17th-century English Translators on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The 17th century lasted from January 1,  By the end of the century, Europeans were masters of logarithms, electricity, the telescope and microscope, calculus, universal gravitation, Newton's Laws of Motion, air pressure, and calculating machines due to the work of the first scientists of the Scientific Revolution, including Galileo Galilei, Johannes Kepler, René Descartes, Pierre Fermat, Blaise Pascal, Robert Boyle, Christiaan Huygens, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, Robert Hooke, Isaac Newton, and Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz. It was also a period of development of culture in general (especially theater, music, visual arts and philosophy). Some of the greatest inventions took place in this century.
It was during this period that the European colonization of the Americas began in earnest, including the exploitation of the silver deposits, which resulted in bouts of inflation as wealth was drawn into Europe. Also during this period, there would be a more intense European presence in Southeast Asia and East Asia (such as the colonization of Taiwan). These foreign elements would contribute to a revolution in Ayutthaya. While the Mataram Sultanate and the Aceh Sultanate would be the major powers of the region, especially during the first half of the century.
In the Islamic world, the gunpowder empires – the Ottoman, Safavid, and Mughal – grew in strength as well. The southern half of India would see the decline of the Deccan Sultanates and extinction of the Vijayanagara Empire. The Dutch would colonize Ceylon and endure hostilities with Kandy. The end of the 17th century saw the first major surrender of Ottoman territory in Europe when the Treaty of Karlowitz ceded most of Hungary to the Habsburgs in 1699.
In Japan, Tokugawa Ieyasu established the Tokugawa shogunate at the beginning of the century, beginning the Edo period; the isolationist Sakoku policy began in the 1630s and lasted until the 19th century. In China, the collapsing Ming dynasty was challenged by a series of conquests led by the Manchu warlord Nurhaci, which were consolidated by his son Hong Taiji and finally consummated by his grandson, the Shunzhi Emperor, founder of the Qing dynasty. Qing China spent decades of this century with economic problems (results of civil wars between the Qing and former Ming dynasty loyalists), only recovering well at the end of the century.
The greatest military conflicts of the century were the Thirty Years' War, Dutch–Portuguese War, the Great Turkish War, the Nine Years' War, Mughal–Safavid Wars, and the Qing annexation of the Ming.
By the end of the century, Europeans were masters of logarithms, electricity, the telescope and microscope, calculus, universal gravitation, Newton's Laws of Motion, air pressure, and calculating machines due to the work of the first scientists of the Scientific Revolution, including Galileo Galilei, Johannes Kepler, René Descartes, Pierre Fermat, Blaise Pascal, Robert Boyle, Christiaan Huygens, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, Robert Hooke, Isaac Newton, and Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz. It was also a period of development of culture in general (especially theater, music, visual arts and philosophy). Some of the greatest inventions took place in this century.
It was during this period that the European colonization of the Americas began in earnest, including the exploitation of the silver deposits, which resulted in bouts of inflation as wealth was drawn into Europe. Also during this period, there would be a more intense European presence in Southeast Asia and East Asia (such as the colonization of Taiwan). These foreign elements would contribute to a revolution in Ayutthaya. While the Mataram Sultanate and the Aceh Sultanate would be the major powers of the region, especially during the first half of the century.
In the Islamic world, the gunpowder empires – the Ottoman, Safavid, and Mughal – grew in strength as well. The southern half of India would see the decline of the Deccan Sultanates and extinction of the Vijayanagara Empire. The Dutch would colonize Ceylon and endure hostilities with Kandy. The end of the 17th century saw the first major surrender of Ottoman territory in Europe when the Treaty of Karlowitz ceded most of Hungary to the Habsburgs in 1699.
In Japan, Tokugawa Ieyasu established the Tokugawa shogunate at the beginning of the century, beginning the Edo period; the isolationist Sakoku policy began in the 1630s and lasted until the 19th century. In China, the collapsing Ming dynasty was challenged by a series of conquests led by the Manchu warlord Nurhaci, which were consolidated by his son Hong Taiji and finally consummated by his grandson, the Shunzhi Emperor, founder of the Qing dynasty. Qing China spent decades of this century with economic problems (results of civil wars between the Qing and former Ming dynasty loyalists), only recovering well at the end of the century.
The greatest military conflicts of the century were the Thirty Years' War, Dutch–Portuguese War, the Great Turkish War, the Nine Years' War, Mughal–Safavid Wars, and the Qing annexation of the Ming.
 * 1605– 1627: The reign of Mughal emperor Jahangir after the death of emperor Akbar.
* 1606: The Long Turkish War between the
* 1605– 1627: The reign of Mughal emperor Jahangir after the death of emperor Akbar.
* 1606: The Long Turkish War between the
UST.edu.ph. Retrieved December 21, 2008. * 1611: The first publication of the King James Bible. * 1612: The first Cotswold Olympic Games, an annual public celebration of games and sports begins in the Cotswolds, England. * 1613: The Time of Troubles in Russia ends with the establishment of the House of Romanov, which rules until 1917. * 1613– 1617: Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth is invaded by the Tatars dozens of times. * 1613: The Dutch East India Company is forced to evacuate Gresik due to the Mataram siege in neighboring Surabaya. The dutch negotiates with Mataram and is allowed to set up a trading post in Jepara.
* 1614– 1615: The Siege of Osaka (last major threat to Tokugawa shogunate) ends.
* 1616: The last remaining Moriscos (Moors who had nominally converted to Christianity) in Spain are expelled.
* 1616: English poet and playwright
* 1613: The Dutch East India Company is forced to evacuate Gresik due to the Mataram siege in neighboring Surabaya. The dutch negotiates with Mataram and is allowed to set up a trading post in Jepara.
* 1614– 1615: The Siege of Osaka (last major threat to Tokugawa shogunate) ends.
* 1616: The last remaining Moriscos (Moors who had nominally converted to Christianity) in Spain are expelled.
* 1616: English poet and playwright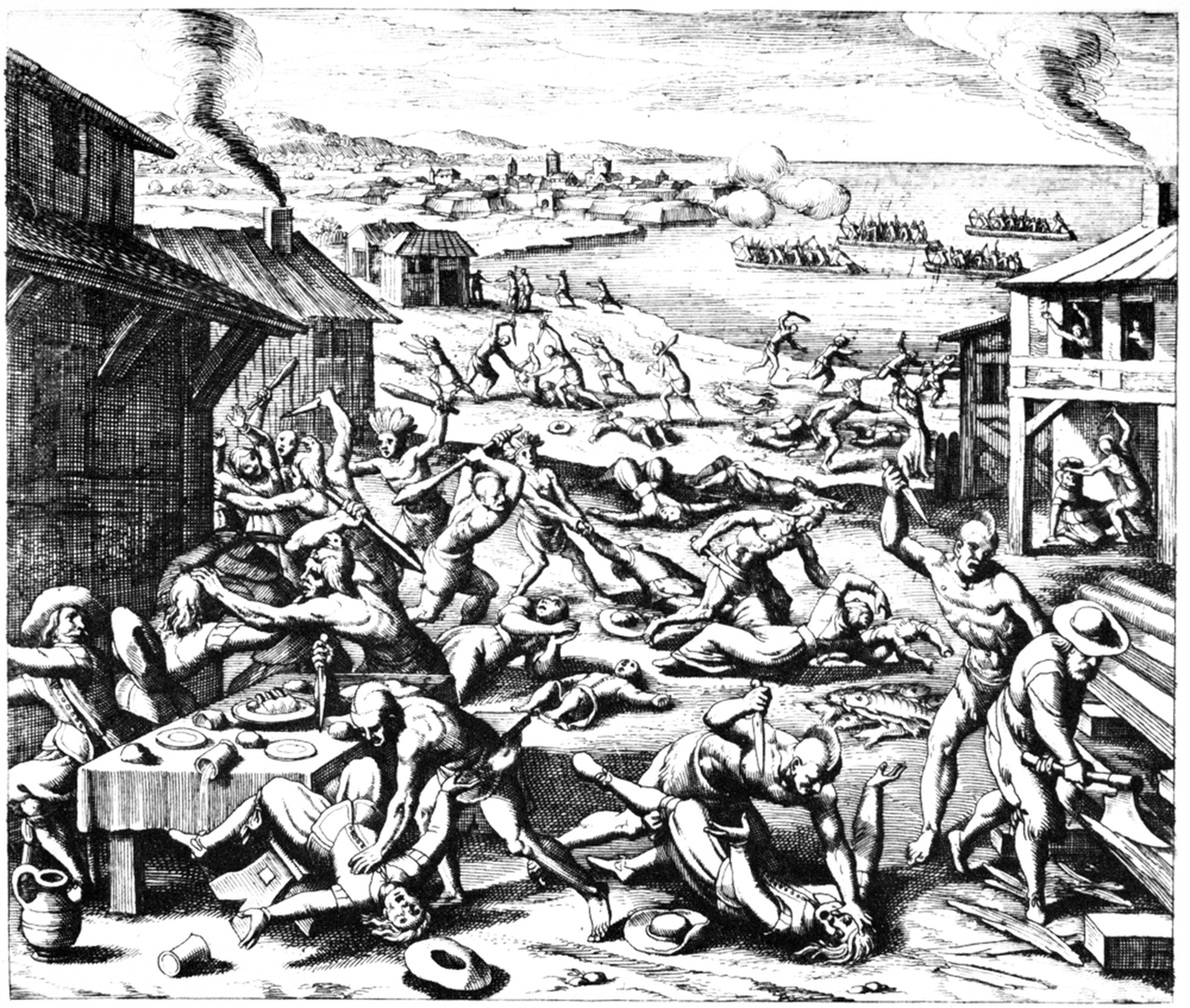  * 1621: The Battle of Chocim: Poles and Cossacks under Jan Karol Chodkiewicz defeat the Ottomans.
* 1622: Jamestown massacre: Algonquian natives kill 347 English settlers outside Jamestown, Virginia (approximately one-third of the colony's population) and burn the Henricus settlement.
* 1624– 1642: As chief minister, Cardinal Richelieu centralises power in
* 1621: The Battle of Chocim: Poles and Cossacks under Jan Karol Chodkiewicz defeat the Ottomans.
* 1622: Jamestown massacre: Algonquian natives kill 347 English settlers outside Jamestown, Virginia (approximately one-third of the colony's population) and burn the Henricus settlement.
* 1624– 1642: As chief minister, Cardinal Richelieu centralises power in  * 1648– 1653: Fronde civil war in
* 1648– 1653: Fronde civil war in
 * 1672– 1678: Franco-Dutch War.
* 1673: The Bruneian Civil War ends with Muhiyiddin winning the war.
* 1674: Shivaji founded the Maratha Empire and crowned himself as first Chatrapati of the empire.
* 1676– 1681: Russia and the
* 1672– 1678: Franco-Dutch War.
* 1673: The Bruneian Civil War ends with Muhiyiddin winning the war.
* 1674: Shivaji founded the Maratha Empire and crowned himself as first Chatrapati of the empire.
* 1676– 1681: Russia and the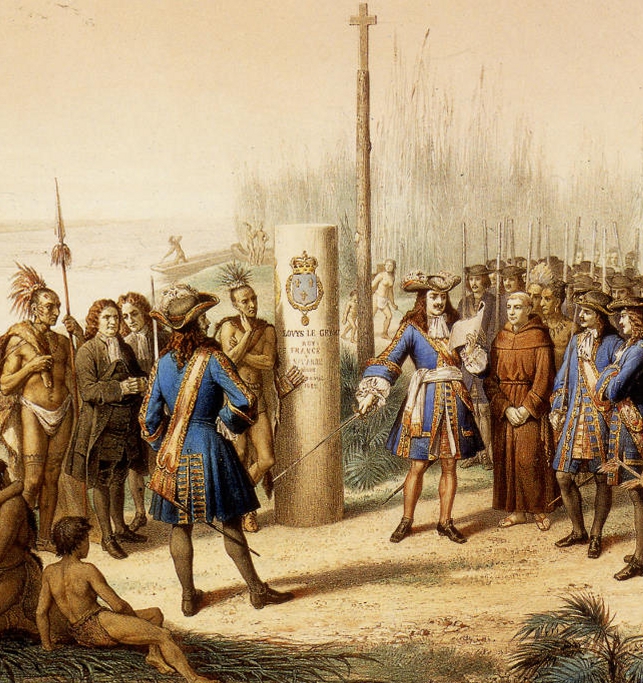  * 1680: The Pueblo Revolt drives the Spanish out of New Mexico until 1692.
* 1680: Prince Sambhaji crowned himself as the second '' Chatrapati'' of Maratha Empire 20 July.
* 1682: French explorer Robert La Salle claims all the land east of the Mississippi River.
* 1683:
* 1680: The Pueblo Revolt drives the Spanish out of New Mexico until 1692.
* 1680: Prince Sambhaji crowned himself as the second '' Chatrapati'' of Maratha Empire 20 July.
* 1682: French explorer Robert La Salle claims all the land east of the Mississippi River.
* 1683: 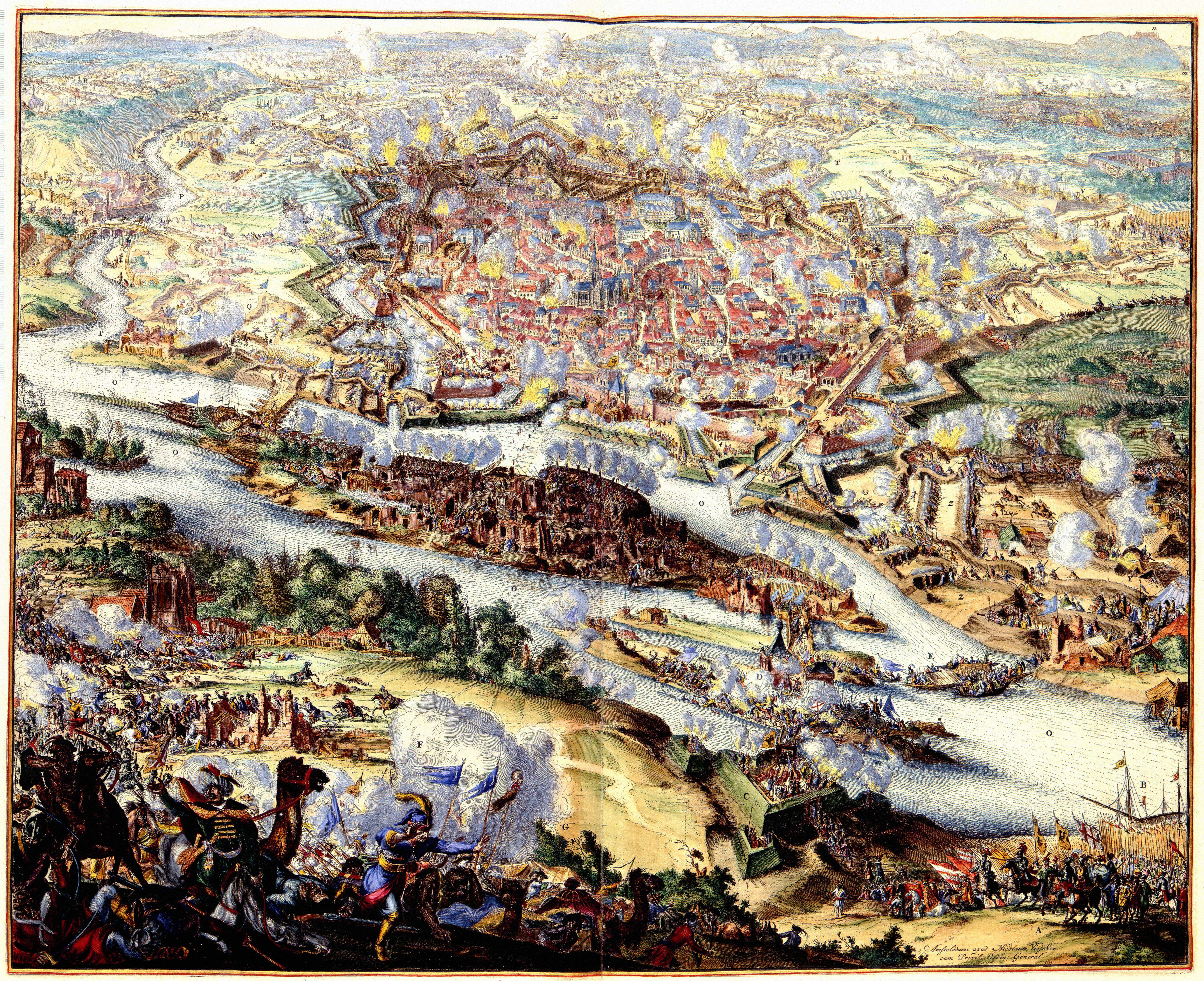 * 1689: Bill of Rights gains royal consent.
* 1689: John Locke publishes '' Two Treatises of Government'' and '' A Letter Concerning Toleration.''
* 1690: The Battle of the Boyne in Ireland.
* 1692: Port Royal in Jamaica is struck by an earthquake and a tsunami. Approximately 2,000 people die and 2,300 are injured.
* 1692– 1694: Famine in France kills two million.
* 1693: College of William & Mary is founded in Williamsburg, Virginia, by a royal charter.
* 1694: The Bank of England is established.
* 1695: The Mughal Empire nearly bans the East India Company in response to pirate Henry Every's capture of the trading ship '' Ganj-i-Sawai''.
* 1696– 1697: Famine in
* 1689: Bill of Rights gains royal consent.
* 1689: John Locke publishes '' Two Treatises of Government'' and '' A Letter Concerning Toleration.''
* 1690: The Battle of the Boyne in Ireland.
* 1692: Port Royal in Jamaica is struck by an earthquake and a tsunami. Approximately 2,000 people die and 2,300 are injured.
* 1692– 1694: Famine in France kills two million.
* 1693: College of William & Mary is founded in Williamsburg, Virginia, by a royal charter.
* 1694: The Bank of England is established.
* 1695: The Mughal Empire nearly bans the East India Company in response to pirate Henry Every's capture of the trading ship '' Ganj-i-Sawai''.
* 1696– 1697: Famine in
Famine in Scotland: The 'Ill Years' of the 1690s
'". Edinburgh University Press. p. 20. * 1697– 1699: Grand Embassy of Peter the Great to Western Europe. * 1699: Thomas Savery demonstrates his first steam engine to the Royal Society.
File:Albrecht Wallenstein.jpeg, Catholic general Albrecht von Wallenstein (1583–1634), supreme commander of the armies of the Imperial Army during the Thirty Years War
File:Jan Pieterszoon Coen.jpg, Jan Pieterszoon Coen (1587–1629), the founder of Batavia, was an officer of the Dutch East India Company (VOC), holding two terms as its Governor-General of the Dutch East Indies
File:René Descartes i samtal med Sveriges drottning, Kristina.jpg, René Descartes (1596–1650) with Queen Christina of Sweden (1626–1689)
File:Cardinal Mazarin by Pierre Mignard (Musée Condé).jpg, Cardinal Mazarin (1602–1661), who served as the chief minister to the kings of France Louis XIII and Louis XIV
File:Aurangzeb-portrait.jpg, Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb (1618–1707), who ruled over almost the entire Indian subcontinent for a period of 49 years
File:Shivaji British Museum.jpg, Chhatrapati Shivaji (1630–1680) founder of Maratha Empire is widely regarded as one of the greatest Hindu rulers
File:Portrait of the Kangxi Emperor in Court Dress.jpg, Kangxi Emperor (1661–1722) one of the most influential emperors of the Qing dynasty
File:Tokugawa Ieyasu2.JPG, '' Shōgun'' Tokugawa Ieyasu was the founder of Japan's final shogunate, which lasted well into the 19th century
 * Chang, Chun-shu, and Shelley Hsueh-lun Chang. ''Crisis and Transformation in Seventeenth-Century China'' (1998).
* Langer, William. ''An Encyclopedia of World History'' (5th ed. 1973); highly detailed outline of event
* Chang, Chun-shu, and Shelley Hsueh-lun Chang. ''Crisis and Transformation in Seventeenth-Century China'' (1998).
* Langer, William. ''An Encyclopedia of World History'' (5th ed. 1973); highly detailed outline of event
online free
* Reid, A. J. S. ''Trade and State Power in 16th & 17th Century Southeast Asia'' (1977). * Spence, J. D. ''The Death of Woman Wang: Rural Life in China in the 17th Century'' (1978).
in JSTOR
* Ogg, David. ''Europe in the Seventeenth Century'' (6th ed. 1965). * Rowbotham, Sheila. ''Hidden from history: Rediscovering women in history from the 17th century to the present'' (1976). * Trevor-Roper, Hugh R. "The general crisis of the 17th century." '' Past & Present'' 16 (1959): 31–64.
Vistorica
Timelines of 17th century events, science, culture and persons {{Authority control 2nd millennium Centuries Early modern period
1601
This Epoch (reference date)#Computing, epoch is the beginning of the 400-year Gregorian leap-year cycle within which digital files first existed; the last year of any such cycle is the only leap year whose year number is divisible by 100.
Jan ...
(represented by the Roman numerals
Roman numerals are a numeral system that originated in ancient Rome and remained the usual way of writing numbers throughout Europe well into the Late Middle Ages. Numbers are written with combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet, eac ...
MDCI), to December 31, 1700 (MDCC).
It falls into the early modern period of Europe and in that continent (whose impact on the world was increasing) was characterized by the Baroque cultural movement, the latter part of the Spanish Golden Age, the Dutch Golden Age, the French '' Grand Siècle'' dominated by Louis XIV, the Scientific Revolution, the world's first public company and megacorporation known as the Dutch East India Company, and according to some historians, the General Crisis.
From the mid-17th century, European politics were increasingly dominated by the Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the Middle Ages, medieval and Early modern France, early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe from th ...
of Louis XIV, where royal power was solidified domestically in the civil war of the Fronde. The semi-feudal territorial French nobility was weakened and subjugated to the power of an absolute monarchy through the reinvention of the Palace of Versailles from a hunting lodge to a gilded prison, in which a greatly expanded royal court could be more easily kept under surveillance. With domestic peace assured, Louis XIV caused the borders of France to be expanded. It was during this century that the English monarch became increasingly involved in conflicts with the Parliament - this would culminate in the English civil war and an end to the dominance of the English monarchy. By the end of the century, Europeans were masters of logarithms, electricity, the telescope and microscope, calculus, universal gravitation, Newton's Laws of Motion, air pressure, and calculating machines due to the work of the first scientists of the Scientific Revolution, including Galileo Galilei, Johannes Kepler, René Descartes, Pierre Fermat, Blaise Pascal, Robert Boyle, Christiaan Huygens, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, Robert Hooke, Isaac Newton, and Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz. It was also a period of development of culture in general (especially theater, music, visual arts and philosophy). Some of the greatest inventions took place in this century.
It was during this period that the European colonization of the Americas began in earnest, including the exploitation of the silver deposits, which resulted in bouts of inflation as wealth was drawn into Europe. Also during this period, there would be a more intense European presence in Southeast Asia and East Asia (such as the colonization of Taiwan). These foreign elements would contribute to a revolution in Ayutthaya. While the Mataram Sultanate and the Aceh Sultanate would be the major powers of the region, especially during the first half of the century.
In the Islamic world, the gunpowder empires – the Ottoman, Safavid, and Mughal – grew in strength as well. The southern half of India would see the decline of the Deccan Sultanates and extinction of the Vijayanagara Empire. The Dutch would colonize Ceylon and endure hostilities with Kandy. The end of the 17th century saw the first major surrender of Ottoman territory in Europe when the Treaty of Karlowitz ceded most of Hungary to the Habsburgs in 1699.
In Japan, Tokugawa Ieyasu established the Tokugawa shogunate at the beginning of the century, beginning the Edo period; the isolationist Sakoku policy began in the 1630s and lasted until the 19th century. In China, the collapsing Ming dynasty was challenged by a series of conquests led by the Manchu warlord Nurhaci, which were consolidated by his son Hong Taiji and finally consummated by his grandson, the Shunzhi Emperor, founder of the Qing dynasty. Qing China spent decades of this century with economic problems (results of civil wars between the Qing and former Ming dynasty loyalists), only recovering well at the end of the century.
The greatest military conflicts of the century were the Thirty Years' War, Dutch–Portuguese War, the Great Turkish War, the Nine Years' War, Mughal–Safavid Wars, and the Qing annexation of the Ming.
By the end of the century, Europeans were masters of logarithms, electricity, the telescope and microscope, calculus, universal gravitation, Newton's Laws of Motion, air pressure, and calculating machines due to the work of the first scientists of the Scientific Revolution, including Galileo Galilei, Johannes Kepler, René Descartes, Pierre Fermat, Blaise Pascal, Robert Boyle, Christiaan Huygens, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, Robert Hooke, Isaac Newton, and Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz. It was also a period of development of culture in general (especially theater, music, visual arts and philosophy). Some of the greatest inventions took place in this century.
It was during this period that the European colonization of the Americas began in earnest, including the exploitation of the silver deposits, which resulted in bouts of inflation as wealth was drawn into Europe. Also during this period, there would be a more intense European presence in Southeast Asia and East Asia (such as the colonization of Taiwan). These foreign elements would contribute to a revolution in Ayutthaya. While the Mataram Sultanate and the Aceh Sultanate would be the major powers of the region, especially during the first half of the century.
In the Islamic world, the gunpowder empires – the Ottoman, Safavid, and Mughal – grew in strength as well. The southern half of India would see the decline of the Deccan Sultanates and extinction of the Vijayanagara Empire. The Dutch would colonize Ceylon and endure hostilities with Kandy. The end of the 17th century saw the first major surrender of Ottoman territory in Europe when the Treaty of Karlowitz ceded most of Hungary to the Habsburgs in 1699.
In Japan, Tokugawa Ieyasu established the Tokugawa shogunate at the beginning of the century, beginning the Edo period; the isolationist Sakoku policy began in the 1630s and lasted until the 19th century. In China, the collapsing Ming dynasty was challenged by a series of conquests led by the Manchu warlord Nurhaci, which were consolidated by his son Hong Taiji and finally consummated by his grandson, the Shunzhi Emperor, founder of the Qing dynasty. Qing China spent decades of this century with economic problems (results of civil wars between the Qing and former Ming dynasty loyalists), only recovering well at the end of the century.
The greatest military conflicts of the century were the Thirty Years' War, Dutch–Portuguese War, the Great Turkish War, the Nine Years' War, Mughal–Safavid Wars, and the Qing annexation of the Ming.
Events
1601–1650
*1601
This Epoch (reference date)#Computing, epoch is the beginning of the 400-year Gregorian leap-year cycle within which digital files first existed; the last year of any such cycle is the only leap year whose year number is divisible by 100.
Jan ...
: 4th Spanish Armada; in the Battle of Kinsale, England defeats Irish and Spanish forces, driving the Gaelic aristocracy out of Ireland and destroying the Gaelic clan system.
* 1601
This Epoch (reference date)#Computing, epoch is the beginning of the 400-year Gregorian leap-year cycle within which digital files first existed; the last year of any such cycle is the only leap year whose year number is divisible by 100.
Jan ...
– 1603: The Russian famine of 1601–1603 kills perhaps one-third of Russia.
* 1602: Matteo Ricci produces the Map of the Myriad Countries of the World (坤輿萬國全圖, ''Kūnyú Wànguó Quántú''), a world map that will be used throughout East Asia for centuries.
* 1602: The Dutch East India Company (VOC) is established by merging competing Dutch trading companies.Ricklefs (1991), page 28 Its success contributes to the Dutch Golden Age.
* 1603: Elizabeth I of England dies and is succeeded by her cousin King James VI of Scotland, uniting the crowns of Scotland and England.
* 1603: Tokugawa Ieyasu takes the title of '' shōgun'', establishing the Tokugawa shogunate. This begins the Edo period, which will last until 1868.
* 1603: In Nagasaki, the Portuguese Jesuit missionary João Rodrigues publishes '' Nippo Jisho'', the first dictionary of Japanese to a European (Portuguese) language.
* 1605: The King of Gowa, a Makassarese kingdom in South Sulawesi, converts to Islam. * 1605– 1627: The reign of Mughal emperor Jahangir after the death of emperor Akbar.
* 1606: The Long Turkish War between the
* 1605– 1627: The reign of Mughal emperor Jahangir after the death of emperor Akbar.
* 1606: The Long Turkish War between the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
and Austria is ended with the Peace of Zsitvatorok—Austria abandons Transylvania.
* 1606: Treaty of Vienna ends an anti-Habsburg uprising in Royal Hungary.
* 1606: Willem Janszoon captained the first recorded European landing on the Australian continent, sailing from Bantam, Java, in the '' Duyfken''.
* 1607: Flight of the Earls (the fleeing of most of the native Gaelic aristocracy) occurs from County Donegal in the west of Ulster in Ireland.
* 1607: Iskandar Muda becomes the Sultan of Aceh for 30 years. He will launch a series of naval conquests that will transform Aceh into a great power in the western Malay Archipelago.
* 1610: The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth army defeats combined Russian–Swedish forces at the Battle of Klushino and conquers Moscow.
* 1610: King Henry IV of France is assassinated by François Ravaillac.
* 1611: The Pontifical and Royal University of Santo Tomas, the oldest existing university in Asia, is established by the Dominican Order in ManilaHistory of USTUST.edu.ph. Retrieved December 21, 2008. * 1611: The first publication of the King James Bible. * 1612: The first Cotswold Olympic Games, an annual public celebration of games and sports begins in the Cotswolds, England. * 1613: The Time of Troubles in Russia ends with the establishment of the House of Romanov, which rules until 1917. * 1613– 1617: Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth is invaded by the Tatars dozens of times.
 * 1613: The Dutch East India Company is forced to evacuate Gresik due to the Mataram siege in neighboring Surabaya. The dutch negotiates with Mataram and is allowed to set up a trading post in Jepara.
* 1614– 1615: The Siege of Osaka (last major threat to Tokugawa shogunate) ends.
* 1616: The last remaining Moriscos (Moors who had nominally converted to Christianity) in Spain are expelled.
* 1616: English poet and playwright
* 1613: The Dutch East India Company is forced to evacuate Gresik due to the Mataram siege in neighboring Surabaya. The dutch negotiates with Mataram and is allowed to set up a trading post in Jepara.
* 1614– 1615: The Siege of Osaka (last major threat to Tokugawa shogunate) ends.
* 1616: The last remaining Moriscos (Moors who had nominally converted to Christianity) in Spain are expelled.
* 1616: English poet and playwright William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 23 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's nation ...
dies.
* 1618: The Defenestration of Prague.
* 1618: The Bohemian Revolt precipitates the Thirty Years' War, which devastates Europe in the years 1618–48.
* 1618: The Manchus start invading China. Their conquest eventually topples the Ming dynasty.
* 1619: European slaving reaches America when the first Africans are brought to the present-day United States.
* 1619: The Dutch East India Company storm Jayakarta and withstand a months-long siege by the combined English, Bantenese and Jayakartan forces. They are relieved by Jan Pieterszoon Coen and a fleet of ships from Ambon. The dutch destroys Jayakarta and builds its new headquarters, Batavia, on top of it.
* 1620– 1621: Polish–Ottoman War over Moldavia.
* 1620: Bethlen Gabor allies with the Ottomans and an invasion of Moldavia takes place. The Polish suffer a disaster at Cecora on the River Prut.
* 1620: The Mayflower sets sail from Plymouth, England to what became the Plymouth Colony in New England. * 1621: The Battle of Chocim: Poles and Cossacks under Jan Karol Chodkiewicz defeat the Ottomans.
* 1622: Jamestown massacre: Algonquian natives kill 347 English settlers outside Jamestown, Virginia (approximately one-third of the colony's population) and burn the Henricus settlement.
* 1624– 1642: As chief minister, Cardinal Richelieu centralises power in
* 1621: The Battle of Chocim: Poles and Cossacks under Jan Karol Chodkiewicz defeat the Ottomans.
* 1622: Jamestown massacre: Algonquian natives kill 347 English settlers outside Jamestown, Virginia (approximately one-third of the colony's population) and burn the Henricus settlement.
* 1624– 1642: As chief minister, Cardinal Richelieu centralises power in France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
.
* 1626: St. Peter's Basilica in the Vatican completed.
* 1627: Aurochs go extinct.
* 1628– 1629: Sultan Agung of Mataram launches a failed campaign to conquer Dutch Batavia.
* 1629: Abbas I, the Safavids king, died.
* 1629: Cardinal Richelieu allies with Swedish Protestant forces in the Thirty Years' War to counter Ferdinand II's expansion.
* 1630: Birth of Shivaji at Shivneri fort, in present day Maharashtra, India, who later founded Maratha Empire in year 1674.
* 1631: Mount Vesuvius erupts.
* 1632: Battle of Lützen, death of king of Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
Gustav II Adolf.
* 1632: Taj Mahal building work started in Agra, India.
* 1633: Galileo Galilei arrives in Rome for his trial before the Inquisition.
* 1633– 1639: Japan transforms into "locked country".
* 1634: Battle of Nördlingen results in Catholic victory.
* 1636: Harvard University
Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyma ...
is founded in Cambridge, Massachusetts.
* 1637: Shimabara Rebellion of Japanese Christians, rōnin and peasants against Edo.
* 1637: The first opera house, Teatro San Cassiano, opens in Venice.
* 1637: Qing dynasty attacked the Joseon dynasty.
* 1639: Naval Battle of the Downs – Republic of the United Provinces fleet decisively defeats a Spanish fleet in English waters.
* 1639: Disagreements between the Farnese and Barberini Pope Urban VIII escalate into the Wars of Castro and last until 1649.
* 1639– 1651: Wars of the Three Kingdoms, civil wars throughout Scotland, Ireland, and England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
.
* 1640– 1668: The Portuguese Restoration War led to the end of the Iberian Union.
* 1641: The Irish Rebellion, by Irish Catholics who wanted an end to discrimination, greater self-governance, and reverse ownership of the plantations of Ireland.
* 1641: René Descartes publishes ''Meditationes de prima philosophia'' Meditations on First Philosophy.
* 1642: Beginning of English Civil War, conflict will end in 1649 with the execution of King Charles I, the abolition of the monarchy and the establishment of the supremacy of Parliament over the king.
* 1643: L'incoronazione di Poppea, Monterverdi
* 1644: The Manchu conquer China ending the Ming dynasty. The subsequent Qing dynasty rules until 1912.
* 1644– 1674: The Mauritanian Thirty-Year War.
* 1645– 1669: Ottoman war with Venice. The Ottomans invade Crete and capture Canea.
* 1647– 1652: The Great Plague of Seville.
* 1648: The Peace of Westphalia ends the Thirty Years' War and the Eighty Years' War and marks the ends of Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
and the Holy Roman Empire as major European powers. * 1648– 1653: Fronde civil war in
* 1648– 1653: Fronde civil war in France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
.
* 1648– 1657: The Khmelnytsky Uprising – a Cossack rebellion in Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
which turned into a Ukrainian war of liberation from Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
.
* 1648– 1667: The Deluge wars leave Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in ruins.
* 1648– 1669: The Ottomans capture Crete from the Venetians after the Siege of Candia.
* 1649: King Charles I is executed for high treason, the first and only English king to be subjected to legal proceedings in a High Court of Justice
The High Court of Justice in London, known properly as His Majesty's High Court of Justice in England, together with the Court of Appeal (England and Wales), Court of Appeal and the Crown Court, are the Courts of England and Wales, Senior Cour ...
and put to death.
* 1649– 1653: The Cromwellian conquest of Ireland.
1651–1700
* 1651: English Civil War ends with the Parliamentarian victory at the Battle of Worcester. * 1656– 1661: Mehmed Köprülü is Grand Vizier. * 1655– 1661: The Northern Wars cement Sweden's rise as a Great Power. * 1657 : Sambhaji, the second King of Maratha Empire and eldest son of King Shivaji was born at Purandar Fort on 14 May. * 1658: After his father Shah Jahan completes the Taj Mahal, his son Aurangzeb deposes him as ruler of the Mughal Empire. * 1659: King Shivaji killed Adil Shahi dynasty's general Afzal Khan at Pratapgad fort on 9 November. * 1660: The Commonwealth of England ends and the monarchy is brought back during the English Restoration. * 1660: The Royal Society is founded. * 1660: The Bruneian Civil War begins * 1661: The reign of the Kangxi Emperor of China begins. * 1663: Ottoman war against Habsburg Hungary. * 1664: The Battle of St. Gotthard: count Raimondo Montecuccoli defeats the Ottomans. The Peace of Vasvar – intended to keep the peace for 20 years. * 1665: Maratha King Shivaji signed the Treaty of Purandar with Mughal general Jai Singh I after Battle of Purandar. * 1665: Robert Hooke discovers cells using a microscope. * 1665:Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
defeats the Kongo Empire at the Battle of Mbwila.
* 1665– 1667: The Second Anglo-Dutch War fought between England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
and the United Provinces.
* 1666: The Great Fire of London.
* 1666: Shivaji visited Aurangzeb at Agra Fort and forced him into house arrest. Shivaji later escaped and returned to the Maratha kingdom.
* 1667: The Raid on the Medway during the Second Anglo-Dutch War.
* 1667– 1668: The War of Devolution: France invades the Netherlands. The Peace of Aix-la-Chapelle (1668) brings this to a halt.
* 1667– 1699: The Great Turkish War halts the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
's expansion into Europe.
* 1672– 1673: Ottoman campaign to help the Ukrainian Cossacks. John Sobieski defeats the Ottomans at the second battle of Khotyn (1673).
* 1672– 1674: The Third Anglo-Dutch War fought between England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
and the United Provinces
* 1672– 1676: Polish–Ottoman War.Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
commence the Russo-Turkish Wars.
* 1678: The Treaty of Nijmegen ends various interconnected wars among France, the Dutch Republic, Spain, Brandenburg, Sweden, Denmark, the Prince-Bishopric of Münster, and the Holy Roman Empire. * 1680: The Pueblo Revolt drives the Spanish out of New Mexico until 1692.
* 1680: Prince Sambhaji crowned himself as the second '' Chatrapati'' of Maratha Empire 20 July.
* 1682: French explorer Robert La Salle claims all the land east of the Mississippi River.
* 1683:
* 1680: The Pueblo Revolt drives the Spanish out of New Mexico until 1692.
* 1680: Prince Sambhaji crowned himself as the second '' Chatrapati'' of Maratha Empire 20 July.
* 1682: French explorer Robert La Salle claims all the land east of the Mississippi River.
* 1683: China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
conquers the Kingdom of Tungning and annexes Taiwan.
* 1683: The Ottoman Empire is defeated in the second Siege of Vienna.
* 1683– 1699: The Great Turkish War leads to the conquest of most of Ottoman Hungary by the Habsburgs.
* 1687: Isaac Newton publishes '' Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica''.
* 1688: The Siege of Derry, the first major event in the Williamite War in Ireland.
* 1688: Siamese revolution of 1688 ousted French influence and virtually severed all ties with the West until the 19th century.
* 1688– 1689: The Glorious Revolution starts with the Dutch Republic invading England, England becomes a constitutional monarchy.
* 1688– 1691: The War of the Two Kings in Ireland.
* 1688– 1697: The Grand Alliance sought to stop French expansion during the Nine Years' War.
* 1689: The Battle of Killiecrankie is fought between Jacobite and Williamite forces in Highland Perthshire.
* 1689: The Karposh rebellion is crushed in present-day North Macedonia, Skopje is retaken by the Ottoman Turks. Karposh is killed, and the rebels are defeated. * 1689: Bill of Rights gains royal consent.
* 1689: John Locke publishes '' Two Treatises of Government'' and '' A Letter Concerning Toleration.''
* 1690: The Battle of the Boyne in Ireland.
* 1692: Port Royal in Jamaica is struck by an earthquake and a tsunami. Approximately 2,000 people die and 2,300 are injured.
* 1692– 1694: Famine in France kills two million.
* 1693: College of William & Mary is founded in Williamsburg, Virginia, by a royal charter.
* 1694: The Bank of England is established.
* 1695: The Mughal Empire nearly bans the East India Company in response to pirate Henry Every's capture of the trading ship '' Ganj-i-Sawai''.
* 1696– 1697: Famine in
* 1689: Bill of Rights gains royal consent.
* 1689: John Locke publishes '' Two Treatises of Government'' and '' A Letter Concerning Toleration.''
* 1690: The Battle of the Boyne in Ireland.
* 1692: Port Royal in Jamaica is struck by an earthquake and a tsunami. Approximately 2,000 people die and 2,300 are injured.
* 1692– 1694: Famine in France kills two million.
* 1693: College of William & Mary is founded in Williamsburg, Virginia, by a royal charter.
* 1694: The Bank of England is established.
* 1695: The Mughal Empire nearly bans the East India Company in response to pirate Henry Every's capture of the trading ship '' Ganj-i-Sawai''.
* 1696– 1697: Famine in Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
wipes out almost one-third of the population.Karen J. Cullen (2010). "Famine in Scotland: The 'Ill Years' of the 1690s
'". Edinburgh University Press. p. 20. * 1697– 1699: Grand Embassy of Peter the Great to Western Europe. * 1699: Thomas Savery demonstrates his first steam engine to the Royal Society.
Gallery
Inventions, discoveries, introductions
Major changes in philosophy and science take place, often characterized as the Scientific Revolution. * Banknotes reintroduced in Europe. * Ice cream. * Tea and coffee become popular in Europe. * Central Banking in France and modern Finance by Scottish economist John Law. * Minarets, Jamé Mosque of Isfahan, Isfahan, Persia (Iran), are built. * 1604: Supernova SN 1604 is observed in the Milky Way. * 1605: Johannes Kepler starts investigating elliptical orbits of planets. * 1605: Johann Carolus of Germany publishes the 'Relation', the first newspaper. * 1608: Refracting telescopes first appear. Dutch spectacle-maker Hans Lippershey tries to obtain a patent on one, spreading word of the invention. * 1610: The Orion Nebula is identified by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc of France. * 1610: Galileo Galilei and Simon Marius observeJupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined a ...
's Galilean moons.
* 1611: King James Bible or 'Authorized Version' first published.
* 1612: The first flintlock musket likely created for Louis XIII of France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
by gunsmith Marin Bourgeois.
* 1614: John Napier introduces the logarithm to simplify calculations.
* 1616: Niccolò Zucchi describes experiments with a bronze parabolic mirror trying to make a reflecting telescope.
* 1620: Cornelis Drebbel, funded by James I of England, builds the first ' submarine' made of wood and greased leather.
* 1623: The third English dictionary, ''English Dictionarie'', is published by Henry Cockeram, listing difficult words with definitions.
* 1628: William Harvey publishes and elucidates his earlier discovery of the circulatory system.
* 1637: Dutch Bible published.
* 1637: Teatro San Cassiano, the first public opera house, opened in Venice.
* 1637: Pierre de Fermat formulates his so-called Last Theorem, unsolved until 1995.
* 1637: Although Chinese naval mines were earlier described in the 14th century '' Huolongjing'', the ''Tian Gong Kai Wu'' book of Ming dynasty scholar Song Yingxing describes naval mines wrapped in a lacquer bag and ignited by an ambusher pulling a rip cord on the nearby shore that triggers a steel-wheel flint mechanism.
* 1642: Blaise Pascal invents the mechanical calculator called Pascal's calculator.
* 1642: Mezzotint engraving introduces grey tones to printed images.
* 1643: Evangelista Torricelli of Italy invents the mercury barometer.
* 1645: Giacomo Torelli of Venice, Italy invents the first rotating stage.
* 1651: Giovanni Riccioli renames the lunar maria.
* 1656: Christiaan Huygens describes the true shape of the rings of Saturn.
* 1657: Christiaan Huygens develops the first functional pendulum clock based on the learnings of Galileo Galilei.
* 1659: Christiaan Huygens first to observe surface details of Mars.
* 1662: Christopher Merret presents first paper on the production of sparkling wine.
* 1663: James Gregory publishes designs for a reflecting telescope.
* 1669: The first known operational reflecting telescope is built by Isaac Newton.
* 1676: Antonie van Leeuwenhoek discovers Bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
.
* 1676: First measurement of the speed of light.
* 1679: Binary system developed by Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz.
* 1684: Calculus independently developed by both Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz and Sir Isaac Newton and used to formulate classical mechanics.
References
Further reading
 * Chang, Chun-shu, and Shelley Hsueh-lun Chang. ''Crisis and Transformation in Seventeenth-Century China'' (1998).
* Langer, William. ''An Encyclopedia of World History'' (5th ed. 1973); highly detailed outline of event
* Chang, Chun-shu, and Shelley Hsueh-lun Chang. ''Crisis and Transformation in Seventeenth-Century China'' (1998).
* Langer, William. ''An Encyclopedia of World History'' (5th ed. 1973); highly detailed outline of eventonline free
* Reid, A. J. S. ''Trade and State Power in 16th & 17th Century Southeast Asia'' (1977). * Spence, J. D. ''The Death of Woman Wang: Rural Life in China in the 17th Century'' (1978).
Focus on Europe
* Clark, George. ''The Seventeenth Century'' (2nd ed. 1945). * Hampshire, Stuart. ''The Age of Reason the 17th Century Philosophers, Selected, with Introduction and Interpretive Commentary'' (1961). * * Lewitter, Lucian Ryszard. "Poland, the Ukraine and Russia in the 17th Century." '' The Slavonic and East European Review'' (1948): 157–171in JSTOR
* Ogg, David. ''Europe in the Seventeenth Century'' (6th ed. 1965). * Rowbotham, Sheila. ''Hidden from history: Rediscovering women in history from the 17th century to the present'' (1976). * Trevor-Roper, Hugh R. "The general crisis of the 17th century." '' Past & Present'' 16 (1959): 31–64.
External links
Vistorica
Timelines of 17th century events, science, culture and persons {{Authority control 2nd millennium Centuries Early modern period