|
Tambur
The is a fretted string instrument of Turkey and the former lands of the Ottoman Empire. There are two variants, one of which is played with a plectrum (''mızraplı tambur'') and the other with a bow ('' yaylı tambur''). The player is called a ''tamburî''.Tambur Republic of Turkey - Ministry of Culture and Tourism History and development There are several hypotheses as to the origin of the instrument. One suggests that it descended from the kopuz, a string instrument still in use among the Turkic peoples of Central Asia and the Caspian region. The name itself derives from the '' tanbur'' (tunbur), which in turn might have descended from the |
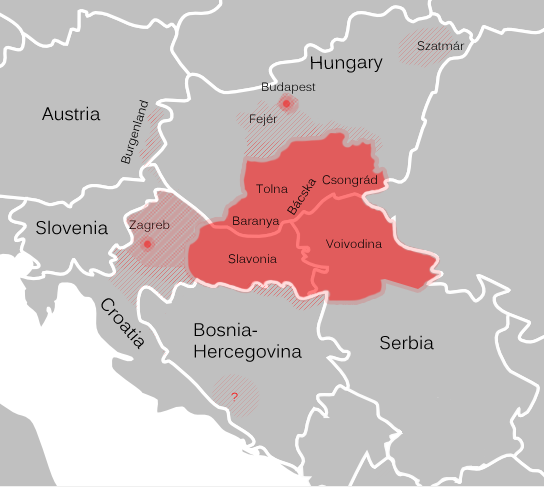
Tamburica
Tamburica ( or ; sometimes written tamburrizza or tamburitza; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", tamburica, тамбурица, little tamboura) or tamboura (; ) refers to a family of long-necked lutes popular in Southeast Europe and southeastern Central Europe, especially Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia (of which it is the national string instrument), Hungary, Serbia (in Vojvodina, Mačva, and Posavo- Tamnava), and Slovenia. It is also known in Burgenland, Austria. All took their name and some characteristics from the Persian tanbur but also resemble the mandolin and guitar in the sense that its strings are plucked and often paired. The frets may be moveable to allow the playing of various modes. The variety of tamburica shapes known today were developed in Serbia and Croatia by a number of indigenous contributors near the end of the 19th century. History There is little reliable data showing how the tamboura entered Central Europe. It already existed during Byzantine Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanbur
The term ''Tanbur'' can refer to various long-necked string instruments originating in Mesopotamia, Southern or Central Asia. According to the ''New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', "terminology presents a complicated situation. Nowadays the term tanbur (or tambur) is applied to a variety of distinct and related long-necked lutes used in art and folk traditions. Similar or identical instruments are also known by other terms." These instruments are used in the traditional music of Iran, Iraq, India, Armenia, Afghanistan, Azerbaijan (especially Avar community), Pakistan, Turkey, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, and Uzbekistan. Origins Tanburs have been present in Mesopotamia since the Akkadian era, or the third millennium BC. Three figurines have been found in Susa that belong to 1500 BC, and in hands of one of them is a tanbur-like instrument. Also an image on the rocks near Mosul that belong to about 1000 BC shows tanbur players. Playing the tanbur was common at least ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cemil Bey
Tanburi Cemil Bey (1873, Istanbul – July 28, 1916, Istanbul) was an Ottoman tanbur, Turkish tambur, yaylı tambur, kemençe, and lavta virtuoso and composer, who has greatly contributed to the ''taksim'' (improvisation on a makam/maqam) genre in Ottoman classical music. His son, Mesut Cemil Bey, was an equally renowned Turkish tambur virtuoso. Biography Cemil Bey was born in Istanbul, Ottoman Empire, in 1871 or 1873; his birth date is uncertain. He took his first lessons in music from Kanuni Ahmet Bey and the violin player Kemani Aleksan, his first instruments thus being the violin and the kanun. After completing middle school, he continued in a school for civil servants (''Mülkiye''), but then devoted himself to music and abandoned his education. He began to play the tanbur quite early in his youth and by the age of 20, his renown had already spread among the tamburis of Istanbul. Reforming the traditional playing technique of the tambur, he developed an energetic te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yaylı Tambur
The ''yaylı tambur'' is a bowed long-neck lute from Turkey. Derived from the older plucked ''mızraplı tambur'' variant of the Turkish tambur, it has a long, fretted neck and a round metal or wooden soundbox which is often covered on the front with a skin or acrylic head similar to that of a banjo. The instrument is held vertically, with the soundbox resting in the player's lap or between the calves or it can be worn on a strap. The bow is grasped sideways, with the little, ring and middle fingers pressing on the horsehairs, while the thumb and index fingers hold the rightmost wooden edge of the bow or it can be held overhand like a Cello Bow to allow for more expressiveness. The leftmost strings of the instrument unite into a single course to form a doubled-string which is tuned to a unison that is lifted slightly from the bridge. This is where all melodic playing takes place. The rest are sympathetic strings numbering from 4 to 6 which are tuned to the octave, fifth and/or fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tambouras
The tambouras ( ) is a Greek traditional string instrument of Byzantine origin. It has existed since at least the 10th century, when it was known in Assyria and Egypt. At that time, it might have had between two and six strings. The characteristic long neck bears two strings, tuned five notes apart. It is also similar to the Turkish ''tambur'' and Indian tanpura. Tanbur, a Persian word, is according to some scholars derived from the Sumerian ''pan tur'', meaning "little bow". History Origins It is considered that the ''tambouras ancestor is the ancient Greek ''pandouris'', also known as '' pandoura'', ''pandouros'' or ''pandourida'' (πανδουρίς, πανδούρα, πάνδουρος), from which the word is derived. The ''tambouras'' is mentioned in the Byzantine epic of Digenis Akritas, when the hero plays his θαμπούριν, ''thambourin'' (medieval form of ''tambouras''): Name The name resembles that of the Indian '' tanpura'', but the Greek ''tambouras'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
String Instrument
In musical instrument classification, string instruments, or chordophones, are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer strums, plucks, strikes or sounds the strings in varying manners. Musicians play some string instruments, like Guitar, guitars, by plucking the String (music), strings with their fingers or a plectrum, plectrum (pick), and others by hitting the strings with a light wooden hammer or by rubbing the strings with a bow (music), bow, like Violin, violins. In some keyboard (music), keyboard instruments, such as the harpsichord, the musician presses a key that plucks the string. Other musical instruments generate sound by striking the string. With bowed instruments, the player pulls a rosined horsehair bow across the strings, causing them to vibrate. With a hurdy-gurdy, the musician cranks a wheel whose rosined edge touches the strings. Bowed instruments include the string section instruments of the orchestra in Western classic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cümbüş
The ''cümbüş'' (; ) is a Turkish stringed instrument of relatively modern origin. It was developed in 1930 by Zeynel Abidin Cümbüş as an oud-like instrument that could be heard as part of a larger ensemble. The cümbüş is shaped like an American banjo, with a spun-aluminum resonator bowl and skin soundboard. Although originally configured as an oud, the instrument has been converted to other instruments by attaching a different set of neck and strings. The standard cümbüş is fretless, but guitar, mandolin and ukulele versions have fretboards. The neck is adjustable, allowing the musician to change the angle of the neck to its strings by turning a screw. One model is made with a wooden resonator bowl, with the effect of a less tinny, softer sound.Zeynel Abidin Cümbüş manufacturers, ''Cumbus Extra' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cemil Özbal
Cemil Özbal was a Turkish doctor and tambur player, considered as one of the last examples of significant tambur players of the classical style. Cemil was born in 1908 in Aintab in the Ottoman Empire to Ayşe and Ökkeş Efendi of the Balhakıkcıoğlu family. He went to Robert College in Istanbul and received medical education there. He married Seher Özbal, who he met during his education. He then returned to his hometown, working in the American hospital as a surgeon between 1946 and 1977. He was regarded as one of the best general surgeons in Gaziantep at the time, later taking charge of the American hospital in the city. Özbal started playing organ and trumpet The trumpet is a brass instrument commonly used in classical and jazz musical ensemble, ensembles. The trumpet group ranges from the piccolo trumpet—with the highest Register (music), register in the brass family—to the bass trumpet, pitche ... at an early age. He received musical education for 6 months from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanburi Büyük Osman Bey
Tanburi Büyük Osman Bey or Tamburi Büyük Osman Bey (1816–1885) was an Ottoman composer and Turkish tambur player. He is considered one of the most outstanding peşrev compositors in Ottoman classical music. Life Tanburi Büyük Osman Bey was born in 1816 in the Tophane district of Istanbul. Most of the information we have on him originates from an oral tradition amongst his pupils and the pupils of those who knew him. His father, Zeki Mehmed Ağa as well as his grandfather Tanburi Numan Ağa were musicians of renown. At the age of eight, he was accepted to the Imperial School of Enderun, where he began his education among the foregoing masters of Turkish classical music, from whom he acquired a firm theoretical basis. His acquaintance with the tanbur also dates back to those years. As his father Zeki Mehmed Ağa is said to have refused to pass on to his son his knowledge of the tambur, most of the work must have come to be incumbent on Osman Bey himself. He is also sai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |