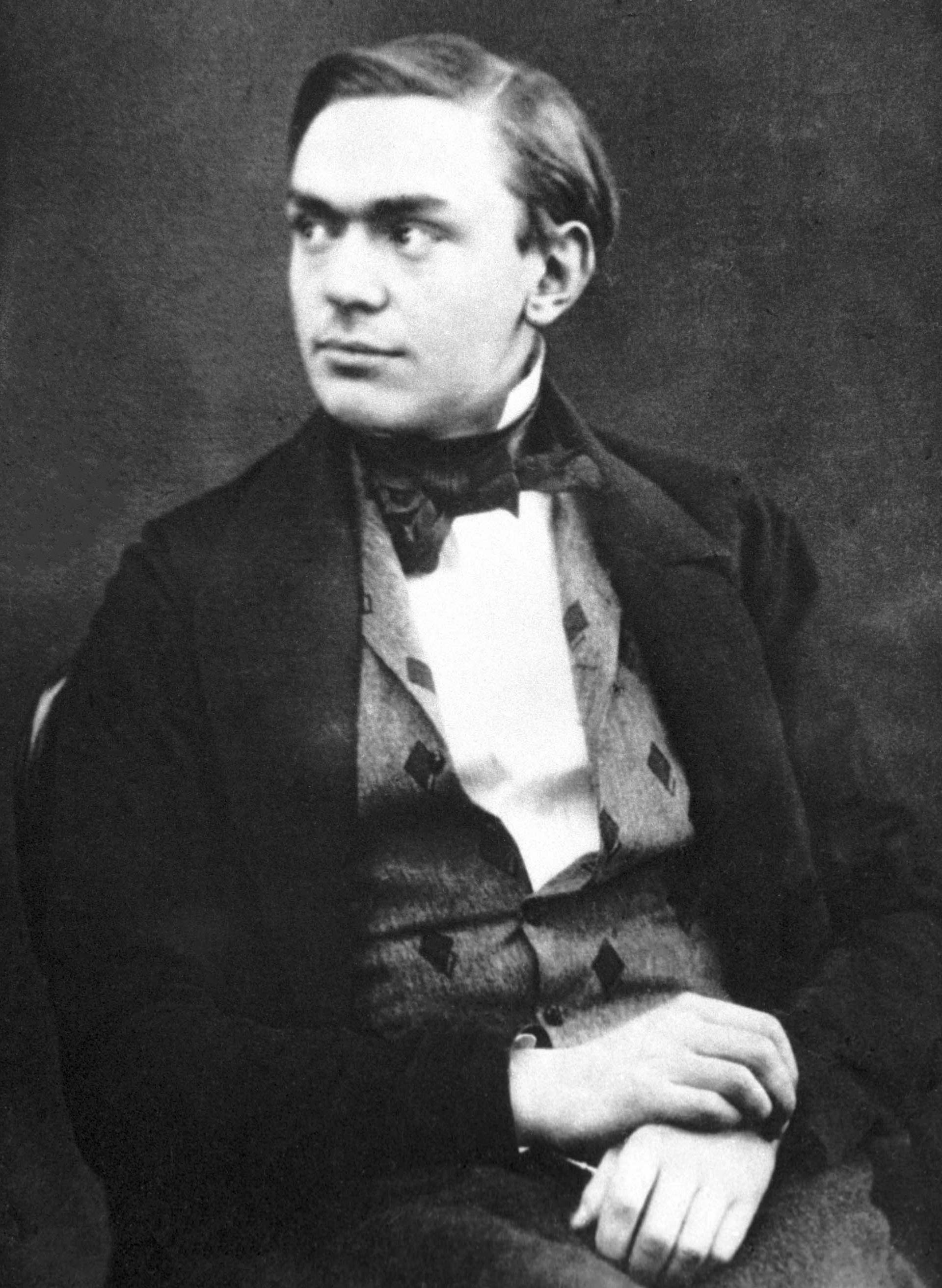|
Nobelium
Nobelium is a synthetic element, synthetic chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol No and atomic number 102. It is named after Alfred Nobel, the inventor of dynamite and benefactor of science. A radioactive metal, it is the tenth transuranium element, the second transfermium, and is the penultimate member of the actinide series. Like all elements with atomic number over 100, nobelium can only be produced in particle accelerators by bombarding lighter elements with charged particles. A total of twelve isotopes of nobelium, nobelium isotopes are known to exist; the most stable is 259No with a half-life of 58 minutes, but the shorter-lived 255No (half-life 3.1 minutes) is most commonly used in chemistry because it can be produced on a larger scale. Chemistry experiments have confirmed that nobelium behaves as a heavier Homologous series, homolog to ytterbium in the periodic table. The chemical properties of nobelium are not completely known: they are mostly only known in aque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotopes Of Nobelium
Nobelium (102No) is a synthetic element, and thus a standard atomic weight cannot be given. Like all synthetic elements, it has no stable isotopes. The first isotope to be synthesized (and correctly identified) was 254No in 1966. There are fourteen known radioisotopes, which are 248No to 260No and 262No, and many nuclear isomer, isomers. The longest-lived isotope is 259No with a half-life of 58 minutes. The longest-lived isomer is 251m1No with a half-life of 1.02 seconds. List of isotopes , -id=Nobelium-248 , 248No , style="text-align:right" , 102 , style="text-align:right" , 146 , 248.08662(24)# , 1.7 μs , IT , 251No , 17/2−# , - , rowspan=3, 252No , rowspan=3 style="text-align:right" , 102 , rowspan=3 style="text-align:right" , 150 , rowspan=3, 252.088966(10) , rowspan=3, , α (70%) , 248Fm , rowspan=3, 0+ , - , SF (29%) , (various) , - , β+ (0.8%) , 252Md , -id=Nobelium-252m1 , style="text-indent:1em" , 252m1No , colspan="3" style="tex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actinides
The actinide () or actinoid () series encompasses at least the 14 metallic chemical elements in the 5f series, with atomic numbers from 89 to 102, actinium through nobelium. Number 103, lawrencium, is also generally included despite being part of the 6d transition series. The actinide series derives its name from the first element in the series, actinium. The informal chemical symbol An is used in general discussions of actinide chemistry to refer to any actinide. The 1985 IUPAC ''Red Book'' recommends that ''actinoid'' be used rather than ''actinide'', since the suffix ''-ide'' normally indicates a negative ion. However, owing to widespread current use, ''actinide'' is still allowed. Actinium through nobelium are f-block elements, while lawrencium is a d-block element and a transition metal. The series mostly corresponds to the filling of the 5f electron shell, although as isolated atoms in the ground state many have anomalous configurations involving the filling of the 6d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discovery Of The Chemical Elements
The discoveries of the 118 chemical elements known to exist as of 2025 are presented here in chronological order. The elements are listed generally in the order in which each was first defined as the pure element, as the exact date of discovery of most elements cannot be accurately determined. There are plans to synthesize more elements, and it is not known how many elements are possible. Each element's list of elements by name, name, atomic number, year of first report, name of the discoverer, and notes related to the discovery are listed. Periodic table of elements Graphical timeline ImageSize = width:1600 height:120 # barincrement:0 PlotArea = top:70 bottom:30 right:10 left:10 AlignBars = justify Colors = id:gray1 value:gray(0.85) legend:Independent id:gray2 value:gray(0.95) DateFormat = yyyy Period = from:1665 till:2025 TimeAxis = orientation:horizontal ScaleMajor = unit:year increment:10 start:1670 ScaleMinor = unit:year increment:1 start:1665 TextData = tex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
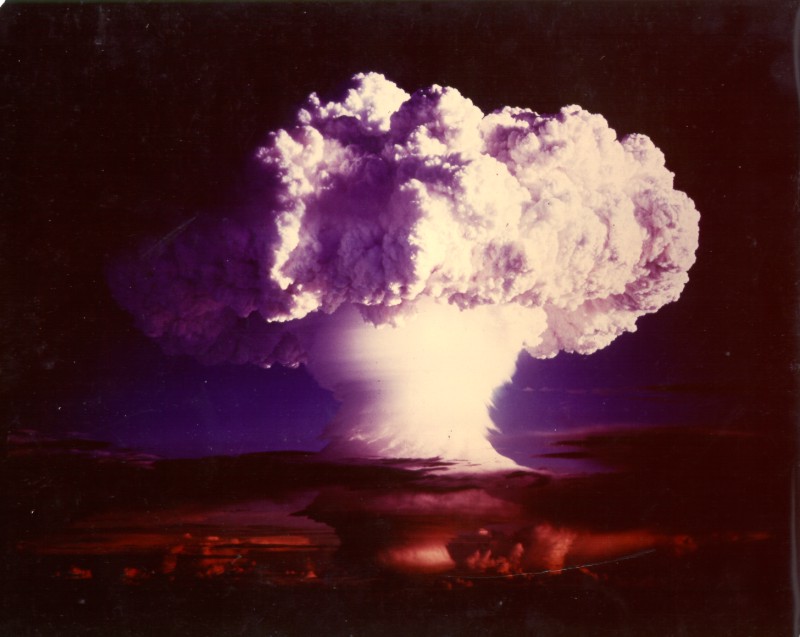
Fermium
Fermium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Fm and atomic number 100. It is an actinide and the heaviest element that can be formed by neutron bombardment of lighter elements, and hence the last element that can be prepared in macroscopic quantities, although pure fermium metal has not been prepared yet. A total of 20 isotopes are known, with 257Fm being the longest-lived with a half-life of 100.5 days. Fermium was discovered in the debris of the first hydrogen bomb explosion in 1952, and named after Enrico Fermi, one of the pioneers of nuclear physics. Its chemistry is typical for the late actinides, with a preponderance of the +3 oxidation state but also an accessible +2 oxidation state. Owing to the small amounts of produced fermium and all of its isotopes having relatively short half-lives, there are currently no uses for it outside basic scientific research. Discovery Fermium was first discovered in the fallout from the 'Ivy Mike' nuclear test (1 Nove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Nobel
Alfred Bernhard Nobel ( ; ; 21 October 1833 – 10 December 1896) was a Swedish chemist, inventor, engineer, and businessman. He is known for inventing dynamite, as well as having bequeathed his fortune to establish the Nobel Prizes. He also made several other important contributions to science, holding 355 patents during his life. Born into the prominent Nobel family in Stockholm, Nobel displayed an early aptitude for science and learning, particularly in chemistry and languages; he became fluent in six languages and filed his first patent at the age of 24. He embarked on many business ventures with his family, most notably owning the company Bofors, which was an iron and steel producer that he had developed into a major manufacturer of cannons and other armaments. Nobel's most famous invention, dynamite, was an explosive made using nitroglycerin, which was patented in 1867. He further invented gelignite in 1875 and ballistite in 1887. Upon his death, Nobel donated his fortun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Element Naming Controversy
The currently accepted names and symbols of the chemical elements are determined by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), usually following recommendations by the recognized discoverers of each element. However, the names of several elements have been the subject of controversies until IUPAC established an official name. In most cases, the controversy was due to a priority dispute as to who first found conclusive evidence for the existence of an element, or as to what evidence was in fact conclusive. Element 23 (Vanadium V) Vanadium (named after Vanadís, another name for Freyja, the Scandinavian goddess of fertility) was originally discovered by Andrés Manuel del Río (a Spanish-born Mexican mineralogist) in Mexico City in 1801. He discovered the element after being sent a sample of "brown lead" ore (''plomo pardo de Zimapán'', now named vanadinite). Through experimentation, he found it to form salts with a wide variety of colors, so he named the eleme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Symbol
Chemical symbols are the abbreviations used in chemistry, mainly for chemical elements; but also for functional groups, chemical compounds, and other entities. Element symbols for chemical elements, also known as atomic symbols, normally consist of one or two letters from the Latin alphabet and are written with the first letter capitalised. History Earlier symbols for chemical elements stem from classical Latin and Greek language, Greek words. For some elements, this is because the material was known in ancient times, while for others, the name is a more recent invention. For example, Pb is the symbol for lead (''plumbum'' in Latin); Hg is the symbol for mercury (element), mercury (''hydrargyrum'' in Greek); and He is the symbol for helium (a Neo-Latin name) because helium was not known in ancient Roman times. Some symbols come from other sources, like W for tungsten (''Wolfram'' in German) which was not known in Roman times. A three-letter Systematic element name, temporary sym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Element
A synthetic element is a known chemical element that does not occur naturally on Earth: it has been created by human manipulation of fundamental particles in a nuclear reactor, a particle accelerator, or the explosion of an atomic bomb; thus, it is called "synthetic", "artificial", or "man-made". The synthetic elements are those with atomic numbers 95–118, as shown in purple on the accompanying periodic table: these 24 elements were first created between 1944 and 2010. The mechanism for the creation of a synthetic element is to force additional protons into the Atomic nucleus, nucleus of an element with an atomic number lower than 95. All known (see: Island of stability) synthetic elements are unstable, but they radioactive decay, decay at widely varying rates; the half-lives of their longest-lived isotopes range from microseconds to millions of years. Five more elements that were first created artificially are strictly speaking not ''synthetic'' because they were later found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transuranium Element
The transuranium (or transuranic) elements are the chemical elements with atomic number greater than 92, which is the atomic number of uranium. All of them are radioactively unstable and decay into other elements. Except for neptunium and plutonium, which have been found in trace amounts in nature, none occur naturally on Earth and they are synthetic. Overview Of the elements with atomic numbers 1 to 92, most can be found in nature, having stable isotopes (such as oxygen) or very long-lived radioisotopes (such as uranium), or existing as common decay products of the decay of uranium and thorium (such as radon). The exceptions are technetium, promethium, astatine, and francium; all four occur in nature, but only in very minor branches of the uranium and thorium decay chains, and thus all save francium were first discovered by synthesis in the laboratory rather than in nature. All elements with higher atomic numbers have been first discovered in the laboratory, with neptunium a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Accelerator
A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel electric charge, charged particles to very high speeds and energies to contain them in well-defined particle beam, beams. Small accelerators are used for fundamental research in particle physics. Accelerators are also used as synchrotron light sources for the study of condensed matter physics. Smaller particle accelerators are used in a wide variety of applications, including particle therapy for oncology, oncological purposes, Isotopes in medicine, radioisotope production for medical diagnostics, Ion implantation, ion implanters for the manufacturing of Semiconductor, semiconductors, and Accelerator mass spectrometry, accelerator mass spectrometers for measurements of rare isotopes such as radiocarbon. Large accelerators include the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider at Brookhaven National Laboratory in New York, and the largest accelerator, the Large Hadron Collider near Geneva, Switzerland, operated b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of its atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei composed of protons and neutrons, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every atom of that element. The atomic number can be used to uniquely identify ordinary chemical elements. In an ordinary uncharged atom, the atomic number is also equal to the number of electrons. For an ordinary atom which contains protons, neutrons and electrons, the sum of the atomic number ''Z'' and the neutron number ''N'' gives the atom's atomic mass number ''A''. Since protons and neutrons have approximately the same mass (and the mass of the electrons is negligible for many purposes) and the mass defect of the nucleon binding is always small compared to the nucleon mass, the atomic mass of any atom, when expressed in daltons (making a quantity called the " relative isotopic mass"), is within 1% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |