|
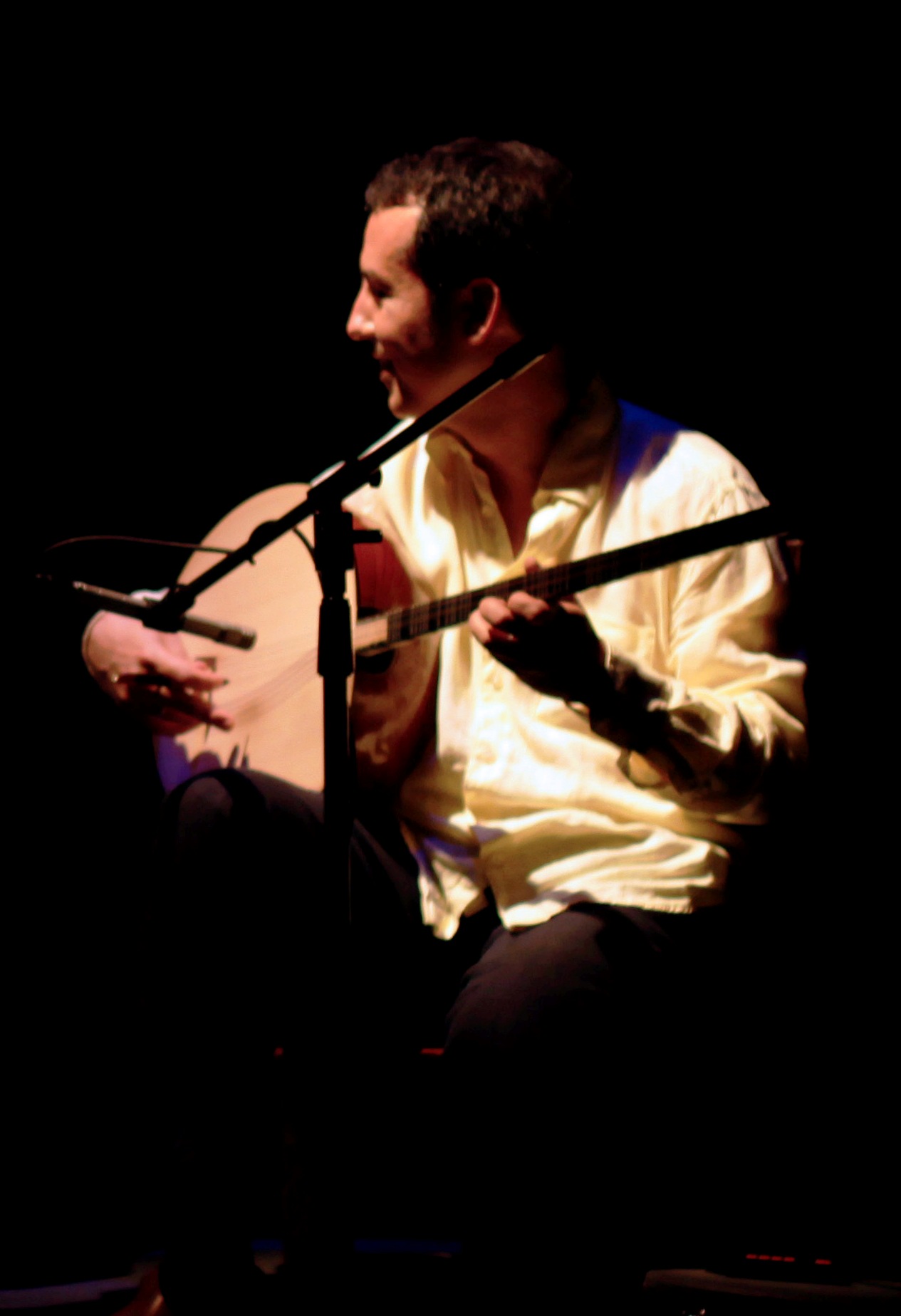
Tamburica
Tamburica ( or ; sometimes written tamburrizza or tamburitza; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", tamburica, тамбурица, little tamboura) or tamboura (; ) refers to a family of long-necked lutes popular in Southeast Europe and southeastern Central Europe, especially Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia (of which it is the national string instrument), Hungary, Serbia (in Vojvodina, Mačva, and Posavo- Tamnava), and Slovenia. It is also known in Burgenland, Austria. All took their name and some characteristics from the Persian tanbur but also resemble the mandolin and guitar in the sense that its strings are plucked and often paired. The frets may be moveable to allow the playing of various modes. The variety of tamburica shapes known today were developed in Serbia and Croatia by a number of indigenous contributors near the end of the 19th century. History There is little reliable data showing how the tamboura entered Central Europe. It already existed during Byzantine Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanbur
The term ''Tanbur'' can refer to various long-necked string instruments originating in Mesopotamia, Southern or Central Asia. According to the ''New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', "terminology presents a complicated situation. Nowadays the term tanbur (or tambur) is applied to a variety of distinct and related long-necked lutes used in art and folk traditions. Similar or identical instruments are also known by other terms." These instruments are used in the traditional music of Iran, Iraq, India, Armenia, Afghanistan, Azerbaijan (especially Avar community), Pakistan, Turkey, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, and Uzbekistan. Origins Tanburs have been present in Mesopotamia since the Akkadian era, or the third millennium BC. Three figurines have been found in Susa that belong to 1500 BC, and in hands of one of them is a tanbur-like instrument. Also an image on the rocks near Mosul that belong to about 1000 BC shows tanbur players. Playing the tanbur was common at least ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chonguri
The choghur (; ka, ჩონგური) is a plucked string musical instrument common in Azerbaijan and Georgia. It has 4 nylon strings. The choghur dates back to the 12th to 16th centuries, the period between the gopuz and the Bağlama. In the Caucasus, Iran and Anatolia, and in Sufi traditions, darvishes and ashugs used an instrument called the "chaghyr" /"chagur"/ "chugur" / "choghur" / "chungur". Presumably, the name "choghur" means "the musical instrument used to appeal to God and truth". In Azerbaijani the word "chaghir" means "to call", "to appeal". It may be assumed that the name of the instrument originates from the expression "chal-chaghyr" (festivity or celebration), which was later changed to "choghur". Various historical sources indicate that the choghur was used to create a high battle spirit among the soldiers of the medieval Safavid state's army. In the " Jahanarai Shah Ismayil Safavi" annals, describing the situation at the beginning of the 16th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tambouras
The tambouras ( ) is a Greek traditional string instrument of Byzantine origin. It has existed since at least the 10th century, when it was known in Assyria and Egypt. At that time, it might have had between two and six strings. The characteristic long neck bears two strings, tuned five notes apart. It is also similar to the Turkish ''tambur'' and Indian tanpura. Tanbur, a Persian word, is according to some scholars derived from the Sumerian ''pan tur'', meaning "little bow". History Origins It is considered that the ''tambouras ancestor is the ancient Greek ''pandouris'', also known as '' pandoura'', ''pandouros'' or ''pandourida'' (πανδουρίς, πανδούρα, πάνδουρος), from which the word is derived. The ''tambouras'' is mentioned in the Byzantine epic of Digenis Akritas, when the hero plays his θαμπούριν, ''thambourin'' (medieval form of ''tambouras''): Name The name resembles that of the Indian '' tanpura'', but the Greek ''tambouras'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balkan Tambura
The tambura is a stringed instrument that is played as a folk instrument in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Hungary, North Macedonia, Serbia (especially Vojvodina), Montenegro and Turkey. It has doubled steel strings and is played with a plectrum, in the same manner as a mandolin. The Bulgarian tambura The Bulgarian tambura has 8 steel strings in 4 doubled courses. All the courses are tuned in unison, with no octaves. It is tuned D3 D3, G3 G3, B3 B3, E4 E4. It has a floating bridge and a metal tailpiece. The instrument body is often carved from a single block of wood. The Macedonian tambura The Macedonian tambura has 4 steel strings in 2 doubled courses. It is tuned A A , D D (or another pitch but at the same relative intervals of a fourth) when playing melodies based on A tonic upon A drone. It also may be tuned G G , D D (or another pitch but at the same relative intervals of a fifth) when playing melodies based on G tonic upon G drone. Sometimes octave strings a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samica (musical Instrument)
The samica (meaning 'alone' in Croatian and Serbian, due to it being played solo) is a small stringed and fretted traditional Croatian and Serbian folk instrument. Its overall shape is similar to that of the dangubica, and has up to four strings. One of these strings is used to play a melody, the rest being used as drones, playing a single note. The samica is often played to accompany dancing and singing. Along with the dangubica, the samica is one of the forerunners of the modern tamburitza Tamburica ( or ; sometimes written tamburrizza or tamburitza; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", tamburica, тамбурица, little tamboura) or tamboura (; ) refers to a family of long-necked lutes popular in Southeast Europe and southeastern .... References *: »TAMBURA«, u: Kovačević, K. (ur.), '' Muzička enciklopedija'', Zagreb: JLZ, 1977., sv. 3, pages. 542-543. *Ćosić, Zlatko: ''Tambura samica'', Cerna: V. Baličević, 1996. *Leopold, Siniša: ''Tambura u Hrvata'', Zagre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dangubica
The dangubica or samica is a small Serbian and Croatian stringed instrument, having either two single or two double strings, a long, fretted neck, and a pear-shaped body. One string (or pair or strings) is used to play the melody, while the second plays a continuous note, known as the drone. Loosely translated, the word danguba means "to lose the day," referring to the instrument's origins among shepherds, who usually played alone as a way to pass the time. This also helps to explain the fact that tuning of the dangubica is widely varied. It is related to the Turkish saz and tamburitza Tamburica ( or ; sometimes written tamburrizza or tamburitza; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", tamburica, тамбурица, little tamboura) or tamboura (; ) refers to a family of long-necked lutes popular in Southeast Europe and southeastern ... orchestra instruments. References {{Authority control Necked bowl lutes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tambur
The is a fretted string instrument of Turkey and the former lands of the Ottoman Empire. There are two variants, one of which is played with a plectrum (''mızraplı tambur'') and the other with a bow ('' yaylı tambur''). The player is called a ''tamburî''.Tambur Republic of Turkey - Ministry of Culture and Tourism History and development There are several hypotheses as to the origin of the instrument. One suggests that it descended from the kopuz, a string instrument still in use among the Turkic peoples of Central Asia and the Caspian region. The name itself derives from the '' tanbur'' (tunbur), which in turn might have descended from the |
Šargija
thumb The ''šargija'' ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, šargija, шаргија; ), anglicized as ''shargia'', is a plucked, fretted long necked lute used in the folk music of various Balkan countries, including Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia, Albania, Kosovo and North Macedonia. The instrument is part of a larger family of instruments which includes the Balkan ''tambura'' and the '' saz'' (or ''tambura saz''), ''tamburica'', and the ''tambouras''. History The instrument was studied by musicologists in the 20th century. Their studies have been characterized as speculative and nationalistic. More recently, an American researcher, Richard March, concluded that the tambura arrived in the Balkans with Turkish people in the 1500s. It was adopted by people living in the Balkans, including "urban Muslim Slavs" and "Bosnia Christians." It also arrived in Croatia with laborers. Today the ''šargija'' is played by Albanians, Bosniaks, Serbs and Croats. The ''sharki'' is used by the Gheg Albanians in n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
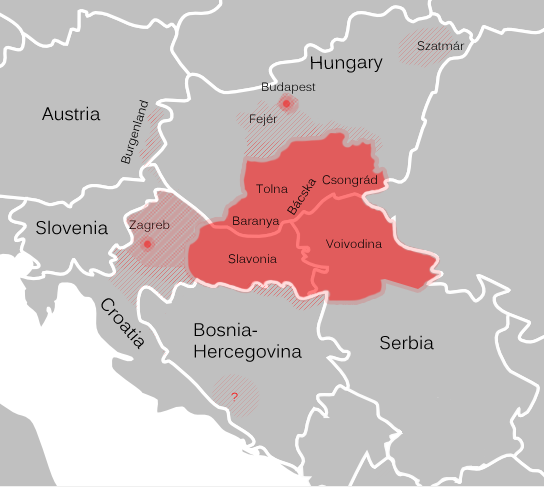
Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( ; sr-Cyrl, Војводина, ), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an Autonomous administrative division, autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia, located in Central Europe. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capital Belgrade and the Sava and Danube Rivers. The administrative centre, Novi Sad, is the second-largest city in Serbia. The historic regions of Banat, Bačka, Syrmia and northernmost part of Mačva overlap the province. Modern Vojvodina is multi-ethnic and multi-cultural, with some 26 ethnic groups and six official languages. Fewer than two million people, nearly 27% of Serbia's population, live in the province. Name ''Vojvodina'' is also the Serbian word for voivodeship, a type of duchy overseen by a voivode. The Voivodeship of Serbia and Banat of Temeschwar, Serbian Voivodeship, a precursor to modern Vojvodina, was an Austrian province from 1849 to 1860. Its official name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mačva
Mačva ( sr-Cyrl, Мачва, ; ) is a geographical and historical region in the northwest of Central Serbia, on a fertile plain between the Sava (river), Sava and Drina rivers. The chief town is Šabac. The modern Mačva District of Serbia is named after the region, although the region of Mačva includes only the northern part of this district. A small northern part of Mačva region is in the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, in the Syrmia District. Name The region is named after a town of Mačva, which existed in the Medieval Ages near the river Sava. In the past, the region was also known as ''Lower Srem'', while the neighbouring region on the northern bank of the river Sava (present-day Syrmia, Srem) was known as ''Upper Srem''. In Serbian Cyrillic alphabet, Serbian Cyrillic, the region is known as Мачва, in Gaj's Latin alphabet, Serbian Latin, Bosnian language, Bosnian and Croatian language, Croatian as ''Mačva'', in Hungarian language, Hungarian as ''Macsó'' or ''Mac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriatic Sea to the southwest, which is part of the Mediterranean Sea. Slovenia is mostly mountainous and forested, covers , and has a population of approximately 2.1 million people. Slovene language, Slovene is the official language. Slovenia has a predominantly temperate continental climate, with the exception of the Slovene Littoral and the Julian Alps. Ljubljana, the capital and List of cities and towns in Slovenia, largest city of Slovenia, is geographically situated near the centre of the country. Other larger urban centers are Maribor, Ptuj, Kranj, Celje, and Koper. Slovenia's territory has been part of many different states: the Byzantine Empire, the Carolingian Empire, the Holy Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Hungary, the Republic of Venice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |