ļČüņĪ░ņäĀ ļ»╝ņŻ╝ņŻ╝ņØś ļ»╝ņĪ▒ĒåĄņØ╝ņĀäņäĀ ņØ╝ļÅÖ on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in
 The modern spelling of Korea first appeared in 1671 in the travel writings of the
The modern spelling of Korea first appeared in 1671 in the travel writings of the
 According to
According to
. Shsu.edu. Retrieved April 17, 2015. Beginning around 300 BC, the Japonic-speaking
 Towards the end of
Towards the end of
 The military of North Korea invaded the
The military of North Korea invaded the
 The post-war 1950s and 1960s saw an ideological shift in North Korea, as Kim Il Sung sought to consolidate his power. Kim Il Sung was highly critical of Soviet premier
The post-war 1950s and 1960s saw an ideological shift in North Korea, as Kim Il Sung sought to consolidate his power. Kim Il Sung was highly critical of Soviet premier  Industry was the favored sector in North Korea. Industrial production returned to pre-war levels by 1957. In 1959, relations with Japan had improved somewhat, and North Korea began allowing the repatriation of Japanese citizens in the country. The same year, North Korea revalued the
Industry was the favored sector in North Korea. Industrial production returned to pre-war levels by 1957. In 1959, relations with Japan had improved somewhat, and North Korea began allowing the repatriation of Japanese citizens in the country. The same year, North Korea revalued the
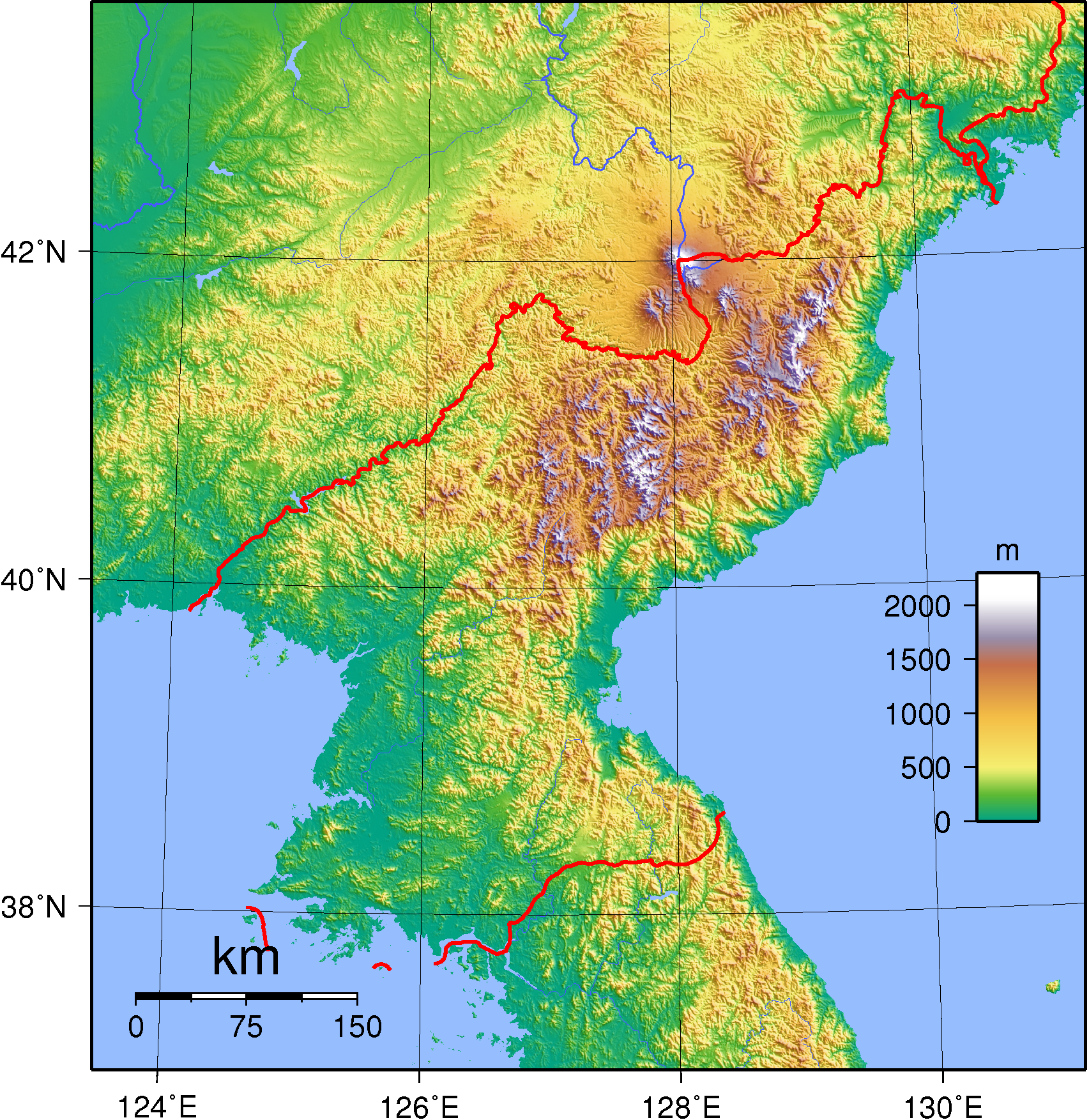 North Korea occupies the northern portion of the
North Korea occupies the northern portion of the
 North Korea experiences a
North Korea experiences a

 Since the founding of the nation, North Korea's supreme leadership has stayed within the Kim family, which in North Korea is referred to as the '' Mount Paektu Bloodline''. It is a three-generation lineage descending from the country's first leader, Kim Il Sung, who developed North Korea around the ''Juche ideology'', and stayed in power until his death. Kim developed a cult of personality closely tied to the state philosophy of Juche, which was later passed on to his successors: his son Kim Jong Il in 1994 and grandson Kim Jong Un in 2011. In 2013, Clause 2 of Article 10 of the newly edited ''Ten Fundamental Principles of the Workers' Party of Korea'' stated that the party and revolution must be carried "eternally" by the "Mount Paektu Bloodline".
According to ''New Focus International'', the cult of personality, particularly surrounding Kim Il Sung, has been crucial for legitimizing the family's hereditary succession. The control the North Korean government exercises over many aspects of the nation's culture is used to perpetuate the
Since the founding of the nation, North Korea's supreme leadership has stayed within the Kim family, which in North Korea is referred to as the '' Mount Paektu Bloodline''. It is a three-generation lineage descending from the country's first leader, Kim Il Sung, who developed North Korea around the ''Juche ideology'', and stayed in power until his death. Kim developed a cult of personality closely tied to the state philosophy of Juche, which was later passed on to his successors: his son Kim Jong Il in 1994 and grandson Kim Jong Un in 2011. In 2013, Clause 2 of Article 10 of the newly edited ''Ten Fundamental Principles of the Workers' Party of Korea'' stated that the party and revolution must be carried "eternally" by the "Mount Paektu Bloodline".
According to ''New Focus International'', the cult of personality, particularly surrounding Kim Il Sung, has been crucial for legitimizing the family's hereditary succession. The control the North Korean government exercises over many aspects of the nation's culture is used to perpetuate the  The song " No Motherland Without You", sung by the North Korean army choir, was created especially for Kim Jong Il and is one of the most popular tunes in the country. Kim Il Sung is still officially revered as the nation's "Eternal President". Several landmarks in North Korea are named for Kim Il Sung, including
The song " No Motherland Without You", sung by the North Korean army choir, was created especially for Kim Jong Il and is one of the most popular tunes in the country. Kim Il Sung is still officially revered as the nation's "Eternal President". Several landmarks in North Korea are named for Kim Il Sung, including
 The
The  The
The
 North Korea is a nuclear-armed state, though the nature and strength of the country's arsenal is uncertain. , estimates of its size ranged between 40 and 116 assembled nuclear warheads. Delivery capabilities are provided by the Rocket Force, which has some 1,000
North Korea is a nuclear-armed state, though the nature and strength of the country's arsenal is uncertain. , estimates of its size ranged between 40 and 116 assembled nuclear warheads. Delivery capabilities are provided by the Rocket Force, which has some 1,000
here
 North Korea has a civil law system based on the Prussian model and influenced by Japanese traditions and communist legal theory. Judiciary procedures are handled by the Central Court (the highest
North Korea has a civil law system based on the Prussian model and influenced by Japanese traditions and communist legal theory. Judiciary procedures are handled by the Central Court (the highest
, ''KCNA'', 22 December 2005.
, ''KCNA'', 8 November 2005. In a 2014 report to the UN, North Korea dismissed accusations of atrocities as wild rumors. The official state media, Korean Central News Agency, KCNA, responded with an article that included homophobic insults against the author of the human rights report, Michael Kirby (judge), Michael Kirby, calling him "a disgusting old lecher with a 40-odd-year-long career of homosexuality ... This practice can never be found in the DPRK boasting of the sound mentality and good morals ... In fact, it is ridiculous for such gay to sponsor dealing with others' human rights issue." The government, however, admitted some human rights issues related to living conditions and stated that it is working to improve them.
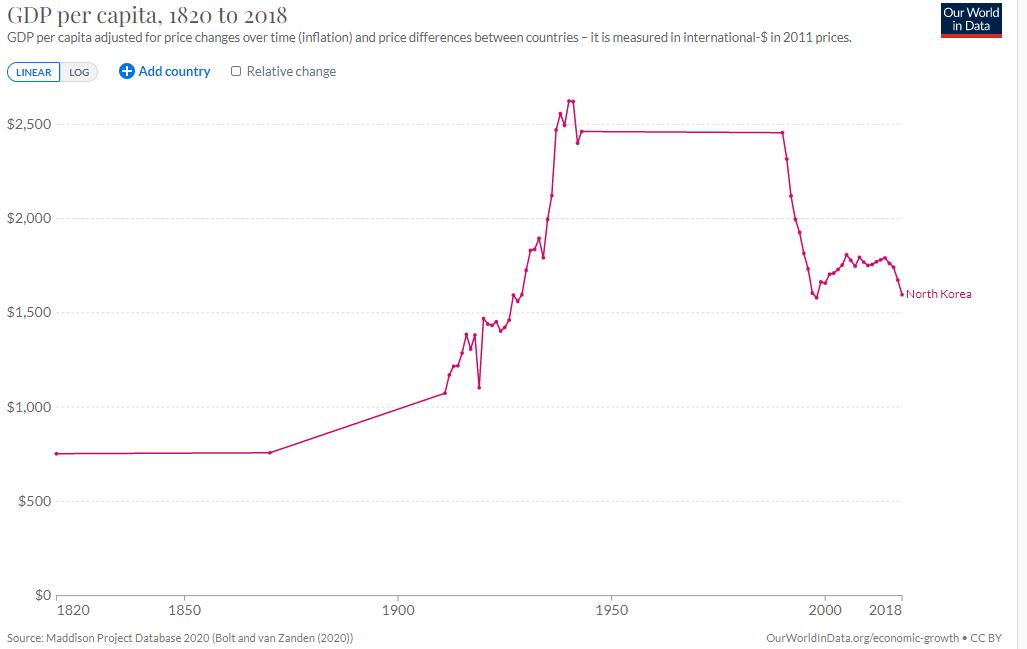 North Korea has maintained one of the most closed and centralized economies in the world since the 1940s. For several decades, it followed the Soviet pattern of five-year plans with the ultimate goal of achieving self-sufficiency. Extensive Soviet and Chinese support allowed North Korea to rapidly recover from the Korean War and register very high growth rates. Systematic inefficiency began to arise around 1960, when the economy shifted from the extensive growth, extensive to the intensive growth, intensive development stage. The shortage of skilled labor, energy, arable land and transportation significantly impeded long-term growth and resulted in consistent failure to meet planning objectives. The major slowdown of the economy contrasted with South Korea, which surpassed the North in terms of absolute Gross domestic product, GDP and per capita income by the 1980s. North Korea declared the last seven-year plan unsuccessful in December 1993 and thereafter stopped announcing plans.
The loss of
North Korea has maintained one of the most closed and centralized economies in the world since the 1940s. For several decades, it followed the Soviet pattern of five-year plans with the ultimate goal of achieving self-sufficiency. Extensive Soviet and Chinese support allowed North Korea to rapidly recover from the Korean War and register very high growth rates. Systematic inefficiency began to arise around 1960, when the economy shifted from the extensive growth, extensive to the intensive growth, intensive development stage. The shortage of skilled labor, energy, arable land and transportation significantly impeded long-term growth and resulted in consistent failure to meet planning objectives. The major slowdown of the economy contrasted with South Korea, which surpassed the North in terms of absolute Gross domestic product, GDP and per capita income by the 1980s. North Korea declared the last seven-year plan unsuccessful in December 1993 and thereafter stopped announcing plans.
The loss of
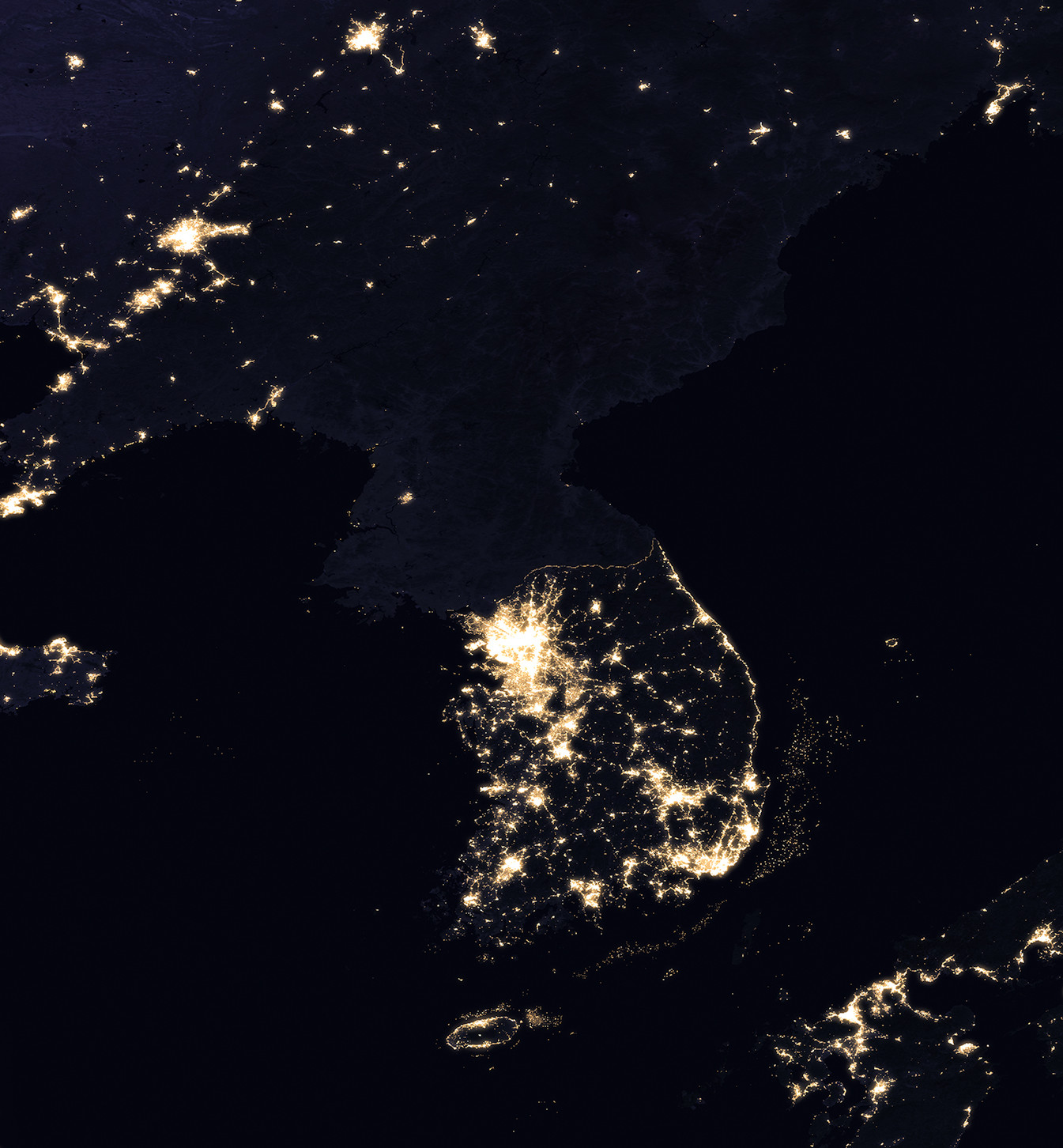 North Korea's energy infrastructure is obsolete and in disrepair. Power shortages are chronic and would not be alleviated even by electricity imports because the poorly maintained grid causes significant losses during transmission. Coal accounts for 70% of primary energy production, followed by hydroelectric power with 17%. The government under Kim Jong Un has increased emphasis on renewable energy projects like wind farms, solar parks, solar heating and biomass. A set of legal regulations adopted in 2014 stressed the development of geothermal, wind and solar energy along with recycling and environmental conservation. North Korea's long-term objective is to curb fossil fuel usage and reach an output of 5 million kilowatts from renewable sources by 2044, up from its current total of 430,000 kilowatts from all sources. Wind power is projected to satisfy 15% of the country's total energy demand under this strategy.
North Korea also strives to develop its own civilian nuclear program. These efforts are under much international dispute due to their military applications and concerns about safety.
North Korea's energy infrastructure is obsolete and in disrepair. Power shortages are chronic and would not be alleviated even by electricity imports because the poorly maintained grid causes significant losses during transmission. Coal accounts for 70% of primary energy production, followed by hydroelectric power with 17%. The government under Kim Jong Un has increased emphasis on renewable energy projects like wind farms, solar parks, solar heating and biomass. A set of legal regulations adopted in 2014 stressed the development of geothermal, wind and solar energy along with recycling and environmental conservation. North Korea's long-term objective is to curb fossil fuel usage and reach an output of 5 million kilowatts from renewable sources by 2044, up from its current total of 430,000 kilowatts from all sources. Wind power is projected to satisfy 15% of the country's total energy demand under this strategy.
North Korea also strives to develop its own civilian nuclear program. These efforts are under much international dispute due to their military applications and concerns about safety.
 Under its "constructing a powerful knowledge economy" slogan, the state has launched a project to concentrate education, scientific research and production into a number of "high-tech development zones". International sanctions remain a significant obstacle to their development. The ''Miraewon'' network of electronic library, electronic libraries was established in 2014 under similar slogans.
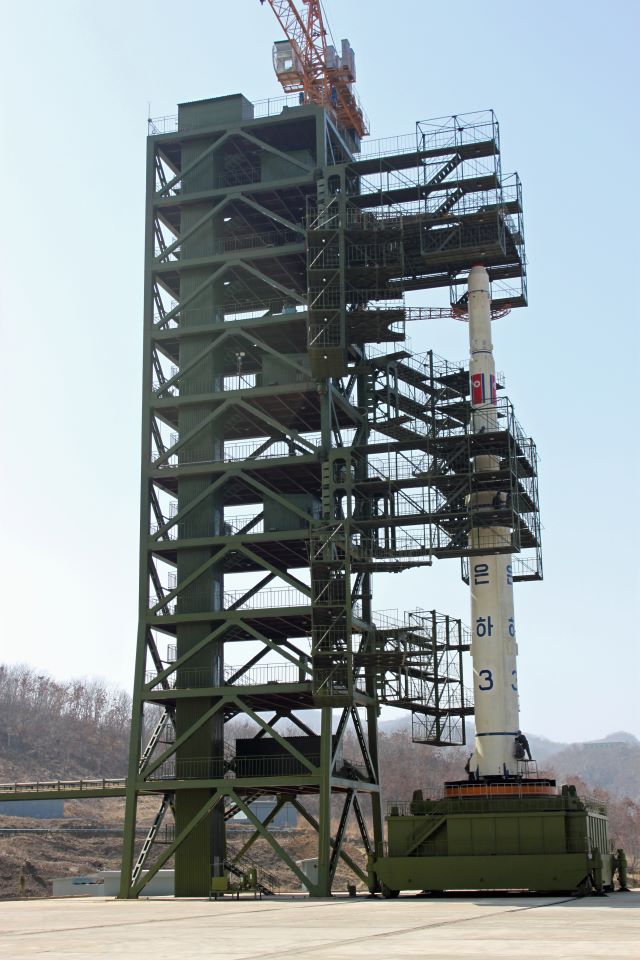
Significant resources have been allocated to the national space program, which is managed by the National Aerospace Technology Administration (formerly managed by the Korean Committee of Space Technology until April 2013). Domestically produced space launch vehicle, launch vehicles and the Kwangmyŏngsŏng program, Kwangmyŏngsŏng satellite class are launched from two spaceports, the Tonghae Satellite Launching Ground and the Sohae Satellite Launching Station. After four failed attempts, North Korea became the Timeline of first orbital launches by country, tenth spacefaring nation with the launch of Kwangmyŏngsŏng-3 Unit 2 in December 2012, which successfully reached orbit but was believed to be crippled and non-operational. It joined the Outer Space Treaty in 2009 and has stated its intentions to undertake human spaceflight, crewed and Exploration of the Moon, Moon missions. The government insisted the space program is for peaceful purposes, but the United States, Japan, South Korea and other countries maintained that it serves to advance North Korea's ballistic missile program. On 7 February 2016, a statement broadcast on Korean Central Television said that a new Earth observation satellite, Kwangmyŏngsŏng-4, Kwangmyongsong-4, had successfully been put into orbit.
Usage of communication technology is controlled by the Ministry of Post and Telecommunications (North Korea), Ministry of Post and Telecommunications. An adequate nationwide fiber-optic communication, fiber-optic telephony, telephone system with 1.18 million fixed lines and expanding mobile coverage is in place. Most phones are installed for senior government officials and installation requires written explanation why the user needs a telephone and how it will be paid for. Cellular coverage is available with a 3G network operated by Koryolink, a joint venture with Orascom Telecom Holding. The number of subscribers has increased from 3,000 in 2002 to almost two million in 2013. International calls through either fixed or cellular service are restricted, and Mobile Web, mobile Internet is not available.
Internet access itself is limited to a handful of elite users and scientists. Instead, North Korea has a Closed platform, walled garden intranet system called Kwangmyong (network), Kwangmyong, which is maintained and monitored by the Korea Computer Center. Its content is limited to state media, chat services, message boards, an e-mail service and an estimated 1,000ŌĆō5,500 websites. Computers employ the Red Star OS, an operating system derived from Linux, with a Shell (computing), user shell visually similar to that of OS X. On 19 September 2016, a TLDR project noticed the North Korean Internet DNS data and top-level domain was left open which allowed global DNS zone transfers. A dump of the data discovered was shared on GitHub.
Under its "constructing a powerful knowledge economy" slogan, the state has launched a project to concentrate education, scientific research and production into a number of "high-tech development zones". International sanctions remain a significant obstacle to their development. The ''Miraewon'' network of electronic library, electronic libraries was established in 2014 under similar slogans.
Significant resources have been allocated to the national space program, which is managed by the National Aerospace Technology Administration (formerly managed by the Korean Committee of Space Technology until April 2013). Domestically produced space launch vehicle, launch vehicles and the Kwangmyŏngsŏng program, Kwangmyŏngsŏng satellite class are launched from two spaceports, the Tonghae Satellite Launching Ground and the Sohae Satellite Launching Station. After four failed attempts, North Korea became the Timeline of first orbital launches by country, tenth spacefaring nation with the launch of Kwangmyŏngsŏng-3 Unit 2 in December 2012, which successfully reached orbit but was believed to be crippled and non-operational. It joined the Outer Space Treaty in 2009 and has stated its intentions to undertake human spaceflight, crewed and Exploration of the Moon, Moon missions. The government insisted the space program is for peaceful purposes, but the United States, Japan, South Korea and other countries maintained that it serves to advance North Korea's ballistic missile program. On 7 February 2016, a statement broadcast on Korean Central Television said that a new Earth observation satellite, Kwangmyŏngsŏng-4, Kwangmyongsong-4, had successfully been put into orbit.
Usage of communication technology is controlled by the Ministry of Post and Telecommunications (North Korea), Ministry of Post and Telecommunications. An adequate nationwide fiber-optic communication, fiber-optic telephony, telephone system with 1.18 million fixed lines and expanding mobile coverage is in place. Most phones are installed for senior government officials and installation requires written explanation why the user needs a telephone and how it will be paid for. Cellular coverage is available with a 3G network operated by Koryolink, a joint venture with Orascom Telecom Holding. The number of subscribers has increased from 3,000 in 2002 to almost two million in 2013. International calls through either fixed or cellular service are restricted, and Mobile Web, mobile Internet is not available.
Internet access itself is limited to a handful of elite users and scientists. Instead, North Korea has a Closed platform, walled garden intranet system called Kwangmyong (network), Kwangmyong, which is maintained and monitored by the Korea Computer Center. Its content is limited to state media, chat services, message boards, an e-mail service and an estimated 1,000ŌĆō5,500 websites. Computers employ the Red Star OS, an operating system derived from Linux, with a Shell (computing), user shell visually similar to that of OS X. On 19 September 2016, a TLDR project noticed the North Korean Internet DNS data and top-level domain was left open which allowed global DNS zone transfers. A dump of the data discovered was shared on GitHub.
 North Korea's population was 10.9 million in 1961. With the exception of a small Chinese people in Korea, Chinese community and a few ethnic Japanese people in North Korea, Japanese, North Korea's people are ethnically homogeneous. Demographic experts in the 20th century estimated that the population would grow to 25.5 million by 2000 and 28 million by 2010, but this increase never occurred due to the
North Korea's population was 10.9 million in 1961. With the exception of a small Chinese people in Korea, Chinese community and a few ethnic Japanese people in North Korea, Japanese, North Korea's people are ethnically homogeneous. Demographic experts in the 20th century estimated that the population would grow to 25.5 million by 2000 and 28 million by 2010, but this increase never occurred due to the
 North Korea has a life expectancy of 72.3 years in 2019, according to HDR 2020. While North Korea is classified as a low-income country, the structure of North Korea's causes of death (2013) is unlike that of other low-income countries. Instead, it is closer to worldwide averages, with non-communicable diseasesŌĆösuch as cardiovascular disease and cancersŌĆöaccounting for 84 percent of the total deaths in 2016.
According to the World Bank report of 2016 (based on World Health Organization, WHO's estimate), only 9.5% of the total deaths recorded in North Korea are attributed to communicable diseases and maternal, prenatal and nutrition conditions, a figure which is slightly lower than that of South Korea (10.1%) and one fifth of other low-income countries (50.1%) but higher than that of high income countries (6.7%). Only one out of ten leading causes of overall deaths in North Korea is attributed to communicable diseases (Lower respiratory tract infection, lower respiratory infection), a disease which is reported to have declined by six percent since 2007.
In 2013, cardiovascular disease as a single disease group was reported as the largest cause of death in North Korea. The three major causes of death in North Korea are stroke, Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, COPD and Coronary artery disease, ischaemic heart disease. Non-communicable diseases risk factors in North Korea include high rates of urbanization, an aging society, and high rates of Smoking in North Korea, smoking and Alcoholic beverage, alcohol consumption amongst men.
Maternal mortality is lower than other low-income countries, but significantly higher than South Korea and other high income countries, at 89 per 100,000 live births. In 2008 child mortality was estimated to be 45 per 1,000, which is much better than other economically comparable countries. Chad for example had a child mortality rate of 120 per 1,000, despite the fact that Chad was most likely wealthier than North Korea at the time.
Healthcare Access and Quality Index, as calculated by Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, IHME, was reported to stand at 62.3, much lower than that of South Korea.
According to a 2003 report by the United States Department of State, almost 100% of the population has access to water and sanitation. Further, 80% of the population had access to improved sanitation facilities in 2015.
North Korea has the highest number of doctors per capita amongst low-income countries, with 3.7 physicians per 1,000 people, a figure which is also significantly higher than that of South Korea, according to World Health Organization, WHO's data.
Conflicting reports between Amnesty and WHO have emerged, where the Amnesty report claimed that North Korea had an inadequate health care system, while the Director of the World Health Organization claimed that North Korea's healthcare system was considered the envy of the developing world and had "no lack of doctors and nurses".
A free universal insurance system is in place. Quality of medical care varies significantly by region and is often low, with severe shortages of equipment, drugs and anesthetics. According to WHO, expenditure on health per capita is one of the lowest in the world. Preventive healthcare, Preventive medicine is emphasized through physical exercise and sports, nationwide monthly checkups and routine spraying of public places against disease. Every individual has a lifetime health card which contains a full medical record.
North Korea has a life expectancy of 72.3 years in 2019, according to HDR 2020. While North Korea is classified as a low-income country, the structure of North Korea's causes of death (2013) is unlike that of other low-income countries. Instead, it is closer to worldwide averages, with non-communicable diseasesŌĆösuch as cardiovascular disease and cancersŌĆöaccounting for 84 percent of the total deaths in 2016.
According to the World Bank report of 2016 (based on World Health Organization, WHO's estimate), only 9.5% of the total deaths recorded in North Korea are attributed to communicable diseases and maternal, prenatal and nutrition conditions, a figure which is slightly lower than that of South Korea (10.1%) and one fifth of other low-income countries (50.1%) but higher than that of high income countries (6.7%). Only one out of ten leading causes of overall deaths in North Korea is attributed to communicable diseases (Lower respiratory tract infection, lower respiratory infection), a disease which is reported to have declined by six percent since 2007.
In 2013, cardiovascular disease as a single disease group was reported as the largest cause of death in North Korea. The three major causes of death in North Korea are stroke, Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, COPD and Coronary artery disease, ischaemic heart disease. Non-communicable diseases risk factors in North Korea include high rates of urbanization, an aging society, and high rates of Smoking in North Korea, smoking and Alcoholic beverage, alcohol consumption amongst men.
Maternal mortality is lower than other low-income countries, but significantly higher than South Korea and other high income countries, at 89 per 100,000 live births. In 2008 child mortality was estimated to be 45 per 1,000, which is much better than other economically comparable countries. Chad for example had a child mortality rate of 120 per 1,000, despite the fact that Chad was most likely wealthier than North Korea at the time.
Healthcare Access and Quality Index, as calculated by Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, IHME, was reported to stand at 62.3, much lower than that of South Korea.
According to a 2003 report by the United States Department of State, almost 100% of the population has access to water and sanitation. Further, 80% of the population had access to improved sanitation facilities in 2015.
North Korea has the highest number of doctors per capita amongst low-income countries, with 3.7 physicians per 1,000 people, a figure which is also significantly higher than that of South Korea, according to World Health Organization, WHO's data.
Conflicting reports between Amnesty and WHO have emerged, where the Amnesty report claimed that North Korea had an inadequate health care system, while the Director of the World Health Organization claimed that North Korea's healthcare system was considered the envy of the developing world and had "no lack of doctors and nurses".
A free universal insurance system is in place. Quality of medical care varies significantly by region and is often low, with severe shortages of equipment, drugs and anesthetics. According to WHO, expenditure on health per capita is one of the lowest in the world. Preventive healthcare, Preventive medicine is emphasized through physical exercise and sports, nationwide monthly checkups and routine spraying of public places against disease. Every individual has a lifetime health card which contains a full medical record.
 Government policies towards film are no different from those applied to other artsŌĆömotion pictures serve to fulfill the targets of "social education". Some of the most influential films are based on historic events (''An Jung-geun shoots It┼Ź Hirobumi'') or folk tales (''Hong Gildong jeon, Hong Gildong''). Most movies have predictable propaganda story lines which make cinema an unpopular entertainment; viewers only see films that feature their favorite actors. Western productions are only available at private showings to high-ranking Party members, although the 1997 film ''Titanic (1997 film), Titanic'' is frequently shown to university students as an example of Western culture. Access to foreign media products is available through smuggled DVDs and television or radio broadcasts in border areas. Western films like ''The Interview'', ''Charlie's Angels (2000 film), Charlie's Angels'', and the aforementioned ''Titanic'' are just a few films that have been smuggled across the borders of North Korea, allowing for access to the North Korean citizens.
North Korean media are under some of the strictest government control in the world. The censorship in North Korea encompasses all the information produced by the media. Monitored heavily by government officials, the media is strictly used to reinforce ideals approved by the government.Journalists, C. T. (25 April 2017). "North Korean censorship". There is no freedom of press in North Korea as all the media is controlled and filtered through governmental censors. Freedom of the press in 2017 was 180th out of 180 countries in Reporters Without Borders' annual Press Freedom Index. According to Freedom House, all media outlets serve as government mouthpieces, all journalists are party members and listening to foreign broadcasts carries the threat of the death penalty. The main news provider is the Korean Central News Agency. All 12 major Newspapers in North Korea, newspapers and 20 periodicals, including ''Rodong Sinmun'', are published in the capital.
There are three state-owned TV stations. Two of them broadcast only on weekends and the Korean Central Television is on air every day in the evenings. Uriminzokkiri and its associated YouTube and Twitter accounts distribute imagery, news and video issued by government media. The Associated Press opened the first Western all-format, full-time bureau in Pyongyang in 2012.
Media coverage of North Korea has often been inadequate as a result of the country's isolation. Stories like Kim Jong Un executing his ex-girlfriend or feeding his uncle to a pack of hungry dogs have been circulated by foreign media as truth despite the lack of a credible source. Many of the claims originate from the South Korean right-wing newspaper ''The Chosun Ilbo''. Max Fisher of ''The Washington Post'' has written that "almost any story [on North Korea] is treated as broadly credible, no matter how outlandish or thinly sourced". Occasional deliberate disinformation on the part of North Korean establishments further complicates the issue.
Government policies towards film are no different from those applied to other artsŌĆömotion pictures serve to fulfill the targets of "social education". Some of the most influential films are based on historic events (''An Jung-geun shoots It┼Ź Hirobumi'') or folk tales (''Hong Gildong jeon, Hong Gildong''). Most movies have predictable propaganda story lines which make cinema an unpopular entertainment; viewers only see films that feature their favorite actors. Western productions are only available at private showings to high-ranking Party members, although the 1997 film ''Titanic (1997 film), Titanic'' is frequently shown to university students as an example of Western culture. Access to foreign media products is available through smuggled DVDs and television or radio broadcasts in border areas. Western films like ''The Interview'', ''Charlie's Angels (2000 film), Charlie's Angels'', and the aforementioned ''Titanic'' are just a few films that have been smuggled across the borders of North Korea, allowing for access to the North Korean citizens.
North Korean media are under some of the strictest government control in the world. The censorship in North Korea encompasses all the information produced by the media. Monitored heavily by government officials, the media is strictly used to reinforce ideals approved by the government.Journalists, C. T. (25 April 2017). "North Korean censorship". There is no freedom of press in North Korea as all the media is controlled and filtered through governmental censors. Freedom of the press in 2017 was 180th out of 180 countries in Reporters Without Borders' annual Press Freedom Index. According to Freedom House, all media outlets serve as government mouthpieces, all journalists are party members and listening to foreign broadcasts carries the threat of the death penalty. The main news provider is the Korean Central News Agency. All 12 major Newspapers in North Korea, newspapers and 20 periodicals, including ''Rodong Sinmun'', are published in the capital.
There are three state-owned TV stations. Two of them broadcast only on weekends and the Korean Central Television is on air every day in the evenings. Uriminzokkiri and its associated YouTube and Twitter accounts distribute imagery, news and video issued by government media. The Associated Press opened the first Western all-format, full-time bureau in Pyongyang in 2012.
Media coverage of North Korea has often been inadequate as a result of the country's isolation. Stories like Kim Jong Un executing his ex-girlfriend or feeding his uncle to a pack of hungry dogs have been circulated by foreign media as truth despite the lack of a credible source. Many of the claims originate from the South Korean right-wing newspaper ''The Chosun Ilbo''. Max Fisher of ''The Washington Post'' has written that "almost any story [on North Korea] is treated as broadly credible, no matter how outlandish or thinly sourced". Occasional deliberate disinformation on the part of North Korean establishments further complicates the issue.
 Most schools have daily practice in association football, basketball, table tennis, gymnastics, boxing and others. The DPR Korea League is popular inside the country and its games are often televised. The national football team, ''Korea DPR national football team, Chollima'', competed in the FIFA World Cup in 2010 FIFA World Cup, 2010, when it lost all three matches against Brazil national football team, Brazil, Portugal national football team, Portugal and Ivory Coast national football team, Ivory Coast. Its 1966 FIFA World Cup, 1966 appearance was much more successful, seeing a surprise 1ŌĆō0 victory over Italy national football team, Italy and a quarter final loss to Portugal by 3ŌĆō5. A North Korea national basketball team, national team represents the nation in international basketball competitions as well. In December 2013, former American basketball professional Dennis Rodman visited North Korea to help train the national team after he developed a friendship with Kim Jong Un.
North Korea's North Korea at the Olympics, first appearance in the Olympics came 1964 Winter Olympics, in 1964. The 1972 Summer Olympics, 1972 Olympics saw its summer games debut and five medals, including one gold. With the exception of the boycotted 1984 Summer Olympics, Los Angeles and 1988 Summer Olympics, Seoul Olympics, North Korean athletes have won medals in all summer games since then. Weightlifter Kim Un-guk broke the world record of the Weightlifting at the 2012 Summer Olympics ŌĆō Men's 62 kg, Men's 62 kg category at the 2012 Summer Olympics in London. Successful Olympians receive luxury apartments from the state in recognition for their achievements.
Most schools have daily practice in association football, basketball, table tennis, gymnastics, boxing and others. The DPR Korea League is popular inside the country and its games are often televised. The national football team, ''Korea DPR national football team, Chollima'', competed in the FIFA World Cup in 2010 FIFA World Cup, 2010, when it lost all three matches against Brazil national football team, Brazil, Portugal national football team, Portugal and Ivory Coast national football team, Ivory Coast. Its 1966 FIFA World Cup, 1966 appearance was much more successful, seeing a surprise 1ŌĆō0 victory over Italy national football team, Italy and a quarter final loss to Portugal by 3ŌĆō5. A North Korea national basketball team, national team represents the nation in international basketball competitions as well. In December 2013, former American basketball professional Dennis Rodman visited North Korea to help train the national team after he developed a friendship with Kim Jong Un.
North Korea's North Korea at the Olympics, first appearance in the Olympics came 1964 Winter Olympics, in 1964. The 1972 Summer Olympics, 1972 Olympics saw its summer games debut and five medals, including one gold. With the exception of the boycotted 1984 Summer Olympics, Los Angeles and 1988 Summer Olympics, Seoul Olympics, North Korean athletes have won medals in all summer games since then. Weightlifter Kim Un-guk broke the world record of the Weightlifting at the 2012 Summer Olympics ŌĆō Men's 62 kg, Men's 62 kg category at the 2012 Summer Olympics in London. Successful Olympians receive luxury apartments from the state in recognition for their achievements.
 The Arirang Mass Games has been recognized by the Guinness World Records as the biggest choreographic event in the world. Some 100,000 athletes perform rhythmic gymnastics and dances while another 40,000 participants create a vast animated screen in the background. The event is an artistic representation of the country's history and pays homage to Kim Il Sung and Kim Jong Il. Rungrado 1st of May Stadium, the List of stadiums by capacity, second largest stadium in the world with its capacity of 114,000, hosts the Festival. The Pyongyang Marathon is another notable sports event. It is an IAAF Road Race Label Events, IAAF Bronze Label Race where amateur runners from around the world can participate.
The Arirang Mass Games has been recognized by the Guinness World Records as the biggest choreographic event in the world. Some 100,000 athletes perform rhythmic gymnastics and dances while another 40,000 participants create a vast animated screen in the background. The event is an artistic representation of the country's history and pays homage to Kim Il Sung and Kim Jong Il. Rungrado 1st of May Stadium, the List of stadiums by capacity, second largest stadium in the world with its capacity of 114,000, hosts the Festival. The Pyongyang Marathon is another notable sports event. It is an IAAF Road Race Label Events, IAAF Bronze Label Race where amateur runners from around the world can participate.
abstract
* * * Hayes, Peter, and Roger Cavazos. "North Korea in 2015." ''Asian Survey'' 56.1 (2016): 68ŌĆō77
abstract
* Hayes, Peter, and Roger Cavazos. "North Korea in 2014." ''Asian Survey'' 55.1 (2015): 119ŌĆō31
abstract
; als
full text online
* , covers 1960s to 2010. * Jackson, Van. "Deterring a Nuclear-Armed Adversary in a Contested Regional Order: The 'Trilemma' of USŌĆōNorth Korea Relations." ''Asia Policy'' 23.1 (2017): 97ŌĆō103
online
* * Lee, Hong Yung. "North Korea in 2013: Economy, Executions, and Nuclear Brinksmanship." ''Asian Survey'' 54.1 (2014): 89ŌĆō100
Online
. * * * * * *
KCNA
() ŌĆō website of the Korean Central News Agency
Naenara
() ŌĆō the official North Korean governmental portal Naenara
DPRK Foreign Ministry
() ŌĆō official North Korean foreign ministry website
The Pyongyang Times
ŌĆō official foreign language newspaper of the DPRK (archived)
Official website of the DPR of Korea
ŌĆō Administered by the Korean Friendship Association
38North
North Korea profile
at BBC News
North Korea
ŌĆō link collection (University of Colorado at Boulder Libraries GovPubs)
NKnews
ŌĆō a news agency covering North Korean topics.
Friend.com.kp
ŌĆō website of the Committee for Cultural Relations with Foreign Countries
Korea Education Fund
''Rodong Sinmun''
ŌĆō the newspaper of the Central Committee of the Workers' Party of Korea ''Rodong Sinmun''
Uriminzokkiri
DPRK Portal
United Nations Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights
ŌĆō Report of the Commission of Inquiry on Human Rights in the Democratic People's Republic of Korea {{Coord, 40, N, 127, E, display=title North Korea, 1948 establishments in North Korea Atheist states Communist states East Asian countries Former Japanese colonies Korea, Korean-speaking countries and territories Member states of the United Nations Northeast Asian countries One-party states Republics States and territories established in 1948 States with limited recognition Totalitarian states
East Asia
East Asia is a geocultural region of Asia. It includes China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan, plus two special administrative regions of China, Hong Kong and Macau. The economies of Economy of China, China, Economy of Ja ...
. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically divided at or near the 38th parallel between North Korea (Dem ...
and borders China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
and Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
to the north at the Yalu (Amnok) and Tumen rivers, and South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the southern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders North Korea along the Korean Demilitarized Zone, with the Yellow Sea to the west and t ...
to the south at the Korean Demilitarized Zone (DMZ). The country's western border is formed by the Yellow Sea
The Yellow Sea, also known as the North Sea, is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean located between mainland China and the Korean Peninsula, and can be considered the northwestern part of the East China Sea.
Names
It is one of four ...
, while its eastern border is defined by the Sea of Japan
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it ...
. North Korea, like South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the southern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders North Korea along the Korean Demilitarized Zone, with the Yellow Sea to the west and t ...
, claims to be the sole legitimate government of the entire peninsula and adjacent islands. Pyongyang
Pyongyang () is the Capital city, capital and largest city of North Korea, where it is sometimes labeled as the "Capital of the Revolution" (). Pyongyang is located on the Taedong River about upstream from its mouth on the Yellow Sea. Accordi ...
is the capital and largest city.
The Korean Peninsula
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically divided at or near the 38th parallel between North Korea (Dem ...
was first inhabited as early as the Lower Paleolithic
The Lower Paleolithic (or Lower Palaeolithic) is the earliest subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. It spans the time from around 3.3 million years ago when the first evidence for stone tool production and use by hominins appears ...
period. Its first kingdom was noted in Chinese records in the early 7th century BCE. Following the unification of the Three Kingdoms of Korea
The Three Kingdoms of Korea or Samhan (Goguryeo, Baekje and Silla) competed for hegemony over the Korea, Korean Peninsula during the ancient period of History of Korea, Korean history. During the Three Kingdoms period (), many states and statele ...
into Silla
Silla (; Old Korean: wikt:ÕŠÉńŠģõ╝É#Old Korean, ÕŠÉńŠģõ╝É, Yale romanization of Korean, Yale: Syerapel, Revised Romanization of Korean, RR: ''Seorabeol''; International Phonetic Alphabet, IPA: ) was a Korean kingdom that existed between ...
and Balhae
Balhae,, , ) also rendered as Bohai or Bohea, and called Jin (; ) early on, was a multiethnic kingdom established in 698 by Dae Joyeong (Da Zuorong). It was originally known as the Kingdom of Jin (ķ£ć, Zhen) until 713 when its name was changed ...
in the late 7th century, Korea was ruled by the Goryeo dynasty
Goryeo (; ) was a Korean state founded in 918, during a time of national division called the Later Three Kingdoms period, that unified and ruled the Korea, Korean Peninsula until the establishment of Joseon in 1392. Goryeo achieved what has b ...
(918ŌĆō1392) and the Joseon dynasty
Joseon ( ; ; also romanized as ''Chosun''), officially Great Joseon (), was a dynastic kingdom of Korea that existed for 505 years. It was founded by Taejo of Joseon in July 1392 and replaced by the Korean Empire in October 1897. The kingdom w ...
(1392ŌĆō1897). The succeeding Korean Empire
The Korean Empire, officially the Empire of Korea or Imperial Korea, was a Korean monarchical state proclaimed in October 1897 by King Gojong of the Joseon dynasty. The empire lasted until the Japanese annexation of Korea in August 1910.
Dur ...
(1897ŌĆō1910) was annexed in 1910 into the Empire of Japan
The Empire of Japan, also known as┬Āthe Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was the Japanese nation state that existed from the Meiji Restoration on January 3, 1868, until the Constitution of Japan took effect on May 3, 1947. From JapanŌĆōKor ...
. In 1945, after the Japanese surrender
The surrender of the Empire of Japan in World War II was announced by Emperor Hirohito on 15 August and formally signed on 2 September 1945, ending the war. By the end of July 1945, the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) was incapable of condu ...
at the end of World War II, Korea was divided into two zones along the 38th parallel, with the north occupied by the Soviet Union and the south occupied by the United States. In 1948, separate governments were formed in Korea: the socialist and Soviet-aligned Democratic People's Republic of Korea in the north, and the capitalist, Western-aligned Republic of Korea in the south. The North Korean invasion of South Korea in 1950 started the Korean War
The Korean War (25 June 1950 ŌĆō 27 July 1953) was an armed conflict on the Korean Peninsula fought between North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea; DPRK) and South Korea (Republic of Korea; ROK) and their allies. North Korea was s ...
. In 1953, the Korean Armistice Agreement
The Korean Armistice Agreement (; zh, t=ķ¤ōÕ£ŗÕü£µł░ÕŹöÕ«Ü / µ£Øķ««Õü£µł░ÕŹöÕ«Ü) is an armistice that brought about a cessation of hostilities of the Korean War. It was signed by United States Army Lieutenant General William Kelly Harrison Jr ...
brought about a ceasefire
A ceasefire (also known as a truce), also spelled cease-fire (the antonym of 'open fire'), is a stoppage of a war in which each side agrees with the other to suspend aggressive actions often due to mediation by a third party. Ceasefires may b ...
and established a demilitarized zone
A demilitarized zone (DMZ or DZ) is an area in which treaties or agreements between states, military powers or contending groups forbid military installations, activities, or personnel. A DZ often lies along an established frontier or boundary ...
(DMZ), but no formal peace treaty
A peace treaty is an treaty, agreement between two or more hostile parties, usually country, countries or governments, which formally ends a declaration of war, state of war between the parties. It is different from an armistice, which is an ag ...
has ever been signed. Post-war North Korea benefited greatly from economic aid and expertise provided by other Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
countries. However, Kim Il Sung
Kim Il Sung (born Kim Song Ju; 15 April 1912 ŌĆō 8 July 1994) was a North Korean politician and the founder of North Korea, which he led as its first Supreme Leader (North Korean title), supreme leader from North Korea#Founding, its establishm ...
, North Korea's first leader, promoted his personal philosophy of ''Juche
''Juche'', officially the ''Juche'' idea, is a component of Ideology of the Workers' Party of Korea#KimilsungismŌĆōKimjongilism, KimilsungismŌĆōKimjongilism, the state ideology of North Korea and the official ideology of the Workers' Party o ...
'' as the state ideology. Pyongyang's international isolation sharply accelerated from the 1980s onwards as the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
came to an end. The fall of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union was formally dissolved as a sovereign state and subject of international law on 26 December 1991 by Declaration No. 142-N of the Soviet of Nationalities, Soviet of the Republics of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union. :s: ...
in 1991 then brought about a sharp decline to the North Korean economy. From 1994 to 1998, North Korea suffered a famine with the population continuing to suffer from malnutrition. In 2024, the DPRK formally abandoned efforts to peacefully reunify Korea.
North Korea is a totalitarian
Totalitarianism is a political system and a form of government that prohibits opposition from political parties, disregards and outlaws the political claims of individual and group opposition to the state, and completely controls the public sph ...
dictatorship
A dictatorship is an autocratic form of government which is characterized by a leader, or a group of leaders, who hold governmental powers with few to no Limited government, limitations. Politics in a dictatorship are controlled by a dictator, ...
with a comprehensive cult of personality around the Kim family. Amnesty International
Amnesty International (also referred to as Amnesty or AI) is an international non-governmental organization focused on human rights, with its headquarters in the United Kingdom. The organization says that it has more than ten million members a ...
considers the country to have the worst human rights record in the world. Officially, North Korea is a communist state
A communist state, also known as a MarxistŌĆōLeninist state, is a one-party state in which the totality of the power belongs to a party adhering to some form of MarxismŌĆōLeninism, a branch of the communist ideology. MarxismŌĆōLeninism was ...
that self-designates as an "independent socialist state
A socialist state, socialist republic, or socialist country is a sovereign state constitutionally dedicated to the establishment of socialism. This article is about states that refer to themselves as socialist states, and not specifically ...
" which holds democratic elections; however, outside observers have described the elections as unfair, uncompetitive, and pre-determined, in a manner similar to elections in the Soviet Union
The electoral system of the Soviet Union was varying over time, being based upon Chapter XIII of the provisional Fundamental Law of 1922, articles 9 and 10 of the 1924 Constitution and Chapter XI of the 1936 Constitution, with the electoral law ...
. The Workers' Party of Korea
The Workers' Party of Korea (WPK), also called the Korean Workers' Party (KWP), is the sole ruling party of North Korea. Founded in 1949 from a merger between the Workers' Party of North Korea and the Workers' Party of South Korea, the WPK is ...
(WPK) is the sole ruling party of North Korea. According to Article 3 of the constitution, KimilsungismŌĆōKimjongilism
Officially, the Workers' Party of Korea (WPK)the ruling party of North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea)is a communist party guided by KimilsungismŌĆōKimjongilism, a synthesis of the ideas of Kim Il Sung and Kim Jong Il. The party ...
is the official ideology of North Korea. The means of production
In political philosophy, the means of production refers to the generally necessary assets and resources that enable a society to engage in production. While the exact resources encompassed in the term may vary, it is widely agreed to include the ...
are owned by the state through state-run enterprises and collectivized farms. Most servicessuch as healthcare
Health care, or healthcare, is the improvement or maintenance of health via the preventive healthcare, prevention, diagnosis, therapy, treatment, wikt:amelioration, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other disability, physic ...
, education
Education is the transmission of knowledge and skills and the development of character traits. Formal education occurs within a structured institutional framework, such as public schools, following a curriculum. Non-formal education als ...
, housing
Housing refers to a property containing one or more Shelter (building), shelter as a living space. Housing spaces are inhabited either by individuals or a collective group of people. Housing is also referred to as a human need and right to ...
, and food production
The food industry is a complex, global network of diverse businesses that supplies most of the food consumed by the World population, world's population. The food industry today has become highly diversified, with manufacturing ranging from sm ...
are subsidized or state-funded.
North Korea follows ''Songun
''Songun'' () is the "military-first" policy of North Korea, prioritizing the Korean People's Army in the affairs of state and allocation of resources. "Military-first" as a principle guides political and economic life in North Korea, with " ...
'', a " military first" policy which prioritizes the Korean People's Army
The Korean People's Army (KPA; ) encompasses the combined military forces of North Korea and the armed wing of the Workers' Party of Korea (WPK). The KPA consists of five branches: the Korean People's Army Ground Force, Ground Force, the Ko ...
in state affairs and the allocation of resources. It possesses nuclear weapons. Its active-duty army of 1.28 million soldiers is the fourth-largest in the world. In addition to being a member of the United Nations since 1991, North Korea is also a member of the Non-Aligned Movement
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 121 countries that Non-belligerent, are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. It was founded with the view to advancing interests of developing countries in the context of Cold W ...
, the G77, and the ASEAN Regional Forum.
Etymology
Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( ; VOC ), commonly known as the Dutch East India Company, was a chartered company, chartered trading company and one of the first joint-stock companies in the world. Established on 20 March 1602 by the States Ge ...
's sailor Hendrick Hamel
Hendrick Hamel (1630 ŌĆō after 1692) was a Dutch sailor. He provided the first Western account of Korea.
Little is known of Hamel's early life and life after his journey to Korea. He was born in the Netherlands in 1630, and sailed to the Dutch ...
.
After the division of the country into North and South Korea, the two sides used different terms to refer to Korea: ''Chosun'' or ''Joseon'' () in North Korea, and ''Hanguk'' () in South Korea. In 1948, North Korea adopted ''Democratic People's Republic of Korea'' (, ''Chos┼Ån Minjuju┼Łi Inmin Konghwaguk''; ) as its official name. In the wider world, because its government controls the northern part of the Korean Peninsula
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically divided at or near the 38th parallel between North Korea (Dem ...
, it is commonly called ''North Korea'' to distinguish it from South Korea, which is officially called the ''Republic of Korea'' in English. Both governments consider themselves to be the legitimate government of the whole of Korea
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically Division of Korea, divided at or near the 38th parallel north, 3 ...
. For this reason, the people do not consider themselves as 'North Koreans' but as Koreans in the same divided country as their compatriots in the South, and foreign visitors are discouraged from using the former term.
History
Korean mythology
Korean mythology () is the group of myths told by historical and modern Koreans. There are two types: the written, literary mythology in traditional histories, mostly about the founding monarchs of List of monarchs of Korea, various historical k ...
in 2333 BC, the Gojoseon
Gojoseon (; ), contemporary name Joseon (; ), was the first kingdom on the Korea, Korean Peninsula. According to Korean mythology, the kingdom was established by the legendary king Dangun. Gojoseon possessed the most advanced culture in th ...
Kingdom was established by the god-king Dangun
Dangun or Tangun (; ), also known as Dangun Wanggeom (; ), was the legendary founder and first king of Gojoseon, the first Korean kingdom. He founded the first kingdom around the northern part of the Korean Peninsula. He is said to be the "gra ...
. Following the end of the Three Kingdoms of Korea into Silla and Balhae in the late 7th century, Korea was subsequently ruled by the Goryeo dynasty (918ŌĆō1392) and the Joseon dynasty
Joseon ( ; ; also romanized as ''Chosun''), officially Great Joseon (), was a dynastic kingdom of Korea that existed for 505 years. It was founded by Taejo of Joseon in July 1392 and replaced by the Korean Empire in October 1897. The kingdom w ...
(1392ŌĆō1897). In 1897, King Gojong proclaimed the Korean Empire
The Korean Empire, officially the Empire of Korea or Imperial Korea, was a Korean monarchical state proclaimed in October 1897 by King Gojong of the Joseon dynasty. The empire lasted until the Japanese annexation of Korea in August 1910.
Dur ...
, which was annexed
Annexation, in international law, is the forcible acquisition and assertion of legal title over one state's territory by another state, usually following military occupation of the territory. In current international law, it is generally held to ...
by the Empire of Japan
The Empire of Japan, also known as┬Āthe Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was the Japanese nation state that existed from the Meiji Restoration on January 3, 1868, until the Constitution of Japan took effect on May 3, 1947. From JapanŌĆōKor ...
in 1910.
Ancient Korea
The Korean Peninsula was inhabited as early as theLower Paleolithic
The Lower Paleolithic (or Lower Palaeolithic) is the earliest subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. It spans the time from around 3.3 million years ago when the first evidence for stone tool production and use by hominins appears ...
period.
According to Korea's founding mythology, the history of Korea begins with the founding of Joseon (also known as "Gojoseon
Gojoseon (; ), contemporary name Joseon (; ), was the first kingdom on the Korea, Korean Peninsula. According to Korean mythology, the kingdom was established by the legendary king Dangun. Gojoseon possessed the most advanced culture in th ...
", or "Old Joseon", to differentiate it from the 14th century dynasty) in 2333 BC by the legendary Dangun
Dangun or Tangun (; ), also known as Dangun Wanggeom (; ), was the legendary founder and first king of Gojoseon, the first Korean kingdom. He founded the first kingdom around the northern part of the Korean Peninsula. He is said to be the "gra ...
.*
:"An extreme manifestation of nationalism and the family cult was the revival of interest in Tangun, the mythical founder of the first Korean state... Most textbooks and professional historians, however, treat him as a myth."
*
:"Although Kija may have truly existed as a historical figure, Tangun is more problematical."
*
:"Most orean historianstreat the angun
Angoon (sometimes formerly spelled Angun, ) is a city on Admiralty Island, Alaska, United States. At the 2000 census the population was 572; by the 2010 census the population had declined to 459. For statistical purposes, it is in the Hoonah- ...
myth as a later creation."
*
:"The Tangun myth became more popular with groups that wanted Korea to be independent; the Kija myth was more useful to those who wanted to show that Korea had a strong affinity to China."
*
:"If a choice is to be made between them, one is faced with the fact that the Tangun, with his supernatural origin, is more clearly a mythological figure than Kija." Gojoseon was noted in Chinese records in the early 7th century. Gojoseon expanded until it controlled the northern Korean Peninsula and parts of Manchuria
Manchuria is a historical region in northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day northeast China and parts of the modern-day Russian Far East south of the Uda (Khabarovsk Krai), Uda River and the Tukuringra-Dzhagdy Ranges. The exact ...
. Gija Joseon
Gija Joseon (1120ŌĆō194 BC) was a dynasty of Gojoseon allegedly founded by the sage Jizi (Gija), a member of the Shang (Yin) dynasty royal house.
Understanding before 20th century Chinese records
Chinese records before the Qin dynasty descr ...
was purportedly founded in the 12th century BC, but its existence and role have been controversial in the modern era. In 108 BC, the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25ŌĆō220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221ŌĆō206 BC ...
defeated Wiman Joseon
Wiman Joseon (194ŌĆō108 BC) was a dynasty of Gojoseon. It began with Wiman's (Wei Man) seizure of the throne from Gija Joseon's King Jun and ended with the death of King Ugeo who was a grandson of Wiman. Apart from archaeological data, the ma ...
and installed four commanderies in the northern Korean peninsula. Three of the commanderies fell or retreated westward within a few decades. As Lelang Commandery
The Lelang Commandery was a Commandery (China), commandery of the Han dynasty established after it had conquered Wiman Joseon in 108 BC and lasted until Goguryeo conquered it in 313. The Lelang Commandery extended the rule of the Four Commande ...
was destroyed and rebuilt around this time, the place gradually moved toward Liaodong. Thus, its force was diminished and only served as a trade center until it was conquered by Goguryeo in 313.Early Korea. Shsu.edu. Retrieved April 17, 2015. Beginning around 300 BC, the Japonic-speaking
Yayoi people
The were an ancient people that immigrated to the Japanese archipelago during the Yayoi period (300 BC–300 AD) and are characterized by the existence of Yayoi material culture. Some argue for an earlier start of the Yayoi period, between 1 ...
from the Korean Peninsula entered the Japanese islands and displaced or intermingled with the original J┼Źmon inhabitants. The linguistic homeland of Proto-Koreans
Koreans are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula. The majority of Koreans live in the two Korean sovereign states of North and South Korea, which are collectively referred to as Korea. As of 2021, an estimated 7.3 m ...
is located somewhere in southern Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
/Manchuria
Manchuria is a historical region in northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day northeast China and parts of the modern-day Russian Far East south of the Uda (Khabarovsk Krai), Uda River and the Tukuringra-Dzhagdy Ranges. The exact ...
, such as the Liao River area or the Amur
The Amur River () or Heilong River ( zh, s=ķ╗æķŠÖµ▒¤) is a perennial river in Northeast Asia, forming the natural border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China (historically the Outer Manchuria, Outer and Inner Manchuria). The Amur ...
River area. Proto-Koreans arrived in the southern part of the Korean Peninsula at around 300 BC, replacing and assimilating Japonic-speakers and likely causing the Yayoi
The Yayoi period (Õ╝źńö¤µÖéõ╗Ż, ''Yayoi jidai'') (c. 300 BC ŌĆō 300 AD) is one of the major historical periods of the Japanese archipelago. It is generally defined as the era between the beginning of food production in Japan and the emergence o ...
migration.
Three Kingdoms of Korea
During theProtoŌĆōThree Kingdoms period
The ProtoŌĆōThree Kingdoms period (or ''Samhan'' period) refers to the proto-historical period in the Korean Peninsula, after the fall of Gojoseon and before the maturation of Goguryeo, Baekje, and Silla into full-fledged kingdoms. It is a su ...
, the states of Buyeo
Buyeo (; ; ), also rendered as Puyŏ or Fuyu, was an ancient kingdom that was centered in northern Manchuria in modern-day northeast China. It had ties to the Yemaek people, who are considered to be the ancestors of modern Koreans. Buyeo is ...
, Okjeo
Okjeo () was an History of Korea, ancient Korean tribal state which arose in the northern Korea, Korean peninsula from perhaps the 2nd century BCE to the 5th century CE.
Dong-okjeo (Eastern Okjeo) occupied roughly the area of the Hamgyong Provin ...
, Dongye, and Samhan
Samhan, or Three Han (), is the collective name of the Byeonhan, Jinhan, and Mahan confederacies that emerged in the first century BC during the ProtoŌĆōThree Kingdoms of Korea, or Samhan, period. Located in the central and southern regions o ...
occupied the whole Korean peninsula and southern Manchuria. From them, the Three Kingdoms of Korea
The Three Kingdoms of Korea or Samhan (Goguryeo, Baekje and Silla) competed for hegemony over the Korea, Korean Peninsula during the ancient period of History of Korea, Korean history. During the Three Kingdoms period (), many states and statele ...
emerged: Goguryeo
Goguryeo (37 BC ŌĆō 668 AD) (; ; Old Korean: Guryeo) also later known as Goryeo (; ; Middle Korean: Ļ│ĀßćóļĪĢŃĆ«, ''kw├▓wly├®y''), was a Korean kingdom which was located on the northern and central parts of the Korea, Korean Peninsula an ...
, Baekje
Baekje or Paekche (; ) was a Korean kingdom located in southwestern Korea from 18 BCE to 660 CE. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla. While the three kingdoms were in separate existence, Baekje had the h ...
, and Silla
Silla (; Old Korean: wikt:ÕŠÉńŠģõ╝É#Old Korean, ÕŠÉńŠģõ╝É, Yale romanization of Korean, Yale: Syerapel, Revised Romanization of Korean, RR: ''Seorabeol''; International Phonetic Alphabet, IPA: ) was a Korean kingdom that existed between ...
.
Goguryeo, the largest and most powerful among them, was a highly militaristic state and competed with various Chinese dynasties during its 700 years of history. Goguryeo experienced a golden age under Gwanggaeto the Great
Gwanggaeto the Great (374ŌĆō412, r. 391ŌĆō412) was the nineteenth monarch of Goguryeo. His full posthumous name means "Entombed in ''Gukgangsang'', Broad Expander of Domain, Peacemaker, Supreme King", sometimes abbreviated to ''Hotaewang'' ...
and his son Jangsu, who both subdued Baekje and Silla during their respective reigns, achieving a brief unification of the Three Kingdoms and becoming the most dominant power on the Korean Peninsula. In addition to contesting control of the Korean Peninsula, Goguryeo had many military conflicts with various Chinese dynasties, most notably the GoguryeoŌĆōSui War
The GoguryeoŌĆōSui War were a series of invasions launched by the Sui dynasty of China against Goguryeo, one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, between AD 598 and AD 614. It resulted in the defeat of the Sui and was one of the pivotal factors in ...
, in which Goguryeo defeated a huge force said to number over a million men.
Baekje was a maritime power, sometimes called the "Phoenicia
Phoenicians were an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syria, Syrian ...
of East Asia". Its maritime ability was instrumental in the dissemination of Buddhism throughout East Asia and spreading continental culture to Japan. Baekje was once a great military power on the Korean Peninsula, especially during the time of Geunchogo, but was critically defeated by Gwanggaeto the Great and declined. Silla was the smallest and weakest of the three, but used opportunistic pacts and alliances with the more powerful Korean kingdoms, and eventually Tang China
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=Õöɵ£Ø), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed ...
, to its advantage.
In 676, the unification of the Three Kingdoms by Silla led to the Northern and Southern States period, in which Balhae
Balhae,, , ) also rendered as Bohai or Bohea, and called Jin (; ) early on, was a multiethnic kingdom established in 698 by Dae Joyeong (Da Zuorong). It was originally known as the Kingdom of Jin (ķ£ć, Zhen) until 713 when its name was changed ...
controlled the northern parts of Goguryeo, and much of the Korean Peninsula was controlled by Later Silla
Unified Silla, or Late Silla, is the name often applied to the historical period of the Korean kingdom of Silla after its conquest of Goguryeo in 668 AD, which marked the end of the Three Kingdoms period. In the 7th century, a SillaŌĆōTang all ...
. Relationships between Korea and China remained relatively peaceful during this time. Balhae was founded by a Goguryeo general and formed as a successor state to Goguryeo. During its height, Balhae controlled most of Manchuria and parts of the Russian Far East and was called the "Prosperous Country in the East".
Late Silla was a wealthy country, and its metropolitan capital of Gyeongju
Gyeongju (, ), historically known as Seorabeol (, ), is a coastal city in the far southeastern corner of North Gyeongsang Province, South Korea. It is the second largest city by area in the province after Andong, covering with a population of ...
grew to become the fourth largest city in the world. It experienced a golden age of art and culture, exemplified by monuments such as Hwangnyongsa, Seokguram, and the Emille Bell. It also carried on the maritime legacy and prowess of Baekje, and during the 8th and 9th centuries dominated the seas of East Asia and the trade between China, Korea, and Japan, most notably during the time of Jang Bogo
Jang Bo-go (787ŌĆō841), whose childhood name was Gungbok or Gungpa (), was a Sillan who rose to prominence in the Later Silla period of Korea as a powerful maritime figure who effectively controlled the Yellow Sea (West Sea), and dominated the ...
. In addition, Silla people made overseas communities in China on the Shandong Peninsula
The Shandong Peninsula or Jiaodong (tsiaotung) Peninsula is a peninsula in Shandong in eastern China, between the Bohai Sea to the north and the Yellow Sea to the south. The latter name refers to the east and Jiaozhou.
Geography
The waters ...
and the mouth of the Yangtze
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ) is the longest river in Eurasia and the third-longest in the world. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains of the Tibetan Plateau and flows including Dam Qu River the longest source of the Yangtze, i ...
River. However, Silla was later weakened due to internal strife and the revival of successor states Baekje
Baekje or Paekche (; ) was a Korean kingdom located in southwestern Korea from 18 BCE to 660 CE. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla. While the three kingdoms were in separate existence, Baekje had the h ...
and Goguryeo
Goguryeo (37 BC ŌĆō 668 AD) (; ; Old Korean: Guryeo) also later known as Goryeo (; ; Middle Korean: Ļ│ĀßćóļĪĢŃĆ«, ''kw├▓wly├®y''), was a Korean kingdom which was located on the northern and central parts of the Korea, Korean Peninsula an ...
, which culminated into the Later Three Kingdoms
The Later Three Kingdoms period (; c. 890s ŌĆō 936 AD) of ancient Korea saw a partial revival of the old three kingdoms which had dominated the peninsula from the 1st century BC to the 7th century. After the Unified Silla kingdom had ruled Kor ...
period in the late 9th century.
Buddhism flourished during this time. Many Korean Buddhists gained great fame among Chinese Buddhist circles and greatly contributed to Chinese Buddhism
Chinese Buddhism or Han Buddhism ( zh, s=µ▒ēõ╝ĀõĮøµĢÖ, t=µ╝óÕé│õĮøµĢÖ, first=t, poj=H├Ān-tho├ón Hu╠Źt-k├Āu, j=Hon3 Cyun4 Fat6 Gaau3, p=H├Ānchu├Īn F├│ji├Āo) is a Chinese form of Mahayana Buddhism. The Chinese Buddhist canonJiang Wu, "The Chin ...
. Examples of significant Korean Buddhists from this period include Woncheuk
Woncheuk (, c. 613ŌĆō696) was a Korean Buddhist monk who worked in seventh century China.Buswell, Robert E. (2004). ''Encyclopedia of Buddhism'', 'W┼Ånch'┼Łk', p. 903. Volumes 1,2. Macmillan Reference. Woncheuk was a follower of Param─ürtha (4 ...
, Wonhyo
W┼Ånhyo (; ; 617 ŌĆō 686, meaning: "Dawnbreak") was one of the most important philosophers and commentators in East Asian Buddhism and the most prolific scholar in Korean Buddhism.Muller, CharlesÕģāµøē Wonhyo, ''Digital Dictionary of Buddhism'' ...
, Uisang
Uisang (; 625ŌĆō702) was one of the most eminent early Silla Korean scholar-monks, a close friend of Wonhyo (Õģāµøē).
He traveled to China, studying at Mount Zhongnan as a student of the influential Huayan master Zhiyan (µÖ║Õä╝) and as a se ...
, Musang, and Kim Gyo-gak. Kim was a Silla prince whose influence made Mount Jiuhua one of the Four Sacred Mountains
Sacred mountains are central to certain religions, and are usually the subjects of many legends. For many, the most symbolic aspect of a mountain is the peak because it is believed that it is closest to heaven or other religious realms. Many reli ...
of Chinese Buddhism.
Unified dynasties
In 936, the Later Three Kingdoms were united by Wang Geon, who establishedGoryeo
Goryeo (; ) was a Korean state founded in 918, during a time of national division called the Later Three Kingdoms period, that unified and ruled the Korea, Korean Peninsula until the establishment of Joseon in 1392. Goryeo achieved what has b ...
as the successor state of Goguryeo. Balhae had fallen to the Khitan Empire in 926, and a decade later the last crown prince of Balhae fled south to Goryeo, where he was warmly welcomed and included in the ruling family by Wang Geon, thus unifying the two successor nations of Goguryeo. Like Silla, Goryeo was a highly cultural state, and invented the metal movable type printing press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a printing, print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in whi ...
. After defeating the Khitan Empire, which was the most powerful empire of its time, in the GoryeoŌĆōKhitan War
The GoryeoŌĆōKhitan War (; ) was a series of 10th- and 11th-century conflicts between the Goryeo dynasty of Korea and the Khitan-led Liao dynasty of China.
GoryeoŌĆōKhitan relations
Silla experienced a period of decline starting in the latter ...
, Goryeo experienced a golden age that lasted a century, during which the Tripitaka Koreana
The is a Korean collection of the ( Buddhist scriptures), carved onto 81,258 wooden printing blocks in the 13th century. They are currently located at the Buddhist temple Haeinsa, in South Gyeongsang Province, South Korea. It is the oldest ...
was completed and significant developments in printing and publishing occurred. This promoted education and the dispersion of knowledge on philosophy, literature, religion, and science. By 1100, there were 12 universities that produced notable scholars.
However, the Mongol invasions
The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire, the Mongol Empire (1206ŌĆō1368), which by 1260 covered large parts of Eurasia. Historians regard the Mongol devastati ...
in the 13th century greatly weakened the kingdom. Goryeo was never conquered by the Mongols, but exhausted after three decades of fighting, the Korean court sent its crown prince
A crown prince or hereditary prince is the heir apparent to the throne in a royal or imperial monarchy. The female form of the title, crown princess, is held by a woman who is heir apparent or is married to the heir apparent.
''Crown prince ...
to the Yuan capital to swear allegiance to Kublai Khan
Kublai Khan (23 September 1215 ŌĆō 18 February 1294), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Shizu of Yuan and his regnal name Setsen Khan, was the founder and first emperor of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty of China. He proclaimed the ...
, who accepted and married one of his daughters to the Korean crown prince. Henceforth, Goryeo continued to rule Korea, though as a tributary ally to the Mongols for the next 86 years. During this period, the two nations became intertwined as all subsequent Korean kings married Mongol princesses, and the last empress of the Yuan dynasty was a Korean princess. In the mid-14th century, Goryeo drove out the Mongols to regain its northern territories, briefly conquered Liaoyang
Liaoyang ( zh, s=ĶŠĮķś│ , t=ķü╝ķÖĮ , p=Li├Īoy├Īng) is a prefecture-level city of east-central Liaoning province, China, situated on the Taizi River. It is approximately one hour south of Shenyang, the provincial capital, by car. Liaoyang is hom ...
, and defeated invasions by the Red Turbans. However, in 1392, General Yi Seong-gye, who had been ordered to attack China, turned his army around and staged a coup.
Yi Seong-gye declared the new name of Korea as "Joseon" in reference to Gojoseon, and moved the capital to Hanseong (one of the old names of Seoul
Seoul, officially Seoul Special Metropolitan City, is the capital city, capital and largest city of South Korea. The broader Seoul Metropolitan Area, encompassing Seoul, Gyeonggi Province and Incheon, emerged as the world's List of cities b ...
). The first 200 years of the Joseon
Joseon ( ; ; also romanized as ''Chosun''), officially Great Joseon (), was a dynastic kingdom of Korea that existed for 505 years. It was founded by Taejo of Joseon in July 1392 and replaced by the Korean Empire in October 1897. The kingdom w ...
dynasty were marked by peace and saw great advancements in science and education, as well as the creation of Hangul
The Korean alphabet is the modern writing system for the Korean language. In North Korea, the alphabet is known as (), and in South Korea, it is known as (). The letters for the five basic consonants reflect the shape of the speech organs ...
by Sejong the Great
Sejong (; 15 May 1397 ŌĆō 8 April 1450), commonly known as Sejong the Great (), was the fourth monarch of the Joseon, Joseon dynasty of Korea. He is regarded as the greatest ruler in Korean history, and is remembered as the inventor of Hangu ...
to promote literacy among the common people. The prevailing ideology of the time was Neo-Confucianism
Neo-Confucianism (, often shortened to ''lŪÉxu├®'' ńÉåÕŁĖ, literally "School of Principle") is a moral, ethical, and metaphysical Chinese philosophy influenced by Confucianism, which originated with Han Yu (768ŌĆō824) and Li Ao (772ŌĆō841) i ...
, which was epitomized by the seonbi
''Seonbi'' () were scholars during the Goryeo and Joseon periods of Korean history. They were generally seen as non-governmental servants of the public, who chose to pass on the benefits and authority of official power in order to develop and sha ...
class: nobles who passed up positions of wealth and power to lead lives of study and integrity. Between 1592 and 1598, Japan under Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and ''daimy┼Ź'' (feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period, Sengoku and Azuchi-Momoyama periods and regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: ...
launched invasions of Korea, but the advance was halted by Korean forces (most notably the Joseon Navy
The Joseon Navy (; Hanja: µ£Øķ««µ░┤Ķ╗Ź) was the navy of the Korean dynasty of Joseon. While originally commissioned to protect merchant vessels and coastal towns from Japanese pirate raids, the Joseon navy is best known for defeating the Japanese n ...
led by Admiral Yi Sun-sin
Yi Sun-sin (; ; April 28, 1545 ŌĆō December 16, 1598) was a Korean admiral and military general known for his victories against the Japanese navy during the Imjin War in the Joseon period. Yi's courtesy name was Y┼Åhae (ņŚ¼ĒĢ┤), and he was po ...
and his renowned "turtle ship
A turtle ship (; ) was a type of warship that was used by the Korean Joseon Navy from the early 15th century up until the 19th century. They were used alongside the panokseon warships in the fight against invading Japanese fleets. The ship's name ...
") with assistance from righteous army
Righteous armies (), sometimes translated as irregular armies or militias, were informal civilian militias that appeared several times in Korean history, when the national armies were in need of assistance.
The first righteous armies emerged d ...
militias formed by Korean civilians, and Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of ...
Chinese troops."Yi's successes gave Korea complete control of the sea lanes around the peninsula, and the Korean navy was able to intercept most of the supplies and communications between Japan and Korea" Through a series of successful battles of attrition, the Japanese forces were eventually forced to withdraw, and relations between all parties became normalized. However, the Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616ŌĆō1636) an ...
took advantage of Joseon's war-weakened state and invaded in 1627 and 1637 and then went on to conquer the destabilized Ming dynasty. After normalizing relations with the new Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the ...
, Joseon experienced a nearly 200-year period of peace. Kings Yeongjo and Jeongjo particularly led a new renaissance of the Joseon dynasty during the 18th century.
In the 19th century, Joseon began experiencing economic difficulties and widespread uprisings, including the Donghak Peasant Revolution
The Donghak Peasant Revolution () was a peasant revolt that took place between 11 January 1894 and 25 December 1895 in Korea. The peasants were primarily followers of Donghak, a Neo-Confucian movement that rejected Western technology and i ...
. The royal in-law families had gained control of the government, leading to mass corruption and weakening of the state. In addition, the strict isolationism of the Joseon government that earned it "the hermit kingdom" became increasing ineffective due to increasing encroachment from powers such as Japan, Russia, and the United States. This is exemplified by the JoseonŌĆōUnited States Treaty of 1882
A Treaty of Peace, Amity, Commerce and Navigation (, Hanja: µ£ØńŠÄõ┐«ÕźĮķĆÜÕĢåµóØń┤ä), also known as the Shufeldt Treaty, was negotiated between representatives of the United States and Korea in 1882.
The treaty was written in English and Hanja, ...
, in which it was compelled to open its borders.
Japanese occupation and World War II
In the late 19th century, Japan became a significant regional power after winning theFirst Sino-Japanese War
The First Sino-Japanese War (25 July 189417 April 1895), or the First ChinaŌĆōJapan War, was a conflict between the Qing dynasty of China and the Empire of Japan primarily over influence in Joseon, Korea. In Chinese it is commonly known as th ...
against Qing China and the Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War (8 February 1904 ŌĆō 5 September 1905) was fought between the Russian Empire and the Empire of Japan over rival imperial ambitions in Manchuria and the Korean Empire. The major land battles of the war were fought on the ...
against the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
. In 1897, King Gojong, the last king of Korea, proclaimed Joseon as the Korean Empire
The Korean Empire, officially the Empire of Korea or Imperial Korea, was a Korean monarchical state proclaimed in October 1897 by King Gojong of the Joseon dynasty. The empire lasted until the Japanese annexation of Korea in August 1910.
Dur ...
. However, Japan compelled Korea to become its protectorate in 1905 and formally annexed it in 1910. From 1910 to the end of World War II in 1945, Korea was under Japanese rule. What followed was a period of forced assimilation, in which Korean language, culture, and history were suppressed. This led to the March First Movement
The March First Movement was a series of protests against Korea under Japanese rule, Japanese colonial rule that was held throughout Korea and internationally by the Korean diaspora beginning on March 1, 1919. Protests were largely concentrated in ...
protests in 1919 and the subsequent foundation of resistance groups in exile, primarily in China. Among the resistance groups was Provisional Government of the Republic of Korea
The Korean Provisional Government (KPG), formally the Provisional Government of the Republic of Korea (), was a Korean government-in-exile based in Republic of China (1912ŌĆō1949), China during Korea under Japanese rule, Japanese rule over K ...
.
During the Japanese colonial period, most Koreans were peasants engaged in subsistence farming
Subsistence agriculture occurs when farmers grow crops on smallholdings to meet the needs of themselves and their families. Subsistence agriculturalists target farm output for survival and for mostly local requirements. Planting decisions occ ...
. In the 1930s, Japan developed mines, hydro-electric dams, steel mills, and manufacturing plants in northern Korea and neighboring Manchuria
Manchuria is a historical region in northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day northeast China and parts of the modern-day Russian Far East south of the Uda (Khabarovsk Krai), Uda River and the Tukuringra-Dzhagdy Ranges. The exact ...
. The Korean industrial working class expanded rapidly, and many Koreans went to work in Manchuria. As a result, 65% of Korea's heavy industry was located in the north, but, due to the rugged terrain, only 37% of its agriculture.
Due to its rule by Japan, northern Korea had little exposure to modern, Western ideas. One partial exception was the penetration of religion. Since the arrival of missionaries in the late nineteenth century, the northwest of Korea, and Pyongyang
Pyongyang () is the Capital city, capital and largest city of North Korea, where it is sometimes labeled as the "Capital of the Revolution" (). Pyongyang is located on the Taedong River about upstream from its mouth on the Yellow Sea. Accordi ...
in particular, had been a stronghold of Christianity. As a result, Pyongyang was called the "Jerusalem of the East".
A Korean guerrilla movement emerged in the mountainous interior and in Manchuria, harassing the Japanese imperial authorities. One of the most prominent guerrilla leaders was the Communist Kim Il Sung
Kim Il Sung (born Kim Song Ju; 15 April 1912 ŌĆō 8 July 1994) was a North Korean politician and the founder of North Korea, which he led as its first Supreme Leader (North Korean title), supreme leader from North Korea#Founding, its establishm ...
.
Division of Korea
 Towards the end of
Towards the end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 ŌĆō 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the U.S. proposed dividing the Korean peninsula into two occupation zones: a U.S. zone and a Soviet zone. Dean Rusk
David Dean Rusk (February 9, 1909December 20, 1994) was the United States secretary of state from 1961 to 1969 under presidents John F. Kennedy and Lyndon B. Johnson, the second-longest serving secretary of state after Cordell Hull from the ...
and Charles H. Bonesteel III suggested the 38th parallel as the dividing line, as it placed Seoul under U.S. control. To the surprise of Rusk and Bonesteel, the Soviets accepted their proposal and agreed to divide Korea.
After the Japanese surrender
The surrender of the Empire of Japan in World War II was announced by Emperor Hirohito on 15 August and formally signed on 2 September 1945, ending the war. By the end of July 1945, the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) was incapable of condu ...
at the end of World War II in 1945, the Korean Peninsula was divided into two occupation zones along the 38th parallel, with the northern half of the peninsula occupied by the Soviet Union and the southern half by the United States. Negotiations on reunification failed. Soviet general Terenty Shtykov
Terentii Fomich Shtykov (; ŌĆō 25 October 1964) was a Soviet general who was the ''de facto'' head of the Soviet 1945ŌĆō1948 military occupation of northern Korea and the first List of ambassadors of Russia to North Korea, Soviet Ambassado ...
recommended the establishment of the Soviet Civil Administration
The Soviet Civil Administration (SCA) was the government of the northern half of Korea from 24 August 1945 to 9 September 1948 though governed concurrently after the setup of the Provisional People's Committee for North Korea in 1946. Even thou ...
in October 1945, and supported Kim Il Sung as chairman of the Provisional People's Committee of North Korea
The Provisional People's Committee of North Korea () was the provisional government of North Korea.
The committee was established on 8 February 1946 in response for the need of the Soviet Civil Administration and the communists to have centraliza ...
, established in February 1946. In September 1946, South Korean citizens rose up against the Allied Military Government. In April 1948, an uprising of the Jeju islanders was violently crushed. The South declared its statehood in May 1948 and two months later the ardent anti-communist Syngman Rhee
Syngman Rhee (; 26 March 1875 ŌĆō 19 July 1965), also known by his art name Unam (), was a South Korean politician who served as the first president of South Korea from 1948 to 1960. Rhee was also the first and last president of the Provisiona ...
became its ruler. The Democratic People's Republic of Korea was established in the North on 9 September 1948. Shtykov served as the first Soviet ambassador, while Kim Il Sung became premier.
Soviet forces withdrew from the North in 1948, and most American forces withdrew from the South in 1949. Ambassador Shtykov suspected Rhee was planning to invade the North and was sympathetic to Kim's goal of Korean unification under socialism. The two successfully lobbied Soviet leader Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
to support a quick war against the South, which culminated in the outbreak of the Korean War.
Korean War
 The military of North Korea invaded the
The military of North Korea invaded the South
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both west and east.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''s┼½├Š'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sun├Ša ...
on 25 June 1950, and swiftly overran most of the country. The United Nations Command
United Nations Command (UNC or UN Command) is the multinational military force established to support the South Korea, Republic of Korea (South Korea) during and after the Korean War. It was the first attempt at collective security by the U ...
(UNC) was subsequently established following the UN Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, an ...
's recognition of North Korean aggression against South Korea. The motion passed because the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
, a close ally of North Korea and a member of the UN Security Council, was boycotting the UN over its recognition of the Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
rather than the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
. The UNC, led by the United States, intervened to defend the South, and rapidly advanced into North Korea. As they neared the border with China, Chinese forces intervened on behalf of North Korea, shifting the balance of the war again. Fighting ended on 27 July 1953, with an armistice that approximately restored the original boundaries between North and South Korea, but no peace treaty was signed. Approximately 3 million people died in the Korean War, with a higher proportional civilian death toll than World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 ŌĆō 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
or the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (1 November 1955 ŌĆō 30 April 1975) was an armed conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia fought between North Vietnam (Democratic Republic of Vietnam) and South Vietnam (Republic of Vietnam) and their allies. North Vietnam w ...
. In both per capita and absolute terms, North Korea was the country most devastated by the war, which resulted in the death of an estimated 12ŌĆō15% of the North Korean population ( 10 million), "a figure close to or surpassing the proportion of Soviet citizens killed in World War II", according to Charles K. Armstrong. As a result of the war, almost every substantial building in North Korea was destroyed. Some have referred to the conflict as a civil war, with other factors involved.
A heavily guarded demilitarized zone
A demilitarized zone (DMZ or DZ) is an area in which treaties or agreements between states, military powers or contending groups forbid military installations, activities, or personnel. A DZ often lies along an established frontier or boundary ...
(DMZ) still divides the peninsula, and an anti-communist and anti-North Korea sentiment remains in South Korea. Since the war, the United States has maintained a strong military presence in the South which is depicted by the North Korean government as an imperialist occupation force. It claims that the Korean War was caused by the United States and South Korea.
In October 2024, North Korea claims that 1.4 million people have joined its military after accusing South Korea of a drone intrusion. In response, South Korea is restricting leaflet launches near the border to prevent potential conflict, while both sides engage in psychological warfare, including disturbing broadcasts at the border.
Leadership of Kim Il Sung
 The post-war 1950s and 1960s saw an ideological shift in North Korea, as Kim Il Sung sought to consolidate his power. Kim Il Sung was highly critical of Soviet premier
The post-war 1950s and 1960s saw an ideological shift in North Korea, as Kim Il Sung sought to consolidate his power. Kim Il Sung was highly critical of Soviet premier Nikita Khrushchev
Nikita Sergeyevich Khrushchev (ŌĆō 11 September 1971) was the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964 and the Premier of the Soviet Union, Chai ...
and his de-Stalinization
De-Stalinization () comprised a series of political reforms in the Soviet Union after Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, the death of long-time leader Joseph Stalin in 1953, and Khrushchev Thaw, the thaw brought about by ascension of Nik ...
policies and critiqued Khrushchev as revisionist. During the 1956 August Faction Incident, Kim Il Sung successfully resisted efforts by the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
and China to depose him in favor of Soviet Koreans or the pro-Chinese Yan'an faction
The Yan'an faction () were a group of pro-China communists in the North Korean government after the division of Korea following World War II.
The group was involved in a power struggle with pro-Soviet factions but Kim Il Sung was eventually able ...
.Chung, Chin O. ''Pyongyang Between Peking and Moscow: North Korea's Involvement in the Sino-Soviet Dispute, 1958ŌĆō1975''. University of Alabama, 1978, p. 45. Some scholars believe that the 1956 August incident was an example of North Korea demonstrating political independence. However, most scholars consider the final withdrawal of Chinese troops from North Korea in October 1958 to be the latest date when North Korea became effectively independent. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, North Korea sought to distinguish itself internationally by becoming a leader of the Non-Aligned Movement
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 121 countries that Non-belligerent, are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. It was founded with the view to advancing interests of developing countries in the context of Cold W ...
and promoting the ideology of ''Juche
''Juche'', officially the ''Juche'' idea, is a component of Ideology of the Workers' Party of Korea#KimilsungismŌĆōKimjongilism, KimilsungismŌĆōKimjongilism, the state ideology of North Korea and the official ideology of the Workers' Party o ...
''. In United States policymaking, North Korea was considered among the Captive Nations. Despite its efforts to break out of the Soviet and Chinese spheres of influence, North Korea remained closely aligned with both countries throughout the Cold War.
 Industry was the favored sector in North Korea. Industrial production returned to pre-war levels by 1957. In 1959, relations with Japan had improved somewhat, and North Korea began allowing the repatriation of Japanese citizens in the country. The same year, North Korea revalued the
Industry was the favored sector in North Korea. Industrial production returned to pre-war levels by 1957. In 1959, relations with Japan had improved somewhat, and North Korea began allowing the repatriation of Japanese citizens in the country. The same year, North Korea revalued the North Korean won
The Korean People's won, more commonly known as the North Korean won (currency symbol, symbol: Ōé®; ISO 4217, code: KPW; ) and sometimes known as the Democratic People's Republic of Korea won (), is the official currency of North Korea. It is ...
, which held greater value than its South Korean counterpart. Until the 1960s, economic growth was higher than in South Korea, and North Korean GDP per capita was equal to that of its southern neighbor as late as 1976. However, by the 1980s, the economy had begun to stagnate; it started its long decline in 1987 and almost completely collapsed after the dissolution of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union was formally dissolved as a sovereign state and subject of international law on 26 December 1991 by Declaration No. 142-N of the Soviet of the Republics of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union. Declaration No. 142-ąØ of ...
in 1991, when all Soviet aid was suddenly halted.
An internal CIA study acknowledged various achievements of the North Korean government post-war: compassionate care for war orphans and children in general, a radical improvement in the status of women, free housing, free healthcare, and health statistics particularly in life expectancy and infant mortality that were comparable to even the most advanced nations up until the North Korean famine
The North Korean famine (), dubbed by the government as the Arduous March (), was a period of mass starvation together with a general economic crisis from 1995 to 2000 in North Korea. During this time there was an increase in defection from N ...
. Life expectancy in the North was 72 before the famine which was only marginally lower than in the South. The country once boasted a comparatively developed healthcare system; pre-famine North Korea had a network of nearly 45,000 family practitioners with some 800 hospitals and 1,000 clinics.
The relative peace between the North and South following the armistice was interrupted by border skirmishes, celebrity abductions, and assassination attempts. The North failed in several assassination attempts on South Korean leaders, such as in 1968, 1974, and the Rangoon bombing
The Rangoon bombing of 9 October 1983, was an assassination attempt against Chun Doo-hwan, the fifth president of South Korea, in Rangoon, Burma. The attempt was orchestrated by North Korea. Although Chun survived, 21 people died in the attac ...
in 1983; tunnels were found under the DMZ
A demilitarized zone (DMZ or DZ) is an area in which treaties or agreements between states, military powers or contending groups forbid military installations, activities, or personnel. A DZ often lies along an established frontier or boundary ...
and tensions flared over the axe murder incident at Panmunjom
Panmunjom (also spelled Panmunjeom) was a village just north of the ''de facto'' border between North Korea and South Korea, where the 1953 Korean Armistice Agreement that ended the Korean War was signed. It was located in what is now Paju, Gy ...
in 1976. For almost two decades after the war, the two states did not seek to negotiate with one another. In 1971, secret, high-level contacts began to be conducted culminating in the 1972 July 4 SouthŌĆōNorth Joint Statement that established principles of working toward peaceful reunification. The talks ultimately failed because in 1973, South Korea declared its preference that the two Koreas should seek separate memberships in international organizations.
Leadership of Kim Jong Il
TheSoviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
was dissolved on 26 December 1991, ending its aid and support to North Korea. In 1992, as Kim Il Sung's health began deteriorating, his son Kim Jong Il
Kim Jong Il (born Yuri Kim; 16 February 1941 or 1942 ŌĆō 17 December 2011) was a North Korean politician who was the second Supreme Leader (North Korean title), supreme leader of North Korea from Death and state funeral of Kim Il Sung, the de ...
slowly began taking over various state tasks. Kim Il Sung died of a heart attack in 1994; Kim Jong Il declared a three-year period of national mourning, afterward officially announcing his position as the new leader.
North Korea promised to halt its development of nuclear weapons under the Agreed Framework
The Agreed Framework between the United States of America and the Democratic People's Republic of Korea () was signed on 21 October 1994, between North Korea (DPRK) and the United States. The objective of the agreement was the freezing and replac ...
, negotiated with U.S. president Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton (n├® Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician and lawyer who was the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, ...
and signed in 1994. Building on Nordpolitik
Nordpolitik ( German for "Northern Policy") was the signature foreign policy of South Korean president Roh Tae-woo. The policy guided South Korean efforts to reach out to the traditional allies of North Korea, with the goal of normalized relatio ...
, South Korea began to engage with the North as part of its Sunshine Policy
The Reconciliation and Cooperation Policy Towards the North (), colloquially referred to as Sunshine Policy () is one of the approaches for South Korea's foreign policy towards North Korea, lasting from 1998 to 2008 and again from 2017 to 2020.
...
. Kim Jong Il instituted a policy called ''Songun
''Songun'' () is the "military-first" policy of North Korea, prioritizing the Korean People's Army in the affairs of state and allocation of resources. "Military-first" as a principle guides political and economic life in North Korea, with " ...
'', or "military first".
Flooding in the mid-1990s exacerbated the economic crisis, severely damaging crops and infrastructure and leading to widespread famine that the government proved incapable of curtailing, resulting in the deaths of between 240,000 and 420,000 people. Which led many North Koreans to flee into China, South Korea and neighboring countries. In China, these illegal North Korea child immigrants are called the Kotjebi. In 1996, the government accepted UN food aid.
The international environment changed once George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician and businessman who was the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Bush family and the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he i ...
became U.S. President in 2001. His administration rejected South Korea's Sunshine Policy and the Agreed Framework. Bush included North Korea in his axis of evil
The phrase "axis of evil" was first used by U.S. president George W. Bush and originally referred to Iran, Ba'athist Iraq, and North Korea. It was used in Bush's State of the Union address on January 29, 2002, less than five months after the ...
in his 2002 State of the Union Address
The 2002 State of the Union Address was given by the 43rd president of the United States, George W. Bush, on January 29, 2002, at 9:00 p.m. Eastern Time Zone, EST, in the chamber of the United States House of Representatives to the 107th United ...
. The U.S. government accordingly treated North Korea as a rogue state
"Rogue state" (or sometimes "outlaw state") is a term applied by some international theorists to states that they consider threatening to the world's peace. These states meet certain criteria, such as being ruled by authoritarian or totalitaria ...
, while North Korea redoubled its efforts to acquire nuclear weapons. On 9 October 2006, North Korea announced it had conducted its first nuclear weapons test.
U.S. President Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II (born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who was the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the first African American president in American history. O ...
adopted a policy of "strategic patience", resisting making deals with North Korea. Tensions with South Korea and the United States increased in 2010 with the sinking of the South Korean warship ''Cheonan'' and North Korea's bombardment of Yeonpyeongdo.
Leadership of Kim Jong Un
On 17 December 2011, Kim Jong Il died from a heart attack. His youngest sonKim Jong Un
Kim Jong Un (born 8 January 1983 or 1984) is a North Korean politician and dictator who has served as supreme leader of North Korea since 2011 and general secretary of the Workers' Party of Korea (WPK) since 2012. He is the third son of Kim ...
was announced as his successor. In the face of international condemnation, North Korea continued to develop its nuclear arsenal, possibly including a hydrogen bomb
A thermonuclear weapon, fusion weapon or hydrogen bomb (H-bomb) is a second-generation nuclear weapon design. Its greater sophistication affords it vastly greater destructive power than first-generation nuclear bombs, a more compact size, a lo ...
and a missile capable of reaching the United States.
Throughout 2017, following Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who is the 47th president of the United States. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he served as the 45 ...
's ascension to the US presidency, tensions between the United States and North Korea increased, and there was heightened rhetoric between the two, with Trump threatening "fire and fury" if North Korea ever attacked U.S. territory amid North Korean threats to test missiles that would land near Guam
Guam ( ; ) is an island that is an Territories of the United States, organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. Guam's capital is Hag├źt├▒a, Guam, Hag├źt├▒a, and the most ...
. The tensions substantially decreased in 2018, and a d├®tente
''D├®tente'' ( , ; for, fr, , relaxation, paren=left, ) is the relaxation of strained relations, especially political ones, through verbal communication. The diplomacy term originates from around 1912, when France and Germany tried unsucces ...
developed. A series of summits took place between Kim Jong Un of North Korea, President Moon Jae-in
Moon Jae-in (, ; born January 24, 1953) is a South Korean politician and former lawyer who served as the 12th president of South Korea from 2017 to 2022. Before his presidency, he served as the senior secretary for civil affairs and the Chief ...
of South Korea, and President Trump.
On 10 January 2021, Kim Jong Un was formally elected as the General Secretary
Secretary is a title often used in organizations to indicate a person having a certain amount of authority, Power (social and political), power, or importance in the organization. Secretaries announce important events and communicate to the org ...
in 8th Congress of the Workers' Party of Korea
The 8th Congress of the Workers' Party of Korea was held at the April 25 House of Culture in Pyongyang from 5 to 12 January 2021. A total of 7,000 people participated in the congress including 5,000 delegates. The Party Congress took place in the ...
, a top title previously held by Kim Il Sung and Kim Jong Il. On 24 March 2022, North Korea conducted a successful ICBM test launch for the first time since the 2017 crisis. In September 2022, North Korea passed a law that declared itself a nuclear state.
On December 30, 2023, North Korean leader Kim Jong Un
Kim Jong Un (born 8 January 1983 or 1984) is a North Korean politician and dictator who has served as supreme leader of North Korea since 2011 and general secretary of the Workers' Party of Korea (WPK) since 2012. He is the third son of Kim ...
provocatively declared South Korea, under the leadership of Yoon Suk Yeol
Yoon Suk Yeol (; born 18 December 1960) is a South Korean politician and former prosecutor who served as the 13th president of South Korea from 2022 until Impeachment of Yoon Suk Yeol, he was removed from office in 2025. The shortest-serving ...
, a "colonial vassal state", marking a significant departure from the longstanding position of mutual claims over the entire Korean Peninsula by both North and South Korea. This statement was followed by a call on January 15, 2024, for a constitutional amendment to redefine the boundary with South Korea as the 'Southern National Borderline,' further intensifying the rhetoric against South Korea. Kim Jong Un also stated that in the event of a war, North Korea would seek to annex the entirety of South Korea. In 2024, North Korea deployed a contingent of troops to Russia in support of Russia's war against Ukraine
The following is a list of major conflicts fought by Ukraine, by Ukrainian people or by regular armies during periods when List of tribes and states in Belarus, Russia and Ukraine, independent states existed on the Geography of Ukraine, modern ...
.
Geography
 North Korea occupies the northern portion of the
North Korea occupies the northern portion of the Korean Peninsula
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically divided at or near the 38th parallel between North Korea (Dem ...
, lying between latitudes 37┬░ and 43┬░N, and longitudes 124┬░ and 131┬░E. It covers an area of . To its west are the Yellow Sea
The Yellow Sea, also known as the North Sea, is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean located between mainland China and the Korean Peninsula, and can be considered the northwestern part of the East China Sea.
Names
It is one of four ...
and Korea Bay
Korea(n) Bay, sometimes West Korea(n) Bay (; ; or ), is a bight and the northern extension of the Yellow Sea, between the southeastern coastline of China's Liaoning Province and the western coastline of North Korea's North Pyongan, South P ...
, and to its east lies Japan across the Sea of Japan
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it ...
.
Early European visitors to Korea remarked that the country resembled "a sea in a heavy gale" because of the many successive mountain range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have aris ...
s that crisscross the peninsula. Some 80 percent of North Korea is composed of mountains and uplands, separated by deep and narrow valleys. All of the Korean Peninsula's mountains with elevations of or more are located in North Korea. The highest point in North Korea is Paektu Mountain
Paektu Mountain or Baekdu Mountain () is an active stratovolcano on the ChineseŌĆōNorth Korean border. In China, it is known as Changbai Mountain (). At , it is the tallest mountain in North Korea and Northeast China and the tallest mounta ...
, a volcanic mountain with an elevation of above sea level. Considered a sacred place by North Koreans, Mount Paektu holds significance in Korean culture and has been incorporated in the elaborate folklore and personality cult around the Kim family. For example, the song, "We Will Go To Mount Paektu" sings in praise of Kim Jong Un and describes a symbolic trek to the mountain. Other prominent ranges are the Hamgyong Range in the extreme northeast and the Rangrim Mountains
The Rangnim Mountains are a mountain range stretching from north to south, west of the Kaema Highlands, in central North Korea. They are the source of several major rivers of North Korea, such as the Taedong and the Ch'ŏngch'ŏn. The moun ...
, which are located in the north-central part of North Korea. Mount Kumgang
Mount Kumgang () or the Kumgang Mountains is a mountain massif, with a peak, in Kangwon-do, North Korea. It is located on the east coast of the country, in Mount Kumgang Tourist Region, formerly part of Kangwŏn Province, and is part of the ...
in the Taebaek Range, which extends into South Korea, is famous for its scenic beauty.
The coastal plains are wide in the west and discontinuous in the east. A great majority of the population lives in the plains and lowlands. According to a United Nations Environmental Programme report in 2003, forest covers over 70 percent of the country, mostly on steep slopes. North Korea had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index
The Forest Landscape Integrity Index (FLII) is an annual global index of forest condition measured by degree of anthropogenic modification. Created by a team of 47 scientists, the FLII, in its measurement of 300m pixels of forest across the globe ...
mean score of 8.02/10, ranking it 28th globally out of 172 countries. The longest river is the Amnok (Yalu) River which flows for . The country contains three terrestrial ecoregions: Central Korean deciduous forests, Changbai Mountains mixed forests
The Changbai Mountains mixed forests ecoregion (WWF ID: PA0414) covers the Changbai Mountains and surrounding foothills in China and North Korea. The region features extensive and naturally preserved deciduous and conifer forests. The region e ...
, and Manchurian mixed forests
The Manchurian mixed forests ecoregion (WWF ID: PA0426) covers the forested hills surrounding the river plains of northern China, Russia, North Korea, and South Korea. The ecoregion supports a number of rare species due to the relative isolation ...
.
Climate
humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir K├Čppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers, and cold ...
within the K├Čppen climate classification
The K├Čppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (te ...
scheme. Winters bring clear weather interspersed with snow storms as a result of northern and northwestern winds that blow from Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
. Summer tends to be by far the hottest, most humid, and rainiest time of year because of the southern and southeastern monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annu ...
winds that carry moist air from the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
. Approximately 60 percent of all precipitation occurs from June to September. Spring and autumn are transitional seasons between summer and winter. The daily average high and low temperatures for Pyongyang
Pyongyang () is the Capital city, capital and largest city of North Korea, where it is sometimes labeled as the "Capital of the Revolution" (). Pyongyang is located on the Taedong River about upstream from its mouth on the Yellow Sea. Accordi ...
are in January and in August.
Government and politics
North Korea functions as a highly centralized,one-party
A one-party state, single-party state, one-party system or single-party system is a governance structure in which only a single political party controls the ruling system. In a one-party state, all opposition parties are either outlawed or en ...
totalitarian
Totalitarianism is a political system and a form of government that prohibits opposition from political parties, disregards and outlaws the political claims of individual and group opposition to the state, and completely controls the public sph ...
dictatorship. According to its constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed.
When these pri ...
, it is a communist state
A communist state, also known as a MarxistŌĆōLeninist state, is a one-party state in which the totality of the power belongs to a party adhering to some form of MarxismŌĆōLeninism, a branch of the communist ideology. MarxismŌĆōLeninism was ...
that self-describes as a revolutionary and socialist state
A socialist state, socialist republic, or socialist country is a sovereign state constitutionally dedicated to the establishment of socialism. This article is about states that refer to themselves as socialist states, and not specifically ...
"guided in its building and activities only by great KimilsungismŌĆōKimjongilism". In addition to the constitution, North Korea is governed by the Ten Principles for the Establishment of a Monolithic Ideological System
Ten Principles for the Establishment of a Monolithic Ideological System (; also known as the Ten Principles of the One-Ideology System) are a set of ten principles and sixty-five clauses establishing standards for governance and guiding the behav ...
(also known as the "Ten Principles of the One-Ideology System") which establishes standards for governance and a guide for the behaviors of North Koreans. The Workers' Party of Korea
The Workers' Party of Korea (WPK), also called the Korean Workers' Party (KWP), is the sole ruling party of North Korea. Founded in 1949 from a merger between the Workers' Party of North Korea and the Workers' Party of South Korea, the WPK is ...
(WPK), a communist party led by a member of the Kim family, has an estimated 6.5 million members and is in control of North Korean politics. It has two satellite parties, the Korean Social Democratic Party
The Korean Social Democratic Party (KSDP; ) is a political party in North Korea that is allied with the ruling Workers' Party of Korea (WPK). It was formed on 3 November 1945 as the Korean Democratic Party by a mixed group of entrepreneurs, mer ...
and the Chondoist Chongu Party.
Kim Jong Un of the Kim family is the current Supreme Leader
A supreme leader or supreme ruler typically refers to powerful figures with an unchallenged authority, such as autocrats, dictators to spiritual and revolutionary leaders. Historic examples are Adolf Hitler () of Nazi Germany, Francisco ...
or ''Suryeong'' of North Korea. He heads all major governing structures: he is the general secretary of the Workers' Party of Korea
The general secretary of the Workers' Party of Korea () is the party leader, leader of the Workers' Party of Korea (WPK), the ruling party in North Korea, and the Supreme Leader (North Korean title), country's supreme leader. Charter of the Wor ...
, chairman of the Central Military Commission and president of the State Affairs. His grandfather Kim Il Sung, the founder and leader of North Korea until his death in 1994, is the country's " eternal President", while his father Kim Jong Il who succeeded Kim Il Sung as the leader was announced " Eternal General Secretary" and "Eternal Chairman of the National Defence Commission" after his death in 2011.
According to the constitution, there are officially three main branches of government. The first of these is the State Affairs Commission (SAC), which acts as "the supreme national guidance organ of state sovereignty". Its role is to deliberate and decide the work on defense building of the State, including major policies of the State, and to carry out the directions of the president of the commission, Kim Jong Un. The SAC also directly supervises the Ministry of Defence
A ministry of defence or defense (see American and British English spelling differences#-ce.2C -se, spelling differences), also known as a department of defence or defense, is the part of a government responsible for matters of defence and Mi ...
, Ministry of State Security and the Ministry of Social Security.
Legislative power
A legislature (, ) is a deliberative assembly with the legal authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country, nation or city on behalf of the people therein. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial powers o ...
is held by the unicameral Supreme People's Assembly
The Supreme People's Assembly (SPA; ) is the legislature of North Korea. It is ostensibly the highest organ of state power and the only branch of government in North Korea, with all state organs subservient to it under the principle of unified ...
(SPA). Its 687 members are elected every five years by universal suffrage
Universal suffrage or universal franchise ensures the right to vote for as many people bound by a government's laws as possible, as supported by the " one person, one vote" principle. For many, the term universal suffrage assumes the exclusion ...
, though the elections have been described by outside observers as similar to elections in the Soviet Union
The electoral system of the Soviet Union was varying over time, being based upon Chapter XIII of the provisional Fundamental Law of 1922, articles 9 and 10 of the 1924 Constitution and Chapter XI of the 1936 Constitution, with the electoral law ...
. Elections in North Korea have also been described as a form of government census, due to the near 100% turnout. Although the elections are not pluralistic, North Korean state media describes the elections as "an expression of the absolute support and trust of all voters in the DPRK government". Supreme People's Assembly sessions are convened by the SPA Standing Committee, whose Chairman
The chair, also chairman, chairwoman, or chairperson, is the presiding officer of an organized group such as a board, committee, or deliberative assembly. The person holding the office, who is typically elected or appointed by members of the gro ...
(Choe Ryong-hae
Choe Ryong-hae (; born 15 January 1950) is a North Korean politician and military officer who currently serves as Chairman of the Standing Committee of the Supreme People's Assembly and First Vice President of the State Affairs Commission, hol ...
since 2019) is the third-ranking official in North Korea. Deputies formally elect the chairman, the vice chairpersons and members of the Standing Committee and take part in the constitutionally appointed activities of the legislature: pass laws, establish domestic and foreign policies, appoint members of the cabinet, review and approve the state economic plan, among others. The SPA itself cannot initiate any legislation independently of party or state organs. It is unknown whether it has ever criticized or amended bills placed before it, and the elections are based around a single list of WPK-approved candidates who stand without opposition.
Executive power
The executive branch is the part of government which executes or enforces the law.
Function
The scope of executive power varies greatly depending on the political context in which it emerges, and it can change over time in a given country. In ...
is vested in the Cabinet of North Korea
The Cabinet of Democratic People's Republic of Korea () is the supreme administrative organ of North Korea. The Cabinet's official newspaper is '' Minju Choson''.
History
In North Korea's first constitution, adopted in 1948, the executive po ...
, which has been headed by Premier
Premier is a title for the head of government in central governments, state governments and local governments of some countries. A second in command to a premier is designated as a deputy premier.
A premier will normally be a head of govern ...
Pak Thae-song
Pak Thae-song (, born 14 September 1955) is a North Korean politician. He is a Vice Chairman of the Workers' Party of Korea and was the Chairman of the Supreme People's Assembly from 2019 to 2023. On 29 December 2024, Pak was appointed Premier of ...
since 29 December 2024, who is officially the second-ranking official after Kim Jong Un. The Premier represents the government and functions independently. His authority extends over two vice premiers, 30 ministers, two cabinet commission chairmen, the cabinet chief secretary, the president of the Central Bank
A central bank, reserve bank, national bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the monetary policy of a country or monetary union. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central bank possesses a monopoly on increasing the mo ...
, the director of the Central Bureau of Statistics and the president of the Academy of Sciences.
North Korea, like its southern counterpart, claims to be the legitimate government of the entire Korean Peninsula
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically divided at or near the 38th parallel between North Korea (Dem ...
and adjacent islands. Despite its official title as the "Democratic People's Republic of Korea", some observers have described North Korea's political system as a "hereditary dictatorship". It has also been described as a Stalinist
Stalinism (, ) is the totalitarian means of governing and MarxistŌĆōLeninist policies implemented in the Soviet Union (USSR) from 1927 to 1953 by dictator Joseph Stalin and in Soviet satellite states between 1944 and 1953. Stalinism in ...
dictatorship
A dictatorship is an autocratic form of government which is characterized by a leader, or a group of leaders, who hold governmental powers with few to no Limited government, limitations. Politics in a dictatorship are controlled by a dictator, ...
.
Political ideology
KimilsungismŌĆōKimjongilism is the official ideology of North Korea and the WPK, and is the cornerstone of party works and government operations. ''Juche
''Juche'', officially the ''Juche'' idea, is a component of Ideology of the Workers' Party of Korea#KimilsungismŌĆōKimjongilism, KimilsungismŌĆōKimjongilism, the state ideology of North Korea and the official ideology of the Workers' Party o ...
'', part of the larger KimilsungismŌĆōKimjongilism along with ''Songun
''Songun'' () is the "military-first" policy of North Korea, prioritizing the Korean People's Army in the affairs of state and allocation of resources. "Military-first" as a principle guides political and economic life in North Korea, with " ...
'' under Kim Jong Un, is viewed by the official North Korean line as an embodiment of Kim Il Sung's wisdom, an expression of his leadership, and an idea which provides "a complete answer to any question that arises in the struggle for national liberation". ''Juche'' was pronounced in December 1955 in a speech called ''On Eliminating Dogmatism and Formalism and Establishing Juche in Ideological Work
''On Eliminating Dogmatism and Formalism and Establishing Juche in Ideological Work'', also known as the "''Juche'' speech", was a speech delivered on 28 December 1955 by Kim Il Sung. The address mentioned his ''Juche'' ideology by name for the ...
'' in order to emphasize a Korea-centered revolution. Its core tenets are economic self-sufficiency, military self-reliance and an independent foreign policy. The roots of ''Juche'' were made up of a complex mixture of factors, including the popularity of Kim Il Sung, the conflict with pro-Soviet and pro-Chinese dissenters, and Korea's centuries-long struggle for independence. ''Juche'' was introduced into the constitution in 1972.
''Juche'' was initially promoted as a "creative application" of MarxismŌĆōLeninism
MarxismŌĆōLeninism () is a communist ideology that became the largest faction of the History of communism, communist movement in the world in the years following the October Revolution. It was the predominant ideology of most communist gov ...
, but in the mid-1970s, it was described by state propaganda as "the only scientific thought... and most effective revolutionary theoretical structure that leads to the future of communist society". ''Juche'' eventually replaced MarxismŌĆōLeninism entirely by the 1980s, and in 1992 references to the latter were omitted from the constitution. The 2009 constitution dropped references to communism and elevated the ''Songun'' military first policy while explicitly confirming the position of Kim Jong Il. However, the constitution retains references to socialism. The WPK reasserted its commitment to communism in 2021. ''Juche''s concepts of self-reliance have evolved with time and circumstances, but still provide the groundwork for the spartan austerity, sacrifice, and discipline demanded by the party.
Kim family
 Since the founding of the nation, North Korea's supreme leadership has stayed within the Kim family, which in North Korea is referred to as the '' Mount Paektu Bloodline''. It is a three-generation lineage descending from the country's first leader, Kim Il Sung, who developed North Korea around the ''Juche ideology'', and stayed in power until his death. Kim developed a cult of personality closely tied to the state philosophy of Juche, which was later passed on to his successors: his son Kim Jong Il in 1994 and grandson Kim Jong Un in 2011. In 2013, Clause 2 of Article 10 of the newly edited ''Ten Fundamental Principles of the Workers' Party of Korea'' stated that the party and revolution must be carried "eternally" by the "Mount Paektu Bloodline".
According to ''New Focus International'', the cult of personality, particularly surrounding Kim Il Sung, has been crucial for legitimizing the family's hereditary succession. The control the North Korean government exercises over many aspects of the nation's culture is used to perpetuate the
Since the founding of the nation, North Korea's supreme leadership has stayed within the Kim family, which in North Korea is referred to as the '' Mount Paektu Bloodline''. It is a three-generation lineage descending from the country's first leader, Kim Il Sung, who developed North Korea around the ''Juche ideology'', and stayed in power until his death. Kim developed a cult of personality closely tied to the state philosophy of Juche, which was later passed on to his successors: his son Kim Jong Il in 1994 and grandson Kim Jong Un in 2011. In 2013, Clause 2 of Article 10 of the newly edited ''Ten Fundamental Principles of the Workers' Party of Korea'' stated that the party and revolution must be carried "eternally" by the "Mount Paektu Bloodline".
According to ''New Focus International'', the cult of personality, particularly surrounding Kim Il Sung, has been crucial for legitimizing the family's hereditary succession. The control the North Korean government exercises over many aspects of the nation's culture is used to perpetuate the cult of personality
A cult of personality, or a cult of the leader,Cas Mudde, Mudde, Cas and Kaltwasser, Crist├│bal Rovira (2017) ''Populism: A Very Short Introduction''. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 63. is the result of an effort which is made to create ...
surrounding Kim Il Sung, and Kim Jong Il. While visiting North Korea in 1979, journalist Bradley Martin wrote that nearly all music, art, and sculpture that he observed glorified "Great Leader" Kim Il Sung, whose personality cult was then being extended to his son, "Dear Leader" Kim Jong Il.
Claims that the family has been deified are contested by B. R. Myers: "Divine powers have never been attributed to either of the two Kims. In fact, the propaganda apparatus in Pyongyang has generally been careful ''not'' to make claims that run directly counter to citizens' experience or common sense." He further explains that the state propaganda painted Kim Jong Il as someone whose expertise lay in military matters and that the famine of the 1990s was partially caused by natural disasters out of Kim Jong Il's control.
 The song " No Motherland Without You", sung by the North Korean army choir, was created especially for Kim Jong Il and is one of the most popular tunes in the country. Kim Il Sung is still officially revered as the nation's "Eternal President". Several landmarks in North Korea are named for Kim Il Sung, including
The song " No Motherland Without You", sung by the North Korean army choir, was created especially for Kim Jong Il and is one of the most popular tunes in the country. Kim Il Sung is still officially revered as the nation's "Eternal President". Several landmarks in North Korea are named for Kim Il Sung, including Kim Il Sung University
Kim Il Sung University () is a public university in Taesong, Pyongyang, North Korea. It was founded on 1 October 1946 and was the first tertiary education institution established in post-war North Korea.
The 15-hectare campus, along with the m ...
, Kim Il Sung Stadium, and Kim Il Sung Square. Defectors have been quoted as saying that North Korean schools deify both father and son. Kim Il Sung rejected the notion that he had created a cult around himself and accused those who suggested this of " factionalism". Following the death of Kim Il Sung, North Koreans were prostrating and weeping to a bronze statue of him in an organized event; similar scenes were broadcast by state television following the death of Kim Jong Il.
Critics maintain that Kim Jong Il's personality cult was inherited from his father. Kim Jong Il was often the center of attention throughout ordinary life. His birthday is one of the most important public holidays in the country. On his 60th birthday (based on his official date of birth), mass celebrations occurred throughout the country. Kim Jong Il's personality cult, although significant, was not as extensive as his father's. One point of view is that Kim Jong Il's cult of personality was solely out of respect for Kim Il Sung or out of fear of punishment for failure to pay homage, while North Korean government sources consider it genuine hero worship.
Administrative divisions
Foreign relations
As a result of its isolation, North Korea is sometimes known as the " hermit kingdom", a term that originally referred to the isolationism in the latter part of the Joseon period. Initially, North Korea had diplomatic ties only with other communist countries, and even today, most of the foreign embassies accredited to North Korea are located inBeijing
Beijing, Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Peking, is the capital city of China. With more than 22 million residents, it is the world's List of national capitals by population, most populous national capital city as well as ...
rather than in Pyongyang
Pyongyang () is the Capital city, capital and largest city of North Korea, where it is sometimes labeled as the "Capital of the Revolution" (). Pyongyang is located on the Taedong River about upstream from its mouth on the Yellow Sea. Accordi ...
. In the 1960s and 1970s, it pursued an independent foreign policy, established relations with many developing countries, and joined the Non-Aligned Movement
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 121 countries that Non-belligerent, are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. It was founded with the view to advancing interests of developing countries in the context of Cold W ...
. In the late 1980s and the 1990s its foreign policy was thrown into turmoil with the collapse of the Soviet Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
. Suffering an economic crisis, it closed a number of its embassies. At the same time, North Korea sought to build relations with developed free market countries.
North Korea joined the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
in 1991 together with South Korea. North Korea is also a member of the Non-Aligned Movement
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 121 countries that Non-belligerent, are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. It was founded with the view to advancing interests of developing countries in the context of Cold W ...
, G77 and the ASEAN Regional Forum. , North Korea had diplomatic relations with 166 countries and embassies in 47 countries. North Korea does not have diplomatic relations with Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
, Botswana
Botswana, officially the Republic of Botswana, is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. Botswana is topographically flat, with approximately 70 percent of its territory part of the Kalahari Desert. It is bordered by South Africa to the sou ...
, Estonia
Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Ru ...
, France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to IraqŌĆōSaudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to IraqŌĆōTurkey border, the north, Iran to IranŌĆōIraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
, Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
, Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
, Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
, the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, and Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which RussiaŌĆōUkraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
. Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
is unusual in maintaining a North Korean embassy. German Ambassador Friedrich Lohr says most of his time in North Korea involved facilitating the delivery of humanitarian aid and agricultural assistance to a population plagued by food shortages.
North Korea enjoys a close relationship with China which is often called North Korea's closest ally. Relations were strained beginning in 2006 because of China's concerns about North Korea's nuclear program. Relations improved after Xi Jinping
Xi Jinping, pronounced (born 15 June 1953) is a Chinese politician who has been the general secretary of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and Chairman of the Central Military Commission (China), chairman of the Central Military Commission ...
, General Secretary of the Chinese Communist Party
The general secretary of the Central Committee of the Chinese Communist Party ( zh, s=õĖŁÕøĮÕģ▒õ║¦ÕģÜõĖŁÕż«Õ¦öÕæśõ╝ܵĆ╗õ╣”Ķ«░, p=Zh┼Źnggu├│ G├▓ngchŪÄndŪÄng Zh┼Źngy─üng W─øiyu├Īnhu├¼ ZŪÆngsh┼½j├¼) is the leader of the Chinese Communist Part ...
and Chinese leader visited North Korea in June 2019. North Korea continues to have strong ties with several Southeast Asian countries such as Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
, Laos
Laos, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic (LPDR), is the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and ...
, Cambodia
Cambodia, officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. It is bordered by Thailand to the northwest, Laos to the north, and Vietnam to the east, and has a coastline ...
, and Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
. Relations with Malaysia were strained in 2017 by the assassination of Kim Jong-nam. North Korea has a close relationship with Russia and has voiced support for the Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, , starting the largest and deadliest war in Europe since World War II, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, conflict between the two countries which began in 2014. The fighting has caused hundreds of thou ...
.
North Korea was previously designated a state sponsor of terrorism by the U.S. because of its alleged involvement in the 1983 Rangoon bombing and the 1987 bombing of a South Korean airliner. On 11 October 2008, the United States removed North Korea from its list of states that sponsor terrorism after Pyongyang agreed to cooperate on issues related to its nuclear program. North Korea was re-designated a state sponsor of terrorism by the U.S. under the administration of Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who is the 47th president of the United States. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he served as the 45 ...
on 20 November 2017 after continued nuclear tests. The kidnapping of at least 13 Japanese citizens by North Korean agents in the 1970s and the 1980s has had a detrimental effect on North Korea's relationship with Japan.
US President Trump met with Kim in Singapore on 12 June 2018. An agreement was signed between the two countries endorsing the 2017 Panmunjom Declaration
The Panmunjom Declaration for Peace, Prosperity and Reunification of the Korean Peninsula was adopted between the Supreme Leader of North Korea, Kim Jong-un, and the President of South Korea, Moon Jae-in, on 27 April 2018, during the 2018 int ...
signed by North and South Korea, pledging to work towards denuclearizing the Korean Peninsula. They met in Hanoi from 27 to 28 February 2019, but failed to achieve an agreement. On 30 June 2019, Trump met with Kim along with South Korean president Moon Jae-in
Moon Jae-in (, ; born January 24, 1953) is a South Korean politician and former lawyer who served as the 12th president of South Korea from 2017 to 2022. Before his presidency, he served as the senior secretary for civil affairs and the Chief ...
at the Korean DMZ.
South Korea
 The
The Korean Demilitarized Zone
The Korean Demilitarized Zone () is a heavily militarized strip of land running across the Korea, Korean Peninsula near the 38th parallel north. The demilitarized zone (DMZ) is a border barrier that divides the peninsula roughly in half. It wa ...
with South Korea remains the most heavily fortified border in the world. Inter-Korean relations are at the core of North Korean diplomacy and have seen numerous shifts in the last few decades. North Korea's policy is to seek reunification without what it sees as outside interference, through a federal structure retaining each side's leadership and systems. In 1972, the two Koreas agreed in principle to achieve reunification through peaceful means and without foreign interference. On 10 October 1980, the then North Korean leader Kim Il Sung proposed a federation between North and South Korea named the Democratic Federal Republic of Korea in which the respective political systems would initially remain. However, relations remained cool well until the early 1990s, with a brief period in the early 1980s when North Korea offered to provide flood relief to its southern neighbor. Although the offer was initially welcomed, talks over how to deliver the relief goods broke down and none of the promised aid ever crossed the border.
The two countries also organized a reunion of 92 separated families.
 The
The Sunshine Policy
The Reconciliation and Cooperation Policy Towards the North (), colloquially referred to as Sunshine Policy () is one of the approaches for South Korea's foreign policy towards North Korea, lasting from 1998 to 2008 and again from 2017 to 2020.
...
instituted by South Korean president Kim Dae-jung
Kim Dae-jung (, ; 6 January 192418 August 2009) was a South Korean politician, activist and statesman who served as the eighth president of South Korea from 1998 to 2003.
Kim entered politics as a member of the new wing of the Democratic Pa ...
in 1998 was a watershed in inter-Korean relations. It encouraged other countries to engage with the North, which allowed Pyongyang to normalize relations with a number of European Union states and contributed to the establishment of joint North-South economic projects. The culmination of the Sunshine Policy was the 2000 inter-Korean summit, when Kim Dae-jung visited Kim Jong Il in Pyongyang. Both North and South Korea signed the June 15th NorthŌĆōSouth Joint Declaration
__NOTOC__
The June 15th NorthŌĆōSouth Joint Declaration was adopted between leaders of North Korea and South Korea in June 2000 after various diplomatic meetings between the North and South. As a result of the talks, numerous separated families ...
, in which both sides promised to seek peaceful reunification. On 4 October 2007, South Korean president Roh Moo-hyun
Roh Moo-hyun (, ; 1 September 1946 ŌĆō 23 May 2009) was a South Korean politician and lawyer who served as the ninth president of South Korea from 2003 to 2008.
Roh's pre-presidential political career was focused on human rights advocacy for ...
and Kim Jong Il signed an eight-point peace agreement.
However, relations worsened when South Korean president Lee Myung-bak
Lee Myung-bak (; born 19 December 1941), often referred to by his initials MB, is a South Korean businessman and politician who served as the tenth president of South Korea from 2008 to 2013. Before his presidency, he was the CEO of Hyundai Engi ...
adopted a more hard-line approach and suspended aid deliveries pending the de-nuclearization of the North. In 2009, North Korea responded by ending all of its previous agreements with the South. It deployed additional ballistic missiles and placed its military on full combat alert after South Korea, Japan and the United States threatened to intercept a Unha-2 space launch vehicle. The next few years witnessed a string of hostilities, including the alleged North Korean involvement in the sinking of South Korean warship ''Cheonan'', mutual ending of diplomatic ties, a North Korean artillery attack on Yeonpyeongdo, and growing international concern over North Korea's nuclear program.
In May 2017, Moon Jae-in
Moon Jae-in (, ; born January 24, 1953) is a South Korean politician and former lawyer who served as the 12th president of South Korea from 2017 to 2022. Before his presidency, he served as the senior secretary for civil affairs and the Chief ...
was elected president of South Korea with a promise to return to the Sunshine Policy. In February 2018, a d├®tente developed at the Winter Olympics held in South Korea. In April, South Korean president Moon Jae-in and Kim Jong Un met at the DMZ, and, in the Panmunjom Declaration
The Panmunjom Declaration for Peace, Prosperity and Reunification of the Korean Peninsula was adopted between the Supreme Leader of North Korea, Kim Jong-un, and the President of South Korea, Moon Jae-in, on 27 April 2018, during the 2018 int ...
, pledged to work for peace and nuclear disarmament. In September, at a joint news conference in Pyongyang, Moon and Kim agreed upon turning the Korean Peninsula
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically divided at or near the 38th parallel between North Korea (Dem ...
into a "land of peace without nuclear weapons and nuclear threats".
In January 2024, North Korea officially announced through its leader Kim Jong Un that it would no longer seek reunification with South Korea. Kim instead called for "completely occupying, subjugating and reclaiming" South Korea if war breaks out. Kim Jong Un also announced to the Supreme People's Assembly that the constitution should be changed such that South Korea would be considered the "primary foe and invariable principal enemy" of North Korea. Additionally, government agencies tasked with promoting reunification were closed.
Military
The North Korean armed forces, or theKorean People's Army
The Korean People's Army (KPA; ) encompasses the combined military forces of North Korea and the armed wing of the Workers' Party of Korea (WPK). The KPA consists of five branches: the Korean People's Army Ground Force, Ground Force, the Ko ...
(KPA), is estimated to comprise 1,280,000 active and 6,300,000 reserve and paramilitary troops, making it one of the largest military institutions in the world. With an active duty army consisting of of its population, North Korea maintains the fourth largest active military force in the world behind China, India and the United States. About 20 percent of men aged 17ŌĆō54 serve in the regular armed forces, and approximately one in every 25 citizens is an enlisted soldier.
The KPA is divided into five branches: Ground Force
''Ground Force'' is a British garden makeover television series originally broadcast by the BBC between 1997 and 2005. The series was originally hosted by Alan Titchmarsh, Charlie Dimmock and Tommy Walsh.
Production
The series was created b ...
, Navy
A navy, naval force, military maritime fleet, war navy, or maritime force is the military branch, branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval warfare, naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral z ...
, Air and Anti-Air Force, Special Operations Force
Special forces or special operations forces (SOF) are military units trained to conduct special operations. NATO has defined special operations as "military activities conducted by specially designated, organized, selected, trained and equip ...
, and Rocket Force. Command of the KPA lies in both the Central Military Commission of the Workers' Party of Korea
The Central Military Commission of the Workers' Party of Korea (CMC) () is an organ of the Central Committee of the Workers' Party of Korea (WPK) which heads the Korean People's Army (KPA).
One of the CMC's primary functions is to authorize ...
and the independent State Affairs Commission, which controls the Ministry of Defence
A ministry of defence or defense (see American and British English spelling differences#-ce.2C -se, spelling differences), also known as a department of defence or defense, is the part of a government responsible for matters of defence and Mi ...
.
Of all the KPA's branches, the Ground Force is the largest, comprising approximately one million personnel divided into 80 infantry divisions
Division may refer to:
Mathematics
*Division (mathematics), the inverse of multiplication
* Division algorithm, a method for computing the result of mathematical division Military
*Division (military), a formation typically consisting of 10,000 t ...
, 30 artillery brigades, 25 special warfare brigades, 20 mechanized brigades, 10 tank brigades and seven tank regiment
A regiment is a military unit. Its role and size varies markedly, depending on the country, military service, service, or administrative corps, specialisation.
In Middle Ages, Medieval Europe, the term "regiment" denoted any large body of l ...
s. It is equipped with 3,700 tanks, 2,100 armored personnel carrier
An armoured personnel carrier (APC) is a broad type of armoured military vehicle designed to transport personnel and equipment in combat zones. Since World War I, APCs have become a very common piece of military equipment around the world.
Acc ...
s and infantry fighting vehicle
An infantry fighting vehicle (IFV), also known as a mechanized infantry combat vehicle (MICV), is a type of armoured fighting vehicle and armoured personnel carrier used to carry infantry into battle and provide direct fire, direct-fire suppo ...
s, 17,900 artillery pieces, 11,000 anti-aircraft guns and some 10,000 MANPADS
Man-portable air-defense systems (MANPADS or MPADS) are portable shoulder-launched surface-to-air missiles. They are guided weapons and are a threat to low-flying aircraft, especially helicopters and also used against low-flying cruise missi ...
and anti-tank guided missile
An anti-tank guided missile (ATGM), anti-tank missile, anti-tank guided weapon (ATGW) or anti-armor guided weapon is a guided missile primarily designed to hit and destroy heavily armored military vehicles. ATGMs range in size from shoulde ...
s. The Air Force is estimated to possess around 1,600 aircraft (with between 545 ŌĆō 810 serving combat roles), while the Navy operates approximately 800 vessels, including the largest submarine fleet in the world. The KPA's Special Operation Force is also the world's largest special forces unit.
ballistic missile
A ballistic missile is a type of missile that uses projectile motion to deliver warheads on a target. These weapons are powered only during relatively brief periodsŌĆömost of the flight is unpowered. Short-range ballistic missiles (SRBM) typic ...
s with a range of up to .
According to a 2004 South Korean assessment, North Korea also possesses a stockpile of chemical weapon
A chemical weapon (CW) is a specialized munition that uses chemicals formulated to inflict death or harm on humans. According to the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW), this can be any chemical compound intended as ...
s estimated to amount to between 2,500 and 5,000 tons, including nerve, blister, blood, and vomiting agents, as well as the ability to cultivate and produce biological weapons
Biological agents, also known as biological weapons or bioweapons, are pathogens used as weapons. In addition to these living or replicating pathogens, toxins and biotoxins are also included among the bio-agents. More than 1,200 different kin ...
including anthrax
Anthrax is an infection caused by the bacterium '' Bacillus anthracis'' or ''Bacillus cereus'' biovar ''anthracis''. Infection typically occurs by contact with the skin, inhalation, or intestinal absorption. Symptom onset occurs between one ...
, smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by Variola virus (often called Smallpox virus), which belongs to the genus '' Orthopoxvirus''. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (W ...
, and cholera
Cholera () is an infection of the small intestine by some Strain (biology), strains of the Bacteria, bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea last ...
. As a result of its nuclear and missile tests, North Korea has been sanctioned under United Nations Security Council resolutions 1695
Events
JanuaryŌĆōMarch
* January 7 (December 28, 1694 O.S.) ŌĆō The United Kingdom's last joint monarchy, the reign of husband-and-wife King William III and Queen Mary II comes to an end with the death of Queen Mary, at the age of 3 ...
of July 2006, 1718 of October 2006, 1874
Events
January
* January 1 – New York City annexes The Bronx.
* January 2 – Ignacio Mar├Ła Gonz├Īlez becomes head of state of the Dominican Republic for the first time.
* January 3 – Third Carlist War: Battle of Caspe &n ...
of June 2009, 2087
In contemporary history, the third millennium is the current millennium in the ''Anno Domini'' or Common Era, under the Gregorian calendar. It began on 1 January 2001 ( MMI) and will end on 31 December 3000 ( MMM), spanning the 21st to 30t ...
of January 2013, and 2397 in December 2017.
The sale of weapons to North Korea by other states is prohibited by UN sanctions, and the KPA's conventional capabilities are limited by a number of factors including obsolete equipment, insufficient fuel supplies and a shortage of digital command and control assets. To compensate for these deficiencies, the KPA has deployed a wide range of asymmetric warfare
Asymmetric warfare (or asymmetric engagement) is a type of war between belligerents whose relative military power, strategy or tactics differ significantly. This type of warfare often, but not necessarily, involves insurgents, terrorist grou ...
technologies including anti-personnel blinding lasers, GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based hyperbolic navigation system owned by the United States Space Force and operated by Mission Delta 31. It is one of the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that provide geol ...
jammers, midget submarine
A midget submarine is any submarine under 150 tons, typically operated by a crew of one or two but sometimes up to six or nine, with little or no on-board living accommodation. They normally work with mother ships, from which they are launched an ...
s and human torpedo
Human torpedoes or manned torpedoes are a type of diver propulsion vehicle on which the diver rides, generally in a seated position behind a fairing. They were used as secret naval weapons in World War┬ĀII. The basic concept is still in use.
...
es, stealth
Stealth may refer to:
Military
*Stealth technology, technology used to conceal ships, aircraft, and missiles
**Stealth aircraft, aircraft which use stealth technology
** Stealth ground vehicle, ground vehicles which use stealth technology
** Ste ...
paint, and cyberwarfare
Cyberwarfare is the use of cyberattack, cyber attacks against an enemy State (polity), state, causing comparable harm to actual warfare and/or disrupting vital computer systems. Some intended outcomes could be espionage, sabotage, propaganda, ...
units. In 2015, North Korea was reported to employ 6,000 sophisticated computer security personnel in a cyberwarfare unit operating out of China. KPA units were blamed for the 2014 Sony Pictures hack
On November 24, 2014, the hacker group " Guardians of Peace" leaked confidential data from the film studio Sony Pictures Entertainment (SPE). The data included employee emails, personal and family information, executive salaries, copies of th ...
and have allegedly attempted to jam South Korean military satellites.
Much of the equipment in use by the KPA is engineered and manufactured by the domestic defense industry. Weapons are manufactured in roughly 1,800 underground defense industry plants scattered throughout the country, most of them located in Chagang Province
Chagang Province (; ) is a province of North Korea; it is bordered by China's Jilin and Liaoning provinces to the north, Ryanggang and South Hamgyong to the east, South Pyongan to the south, and North Pyongan to the west. Chagang was formed ...
. The defense industry is capable of producing a full range of individual and crew-operated weapons, artillery, armored vehicles, tanks, missiles, helicopters, submarines, landing and infiltration craft and Yak-18 trainers, and may even have limited jet aircraft manufacturing capacity. According to North Korean state media, military expenditure amounted to 15.8 percent of the state budget in 2010. The U.S. State Department has estimated that North Korea's military spending averaged 23% of its GDP from 2004 to 2014, the highest level in the world. North Korea successfully tested a new type of submarine-launched ballistic missile
A submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) is a ballistic missile capable of being launched from Ballistic missile submarine, submarines. Modern variants usually deliver multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs), each of which ...
, named Hwasong-11S on 19 October 2021. For the Excel file, sehere
Law enforcement and internal security
 North Korea has a civil law system based on the Prussian model and influenced by Japanese traditions and communist legal theory. Judiciary procedures are handled by the Central Court (the highest
North Korea has a civil law system based on the Prussian model and influenced by Japanese traditions and communist legal theory. Judiciary procedures are handled by the Central Court (the highest court of appeal
An appellate court, commonly called a court of appeal(s), appeal court, court of second instance or second instance court, is any court of law that is empowered to Hearing (law), hear a Legal case, case upon appeal from a trial court or other ...
), provincial or special city-level courts, people's courts, and special courts. People's courts are at the lowest level of the system and operate in cities, counties and urban districts, while different kinds of special courts handle cases related to military, railroad, or maritime matters.
Judges are elected by their respective local people's assemblies, but this vote tends to be overruled by the Workers' Party of Korea. The penal code
A criminal code or penal code is a document that compiles all, or a significant amount of, a particular jurisdiction's criminal law. Typically a criminal code will contain Crime, offences that are recognised in the jurisdiction, penalties that ...
is based on the principle of '' nullum crimen sine lege'' (no crime without a law), but remains a tool for political control despite several amendments reducing ideological influence. Courts carry out legal procedures related to not only criminal and civil matters, but also political cases as well. Political prisoners are sent to labor camp
A labor camp (or labour camp, see British and American spelling differences, spelling differences) or work camp is a detention facility where inmates are unfree labour, forced to engage in penal labor as a form of punishment. Labor camps have ...
s, while criminal offenders are incarcerated in a separate system.
The Ministry of Social Security maintains most law enforcement activities. It is one of the most powerful state institutions in North Korea and oversees the national police force, investigates criminal cases and manages non-political correctional facilities. It handles other aspects of domestic security like civil registration, traffic control, fire departments and railroad security. The Ministry of State Security was separated from the Ministry of Public Security in 1973 to conduct domestic and foreign intelligence, counterintelligence and manage the political prison system. Political camps can be short-term reeducation zones or " kwalliso" (total control zones) for lifetime detention. Camp 15 in Yodok and Camp 18 in Pukchang have been described in detailed testimonies.
The security apparatus is extensive, exerting strict control over residence, travel, employment, clothing, food and family life. Security forces employ mass surveillance
Mass surveillance is the intricate surveillance of an entire or a substantial fraction of a population in order to monitor that group of citizens. The surveillance is often carried out by Local government, local and federal governments or intell ...
. It is believed they tightly monitor cellular and digital communications.
North Korea has updated its constitution, labeling South Korea as a "hostile state" and abandoning its previous goal of peaceful reunification. This shift coincides with the destruction of inter-Korean connections and increased border defenses.
Human rights
The state ofhuman rights
Human rights are universally recognized Morality, moral principles or Social norm, norms that establish standards of human behavior and are often protected by both Municipal law, national and international laws. These rights are considered ...
in North Korea has been widely condemned. A 2014 UN inquiry into the DPRK's human rights record found evidence for "systematic, widespread and gross human rights violations" and stated that "the gravity, scale and nature of these violations reveal a state that does not have any parallel in the contemporary world", with Amnesty International
Amnesty International (also referred to as Amnesty or AI) is an international non-governmental organization focused on human rights, with its headquarters in the United Kingdom. The organization says that it has more than ten million members a ...
and Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. Headquartered in New York City, the group investigates and reports on issues including War crime, war crimes, crim ...
holding similar views. North Koreans have been referred to as "some of the world's most brutalized people" by Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. Headquartered in New York City, the group investigates and reports on issues including War crime, war crimes, crim ...
, because of the severe restrictions placed on their political
Politics () is the set of activities that are associated with decision-making, making decisions in social group, groups, or other forms of power (social and political), power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of Social sta ...
and economic freedoms. The North Korean population is strictly managed by the state and all aspects of daily life are subordinated to party and state planning. According to US government reports, employment is managed by the party on the basis of political reliability, and travel is tightly controlled by the Ministry of People's Security. The US State Department says that North Koreans do not have a choice in the jobs they work and are not free to change jobs at will.
There are restrictions on the freedom of association, expression and movement; arbitrary detention, torture and other ill-treatment result in death and execution. Citizens in North Korea are generally not permitted to leave the country at will and its government denies access to UN human rights observers.
The Ministry of State Security extrajudicially apprehends and imprisons those accused of political crimes without due process. People perceived as hostile to the government, such as Christians or critics of the leadership, are deported to labor camps without trial, often with their whole family and mostly without any chance of being released. Forced labor is part of an established system of political repression
Political repression is the act of a state entity controlling a citizenry by force for political reasons, particularly for the purpose of restricting or preventing the citizenry's ability to take part in the political life of a society, thereby ...
.
Based on satellite images and defector testimonies, an estimated 200,000 prisoners are held in six large prison camps, where they are made to work to right their wrongdoings. Supporters of the government who deviate from the government line are subject to reeducation in sections of labor camp
A labor camp (or labour camp, see British and American spelling differences, spelling differences) or work camp is a detention facility where inmates are unfree labour, forced to engage in penal labor as a form of punishment. Labor camps have ...
s set aside for that purpose. Those who are deemed politically rehabilitated may reassume responsible government positions on their release.
The United Nations Commission of Inquiry
A United Nations fact-finding mission, also called a United Nations commission of inquiry, is a United Nations mission carried out with the intention to discover facts. Fact-finding missions have been sent by the UN to a number of conflict areas ...
has accused North Korea of crimes against humanity
Crimes against humanity are certain serious crimes committed as part of a large-scale attack against civilians. Unlike war crimes, crimes against humanity can be committed during both peace and war and against a state's own nationals as well as ...
. The International Coalition to Stop Crimes Against Humanity in North Korea
The International Coalition to Stop Crimes Against Humanity in North Korea (ICNK) was formed on September 8, 2011. It comprises Amnesty International, Human Rights Watch and the International Federation for Human Rights and has support from over 4 ...
(ICNK) estimates that over 10,000 people die in North Korean prison camps every year.
With 1,100,000 people in modern slavery (via forced labor), North Korea is ranked highest in the world in terms of the percentage of population in modern slavery, with 10.4 percent enslaved according to the Walk Free's 2018 Global Slavery Index. North Korea is the only country in the world that has not explicitly criminalized some form of modern slavery. A United Nations report listed slavery among the crimes against humanity occurring in North Korea.
According to the US State Department, the North Korean government does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of human trafficking and is not making significant efforts to do so. North Korea has trafficked thousands of its own citizens allegedly as forced laborers to Russia, Poland, Malaysia, various parts of Africa and the Arab states of the Persian Gulf, Persian Gulf where most of the laborers' earnings are pocketed by Pyongyang.
The North Korean government rejects the human rights abuse claims, calling them a smear campaign and a human rights racket made to topple the government.KCNA Assails Role Played by Japan for UN Passage of "Human Rights" Resolution against DPRK, ''KCNA'', 22 December 2005.
, ''KCNA'', 8 November 2005. In a 2014 report to the UN, North Korea dismissed accusations of atrocities as wild rumors. The official state media, Korean Central News Agency, KCNA, responded with an article that included homophobic insults against the author of the human rights report, Michael Kirby (judge), Michael Kirby, calling him "a disgusting old lecher with a 40-odd-year-long career of homosexuality ... This practice can never be found in the DPRK boasting of the sound mentality and good morals ... In fact, it is ridiculous for such gay to sponsor dealing with others' human rights issue." The government, however, admitted some human rights issues related to living conditions and stated that it is working to improve them.
Economy
 North Korea has maintained one of the most closed and centralized economies in the world since the 1940s. For several decades, it followed the Soviet pattern of five-year plans with the ultimate goal of achieving self-sufficiency. Extensive Soviet and Chinese support allowed North Korea to rapidly recover from the Korean War and register very high growth rates. Systematic inefficiency began to arise around 1960, when the economy shifted from the extensive growth, extensive to the intensive growth, intensive development stage. The shortage of skilled labor, energy, arable land and transportation significantly impeded long-term growth and resulted in consistent failure to meet planning objectives. The major slowdown of the economy contrasted with South Korea, which surpassed the North in terms of absolute Gross domestic product, GDP and per capita income by the 1980s. North Korea declared the last seven-year plan unsuccessful in December 1993 and thereafter stopped announcing plans.
The loss of
North Korea has maintained one of the most closed and centralized economies in the world since the 1940s. For several decades, it followed the Soviet pattern of five-year plans with the ultimate goal of achieving self-sufficiency. Extensive Soviet and Chinese support allowed North Korea to rapidly recover from the Korean War and register very high growth rates. Systematic inefficiency began to arise around 1960, when the economy shifted from the extensive growth, extensive to the intensive growth, intensive development stage. The shortage of skilled labor, energy, arable land and transportation significantly impeded long-term growth and resulted in consistent failure to meet planning objectives. The major slowdown of the economy contrasted with South Korea, which surpassed the North in terms of absolute Gross domestic product, GDP and per capita income by the 1980s. North Korea declared the last seven-year plan unsuccessful in December 1993 and thereafter stopped announcing plans.
The loss of Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
trading partners and a series of natural disasters throughout the 1990s caused severe hardships, including widespread famine. By 2000, the situation improved owing to a massive international food assistance effort, but the economy continues to suffer from food shortages, dilapidated infrastructure and a critically low energy supply. In an attempt to recover from the collapse, the government began structural reforms in 1998 that formally legalized private property, private ownership of assets and decentralized control over production. A second round of reforms in 2002 led to an expansion of market activities, partial monetization, flexible prices and salaries, and the introduction of incentives and accountability techniques. Despite these changes, North Korea remains a command economy where the state owns almost all means of production and development priorities are defined by the government.
North Korea has the structural profile of a relatively industrialized country where nearly half of the gross domestic product is generated by Industrial sector, industry and Human Development Index, human development is at medium levels. Purchasing power parity (PPP) GDP is estimated at $40 billion, with a very low per capita value of $1,800. In 2012, gross national income per capita was $1,523, compared to $28,430 in South Korea. The North Korean won
The Korean People's won, more commonly known as the North Korean won (currency symbol, symbol: Ōé®; ISO 4217, code: KPW; ) and sometimes known as the Democratic People's Republic of Korea won (), is the official currency of North Korea. It is ...
is the national currency, issued by the Central Bank of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea. The economy has been developing dramatically in recent years despite sanctions. The Sejong Institute describes these changes as "astonishing".
The economy is heavily nationalized. Food and housing are extensively subsidized by the state; education and healthcare are free; and the payment of taxes was officially abolished in 1974. A variety of goods are available in department stores and supermarkets in Pyongyang, though most of the population relies on small-scale ''jangmadang'' markets. In 2009, the government attempted to stem the expanding free market by banning jangmadang and the use of foreign currency, heavily devaluing the won and restricting the convertibility of savings in the old currency, but the resulting inflation spike and rare public protests caused a reversal of these policies. Private trade is dominated by women because most men are required to be present at their workplace, even though many state-owned enterprises are non-operational.
Industry and services employ 65% of North Korea's 12.6 million labor force. Major industries include machine building, military equipment, chemicals, mining, metallurgy, textiles, food processing and Tourism in North Korea, tourism. Iron ore and coal production are among the few sectors where North Korea performs significantly better than its South Korea, southern neighborŌĆöit produces about 10 times more of each resource. Using ex-Romanian drilling rigs, several oil exploration companies have confirmed significant oil reserves in the North Korean shelf of the Sea of Japan, and in areas south of Pyongyang. The agricultural sector was shattered by the natural disasters of the 1990s. Its 3,500 agricultural cooperative, cooperatives and state farms were moderately successful until the mid-1990s but now experience chronic fertilizer and equipment shortages. Rice, corn, soybeans and Potato production in North Korea, potatoes are some of the primary crops. A significant contribution to the food supply comes from commercial fishing and aquaculture. Smaller specialized farms, managed by the state, also produce high-value crops, including ginseng, honey, matsutake and herbs for traditional Korean medicine, traditional Korean and traditional Chinese medicine, Chinese medicine. Tourism in North Korea, Tourism has been a growing sector for the past decade. North Korea has been aiming to increase the number of foreign visitors through projects like the Masikryong Ski Resort. On 22 January 2020, North Korea closed its borders to foreign tourists in response to the threat of the COVID-19 pandemic in North Korea.
Foreign trade surpassed pre-crisis levels in 2005 and continues to expand. North Korea has a number of special economic zones (SEZs) and Special cities of North Korea, Special Administrative Regions where foreign companies can operate with tax and tariff incentives while North Korean establishments gain access to improved technology. Initially four such zones existed, but they yielded little overall success. The SEZ system was overhauled in 2013 when 14 new zones were opened and the Rason Special Economic Zone was reformed as a joint Chinese-North Korean project. The Kaesong Industrial Region is a special economic zone where more than 100 South Korean companies employ some 52,000 North Korean workers. , China is the biggest trading partner of North Korea outside inter-Korean trade, accounting for more than 84% of the total external trade ($5.3 billion) followed by India at 3.3% share ($205 million). In 2014, Russia wrote off 90% of North Korea's debt and the two countries agreed to conduct all transactions in Russian ruble, rubles. Overall, external trade in 2013 reached a total of $7.3 billion (the highest amount since 1990), while inter-Korean trade dropped to an eight-year low of $1.1 billion.
Transportation
Transport infrastructure in North Korea includes railways, highways, water and air routes, but rail transport is by far the most widespread. North Korea has some of railways mostly in standard gauge which carry 80% of annual passenger traffic and 86% of freight, but electricity shortages undermine their efficiency. Construction of a high-speed railway connecting Kaesong, Pyongyang and Sinuiju with speeds exceeding was approved in 2013. North Korea connects with the Trans-Siberian Railway through Rajin station, Rajin. Road transport is very limitedŌĆöonly of the road network are paved, and maintenance on most roads is poor. Only 2% of the freight capacity is supported by river and sea transport, and air traffic is negligible. All port facilities are ice-free and host a merchant fleet of 158 vessels. Eighty-two airports and 23 helipads are operational and the largest serve the state-run airline, Air Koryo. Cars are relatively rare, but bicycles are common. There is only one international airportŌĆöPyongyang International AirportŌĆöserviced by Russia and China (see List of airports in North Korea#Public airports, List of public airports in North Korea)Energy
 North Korea's energy infrastructure is obsolete and in disrepair. Power shortages are chronic and would not be alleviated even by electricity imports because the poorly maintained grid causes significant losses during transmission. Coal accounts for 70% of primary energy production, followed by hydroelectric power with 17%. The government under Kim Jong Un has increased emphasis on renewable energy projects like wind farms, solar parks, solar heating and biomass. A set of legal regulations adopted in 2014 stressed the development of geothermal, wind and solar energy along with recycling and environmental conservation. North Korea's long-term objective is to curb fossil fuel usage and reach an output of 5 million kilowatts from renewable sources by 2044, up from its current total of 430,000 kilowatts from all sources. Wind power is projected to satisfy 15% of the country's total energy demand under this strategy.
North Korea also strives to develop its own civilian nuclear program. These efforts are under much international dispute due to their military applications and concerns about safety.
North Korea's energy infrastructure is obsolete and in disrepair. Power shortages are chronic and would not be alleviated even by electricity imports because the poorly maintained grid causes significant losses during transmission. Coal accounts for 70% of primary energy production, followed by hydroelectric power with 17%. The government under Kim Jong Un has increased emphasis on renewable energy projects like wind farms, solar parks, solar heating and biomass. A set of legal regulations adopted in 2014 stressed the development of geothermal, wind and solar energy along with recycling and environmental conservation. North Korea's long-term objective is to curb fossil fuel usage and reach an output of 5 million kilowatts from renewable sources by 2044, up from its current total of 430,000 kilowatts from all sources. Wind power is projected to satisfy 15% of the country's total energy demand under this strategy.
North Korea also strives to develop its own civilian nuclear program. These efforts are under much international dispute due to their military applications and concerns about safety.
Science and technology
R&D efforts are concentrated at the State Academy of Sciences, which runs 40 research institutes, 200 smaller research centers, a scientific equipment factory and six publishing houses. The government considers science and technology to be directly linked to economic development. A five-year scientific plan emphasizing IT, biotechnology, nanotechnology, marine technology, and laser and plasma research was carried out in the early 2000s. A 2010 report by the South Korean Science and Technology Policy Institute identified polymer chemistry, single carbon materials, nanoscience, mathematics, software, nuclear technology and rocketry as potential areas of inter-Korean scientific cooperation. North Korean institutes are strong in these fields of research, although their engineers require additional training, and laboratories need equipment upgrades. Under its "constructing a powerful knowledge economy" slogan, the state has launched a project to concentrate education, scientific research and production into a number of "high-tech development zones". International sanctions remain a significant obstacle to their development. The ''Miraewon'' network of electronic library, electronic libraries was established in 2014 under similar slogans.
Significant resources have been allocated to the national space program, which is managed by the National Aerospace Technology Administration (formerly managed by the Korean Committee of Space Technology until April 2013). Domestically produced space launch vehicle, launch vehicles and the Kwangmyŏngsŏng program, Kwangmyŏngsŏng satellite class are launched from two spaceports, the Tonghae Satellite Launching Ground and the Sohae Satellite Launching Station. After four failed attempts, North Korea became the Timeline of first orbital launches by country, tenth spacefaring nation with the launch of Kwangmyŏngsŏng-3 Unit 2 in December 2012, which successfully reached orbit but was believed to be crippled and non-operational. It joined the Outer Space Treaty in 2009 and has stated its intentions to undertake human spaceflight, crewed and Exploration of the Moon, Moon missions. The government insisted the space program is for peaceful purposes, but the United States, Japan, South Korea and other countries maintained that it serves to advance North Korea's ballistic missile program. On 7 February 2016, a statement broadcast on Korean Central Television said that a new Earth observation satellite, Kwangmyŏngsŏng-4, Kwangmyongsong-4, had successfully been put into orbit.
Usage of communication technology is controlled by the Ministry of Post and Telecommunications (North Korea), Ministry of Post and Telecommunications. An adequate nationwide fiber-optic communication, fiber-optic telephony, telephone system with 1.18 million fixed lines and expanding mobile coverage is in place. Most phones are installed for senior government officials and installation requires written explanation why the user needs a telephone and how it will be paid for. Cellular coverage is available with a 3G network operated by Koryolink, a joint venture with Orascom Telecom Holding. The number of subscribers has increased from 3,000 in 2002 to almost two million in 2013. International calls through either fixed or cellular service are restricted, and Mobile Web, mobile Internet is not available.
Internet access itself is limited to a handful of elite users and scientists. Instead, North Korea has a Closed platform, walled garden intranet system called Kwangmyong (network), Kwangmyong, which is maintained and monitored by the Korea Computer Center. Its content is limited to state media, chat services, message boards, an e-mail service and an estimated 1,000ŌĆō5,500 websites. Computers employ the Red Star OS, an operating system derived from Linux, with a Shell (computing), user shell visually similar to that of OS X. On 19 September 2016, a TLDR project noticed the North Korean Internet DNS data and top-level domain was left open which allowed global DNS zone transfers. A dump of the data discovered was shared on GitHub.
Under its "constructing a powerful knowledge economy" slogan, the state has launched a project to concentrate education, scientific research and production into a number of "high-tech development zones". International sanctions remain a significant obstacle to their development. The ''Miraewon'' network of electronic library, electronic libraries was established in 2014 under similar slogans.
Significant resources have been allocated to the national space program, which is managed by the National Aerospace Technology Administration (formerly managed by the Korean Committee of Space Technology until April 2013). Domestically produced space launch vehicle, launch vehicles and the Kwangmyŏngsŏng program, Kwangmyŏngsŏng satellite class are launched from two spaceports, the Tonghae Satellite Launching Ground and the Sohae Satellite Launching Station. After four failed attempts, North Korea became the Timeline of first orbital launches by country, tenth spacefaring nation with the launch of Kwangmyŏngsŏng-3 Unit 2 in December 2012, which successfully reached orbit but was believed to be crippled and non-operational. It joined the Outer Space Treaty in 2009 and has stated its intentions to undertake human spaceflight, crewed and Exploration of the Moon, Moon missions. The government insisted the space program is for peaceful purposes, but the United States, Japan, South Korea and other countries maintained that it serves to advance North Korea's ballistic missile program. On 7 February 2016, a statement broadcast on Korean Central Television said that a new Earth observation satellite, Kwangmyŏngsŏng-4, Kwangmyongsong-4, had successfully been put into orbit.
Usage of communication technology is controlled by the Ministry of Post and Telecommunications (North Korea), Ministry of Post and Telecommunications. An adequate nationwide fiber-optic communication, fiber-optic telephony, telephone system with 1.18 million fixed lines and expanding mobile coverage is in place. Most phones are installed for senior government officials and installation requires written explanation why the user needs a telephone and how it will be paid for. Cellular coverage is available with a 3G network operated by Koryolink, a joint venture with Orascom Telecom Holding. The number of subscribers has increased from 3,000 in 2002 to almost two million in 2013. International calls through either fixed or cellular service are restricted, and Mobile Web, mobile Internet is not available.
Internet access itself is limited to a handful of elite users and scientists. Instead, North Korea has a Closed platform, walled garden intranet system called Kwangmyong (network), Kwangmyong, which is maintained and monitored by the Korea Computer Center. Its content is limited to state media, chat services, message boards, an e-mail service and an estimated 1,000ŌĆō5,500 websites. Computers employ the Red Star OS, an operating system derived from Linux, with a Shell (computing), user shell visually similar to that of OS X. On 19 September 2016, a TLDR project noticed the North Korean Internet DNS data and top-level domain was left open which allowed global DNS zone transfers. A dump of the data discovered was shared on GitHub.
Demographics
North Korean famine
The North Korean famine (), dubbed by the government as the Arduous March (), was a period of mass starvation together with a general economic crisis from 1995 to 2000 in North Korea. During this time there was an increase in defection from N ...
. The famine began in 1995, lasted for three years, and resulted in the deaths of between 240,000 and 420,000 North Koreans.
International donors led by the United States initiated shipments of food through the World Food Program in 1997 to combat the famine. Despite a drastic reduction of aid under the Presidency of George W. Bush, George W. Bush administration, the situation gradually improved: the number of malnourished children declined from 60% in 1998 to 37% in 2006 and 28% in 2013. Domestic food production almost recovered to the recommended annual level of 5.37 million tons of cereal equivalent in 2013, but the World Food Program reported a continuing lack of dietary diversity and access to fats and proteins. By the mid-2010s national levels of severe wasting, an indication of famine-like conditions, were lower than in other low-income countries and about on par with developing nations in the Pacific and East Asia. Children's health and nutrition is significantly better on a number of indicators than in many other Asian countries.
The famine had a significant impact on the population growth rate, which declined to 0.9% annually in 2002. It was 0.5% in 2014. Late marriages after military service, limited housing space and long hours of work or political studies further exhaust the population and reduce growth. The national birth rate is 14.5 births per year per 1,000 population. Two-thirds of households consist of extended family, extended families mostly living in two-room units. Marriage is virtually universal and divorce is extremely rare.
Language
North Korea shares the Korean language with South Korea, although some NorthŌĆōSouth differences in the Korean language, dialectal differences exist within both Koreas. North Koreans refer to their Pyongan dialect as ''munhwa┼Å'' ("cultured language") as opposed to the dialects of South Korea, especially the Seoul dialect or ''p'yojun'┼Å'' ("standard language"), which are viewed as decadent because of its use of loanwords from Chinese language, Chinese and European languages (particularly English language, English). Words of Chinese, Manchu or Western origin have been eliminated from ''munhwa'' along with the usage of Chinese hancha characters. Written language uses only the Chos┼Ån'g┼Łl (Hangul) phonetic alphabet, developed underSejong the Great
Sejong (; 15 May 1397 ŌĆō 8 April 1450), commonly known as Sejong the Great (), was the fourth monarch of the Joseon, Joseon dynasty of Korea. He is regarded as the greatest ruler in Korean history, and is remembered as the inventor of Hangu ...
(1418ŌĆō1450).
Religion
North Korea is officially an atheist state. Its constitution guarantees Freedom of religion in North Korea, freedom of religion under Article 68, but this principle is limited by the requirement that religion may not be used as a pretext to harm the state, introduce foreign forces, or harm the existing social order. Religious practice is therefore restricted, despite nominal constitutional protections. Proselytizing is also prohibited due to concerns about foreign influence. The number of Christian churchgoers nonetheless more than doubled between the 1980s and the early 2000s due to the recruitment of Christians who previously worshipped privately or in small house churches. The Open Doors mission, a Protestant group based in the United States and founded during the Cold War era, claims the most severe persecution of Christians in the world occurs in North Korea. There are no known official statistics of religions in North Korea. According to a 2020 study published by the Centre for the Study of World Christianity, 73% of the population are irreligion, irreligious (58% agnostic, 15% atheist), 13% practice Cheondoism, Chondoism, 12% practice Korean shamanism, 1.5% are Korean Buddhism, Buddhist, and less than 0.5% practice another religion such as Christianity in Korea, Christianity, Islam in Korea, Islam, or Chinese folk religion. Amnesty International has expressed concerns about religious persecution in North Korea. Pro-North groups such as the Paektu Solidarity Alliance deny these claims, saying that multiple religious facilities exist across the nation. Some religious places of worship are located in foreign embassies in the capital city of Pyongyang. Five Christian churches built with state funds stand in Pyongyang: three Protestant, one Roman Catholic, and one Russian Orthodox. Critics claim these are showcases for foreigners. Buddhism and Korean Confucianism, Confucianism still influence spirituality. Chondoism ("Heavenly Way") is an indigenous syncretism, syncretic belief combining elements of Korean shamanism, Buddhism, Taoism in Korea, Taoism and Catholicism that is officially represented by the WPK-controlled Chondoist Chongu Party. Chondoism is recognized and favored by the government, being seen as an indigenous form of "revolutionary religion".Education
The 2008 North Korea census, 2008 census listed the entire population as literate. An 11-year free, compulsory cycle of primary and secondary education is provided in more than 27,000 nursery schools, 14,000 kindergartens, 4,800 four-year primary and 4,700 six-year secondary schools. 77% of males and 79% of females aged 30ŌĆō34 have finished secondary school. An additional 300 universities and colleges offer higher education. Most graduates from the compulsory program do not attend university but begin their obligatory military service or proceed to work in farms or factories instead. The main deficiencies of higher education are the heavy presence of ideological subjects, which comprise 50% of courses in social studies and 20% in sciences, and the imbalances in curriculum. The study of natural sciences is greatly emphasized while social sciences are neglected. Heuristics is actively applied to develop the independence and creativity of students throughout the system. The study of Russian language, Russian and English language, English was made compulsory in upper middle schools in 1978.Health
 North Korea has a life expectancy of 72.3 years in 2019, according to HDR 2020. While North Korea is classified as a low-income country, the structure of North Korea's causes of death (2013) is unlike that of other low-income countries. Instead, it is closer to worldwide averages, with non-communicable diseasesŌĆösuch as cardiovascular disease and cancersŌĆöaccounting for 84 percent of the total deaths in 2016.
According to the World Bank report of 2016 (based on World Health Organization, WHO's estimate), only 9.5% of the total deaths recorded in North Korea are attributed to communicable diseases and maternal, prenatal and nutrition conditions, a figure which is slightly lower than that of South Korea (10.1%) and one fifth of other low-income countries (50.1%) but higher than that of high income countries (6.7%). Only one out of ten leading causes of overall deaths in North Korea is attributed to communicable diseases (Lower respiratory tract infection, lower respiratory infection), a disease which is reported to have declined by six percent since 2007.
In 2013, cardiovascular disease as a single disease group was reported as the largest cause of death in North Korea. The three major causes of death in North Korea are stroke, Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, COPD and Coronary artery disease, ischaemic heart disease. Non-communicable diseases risk factors in North Korea include high rates of urbanization, an aging society, and high rates of Smoking in North Korea, smoking and Alcoholic beverage, alcohol consumption amongst men.
Maternal mortality is lower than other low-income countries, but significantly higher than South Korea and other high income countries, at 89 per 100,000 live births. In 2008 child mortality was estimated to be 45 per 1,000, which is much better than other economically comparable countries. Chad for example had a child mortality rate of 120 per 1,000, despite the fact that Chad was most likely wealthier than North Korea at the time.
Healthcare Access and Quality Index, as calculated by Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, IHME, was reported to stand at 62.3, much lower than that of South Korea.
According to a 2003 report by the United States Department of State, almost 100% of the population has access to water and sanitation. Further, 80% of the population had access to improved sanitation facilities in 2015.
North Korea has the highest number of doctors per capita amongst low-income countries, with 3.7 physicians per 1,000 people, a figure which is also significantly higher than that of South Korea, according to World Health Organization, WHO's data.
Conflicting reports between Amnesty and WHO have emerged, where the Amnesty report claimed that North Korea had an inadequate health care system, while the Director of the World Health Organization claimed that North Korea's healthcare system was considered the envy of the developing world and had "no lack of doctors and nurses".
A free universal insurance system is in place. Quality of medical care varies significantly by region and is often low, with severe shortages of equipment, drugs and anesthetics. According to WHO, expenditure on health per capita is one of the lowest in the world. Preventive healthcare, Preventive medicine is emphasized through physical exercise and sports, nationwide monthly checkups and routine spraying of public places against disease. Every individual has a lifetime health card which contains a full medical record.
North Korea has a life expectancy of 72.3 years in 2019, according to HDR 2020. While North Korea is classified as a low-income country, the structure of North Korea's causes of death (2013) is unlike that of other low-income countries. Instead, it is closer to worldwide averages, with non-communicable diseasesŌĆösuch as cardiovascular disease and cancersŌĆöaccounting for 84 percent of the total deaths in 2016.
According to the World Bank report of 2016 (based on World Health Organization, WHO's estimate), only 9.5% of the total deaths recorded in North Korea are attributed to communicable diseases and maternal, prenatal and nutrition conditions, a figure which is slightly lower than that of South Korea (10.1%) and one fifth of other low-income countries (50.1%) but higher than that of high income countries (6.7%). Only one out of ten leading causes of overall deaths in North Korea is attributed to communicable diseases (Lower respiratory tract infection, lower respiratory infection), a disease which is reported to have declined by six percent since 2007.
In 2013, cardiovascular disease as a single disease group was reported as the largest cause of death in North Korea. The three major causes of death in North Korea are stroke, Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, COPD and Coronary artery disease, ischaemic heart disease. Non-communicable diseases risk factors in North Korea include high rates of urbanization, an aging society, and high rates of Smoking in North Korea, smoking and Alcoholic beverage, alcohol consumption amongst men.
Maternal mortality is lower than other low-income countries, but significantly higher than South Korea and other high income countries, at 89 per 100,000 live births. In 2008 child mortality was estimated to be 45 per 1,000, which is much better than other economically comparable countries. Chad for example had a child mortality rate of 120 per 1,000, despite the fact that Chad was most likely wealthier than North Korea at the time.
Healthcare Access and Quality Index, as calculated by Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, IHME, was reported to stand at 62.3, much lower than that of South Korea.
According to a 2003 report by the United States Department of State, almost 100% of the population has access to water and sanitation. Further, 80% of the population had access to improved sanitation facilities in 2015.
North Korea has the highest number of doctors per capita amongst low-income countries, with 3.7 physicians per 1,000 people, a figure which is also significantly higher than that of South Korea, according to World Health Organization, WHO's data.
Conflicting reports between Amnesty and WHO have emerged, where the Amnesty report claimed that North Korea had an inadequate health care system, while the Director of the World Health Organization claimed that North Korea's healthcare system was considered the envy of the developing world and had "no lack of doctors and nurses".
A free universal insurance system is in place. Quality of medical care varies significantly by region and is often low, with severe shortages of equipment, drugs and anesthetics. According to WHO, expenditure on health per capita is one of the lowest in the world. Preventive healthcare, Preventive medicine is emphasized through physical exercise and sports, nationwide monthly checkups and routine spraying of public places against disease. Every individual has a lifetime health card which contains a full medical record.
Songbun
According to North Korean documents and refugee testimonies, all North Koreans are sorted into groups according to their Songbun, an ascribed status system based on a citizen's assessed loyalty to the government. Based on their own behavior and the political, social, and economic background of their family for three generations as well as behavior by relatives within that range, Songbun is allegedly used to determine whether an individual is trusted with responsibility or given certain opportunities. Songbun allegedly affects access to educational and employment opportunities and particularly whether a person is eligible to join North Korea's ruling party. There are 3 main classifications and about 50 sub-classifications. According to Kim Il Sung, speaking in 1958, the loyal "core class" constituted 25% of the North Korean population, the "wavering class" 55%, and the "hostile class" 20%. The highest status is accorded to individuals descended from those who participated with Kim Il Sung in the resistance against Japanese occupation before and during World War II and to those who were factory workers, laborers, or peasants in 1950. While some analysts believe private commerce recently changed the Songbun system to some extent, most North Korean refugees say it remains a commanding presence in everyday life. The North Korean government claims all citizens are equal and denies any discrimination on the basis of family background.Culture
Despite a historically strong Chinese influence, Korean culture has shaped its own unique identity. It came under attack during the Korea under Japanese rule, Japanese rule from 1910 to 1945, when Japan enforced a cultural assimilation policy. Koreans were forced to learn and speak Japanese, adopt the Japanese family name system and Shinto religion, and were forbidden to write or speak the Korean language in schools, businesses, or public places. After the peninsula was divided in 1945, two distinct cultures formed out of the common Korean heritage. North Koreans have little exposure to foreign influence. The revolutionary struggle and the brilliance of the leadership are some of the main themes in art. "Reactionary" elements from traditional culture have been discarded and cultural forms with a "folk" spirit have been reintroduced. Korean heritage is protected and maintained by the state. Over 190 historical sites and objects of national significance are cataloged as National Treasures of North Korea, while some 1,800 less valuable artifacts are included in a list of Cultural assets of North Korea, Cultural Assets. The Historic Monuments and Sites in Kaesong and the Complex of Koguryo Tombs are UNESCO World Heritage Sites. The Goguryeo tombs are registered on UNESCO's list of World Heritage Sites. These remains were registered as the first World Heritage property of North Korea in the UNESCO World Heritage Committee (WHC) in July 2004. There are 63 burial mounds on the site, with clear murals preserved. The burial customs of the Goguryeo culture have influenced Asian civilizations beyond Korea, including Japan.Art
Visual arts are generally produced in the aesthetic of socialist realism. North Korean painting combines the influence of Soviet and Japanese visual expression to instill a sentimental loyalty to the system. All artists in North Korea are required to join the Artists' Union, and the best among them can receive an official license to portray the leaders. Portraits and sculptures depicting Kim Il Sung, Kim Jong Il and Kim Jong Un are classed as "Number One works". Most aspects of art have been dominated by Mansudae Art Studio since its establishment in 1959. It employs around 1,000 artists in what is likely the biggest art factory in the world where paintings, murals, posters and monuments are designed and produced. The studio has commercialized its activity and sells its works to collectors in a variety of countries including China, where it is in high demand. Mansudae Overseas Projects is a subdivision of Mansudae Art Studio that carries out construction of large-scale monuments for international customers. Some of the projects include the African Renaissance Monument in Senegal, and the Heroes' Acre (Namibia), Heroes' Acre in Namibia.Literature
All publishing houses are owned by the government or the WPK because they are considered an important tool for agitprop. The Workers' Party of Korea Publishing House is the most authoritative among them and publishes all Kim Il Sung bibliography, works of Kim Il Sung, ideological education materials and party policy documents. The availability of foreign literature is limited, examples being North Korean editions of Indian, German, Chinese and Russian fairy tales, ''Tales from Shakespeare'', some works of Bertolt Brecht and Erich K├żstner, and the Harry Potter series, ''Harry Potter'' series. Kim Il Sung's personal works are considered "classical masterpieces" while the ones created under his instruction are labeled "models of ''Juche'' literature". These include ''The Fate of a Self-Defense Corps Man'', ''The Song of Korea'' and ''Immortal History'', a series of historical novels depicting the suffering of Koreans under Japanese occupation. More than four million literary works were published between the 1980s and the early 2000s, but almost all of them belong to a narrow variety of political genres like "army-first revolutionary literature". Science fiction is considered a secondary genre because it somewhat departs from the traditional standards of detailed descriptions and metaphors of the leader. The exotic settings of the stories give authors more freedom to depictcyberwarfare
Cyberwarfare is the use of cyberattack, cyber attacks against an enemy State (polity), state, causing comparable harm to actual warfare and/or disrupting vital computer systems. Some intended outcomes could be espionage, sabotage, propaganda, ...
, violence, sexual abuse, and crime, which are absent in other genres. Sci-fi works glorify technology and promote the ''Juche'' concept of Anthropocentrism, anthropocentric existence through depictions of robotics, space exploration, and immortality.
Music
The government emphasized optimistic folk-based tunes and revolutionary music throughout most of the 20th century. Ideological messages are conveyed through massive orchestral pieces like the "Korean revolutionary opera, Five Great Revolutionary Operas" based on traditional Korean ''Changgeuk, ch'angguk''. Revolutionary operas differ from their Western counterparts by adding traditional instruments to the orchestra and avoiding recitative segments. ''Sea of Blood'' is the most widely performed of the Five Great Operas: since its premiere in 1971, it has been played over 1,500 times, and its 2010 tour in China was a major success. Western classical music by Johannes Brahms, Brahms, Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky, Tchaikovsky, Igor Stravinsky, Stravinsky and other composers is performed both by the State Symphony Orchestra of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea, State Symphony Orchestra and student orchestras. Pop music appeared in the 1980s with the Pochonbo Electronic Ensemble and Wangjaesan Light Music Band. Improved relations with South Korea following the 2000 inter-Korean summit caused a decline in direct ideological messages in pop songs, but themes like comradeship, nostalgia and the construction of a powerful country remained. In 2014, the All-female band, all-girl Moranbong Band was described as the most popular group in the country. North Koreans also listen to K-pop which spreads through illegal markets.Media
Cuisine
Korean cuisine has evolved through centuries of social and political change. Originating from ancient Prehistoric Korea, agricultural and nomadic traditions in southernManchuria
Manchuria is a historical region in northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day northeast China and parts of the modern-day Russian Far East south of the Uda (Khabarovsk Krai), Uda River and the Tukuringra-Dzhagdy Ranges. The exact ...
and the Korean Peninsula
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically divided at or near the 38th parallel between North Korea (Dem ...
, it has gone through a complex interaction of the natural environment and different cultural trends. Rice dishes and kimchi are staple Korean food. In a traditional meal, they accompany both side dishes (''Banchan, panch'an'') and main courses like ''Juk (food), juk'', ''Bulgogi, pulgogi'' or noodles. ''Soju'' liquor is the best-known traditional Korean spirit.
North Korea's most famous restaurant, Okryu-gwan, located in Pyongyang, is known for its ''Naengmyeon, raengmyeon'' cold noodles. Other dishes served there include Mullet (fish), gray mullet soup with boiled rice, Galbitang, beef rib soup, green bean pancake, ''sinseollo, sinsollo'' and dishes made from diamondback terrapin, terrapin. Okryu-gwan sends research teams into the countryside to collect data on Korean cuisine and introduce new recipes. Some Asian cities host branches of the Pyongyang (restaurant chain), Pyongyang restaurant chain where waitresses perform music and dance.
Sports
 Most schools have daily practice in association football, basketball, table tennis, gymnastics, boxing and others. The DPR Korea League is popular inside the country and its games are often televised. The national football team, ''Korea DPR national football team, Chollima'', competed in the FIFA World Cup in 2010 FIFA World Cup, 2010, when it lost all three matches against Brazil national football team, Brazil, Portugal national football team, Portugal and Ivory Coast national football team, Ivory Coast. Its 1966 FIFA World Cup, 1966 appearance was much more successful, seeing a surprise 1ŌĆō0 victory over Italy national football team, Italy and a quarter final loss to Portugal by 3ŌĆō5. A North Korea national basketball team, national team represents the nation in international basketball competitions as well. In December 2013, former American basketball professional Dennis Rodman visited North Korea to help train the national team after he developed a friendship with Kim Jong Un.
North Korea's North Korea at the Olympics, first appearance in the Olympics came 1964 Winter Olympics, in 1964. The 1972 Summer Olympics, 1972 Olympics saw its summer games debut and five medals, including one gold. With the exception of the boycotted 1984 Summer Olympics, Los Angeles and 1988 Summer Olympics, Seoul Olympics, North Korean athletes have won medals in all summer games since then. Weightlifter Kim Un-guk broke the world record of the Weightlifting at the 2012 Summer Olympics ŌĆō Men's 62 kg, Men's 62 kg category at the 2012 Summer Olympics in London. Successful Olympians receive luxury apartments from the state in recognition for their achievements.
Most schools have daily practice in association football, basketball, table tennis, gymnastics, boxing and others. The DPR Korea League is popular inside the country and its games are often televised. The national football team, ''Korea DPR national football team, Chollima'', competed in the FIFA World Cup in 2010 FIFA World Cup, 2010, when it lost all three matches against Brazil national football team, Brazil, Portugal national football team, Portugal and Ivory Coast national football team, Ivory Coast. Its 1966 FIFA World Cup, 1966 appearance was much more successful, seeing a surprise 1ŌĆō0 victory over Italy national football team, Italy and a quarter final loss to Portugal by 3ŌĆō5. A North Korea national basketball team, national team represents the nation in international basketball competitions as well. In December 2013, former American basketball professional Dennis Rodman visited North Korea to help train the national team after he developed a friendship with Kim Jong Un.
North Korea's North Korea at the Olympics, first appearance in the Olympics came 1964 Winter Olympics, in 1964. The 1972 Summer Olympics, 1972 Olympics saw its summer games debut and five medals, including one gold. With the exception of the boycotted 1984 Summer Olympics, Los Angeles and 1988 Summer Olympics, Seoul Olympics, North Korean athletes have won medals in all summer games since then. Weightlifter Kim Un-guk broke the world record of the Weightlifting at the 2012 Summer Olympics ŌĆō Men's 62 kg, Men's 62 kg category at the 2012 Summer Olympics in London. Successful Olympians receive luxury apartments from the state in recognition for their achievements.
See also
* Bibliography of North Korea * ChinaŌĆōNorth Korea border * Outline of North KoreaNotes
References
Citations
General and cited sources
* * * * * Armstrong, Charles K. "North Korea in 2016." ''Asian Survey'' 57.1 (2017): 119ŌĆō27abstract
* * * Hayes, Peter, and Roger Cavazos. "North Korea in 2015." ''Asian Survey'' 56.1 (2016): 68ŌĆō77
abstract
* Hayes, Peter, and Roger Cavazos. "North Korea in 2014." ''Asian Survey'' 55.1 (2015): 119ŌĆō31
abstract
; als
full text online
* , covers 1960s to 2010. * Jackson, Van. "Deterring a Nuclear-Armed Adversary in a Contested Regional Order: The 'Trilemma' of USŌĆōNorth Korea Relations." ''Asia Policy'' 23.1 (2017): 97ŌĆō103
online
* * Lee, Hong Yung. "North Korea in 2013: Economy, Executions, and Nuclear Brinksmanship." ''Asian Survey'' 54.1 (2014): 89ŌĆō100
Online
. * * * * * *
External links
Government websites
KCNA
() ŌĆō website of the Korean Central News Agency
Naenara
() ŌĆō the official North Korean governmental portal Naenara
DPRK Foreign Ministry
() ŌĆō official North Korean foreign ministry website
The Pyongyang Times
ŌĆō official foreign language newspaper of the DPRK (archived)
General websites
*Official website of the DPR of Korea
ŌĆō Administered by the Korean Friendship Association
38North
North Korea profile
at BBC News
North Korea
ŌĆō link collection (University of Colorado at Boulder Libraries GovPubs)
NKnews
ŌĆō a news agency covering North Korean topics.
Friend.com.kp
ŌĆō website of the Committee for Cultural Relations with Foreign Countries
Korea Education Fund
''Rodong Sinmun''
ŌĆō the newspaper of the Central Committee of the Workers' Party of Korea ''Rodong Sinmun''
Uriminzokkiri
DPRK Portal
United Nations Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights
ŌĆō Report of the Commission of Inquiry on Human Rights in the Democratic People's Republic of Korea {{Coord, 40, N, 127, E, display=title North Korea, 1948 establishments in North Korea Atheist states Communist states East Asian countries Former Japanese colonies Korea, Korean-speaking countries and territories Member states of the United Nations Northeast Asian countries One-party states Republics States and territories established in 1948 States with limited recognition Totalitarian states