks.
By 371 BC, Thebes was in the ascendancy, defeating Sparta at the Battle of Leuctra
The Battle of Leuctra (, ) was fought on 6 July 371 BC between the Boeotians led by the Thebes (Greece), Thebans, and the History of Sparta, Spartans along with their allies amidst the post–Corinthian War conflict. The battle took place in the ...
, killing the Spartan king Cleombrotus I, and invading Laconia. Further Theban successes against Sparta in 369 led to Messenia gaining independence; Sparta never recovered from the loss of Messenia's fertile land and the helot workforce it provided. The rising power of Thebes led Sparta and Athens to join forces; in 362 they were defeated by Thebes at the Battle of Mantinea. In the aftermath of Mantinea, none of the major Greek states were able to dominate. Though Thebes had won the battle, their general Epaminondas was killed, and they spent the following decades embroiled in wars with their neighbours; Athens, meanwhile, saw its second naval alliance, formed in 377, collapse in the mid-350s.
The power vacuum in Greece after the Battle of Mantinea was filled by Macedon, under Philip II. In 338 BC, he defeated a Greek alliance at the Battle of Chaeronea, and subsequently formed the League of Corinth
The League of Corinth, also referred to as the Hellenic League (, ''koinòn tõn Hellḗnōn''; or simply , ''the Héllēnes''), was a federation of Greek states created by Philip IIDiodorus Siculus, Book 16, 89. «διόπερ ἐν Κορί� ...
. Philip planned to lead the League to invade Persia, but was murdered in 336 BC. His son Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
was left to fulfil his father's ambitions. After campaigns against Macedon's western and northern enemies, and those Greek states that had broken from the League of Corinth following the death of Philip, Alexander began his campaign against Persia in 334 BC. He conquered Persia, defeating Darius III at the Battle of Issus in 333 BC, and after the Battle of Gaugamela in 331 BC proclaimed himself king of Asia. From 329 BC he led expeditions to Bactria and then India; further plans to invade Arabia and North Africa were halted by his death in 323 BC.
Hellenistic Greece
 The period from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC until the death of
The period from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC until the death of Cleopatra
Cleopatra VII Thea Philopator (; The name Cleopatra is pronounced , or sometimes in both British and American English, see and respectively. Her name was pronounced in the Greek dialect of Egypt (see Koine Greek phonology). She was ...
, the last Macedonian ruler of Egypt, is known as the Hellenistic period. In the early part of this period, a new form of kingship developed based on Macedonian and Near Eastern traditions. The first Hellenistic kings were previously Alexander's generals, and took power in the period following his death, though they were not part of existing royal lineages and lacked historic claims to the territories they controlled. The most important of these rulers in the decades after Alexander's death were Antigonus I and his son Demetrius in Macedonia and the rest of Greece, Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
in Egypt, and Seleucus I in Syria and the former Persian empire; smaller Hellenistic kingdoms included the Attalids in Anatolia and the Greco-Bactrian kingdom
The Greco-Bactrian Kingdom () was a Ancient Greece, Greek state of the Hellenistic period located in Central Asia, Central-South Asia. The kingdom was founded by the Seleucid Empire, Seleucid satrap Diodotus I, Diodotus I Soter in about 256 BC, ...
.
 In the early part of the Hellenistic period, the exact borders of the Hellenistic kingdoms were not settled. Antigonus attempted to expand his territory by attacking the other successor kingdoms until they joined against him, and he was killed at the Battle of Ipsus in 301 BC. His son Demetrius spent many years in Seleucid captivity, and his son, Antigonus II, only reclaimed the Macedonian throne around 276. Meanwhile, the Seleucid kingdom gave up territory in the east to the Indian king
In the early part of the Hellenistic period, the exact borders of the Hellenistic kingdoms were not settled. Antigonus attempted to expand his territory by attacking the other successor kingdoms until they joined against him, and he was killed at the Battle of Ipsus in 301 BC. His son Demetrius spent many years in Seleucid captivity, and his son, Antigonus II, only reclaimed the Macedonian throne around 276. Meanwhile, the Seleucid kingdom gave up territory in the east to the Indian king Chandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta Maurya (Sanskrit: elp:IPA/Sanskrit, t̪͡ɕɐn̪d̪ɾɐgupt̪ɐ mɐʊɾjɐ (reigned 320 BCE – c. 298 BCE) was the founder and the first emperor of the Maurya Empire, based in Magadha (present-day Bihar) in the Indian ...
in exchange for war elephants, and later lost large parts of Persia to the Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power centered in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe ...
. By the mid-3rd century, the kingdoms of Alexander's successors was mostly stable, though there continued to be disputes over border areas.
The great capitals of Hellenistic culture were Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile ...
in the Ptolemaic Kingdom
The Ptolemaic Kingdom (; , ) or Ptolemaic Empire was an ancient Greek polity based in Ancient Egypt, Egypt during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 305 BC by the Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general Ptolemy I Soter, a Diadochi, ...
and Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; , ) "Antioch on Daphne"; or "Antioch the Great"; ; ; ; ; ; ; . was a Hellenistic Greek city founded by Seleucus I Nicator in 300 BC. One of the most important Greek cities of the Hellenistic period, it served as ...
in the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire ( ) was a Greek state in West Asia during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 312 BC by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire founded by Alexander the Great ...
.
The conquests of Alexander had numerous consequences for the Greek city-states. It greatly widened the horizons of the Greeks and led to a steady emigration of the young and ambitious to the new Greek empires in the east. Many Greeks migrated to Alexandria, Antioch and the many other new Hellenistic cities founded in Alexander's wake, as far away as present-day Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
and Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
, where the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom
The Greco-Bactrian Kingdom () was a Ancient Greece, Greek state of the Hellenistic period located in Central Asia, Central-South Asia. The kingdom was founded by the Seleucid Empire, Seleucid satrap Diodotus I, Diodotus I Soter in about 256 BC, ...
and the Indo-Greek Kingdom
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, also known as the Yavana Kingdom, was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Ancient Greece, Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India.
The term "Indo-Greek Kingdom" ...
survived until the end of the 1st century BC.
The city-states within Greece formed themselves into two leagues; the Achaean League
The Achaean League () was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era confederation of polis, Greek city-states on the northern and central Peloponnese. The league was named after the region of Achaea (ancient region), Achaea in the northwestern Pelopon ...
(including Corinth and Argos) and the Aetolian League (including Sparta and Athens). For much of the period until the Roman conquest, these leagues were at war, often participating in the conflicts between the Diadochi
The Diadochi were the rival generals, families, and friends of Alexander the Great who fought for control over his empire after his death in 323 BC. The Wars of the Diadochi mark the beginning of the Hellenistic period from the Mediterran ...
(the successor states to Alexander's empire).
The Antigonid Kingdom became involved in a war with the Roman Republic in the late 3rd century. Although the First Macedonian War was inconclusive, the Romans, in typical fashion, continued to fight Macedon until it was completely absorbed into the Roman Republic (by 149 BC). In the east, the unwieldy Seleucid Empire gradually disintegrated, although a rump survived until 64 BC, whilst the Ptolemaic Kingdom continued in Egypt until 30 BC when it too was conquered by the Romans. The Aetolian league grew wary of Roman involvement in Greece, and sided with the Seleucids in the Roman–Seleucid War; when the Romans were victorious, the league was effectively absorbed into the Republic. Although the Achaean league outlasted both the Aetolian league and Macedon, it was also soon defeated and absorbed by the Romans in 146 BC, bringing Greek independence to an end.
Roman Greece
The Greek peninsula came under Roman rule during the 146 BC conquest of Greece after the Battle of Corinth. Macedonia became aRoman province
The Roman provinces (, pl. ) were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as Roman g ...
while southern Greece came under the surveillance of Macedonia's prefect
Prefect (from the Latin ''praefectus'', substantive adjectival form of ''praeficere'': "put in front", meaning in charge) is a magisterial title of varying definition, but essentially refers to the leader of an administrative area.
A prefect' ...
; however, some Greek ''poleis'' managed to maintain a partial independence and avoid taxation. The Aegean Islands were added to this territory in 133 BC. Athens and other Greek cities revolted in 88 BC, and the peninsula was crushed by the Roman general Sulla
Lucius Cornelius Sulla Felix (, ; 138–78 BC), commonly known as Sulla, was a Roman people, Roman general and statesman of the late Roman Republic. A great commander and ruthless politician, Sulla used violence to advance his career and his co ...
. The Roman civil wars devastated the land even further, until Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
organized the peninsula as the province of Achaea
Achaea () or Achaia (), sometimes transliterated from Greek language, Greek as Akhaia (, ''Akhaḯa'', ), is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the modern regions of Greece, region of Western Greece and is situated in the northwest ...
in 27 BC.
Greece was a key eastern province of the Roman Empire, as the Roman culture had long been in fact Greco-Roman. The Greek language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy (in Calabria and Salento), south ...
served as a ''lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, link language or language of wider communication (LWC), is a Natural language, language systematically used to make co ...
'' in the East and in Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, and many Greek intellectuals such as Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus (; September 129 – AD), often Anglicization, anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Ancient Rome, Roman and Greeks, Greek physician, surgeon, and Philosophy, philosopher. Considered to be one o ...
would perform most of their work in Rome.
Geography
Regions
 The territory of Greece is mountainous, and as a result, ancient Greece consisted of many smaller regions, each with its own dialect, cultural peculiarities, and identity. Regionalism and regional conflicts were prominent features of ancient Greece. Cities tended to be located in valleys between mountains, or on coastal plains, and dominated a certain area around them.
In the south lay the
The territory of Greece is mountainous, and as a result, ancient Greece consisted of many smaller regions, each with its own dialect, cultural peculiarities, and identity. Regionalism and regional conflicts were prominent features of ancient Greece. Cities tended to be located in valleys between mountains, or on coastal plains, and dominated a certain area around them.
In the south lay the Peloponnese
The Peloponnese ( ), Peloponnesus ( ; , ) or Morea (; ) is a peninsula and geographic region in Southern Greece, and the southernmost region of the Balkans. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridg ...
, consisting of the regions of Laconia (southeast), Messenia (southwest), Elis (west), Achaia (north), Korinthia (northeast), Argolis (east), and Arcadia (center). These names survive to the present day as regional units of modern Greece, though with somewhat different boundaries. Mainland Greece to the north, nowadays known as Central Greece, consisted of Aetolia and Acarnania
Acarnania () is a region of west-central Greece that lies along the Ionian Sea, west of Aetolia, with the Achelous River for a boundary, and north of the gulf of Calydon, which is the entrance to the Gulf of Corinth. Today it forms the western part ...
in the west, Locris, Doris, and Phocis
Phocis (; ; ) is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the administrative region of Central Greece. It stretches from the western mountainsides of Parnassus on the east to the mountain range of Vardousia on the west, upon the Gu ...
in the center, while in the east lay Boeotia
Boeotia ( ), sometimes Latinisation of names, Latinized as Boiotia or Beotia (; modern Greek, modern: ; ancient Greek, ancient: ), is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the modern regions of Greece, region of Central Greece (adm ...
, Attica
Attica (, ''Attikḗ'' (Ancient Greek) or , or ), or the Attic Peninsula, is a historical region that encompasses the entire Athens metropolitan area, which consists of the city of Athens, the capital city, capital of Greece and the core cit ...
, and Megaris :''This is also the ancient Greek name of Megaris (Naples), a small island off Naples, site of the Castel dell'Ovo.''
Megaris () was a small but populous Sovereign state, state of ancient Greece, west of Attica and north of Corinthia, whose inhabi ...
. Northeast lay Thessaly
Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, a ...
, while Epirus
Epirus () is a Region#Geographical regions, geographical and historical region, historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay ...
lay to the northwest. Epirus stretched from the Ambracian Gulf in the south to the Ceraunian Mountains and the Aoos river in the north, and consisted of Chaonia (north), Molossia (center), and Thesprotia (south). In the northeast corner was Macedonia, originally consisting Lower Macedonia and its regions, such as Elimeia, Pieria, and Orestis. Around the time of Alexander I of Macedon, the Argead kings of Macedon started to expand into Upper Macedonia, lands inhabited by independent Macedonian tribes like the Lyncestae, Orestae and the Elimiotis, Elimiotae and to the west, beyond the Axius river, into Eordaia, Bottiaea, Mygdonia, and Almopia, regions settled by Thracian tribes. To the north of Macedonia lay various non-Greek peoples such as the Paeonians due north, the Thracians to the northeast, and the Illyrians, with whom the Ancient Macedonians, Macedonians were frequently in conflict, to the northwest. Chalcidice was settled early on by southern Greek colonists and was considered part of the Greek world, while from the late 2nd millennium BC substantial Greek settlement also occurred on the eastern shores of the Aegean Sea, Aegean, in Anatolia.
Colonies

Politics and society
Political structure
 Ancient Greece consisted of several hundred relatively independent city-states ('' poleis''). This was a situation unlike that in most other contemporary societies, which were either tribal or Realm, kingdoms ruling over relatively large territories. Undoubtedly, the geography of Greece—divided and sub-divided by hills, mountains, and rivers—contributed to the fragmentary nature of ancient Greece. On the one hand, the ancient Greeks had no doubt that they were "one people"; they had the same State religion, religion, same basic culture, and same language. Furthermore, the Greeks were very aware of their tribal origins;
Ancient Greece consisted of several hundred relatively independent city-states ('' poleis''). This was a situation unlike that in most other contemporary societies, which were either tribal or Realm, kingdoms ruling over relatively large territories. Undoubtedly, the geography of Greece—divided and sub-divided by hills, mountains, and rivers—contributed to the fragmentary nature of ancient Greece. On the one hand, the ancient Greeks had no doubt that they were "one people"; they had the same State religion, religion, same basic culture, and same language. Furthermore, the Greeks were very aware of their tribal origins; Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
was able to extensively categorise the city-states by tribe. Yet, although these higher-level relationships existed, they seem to have rarely had a major role in Greek politics. The independence of the ''poleis'' was fiercely defended; unification was something rarely contemplated by the ancient Greeks. Even when, during the second Persian invasion of Greece, a group of city-states allied themselves to defend Greece, the vast majority of ''poleis'' remained neutral, and after the Persian defeat, the allies quickly returned to infighting.
Thus, the major peculiarities of the ancient Greek political system were its fragmented nature (and that this does not particularly seem to have tribal origin), and the particular focus on urban centers within otherwise tiny states. The peculiarities of the Greek system are further evidenced by the colonies that they set up throughout the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
, which, though they might count a certain Greek ''polis'' as their 'mother' (and remain sympathetic to her), were completely independent of the founding city.
Inevitably smaller ''poleis'' might be dominated by larger neighbors, but conquest or direct rule by another city-state appears to have been quite rare. Instead the ''poleis'' grouped themselves into leagues, membership of which was in a constant state of flux. Later in the Classical period, the leagues would become fewer and larger, be dominated by one city (particularly Athens, Sparta and Thebes, Greece, Thebes); and often ''poleis'' would be compelled to join under threat of war (or as part of a peace treaty). Even after Philip II of Macedon conquered the heartlands of ancient Greece, he did not attempt to annex the territory or unify it into a new province, but compelled most of the ''poleis'' to join his own Corinthian League.
Government and law
 Initially many Greek city-states seem to have been petty kingdoms; there was often a city official carrying some residual, ceremonial functions of the king (''basileus''), e.g., the ''archon basileus'' in Athens. However, by the Archaic period and the first historical consciousness, most had already become aristocratic oligarchies. It is unclear exactly how this change occurred. For instance, in Athens, the kingship had been reduced to a hereditary, lifelong chief magistracy (''Archon of Athens, archon'') by ; by 753 BC this had become a decennial, elected archonship, and finally an annually elected archonship by 683 BC. Through each stage, more power would have been transferred to the aristocracy as a whole, and away from a single individual.
Inevitably, the domination of politics and concomitant aggregation of wealth by small groups of families was apt to cause social unrest in many ''poleis''. In many cities a tyrant (not in the modern sense of repressive autocracies), would at some point seize control and govern according to their own will; often a populist agenda would help sustain them in power. In a system wracked with class conflict, government by a 'strongman' was often the best solution.
Athens fell under a tyranny in the second half of the 6th century BC. When this tyranny was ended, the Athenians founded Athenian democracy, the world's first democracy as a radical solution to prevent the aristocracy regaining power. A Popular assembly, citizens' assembly (the ''Ecclesia (ancient Athens), Ecclesia''), for the discussion of city policy, had existed since the reforms of Draco in 621 BC; all citizens were permitted to attend after the reforms of
Initially many Greek city-states seem to have been petty kingdoms; there was often a city official carrying some residual, ceremonial functions of the king (''basileus''), e.g., the ''archon basileus'' in Athens. However, by the Archaic period and the first historical consciousness, most had already become aristocratic oligarchies. It is unclear exactly how this change occurred. For instance, in Athens, the kingship had been reduced to a hereditary, lifelong chief magistracy (''Archon of Athens, archon'') by ; by 753 BC this had become a decennial, elected archonship, and finally an annually elected archonship by 683 BC. Through each stage, more power would have been transferred to the aristocracy as a whole, and away from a single individual.
Inevitably, the domination of politics and concomitant aggregation of wealth by small groups of families was apt to cause social unrest in many ''poleis''. In many cities a tyrant (not in the modern sense of repressive autocracies), would at some point seize control and govern according to their own will; often a populist agenda would help sustain them in power. In a system wracked with class conflict, government by a 'strongman' was often the best solution.
Athens fell under a tyranny in the second half of the 6th century BC. When this tyranny was ended, the Athenians founded Athenian democracy, the world's first democracy as a radical solution to prevent the aristocracy regaining power. A Popular assembly, citizens' assembly (the ''Ecclesia (ancient Athens), Ecclesia''), for the discussion of city policy, had existed since the reforms of Draco in 621 BC; all citizens were permitted to attend after the reforms of Solon
Solon (; ; BC) was an Archaic Greece#Athens, archaic History of Athens, Athenian statesman, lawmaker, political philosopher, and poet. He is one of the Seven Sages of Greece and credited with laying the foundations for Athenian democracy. ...
(early 6th century), but the poorest citizens could not address the assembly or run for office. With the establishment of the democracy, the assembly became the ''de jure'' mechanism of government; all citizens had equal privileges in the assembly. However, non-citizens, such as metics (foreigners living in Athens) or Slavery in ancient Greece, slaves, had no political rights at all.
After the rise of democracy in Athens, other city-states founded democracies. However, many retained more traditional forms of government. As so often in other matters, Sparta was a notable exception to the rest of Greece, ruled through the whole period by not one, but two hereditary monarchs. This was a form of diarchy. The Kings of Sparta belonged to the Agiads and the Eurypontids, descendants respectively of Eurysthenes and Procles. Both dynasties' founders were believed to be twin sons of Aristodemus, a Heraclid ruler. However, the powers of these kings were held in check by both a council of elders (the ''Gerousia'') and magistrates specifically appointed to watch over the kings (the ''Ephors'').
Social structure
Only free, land-owning, native-born men could be citizens entitled to the full protection of the law in a city-state. In most city-states, unlike the situation in Ancient Rome, Rome, social prominence did not allow special rights. Sometimes families controlled public religious functions, but this ordinarily did not give any extra power in the government. In Athens, the population was divided into four social classes based on wealth. People could change classes if they made more money. In Sparta, all male citizens were called ''homoioi'', meaning "peers". However, Spartan kings, who served as the city-state's dual military and religious leaders, came from two families. Women in Greece#Women in ancient Greece, Women in Ancient Greece appear to have primarily performed domestic tasks, managed households, and borne and reared children.Slavery
 Slaves had no power or status. Slaves had the right to have a family and own property, subject to their master's goodwill and permission, but they had no political rights. By 600 BC, chattel slavery had spread in Greece. By the 5th century BC, slaves made up one-third of the total population in some city-states. Between 40 and 80% of the population of Classical Athens were slaves. Slaves outside of Sparta almost never revolted because they were made up of too many nationalities and were too scattered to organize. However, unlike later Western culture, the ancient Greeks did not think in terms of race (human categorization), race.
Most families owned slaves as household servants and laborers, and even poor families might have owned a few slaves. Owners were not allowed to beat or kill their slaves. Owners often promised to free slaves in the future to encourage slaves to work hard. Unlike in Rome, freedmen did not become citizens. Instead, they were mixed into the population of ''metics'', which included people from foreign countries or other city-states who were officially allowed to live in the state.
City-states legally owned slaves. These public slaves had a larger measure of independence than slaves owned by families, living on their own and performing specialized tasks. In Athens, public slaves were trained to look out for counterfeit coinage, while temple slaves acted as servants of the temple's Lists of Greek mythological figures, deity and Scythian slaves were employed in Athens as a police force corralling citizens to political functions.
Sparta had a special type of slaves called ''helots''. Helots were Messenians enslaved en masse during the First Messenian War, Messenian Wars by the state and assigned to families where they were forced to stay. Helots raised food and did household chores so that women could concentrate on raising strong children while men could devote their time to training as hoplites. Their masters treated them harshly, and helots slave rebellion, revolted against their masters several times. In 370/369 BC, as a result of Epaminondas' liberation of Messenia from Spartan rule, the helot system there came to an end and the helots won their freedom. However, it persisted in Laconia until the 2nd century BC.
Slaves had no power or status. Slaves had the right to have a family and own property, subject to their master's goodwill and permission, but they had no political rights. By 600 BC, chattel slavery had spread in Greece. By the 5th century BC, slaves made up one-third of the total population in some city-states. Between 40 and 80% of the population of Classical Athens were slaves. Slaves outside of Sparta almost never revolted because they were made up of too many nationalities and were too scattered to organize. However, unlike later Western culture, the ancient Greeks did not think in terms of race (human categorization), race.
Most families owned slaves as household servants and laborers, and even poor families might have owned a few slaves. Owners were not allowed to beat or kill their slaves. Owners often promised to free slaves in the future to encourage slaves to work hard. Unlike in Rome, freedmen did not become citizens. Instead, they were mixed into the population of ''metics'', which included people from foreign countries or other city-states who were officially allowed to live in the state.
City-states legally owned slaves. These public slaves had a larger measure of independence than slaves owned by families, living on their own and performing specialized tasks. In Athens, public slaves were trained to look out for counterfeit coinage, while temple slaves acted as servants of the temple's Lists of Greek mythological figures, deity and Scythian slaves were employed in Athens as a police force corralling citizens to political functions.
Sparta had a special type of slaves called ''helots''. Helots were Messenians enslaved en masse during the First Messenian War, Messenian Wars by the state and assigned to families where they were forced to stay. Helots raised food and did household chores so that women could concentrate on raising strong children while men could devote their time to training as hoplites. Their masters treated them harshly, and helots slave rebellion, revolted against their masters several times. In 370/369 BC, as a result of Epaminondas' liberation of Messenia from Spartan rule, the helot system there came to an end and the helots won their freedom. However, it persisted in Laconia until the 2nd century BC.
Education
For most of Greek history, education was private, except in Sparta. During the Hellenistic period, some city-states established Public school (government funded), public schools. Only wealthy families could afford a teacher. Boys learned how to read, write and quote literature. They also learned to sing and play one musical instrument and were trained as athletes for military service. They studied not for a job but to become an effective citizen. Girls also learned to read, write and do simple arithmetic so they could manage the household. They almost never received education after childhood. Boys went to school at the age of seven, or went to the barracks, if they lived in Sparta. The three types of teachings were: grammatistes for arithmetic, kitharistes for music and dancing, and Paedotribae for sports. Boys from wealthy families attending the private school lessons were taken care of by a ''paidagogos'', a household slave selected for this task who accompanied the boy during the day. Classes were held in teachers' private houses and included reading, writing, mathematics, singing, and playing the lyre and flute. When the boy became 12 years old the schooling started to include sports such as wrestling, running, and throwing discus and javelin. In Athens, some older youths attended academy for the finer disciplines such as culture, sciences, music, and the arts. The schooling ended at age 18, followed by military training in the army usually for one or two years. Some of Athens' greatest such schools included the Lyceum (the so-called Peripatetic school founded byAristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
of Stageira) and the Platonic Academy (founded by Plato
Plato ( ; Greek language, Greek: , ; born BC, died 348/347 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher of the Classical Greece, Classical period who is considered a foundational thinker in Western philosophy and an innovator of the writte ...
of Athens). The education system of the wealthy ancient Greeks is also called Paideia.
Economy
At its economic height in the 5th and 4th centuries BC, the free citizenry ofClassical Greece
Classical Greece was a period of around 200 years (the 5th and 4th centuries BC) in ancient Greece,The "Classical Age" is "the modern designation of the period from about 500 B.C. to the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C." ( Thomas R. Mar ...
represented perhaps the most prosperous society in the ancient world, some economic historians considering Greece one of the most advanced pre-industrial economies. In terms of wheat, wages reached an estimated daily for an unskilled worker in urban Athens, 2–3 times the of an unskilled rural labourer in Roman Egypt, though Greek farm incomes too were on average lower than those available to urban workers.
While slave conditions varied widely, the institution served to sustain the incomes of the free citizenry: an estimate of economic development drawn from the latter (or derived from urban incomes alone) is therefore likely to overstate the true overall level despite widespread evidence for high living standards.
Warfare
 At least in the Archaic period, the fragmentary nature of ancient Greece, with many competing city-states, increased the frequency of conflict but conversely limited the scale of warfare. Unable to maintain professional armies, the city-states relied on their own citizens to fight. This inevitably reduced the potential duration of campaigns, as citizens would need to return to their own professions (especially in the case of, for example, farmers). Campaigns would therefore often be restricted to summer. When battles occurred, they were usually set piece and intended to be decisive. Casualties were slight compared to later battles, rarely amounting to more than five percent of the losing side, but the slain often included the most prominent citizens and generals who led from the front.
The scale and scope of warfare in ancient Greece changed dramatically as a result of the
At least in the Archaic period, the fragmentary nature of ancient Greece, with many competing city-states, increased the frequency of conflict but conversely limited the scale of warfare. Unable to maintain professional armies, the city-states relied on their own citizens to fight. This inevitably reduced the potential duration of campaigns, as citizens would need to return to their own professions (especially in the case of, for example, farmers). Campaigns would therefore often be restricted to summer. When battles occurred, they were usually set piece and intended to be decisive. Casualties were slight compared to later battles, rarely amounting to more than five percent of the losing side, but the slain often included the most prominent citizens and generals who led from the front.
The scale and scope of warfare in ancient Greece changed dramatically as a result of the Greco-Persian Wars
The Greco-Persian Wars (also often called the Persian Wars) were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Polis, Greek city-states that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world ...
. To fight the enormous armies of the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, i ...
was effectively beyond the capabilities of a single city-state. The eventual triumph of the Greeks was achieved by alliances of city-states (the exact composition changing over time), allowing the pooling of resources and division of labor. Although alliances between city-states occurred before this time, nothing on this scale had been seen before. The rise of Athens and Sparta as pre-eminent powers during this conflict led directly to the Peloponnesian War
The Second Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), often called simply the Peloponnesian War (), was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek war fought between Classical Athens, Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Ancien ...
, which saw further development of the nature of warfare, strategy and tactics. Fought between leagues of cities dominated by Athens and Sparta, the increased manpower and financial resources increased the scale and allowed the diversification of warfare. Set-piece battles during the Peloponnesian war proved indecisive and instead there was increased reliance on attritionary strategies, naval battles and blockades and sieges. These changes greatly increased the number of casualties and the disruption of Greek society.
Athens owned one of the largest war fleets in ancient Greece. It had over 200 triremes each powered by 170 oarsmen who were seated in 3 rows on each side of the ship. The city could afford such a large fleet—it had over 34,000 oarsmen—because it owned a lot of silver mines that were worked by slaves.
According to Josiah Ober, Greek city-states faced approximately a one-in-three chance of destruction during the archaic and classical period.
Culture
Philosophy
 Ancient Greek philosophy focused on the role of reason and inquiry. In many ways, it had an important influence on modern philosophy, as well as modern science. Clear unbroken lines of influence lead from ancient Greek and Hellenistic philosophers, to medieval Early Islamic philosophy, Muslim philosophers and Islamic science, Islamic scientists, to the European Renaissance and Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment, to the secular sciences of the modern day.
Neither reason nor inquiry began with the ancient Greeks. Defining the difference between the Greek quest for knowledge and the quests of the elder civilizations, such as the ancient Egyptians and Babylonians, has long been a topic of study by theorists of civilization.
The first known philosophers of Greece were the pre-Socratics, who attempted to provide naturalistic, non-mythical descriptions of the world. They were followed by Socrates, one of the first philosophers based in Athens during fifth-century Athens, its golden age whose ideas, despite being known by second-hand accounts instead of writings of his own, laid the basis of Western philosophy. Socrates' disciple
Ancient Greek philosophy focused on the role of reason and inquiry. In many ways, it had an important influence on modern philosophy, as well as modern science. Clear unbroken lines of influence lead from ancient Greek and Hellenistic philosophers, to medieval Early Islamic philosophy, Muslim philosophers and Islamic science, Islamic scientists, to the European Renaissance and Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment, to the secular sciences of the modern day.
Neither reason nor inquiry began with the ancient Greeks. Defining the difference between the Greek quest for knowledge and the quests of the elder civilizations, such as the ancient Egyptians and Babylonians, has long been a topic of study by theorists of civilization.
The first known philosophers of Greece were the pre-Socratics, who attempted to provide naturalistic, non-mythical descriptions of the world. They were followed by Socrates, one of the first philosophers based in Athens during fifth-century Athens, its golden age whose ideas, despite being known by second-hand accounts instead of writings of his own, laid the basis of Western philosophy. Socrates' disciple Plato
Plato ( ; Greek language, Greek: , ; born BC, died 348/347 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher of the Classical Greece, Classical period who is considered a foundational thinker in Western philosophy and an innovator of the writte ...
, who wrote ''The Republic (Plato), The Republic'' and established a radical difference between ideas and the concrete world, and Plato's disciple Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
, who wrote extensively about nature and ethics, are also immensely influential in Western philosophy to this day. The later Hellenistic philosophy, also originating in Greece, is defined by names such as Antisthenes (cynicism (philosophy), cynicism), Zeno of Citium (stoicism) and Plotinus (Neoplatonism).
Literature and theatre
The earliest Greek literature was poetry and was composed for performance rather than private consumption. The earliest Greek poet known is Homer, although he was certainly part of an existing tradition of oral poetry. Homer's poetry, though it was developed around the same time that the Greeks developed writing, would have been composed orally; the first poet to certainly compose their work in writing was Archilochus, a Greek lyric, lyric poet from the mid-7th century BC. Greek tragedy, Tragedy developed around the end of the archaic period, taking elements from across the pre-existing genres of late archaic poetry. Towards the beginning of the classical period, comedy began to develop—the earliest date associated with the genre is 486 BC, when a competition for comedy became an official event at the City Dionysia in Athens, though the first preserved ancient comedy is Aristophanes' ''Acharnians'', produced in 425. Like poetry, Greek prose had its origins in the archaic period, and the earliest writers of Greek philosophy, history, and medical literature all date to the 6th century BC. Prose first emerged as the writing style adopted by the presocratic philosophers Anaximander and Anaximenes of Miletus, Anaximenes—though Thales of Miletus, considered the first Greek philosopher, apparently wrote nothing. Prose as a genre reached maturity in the classical era, and the major Greek prose genres—philosophy, history, rhetoric, and dialogue—developed in this period.
The Hellenistic period saw the literary centre of the Greek world move from Athens, where it had been in the classical period, to Alexandria. At the same time, other Hellenistic kings such as the Antigonids and the Attalids were patrons of scholarship and literature, turning Pella and Pergamon respectively into cultural centres. It was thanks to this cultural patronage by Hellenistic kings, and especially the Museum at Alexandria, that so much ancient Greek literature has survived. The Library of Alexandria, part of the Museum, had the previously unenvisaged aim of collecting together copies of all known authors in Greek. Almost all of the surviving non-technical Hellenistic literature is poetry, and Hellenistic poetry tended to be highly intellectual, blending different genres and traditions, and avoiding linear narratives. The Hellenistic period also saw a shift in the ways literature was consumed—while in the archaic and classical periods literature had typically been experienced in public performance, in the Hellenistic period it was more commonly read privately. At the same time, Hellenistic poets began to write for private, rather than public, consumption.
With Octavian's victory at Actium in 31 BC, Rome began to become a major centre of Greek literature, as important Greek authors such as Strabo and Dionysius of Halicarnassus came to Rome. The period of greatest innovation in Greek literature under Rome was the "long second century" from approximately 80 AD to around 230 AD. This innovation was especially marked in prose, with the development of the novel and a revival of prominence for display oratory both dating to this period.
Like poetry, Greek prose had its origins in the archaic period, and the earliest writers of Greek philosophy, history, and medical literature all date to the 6th century BC. Prose first emerged as the writing style adopted by the presocratic philosophers Anaximander and Anaximenes of Miletus, Anaximenes—though Thales of Miletus, considered the first Greek philosopher, apparently wrote nothing. Prose as a genre reached maturity in the classical era, and the major Greek prose genres—philosophy, history, rhetoric, and dialogue—developed in this period.
The Hellenistic period saw the literary centre of the Greek world move from Athens, where it had been in the classical period, to Alexandria. At the same time, other Hellenistic kings such as the Antigonids and the Attalids were patrons of scholarship and literature, turning Pella and Pergamon respectively into cultural centres. It was thanks to this cultural patronage by Hellenistic kings, and especially the Museum at Alexandria, that so much ancient Greek literature has survived. The Library of Alexandria, part of the Museum, had the previously unenvisaged aim of collecting together copies of all known authors in Greek. Almost all of the surviving non-technical Hellenistic literature is poetry, and Hellenistic poetry tended to be highly intellectual, blending different genres and traditions, and avoiding linear narratives. The Hellenistic period also saw a shift in the ways literature was consumed—while in the archaic and classical periods literature had typically been experienced in public performance, in the Hellenistic period it was more commonly read privately. At the same time, Hellenistic poets began to write for private, rather than public, consumption.
With Octavian's victory at Actium in 31 BC, Rome began to become a major centre of Greek literature, as important Greek authors such as Strabo and Dionysius of Halicarnassus came to Rome. The period of greatest innovation in Greek literature under Rome was the "long second century" from approximately 80 AD to around 230 AD. This innovation was especially marked in prose, with the development of the novel and a revival of prominence for display oratory both dating to this period.
Music and dance
In Ancient Greek society, music was ever-present and considered a fundamental component of civilisation. It was an important part of public religious worship, private ceremonies such as weddings and funerals, and household entertainment. Men sang and played music at the symposium; both men and women sang at work; and children's games involved song and dance. Ancient Greek music was primarily vocal, sung either by a solo singer or a chorus, and usually accompanied by an instrument; purely instrumental music was less common. The Greeks used stringed instruments, including lyres, harps, and lutes; and wind instruments, of which the most important was the , a reed instrument. Percussion instruments played a relatively unimportant role supporting stringed and wind instruments, and were used in certain religious cults.Science and technology
Ancient Greek mathematics contributed many important developments to mathematics, including the basic rules of geometry, the idea of formal proof, formal mathematical proof, and discoveries in number theory, mathematical analysis, applied mathematics, and approached close to establishing integral calculus. The discoveries of several Greek mathematicians, including Pythagoras, Euclid, and Archimedes, are still used in mathematical teaching today. The Greeks developed astronomy, which they treated as a branch of mathematics, to a highly sophisticated level. The first geometrical, three-dimensional models to explain the apparent motion of the planets were developed in the 4th century BC by Eudoxus of Cnidus and Callippus of Cyzicus. Their younger contemporary Heraclides Ponticus proposed that the Earth rotates around its axis. In the 3rd century BC, Aristarchus of Samos was the first to suggest a heliocentric system. Archimedes in his treatise The Sand Reckoner#Estimation of the size of the universe, The Sand Reckoner revives Aristarchus' hypothesis that ''"the fixed stars and the Sun remain unmoved, while the Earth revolves about the Sun on the circumference of a circle"''. Otherwise, only fragmentary descriptions of Aristarchus' idea survive. Eratosthenes, using the angles of shadows created at widely separated regions, estimated the circumference of the Earth with great accuracy. In the 2nd century BC Hipparchus of Nicea made a number of contributions, including the first measurement of precession and the compilation of the first star catalog in which he proposed the modern system of apparent magnitudes. The Antikythera mechanism, a device for calculating the movements of planets, dates from about 80 BC and was the first ancestor of the astronomical computer. It was discovered in an ancient shipwreck off the Greek island of Antikythera, between Kythera and Crete. The device became famous for its use of a differential gear, previously believed to have been invented in the 16th century, and the miniaturization and complexity of its parts, comparable to a clock made in the 18th century. The original mechanism is displayed in the Bronze collection of the National Archaeological Museum of Athens, accompanied by a replica. The ancient Greeks also made important discoveries in the medical field. Hippocrates was a physician of the Classical period, and is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine. He is referred to as the "List of persons considered father or mother of a field#Natural and social sciences, father of medicine"Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2006. Microsoft Corporation
31 October 2009. in recognition of his lasting contributions to the field as the founder of the Hippocratic school of medicine. This intellectual school revolutionized medicine in ancient Greece, establishing it as a discipline distinct from other fields that it had traditionally been associated with (notably theurgy and philosophy), thus making medicine a profession.
Art and architecture
The art of ancient Greece has exercised an enormous influence on the culture of many countries from ancient times to the present day, particularly in the areas of sculpture and architecture. In the West, the art of theRoman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
was largely derived from Greek models. In the East, Alexander the Great's conquests initiated several centuries of exchange between Greek, Central Asian and Indian cultures, resulting in Greco-Buddhist art, with ramifications as far as Japan. Following the Renaissance in Europe, the humanist aesthetic and the high technical standards of Greek art inspired generations of European artists. Well into the 19th century, the classical tradition derived from Greece dominated the art of the Western world.
Religion
Religion was a central part of ancient Greek life. Though the Greeks of different cities and ancient Greek tribes, tribes worshipped similar gods, religious practices were not uniform and the gods were thought of differently in different places. The Greeks were polytheistic, worshipping many gods, but as early as the 6th century BC a pantheon of twelve Olympians began to develop. Greek religion was influenced by the practices of the Greeks' near eastern neighbours at least as early as the archaic period, and by the Hellenistic period this influence was seen in both directions. The most important religious act in ancient Greece was animal sacrifice, most commonly of sheep and goats. Sacrifice was accompanied by public prayer, and prayer and hymns were themselves a major part of ancient Greek religious life.Legacy
The civilization of ancient Greece has been immensely influential on language, politics, educational systems, philosophy, science, and the arts. It became the ''Leitkultur'' of the Roman Empire to the point of marginalizing native Iron Age Italy, Italic traditions. As Horace put it, Via the Roman Empire, Greek culture came to be foundational to Western culture in general. The Byzantine Empire inherited Classical Greek-Hellenistic culture directly, without Latin intermediation, and the preservation of Classical Greek learning in medieval Byzantine tradition further exerted a strong influence on the Slavs and later on the Islamic Golden Age and the Western European Renaissance. A modern revival of Classical Greek learning took place in the Neoclassicism movement in 18th- and 19th-century Europe and the Americas.See also
* List of ancient Greek writers * Classical demography * List of adjectival and demonymic forms of place names#Regions in Greco-Roman antiquity, Regions in Greco-Roman antiquity * Science in classical antiquity * List of archaeologically attested women from the ancient Mediterranean regionNotes
References
Notes
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * Brock, Roger, and Stephen Hodkinson, eds. 2000. ''Alternatives to Athens: Varieties of political organization and community in ancient Greece''. Oxford and New York: Oxford Univ. Press. * Cartledge, Paul, Edward E. Cohen, and Lin Foxhall. 2002. ''Money, labour and land: Approaches to the economies of ancient Greece''. London and New York: Routledge. * Cohen, Edward. 1992. ''Athenian economy and society: A banking perspective''. Princeton, NJ: Princeton Univ. Press. * Hurwit, Jeffrey. 1987. ''The art and culture of early Greece, 1100–480 B.C.'' Ithaca, NY: Cornell Univ. Press. * Kinzl, Konrad, ed. 2006. ''A companion to the Classical Greek world''. Oxford and Malden, MA: Blackwell. * Morris, Ian, ed. 1994. ''Classical Greece: Ancient histories and modern archaeologies''. Cambridge, UK, and New York: Cambridge Univ. Press. * Sarah B. Pomeroy, Pomeroy, Sarah, Stanley M. Burstein, Walter Donlan, and Jennifer Tolbert Roberts. 2008. ''Ancient Greece: A political, social, and cultural history''. 2d ed. New York: Oxford Univ. Press. * Rhodes, Peter J. 2006. ''A history of the Classical Greek world: 478–323 BC''. Blackwell History of the Ancient World. Malden, MA: Blackwell. * Whitley, James. 2001. ''The archaeology of ancient Greece''. Cambridge, UK, and New York: Cambridge Univ. Press.External links
The Canadian Museum of Civilization—Greece Secrets of the Past
Ancient Greece
website from the British Museum
Economic history of ancient Greece
(archived 2 May 2006)
The Greek currency history
Limenoscope
an ancient Greek ports database (archived 11 May 2011)
Greek and Roman theatre architecture
Illustrated Greek History
Janice Siegel, Department of Classics, Hampden–Sydney College, Virginia {{Authority control Ancient Greece, Articles which contain graphical timelines