Adipositas on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a
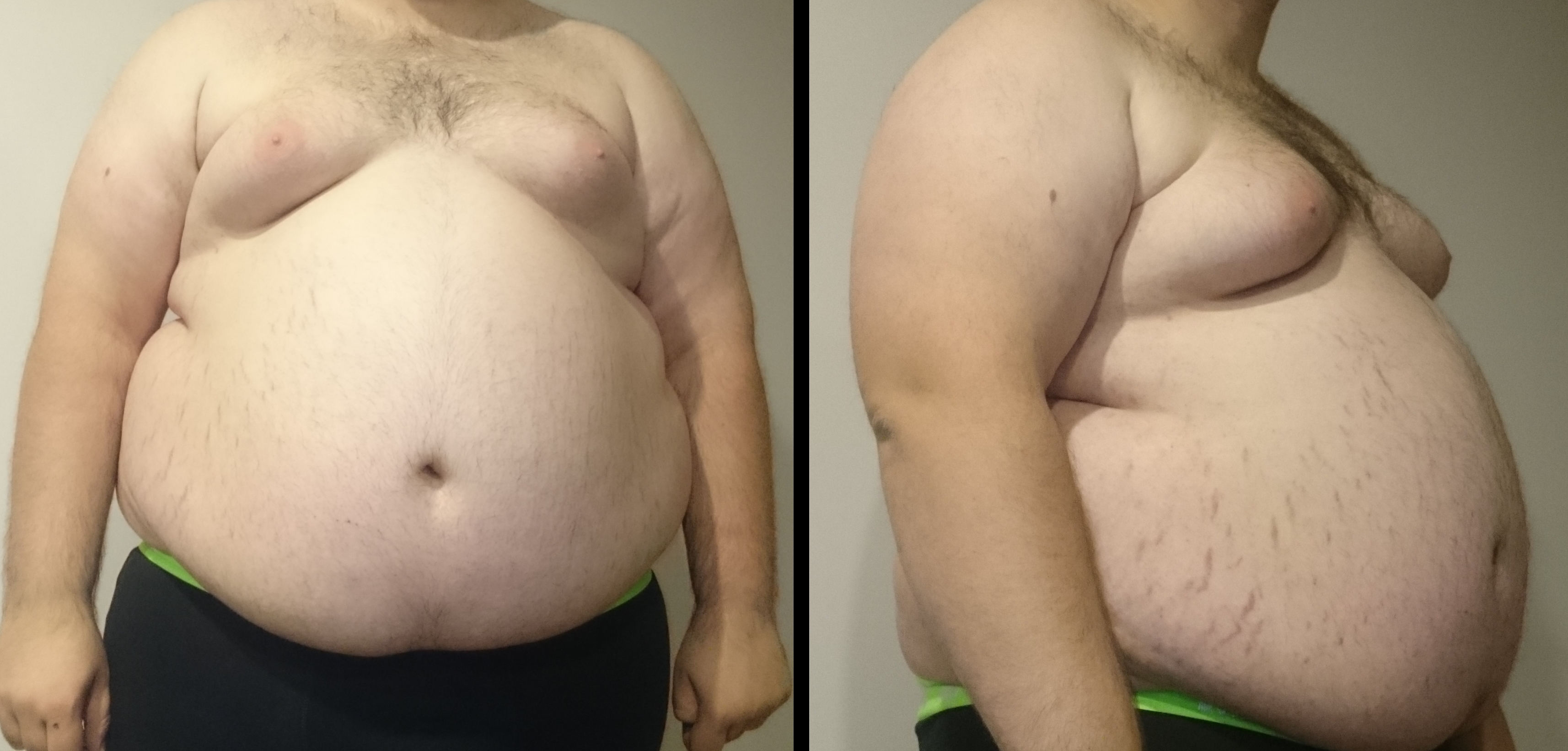 Obesity is typically defined as a substantial accumulation of
Obesity is typically defined as a substantial accumulation of
 Excess appetite for palatable, high-calorie food (especially fat, sugar, and certain animal proteins) is seen as the primary factor driving obesity worldwide, likely because of imbalances in
Excess appetite for palatable, high-calorie food (especially fat, sugar, and certain animal proteins) is seen as the primary factor driving obesity worldwide, likely because of imbalances in  The widespread availability of
The widespread availability of
 While genetic influences are important to understanding obesity, they cannot completely explain the dramatic increase seen within specific countries or globally. Though it is accepted that energy consumption in excess of energy expenditure leads to increases in body weight on an individual basis, the cause of the shifts in these two factors on the societal scale is much debated. There are a number of theories as to the cause but most believe it is a combination of various factors.
The correlation between
While genetic influences are important to understanding obesity, they cannot completely explain the dramatic increase seen within specific countries or globally. Though it is accepted that energy consumption in excess of energy expenditure leads to increases in body weight on an individual basis, the cause of the shifts in these two factors on the societal scale is much debated. There are a number of theories as to the cause but most believe it is a combination of various factors.
The correlation between
 Two distinct but related processes are considered to be involved in the development of obesity: sustained positive energy balance (energy intake exceeding energy expenditure) and the resetting of the body weight "set point" at an increased value. The second process explains why finding effective obesity treatments has been difficult. While the underlying biology of this process still remains uncertain, research is beginning to clarify the mechanisms.
At a biological level, there are many possible pathophysiology, pathophysiological mechanisms involved in the development and maintenance of obesity. This field of research had been almost unapproached until the leptin gene was discovered in 1994 by J. M. Friedman's laboratory. While leptin and ghrelin are produced peripherally, they control appetite through their actions on the central nervous system. In particular, they and other appetite-related hormones act on the hypothalamus, a region of the brain central to the regulation of food intake and energy expenditure. There are several circuits within the hypothalamus that contribute to its role in integrating appetite, the melanocortin pathway being the most well understood. The circuit begins with an area of the hypothalamus, the arcuate nucleus, that has outputs to the lateral hypothalamus (LH) and ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH), the brain's feeding and satiety centers, respectively.
The arcuate nucleus contains two distinct groups of neurons. The first group coexpresses neuropeptide Y (NPY) and agouti-related peptide (AgRP) and has stimulatory inputs to the LH and inhibitory inputs to the VMH. The second group coexpresses pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) and cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) and has stimulatory inputs to the VMH and inhibitory inputs to the LH. Consequently, NPY/AgRP neurons stimulate feeding and inhibit satiety, while POMC/CART neurons stimulate satiety and inhibit feeding. Both groups of arcuate nucleus neurons are regulated in part by leptin. Leptin inhibits the NPY/AgRP group while stimulating the POMC/CART group. Thus a deficiency in leptin signaling, either via leptin deficiency or leptin resistance, leads to overfeeding and may account for some genetic and acquired forms of obesity.
Two distinct but related processes are considered to be involved in the development of obesity: sustained positive energy balance (energy intake exceeding energy expenditure) and the resetting of the body weight "set point" at an increased value. The second process explains why finding effective obesity treatments has been difficult. While the underlying biology of this process still remains uncertain, research is beginning to clarify the mechanisms.
At a biological level, there are many possible pathophysiology, pathophysiological mechanisms involved in the development and maintenance of obesity. This field of research had been almost unapproached until the leptin gene was discovered in 1994 by J. M. Friedman's laboratory. While leptin and ghrelin are produced peripherally, they control appetite through their actions on the central nervous system. In particular, they and other appetite-related hormones act on the hypothalamus, a region of the brain central to the regulation of food intake and energy expenditure. There are several circuits within the hypothalamus that contribute to its role in integrating appetite, the melanocortin pathway being the most well understood. The circuit begins with an area of the hypothalamus, the arcuate nucleus, that has outputs to the lateral hypothalamus (LH) and ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH), the brain's feeding and satiety centers, respectively.
The arcuate nucleus contains two distinct groups of neurons. The first group coexpresses neuropeptide Y (NPY) and agouti-related peptide (AgRP) and has stimulatory inputs to the LH and inhibitory inputs to the VMH. The second group coexpresses pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) and cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) and has stimulatory inputs to the VMH and inhibitory inputs to the LH. Consequently, NPY/AgRP neurons stimulate feeding and inhibit satiety, while POMC/CART neurons stimulate satiety and inhibit feeding. Both groups of arcuate nucleus neurons are regulated in part by leptin. Leptin inhibits the NPY/AgRP group while stimulating the POMC/CART group. Thus a deficiency in leptin signaling, either via leptin deficiency or leptin resistance, leads to overfeeding and may account for some genetic and acquired forms of obesity.
 Obesity can lead to social stigmatization and disadvantages in employment. When compared to their ideal weight counterparts, workers with obesity, on average have higher rates of absenteeism from work and take more disability leave, thus increasing costs for employers and decreasing productivity. A study examining Duke University employees found that people with a BMI over 40 kg/m2 filed twice as many workers' compensation claims as those whose BMI was 18.5–24.9 kg/m2. They also had more than 12 times as many lost work days. The most common injuries in this group were due to falls and lifting, thus affecting the lower extremities, wrists or hands, and backs. The Alabama State Employees' Insurance Board approved a controversial plan to charge obese workers $25 a month for health insurance that would otherwise be free unless they take steps to lose weight and improve their health. These measures started in January 2010 and apply to those state workers whose BMI exceeds 35 kg/m2 and who fail to make improvements in their health after one year. This becomes a Catch 22 position as many insurance companies will refuse to pay for treatment methods for workers living with obesity.
Some research shows that people with obesity are less likely to be hired for a job and are less likely to be promoted. People with obesity are also paid less than their counterparts who do not live with obesity for an equivalent job; women with obesity on average make 6% less and men with obesity make 3% less.
Specific industries, such as the airline, healthcare and food industries, have special concerns. Due to rising rates of obesity, airlines face higher fuel costs and pressures to increase seating width. In 2000, the extra weight of passengers with obesity cost airlines US$275 million. The healthcare industry has had to invest in special facilities for handling patients with class III obesity, including special lifting equipment and bariatric ambulances. Costs for restaurants are increased by litigation accusing them of causing obesity. In 2005, the US Congress discussed legislation to prevent civil lawsuits against the food industry in relation to obesity; however, it did not become law.
With the
Obesity can lead to social stigmatization and disadvantages in employment. When compared to their ideal weight counterparts, workers with obesity, on average have higher rates of absenteeism from work and take more disability leave, thus increasing costs for employers and decreasing productivity. A study examining Duke University employees found that people with a BMI over 40 kg/m2 filed twice as many workers' compensation claims as those whose BMI was 18.5–24.9 kg/m2. They also had more than 12 times as many lost work days. The most common injuries in this group were due to falls and lifting, thus affecting the lower extremities, wrists or hands, and backs. The Alabama State Employees' Insurance Board approved a controversial plan to charge obese workers $25 a month for health insurance that would otherwise be free unless they take steps to lose weight and improve their health. These measures started in January 2010 and apply to those state workers whose BMI exceeds 35 kg/m2 and who fail to make improvements in their health after one year. This becomes a Catch 22 position as many insurance companies will refuse to pay for treatment methods for workers living with obesity.
Some research shows that people with obesity are less likely to be hired for a job and are less likely to be promoted. People with obesity are also paid less than their counterparts who do not live with obesity for an equivalent job; women with obesity on average make 6% less and men with obesity make 3% less.
Specific industries, such as the airline, healthcare and food industries, have special concerns. Due to rising rates of obesity, airlines face higher fuel costs and pressures to increase seating width. In 2000, the extra weight of passengers with obesity cost airlines US$275 million. The healthcare industry has had to invest in special facilities for handling patients with class III obesity, including special lifting equipment and bariatric ambulances. Costs for restaurants are increased by litigation accusing them of causing obesity. In 2005, the US Congress discussed legislation to prevent civil lawsuits against the food industry in relation to obesity; however, it did not become law.
With the
 The principal goal of the fat acceptance movement is to decrease discrimination against people who are overweight and obese. However, some in the movement are also attempting to challenge the established relationship between obesity and negative health outcomes.
A number of organizations exist that promote the acceptance of obesity. They have increased in prominence in the latter half of the 20th century. The US-based National Association to Advance Fat Acceptance (NAAFA) was formed in 1969 and describes itself as a civil rights organization dedicated to ending size discrimination.
The International Size Acceptance Association (ISAA) is a non-governmental organization (NGO) which was founded in 1997. It has more of a global orientation and describes its mission as promoting size acceptance and helping to end weight-based discrimination. These groups often argue for the recognition of obesity as a disability under the US Americans With Disabilities Act (ADA). The American legal system, however, has decided that the potential public health costs exceed the benefits of extending this anti-discrimination law to cover obesity.
The principal goal of the fat acceptance movement is to decrease discrimination against people who are overweight and obese. However, some in the movement are also attempting to challenge the established relationship between obesity and negative health outcomes.
A number of organizations exist that promote the acceptance of obesity. They have increased in prominence in the latter half of the 20th century. The US-based National Association to Advance Fat Acceptance (NAAFA) was formed in 1969 and describes itself as a civil rights organization dedicated to ending size discrimination.
The International Size Acceptance Association (ISAA) is a non-governmental organization (NGO) which was founded in 1997. It has more of a global orientation and describes its mission as promoting size acceptance and helping to end weight-based discrimination. These groups often argue for the recognition of obesity as a disability under the US Americans With Disabilities Act (ADA). The American legal system, however, has decided that the potential public health costs exceed the benefits of extending this anti-discrimination law to cover obesity.
WHO fact sheet on obesity and overweight
{{Authority control Obesity, Bariatrics Body shape Nutrition
disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function (biology), function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical condi ...
, in which excess body fat
Adipose tissue (also known as body fat or simply fat) is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. It also contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, Blood vessel, vascular endothel ...
has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health
Health has a variety of definitions, which have been used for different purposes over time. In general, it refers to physical and emotional well-being, especially that associated with normal functioning of the human body, absent of disease, p ...
. People are classified as obese when their body mass index
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (Mass versus weight, weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the human body weight, body mass divided by the square (algebra), square of the human height, body height, and is ...
(BMI)—a person's weight divided by the square of the person's height—is over ; the range is defined as overweight
Being overweight is having more body fat than is optimally healthy. Being overweight is especially common where food supplies are plentiful and lifestyles are sedentary.
, excess weight reached epidemic proportions globally, with more than ...
. Some East Asia
East Asia is a geocultural region of Asia. It includes China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan, plus two special administrative regions of China, Hong Kong and Macau. The economies of Economy of China, China, Economy of Ja ...
n countries use lower values to calculate obesity. Obesity is a major cause of disability and is correlated with various diseases and conditions, particularly cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumati ...
s, type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent ...
, obstructive sleep apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common sleep-related breathing disorder and is characterized by recurrent episodes of complete or partial airway obstruction, obstruction of the respiratory tract#Upper respiratory tract, upper airway lea ...
, certain types of cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
, and osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of articular cartilage, joint cartilage and underlying bone. A form of arthritis, it is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the world, affect ...
.
Obesity has individual, socioeconomic, and environmental causes. Some known causes are diet
Diet may refer to:
Food
* Diet (nutrition), the sum of the food consumed by an organism or group
* Dieting, the deliberate selection of food to control body weight or nutrient intake
** Diet food, foods that aid in creating a diet for weight loss ...
, low physical activity, automation
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, mainly by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machine ...
, urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation in British English) is the population shift from Rural area, rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. ...
, genetic susceptibility
Public health genomics is the use of genomics information to benefit public health. This is visualized as more effective preventive care and disease treatments with better specificity, tailored to the genetic makeup of each patient. According to ...
, medications
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to medical diagnosis, diagnose, cure, treat, or preventive medicine, prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmaco ...
, mental disorder
A mental disorder, also referred to as a mental illness, a mental health condition, or a psychiatric disability, is a behavioral or mental pattern that causes significant distress or impairment of personal functioning. A mental disorder is ...
s, economic policies
''Economic Policy'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal published by Oxford Academic on behalf of the Centre for Economic Policy Research, the Center for Economic Studies (University of Munich), and the Paris School of Economics. The jo ...
, endocrine disorders, and exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals.
While many people living with obesity attempt to lose weight and are often successful, maintaining weight loss long-term is rare. Obesity prevention requires a complex approach, including interventions at medical, societal, community, family, and individual levels. Changes to diet
Diet may refer to:
Food
* Diet (nutrition), the sum of the food consumed by an organism or group
* Dieting, the deliberate selection of food to control body weight or nutrient intake
** Diet food, foods that aid in creating a diet for weight loss ...
as well as exercising are the main treatments recommended by health professionals. Diet quality can be improved by reducing the consumption of energy-dense foods, such as those high in fat or sugars, and by increasing the intake of dietary fiber
Dietary fiber (fibre in English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English) or roughage is the portion of plant-derived food that cannot be completely broken down by human digestive enzymes. Dietary fibers are diverse in chemical co ...
. The World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
stresses that the disease is a societal responsibility and that these dietary choices should be made the most available, affordable, and accessible options. Medications
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to medical diagnosis, diagnose, cure, treat, or preventive medicine, prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmaco ...
can be used, along with a suitable diet, to reduce appetite or decrease fat absorption. If diet, exercise, and medication are not effective, a gastric balloon
A gastric balloon, also known as an intragastric balloon (IGB) or a stomach balloon, is an inflatable medical device that is temporarily placed into the stomach to help reduce weight. It is designed to help provide weight loss when diet and exe ...
or surgery
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery s ...
may be performed to reduce stomach volume or length of the intestines, leading to feeling full earlier, or a reduced ability to absorb nutrients from food. Many do not realize that metabolic surgery is not only about reducing intake, it has also been shown to alter gut hormones for a period of time.
Obesity is a leading preventable cause of death worldwide, with increasing rates in adults and children
A child () is a human being between the stages of childbirth, birth and puberty, or between the Development of the human body, developmental period of infancy and puberty. The term may also refer to an unborn human being. In English-speaking ...
. In 2022, over 1 billion people lived with obesity worldwide (879 million adults and 159 million children), representing more than a double of adult cases (and four times higher than cases among children) registered in 1990. Obesity is more common in women than in men. Today, obesity is stigmatized
Stigma, originally referring to the visible marking of people considered inferior, has evolved to mean a negative perception or sense of disapproval that a society places on a group or individual based on certain characteristics such as their ...
in most of the world. Conversely, some cultures, past and present, have a favorable view of obesity, seeing it as a symbol of wealth and fertility. The World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
, the US, Canada, Japan, Portugal, Germany, the European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the two legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and informally as the Council of Ministers), it ...
and medical societies, e.g. the American Medical Association
The American Medical Association (AMA) is an American professional association and lobbying group of physicians and medical students. This medical association was founded in 1847 and is headquartered in Chicago, Illinois. Membership was 271,660 ...
, classify obesity as a disease. Others, such as the UK, do not.
Classification
body fat
Adipose tissue (also known as body fat or simply fat) is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. It also contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, Blood vessel, vascular endothel ...
that could impact health. Medical organizations tend to classify people living with obesity as based on body mass index
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (Mass versus weight, weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the human body weight, body mass divided by the square (algebra), square of the human height, body height, and is ...
(BMI) – a ratio of a person's weight in kilogram
The kilogram (also spelled kilogramme) is the base unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI), equal to one thousand grams. It has the unit symbol kg. The word "kilogram" is formed from the combination of the metric prefix kilo- (m ...
s to the square
In geometry, a square is a regular polygon, regular quadrilateral. It has four straight sides of equal length and four equal angles. Squares are special cases of rectangles, which have four equal angles, and of rhombuses, which have four equal si ...
of their height in meter
The metre (or meter in US spelling; symbol: m) is the base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI). Since 2019, the metre has been defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of of ...
s. For adults, the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
(WHO) defines "overweight
Being overweight is having more body fat than is optimally healthy. Being overweight is especially common where food supplies are plentiful and lifestyles are sedentary.
, excess weight reached epidemic proportions globally, with more than ...
" as a BMI 25 or higher, and "obesity" as a BMI 30 or higher. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
(CDC) further subdivides obesity based on BMI, with a BMI 30 to 35 called class 1 obesity; 35 to 40, class 2 obesity; and 40+, class 3 obesity.
For children, obesity measures take age into consideration along with height and weight. For children aged 5–19, the WHO defines obesity as a BMI two standard deviation
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation of the values of a variable about its Expected value, mean. A low standard Deviation (statistics), deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean ( ...
s above the median
The median of a set of numbers is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a Sample (statistics), data sample, a statistical population, population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as the “ ...
for their age (a BMI around 18 for a five-year old; around 30 for a 19-year old). For children under five, the WHO defines obesity as a weight three standard deviations above the median for their height.
Some modifications to the WHO definitions have been made by particular organizations. The surgical literature breaks down class II and III or only class III obesity into further categories whose exact values are still disputed.
* Any BMI ≥ 35 or 40 kg/m2 is ''severe obesity''.
* A BMI of ≥ 35 kg/m2 and experiencing obesity-related health conditions or ≥ 40 or 45 kg/m2 is ''morbid obesity''.
* A BMI of ≥ 45 or 50 kg/m2 is ''super obesity''.
As Asian populations develop negative health consequences at a lower BMI than Caucasians, some nations have redefined obesity; Japan has defined obesity as any BMI greater than 25 kg/m2 while China uses a BMI of greater than 28 kg/m2.; Originally printed as
The preferred obesity metric in scholarly circles is the body fat percentage
The body fat percentage of an organism is the total mass of its fat divided by its total body mass, multiplied by 100; body fat includes essential body fat and storage body fat. Essential body fat is necessary to maintain life and reproductive fu ...
(BF%) – the ratio of the total weight of person's fat to his or her body weight, and BMI is viewed merely as a way to approximate BF%. According to ''American Society of Bariatric Physicians'', levels in excess of 32% for women and 25% for men are generally considered to indicate obesity.
BMI is now viewed as outdated in numerous countries. It ignores variations between individuals in amounts of lean body mass, particularly muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
mass. Individuals involved in heavy physical labor or sports may have high BMI values despite having little fat. For example, more than half of all NFL
The National Football League (NFL) is a professional American football league in the United States. Composed of 32 teams, it is divided equally between the American Football Conference (AFC) and the National Football Conference (NFC). The N ...
players are classified as "obese" (BMI ≥ 30), and 1 in 4 are classified as "extremely obese" (BMI ≥ 35), according to the BMI metric. However, their mean body fat percentage
The body fat percentage of an organism is the total mass of its fat divided by its total body mass, multiplied by 100; body fat includes essential body fat and storage body fat. Essential body fat is necessary to maintain life and reproductive fu ...
, 14%, is well within what is considered a healthy range. Similarly, Sumo
is a form of competitive full-contact wrestling where a ''rikishi'' (wrestler) attempts to force his opponent out of a circular ring (''dohyō'') or into touching the ground with any body part other than the soles of his feet (usually by th ...
wrestlers are typically categorized by BMI as "severely obese" or "very severely obese"; but one study of college-aged Sumo wrestlers found that 40% of them were no longer categorized as obese when body fat percentage (with a cutoff of <25%) was used instead of BMI; this was attributed to their very high lean body mass.
Canada utilises BMI sparingly within their method of defining levels of obesity through use of the Edmonton Scale (for adult obesity). This scale also introduces factors such as Quality of Life, Mental Health & Mobility amongst others. In recent years, Canada chose to allow both Chile & Ireland to adapt their obesity guidelines to suit both countries' health systems. In Ireland, obesity is now defined as "a Complex, Chronic & Relapsing Disease".
Effects on health
Obesity increases a person's risk of developing various metabolic diseases,cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumati ...
, osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of articular cartilage, joint cartilage and underlying bone. A form of arthritis, it is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the world, affect ...
, Alzheimer disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems with ...
, depression, and certain types of cancer. Depending on the degree of obesity and the presence of comorbid disorders, obesity is associated with an estimated 2–20 year shorter life expectancy. High BMI is a marker of risk for, but not a direct cause of, diseases caused by diet and physical activity.
Mortality
Obesity is one of the leadingpreventable causes of death
Preventable causes of death are causes of death related to risk factors which could have been avoided. The World Health Organization has traditionally classified death according to the primary type of disease or injury. However, causes of death ...
worldwide. The mortality risk is lowest at a BMI of 20–25 kg/m2 in non-smokers and at 24–27 kg/m2 in current smokers, with risk increasing along with changes in either direction. This appears to apply in at least four continents. Other research suggests that the association of BMI and waist circumference with mortality is U- or J-shaped, while the association between waist-to-hip ratio and waist-to-height ratio
The waist-to-height ratio (WHtR, or WSR: waist-to-stature ratio) is the waist circumference divided by body height, both measured in the same units.
WHtR is a measure of the distribution of body fat. Higher values of WHtR indicate higher risk of ...
with mortality is more positive. In Asians the risk of negative health effects begins to increase between 22 and 25 kg/m2. In 2021, the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
estimated that obesity caused at least 2.8 million deaths annually. On average, obesity reduces life expectancy by six to seven years, a BMI of 30–35 kg/m2 reduces life expectancy by two to four years, while severe obesity (BMI ≥ 40 kg/m2) reduces life expectancy by ten years.
Morbidity
Obesity increases the risk of many physical and mental conditions. These comorbidities are most commonly shown inmetabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a clustering of at least three of the following five medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high serum triglycerides, and low serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
Metabolic syndro ...
, a combination of medical disorders which includes: diabetes mellitus type 2
Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent ...
, high blood pressure
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms itself. It is, however, a major ri ...
, high blood cholesterol, and high triglyceride levels. A study from the RAK Hospital found that obese people are at a greater risk of developing long COVID
Long may refer to:
Measurement
* Long, characteristic of something of great duration
* Long, characteristic of something of great length
* Longitude (abbreviation: long.), a geographic coordinate
* Longa (music), note value in early music mens ...
. The CDC has found that obesity is the single strongest risk factor for severe COVID-19 illness.
Complications may be either directly caused by obesity or indirectly related through mechanisms sharing a common cause such as a poor diet or a sedentary lifestyle
Sedentary lifestyle is a Lifestyle (social sciences), lifestyle type, in which one is physically inactive and does little or no physical movement and/or exercise. A person living a sedentary lifestyle is often sitting or lying down while enga ...
. The strength of the link between obesity and specific conditions varies. One of the strongest is the link with type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent ...
. Excess body fat underlies 64% of cases of diabetes in men and 77% of cases in women.
Health consequences fall into two broad categories: those attributable to the effects of increased fat mass (such as osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of articular cartilage, joint cartilage and underlying bone. A form of arthritis, it is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the world, affect ...
, obstructive sleep apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common sleep-related breathing disorder and is characterized by recurrent episodes of complete or partial airway obstruction, obstruction of the respiratory tract#Upper respiratory tract, upper airway lea ...
, social stigmatization) and those due to the increased number of fat cells
Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cell (biology), cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Adipocytes are derived from mesenchymal stem cells which give rise to adipocytes through ...
(diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
, cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
, cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumati ...
, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
An alcohol-free or non-alcoholic drink, also known as a temperance drink, is a version of an alcoholic drink made without alcohol, or with the alcohol removed or reduced to almost zero. These may take the form of a non-alcoholic mixed drink or n ...
). Increases in body fat alter the body's response to insulin, potentially leading to insulin resistance
Insulin resistance (IR) is a pathological response in which cells in insulin-sensitive tissues in the body fail to respond normally to the hormone insulin or downregulate insulin receptors in response to hyperinsulinemia.
Insulin is a horm ...
. Increased fat also creates a proinflammatory state, and a prothrombotic state.
Metrics of health
Newer research has focused on methods of identifying healthier obese people by clinicians, and not treating obese people as a monolithic group. Obese people who do not experience medical complications from their obesity are sometimes called '' (metabolically) healthy obese'', but the extent to which this group exists (especially among older people) is in dispute. The number of people considered ''metabolically healthy'' depends on the definition used, and there is no universally accepted definition. There are numerous obese people who have relatively few metabolic abnormalities, and a minority of obese people have no medical complications. The guidelines of theAmerican Association of Clinical Endocrinologists
The American Association of Clinical Endocrinology (AACE) is a professional community of physicians specializing in endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism. AACE's mission is elevating clinical endocrinology to improve global health. The associ ...
call for physicians to use risk stratification with obese patients when considering how to assess their risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
In 2014, the BioSHaRE– EU Healthy Obese Project (sponsored by Maelstrom Research, a team under the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre
The McGill University Health Centre (MUHC; ) is one of two major healthcare networks in the city of Montreal, Montreal, Quebec. It is affiliated with McGill University and one of the largest medical complexes in Montreal. It is the largest hospita ...
) came up with two definitions for ''healthy obesity'', one more strict and one less so:
To come up with these criteria, BioSHaRE controlled for age and tobacco use, researching how both may effect the metabolic syndrome associated with obesity, but not found to exist in the metabolically healthy obese. Other definitions of metabolically healthy obesity exist, including ones based on waist circumference rather than BMI, which is unreliable in certain individuals.
Another identification metric for health in obese people is calf strength
Strength may refer to:
Personal trait
*Physical strength, as in people or animals
*Character strengths like those listed in the Values in Action Inventory
*The exercise of willpower
Physics
* Mechanical strength, the ability to withstand ...
, which is positively correlated with physical fitness
Physical fitness is a state of health and well-being and, more specifically, the ability to perform aspects of Outline of sports, sports, occupations, and daily activities. Physical fitness is generally achieved through proper nutrition, modera ...
in obese people. Body composition
In physical fitness, body composition refers to quantifying the different components (or "compartments") of a human body. The selection of compartments varies by model but may include fat, bone, water, and muscle. Two people of the same gender, h ...
in general is hypothesized to help explain the existence of metabolically healthy obesity—the metabolically healthy obese are often found to have low amounts of ectopic fat (fat stored in tissues other than adipose tissue) despite having overall fat mass equivalent in weight to obese people with metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a clustering of at least three of the following five medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high serum triglycerides, and low serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
Metabolic syndro ...
.
Survival paradox
Although the negative health consequences of obesity in the general population are well supported by the available research evidence, health outcomes in certain subgroups seem to be improved at an increased BMI, a phenomenon known as the obesity survival paradox. The paradox was first described in 1999 in overweight and obese people undergoinghemodialysis
Hemodialysis, American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, also spelled haemodialysis, or simply ''"'dialysis'"'', is a process of filtering the blood of a person whose kidneys are not working normally. This type of Kidney dialys ...
and has subsequently been found in those with heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome caused by an impairment in the heart's ability to Cardiac cycle, fill with and pump blood.
Although symptoms vary based on which side of the heart is affected, HF ...
and peripheral artery disease
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a vascular disorder that causes abnormal narrowing of arteries other than those that supply the heart or brain. PAD can happen in any blood vessel, but it is more common in the legs than the arms.
When narr ...
(PAD).
In people with heart failure, those with a BMI between 30.0 and 34.9 had lower mortality than those with a normal weight. This has been attributed to the fact that people often lose weight as they become progressively more ill. Similar findings have been made in other types of heart disease. People with class I obesity and heart disease do not have greater rates of further heart problems than people of normal weight who also have heart disease. In people with greater degrees of obesity, however, the risk of further cardiovascular events is increased. Even after cardiac bypass surgery, no increase in mortality is seen in the overweight and obese. One study found that the improved survival could be explained by the more aggressive treatment obese people receive after a cardiac event. Another study found that if one takes into account chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by chronic respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. GOLD defines COPD as a heterogeneous lung condition characterized by chronic respiratory s ...
(COPD) in those with PAD, the benefit of obesity no longer exists.
Causes
The "a calorie is a calorie
''"A calorie is a calorie"'' is an expression used to convey the concept that sources of dietary energy are interchangeable. This concept has been subject of debate since its emergence in the early 19th century.
History
In 1883, German nutriti ...
" model of obesity posits a combination of excessive food energy
Food energy is chemical energy that animals and humans derive from food to sustain their metabolism and muscular activity.
Most animals derive most of their energy from aerobic respiration, namely combining the carbohydrates, fats, and protein ...
intake and a lack of physical activity
Physical activity is defined as any voluntary movement produced by skeletal muscles that requires energy expenditure.Global Recommendations on Physical Activity for Health, 2009. World Health Organization. Geneva, Switzerland. Accessed 13/07/2018 ...
as the cause of most cases of obesity. A limited number of cases are due primarily to genetics, medical reasons, or psychiatric illness. The satiety value
Satiety value is the degree at which food gives a human the feeling of satiety per calorie. The concept of the Satiety Value and Satiety Index was developed by Australians, Australian researcher and doctor, Susanna Holt. Highest satiety value is ex ...
shows that the feeling of satiety
Satiety ( /səˈtaɪ.ə.ti/ ''sə-TYE-ə-tee'') is a state or condition of fullness gratified beyond the point of satisfaction, the opposite of hunger. Following satiation (meal termination), satiety is a feeling of fullness lasting until the next ...
per calorie
The calorie is a unit of energy that originated from the caloric theory of heat. The large calorie, food calorie, dietary calorie, kilocalorie, or kilogram calorie is defined as the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one liter o ...
varies between food types. Increasing rates of obesity at a societal level are felt to be due to an easily accessible and palatable diet
Diet may refer to:
Food
* Diet (nutrition), the sum of the food consumed by an organism or group
* Dieting, the deliberate selection of food to control body weight or nutrient intake
** Diet food, foods that aid in creating a diet for weight loss ...
, increased reliance on cars, and mechanized manufacturing.
Some other factors have been proposed as causes towards rising rates of obesity worldwide, including insufficient sleep
Sleep deprivation, also known as sleep insufficiency or sleeplessness, is the condition of not having adequate duration and/or quality of sleep to support decent alertness, performance, and health. It can be either chronic or acute and may v ...
, endocrine disruptor
Endocrine disruptors, sometimes also referred to as hormonally active agents, endocrine disrupting chemicals, or endocrine disrupting compounds are chemicals that can interfere with endocrine (or hormonal) systems. These disruptions can cause ...
s, increased usage of certain medications (such as atypical antipsychotics
The atypical antipsychotics (AAP), also known as second generation antipsychotics (SGAs) and serotonin–dopamine antagonists (SDAs), are a group of antipsychotic drugs (antipsychotic drugs in general are also known as tranquilizers and neuro ...
), increases in ambient temperature, decreased rates of smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is combusted, and the resulting smoke is typically inhaled to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream of a person. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, whi ...
, demographic changes, increasing maternal age of first-time mothers, changes to epigenetic
In biology, epigenetics is the study of changes in gene expression that happen without changes to the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix ''epi-'' (ἐπι- "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are "on top of" or "in ...
dysregulation from the environment, increased phenotypic variance via assortative mating, social pressure to diet
Diet may refer to:
Food
* Diet (nutrition), the sum of the food consumed by an organism or group
* Dieting, the deliberate selection of food to control body weight or nutrient intake
** Diet food, foods that aid in creating a diet for weight loss ...
, among others. According to one study, factors like these may play as big of a role as excessive food energy intake and a lack of physical activity; however, the relative magnitudes of the effects of any proposed cause of obesity is varied and uncertain, as there is a general need for randomized controlled trials on humans before definitive statement can be made.
According to the Endocrine Society
The Endocrine Society is a professional, international medical organization in the field of endocrinology and metabolism, founded in 1916 as The Association for the Study of Internal Secretions. The official name of the organization was changed t ...
, there is "growing evidence suggesting that obesity is a disorder of the energy homeostasis
In biology, energy homeostasis, or the homeostatic control of energy balance, is a biological process that involves the coordinated homeostatic regulation of food intake (energy inflow) and energy expenditure (energy outflow). The human brain, p ...
system, rather than simply arising from the passive accumulation of excess weight".
Diet
1961
2001–03
Map of dietary energy availability per person per day in 1961 (left) and 2001–2003 (right) Calories per person per day (kilojoules per person per day)
 Excess appetite for palatable, high-calorie food (especially fat, sugar, and certain animal proteins) is seen as the primary factor driving obesity worldwide, likely because of imbalances in
Excess appetite for palatable, high-calorie food (especially fat, sugar, and certain animal proteins) is seen as the primary factor driving obesity worldwide, likely because of imbalances in neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotra ...
s affecting the drive to eat, as well as changes to the duodenum impacting nutrient sensing and signaling. Dietary energy supply per capita varies markedly between different regions and countries. It has also changed significantly over time. From the early 1970s to the late 1990s the average food energy
Food energy is chemical energy that animals and humans derive from food to sustain their metabolism and muscular activity.
Most animals derive most of their energy from aerobic respiration, namely combining the carbohydrates, fats, and protein ...
available per person per day (the amount of food bought) increased in all parts of the world except Eastern Europe. The United States had the highest availability with per person in 1996. This increased further in 2003 to . During the late 1990s, Europeans had per person, in the developing areas of Asia there were per person, and in sub-Saharan Africa people had per person. Total food energy consumption has been found to be related to obesity.
dietary guidelines
A healthy diet is a Diet (nutrition), diet that maintains or improves overall health. A healthy diet provides the body with essential Human nutrition, nutrition: fluid, macronutrients such as protein, micronutrients such as vitamins, and adequat ...
has done little to address the problems of overeating and poor dietary choice. From 1971 to 2000, obesity rates in the United States increased from 14.5% to 30.9%. During the same period, an increase occurred in the average amount of food energy consumed. For women, the average increase was per day ( in 1971 and in 2004), while for men the average increase was per day ( in 1971 and in 2004). Most of this extra food energy came from an increase in carbohydrate consumption rather than fat consumption. The primary sources of these extra carbohydrates are sweetened beverages, which now account for almost 25 percent of daily food energy in young adults in America, and potato chips. Consumption of sweetened beverages such as soft drinks, fruit drinks, and iced tea is believed to be contributing to the rising rates of obesity and to an increased risk of metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a clustering of at least three of the following five medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high serum triglycerides, and low serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
Metabolic syndro ...
and type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent ...
. Vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency or hypovitaminosis D is a vitamin D level that is below normal. It most commonly occurs in people when they have inadequate exposure to sunlight, particularly sunlight with adequate ultraviolet B rays (UVB). Vitamin D def ...
is related to diseases associated with obesity.
As societies become increasingly reliant on energy-dense, big-portions, and fast-food
Fast food is a type of mass-produced food designed for commercial resale, with a strong priority placed on speed of service. ''Fast food'' is a commercial term, limited to food sold in a restaurant or store with frozen, preheated or precooked ...
meals, the association between fast-food consumption and obesity becomes more concerning. In the United States, consumption of fast-food meals tripled and food energy intake from these meals quadrupled between 1977 and 1995.
Agricultural policy
Agricultural policy describes a set of laws relating to domestic agriculture and imports of foreign agricultural products. Governments usually implement agricultural policies with the goal of achieving a specific outcome in the domestic agricultu ...
and techniques in the United States and Europe have led to lower food prices
Food prices refer to the average price level for food across countries, regions and on a global scale. Food prices affect producers and consumers of food. Price levels depend on the food production process, including food marketing and food di ...
. In the United States, subsidization of corn, soy, wheat, and rice through the U.S. farm bill has made the main sources of processed food cheap compared to fruits and vegetables. Calorie count laws
Calorie count laws are a type of law that require restaurants (typically only larger restaurant chains) to post food energy
Food energy is chemical energy that animals and humans derive from food to sustain their metabolism and muscular activit ...
and nutrition facts label
The nutrition facts label (also known as the nutrition information panel, and other slight variations) is a label required on most convenience food, packaged food in many countries, showing what nutrients and other ingredients (to limit and get e ...
s attempt to steer people toward making healthier food choices, including awareness of how much food energy is being consumed.
Obese people consistently under-report their food consumption as compared to people of normal weight. This is supported both by tests of people carried out in a calorimeter
A calorimeter is a device used for calorimetry, or the process of measuring the heat of chemical reactions or physical changes as well as heat capacity. Differential scanning calorimeters, isothermal micro calorimeters, titration calorimeters ...
room and by direct observation.
Sedentary lifestyle
A sedentary lifestyle may play a significant role in obesity. Worldwide there has been a large shift towards less physically demanding work, and currently at least 30% of the world's population gets insufficient exercise. This is primarily due to increasing use of mechanized transportation and a greater prevalence of labor-saving technology in the home. In children, there appear to be declines in levels of physical activity (with particularly strong declines in the amount of walking and physical education), likely due to safety concerns, changes in social interaction (such as fewer relationships with neighborhood children), and inadequate urban design (such as too few public spaces for safe physical activity). World trends in active leisure timephysical activity
Physical activity is defined as any voluntary movement produced by skeletal muscles that requires energy expenditure.Global Recommendations on Physical Activity for Health, 2009. World Health Organization. Geneva, Switzerland. Accessed 13/07/2018 ...
are less clear. The World Health Organization indicates people worldwide are taking up less active recreational pursuits, while research from Finland found an increase and research from the United States found leisure-time physical activity has not changed significantly. Physical activity in children may not be a significant contributor.
In both children and adults, there is an association between television viewing time and the risk of obesity. Increased media exposure increases the rate of childhood obesity, with rates increasing proportionally to time spent watching television.
Genetics
Like many other medical conditions, obesity is the result of an interplay between genetic and environmental factors. Polymorphisms in variousgene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
s controlling appetite
Appetite is the desire to eat food items, usually due to hunger. Appealing foods can stimulate appetite even when hunger is absent, although appetite can be greatly reduced by satiety. Appetite exists in all higher life-forms, and serves to reg ...
and metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
predispose to obesity when sufficient food energy is present. As of 2006, more than 41 of these sites on the human genome have been linked to the development of obesity when a favorable environment is present. People with two copies of the FTO gene
Fat mass and obesity-associated protein, also known as alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase FTO, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''FTO'' gene located on chromosome 16. As one homolog in the AlkB family proteins, it is the firs ...
(fat mass and obesity associated gene) have been found on average to weigh 3–4 kg more and have a 1.67-fold greater risk of obesity compared with those without the risk allele
An allele is a variant of the sequence of nucleotides at a particular location, or Locus (genetics), locus, on a DNA molecule.
Alleles can differ at a single position through Single-nucleotide polymorphism, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), ...
. The differences in BMI between people that are due to genetics varies depending on the population examined from 6% to 85%.
Obesity is a major feature in several syndromes, such as Prader–Willi syndrome
Prader–Willi syndrome (PWS) is a rare genetic disorder caused by a loss of function of specific genes on chromosome 15. In newborns, symptoms include hypotonia, weak muscles, poor feeding, and slow development. Beginning in childhood, those ...
, Bardet–Biedl syndrome
Bardet–Biedl syndrome (BBS) is a ciliopathic human genetic disorder that produces many effects and affects many body systems. It is characterized by rod/cone dystrophy, polydactyly, central obesity, hypogonadism, and kidney dysfunction in ...
, Cohen syndrome
Cohen syndrome (also known as Pepper syndrome or Cervenka syndrome) is a very rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder with varied expression, characterised by obesity, intellectual disability, distinct craniofacial abnormalities and potential ocu ...
, and MOMO syndrome
MOMO syndrome is an extremely rare genetic disorder which belongs to the overgrowth syndromes and has been diagnosed in only seven cases around the world, and occurs in 1 in 100 million births. The name is an acronym of the four primary aspects o ...
. (The term "non-syndromic obesity" is sometimes used to exclude these conditions.) In people with early-onset severe obesity (defined by an onset before 10 years of age and body mass index over three standard deviation
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation of the values of a variable about its Expected value, mean. A low standard Deviation (statistics), deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean ( ...
s above normal), 7% harbor a single point DNA mutation.
Studies that have focused on inheritance patterns rather than on specific genes have found that 80% of the offspring of two obese parents were also obese, in contrast to less than 10% of the offspring of two parents who were of normal weight. Different people exposed to the same environment have different risks of obesity due to their underlying genetics.
The thrifty gene hypothesis
The thrifty gene hypothesis is an attempt by geneticist James V. Neel to explain why certain populations and subpopulations in the modern day are prone to diabetes mellitus type 2. He proposed the hypothesis in 1962 to resolve a problem: diabetes ...
postulates that, due to dietary scarcity during human evolution, people are prone to obesity. Their ability to take advantage of rare periods of abundance by storing energy as fat would be advantageous during times of varying food availability, and individuals with greater adipose reserves would be more likely to survive famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food caused by several possible factors, including, but not limited to war, natural disasters, crop failure, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenom ...
. This tendency to store fat, however, would be maladaptive in societies with stable food supplies. This theory has received various criticisms, and other evolutionarily-based theories such as the drifty gene hypothesis The "drifty gene hypothesis" was proposed by the British biologist John Speakman as an alternative to the thrifty gene hypothesis originally proposed by James V Neel in 1962.
Speakman's critique of the thrifty gene hypothesis is based on an analy ...
and the thrifty phenotype hypothesis have also been proposed.
Other illnesses
Certain physical and mental illnesses and the pharmaceutical substances used to treat them can increase risk of obesity. Medical illnesses that increase obesity risk include several rare genetic syndromes (listed above) as well as some congenital or acquired conditions:hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is an endocrine disease in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as cold intolerance, poor ability to tolerate cold, fatigue, extreme fatigue, muscle aches, co ...
, Cushing's syndrome
Cushing's syndrome is a collection of signs and symptoms due to prolonged exposure to glucocorticoids such as cortisol. Signs and symptoms may include high blood pressure, abdominal obesity but with thin arms and legs, reddish stretch marks, ...
, growth hormone deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency (GHD), or hyposomatotropism, is a medical condition resulting from not enough growth hormone (GH). Generally the most noticeable symptom is that an individual attains a short height. Newborns may also present low blood ...
, and some eating disorder
An eating disorder is a mental disorder defined by abnormal eating behaviors that adversely affect a person's health, physical or mental health, mental health. These behaviors may include eating too much food or too little food. Types of eatin ...
s such as binge eating disorder
Binge eating disorder (BED) is an eating disorder characterized by frequent and recurrent binge eating episodes with associated negative psychological and social problems, but without the compensatory behaviors common to bulimia nervosa, OSFE ...
and night eating syndrome
Night eating syndrome (NES) is classified as an Other Specified Feeding or Eating Disorder (OSFED) under the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition (DSM-5).American Psychiatric Association. (2013). ''Diagnostic and st ...
. However, obesity is not regarded as a psychiatric disorder, and therefore is not listed in the DSM-IVR as a psychiatric illness. The risk of overweight and obesity is higher in patients with psychiatric disorders than in persons without psychiatric disorders. Obesity and depression influence each other mutually, with obesity increasing the risk of clinical depression, and also depression leading to a higher chance of developing obesity.
Drug-induced obesity
Certain medications may cause weight gain or changes inbody composition
In physical fitness, body composition refers to quantifying the different components (or "compartments") of a human body. The selection of compartments varies by model but may include fat, bone, water, and muscle. Two people of the same gender, h ...
; these include insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
, sulfonylurea
Sulfonylureas or sulphonylureas are a class of organic compounds used in medicine and agriculture. The functional group consists of a sulfonyl group (-S(=O)2) with its sulphur atom bonded to a nitrogen atom of a ureylene group (N,N-dehydrourea ...
s, thiazolidinedione
The thiazolidinediones , abbreviated as TZD, also known as glitazones after the prototypical drug ciglitazone, are a class of heterocyclic compounds consisting of a five-membered C3NS ring. The term usually refers to a family of drugs used i ...
s, atypical antipsychotic
The atypical antipsychotics (AAP), also known as second generation antipsychotics (SGAs) and serotonin–dopamine antagonists (SDAs), are a group of antipsychotic drugs (antipsychotic drugs in general are also known as tranquilizers and neurol ...
s, antidepressant
Antidepressants are a class of medications used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain, and addiction.
Common side effects of antidepressants include Xerostomia, dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, headaches, akathi ...
s, steroids
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration.
Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter mem ...
, certain anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs, antiseizure drugs, or anti-seizure medications (ASM)) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also used in the treatme ...
s (phenytoin
Phenytoin (PHT), sold under the brand name Dilantin among others, is an anticonvulsant, anti-seizure medication. It is useful for the prevention of tonic-clonic seizures (also known as grand mal seizures) and focal seizures, but not absence se ...
and valproate
Valproate (valproic acid, VPA, sodium valproate, and valproate semisodium forms) are medications primarily used to treat epilepsy and bipolar disorder and prevent migraine headaches. They are useful for the prevention of seizures in those with ...
), pizotifen
Pizotifen, also known as pizotyline and sold under the brand names Sandomigran and Mosegor among others, is an antimigraine agent of the tricyclic group which is used primarily as a preventative to reduce the frequency of recurrent migraine h ...
, and some forms of hormonal contraception
Hormonal contraception refers to birth control methods that act on the endocrine system. Almost all methods are composed of steroid hormones, although in India one selective estrogen receptor modulator is marketed as a contraceptive. The original ...
.
Social determinants
social class
A social class or social stratum is a grouping of people into a set of Dominance hierarchy, hierarchical social categories, the most common being the working class and the Bourgeoisie, capitalist class. Membership of a social class can for exam ...
and BMI varies globally. Research in 1989 found that in developed countries women of a high social class were less likely to be obese. No significant differences were seen among men of different social classes. In the developing world, women, men, and children from high social classes had greater rates of obesity. In 2007 repeating the same research found the same relationships, but they were weaker. The decrease in strength of correlation was felt to be due to the effects of globalization
Globalization is the process of increasing interdependence and integration among the economies, markets, societies, and cultures of different countries worldwide. This is made possible by the reduction of barriers to international trade, th ...
. Among developed countries, levels of adult obesity, and percentage of teenage children who are overweight, are correlated with income inequality
In economics, income distribution covers how a country's total GDP is distributed amongst its population. Economic theory and economic policy have long seen income and its distribution as a central concern. Unequal distribution of income causes ...
. A similar relationship is seen among US states: more adults, even in higher social classes, are obese in more unequal states.
Many explanations have been put forth for associations between BMI and social class. It is thought that in developed countries, the wealthy are able to afford more nutritious food, they are under greater social pressure to remain slim, and have more opportunities along with greater expectations for physical fitness
Physical fitness is a state of health and well-being and, more specifically, the ability to perform aspects of Outline of sports, sports, occupations, and daily activities. Physical fitness is generally achieved through proper nutrition, modera ...
. In undeveloped countries
The least developed countries (LDCs) are developing countries listed by the United Nations that exhibit the lowest indicators of socioeconomic development. The concept of LDCs originated in the late 1960s and the first group of LDCs was listed by ...
the ability to afford food, high energy expenditure with physical labor, and cultural values favoring a larger body size are believed to contribute to the observed patterns. Attitudes toward body weight held by people in one's life may also play a role in obesity. A correlation in BMI changes over time has been found among friends, siblings, and spouses. Stress and perceived low social status appear to increase risk of obesity.
Smoking has a significant effect on an individual's weight. Those who quit smoking gain an average of 4.4 kilograms (9.7 lb) for men and 5.0 kilograms (11.0 lb) for women over ten years. However, changing rates of smoking have had little effect on the overall rates of obesity.
In the United States, the number of children a person has is related to their risk of obesity. A woman's risk increases by 7% per child, while a man's risk increases by 4% per child. This could be partly explained by the fact that having dependent children decreases physical activity in Western parents.
In the developing world urbanization is playing a role in increasing rate of obesity. In China overall rates of obesity are below 5%; however, in some cities rates of obesity are greater than 20%. In part, this may be because of urban design issues (such as inadequate public spaces for physical activity). Time spent in motor vehicles, as opposed to active transportation options such as cycling or walking, is correlated with increased risk of obesity.
Malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
in early life is believed to play a role in the rising rates of obesity in the developing world
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreeme ...
. Endocrine changes that occur during periods of malnutrition may promote the storage of fat once more food energy becomes available.
Gut bacteria
The study of the effect of infectious agents on metabolism is still in its early stages. Gut flora has been shown to differ between lean and obese people. There is an indication that gut flora can affect the metabolic potential. This apparent alteration is believed to confer a greater capacity to harvest energy contributing to obesity. Whether these differences are the direct cause or the result of obesity has yet to be determined unequivocally. The use of antibiotics among children has also been associated with obesity later in life. An association between viruses and obesity has been found in humans and several different animal species. The amount that these associations may have contributed to the rising rate of obesity is yet to be determined.Other factors
Not getting enough sleep sleep and weight, is also associated with obesity. Whether one causes the other is unclear. Even if short sleep does increase weight gain, it is unclear if this is to a meaningful degree or if increasing sleep would be of benefit. Some have proposed that chemical compounds called "obesogens" may play a role in obesity. Certain aspects of personality are associated with being obese. Loneliness, neuroticism, impulsivity, and sensitivity to reward are more common in people who are obese while conscientiousness and self-control are less common in people who are obese. Because most of the studies on this topic are questionnaire-based, it is possible that these findings overestimate the relationships between personality and obesity: people who are obese might be aware of the social stigma of obesity and their questionnaire responses might be biased accordingly. Similarly, the personalities of people who are obese as children might be influenced by obesity stigma, rather than these personality factors acting as risk factors for obesity. In relation to globalization, it is known that trade liberalization is linked to obesity; research, based on data from 175 countries during 1975–2016, showed that obesity prevalence was positively correlated with trade openness, and the correlation was stronger in developing countries.Pathophysiology
 Two distinct but related processes are considered to be involved in the development of obesity: sustained positive energy balance (energy intake exceeding energy expenditure) and the resetting of the body weight "set point" at an increased value. The second process explains why finding effective obesity treatments has been difficult. While the underlying biology of this process still remains uncertain, research is beginning to clarify the mechanisms.
At a biological level, there are many possible pathophysiology, pathophysiological mechanisms involved in the development and maintenance of obesity. This field of research had been almost unapproached until the leptin gene was discovered in 1994 by J. M. Friedman's laboratory. While leptin and ghrelin are produced peripherally, they control appetite through their actions on the central nervous system. In particular, they and other appetite-related hormones act on the hypothalamus, a region of the brain central to the regulation of food intake and energy expenditure. There are several circuits within the hypothalamus that contribute to its role in integrating appetite, the melanocortin pathway being the most well understood. The circuit begins with an area of the hypothalamus, the arcuate nucleus, that has outputs to the lateral hypothalamus (LH) and ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH), the brain's feeding and satiety centers, respectively.
The arcuate nucleus contains two distinct groups of neurons. The first group coexpresses neuropeptide Y (NPY) and agouti-related peptide (AgRP) and has stimulatory inputs to the LH and inhibitory inputs to the VMH. The second group coexpresses pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) and cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) and has stimulatory inputs to the VMH and inhibitory inputs to the LH. Consequently, NPY/AgRP neurons stimulate feeding and inhibit satiety, while POMC/CART neurons stimulate satiety and inhibit feeding. Both groups of arcuate nucleus neurons are regulated in part by leptin. Leptin inhibits the NPY/AgRP group while stimulating the POMC/CART group. Thus a deficiency in leptin signaling, either via leptin deficiency or leptin resistance, leads to overfeeding and may account for some genetic and acquired forms of obesity.
Two distinct but related processes are considered to be involved in the development of obesity: sustained positive energy balance (energy intake exceeding energy expenditure) and the resetting of the body weight "set point" at an increased value. The second process explains why finding effective obesity treatments has been difficult. While the underlying biology of this process still remains uncertain, research is beginning to clarify the mechanisms.
At a biological level, there are many possible pathophysiology, pathophysiological mechanisms involved in the development and maintenance of obesity. This field of research had been almost unapproached until the leptin gene was discovered in 1994 by J. M. Friedman's laboratory. While leptin and ghrelin are produced peripherally, they control appetite through their actions on the central nervous system. In particular, they and other appetite-related hormones act on the hypothalamus, a region of the brain central to the regulation of food intake and energy expenditure. There are several circuits within the hypothalamus that contribute to its role in integrating appetite, the melanocortin pathway being the most well understood. The circuit begins with an area of the hypothalamus, the arcuate nucleus, that has outputs to the lateral hypothalamus (LH) and ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH), the brain's feeding and satiety centers, respectively.
The arcuate nucleus contains two distinct groups of neurons. The first group coexpresses neuropeptide Y (NPY) and agouti-related peptide (AgRP) and has stimulatory inputs to the LH and inhibitory inputs to the VMH. The second group coexpresses pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) and cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) and has stimulatory inputs to the VMH and inhibitory inputs to the LH. Consequently, NPY/AgRP neurons stimulate feeding and inhibit satiety, while POMC/CART neurons stimulate satiety and inhibit feeding. Both groups of arcuate nucleus neurons are regulated in part by leptin. Leptin inhibits the NPY/AgRP group while stimulating the POMC/CART group. Thus a deficiency in leptin signaling, either via leptin deficiency or leptin resistance, leads to overfeeding and may account for some genetic and acquired forms of obesity.
Management
The main treatment for obesity consists of weight loss via lifestyle interventions, including prescribed Diet (nutrition), diets and physical exercise. Although it is unclear what diets might support long-term weight loss, and although the effectiveness of Calorie restriction, low-calorie diets is debated, lifestyle changes that reduce calorie consumption or increase physical exercise over the long term also tend to produce some sustained weight loss, despite slow weight regain over time. Although 87% of participants in the National Weight Control Registry were able to maintain 10% body weight loss for 10 years, the most appropriate dietary approach for long term weight loss maintenance is still unknown. In the US, intensive behavioral interventions combining both dietary changes and exercise are recommended. Intermittent fasting has no additional benefit of weight loss compared to continuous energy restriction. Adherence is a more important factor in weight loss success than whatever kind of diet an individual undertakes. Several hypo-caloric diets are effective. In the short-term Low-carbohydrate diet, low carbohydrate diets appear better than Low-fat diet, low fat diets for weight loss. In the long term, however, all types of low-carbohydrate and low-fat diets appear equally beneficial. Heart disease and diabetes risks associated with different diets appear to be similar. Promotion of the Mediterranean diets among the obese may lower the risk of heart disease. Decreased intake of sweet drinks is also related to weight-loss. Success rates of long-term weight loss maintenance with lifestyle changes are low, ranging from 2–20%. Dietary and lifestyle changes are effective in limiting excessive weight gain in pregnancy and improve outcomes for both the mother and the child. Intensive behavioral counseling is recommended in those who are both obese and have other risk factors for heart disease.Health policy
Obesity is a complex public health and policy problem because of its prevalence, costs, and health effects. As such, managing it requires changes in the wider societal context and effort by communities, local authorities, and governments. Public health efforts seek to understand and correct the Obesity and the environment, environmental factors responsible for the increasing prevalence of obesity in the population. Solutions look at changing the factors that cause excess food energy consumption and inhibit physical activity. Efforts include federally reimbursed meal programs in schools, limiting direct junk food, junk food marketing to children, and decreasing access to sugar-sweetened beverages in schools. The World Health Organization recommends the taxing of sugary drinks. When constructing urban environments, efforts have been made to increase access to parks and to develop pedestrian routes. Efforts also exist to address the occurrence of Food swamp, food swamps, or areas with an overabundance of convenient or fast food options, as these has been found to be strongly predictive of obesity rates. Mass media campaigns seem to have limited effectiveness in changing behaviors that influence obesity, but may increase knowledge and awareness regarding physical activity and diet, which might lead to changes in the long term. Campaigns might also be able to reduce the amount of time spent Sedentary lifestyle, sitting or lying down and positively affect the intention to be active physically. Nutrition facts label, Nutritional labelling with energy information on menus might be able to help reducing energy intake while dining in restaurants. Some call for policy against ultra-processed foods.Medical interventions
Medication
Since the introduction of medicines for the management of obesity in the 1930s, many compounds have been tried. Most of them reduce body weight by small amounts, and several of them are no longer marketed for obesity because of their side effects. Out of 25 anti-obesity medications withdrawn from the market between 1964 and 2009, 23 acted by altering the functions of chemical neurotransmitters in the brain. The most common side effects of these drugs that led to withdrawals were mental disturbances, cardiac side effects, and Substance abuse, drug abuse or drug dependence. Deaths were reportedly associated with seven products. Five medications beneficial for long-term use are: orlistat, lorcaserin, liraglutide, Phentermine/topiramate, phentermine–topiramate, and naltrexone/bupropion, naltrexone–bupropion. They result in weight loss after one year ranged from 3.0 to 6.7 kg (6.6-14.8 lbs) over placebo. Orlistat, liraglutide, and naltrexone–bupropion are available in both the United States and Europe, phentermine–topiramate is available only in the United States. European regulatory authorities rejected lorcaserin and phentermine-topiramate, in part because of associations of heart valve problems with lorcaserin and more general heart and blood vessel problems with phentermine–topiramate. Lorcaserin was available in the United States and then removed from the market in 2020 due to its association with cancer. Orlistat use is associated with high rates of gastrointestinal side effects and concerns have been raised about negative effects on the kidneys. There is no information on how these drugs affect longer-term complications of obesity such as cardiovascular disease or death; however, liraglutide, when used for type 2 diabetes, does reduce cardiovascular events. In 2019 a systematic review compared the effects on weight of various doses of fluoxetine (60 mg/d, 40 mg/d, 20 mg/d, 10 mg/d) in obese adults. When compared to placebo, all dosages of fluoxetine appeared to contribute to weight loss but lead to increased risk of experiencing side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, insomnia and nausea during period of treatment. However, these conclusions were from low certainty evidence. When comparing, in the same review, the effects of fluoxetine on weight of obese adults, to other Anorectic, anti-obesity agents, Omega-3 fatty acid, omega-3 gel and not receiving a treatment, the authors could not reach conclusive results due to poor quality of evidence. Among antipsychotic drugs for treating schizophrenia clozapine is the most effective, but it also has the highest risk of causing themetabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a clustering of at least three of the following five medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high serum triglycerides, and low serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
Metabolic syndro ...
, of which obesity is the main feature. For people who gain weight because of clozapine, taking metformin may reportedly improve three of the five components of the metabolic syndrome: waist circumference, fasting glucose, and fasting triglycerides.
Surgery
The most effective treatment for obesity is bariatric surgery. The types of procedures include laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, vertical-sleeve gastrectomy, and biliopancreatic diversion. Surgery for severe obesity is associated with long-term weight loss, improvement in obesity-related conditions, and decreased overall mortality; however, improved metabolic health results from the weight loss, not the surgery. One study found a weight loss of between 14% and 25% (depending on the type of procedure performed) at 10 years, and a 29% reduction in all cause mortality when compared to standard weight loss measures. Complications occur in about 17% of cases and reoperation is needed in 7% of cases.Epidemiology
In earlier historical periods obesity was rare and achievable only by a small elite, although already recognised as a problem for health. But as prosperity increased in the Early Modern period, it affected increasingly larger groups of the population. Prior to the 1970s, obesity was a relatively rare condition even in the wealthiest of nations, and when it did exist it tended to occur among the wealthy. Then, a confluence of events started to change the human condition. The average BMI of populations in first-world countries started to increase, and consequently there was a rapid increase in the proportion of people overweight and obese. In 1997, the WHO formally recognized obesity as a global epidemic. As of 2008, the WHO estimates that at least 500 million adults (greater than 10%) are obese, with higher rates among women than men. The global prevalence of obesity more than doubled between 1980 and 2014. In 2014, more than 600 million adults were obese, equal to about 13 percent of the world's adult population, with that figure growing to 16% by 2022, according to the World Health Organisation. The percentage of adults affected in the United States as of 2015–2016 is about 39.6% overall (37.9% of males and 41.1% of females). In 2000, theWorld Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
(WHO) stated that overweight
Being overweight is having more body fat than is optimally healthy. Being overweight is especially common where food supplies are plentiful and lifestyles are sedentary.
, excess weight reached epidemic proportions globally, with more than ...
and obesity were replacing more traditional public health concerns such as undernutrition and infectious diseases as one of the most significant cause of poor health.
The rate of obesity also increases with age at least up to 50 or 60 years old and severe obesity in the United States, Australia, and Canada is increasing faster than the overall rate of obesity. The OECD has projected an increase in obesity rates until at least 2030, especially in the United States, Mexico and England with rates reaching 47%, 39% and 35%, respectively.
Once considered a problem only of high-income countries, obesity rates are rising worldwide and affecting both the developed and developing world. These increases have been felt most dramatically in urban settings. In 2021, nearly half the global adult population - a billion men and 1.11 billion women aged 25 or older - were overweight or obese. It was predicted that if these trends continue about 57.4% of men and 60.3% of women would be overweight or obese by 2050.
Sex- and gender-based differences influence the prevalence of obesity. Globally there are more obese women than men, but the numbers differ depending on how obesity is measured.
History
Etymology
''Obesity'' is from the Latin ''obesitas'', which means "stout, fat, or plump". ''Ēsus'' is the past participle of ''edere'' (to eat), with ''ob'' (over) added to it. ''The Oxford English Dictionary'' documents its first usage in 1611 by Randle Cotgrave.Historical attitudes
Ancient Greek medicine recognizes obesity as a medical disorder and records that the Ancient Egyptians saw it in the same way. Hippocrates wrote that "Corpulence is not only a disease itself, but the harbinger of others". The Indian surgeon Sushruta (6th century BCE) related obesity to diabetes and heart disorders. He recommended physical work to help cure it and its side effects. For most of human history, mankind struggled with food scarcity. Obesity has thus historically been viewed as a sign of wealth and prosperity. It was common among high officials in Ancient East Asian civilizations. In the 17th century, English medical author Tobias Venner is credited with being one of the first to refer to the term as a societal disease in a published English language book. With the onset of the Industrial Revolution, it was realized that the military and economic might of nations were dependent on both the body size and strength of their soldiers and workers. Increasing the average body mass index from what is now considered underweight to what is now the normal range played a significant role in the development of industrialized societies. Height and weight thus both increased through the 19th century in the developed world. During the 20th century, as populations reached their genetic potential for height, weight began increasing much more than height, resulting in obesity. In the 1950s, increasing wealth in the developed world decreased child mortality, but as body weight increased, heart and kidney disease became more common. During this time period, insurance companies realized the connection between weight and life expectancy and increased premiums for the obese. Many cultures throughout history have viewed obesity as the result of a character flaw. The ''obesus'' or fat character in Ancient Greek comedy was a glutton and figure of mockery. During Christian times, food was viewed as a gateway to the sins of Sloth (deadly sin), sloth and lust. In modern Western culture, excess weight is often regarded as unattractive, and obesity is commonly associated with various negative stereotypes. People of all ages can face social stigmatization and may be targeted by bullies or shunned by their peers. Public perceptions in Western society regarding healthy body weight differ from those regarding the weight that is considered ideal – and both have changed since the beginning of the 20th century. The weight that is viewed as an ideal has become lower since the 1920s. This is illustrated by the fact that the average height of Miss America pageant winners increased by 2% from 1922 to 1999, while their average weight decreased by 12%. On the other hand, people's views concerning healthy weight have changed in the opposite direction. In Britain, the weight at which people considered themselves to be overweight was significantly higher in 2007 than in 1999. These changes are believed to be due to increasing rates of adiposity leading to increased acceptance of extra body fat as being normal. Obesity is still seen as a sign of wealth and well-being in many parts of Africa. This has become particularly common since the HIV epidemic began.The arts
The first sculptural representations of the human body 20,000–35,000 years ago depict obese females. Some attribute the Venus figurines to the tendency to emphasize fertility while others feel they represent "fatness" in the people of the time. Corpulence is, however, absent in both Greek and Roman art, probably in keeping with their ideals regarding moderation. This continued through much of Christian European history, with only those of low socioeconomic status being depicted as obese. During the Renaissance some of the upper class began flaunting their large size, as can be seen in portraits of Henry VIII of England and Alessandro dal Borro. Peter Paul Rubens, Rubens (1577–1640) regularly depicted heavyset women in his pictures, from which derives the term Peter Paul Rubens#Work, Rubenesque. These women, however, still maintained the "hourglass" shape with its relationship to fertility. During the 19th century, views on obesity changed in the Western world. After centuries of obesity being synonymous with wealth and social status, slimness began to be seen as the desirable standard. In his 1819 print, ''The Belle Alliance, or the Female Reformers of Blackburn!!!,'' artist George Cruikshank criticised the work of female reformers in Blackburn and used fatness as a means to portray them as unfeminine.Society and culture
Economic impact
In addition to its health impacts, obesity leads to many problems, including disadvantages in employment and increased business costs. In 2005, the medical costs attributable to obesity in the US were an estimated $190.2 billion or 20.6% of all medical expenditures, while the cost of obesity in Canada was estimated at CA$2 billion in 1997 (2.4% of total health costs). The total annual direct cost of overweight and obesity in Australia in 2005 was A$21 billion. Overweight and obese Australians also received A$35.6 billion in government subsidies. The estimated range for annual expenditures on diet products is $40 billion to $100 billion in the US alone. The Lancet Commission on Obesity in 2019 called for a global treaty—modelled on the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control—committing countries to address obesity and undernutrition, explicitly excluding the food industry from policy development. They estimate the global cost of obesity $2 trillion a year, about or 2.8% of world GDP. Obesity prevention programs have been found to reduce the cost of treating obesity-related disease. However, the longer people live, the more medical costs they incur. Researchers, therefore, conclude that reducing obesity may improve the public's health, but it is unlikely to reduce overall health spending. Sin taxes such as a sugary drink tax have been implemented in certain countries globally to curb dietary and consumer habits, and as an effort to offset the economic tolls. Obesity can lead to social stigmatization and disadvantages in employment. When compared to their ideal weight counterparts, workers with obesity, on average have higher rates of absenteeism from work and take more disability leave, thus increasing costs for employers and decreasing productivity. A study examining Duke University employees found that people with a BMI over 40 kg/m2 filed twice as many workers' compensation claims as those whose BMI was 18.5–24.9 kg/m2. They also had more than 12 times as many lost work days. The most common injuries in this group were due to falls and lifting, thus affecting the lower extremities, wrists or hands, and backs. The Alabama State Employees' Insurance Board approved a controversial plan to charge obese workers $25 a month for health insurance that would otherwise be free unless they take steps to lose weight and improve their health. These measures started in January 2010 and apply to those state workers whose BMI exceeds 35 kg/m2 and who fail to make improvements in their health after one year. This becomes a Catch 22 position as many insurance companies will refuse to pay for treatment methods for workers living with obesity.
Some research shows that people with obesity are less likely to be hired for a job and are less likely to be promoted. People with obesity are also paid less than their counterparts who do not live with obesity for an equivalent job; women with obesity on average make 6% less and men with obesity make 3% less.
Specific industries, such as the airline, healthcare and food industries, have special concerns. Due to rising rates of obesity, airlines face higher fuel costs and pressures to increase seating width. In 2000, the extra weight of passengers with obesity cost airlines US$275 million. The healthcare industry has had to invest in special facilities for handling patients with class III obesity, including special lifting equipment and bariatric ambulances. Costs for restaurants are increased by litigation accusing them of causing obesity. In 2005, the US Congress discussed legislation to prevent civil lawsuits against the food industry in relation to obesity; however, it did not become law.
With the
Obesity can lead to social stigmatization and disadvantages in employment. When compared to their ideal weight counterparts, workers with obesity, on average have higher rates of absenteeism from work and take more disability leave, thus increasing costs for employers and decreasing productivity. A study examining Duke University employees found that people with a BMI over 40 kg/m2 filed twice as many workers' compensation claims as those whose BMI was 18.5–24.9 kg/m2. They also had more than 12 times as many lost work days. The most common injuries in this group were due to falls and lifting, thus affecting the lower extremities, wrists or hands, and backs. The Alabama State Employees' Insurance Board approved a controversial plan to charge obese workers $25 a month for health insurance that would otherwise be free unless they take steps to lose weight and improve their health. These measures started in January 2010 and apply to those state workers whose BMI exceeds 35 kg/m2 and who fail to make improvements in their health after one year. This becomes a Catch 22 position as many insurance companies will refuse to pay for treatment methods for workers living with obesity.
Some research shows that people with obesity are less likely to be hired for a job and are less likely to be promoted. People with obesity are also paid less than their counterparts who do not live with obesity for an equivalent job; women with obesity on average make 6% less and men with obesity make 3% less.
Specific industries, such as the airline, healthcare and food industries, have special concerns. Due to rising rates of obesity, airlines face higher fuel costs and pressures to increase seating width. In 2000, the extra weight of passengers with obesity cost airlines US$275 million. The healthcare industry has had to invest in special facilities for handling patients with class III obesity, including special lifting equipment and bariatric ambulances. Costs for restaurants are increased by litigation accusing them of causing obesity. In 2005, the US Congress discussed legislation to prevent civil lawsuits against the food industry in relation to obesity; however, it did not become law.
With the American Medical Association
The American Medical Association (AMA) is an American professional association and lobbying group of physicians and medical students. This medical association was founded in 1847 and is headquartered in Chicago, Illinois. Membership was 271,660 ...
's 2013 classification of obesity as a chronic disease, it is thought that health insurance companies will more likely pay for obesity treatment, counseling and surgery, and the cost of research and development of adipose treatment pills or gene therapy treatments should be more affordable if insurers help to subsidize their cost. The AMA classification is not legally binding, however, so health insurers still have the right to reject coverage for a treatment or procedure.
In 2014, The European Court of Justice ruled that morbid obesity is a disability. The Court said that if an employee's obesity prevents them from "full and effective participation of that person in professional life on an equal basis with other workers", then it shall be considered a disability and that firing someone on such grounds is discriminatory.
In low-income countries, obesity can be a signal of wealth. A 2023 experimental study found that obese individuals in Uganda were more likely to access credit.
Size acceptance
 The principal goal of the fat acceptance movement is to decrease discrimination against people who are overweight and obese. However, some in the movement are also attempting to challenge the established relationship between obesity and negative health outcomes.
A number of organizations exist that promote the acceptance of obesity. They have increased in prominence in the latter half of the 20th century. The US-based National Association to Advance Fat Acceptance (NAAFA) was formed in 1969 and describes itself as a civil rights organization dedicated to ending size discrimination.
The International Size Acceptance Association (ISAA) is a non-governmental organization (NGO) which was founded in 1997. It has more of a global orientation and describes its mission as promoting size acceptance and helping to end weight-based discrimination. These groups often argue for the recognition of obesity as a disability under the US Americans With Disabilities Act (ADA). The American legal system, however, has decided that the potential public health costs exceed the benefits of extending this anti-discrimination law to cover obesity.
The principal goal of the fat acceptance movement is to decrease discrimination against people who are overweight and obese. However, some in the movement are also attempting to challenge the established relationship between obesity and negative health outcomes.
A number of organizations exist that promote the acceptance of obesity. They have increased in prominence in the latter half of the 20th century. The US-based National Association to Advance Fat Acceptance (NAAFA) was formed in 1969 and describes itself as a civil rights organization dedicated to ending size discrimination.
The International Size Acceptance Association (ISAA) is a non-governmental organization (NGO) which was founded in 1997. It has more of a global orientation and describes its mission as promoting size acceptance and helping to end weight-based discrimination. These groups often argue for the recognition of obesity as a disability under the US Americans With Disabilities Act (ADA). The American legal system, however, has decided that the potential public health costs exceed the benefits of extending this anti-discrimination law to cover obesity.
Industry influence on research
In 2015, the ''New York Times'' published an article on the Global Energy Balance Network, a nonprofit founded in 2014 that advocated for people to focus on increasing exercise rather than reducing calorie intake to avoid obesity and to be healthy. The organization was founded with at least $1.5M in funding from the Coca-Cola Company, and the company has provided $4M in research funding to the two founding scientists Gregory A. Hand and Steven Blair, Steven N. Blair since 2008.Reports
Many organizations have published reports pertaining to obesity. In 1998, the first US Federal guidelines were published, titled "Clinical Guidelines on the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults: The Evidence Report". In 2006, the Canadian Obesity Network, now known as Obesity Canada published the "Canadian Clinical Practice Guidelines (CPG) on the Management and Prevention of Obesity in Adults and Children". This is a comprehensive evidence-based guideline to address the management and prevention of overweight and obesity in adults and children. In 2004, the United Kingdom Royal College of Physicians, the Faculty of Public Health and the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health released the report "Storing up Problems", which highlighted the growing problem of obesity in the UK. The same year, the British House of Commons, House of Commons Health Select Committee published its "most comprehensive inquiry [...] ever undertaken" into the impact of obesity on health and society in the UK and possible approaches to the problem. In 2006, the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) issued a guideline on the diagnosis and management of obesity, as well as policy implications for non-healthcare organizations such as local councils. A 2007 report produced by Derek Wanless for the King's Fund warned that unless further action was taken, obesity had the capacity to debilitate the National Health Service financially. In 2022 the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) published a comprehensive review of research on what Local government in England, local authorities can do to reduce obesity. The Obesity Policy Action (OPA) framework divides measure into ''upstream'' policies, ''midstream'' policies, and ''downstream'' policies. Upstream policies have to do with changing society, while midstream policies try to alter behaviors believed to contribute to obesity at the individual level, while downstream policies treat currently obese people.Childhood obesity
The healthy BMI range varies with the age and sex of the child. Obesity in children and adolescents is defined as a BMI greater than the 95th percentile. The reference data that these percentiles are based on is from 1963 to 1994 and thus has not been affected by the recent increases in rates of obesity. Childhood obesity has reached epidemic proportions in the 21st century, with rising rates in both the developed and the developing world. Rates of obesity in Canadian boys have increased from 11% in the 1980s to over 30% in the 1990s, while during this same time period rates increased from 4 to 14% in Brazilian children. In the UK, there were 60% more obese children in 2005 compared to 1989. In the US, the percentage of overweight and obese children increased to 16% in 2008, a 300% increase over the prior 30 years. As with obesity in adults, many factors contribute to the rising rates of childhood obesity. Changing diet and decreasing physical activity are believed to be the two most important causes for the recent increase in the incidence of child obesity. Food marketing toward children, Advertising of unhealthy foods to children also contributes, as it increases their consumption of the product. Antibiotics in the first 6 months of life have been associated with excess weight at age seven to twelve years of age. Because childhood obesity often persists into adulthood and is associated with numerous chronic illnesses, children who are obese are often tested for hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and fatty liver disease. Treatments used in children are primarily lifestyle interventions and behavioral techniques, although efforts to increase activity in children have had little success. In the United States, medications are not FDA approved for use in this age group. Brief weight management interventions in primary care (e.g. delivered by a physician or nurse practitioner) have only a marginal positive effect in reducing childhood overweight or obesity. Multi-component behaviour change interventions that include changes to dietary and physical activity may reduce BMI in the short term in children aged 6 to 11 years, although the benefits are small and quality of evidence is low.Other animals
Obesity in pets is common in many countries. In the United States, 23–41% of dogs are overweight, and about 5.1% are obese. The rate of obesity in cats was slightly higher at 6.4%. In Australia, the rate of obesity among dogs in a veterinary setting has been found to be 7.6%. The risk of obesity in dogs is related to whether or not their owners are obese; however, there is no similar correlation between cats and their owners.See also
* Portal-visceral hypothesis * Anti-Obesity Day * Health effects of ultra-processed foodsReferences
Citations
Further reading
* * * * *External links
*WHO fact sheet on obesity and overweight
{{Authority control Obesity, Bariatrics Body shape Nutrition