Americium Dichloride on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Americium is a synthetic chemical element; it has
 Although americium was likely produced in previous nuclear experiments, it was first intentionally synthesized, isolated and identified in late autumn 1944, at the
Although americium was likely produced in previous nuclear experiments, it was first intentionally synthesized, isolated and identified in late autumn 1944, at the
 The longest-lived and most common isotopes of americium, 241Am and 243Am, have half-lives of 432.2 and 7,370 years, respectively. Therefore, any
The longest-lived and most common isotopes of americium, 241Am and 243Am, have half-lives of 432.2 and 7,370 years, respectively. Therefore, any
, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Retrieved 28 November 2010 Americium is produced mostly artificially in small quantities, for research purposes. A tonne of spent nuclear fuel contains about 100 grams of various americium isotopes, mostly 241Am and 243Am. Their prolonged radioactivity is undesirable for the disposal, and therefore americium, together with other long-lived actinides, must be neutralized. The associated procedure may involve several steps, where americium is first separated and then converted by neutron bombardment in special reactors to short-lived nuclides. This procedure is well known as
 Americium has been produced in small quantities in
Americium has been produced in small quantities in
, World Nuclear Association, January 2009, Retrieved 28 November 2010 The heavier isotope 243Am is produced in much smaller amounts; it is thus more difficult to separate, resulting in a higher cost of the order .Hammond C. R. "The elements" in Americium is not synthesized directly from uranium – the most common reactor material – but from the plutonium isotope 239Pu. The latter needs to be produced first, according to the following nuclear process: :^_U -> ce^_U -> beta^-23.5 \ \ce] ^_Np -> beta^-2.3565 \ \ce] ^_Pu
The capture of two neutrons by 239Pu (a so-called (n,γ) reaction), followed by a β-decay, results in 241Am:
: ^_Pu -> ce^_Pu -> beta^-14.35 \ \ce] ^_Am
The plutonium present in spent nuclear fuel contains about 12% of 241Pu. Because it ^_Pu -> ce\ ^_Pu -> beta^-4.956 \ \ce] ^_Am
 In the
In the
+ \underset -> \atop 400 - 500 ^\circ \ce C +
Americium(III) fluoride (AmF3) is poorly soluble and precipitates upon reaction of Am3+ and fluoride ions in weak acidic solutions:
: Am^3+ + 3F^- -> AmF3(v)
The tetravalent americium(IV) fluoride (AmF4) is obtained by reacting solid americium(III) fluoride with molecular 2AmF3 + F2 -> 2AmF4
Another known form of solid tetravalent americium fluoride is KAmF5.Penneman, p. 6 Tetravalent americium has also been observed in the aqueous phase. For this purpose, black Am(OH)4 was dissolved in 15- M NH4F with the americium concentration of 0.01 M. The resulting reddish solution had a characteristic optical absorption spectrum which is similar to that of AmF4 but differed from other oxidation states of americium. Heating the Am(IV) solution to 90 °C did not result in its disproportionation or reduction, however a slow reduction was observed to Am(III) and assigned to self-irradiation of americium by alpha particles.
Most americium(III) halides form hexagonal crystals with slight variation of the color and exact structure between the halogens. So, chloride (AmCl3) is reddish and has a structure isotypic to
 Analogous to
Analogous to
"Evaluation of nuclear criticality safety data and limits for actinides in transport"
p. 16. Scarcity and high price yet hinder application of americium as a
Performance of Home Smoke Alarms Analysis of the Response of Several Available Technologies in Residential Fire Settings
, NIST Technical Note 1455-1
, G.L. Kulcinski, NEEP 602 Course Notes (Spring 2000), Nuclear Power in Space, University of Wisconsin Fusion Technology Institute (see last page) Although americium produces less heat and electricity – the power yield is 114.7 mW/g for 241Am and 6.31 mW/g for 243Am (cf. 390 mW/g for 238Pu) – and its radiation poses more threat to humans owing to neutron emission, the
^_Am -> ^_Np + ^_He + \gamma
: ^_Be + ^_He -> ^_C + ^_n + \gamma
The most widespread use of 241AmBe neutron sources is a
^_Am -> ce^_Am -> beta^-10.1 \ \ce] ^_Cm
Irradiation of 241Am by 12C or 22Ne ions yields the isotopes 247Es (
The Radioactive Boy Scout: When a teenager attempts to build a breeder reactor
''Harper's Magazine'', November 1998 There have been a few cases of exposure to americium, the worst case being that of Chemical technologist, chemical operations technician Harold McCluskey, who at the age of 64 was exposed to 500 times the occupational standard for americium-241 as a result of an explosion in his lab. McCluskey died at the age of 75 of unrelated pre-existing disease.
The radiochemistry of americium and curium
University of California, Los Alamos, California, 1960 *
at ''The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham)
ATSDR – Public Health Statement: Americium
{{Authority control Americium, Chemical elements Chemical elements with double hexagonal close-packed structure Actinides Carcinogens Synthetic elements
symbol
A symbol is a mark, Sign (semiotics), sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, physical object, object, or wikt:relationship, relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by cr ...
Am and atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of its atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei composed of protons and neutrons, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of pro ...
95. It is radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is conside ...
and a transuranic
The transuranium (or transuranic) elements are the chemical elements with atomic number greater than 92, which is the atomic number of uranium. All of them are radioactively unstable and decay into other elements. Except for neptunium and pluton ...
member of the actinide
The actinide () or actinoid () series encompasses at least the 14 metallic chemical elements in the 5f series, with atomic numbers from 89 to 102, actinium through nobelium. Number 103, lawrencium, is also generally included despite being part ...
series in the periodic table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the elements, is an ordered arrangement of the chemical elements into rows (" periods") and columns (" groups"). It is an icon of chemistry and is widely used in physics and other s ...
, located under the lanthanide
The lanthanide () or lanthanoid () series of chemical elements comprises at least the 14 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers 57–70, from lanthanum through ytterbium. In the periodic table, they fill the 4f orbitals. Lutetium (el ...
element europium
Europium is a chemical element; it has symbol Eu and atomic number 63. It is a silvery-white metal of the lanthanide series that reacts readily with air to form a dark oxide coating. Europium is the most chemically reactive, least dense, and soft ...
and was thus named after the Americas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a sing ...
by analogy.
Americium was first produced in 1944 by the group of Glenn T. Seaborg
Glenn Theodore Seaborg ( ; April 19, 1912February 25, 1999) was an American chemist whose involvement in the synthesis, discovery and investigation of ten transuranium elements earned him a share of the 1951 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. His work i ...
from Berkeley, California
Berkeley ( ) is a city on the eastern shore of San Francisco Bay in northern Alameda County, California, United States. It is named after the 18th-century Anglo-Irish bishop and philosopher George Berkeley. It borders the cities of Oakland, Cali ...
, at the Metallurgical Laboratory
The Metallurgical Laboratory (or Met Lab) was a scientific laboratory from 1942 to 1946 at the University of Chicago. It was established in February 1942 and became the Argonne National Laboratory in July 1946.
The laboratory was established i ...
of the University of Chicago
The University of Chicago (UChicago, Chicago, or UChi) is a Private university, private research university in Chicago, Illinois, United States. Its main campus is in the Hyde Park, Chicago, Hyde Park neighborhood on Chicago's South Side, Chic ...
, as part of the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development program undertaken during World War II to produce the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States in collaboration with the United Kingdom and Canada.
From 1942 to 1946, the ...
. Although it is the third element in the transuranic series, it was discovered fourth, after the heavier curium
Curium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This transuranic actinide element was named after eminent scientists Marie and Pierre Curie, both known for their research on radioactivity. Curium was first inten ...
. The discovery was kept secret and only released to the public in November 1945. Most americium is produced by uranium
Uranium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Ura ...
or plutonium
Plutonium is a chemical element; it has symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is a silvery-gray actinide metal that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four ...
being bombarded with neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , that has no electric charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. The Discovery of the neutron, neutron was discovered by James Chadwick in 1932, leading to the discovery of nucle ...
s in nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a Nuclear fission, fission nuclear chain reaction. They are used for Nuclear power, commercial electricity, nuclear marine propulsion, marine propulsion, Weapons-grade plutonium, weapons ...
s – one tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1,000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton in the United States to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the s ...
of spent nuclear fuel
Spent nuclear fuel, occasionally called used nuclear fuel, is nuclear fuel that has been irradiated in a nuclear reactor (usually at a nuclear power plant). It is no longer useful in sustaining a nuclear reaction in an ordinary thermal reactor and ...
contains about 100 grams of americium. It is widely used in commercial ionization chamber
The ionization chamber is the simplest type of gaseous ionisation detector, and is widely used for the detection and measurement of many types of ionizing radiation, including X-rays, gamma rays, alpha particles and beta particles. Conventionall ...
smoke detector
A smoke detector is a device that senses smoke, typically as an indicator of fire. Smoke detectors/alarms are usually housed in plastic enclosures, typically shaped like a disk about in diameter and thick, but shape and size vary. Smoke can be ...
s, as well as in neutron source
A neutron source is any device that emits neutrons, irrespective of the mechanism used to produce the neutrons. Neutron sources are used in physics, engineering, medicine, nuclear weapons, petroleum exploration, biology, chemistry, and nuclear p ...
s and industrial gauges. Several unusual applications, such as nuclear batteries or fuel for space ships with nuclear propulsion
Propulsion is the generation of force by any combination of pushing or pulling to modify the translational motion of an object, which is typically a rigid body (or an articulated rigid body) but may also concern a fluid. The term is derived from ...
, have been proposed for the isotope
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their Atomic nucleus, nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemica ...
242mAm, but they are as yet hindered by the scarcity and high price of this nuclear isomer
A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus, in which one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) occupy excited state levels (higher energy levels). "Metastable" describes nuclei whose excited states have Half-life, half-lives of ...
.
Americium is a relatively soft radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is conside ...
metal with a silvery appearance. Its most common isotopes
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), but ...
are 241Am and 243Am. In chemical compounds, americium usually assumes the oxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical Electrical charge, charge of an atom if all of its Chemical bond, bonds to other atoms are fully Ionic bond, ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons ...
+3, especially in solutions. Several other oxidation states are known, ranging from +2 to +7, and can be identified by their characteristic optical absorption
In physics, absorption of electromagnetic radiation is how matter (typically electrons bound in atoms) takes up a photon's energy—and so transforms electromagnetic energy into internal energy of the absorber (for example, thermal energy).
A ...
spectra. The crystal lattices of solid americium and its compounds contain small intrinsic radiogenic defects, due to metamictization
Metamictisation (sometimes called metamictization or metamiction) is a natural process resulting in the gradual and ultimately complete destruction of a mineral's crystal structure, leaving the mineral amorphous. The affected material is therefore ...
induced by self-irradiation with alpha particles, which accumulates with time; this can cause a drift of some material properties over time, more noticeable in older samples.
History
 Although americium was likely produced in previous nuclear experiments, it was first intentionally synthesized, isolated and identified in late autumn 1944, at the
Although americium was likely produced in previous nuclear experiments, it was first intentionally synthesized, isolated and identified in late autumn 1944, at the University of California, Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley, Berkeley, Cal, or California), is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Berkeley, California, United States. Founded in 1868 and named after t ...
, by Glenn T. Seaborg
Glenn Theodore Seaborg ( ; April 19, 1912February 25, 1999) was an American chemist whose involvement in the synthesis, discovery and investigation of ten transuranium elements earned him a share of the 1951 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. His work i ...
, Leon O. Morgan, Ralph A. James, and Albert Ghiorso
Albert Ghiorso (July 15, 1915 – December 26, 2010) was an American nuclear scientist and co-discoverer of a record 12 chemical elements on the periodic table. His research career spanned six decades, from the early 1940s to the late 1990s.
Biog ...
. They used a 60-inch cyclotron
A cyclotron is a type of particle accelerator invented by Ernest Lawrence in 1929–1930 at the University of California, Berkeley, and patented in 1932. Lawrence, Ernest O. ''Method and apparatus for the acceleration of ions'', filed: Januar ...
at the University of California, Berkeley. The element was chemically identified at the Metallurgical Laboratory (now Argonne National Laboratory
Argonne National Laboratory is a Federally funded research and development centers, federally funded research and development center in Lemont, Illinois, Lemont, Illinois, United States. Founded in 1946, the laboratory is owned by the United Sta ...
) of the University of Chicago
The University of Chicago (UChicago, Chicago, or UChi) is a Private university, private research university in Chicago, Illinois, United States. Its main campus is in the Hyde Park, Chicago, Hyde Park neighborhood on Chicago's South Side, Chic ...
. Following the lighter neptunium
Neptunium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactivity, radioactive actinide metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element. It is named after Neptune, the planet beyond Uranus in the Solar Syste ...
, plutonium
Plutonium is a chemical element; it has symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is a silvery-gray actinide metal that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four ...
, and heavier curium
Curium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This transuranic actinide element was named after eminent scientists Marie and Pierre Curie, both known for their research on radioactivity. Curium was first inten ...
, americium was the fourth transuranium element
The transuranium (or transuranic) elements are the chemical elements with atomic number greater than 92, which is the atomic number of uranium. All of them are radioactively unstable and decay into other elements. Except for neptunium and pluton ...
to be discovered. At the time, the periodic table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the elements, is an ordered arrangement of the chemical elements into rows (" periods") and columns (" groups"). It is an icon of chemistry and is widely used in physics and other s ...
had been restructured by Seaborg to its present layout, containing the actinide row below the lanthanide
The lanthanide () or lanthanoid () series of chemical elements comprises at least the 14 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers 57–70, from lanthanum through ytterbium. In the periodic table, they fill the 4f orbitals. Lutetium (el ...
one. This led to americium being located right below its twin lanthanide element europium; it was thus by analogy named after the Americas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a sing ...
: "The name americium (after the Americas) and the symbol Am are suggested for the element on the basis of its position as the sixth member of the actinide rare-earth series, analogous to europium, Eu, of the lanthanide series."Greenwood, p. 1252
The new element was isolated from its oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion (anion bearing a net charge of −2) of oxygen, an O2− ion with oxygen in the oxidation st ...
s in a complex, multi-step process. First plutonium
Plutonium is a chemical element; it has symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is a silvery-gray actinide metal that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four ...
-239 nitrate (239PuNO3) solution was coated on a platinum
Platinum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a density, dense, malleable, ductility, ductile, highly unreactive, precious metal, precious, silverish-white transition metal. Its name origina ...
foil of about 0.5 cm2 area, the solution was evaporated and the residue was converted into plutonium dioxide (PuO2) by calcining
Calcination is thermal treatment of a solid chemical compound (e.g. mixed carbonate ores) whereby the compound is raised to high temperature without melting under restricted supply of ambient oxygen (i.e. gaseous O2 fraction of air), generally fo ...
. After cyclotron irradiation, the coating was dissolved with nitric acid
Nitric acid is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into nitrogen oxide, oxides of nitrogen. Most com ...
, and then precipitated as the hydroxide using concentrated aqueous ammonia solution
Ammonia solution, also known as ammonia water, ammonium hydroxide, ammoniacal liquor, ammonia liquor, aqua ammonia, aqueous ammonia, or (inaccurately) ammonia, is a solution of ammonia in water. It can be denoted by the symbols NH3(aq). Although ...
. The residue was dissolved in perchloric acid
Perchloric acid is a mineral acid with the formula H Cl O4. It is an oxoacid of chlorine. Usually found as an aqueous solution, this colorless compound is a stronger acid than sulfuric acid, nitric acid and hydrochloric acid. It is a powerful oxid ...
. Further separation was carried out by ion exchange
Ion exchange is a reversible interchange of one species of ion present in an insoluble solid with another of like charge present in a solution surrounding the solid. Ion exchange is used in softening or demineralizing of water, purification of ch ...
, yielding a certain isotope of curium. The separation of curium and americium was so painstaking that those elements were initially called by the Berkeley group as '' pandemonium'' (from Greek for ''all demons'' or ''hell'') and ''delirium
Delirium (formerly acute confusional state, an ambiguous term that is now discouraged) is a specific state of acute confusion attributable to the direct physiological consequence of a medical condition, effects of a psychoactive substance, or ...
'' (from Latin for ''madness'').
Initial experiments yielded four americium isotopes: 241Am, 242Am, 239Am and 238Am. Americium-241
Americium-241 (Am, Am-241) is an isotope of americium. Like all isotopes of americium, it is radioactive, with a half-life of . Am is the most common isotope of americium as well as the most prevalent isotope of americium in nuclear waste. It ...
was directly obtained from plutonium upon absorption of two neutrons. It decays by emission of a α-particle
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay but may also be produc ...
to 237Np; the half-life Half-life is a mathematical and scientific description of exponential or gradual decay.
Half-life, half life or halflife may also refer to:
Film
* Half-Life (film), ''Half-Life'' (film), a 2008 independent film by Jennifer Phang
* ''Half Life: ...
of this decay was first determined as years but then corrected to 432.2 years.
:
: The times are half-lives Half-life is a mathematical and scientific description of exponential or gradual decay.
Half-life, half life or halflife may also refer to:
Film
* ''Half-Life'' (film), a 2008 independent film by Jennifer Phang
* '' Half Life: A Parable for t ...
The second isotope 242Am was produced upon neutron bombardment of the already-created 241Am. Upon rapid β-decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron), transforming into an isobar of that nuclide. For example, beta decay of a neutron t ...
, 242Am converts into the isotope of curium 242Cm (which had been discovered previously). The half-life of this decay was initially determined at 17 hours, which was close to the presently accepted value of 16.02 h.
:
The discovery of americium and curium in 1944 was closely related to the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development program undertaken during World War II to produce the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States in collaboration with the United Kingdom and Canada.
From 1942 to 1946, the ...
; the results were confidential and declassified only in 1945. Seaborg leaked the synthesis of the elements 95 and 96 on the U.S. radio show for children ''Quiz Kids
''Quiz Kids'' is a radio and TV series originally broadcast in the 1940s and 1950s. Created by Chicago public relations and advertising man Louis G. Cowan, and originally sponsored by Alka-Seltzer, the series was first broadcast on NBC from ...
'' five days before the official presentation at an American Chemical Society
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a scientific society based in the United States that supports scientific inquiry in the field of chemistry. Founded in 1876 at New York University, the ACS currently has more than 155,000 members at all ...
meeting on 11 November 1945, when one of the listeners asked whether any new transuranium element besides plutonium and neptunium had been discovered during the war. After the discovery of americium isotopes 241Am and 242Am, their production and compounds were patented listing only Seaborg as the inventor. The initial americium samples weighed a few micrograms; they were barely visible and were identified by their radioactivity. The first substantial amounts of metallic americium weighing 40–200 micrograms were not prepared until 1951 by reduction of americium(III) fluoride
Americium(III) fluoride or americium trifluoride is the chemical compound composed of americium and fluorine with the formula
In science, a formula is a concise way of expressing information symbolically, as in a mathematical formula or a ''c ...
with barium
Barium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in group 2 and is a soft, silvery alkaline earth metal. Because of its high chemical reactivity, barium is never found in nature as a free element.
Th ...
metal in high vacuum at 1100 °C.
Occurrence
 The longest-lived and most common isotopes of americium, 241Am and 243Am, have half-lives of 432.2 and 7,370 years, respectively. Therefore, any
The longest-lived and most common isotopes of americium, 241Am and 243Am, have half-lives of 432.2 and 7,370 years, respectively. Therefore, any primordial
Primordial may refer to:
* Primordial era, an era after the Big Bang. See Chronology of the universe
* Primordial soup, hypothetical conditions under which life on Earth may have begun
* Primordial nuclide, nuclides, a few radioactive, that form ...
americium (americium that was present on Earth during its formation) should have decayed by now. Trace amounts of americium probably occur naturally in uranium minerals as a result of neutron capture and beta decay (238U → 239Pu → 240Pu → 241Am), though the quantities would be tiny and this has not been confirmed. Extraterrestrial long-lived 247Cm is probably also deposited on Earth and has 243Am as one of its intermediate decay products, but again this has not been confirmed.
Existing americium is concentrated in the areas used for the atmospheric nuclear weapons tests conducted between 1945 and 1980, as well as at the sites of nuclear incidents, such as the Chernobyl disaster
On 26 April 1986, the no. 4 reactor of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, located near Pripyat, Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, Ukrainian SSR, Soviet Union (now Ukraine), exploded. With dozens of direct casualties, it is one of only ...
. For example, the analysis of the debris at the testing site of the first U.S. hydrogen bomb
A thermonuclear weapon, fusion weapon or hydrogen bomb (H-bomb) is a second-generation nuclear weapon design. Its greater sophistication affords it vastly greater destructive power than first-generation nuclear bombs, a more compact size, a lo ...
, Ivy Mike
Ivy Mike was the code name, codename given to the first full-scale test of a Thermonuclear weapon, thermonuclear device, in which a significant fraction of the explosive nuclear weapon yield, yield comes from nuclear fusion.
Ivy Mike was detona ...
, (1 November 1952, Enewetak Atoll
Enewetak Atoll (; also spelled Eniwetok Atoll or sometimes Eniewetok; , , or , ; known to the Japanese as Brown Atoll or Brown Island; ) is a large coral atoll of 40 islands in the Pacific Ocean and with its 296 people (as of 2021) forms a leg ...
), revealed high concentrations of various actinides including americium; but due to military secrecy, this result was not published until later, in 1956. Trinitite
Trinitite, also known as atomsite or Alamogordo glass, is the glassy residue left on the desert floor after the plutonium-based Trinity (nuclear test), Trinity nuclear bomb test on July 16, 1945, near Alamogordo, New Mexico. The glass is primaril ...
, the glassy residue left on the desert floor near Alamogordo, New Mexico
Alamogordo () is a city in and the county seat of Otero County, New Mexico, United States. A city in the Tularosa Basin of the Chihuahuan Desert, it is bordered on the east by the Sacramento Mountains and to the west by Holloman Air Force ...
, after the plutonium
Plutonium is a chemical element; it has symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is a silvery-gray actinide metal that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four ...
-based Trinity
The Trinity (, from 'threefold') is the Christian doctrine concerning the nature of God, which defines one God existing in three, , consubstantial divine persons: God the Father, God the Son (Jesus Christ) and God the Holy Spirit, thr ...
nuclear bomb test on 16 July 1945, contains traces of americium-241. Elevated levels of americium were also detected at the crash site of a US Boeing B-52
The Boeing B-52 Stratofortress is an American long-range, subsonic aircraft, subsonic, jet-powered strategic bomber. The B-52 was designed and built by Boeing, which has continued to provide support and upgrades. It has been operated by the ...
bomber aircraft, which carried four hydrogen bombs, in 1968 in Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous territory in the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. It is by far the largest geographically of three constituent parts of the kingdom; the other two are metropolitan Denmark and the Faroe Islands. Citizens of Greenlan ...
.
In other regions, the average radioactivity of surface soil due to residual americium is only about 0.01 picocuries per gram (0.37 mBq/g). Atmospheric americium compounds are poorly soluble in common solvents and mostly adhere to soil particles. Soil analysis revealed about 1,900 times higher concentration of americium inside sandy soil particles than in the water present in the soil pores; an even higher ratio was measured in loam
Loam (in geology and soil science) is soil composed mostly of sand (particle size > ), silt (particle size > ), and a smaller amount of clay (particle size < ). By weight, its mineral composition is about 40–40–20% concentration of sand–si ...
soils.Human Health Fact Sheet on Americium, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Retrieved 28 November 2010 Americium is produced mostly artificially in small quantities, for research purposes. A tonne of spent nuclear fuel contains about 100 grams of various americium isotopes, mostly 241Am and 243Am. Their prolonged radioactivity is undesirable for the disposal, and therefore americium, together with other long-lived actinides, must be neutralized. The associated procedure may involve several steps, where americium is first separated and then converted by neutron bombardment in special reactors to short-lived nuclides. This procedure is well known as
nuclear transmutation
Nuclear transmutation is the conversion of one chemical element or an isotope into another chemical element. Nuclear transmutation occurs in any process where the number of protons or neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is changed.
A transmutat ...
, but it is still being developed for americium.
The transuranic element
The transuranium (or transuranic) elements are the chemical elements with atomic number greater than 92, which is the atomic number of uranium. All of them are radioactively unstable and decay into other elements. Except for neptunium and pluton ...
s up to fermium
Fermium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Fm and atomic number 100. It is an actinide and the heaviest element that can be formed by neutron bombardment of lighter elements, and hence the last element that can be prepared in macros ...
, including americium, should have been present in the natural nuclear fission reactor
A natural nuclear fission reactor is a uranium deposit where self-sustaining nuclear chain reactions occur. The idea of a nuclear reactor existing ''in situ'' within an ore body moderated by groundwater was briefly explored by Paul Kuroda in 19 ...
at Oklo
Oklo is a region near Franceville in the Haut-Ogooué Province of Gabon. Several natural nuclear fission reactors were discovered in the uranium mines in the region in 1972.
History
Gabon was a French colony when prospectors from the Comm ...
, but no longer do so.
Synthesis and extraction
Isotope nucleosynthesis
 Americium has been produced in small quantities in
Americium has been produced in small quantities in nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a Nuclear fission, fission nuclear chain reaction. They are used for Nuclear power, commercial electricity, nuclear marine propulsion, marine propulsion, Weapons-grade plutonium, weapons ...
s for decades, and kilograms of its 241Am and 243Am isotopes have been accumulated by now.Greenwood, p. 1262 Nevertheless, since it was first offered for sale in 1962, its price, about of 241Am, remains almost unchanged owing to the very complex separation procedure.Smoke detectors and americium, World Nuclear Association, January 2009, Retrieved 28 November 2010 The heavier isotope 243Am is produced in much smaller amounts; it is thus more difficult to separate, resulting in a higher cost of the order .Hammond C. R. "The elements" in Americium is not synthesized directly from uranium – the most common reactor material – but from the plutonium isotope 239Pu. The latter needs to be produced first, according to the following nuclear process: :
beta-decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron), transforming into an isobar of that nuclide. For example, beta decay of a neutron t ...
s to 241Am, 241Pu can be extracted and may be used to generate further 241Am. However, this process is rather slow: half of the original amount of 241Pu decays to 241Am after about 15 years, and the 241Am amount reaches a maximum after 70 years.
The obtained 241Am can be used for generating heavier americium isotopes by further neutron capture inside a nuclear reactor. In a light water reactor
The light-water reactor (LWR) is a type of thermal-neutron reactor that uses normal water, as opposed to heavy water, as both its coolant and neutron moderator; furthermore a solid form of fissile elements is used as fuel. Thermal-neutron react ...
(LWR), 79% of 241Am converts to 242Am and 10% to its nuclear isomer
A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus, in which one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) occupy excited state levels (higher energy levels). "Metastable" describes nuclei whose excited states have Half-life, half-lives of ...
242mAm:The "metastable" state is marked by the letter m.
:
Americium-242 has a half-life of only 16 hours, which makes its further conversion to 243Am extremely inefficient. The latter isotope is produced instead in a process where 239Pu captures four neutrons under high neutron flux
The neutron flux is a scalar quantity used in nuclear physics and nuclear reactor physics. It is the total distance travelled by all free neutrons per unit time and volume. Equivalently, it can be defined as the number of neutrons travelling ...
:
: Metal generation
Most synthesis routines yield a mixture of different actinide isotopes in oxide forms, from which isotopes of americium can be separated. In a typical procedure, the spent reactor fuel (e.g.MOX fuel
Mixed oxide fuel (MOX fuel) is nuclear fuel that contains more than one oxide of fissile material, usually consisting of plutonium blended with natural uranium, reprocessed uranium, or depleted uranium. MOX fuel is an alternative to the low-enr ...
) is dissolved in nitric acid
Nitric acid is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into nitrogen oxide, oxides of nitrogen. Most com ...
, and the bulk of uranium and plutonium is removed using a PUREX
PUREX (plutonium uranium reduction extraction) is a chemical method used to purify fuel for nuclear reactors or nuclear weapons. It is based on liquid–liquid extraction ion-exchange. PUREX is the '' de facto'' standard aqueous nuclear reproc ...
-type extraction (Plutonium–URanium EXtraction) with tributyl phosphate
Tributyl phosphate, known commonly as TBP, is an organophosphorus compound with the chemical formula (CH3CH2CH2CH2O)3PO. This colourless, odorless liquid finds some applications as an extractant and a plasticizer. It is an ester of phosphoric a ...
in a hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and Hydrophobe, hydrophobic; their odor is usually fain ...
. The lanthanides and remaining actinides are then separated from the aqueous residue (raffinate
In chemical separation terminology, the raffinate (from French ''raffiner'', to refine) is a product which has had a component or components removed. The product having the removed materials is referred to as the extract. For example, in solvent e ...
) by a diamide-based extraction, to give, after stripping, a mixture of trivalent actinides and lanthanides. Americium compounds are then selectively extracted using multi-step chromatographic and centrifugation techniques with an appropriate reagent. A large amount of work has been done on the solvent extraction
A solvent (from the Latin language, Latin ''wikt:solvo#Latin, solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a Solution (chemistry), solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas ...
of americium. For example, a 2003 EU-funded project codenamed "EUROPART" studied triazine
Triazines are a class of nitrogen-containing heterocycles. The parent molecules' molecular formula is . They exist in three isomeric forms, 1,3,5-triazines being common.
Structure
The triazines have planar six-membered benzene-like ring but ...
s and other compounds as potential extraction agents. A ''bis''-triazinyl bipyridine complex was proposed in 2009 as such a reagent is highly selective to americium (and curium). Separation of americium from the highly similar curium can be achieved by treating a slurry of their hydroxides in aqueous sodium bicarbonate
Sodium bicarbonate ( IUPAC name: sodium hydrogencarbonate), commonly known as baking soda or bicarbonate of soda (or simply “bicarb” especially in the UK) is a chemical compound with the formula NaHCO3. It is a salt composed of a sodium cat ...
with ozone
Ozone () (or trioxygen) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , break ...
, at elevated temperatures. Both Am and Cm are mostly present in solutions in the +3 valence state; whereas curium remains unchanged, americium oxidizes to soluble Am(IV) complexes which can be washed away.
Metallic americium is obtained by reduction from its compounds. Americium(III) fluoride
Americium(III) fluoride or americium trifluoride is the chemical compound composed of americium and fluorine with the formula
In science, a formula is a concise way of expressing information symbolically, as in a mathematical formula or a ''c ...
was first used for this purpose. The reaction was conducted using elemental barium
Barium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in group 2 and is a soft, silvery alkaline earth metal. Because of its high chemical reactivity, barium is never found in nature as a free element.
Th ...
as reducing agent in a water- and oxygen-free environment inside an apparatus made of tantalum
Tantalum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ta and atomic number 73. It is named after Tantalus, a figure in Greek mythology. Tantalum is a very hard, ductility, ductile, lustre (mineralogy), lustrous, blue-gray transition ...
and tungsten
Tungsten (also called wolfram) is a chemical element; it has symbol W and atomic number 74. It is a metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively in compounds with other elements. It was identified as a distinct element in 1781 and first ...
.''Gmelin Handbook of Inorganic Chemistry'', System No. 71, transuranics, Part B 1, pp. 57–67.Penneman, p. 3
:
An alternative is the reduction of americium dioxide
Americium dioxide (AmO2) is a black compound of americium. In the solid state, AmO2 adopts a fluorite structure (like CaF2). It is used as a source of alpha particles.
Historical context
The demand for americium dioxide stems from the difficulty ...
by metallic lanthanum
Lanthanum is a chemical element; it has symbol La and atomic number 57. It is a soft, ductile, silvery-white metal that tarnishes slowly when exposed to air. It is the eponym of the lanthanide series, a group of 15 similar elements bet ...
or thorium
Thorium is a chemical element; it has symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is a weakly radioactive light silver metal which tarnishes olive grey when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft, malleable, and ha ...
:
:
Physical properties
 In the
In the periodic table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the elements, is an ordered arrangement of the chemical elements into rows (" periods") and columns (" groups"). It is an icon of chemistry and is widely used in physics and other s ...
, americium is located to the right of plutonium, to the left of curium, and below the lanthanide europium
Europium is a chemical element; it has symbol Eu and atomic number 63. It is a silvery-white metal of the lanthanide series that reacts readily with air to form a dark oxide coating. Europium is the most chemically reactive, least dense, and soft ...
, with which it shares many physical and chemical properties. Americium is a highly radioactive element. When freshly prepared, it has a silvery-white metallic lustre, but then slowly tarnishes in air. With a density of 12 g/cm3, americium is less dense than both curium (13.52 g/cm3) and plutonium (19.8 g/cm3); but has a higher density than europium (5.264 g/cm3)—mostly because of its higher atomic mass. Americium is relatively soft and easily deformable and has a significantly lower bulk modulus
The bulk modulus (K or B or k) of a substance is a measure of the resistance of a substance to bulk compression. It is defined as the ratio of the infinitesimal pressure increase to the resulting ''relative'' decrease of the volume.
Other mo ...
than the actinides before it: Th, Pa, U, Np and Pu. Its melting point of 1173 °C is significantly higher than that of plutonium (639 °C) and europium (826 °C), but lower than for curium (1340 °C).
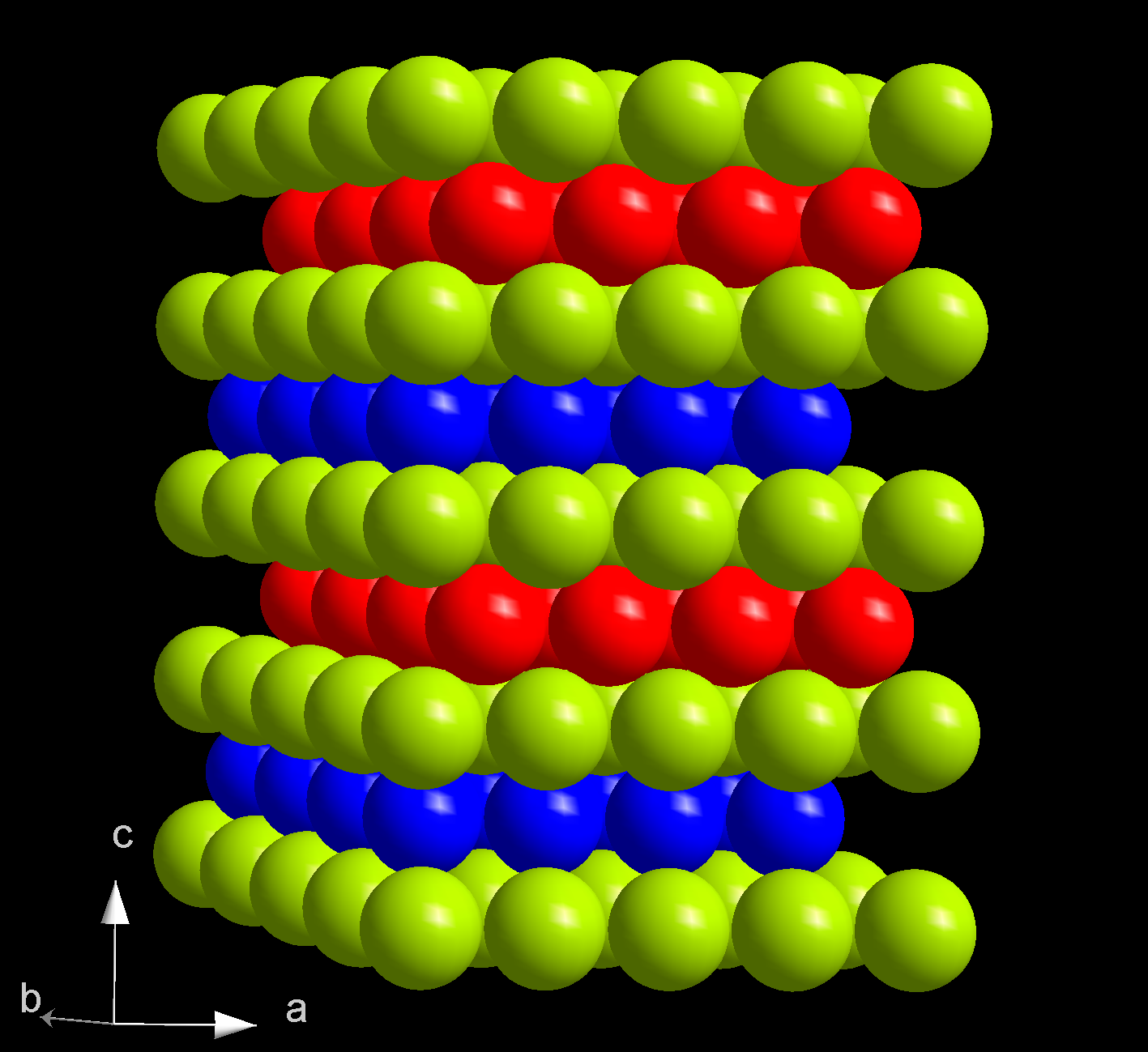
At ambient conditions, americium is present in its most stable α form which has a hexagonal crystal symmetry, and a space group
In mathematics, physics and chemistry, a space group is the symmetry group of a repeating pattern in space, usually in three dimensions. The elements of a space group (its symmetry operations) are the rigid transformations of the pattern that ...
P63/mmc with cell parameters ''a'' = 346.8 pm and ''c'' = 1124 pm, and four atoms per unit cell
In geometry, biology, mineralogy and solid state physics, a unit cell is a repeating unit formed by the vectors spanning the points of a lattice. Despite its suggestive name, the unit cell (unlike a unit vector
In mathematics, a unit vector i ...
. The crystal consists of a double-hexagonal close packing
In geometry, close-packing of equal spheres is a dense arrangement of congruent spheres in an infinite, regular arrangement (or lattice). Carl Friedrich Gauss proved that the highest average density – that is, the greatest fraction of space occ ...
with the layer sequence ABAC and so is isotypic with α-lanthanum and several actinides such as α-curium. The crystal structure of americium changes with pressure and temperature. When compressed at room temperature to 5 GPa, α-Am transforms to the β modification, which has a face-centered cubic
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals.
There are three main varieties o ...
(''fcc'') symmetry, space group Fmm and lattice constant ''a'' = 489 pm. This ''fcc'' structure is equivalent to the closest packing with the sequence ABC. Upon further compression to 23 GPa, americium transforms to an orthorhombic
In crystallography, the orthorhombic crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Orthorhombic Lattice (group), lattices result from stretching a cubic crystal system, cubic lattice along two of its orthogonal pairs by two different factors, res ...
γ-Am structure similar to that of α-uranium. There are no further transitions observed up to 52 GPa, except for an appearance of a monoclinic phase at pressures between 10 and 15 GPa. There is no consistency on the status of this phase in the literature, which also sometimes lists the α, β and γ phases as I, II and III. The β-γ transition is accompanied by a 6% decrease in the crystal volume; although theory also predicts a significant volume change for the α-β transition, it is not observed experimentally. The pressure of the α-β transition decreases with increasing temperature, and when α-americium is heated at ambient pressure, at 770 °C it changes into an ''fcc'' phase which is different from β-Am, and at 1075 °C it converts to a body-centered cubic
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the Crystal structure#Unit cell, unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals.
There ...
structure. The pressure-temperature phase diagram of americium is thus rather similar to those of lanthanum, praseodymium
Praseodymium is a chemical element; it has symbol Pr and atomic number 59. It is the third member of the lanthanide series and is considered one of the rare-earth metals. It is a soft, silvery, malleable and ductile metal, valued for its magnetic ...
and neodymium
Neodymium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is the fourth member of the lanthanide series and is considered to be one of the rare-earth element, rare-earth metals. It is a hard (physics), hard, sli ...
.
As with many other actinides, self-damage of the crystal structure due to alpha-particle irradiation is intrinsic to americium. It is especially noticeable at low temperatures, where the mobility of the produced structure defects is relatively low, by broadening of X-ray diffraction
X-ray diffraction is a generic term for phenomena associated with changes in the direction of X-ray beams due to interactions with the electrons around atoms. It occurs due to elastic scattering, when there is no change in the energy of the waves. ...
peaks. This effect makes somewhat uncertain the temperature of americium and some of its properties, such as electrical resistivity
Electrical resistivity (also called volume resistivity or specific electrical resistance) is a fundamental specific property of a material that measures its electrical resistance or how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity i ...
. So for americium-241, the resistivity at 4.2 K increases with time from about 2 μOhm·cm to 10 μOhm·cm after 40 hours, and saturates at about 16 μOhm·cm after 140 hours. This effect is less pronounced at room temperature, due to annihilation of radiation defects; also heating to room temperature the sample which was kept for hours at low temperatures restores its resistivity. In fresh samples, the resistivity gradually increases with temperature from about 2 μOhm·cm at liquid helium
Liquid helium is a physical state of helium at very low temperatures at standard atmospheric pressures. Liquid helium may show superfluidity.
At standard pressure, the chemical element helium exists in a liquid form only at the extremely low temp ...
to 69 μOhm·cm at room temperature; this behavior is similar to that of neptunium, uranium, thorium and protactinium
Protactinium is a chemical element; it has symbol Pa and atomic number 91. It is a dense, radioactive, silvery-gray actinide metal which readily reacts with oxygen, water vapor, and inorganic acids. It forms various chemical compounds, in which p ...
, but is different from plutonium and curium which show a rapid rise up to 60 K followed by saturation. The room temperature value for americium is lower than that of neptunium, plutonium and curium, but higher than for uranium, thorium and protactinium.
Americium is paramagnetic
Paramagnetism is a form of magnetism whereby some materials are weakly attracted by an externally applied magnetic field, and form internal, induced magnetic fields in the direction of the applied magnetic field. In contrast with this behavior, ...
in a wide temperature range, from that of liquid helium
Liquid helium is a physical state of helium at very low temperatures at standard atmospheric pressures. Liquid helium may show superfluidity.
At standard pressure, the chemical element helium exists in a liquid form only at the extremely low temp ...
, to room temperature and above. This behavior is markedly different from that of its neighbor curium which exhibits antiferromagnetic transition at 52 K. The thermal expansion
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to increase in length, area, or volume, changing its size and density, in response to an increase in temperature (usually excluding phase transitions).
Substances usually contract with decreasing temp ...
coefficient of americium is slightly anisotropic and amounts to along the shorter ''a'' axis and for the longer ''c'' hexagonal axis. The enthalpy of dissolution of americium metal in hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid or spirits of salt, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride (HCl). It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungency, pungent smell. It is classified as a acid strength, strong acid. It is ...
at standard conditions is , from which the standard enthalpy change of formation
In chemistry and thermodynamics, the standard enthalpy of formation or standard heat of formation of a compound is the change of enthalpy during the formation of 1 mole of the substance from its constituent elements in their reference state, wi ...
(Δf''H''°) of aqueous Am3+ ion is . The standard potential
In electrochemistry, standard electrode potential E^\ominus, or E^\ominus_, is the electrode potential (a measure of the reducing power of any element or compound) which the IUPAC "Gold Book" defines as ''"the value of the standard emf (electromo ...
Am3+/Am0 is .
Chemical properties
Americium metal readily reacts with oxygen and dissolves in aqueousacid
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis ...
s. The most stable oxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical Electrical charge, charge of an atom if all of its Chemical bond, bonds to other atoms are fully Ionic bond, ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons ...
for americium is +3.Penneman, p. 4 The chemistry of americium(III) has many similarities to the chemistry of lanthanide
The lanthanide () or lanthanoid () series of chemical elements comprises at least the 14 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers 57–70, from lanthanum through ytterbium. In the periodic table, they fill the 4f orbitals. Lutetium (el ...
(III) compounds. For example, trivalent americium forms insoluble fluoride
Fluoride (). According to this source, is a possible pronunciation in British English. is an Inorganic chemistry, inorganic, Monatomic ion, monatomic Ion#Anions and cations, anion of fluorine, with the chemical formula (also written ), whose ...
, oxalate
Oxalate (systematic IUPAC name: ethanedioate) is an anion with the chemical formula . This dianion is colorless. It occurs naturally, including in some foods. It forms a variety of salts, for example sodium oxalate (), and several esters such as ...
, iodate
An iodate is the polyatomic anion with the formula . It is the most common form of iodine in nature, as it comprises the major iodine-containing ores. Iodate salts are often colorless. They are the salts of iodic acid.
Structure
Iodate is pyra ...
, hydroxide
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and hydrogen atom held together by a single covalent bond, and carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. It ...
, phosphate
Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus.
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthop ...
and other salts. Compounds of americium in oxidation states +2, +4, +5, +6 and +7 have also been studied. This is the widest range that has been observed with actinide elements. The color of americium compounds in aqueous solution is as follows: Am3+ (yellow-reddish), Am4+ (yellow-reddish), ; (yellow), (brown) and (dark green).Greenwood, p. 1265 The absorption spectra have sharp peaks, due to ''f''-''f'' transitions' in the visible and near-infrared regions. Typically, Am(III) has absorption maxima at ca. 504 and 811 nm, Am(V) at ca. 514 and 715 nm, and Am(VI) at ca. 666 and 992 nm.
Americium compounds with oxidation state +4 and higher are strong oxidizing agents, comparable in strength to the permanganate
A permanganate () is a chemical compound with the manganate(VII) ion, , the conjugate base of permanganic acid. Because the manganese atom has a +7 oxidation state, the permanganate(VII) ion is a strong oxidising agent. The ion is a transition ...
ion () in acidic solutions.Wiberg, p. 1956 Whereas the Am4+ ions are unstable in solutions and readily convert to Am3+, compounds such as americium dioxide
Americium dioxide (AmO2) is a black compound of americium. In the solid state, AmO2 adopts a fluorite structure (like CaF2). It is used as a source of alpha particles.
Historical context
The demand for americium dioxide stems from the difficulty ...
(AmO2) and americium(IV) fluoride
Americium(IV) fluoride is the inorganic compound
An inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bondsthat is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of c ...
(AmF4) are stable in the solid state.
The pentavalent oxidation state of americium was first observed in 1951. In acidic aqueous solution the ion is unstable with respect to disproportionation
In chemistry, disproportionation, sometimes called dismutation, is a redox reaction in which one compound of intermediate oxidation state converts to two compounds, one of higher and one of lower oxidation state. The reverse of disproportionatio ...
.Greenwood, p. 1275 The reaction
:
is typical. The chemistry of Am(V) and Am(VI) is comparable to the chemistry of uranium
Uranium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Ura ...
in those oxidation states. In particular, compounds like and are comparable to uranate
A uranate is a ternary oxide involving the element uranium in one of the oxidation states 4, 5 or 6. A typical chemical formula is MxUyOz, where M represents a cation. The uranium atom in uranates(VI) has two short collinear U–O bonds and eith ...
s and the ion is comparable to the uranyl
The uranyl ion with the chemical formula has a linear structure with short U–O bonds, indicative of the presence of multiple bonds between uranium and oxygen, with uranium in the oxidation state +6. Four or more ligands may be bound to the u ...
ion, . Such compounds can be prepared by oxidation of Am(III) in dilute nitric acid with ammonium persulfate
Ammonium persulfate (APS) is the inorganic compound with the formula (NH4)2S2O8. It is a colourless (white) salt that is highly soluble in water, much more so than the related potassium salt. It is a strong oxidizing agent that is used as a cataly ...
. Other oxidising agents that have been used include silver(I) oxide
Silver oxide is the chemical compound with the formula Ag2 O. It is a fine black or dark brown powder that is used to prepare other silver compounds.
Preparation
Silver oxide can be prepared by combining aqueous solutions of silver nitrate and ...
, ozone
Ozone () (or trioxygen) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , break ...
and sodium persulfate
Sodium persulfate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2 S2 O8. It is the sodium salt of peroxydisulfuric acid, H2S2O8, an oxidizing agent. It is a white solid that dissolves in water. It is almost non-hygroscopic and has good shelf-life. ...
.
Chemical compounds
Oxygen compounds
Three americium oxides are known, with the oxidation states +2 (AmO), +3 (Am2O3) and +4 (AmO2).Americium(II) oxide
Americium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Am and atomic number 95. It is radioactive and a transuranic member of the actinide series in the periodic table, located under the lanthanide element europium and was thus named after th ...
was prepared in minute amounts and has not been characterized in detail. Americium(III) oxide
Americium(III) oxide or americium sesquioxide is an oxide of the element americium. It has the empirical formula Am2O3. Since all isotopes of americium are only artificially produced, americium (III) oxide has no natural occurrence. The colour depe ...
is a red-brown solid with a melting point of 2205 °C.Wiberg, p. 1972 Americium(IV) oxide is the main form of solid americium which is used in nearly all its applications. As most other actinide dioxides, it is a black solid with a cubic (fluorite
Fluorite (also called fluorspar) is the mineral form of calcium fluoride, CaF2. It belongs to the halide minerals. It crystallizes in isometric cubic habit, although octahedral and more complex isometric forms are not uncommon.
The Mohs scal ...
) crystal structure.Greenwood, p. 1267
The oxalate of americium(III), vacuum dried at room temperature, has the chemical formula Am2(C2O4)3·7H2O. Upon heating in vacuum, it loses water at 240 °C and starts decomposing into AmO2 at 300 °C, the decomposition completes at about 470 °C. The initial oxalate dissolves in nitric acid with the maximum solubility of 0.25 g/L.Penneman, p. 5
Halides
Halide
In chemistry, a halide (rarely halogenide) is a binary chemical compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative (or more electropositive) than the halogen, to make a fl ...
s of americium are known for the oxidation states +2, +3 and +4,Wiberg, p. 1969 where the +3 is most stable, especially in solutions.
Reduction of Am(III) compounds with sodium amalgam
Amalgam most commonly refers to:
* Amalgam (chemistry), mercury alloy
* Amalgam (dentistry), material of silver tooth fillings
** Bonded amalgam, used in dentistry
Amalgam may also refer to:
* Amalgam Comics, a publisher
* Amalgam Digital, an in ...
yields Am(II) salts – the black halides AmCl2, AmBr2 and AmI2. They are very sensitive to oxygen and oxidize in water, releasing hydrogen and converting back to the Am(III) state. Specific lattice constants are:
* Orthorhombic
In crystallography, the orthorhombic crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Orthorhombic Lattice (group), lattices result from stretching a cubic crystal system, cubic lattice along two of its orthogonal pairs by two different factors, res ...
AmCl2: ''a'' = , ''b'' = and ''c'' =
* Tetragonal
In crystallography, the tetragonal crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Tetragonal crystal lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along one of its lattice vectors, so that the Cube (geometry), cube becomes a rectangular Pri ...
AmBr2: ''a'' = and ''c'' = . They can also be prepared by reacting metallic americium with an appropriate mercury halide HgX2, where X = Cl, Br or I:Greenwood, p. 1272
: fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at Standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions as pale yellow Diatomic molecule, diatomic gas. Fluorine is extre ...
:Greenwood, p. 1271
: uranium(III) chloride
Uranium(III) chloride, UCl3, is a water soluble salt of uranium. UCl3 is used mostly to reprocess spent nuclear fuel. Uranium(III) chloride is synthesized in various ways from uranium(IV) chloride; however, UCl3 is less stable than UCl4.
Prepar ...
(space group P63/m) and the melting point of 715 °C. The fluoride is isotypic to LaF3 (space group P63/mmc) and the iodide to BiI3 (space group R). The bromide is an exception with the orthorhombic PuBr3-type structure and space group Cmcm. Crystals of americium(III) chloride hexahydrate (AmCl3·6H2O) can be prepared by dissolving americium dioxide in hydrochloric acid and evaporating the liquid. Those crystals are hygroscopic and have yellow-reddish color and a monoclinic
In crystallography, the monoclinic crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems. A crystal system is described by three Vector (geometric), vectors. In the monoclinic system, the crystal is described by vectors of unequal lengths, as in t ...
crystal structure.
Oxyhalides of americium in the form AmVIO2X2, AmVO2X, AmIVOX2 and AmIIIOX can be obtained by reacting the corresponding americium halide with oxygen or Sb2O3, and AmOCl can also be produced by vapor phase hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
:
: AmCl3 + H2O -> AmOCl + 2HCl
Chalcogenides and pnictides
The knownchalcogenide
: 220px, Cadmium sulfide, a prototypical metal chalcogenide, is used as a yellow pigment.
A chalcogenide is a chemical compound consisting of at least one chalcogen anion and at least one more electropositive element. Although all group 16 elemen ...
s of americium include the sulfide
Sulfide (also sulphide in British English) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. ''Sulfide'' also refers to large families o ...
AmS2, selenide
A selenide is a chemical compound containing a selenium with oxidation number of −2. Similar to sulfide, selenides occur both as inorganic compounds and as organic derivatives, which are called organoselenium compound.
Inorganic selenides
Th ...
s AmSe2 and Am3Se4, and tellurides
The telluride ion is the anion Te2− and its derivatives. It is analogous to the other chalcogenide anions, the lighter O2−, S2−, and Se2−, and the heavier Po2−.
In principle, Te2− is formed by the two-e− reduction of telluriu ...
Am2Te3 and AmTe2. The pnictides
, -
! colspan=2 style="text-align:left;" , ↓ Period
, -
! 2
,
, -
! 3
,
, -
! 4
,
, -
! 5
,
, -
! 6
,
, -
! 7
,
, -
, colspan="2",
----
''Legend''
A pnictogen ( or ; from "to choke" and -gen, "generator") is any o ...
of americium (243Am) of the AmX type are known for the elements phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol P and atomic number 15. All elemental forms of phosphorus are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive and are therefore never found in nature. They can nevertheless be prepared ar ...
, arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is not ...
, antimony
Antimony is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Sb () and atomic number 51. A lustrous grey metal or metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite (). Antimony compounds have been known since ancient t ...
and bismuth
Bismuth is a chemical element; it has symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens, with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth occurs nat ...
. They crystallize in the rock-salt lattice.
Silicides and borides
Americium monosilicide (AmSi) and "disilicide" (nominally AmSix with: 1.87 < x < 2.0) were obtained by reduction of americium(III) fluoride with elementarysilicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a membe ...
in vacuum at 1050 °C (AmSi) and 1150−1200 °C (AmSix). AmSi is a black solid isomorphic with LaSi, it has an orthorhombic crystal symmetry. AmSix has a bright silvery lustre and a tetragonal crystal lattice (space group ''I''41/amd), it is isomorphic with PuSi2 and ThSi2. Boride
A boride is a compound between boron and a less electronegative element, for example silicon boride (SiB3 and SiB6). The borides are a very large group of compounds that are generally high melting and are covalent more than ionic in nature. Some b ...
s of americium include AmB4 and AmB6. The tetraboride can be obtained by heating an oxide or halide of americium with magnesium diboride
Magnesium diboride is the inorganic compound of magnesium and boron with the formula MgB2. It is a dark gray, water-insoluble solid. The compound becomes superconducting at 39 K (−234 °C), which has attracted attention. In terms of its ...
in vacuum or inert atmosphere.
Organoamericium compounds
 Analogous to
Analogous to uranocene
Uranocene, U(C8H8)2, is an organouranium compound composed of a uranium atom sandwiched between two cyclooctatetraene, cyclooctatetraenide rings. It was one of the first Organoactinide chemistry, organoactinide compounds to be synthesized. It is a ...
, americium is predicted to form the organometallic compound amerocene with two cyclooctatetraene
1,3,5,7-Cyclooctatetraene (COT) is an unsaturated derivative of cyclooctane, with the formula C8H8. It is also known as nnulene. This polyunsaturated hydrocarbon is a colorless to light yellow flammable liquid at room temperature. Because of ...
ligands, with the chemical formula (η8-C8H8)2Am. A cyclopentadienyl complex
A cyclopentadienyl complex is a coordination complex of a metal and cyclopentadienyl groups (, abbreviated as Cp−). Cyclopentadienyl ligands almost invariably bind to metals as a pentahapto (''η''5-) bonding mode. The metal–cyclopentadien ...
is also known that is likely to be stoichiometrically AmCp3.
Formation of the complexes of the type Am(n-C3H7-BTP)3, where BTP stands for 2,6-di(1,2,4-triazin-3-yl)pyridine, in solutions containing n-C3H7-BTP and Am3+ ions has been confirmed by EXAFS. Some of these BTP-type complexes selectively interact with americium and therefore are useful in its selective separation from lanthanides and another actinides.
Biological aspects
Americium is an artificial element of recent origin, and thus does not have a biological requirement. It is harmful tolife
Life, also known as biota, refers to matter that has biological processes, such as Cell signaling, signaling and self-sustaining processes. It is defined descriptively by the capacity for homeostasis, Structure#Biological, organisation, met ...
. It has been proposed to use bacteria for removal of americium and other heavy metals
upright=1.2, Crystals of lead.html" ;"title="osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead">osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead
Heavy metals is a controversial and ambiguous term for metallic elements with relatively h ...
from rivers and streams. Thus, Enterobacteriaceae
Enterobacteriaceae is a large family (biology), family of Gram-negative bacteria. It includes over 30 genera and more than 100 species. Its classification above the level of Family (taxonomy), family is still a subject of debate, but one class ...
of the genus ''Citrobacter
''Citrobacter'' is a genus of Gram-negative, aerobic, rod-shaped coliform bacteria of the Enterobacteriaceae family.
''Citrobacter'' spp. cause opportunistic infections (including urinary tract infections, gastroenteritis, and bacteremia).
...
'' precipitate americium ions from aqueous solutions, binding them into a metal-phosphate complex at their cell walls. Several studies have been reported on the biosorption
Biosorption is a physiochemical process that occurs naturally in certain biomass which allows it to passively concentrate and bind contaminants onto its cellular structure. Biosorption can be defined as the ability of biological materials to accumu ...
and bioaccumulation
Bioaccumulation is the gradual accumulation of substances, such as pesticides or other chemicals, in an organism. Bioaccumulation occurs when an organism absorbs a substance faster than it can be lost or eliminated by catabolism and excretion. T ...
of americium by bacteria and fungi. In the laboratory, both americium and curium were found to support the growth of methylotroph
Methylotrophs are a diverse group of microorganisms that can use reduced one-carbon compounds, such as methanol or methane, as the carbon source for their growth; and multi-carbon compounds that contain no carbon-carbon bonds, such as dimethyl eth ...
s.
Fission
The isotope 242mAm (half-life 141 years) has the largest cross sections for absorption of thermal neutrons (5,700barns
A barn is an agricultural building usually on farms and used for various purposes. In North America, a barn refers to structures that house livestock, including cattle and horses, as well as equipment and fodder, and often grain.Allen G. ...
),Pfennig, G.; Klewe-Nebenius, H and Seelmann Eggebert, W. (Eds.): Karlsruhe nuclide
Nuclides (or nucleides, from nucleus, also known as nuclear species) are a class of atoms characterized by their number of protons, ''Z'', their number of neutrons, ''N'', and their nuclear energy state.
The word ''nuclide'' was coined by the A ...
, 7 Edition 2006. that results in a small critical mass
In nuclear engineering, critical mass is the minimum mass of the fissile material needed for a sustained nuclear chain reaction in a particular setup. The critical mass of a fissionable material depends upon its nuclear properties (specific ...
for a sustained nuclear chain reaction
In nuclear physics, a nuclear chain reaction occurs when one single nuclear reaction causes an average of one or more subsequent nuclear reactions, thus leading to the possibility of a self-propagating series or "positive feedback loop" of thes ...
. The critical mass for a bare 242mAm sphere is about 9–14 kg (the uncertainty results from insufficient knowledge of its material properties). It can be lowered to 3–5 kg with a metal reflector and should become even smaller with a water reflector. Such small critical mass is favorable for portable nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission or atomic bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear weapon), producing a nuclear exp ...
s, but those based on 242mAm are not known yet, probably because of its scarcity and high price. The critical masses of the two readily available isotopes, 241Am and 243Am, are relatively high – 57.6 to 75.6 kg for 241Am and 209 kg for 243Am.Institut de Radioprotection et de Sûreté Nucléaire"Evaluation of nuclear criticality safety data and limits for actinides in transport"
p. 16. Scarcity and high price yet hinder application of americium as a
nuclear fuel
Nuclear fuel refers to any substance, typically fissile material, which is used by nuclear power stations or other atomic nucleus, nuclear devices to generate energy.
Oxide fuel
For fission reactors, the fuel (typically based on uranium) is ...
in nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a Nuclear fission, fission nuclear chain reaction. They are used for Nuclear power, commercial electricity, nuclear marine propulsion, marine propulsion, Weapons-grade plutonium, weapons ...
s.
There are proposals of very compact 10-kW high-flux reactors using as little as 20 grams of 242mAm. Such low-power reactors would be relatively safe to use as neutron source
A neutron source is any device that emits neutrons, irrespective of the mechanism used to produce the neutrons. Neutron sources are used in physics, engineering, medicine, nuclear weapons, petroleum exploration, biology, chemistry, and nuclear p ...
s for radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a therapy, treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of treatment of cancer, cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignancy, malignant cell (biology), ...
in hospitals.
Isotopes
About 18isotope
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their Atomic nucleus, nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemica ...
s and 11 nuclear isomer
A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus, in which one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) occupy excited state levels (higher energy levels). "Metastable" describes nuclei whose excited states have Half-life, half-lives of ...
s are known for americium, having mass numbers 229, 230, and 232 through 247. There are two long-lived alpha-emitters; 243Am has a half-life of 7,370 years and is the most stable isotope, and 241Am has a half-life of 432.2 years. The most stable nuclear isomer is 242m1Am; it has a long half-life of 141 years. The half-lives of other isotopes and isomers range from 0.64 microseconds for 245m1Am to 50.8 hours for 240Am. As with most other actinides, the isotopes of americium with odd number of neutrons have relatively high rate of nuclear fission and low critical mass.
Americium-241
Americium-241 (Am, Am-241) is an isotope of americium. Like all isotopes of americium, it is radioactive, with a half-life of . Am is the most common isotope of americium as well as the most prevalent isotope of americium in nuclear waste. It ...
decays to 237Np emitting alpha particles of 5 different energies, mostly at 5.486 MeV (85.2%) and 5.443 MeV (12.8%). Because many of the resulting states are metastable, they also emit gamma ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol ), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from high energy interactions like the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei or astronomical events like solar flares. It consists o ...
s with the discrete energies between 26.3 and 158.5 keV.
Americium-242 is a short-lived isotope with a half-life of 16.02 h. It mostly (82.7%) converts by β-decay to 242Cm, but also by electron capture
Electron capture (K-electron capture, also K-capture, or L-electron capture, L-capture) is a process in which the proton-rich nucleus of an electrically neutral atom absorbs an inner atomic electron, usually from the K or L electron shells. Th ...
to 242Pu (17.3%). Both 242Cm and 242Pu transform via nearly the same decay chain through 238Pu down to 234U.
Nearly all (99.541%) of 242m1Am decays by internal conversion
Internal conversion is an atomic decay process where an excited nucleus interacts electromagnetically with one of the orbital electrons of an atom. This causes the electron to be emitted (ejected) from the atom. Thus, in internal conversion (o ...
to 242Am and the remaining 0.459% by α-decay to 238Np. The latter subsequently decays to 238Pu and then to 234U.
Americium-243 transforms by α-emission into 239Np, which converts by β-decay to 239Pu, and the 239Pu changes into 235U by emitting an α-particle.
Applications
Ionization-type smoke detector
Americium is used in the most common type of householdsmoke detector
A smoke detector is a device that senses smoke, typically as an indicator of fire. Smoke detectors/alarms are usually housed in plastic enclosures, typically shaped like a disk about in diameter and thick, but shape and size vary. Smoke can be ...
, which uses 241Am in the form of americium dioxide as its source of ionizing radiation
Ionizing (ionising) radiation, including Radioactive decay, nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have enough energy per individual photon or particle to ionization, ionize atoms or molecules by detaching ...
. This isotope is preferred over 226 Ra because it emits 5 times more alpha particles and relatively little harmful gamma radiation.
The amount of americium in a typical new smoke detector is 1 microcurie
The curie (symbol Ci) is a non- SI unit of radioactivity originally defined in 1910. According to a notice in ''Nature'' at the time, it was to be named in honour of Pierre Curie, but was considered at least by some to be in honour of Marie Skło ...
(37 kBq) or 0.29 microgram
In the metric system, a microgram or microgramme is a unit of mass equal to one millionth () of a gram. The unit symbol is μg according to the International System of Units (SI); the recommended symbol in the United States and United Kingdom wh ...
. This amount declines slowly as the americium decays into neptunium
Neptunium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactivity, radioactive actinide metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element. It is named after Neptune, the planet beyond Uranus in the Solar Syste ...
-237, a different transuranic element with a much longer half-life (about 2.14 million years). With its half-life of 432.2 years, the americium in a smoke detector includes about 3% neptunium
Neptunium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactivity, radioactive actinide metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element. It is named after Neptune, the planet beyond Uranus in the Solar Syste ...
after 19 years, and about 5% after 32 years. The radiation passes through an ionization chamber
The ionization chamber is the simplest type of gaseous ionisation detector, and is widely used for the detection and measurement of many types of ionizing radiation, including X-rays, gamma rays, alpha particles and beta particles. Conventionall ...
, an air-filled space between two electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or a gas). In electrochemical cells, electrodes are essential parts that can consist of a varie ...
s, and permits a small, constant current
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (hydr ...
between the electrodes. Any smoke that enters the chamber absorbs the alpha particles, which reduces the ionization and affects this current, triggering the alarm. Compared to the alternative optical smoke detector, the ionization smoke detector is cheaper and can detect particles which are too small to produce significant light scattering; however, it is more prone to false alarms
A false alarm, also called a nuisance alarm, is the deceptive or erroneous report of an emergency, causing unnecessary panic and/or bringing resources (such as emergency services) to a place where they are not needed. False alarms may occur with ...
.Bukowski, R. W. ''et al''. (2007Performance of Home Smoke Alarms Analysis of the Response of Several Available Technologies in Residential Fire Settings
, NIST Technical Note 1455-1
Radionuclide
As 241Am has a roughly similar half-life to 238Pu (432.2 years vs. 87 years), it has been proposed as an active element ofradioisotope thermoelectric generator
A radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG, RITEG), or radioisotope power system (RPS), is a type of nuclear battery that uses an array of thermocouples to convert the Decay heat, heat released by the decay of a suitable radioactive material i ...
s, for example in spacecraft.Basic elements of static RTGs, G.L. Kulcinski, NEEP 602 Course Notes (Spring 2000), Nuclear Power in Space, University of Wisconsin Fusion Technology Institute (see last page) Although americium produces less heat and electricity – the power yield is 114.7 mW/g for 241Am and 6.31 mW/g for 243Am (cf. 390 mW/g for 238Pu) – and its radiation poses more threat to humans owing to neutron emission, the
European Space Agency
The European Space Agency (ESA) is a 23-member International organization, international organization devoted to space exploration. With its headquarters in Paris and a staff of around 2,547 people globally as of 2023, ESA was founded in 1975 ...
is considering using americium for its space probes.
Another proposed space-related application of americium is a fuel for space ships with nuclear propulsion. It relies on the very high rate of nuclear fission of 242mAm, which can be maintained even in a micrometer-thick foil. Small thickness avoids the problem of self-absorption of emitted radiation. This problem is pertinent to uranium or plutonium rods, in which only surface layers provide alpha-particles. The fission products of 242mAm can either directly propel the spaceship or they can heat a thrusting gas. They can also transfer their energy to a fluid and generate electricity through a magnetohydrodynamic generator
A magnetohydrodynamic generator (MHD generator) is a magnetohydrodynamic converter that transforms thermal energy and kinetic energy directly into electricity. An MHD generator, like a conventional generator, relies on moving a conductor through ...
.
One more proposal which utilizes the high nuclear fission rate of 242mAm is a nuclear battery. Its design relies not on the energy of the emitted by americium alpha particles, but on their charge, that is the americium acts as the self-sustaining "cathode". A single 3.2 kg 242mAm charge of such battery could provide about 140 kW of power over a period of 80 days. Even with all the potential benefits, the current applications of 242mAm are as yet hindered by the scarcity and high price of this particular nuclear isomer
A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus, in which one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) occupy excited state levels (higher energy levels). "Metastable" describes nuclei whose excited states have Half-life, half-lives of ...
.
In 2019, researchers at the UK National Nuclear Laboratory
The United Kingdom National Nuclear Laboratory (UKNNL, formerly National Nuclear Laboratory and earlier Nexia Solutions) is a UK government owned and operated nuclear services technology provider covering the whole of the nuclear fuel cycle. It ...
and the University of Leicester
The University of Leicester ( ) is a public university, public research university based in Leicester, England. The main campus is south of the city centre, adjacent to Victoria Park, Leicester, Victoria Park. The university's predecessor, Univ ...
demonstrated the use of heat generated by americium to illuminate a small light bulb. This technology could lead to systems to power missions with durations up to 400 years into interstellar space, where solar panels do not function.
Neutron source
The oxide of 241Am pressed withberyllium
Beryllium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a steel-gray, hard, strong, lightweight and brittle alkaline earth metal. It is a divalent element that occurs naturally only in combination with ...
is an efficient neutron source
A neutron source is any device that emits neutrons, irrespective of the mechanism used to produce the neutrons. Neutron sources are used in physics, engineering, medicine, nuclear weapons, petroleum exploration, biology, chemistry, and nuclear p ...
. Here americium acts as the alpha source, and beryllium produces neutrons owing to its large cross-section for the (α,n) nuclear reaction:
: neutron probe
A neutron probe is a device used to measure the quantity of water present in soil.
A typical neutron probe contains a pellet of americium-241 and beryllium. The alpha particles emitted by the decay of the americium collide with the light beryllium ...
– a device used to measure the quantity of water present in soil, as well as moisture/density for quality control in highway construction. 241Am neutron sources are also used in well logging applications, as well as in neutron radiography
Neutron imaging is the process of making an image with neutrons. The resulting image is based on the neutron attenuation properties of the imaged object. The resulting images have much in common with industrial X-ray images, but since the image i ...
, tomography and other radiochemical investigations.
Production of other elements
Americium is a starting material for the production of other transuranic elements andtransactinide
Superheavy elements, also known as transactinide elements, transactinides, or super-heavy elements, or superheavies for short, are the chemical elements with atomic number greater than 104. The superheavy elements are those beyond the actinides in ...
s – for example, 82.7% of 242Am decays to 242Cm and 17.3% to 242Pu. In the nuclear reactor, 242Am is also up-converted by neutron capture to 243Am and 244Am, which transforms by β-decay to 244Cm:
: einsteinium
Einsteinium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Es and atomic number 99 and is a member of the actinide series and the seventh transuranium element.
Einsteinium was discovered as a component of the debris of the first hydrogen bomb ...
) or 260Db (dubnium
Dubnium is a synthetic element, synthetic chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Db and atomic number 105. It is highly radioactive: the most stable known isotopes of dubnium, isotope, dubnium-268, has a half-life of about 16 hours. ...
), respectively. Furthermore, the element berkelium
Berkelium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Bk and atomic number 97. It is a member of the actinide and transuranium element series. It is named after the city of Berkeley, California, the location of the Lawrence Berkeley National ...
(243Bk isotope) had been first intentionally produced and identified by bombarding 241Am with alpha particles, in 1949, by the same Berkeley group, using the same 60-inch cyclotron. Similarly, nobelium
Nobelium is a synthetic element, synthetic chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol No and atomic number 102. It is named after Alfred Nobel, the inventor of dynamite and benefactor of science. A radioactive metal, it is the tenth transura ...
was produced at the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research
The Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (JINR, ), in Dubna, Moscow Oblast (110 km north of Moscow), Russia, is an international research center for nuclear sciences, with 5,500 staff members including 1,200 researchers holding over 1,000 ...
, Dubna
Dubna ( rus, Дубна́, p=dʊbˈna) is a town in Moscow Oblast, Russia. It has a status of '' naukograd'' (i.e. town of science), being home to the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, an international nuclear physics research center and o ...
, Russia, in 1965 in several reactions, one of which included irradiation of 243Am with 15N ions. Besides, one of the synthesis reactions for lawrencium
Lawrencium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Lr (formerly Lw) and atomic number 103. It is named after Ernest Lawrence, inventor of the cyclotron, a device that was used to discover many artificial radioactive elements. A radioactiv ...
, discovered by scientists at Berkeley and Dubna, included bombardment of 243Am with 18O.
Spectrometer
Americium-241 has been used as a portable source of both gamma rays and alpha particles for a number of medical and industrial uses. The 59.5409 keV gamma ray emissions from 241Am in such sources can be used for indirect analysis of materials inradiography
Radiography is an imaging technology, imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical ("diagnostic" radiog ...
and X-ray fluorescence
X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is the emission of characteristic "secondary" (or fluorescent) X-rays from a material that has been excited by being bombarded with high-energy X-rays or gamma rays. The phenomenon is widely used for elemental analysis ...
spectroscopy, as well as for quality control in fixed nuclear density gauge
Nuclear densitometry is a technique used in civil construction and the petroleum industry, as well as for mining and archaeology purposes, to measure the density and inner structure of the test material. The processes uses a nuclear density gauge, ...
s and nuclear densometer
Nuclear densitometry is a technique used in civil construction and the petroleum industry, as well as for mining and archaeology purposes, to measure the density and inner structure of the test material. The processes uses a nuclear density gauge, ...
s. For example, the element has been employed to gauge glass
Glass is an amorphous (non-crystalline solid, non-crystalline) solid. Because it is often transparency and translucency, transparent and chemically inert, glass has found widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in window pane ...
thickness to help create flat glass. Americium-241 is also suitable for calibration of gamma-ray spectrometers in the low-energy range, since its spectrum consists of nearly a single peak and negligible Compton continuum (at least three orders of magnitude lower intensity). Americium-241 gamma rays were also used to provide passive diagnosis of thyroid function. This medical application is however obsolete.
Health concerns
As a highly radioactive element, americium and its compounds must be handled only in an appropriate laboratory under special arrangements. Although most americium isotopes predominantly emit alpha particles which can be blocked by thin layers of common materials, many of the daughter products emit gamma-rays and neutrons which have a long penetration depth. If consumed, most of the americium is excreted within a few days, with only 0.05% absorbed in the blood, of which roughly 45% goes to theliver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
and 45% to the bones, and the remaining 10% is excreted. The uptake to the liver depends on the individual and increases with age. In the bones, americium is first deposited over Cortex (anatomy), cortical and trabecular surfaces and slowly redistributes over the bone with time. The biological half-life of 241Am is 50 years in the bones and 20 years in the liver, whereas in the gonads (testicles and ovaries) it remains permanently; in all these organs, americium promotes formation of cancer cells as a result of its radioactivity.
Americium often enters landfills from discarded smoke detector
A smoke detector is a device that senses smoke, typically as an indicator of fire. Smoke detectors/alarms are usually housed in plastic enclosures, typically shaped like a disk about in diameter and thick, but shape and size vary. Smoke can be ...
s. The rules associated with the disposal of smoke detectors are relaxed in most jurisdictions. In 1994, 17-year-old David Hahn extracted the americium from about 100 smoke detectors in an attempt to build a breeder nuclear reactor.Ken SilversteinThe Radioactive Boy Scout: When a teenager attempts to build a breeder reactor
''Harper's Magazine'', November 1998 There have been a few cases of exposure to americium, the worst case being that of Chemical technologist, chemical operations technician Harold McCluskey, who at the age of 64 was exposed to 500 times the occupational standard for americium-241 as a result of an explosion in his lab. McCluskey died at the age of 75 of unrelated pre-existing disease.
See also
* Actinides in the environment * :Americium compoundsNotes
References
Bibliography
* * Penneman, R. A. and Keenan T. KThe radiochemistry of americium and curium
University of California, Los Alamos, California, 1960 *
Further reading
* ''Nuclides and Isotopes – 14th Edition'', GE Nuclear Energy, 1989. * *External links
at ''The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham)
ATSDR – Public Health Statement: Americium
{{Authority control Americium, Chemical elements Chemical elements with double hexagonal close-packed structure Actinides Carcinogens Synthetic elements