|
Tanbur
The term ''Tanbur'' can refer to various long-necked string instruments originating in Mesopotamia, Southern or Central Asia. According to the ''New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', "terminology presents a complicated situation. Nowadays the term tanbur (or tambur) is applied to a variety of distinct and related long-necked lutes used in art and folk traditions. Similar or identical instruments are also known by other terms." These instruments are used in the traditional music of Iran, Iraq, India, Armenia, Afghanistan, Azerbaijan (especially Avar community), Pakistan, Turkey, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, and Uzbekistan. Origins Tanburs have been present in Mesopotamia since the Akkadian era, or the third millennium BC. Three figurines have been found in Susa that belong to 1500 BC, and in hands of one of them is a tanbur-like instrument. Also an image on the rocks near Mosul that belong to about 1000 BC shows tanbur players. Playing the tanbur was common at least ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkish Tambur
The is a fretted string instrument of Turkey and the former lands of the Ottoman Empire. There are two variants, one of which is played with a plectrum (''mızraplı tambur'') and the other with a bow ('' yaylı tambur''). The player is called a ''tamburî''.Tambur Republic of Turkey - Ministry of Culture and Tourism History and development There are several hypotheses as to the origin of the instrument. One suggests that it descended from the kopuz, a string instrument still in use among the Turkic peoples of Central Asia and the Caspian region. The name itself derives from the '''' (tunbur), which in turn might have descended from ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yaylı Tambur
The ''yaylı tambur'' is a bowed long-neck lute from Turkey. Derived from the older plucked ''mızraplı tambur'' variant of the Turkish tambur, it has a long, fretted neck and a round metal or wooden soundbox which is often covered on the front with a skin or acrylic head similar to that of a banjo. The instrument is held vertically, with the soundbox resting in the player's lap or between the calves or it can be worn on a strap. The bow is grasped sideways, with the little, ring and middle fingers pressing on the horsehairs, while the thumb and index fingers hold the rightmost wooden edge of the bow or it can be held overhand like a Cello Bow to allow for more expressiveness. The leftmost strings of the instrument unite into a single course to form a doubled-string which is tuned to a unison that is lifted slightly from the bridge. This is where all melodic playing takes place. The rest are sympathetic strings numbering from 4 to 6 which are tuned to the octave, fifth and/or fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Setar
A setar (, ) (lit: "Three String (music), Strings") is a stringed instrument, a type of lute used in Persian traditional music, played solo or accompanying voice. It is a member of the tanbur family of long-necked lutes with a range of more than two and a half Octave, octaves. Originally a three stringed instrument, a fourth string was added by Mushtaq Ali Shah by the mid 19th century. It is played with the index finger of the right hand. It has been speculated that the setar originated in Persia by the 9th century AD A more conservative estimate says "it originated in the 15th century, or even earlier." Although related to the tanbur, in recent centuries, the setar has evolved so that, musically, it more closely resembles the Tar (string instrument), tar, both in Musical tuning, tuning and playing style. Etymology According to Curt Sachs, Persians chose to name their lutes around the word ''tar'', meaning string, combined with a word for the number of strings. Du + tar is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanpura
The tanpura (; also referred to as tambura, tanpuri, tamboura, or tanpoura) is a long-necked, plucked, four-stringed instrument originating in the Indian subcontinent, found in various forms in Indian music. Visually, the tanpura resembles a simplified sitar or similar lute-like instrument, and is likewise crafted out of a gourd or pumpkin. The tanpura does not play a melody, but rather creates a meditative ambience, supporting and sustaining the performance of another musician or vocalist, as well as for musicians accompanying a dance performance. The instrument's four strings are tuned to specific notes of a given scale or musical key, normally the fifth (''Pa''; Solfège, “So”) and the root tonic (''Sa''; “Do”). The strings are generally tuned 5-8-8-1. One of the three strings tuned to the tonic is thus an octave below the others, adding greater resonance and depth to the ambient drone. Through continuous, rhythmic plucking of its strings, the tanpura creates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bağlama
The bağlama or saz is a family of plucked string instruments and long-necked lutes used in Europe, Balkans, Caucasus, Middle East, Khazar, Central Asia including Germany, France, Belgium, TRNC, Netherlands, Albania, Greece,Bosnia, Serbia, Croatia, Bulgaria, North Macedonia, Russia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Iran, Iraq, Syria, Lebanon and Turkey. It is commonly used by Ashik, ashiks. Name According to ''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', "the terms 'bağlama' and 'saz' are used somewhat interchangeably in Turkey. 'Saz' is generally used interchangeably with 'enstrüman' (instrument) and it is used to refer single or group of musical instruments like 'üflemeli sazlar' (Wind instrument, wind instruments). Bağlama scale The scale (music), musical scale of the bağlama differs from that of many western instruments – such as the guitar – in that it features ratios that are close to quarter tones. The traditional ratios for bağla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tambouras
The tambouras ( ) is a Greek traditional string instrument of Byzantine origin. It has existed since at least the 10th century, when it was known in Assyria and Egypt. At that time, it might have had between two and six strings. The characteristic long neck bears two strings, tuned five notes apart. It is also similar to the Turkish ''tambur'' and Indian tanpura. Tanbur, a Persian word, is according to some scholars derived from the Sumerian ''pan tur'', meaning "little bow". History Origins It is considered that the ''tambouras ancestor is the ancient Greek ''pandouris'', also known as '' pandoura'', ''pandouros'' or ''pandourida'' (πανδουρίς, πανδούρα, πάνδουρος), from which the word is derived. The ''tambouras'' is mentioned in the Byzantine epic of Digenis Akritas, when the hero plays his θαμπούριν, ''thambourin'' (medieval form of ''tambouras''): Name The name resembles that of the Indian '' tanpura'', but the Greek ''tambouras'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
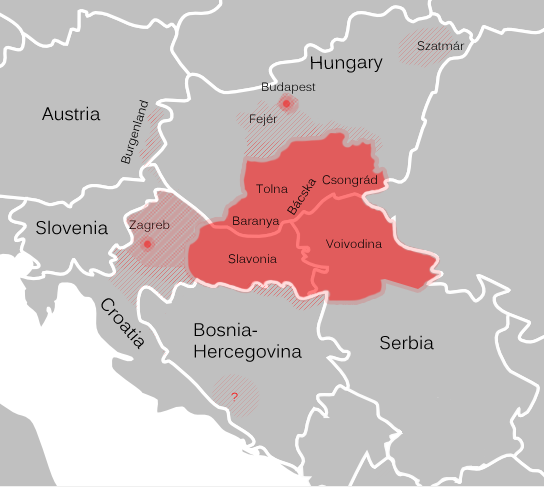
Tamburica
Tamburica ( or ; sometimes written tamburrizza or tamburitza; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", tamburica, тамбурица, little tamboura) or tamboura (; ) refers to a family of long-necked lutes popular in Southeast Europe and southeastern Central Europe, especially Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia (of which it is the national string instrument), Hungary, Serbia (in Vojvodina, Mačva, and Posavo- Tamnava), and Slovenia. It is also known in Burgenland, Austria. All took their name and some characteristics from the Persian tanbur but also resemble the mandolin and guitar in the sense that its strings are plucked and often paired. The frets may be moveable to allow the playing of various modes. The variety of tamburica shapes known today were developed in Serbia and Croatia by a number of indigenous contributors near the end of the 19th century. History There is little reliable data showing how the tamboura entered Central Europe. It already existed during Byzantine Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sataer
The ''Sataer'' (; zh, 萨它尔) is a traditional Uyghur long-necked bowed lute. It is used by Uyghur people in Xinjiang, western China, and is an important instrument to play maqams. Characteristics The instrument is a long-necked lute, about 140 cm long, with a bowl about 16.5 cm at the widest point, about 15 cm deep. The neck is fretted with 18 tied frets, which may be made of string rather that the inlaid metal frets of western instruments. The soundboard has additionally frets laid on it under the main melody string, approximately 11 or 12 frets. The sataer is strung with between 9 and 17 sympathetic strings which are not played directly but vibrate in reaction to the melody string, in sympathetic resonance. A single melody string is set apart from the sympathetic strings. This is the string that the musician manipulates on the instrument's neck, fretting it to change the notes as the string is bowed. On modern instruments, the bridge is set on the sound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pamiri Rubab
The Pamiri rubab (Russian and Tajiki: рубоб) is a fretless six-strung lute, carved from a single piece of wood with a skin head. It is played in the Badakhshan region of Tajikistan, as part of the Pamiri musical tradition. The Pamiri rubab has six gut strings or nylon strings, one of which, rather than running from the head to the bridge, is attached partway down the neck, similar to the fifth string of the American banjo The banjo is a stringed instrument with a thin membrane stretched over a frame or cavity to form a resonator. The membrane is typically circular, and in modern forms is usually made of plastic, where early membranes were made of animal skin. .... The Institute of Ismaili Studies. The instrument is p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutar
The ''dutar'' (also ''Dotara, dotar''; ; ; ; ; ; ; ) is a traditional Iranian long-necked two-stringed lute found in Iran and Central Asia. Its name comes from the Persian language, Persian word for "two strings", دوتار ''do tār'' (< دو ''do'' "two",تار ''tār'' "string"), although the Herati dutar of Afghanistan has fourteen strings. Dutar is very popular in Tajikistan and Khorasan province, Khorasan province of Iran. When played, the strings are usually plucked by the Uyghur people, Uyghurs of Western China and strummed and plucked by the Tājik people, Tajiks, Turkmen people, Turkmen, Uzbeks. Related instruments include the Kazakhstan, Kazakh dombra. The dutar is also an important instrument among the Kurds of Khorasan, tork of Khorasan amongst whom Haj Qorban Soleimani, Haj Ghorban Soleimani of Quchan was a noted virtuoso. In Kurdish languages, tork one who plays the dutar is known as a (bakhshi) similar to Turkmen language, Turkmen , while in Azerbaijani lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tar (lute)
The tar () is a long-necked, waisted instrument in the lute family, used by many cultures and countries in the Middle East and the Caucasus, including Iran, Azerbaijan, Uzbekistan, Armenia, Georgia, Tajikistan, and Turkey.tar (musical instrument) ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. Retrieved on 1 January 2013. It was originally known as the ''chahartar'' () or ''chartar'' (), which translates into as 'four-stringed'. This is in accordance with a practice common in Persian-speaking areas of distinguishing lutes on the basis of the number of strings originally employed. Beside the ''chartar'', these include the '' |
Balkan Tambura
The tambura is a stringed instrument that is played as a folk instrument in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Hungary, North Macedonia, Serbia (especially Vojvodina), Montenegro and Turkey. It has doubled steel strings and is played with a plectrum, in the same manner as a mandolin. The Bulgarian tambura The Bulgarian tambura has 8 steel strings in 4 doubled courses. All the courses are tuned in unison, with no octaves. It is tuned D3 D3, G3 G3, B3 B3, E4 E4. It has a floating bridge and a metal tailpiece. The instrument body is often carved from a single block of wood. The Macedonian tambura The Macedonian tambura has 4 steel strings in 2 doubled courses. It is tuned A A , D D (or another pitch but at the same relative intervals of a fourth) when playing melodies based on A tonic upon A drone. It also may be tuned G G , D D (or another pitch but at the same relative intervals of a fifth) when playing melodies based on G tonic upon G drone. Sometimes octave strings a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |