|
Tetraiodomethane
Carbon tetraiodide is a tetrahalomethane with the molecular formula . Being bright red, it is a relatively rare example of a highly colored methane derivative. It is only 2.3% by weight carbon, although other methane derivatives are known with still less carbon. Structure The tetrahedral molecule features C-I distances of 2.12 ± 0.02 Å. The molecule is slightly crowded with short contacts between iodine atoms of 3.459 ± 0.03 Å, and possibly for this reason, it is thermally and photochemically unstable. Carbon tetraiodide crystallizes in tetragonal crystal structure (''a'' 6.409, ''c'' 9.558 (.10−1 nm)). It has zero dipole moment due to its symmetrically substituted tetrahedral geometry. Properties, synthesis, and uses Carbon tetraiodide is slightly reactive towards water, giving iodoform and I2. It is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. It decomposes thermally and photochemically to , C2I4. Its synthesis entails AlCl3-catalyzed halide exchange, which is conducted a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Tetrahalomethane
Tetrahalomethanes are fully halogenated methane derivatives of general formula CFkCllBrmInAtp, where:k+l+m+n+p=4Tetrahalomethanes are on the border of inorganic and organic chemistry, thus they can be assigned both inorganic and organic names by IUPAC: tetrafluoromethane - carbon tetrafluoride, tetraiodomethane - carbon tetraiodide, dichlorodifluoromethane - carbon dichloride difluoride. Each halogen ( F, Cl, Br, I, At) forms a corresponding halomethane, but their stability decreases in order CF4 > CCl4 > CBr4 > CI4 from exceptionally stable gaseous tetrafluoromethane with bond energy 515 kJ·mol−1 to solid tetraiodomethane, depending on bond energy. Many mixed halomethanes are also known, such as CBrClF2. Uses Fluorine, chlorine, and sometimes bromine-substituted halomethanes were used as refrigerants, commonly known as CFCs (chlorofluorocarbon Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) are fully or partly Halogenation, halogenated hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Diethyl Ether
Diethyl ether, or simply ether, is an organic compound with the chemical formula , sometimes abbreviated as . It is a colourless, highly Volatility (chemistry), volatile, sweet-smelling ("ethereal odour"), extremely flammable liquid. It belongs to the ether class of organic compounds. It is a common solvent and was formerly used as a general anesthetic. Production Most diethyl ether is produced as a byproduct of the vapor-phase Hydration reaction, hydration of ethylene to make ethanol. This process uses solid-supported phosphoric acid Catalysis, catalysts and can be adjusted to make more ether if the need arises: Vapor-phase Dehydration reaction, dehydration of ethanol over some Aluminium oxide, alumina catalysts can give diethyl ether yields of up to 95%. : Diethyl ether can be prepared both in laboratories and on an industrial scale by the acid ether synthesis. Uses The dominant use of diethyl ether is as a solvent. One particular application is in the production of cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Derivative (chemistry)
In chemistry, a derivative is a compound that is derived from a similar compound by a chemical reaction. In the past, derivative also meant a compound that ''can be imagined to'' arise from another compound, if one atom or group of atoms is replaced with another atom or group of atoms, but modern chemical language now uses the term structural analog for this meaning, thus eliminating ambiguity. The term "structural analogue" is common in organic chemistry. In biochemistry, the word is used for compounds that at least theoretically can be formed from the precursor compound. Chemical derivatives may be used to facilitate analysis. For example, melting point (MP) analysis can assist in identification of many organic compounds. A crystalline derivative may be prepared, such as a semicarbazone or 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone (derived from aldehydes or ketones), as a simple way of verifying the identity of the original compound, assuming that a table of derivative MP values is avai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Inorganic Carbon Compounds
An inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bondsthat is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as ''inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep mantle remain active areas of investigation. All allotropes (structurally different pure forms of an element) and some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon (graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, graphene, etc.), carbon monoxide , carbon dioxide , carbides, and salts of inorganic anions such as carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, thiocyanates, isothiocyanates, etc. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it cannot occur within living things. History Friedrich Wöhler's conversion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Journal Of The American Chemical Society
The ''Journal of the American Chemical Society'' (also known as JACS) is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal that was established in 1879 by the American Chemical Society. The journal has absorbed two other publications in its history, the ''Journal of Analytical and Applied Chemistry'' (July 1893) and the ''American Chemical Journal'' (January 1914). It covers all fields of chemistry. Since 2021, the editor-in-chief is Erick M. Carreira (ETH Zurich). In 2014, the journal moved to a hybrid open access publishing model. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 14.4. Editors-in-chief The following people are or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Median Lethal Dose
In toxicology, the median lethal dose, LD50 (abbreviation for " lethal dose, 50%"), LC50 (lethal concentration, 50%) or LCt50 is a toxic unit that measures the lethal dose of a given substance. The value of LD50 for a substance is the dose required to kill half the members of a tested population after a specified test duration. LD50 figures are frequently used as a general indicator of a substance's acute toxicity. A lower LD50 is indicative of higher toxicity. The term LD50 is generally attributed to John William Trevan. The test was created by J. W. Trevan in 1927. The term semilethal dose is occasionally used in the same sense, in particular with translations of foreign language text, but can also refer to a sublethal dose. LD50 is usually determined by tests on animals such as laboratory mice. In 2011, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved alternative methods to LD50 for testing the cosmetic drug botox without animal tests. Conventions The LD50 is usually expr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Carbon Tetrachloride
Carbon tetrachloride, also known by many other names (such as carbon tet for short and tetrachloromethane, also IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry, recognised by the IUPAC), is a chemical compound with the chemical formula CCl4. It is a non-flammable, dense, colourless liquid with a "sweet" chloroform-like odour that can be detected at low levels. It was formerly widely used in fire extinguishers, as a precursor to refrigerants, an anthelmintic and a cleaning agent, but has since been phased out because of environmental and safety concerns. Exposure to high concentrations of carbon tetrachloride can affect the central nervous system and degenerate the liver and kidneys. Prolonged exposure can be fatal. Properties In the carbon tetrachloride molecule, four chlorine atoms are positioned symmetrically as corners in a tetrahedron, tetrahedral configuration joined to a central carbon atom by single covalent bonds. Because of this symmetric geometry, CCl4 is non-polar. methane, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Appel Reaction
The Appel reaction is an organic reaction that converts an alcohol into an alkyl chloride using triphenylphosphine and carbon tetrachloride. The use of carbon tetrabromide or bromine as a halide source will yield alkyl bromides, whereas using carbon tetraiodide, methyl iodide or iodine gives alkyl iodides. The reaction is credited to and named after Rolf Appel, it had however been described earlier. The use of this reaction is becoming less common, due to carbon tetrachloride being restricted under the Montreal protocol. Drawbacks to the reaction are the use of toxic halogenating agents and the coproduction of organophosphorus product that must be separated from the organic product. The phosphorus reagent can be used in catalytic quantities. The corresponding alkyl bromide can also be synthesised by addition of lithium bromide as a source of bromide ions. A more sustainable version of the Appel reaction has been reported, which uses a catalytic amount of phosphine that is regen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
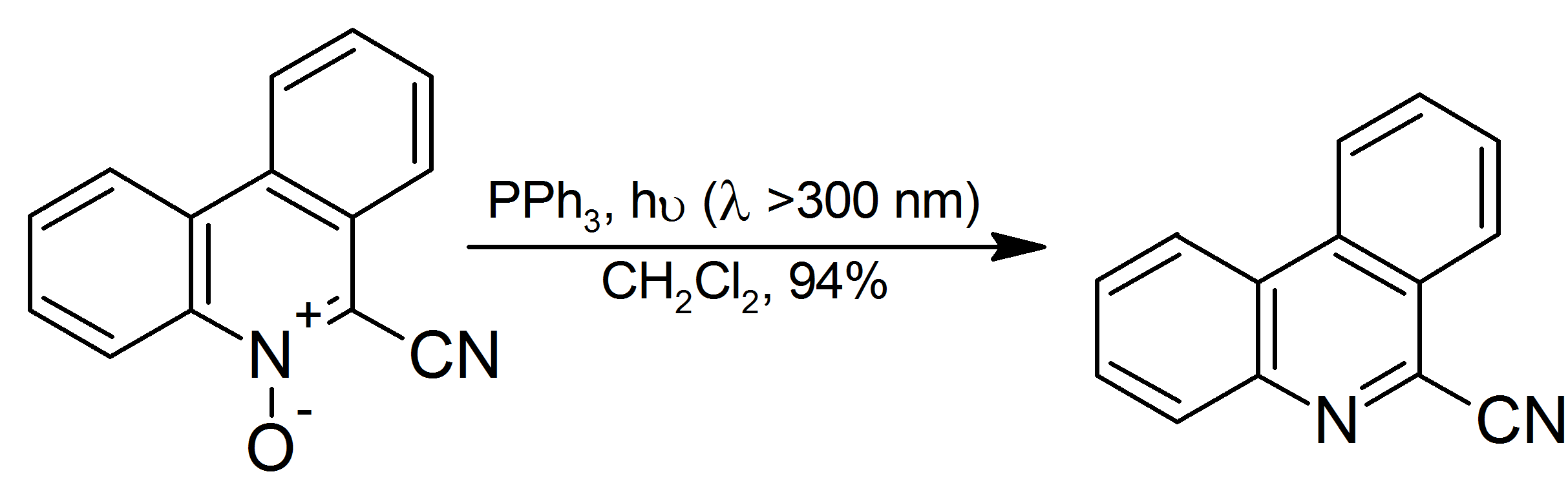 |
Triphenylphosphine
Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to P Ph3 or Ph3P. It is versatile compound that is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis and as a ligand for transition metal complexes, including ones that serve as catalysts in organometallic chemistry. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether. Preparation and structure Triphenylphosphine can be prepared in the laboratory by treatment of phosphorus trichloride with phenylmagnesium bromide or phenyllithium. The industrial synthesis involves the reaction between phosphorus trichloride, chlorobenzene, and sodium: :PCl3 + 3 PhCl + 6 Na → PPh3 + 6 NaCl Triphenylphosphine crystallizes in triclinic and monoclinic modification. In both cases, the molecule adopts a pyramidal structure with propeller-like arrangement of the thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Iodination
In chemistry, halogenation is a chemical reaction which introduces one or more halogens into a chemical compound. Halide-containing compounds are pervasive, making this type of transformation important, e.g. in the production of polymers, drugs. This kind of conversion is in fact so common that a comprehensive overview is challenging. This article mainly deals with halogenation using elemental halogens (). Halides are also commonly introduced using salts of the halides and halogen acids. Many specialized reagents exist for introducing halogens into diverse substrates, e.g. thionyl chloride. Organic chemistry Several pathways exist for the halogenation of organic compounds, including free radical halogenation, ketone halogenation, electrophilic halogenation, and halogen addition reaction. The nature of the substrate determines the pathway. The facility of halogenation is influenced by the halogen. Fluorine and chlorine are more electrophilic and are more aggressive halogenating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Aluminium Chloride
Aluminium chloride, also known as aluminium trichloride, is an inorganic compound with the formula . It forms a hexahydrate with the formula , containing six water molecules of hydration. Both the anhydrous form and the hexahydrate are colourless crystals, but samples are often contaminated with iron(III) chloride, giving them a yellow colour. The anhydrous form is commercially important. It has a low melting and boiling point. It is mainly produced and consumed in the production of aluminium, but large amounts are also used in other areas of the chemical industry. The compound is often cited as a Lewis acid. It is an inorganic compound that reversibly changes from a polymer to a monomer at mild temperature. Structure Anhydrous adopts three structures, depending on the temperature and the state (solid, liquid, gas). Solid has a sheet-like layered structure with cubic close-packed chloride ions. In this framework, the Al centres exhibit octahedral coordination geom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Tetraiodoethylene
Tetraiodoethylene, TIE or diiodoform, is an Organoiodine chemistry, organoiodine compound with the chemical formula . Its structure is . It is an odourless yellow crystalline solid that is soluble in benzene and chloroform, and insoluble in water.Lide, D. R. (1995). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. (Special Student Edition): A Ready-Reference Book of Chemical and Physical Data. CRC-Press. Page 522 It has been used as an antiseptic and a component in pesticide and fungicide formulations. It is the periodinated analogue of ethylene. It is a decomposition product of carbon tetraiodide and diiodoacetylene.''Peculiar Decomposition of Diiodoacetylene'', Victor Meyel and Wilhelm Pemsel (1896) Tetraiodoethylene reacts with ethylamine to give ethylamine di-tetraiodoethylene, , and ethylamine tetraiodoethylene, . Tetraiodoethylene and iodine pentafluoride yield iodopentafluoroethane.Journal of the Chemical Society. (1948). page 2188 Tetraiodoethylene turns brown and emits a character ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |