|
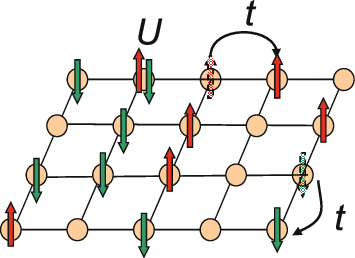
T-J Model
In solid-state physics, the ''t''-''J'' model is a model first derived by Józef Spałek to explain antiferromagnetic properties of Mott insulators, taking into account experimental results about the strength of electron-electron repulsion in these materials. The material is modelled as a lattice with atoms in the sites with conduction electrons (or holes) moving between them, like in the Hubbard model. Unlike the Hubbard model, the electrons are strongly-correlated, meaning the electrons are sensitive to reciprocal coulombic repulsion, and so are less likely to occupy lattice sites already occupied by another electron. In the basic Hubbard model, the repulsion, indicated by ''U'', can be small or even zero, and electrons are more free to jump (''hopping'', parametrized by ''t'' as ''transfer'' or ''tunnel'') from one site to another. In the ''t''-''J'' model, instead of ''U'', there is the parameter ''J'', function of the ratio ''t''/''U''. Like the Hubbard model, it is a pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operator (physics)
An operator is a function over a space of physical states onto another space of states. The simplest example of the utility of operators is the study of symmetry (which makes the concept of a group useful in this context). Because of this, they are useful tools in classical mechanics. Operators are even more important in quantum mechanics, where they form an intrinsic part of the formulation of the theory. They play a central role in describing observables (measurable quantities like energy, momentum, etc.). Operators in classical mechanics In classical mechanics, the movement of a particle (or system of particles) is completely determined by the Lagrangian L(q, \dot, t) or equivalently the Hamiltonian H(q, p, t), a function of the generalized coordinates ''q'', generalized velocities \dot = \mathrm q / \mathrm t and its conjugate momenta: :p = \frac If either ''L'' or ''H'' is independent of a generalized coordinate ''q'', meaning the ''L'' and ''H'' do not change when ''q' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin (physics)
Spin is an Intrinsic and extrinsic properties, intrinsic form of angular momentum carried by elementary particles, and thus by List of particles#Composite particles, composite particles such as hadrons, atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei, and atoms. Spin is quantized, and accurate models for the interaction with spin require relativistic quantum mechanics or quantum field theory. The existence of electron spin angular momentum is inferred from experiments, such as the Stern–Gerlach experiment, in which silver atoms were observed to possess two possible discrete angular momenta despite having no orbital angular momentum. The relativistic spin–statistics theorem connects electron spin quantization to the Pauli exclusion principle: observations of exclusion imply half-integer spin, and observations of half-integer spin imply exclusion. Spin is described mathematically as a vector for some particles such as photons, and as a spinor or bispinor for other particles such as electrons. Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exchange Interaction
In chemistry and physics, the exchange interaction is a quantum mechanical constraint on the states of indistinguishable particles. While sometimes called an exchange force, or, in the case of fermions, Pauli repulsion, its consequences cannot always be predicted based on classical ideas of force. Both bosons and fermions can experience the exchange interaction. The wave function of identical particles, indistinguishable particles is subject to exchange symmetry: the wave function either changes sign (for fermions) or remains unchanged (for bosons) when two particles are exchanged. The exchange symmetry alters the Expectation value (quantum mechanics), expectation value of the distance between two indistinguishable particles when their wave functions overlap. For fermions the expectation value of the distance increases, and for bosons it decreases (compared to distinguishable particles). The exchange interaction arises from the combination of exchange symmetry and the Coulomb's l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tight Binding
In solid-state physics, the tight-binding model (or TB model) is an approach to the calculation of electronic band structure using an approximate set of wave functions based upon superposition of wave functions for isolated atoms located at each atomic site. The method is closely related to the LCAO method (linear combination of atomic orbitals method) used in chemistry. Tight-binding models are applied to a wide variety of solids. The model gives good qualitative results in many cases and can be combined with other models that give better results where the tight-binding model fails. Though the tight-binding model is a one-electron model, the model also provides a basis for more advanced calculations like the calculation of surface states and application to various kinds of many-body problem and quasiparticle calculations. Introduction The name "tight binding" of this electronic band structure model suggests that this quantum mechanical model describes the properties of tigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin Polarization
In particle physics, spin polarization is the degree to which the spin, i.e., the intrinsic angular momentum of elementary particles, is aligned with a given direction. This property may pertain to the spin, hence to the magnetic moment, of conduction electrons in ferromagnetic metals, such as iron, giving rise to spin-polarized currents. It may refer to (static) spin waves, preferential correlation of spin orientation with ordered lattices (semiconductors or insulators). It may also pertain to beams of particles, produced for particular aims, such as polarized neutron scattering or muon spin spectroscopy. Spin polarization of electrons or of nuclei, often called simply magnetization, is also produced by the application of a magnetic field. Curie law is used to produce an induction signal in electron spin resonance (ESR or EPR) and in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). Spin polarization is also important for spintronics, a branch of electronics. Magnetic semiconducto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creation And Annihilation Operator
Creation operators and annihilation operators are mathematical operators that have widespread applications in quantum mechanics, notably in the study of quantum harmonic oscillators and many-particle systems. An annihilation operator (usually denoted \hat) lowers the number of particles in a given state by one. A creation operator (usually denoted \hat^\dagger) increases the number of particles in a given state by one, and it is the adjoint of the annihilation operator. In many subfields of physics and chemistry, the use of these operators instead of wavefunctions is known as second quantization. They were introduced by Paul Dirac. Creation and annihilation operators can act on states of various types of particles. For example, in quantum chemistry and many-body theory the creation and annihilation operators often act on electron states. They can also refer specifically to the ladder operators for the quantum harmonic oscillator. In the latter case, the creation operator is interpr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermion
In particle physics, a fermion is a subatomic particle that follows Fermi–Dirac statistics. Fermions have a half-integer spin (spin 1/2, spin , Spin (physics)#Higher spins, spin , etc.) and obey the Pauli exclusion principle. These particles include all quarks and leptons and all composite particles made of an even and odd, odd number of these, such as all baryons and many atoms and atomic nucleus, nuclei. Fermions differ from bosons, which obey Bose–Einstein statistics. Some fermions are elementary particles (such as electrons), and some are composite particles (such as protons). For example, according to the spin-statistics theorem in Theory of relativity, relativistic quantum field theory, particles with integer Spin (physics), spin are bosons. In contrast, particles with half-integer spin are fermions. In addition to the spin characteristic, fermions have another specific property: they possess conserved baryon or lepton quantum numbers. Therefore, what is usually referr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Lattice
In mathematics, the square lattice is a type of lattice in a two-dimensional Euclidean space. It is the two-dimensional version of the integer lattice, denoted as . It is one of the five types of two-dimensional lattices as classified by their symmetry groups; its symmetry group in IUC notation as , Coxeter notation as , and orbifold notation as . Two orientations of an image of the lattice are by far the most common. They can conveniently be referred to as the upright square lattice and diagonal square lattice; the latter is also called the centered square lattice.. They differ by an angle of 45°. This is related to the fact that a square lattice can be partitioned into two square sub-lattices, as is evident in the colouring of a checkerboard. Symmetry The square lattice's symmetry category is wallpaper group . A pattern with this lattice of translational symmetry cannot have more, but may have less symmetry than the lattice itself. An upright square lattice can be vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-dimensional
A two-dimensional space is a mathematical space with two dimensions, meaning points have two degrees of freedom: their locations can be locally described with two coordinates or they can move in two independent directions. Common two-dimensional spaces are often called '' planes'', or, more generally, '' surfaces''. These include analogs to physical spaces, like flat planes, and curved surfaces like spheres, cylinders, and cones, which can be infinite or finite. Some two-dimensional mathematical spaces are not used to represent physical positions, like an affine plane or complex plane. Flat The most basic example is the flat Euclidean plane, an idealization of a flat surface in physical space such as a sheet of paper or a chalkboard. On the Euclidean plane, any two points can be joined by a unique straight line along which the distance can be measured. The space is flat because any two lines transversed by a third line perpendicular to both of them are parallel, meaning th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world. Its first book was printed in Oxford in 1478, with the Press officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586. It is the second-oldest university press after Cambridge University Press, which was founded in 1534. It is a department of the University of Oxford. It is governed by a group of 15 academics, the Delegates of the Press, appointed by the Vice Chancellor, vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, Oxford, Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho, Oxford, Jericho. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projection (linear Algebra)
In linear algebra and functional analysis, a projection is a linear transformation P from a vector space to itself (an endomorphism) such that P\circ P=P. That is, whenever P is applied twice to any vector, it gives the same result as if it were applied once (i.e. P is idempotent). It leaves its image unchanged. This definition of "projection" formalizes and generalizes the idea of graphical projection. One can also consider the effect of a projection on a geometrical object by examining the effect of the projection on points in the object. Definitions A projection on a vector space V is a linear operator P\colon V \to V such that P^2 = P. When V has an inner product and is complete, i.e. when V is a Hilbert space, the concept of orthogonality can be used. A projection P on a Hilbert space V is called an orthogonal projection if it satisfies \langle P \mathbf x, \mathbf y \rangle = \langle \mathbf x, P \mathbf y \rangle for all \mathbf x, \mathbf y \in V. A projecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |