|
River Great Ouse
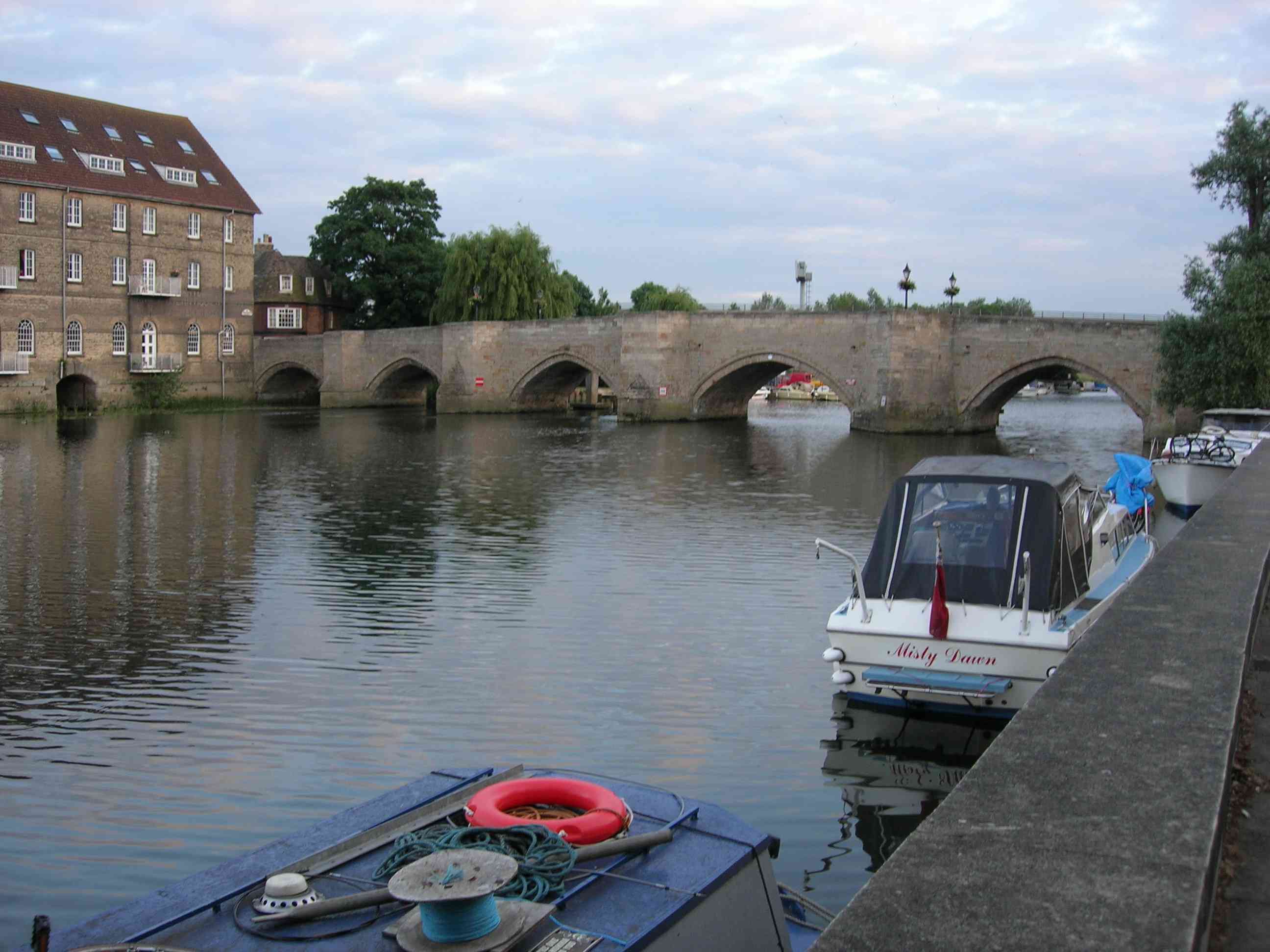
The River Great Ouse ( ) is a river in England, the longest of several British rivers called "Ouse". From Syresham in Northamptonshire, the Great Ouse flows through Buckinghamshire, Bedfordshire, Cambridgeshire and Norfolk to drain into the Wash and the North Sea near Kings Lynn. Authorities disagree both on the river's source and its length, with one quoting and another . Mostly flowing north and east, it is the fifth longest river in the United Kingdom. The Great Ouse has been historically important for commercial navigation, and for draining the low-lying region through which it flows; its best-known tributary is the Cam, which runs through Cambridge. Its lower course passes through drained wetlands and fens and has been extensively modified, or channelised, to relieve flooding and provide a better route for barge traffic. The unmodified river would have changed course regularly after floods. The name ''Ouse'' is from the Celtic or pre-Celtic *''Udso-s'', and probably ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Over, Cambridgeshire
Over is a large village near the River Great Ouse in the English county of Cambridgeshire, just east of the prime meridian. The parish covers an area of approximately . It is east of the town of Huntingdon and is also northwest from the city of Cambridge. Over contains the basic village facilities, including a primary school, shop, one public house (the Admiral Vernon) and St. Mary's Church. In recent years, the village has expanded rapidly, with the inclusion of several housing estates, a community and conference centre and modern sporting facilities. An Over day centre was set up in 1989 by Pamela Cressey. The Over Community Centre was set up with National Lottery funding of almost £1 million in 1999. Over is mentioned in the poem " The Old Vicarage, Grantchester", by Rupert Brooke. History By 1628 the fens and meres to the north of the settlement were enclosed, as was the rest of the village land by 1837. Originally, there were two distinct settlements. One ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Wissey
The River Wissey is a river in Norfolk, eastern England. It rises near Bradenham, and flows for nearly to join the River Great Ouse at Fordham. The lower are navigable. The upper reaches are notable for a number of buildings of historic interest, which are close to the banks. The river passes through the parkland of the Arts and Crafts Pickenham Hall, and further downstream, flows through the Army's Stanford Training Area (STANTA), which was created in 1942 by evacuating six villages. The water provided power for at least two mills, at Hilborough and Northwold. At Whittington, the river becomes navigable, and is surrounded by fenland. A number of pumping stations pump water from drainage ditches into the higher river channel. Although navigation is known to have taken place since at least the time of the Domesday Book, there is less documentary evidence than for other neighbouring rivers, as there was no centre of population at the head of the navigation. A sugar-beet facto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brackley
Brackley is a market town and civil parish in the West Northamptonshire unitary authority area of Northamptonshire, England. It is on the borders with Oxfordshire and Buckinghamshire, east-southeast of Banbury, north-northeast of Oxford, and southwest of Northampton. Historically a market town based on the wool and lace trade, it was built on the intersecting trade routes between London, Birmingham, the Midlands, Cambridge and Oxford. Brackley is close to Silverstone and home to the Mercedes AMG Petronas F1 Team. In 2021 the parish had a population of 16,195. History The place-name 'Brackley' is first attested in the Domesday Book of 1086, where it appears as ''Brachelai''. It appears as ''Brackelea'' in 1173 and as ''Brackeley'' in 1230 in the Pipe Rolls. The name means 'Bracca's glade or clearing'. Brackley was held in 1086 by Earl Alberic, after which it passed to the Earl of Leicester, and to the families of De Quincy and Roland. In the 11th and 12th centuries Brack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wappenham
Wappenham is a linear village and civil parish in Northamptonshire, England. It is south-west of Towcester, north of Syresham and north-west of Silverstone and forms part of West Northamptonshire. At the time of the United Kingdom Census 2001, 2001 census, the parish's population was 266 people, increasing to 294 at the 2011 Census. The village's name means 'homestead/village of Waeppa' or 'hemmed-in land of Waeppa'. Buildings Wappenham has some of the earliest architectural works by Sir George Gilbert Scott.The red-brick vicarage, east of the church, built in 1833 as a home for his father Reverend Thomas Scott who was vicar of Wappenham at the time, was Gilbert Scott's first work, built while he was still an assistant architect. Pevsner describes it as ''"...only remarkable for being Sir George Gilbert Scott's first building"''. The village also contains four other houses designed by Gilbert Scott, and on the village green there is a still-functional red telephone box, red K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleonasm
Pleonasm (; , ) is redundancy in linguistic expression, such as "black darkness", "burning fire", "the man he said", or "vibrating with motion". It is a manifestation of tautology by traditional rhetorical criteria. Pleonasm may also be used for emphasis, or because the phrase has become established in a certain form. Tautology and pleonasm are not consistently differentiated in literature. Usage Most often, ''pleonasm'' is understood to mean a word or phrase which is useless, clichéd, or repetitive, but a pleonasm can also be simply an unremarkable use of idiom. It can aid in achieving a specific linguistic effect, be it social, poetic or literary. Pleonasm sometimes serves the same function as rhetorical repetition—it can be used to reinforce an idea, contention or question, rendering writing clearer and easier to understand. Pleonasm can serve as a redundancy check; if a word is unknown, misunderstood, misheard, or if the medium of communication is poor—a static-fille ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indogermanisches Etymologisches Wörterbuch
The ''Indogermanisches etymologisches Wörterbuch'' (''IEW''; "Indo-European Etymological Dictionary") was published in 1959 by the Austrian-Czech comparative linguist and Celtic languages expert Julius Pokorny. It is an updated and slimmed-down reworking of the three-volume ''Vergleichendes Wörterbuch der indogermanischen Sprachen'' (1927–1932, by Alois Walde and Julius Pokorny). Both of these works aim to provide an overview of the lexical knowledge of the Proto-Indo-European language accumulated through the early 20th century. The ''IEW'' is now significantly outdated, especially as it was conservative even when it was written, ignoring the now integral laryngeal theory, and hardly including any Anatolian material. Editions *A. Francke, 1st ed. (1959) three vols. in one, via Internet Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Engineering
River engineering is a discipline of civil engineering which studies human intervention in the course, characteristics, or flow of a river with the intention of producing some defined benefit. People have intervened in the natural course and behaviour of rivers since before recorded history—to manage the water resources, to protect against flooding, or to make passage along or across rivers easier. Since the Yuan Dynasty and Ancient Roman times, rivers have been used as a source of hydropower. From the late 20th century onward, the practice of river engineering has responded to environmental concerns broader than immediate human benefit. Some river engineering projects have focused exclusively on the restoration or protection of natural characteristics and habitats. Hydromodification Hydromodification encompasses the systematic response to alterations to riverine and non-riverine water bodies such as coastal waters (estuaries and bays) and lakes. The U.S. Environmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetlands
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially in the soils. Wetlands form a transitional zone between waterbodies and dry lands, and are different from other terrestrial or aquatic ecosystems due to their vegetation's roots having adapted to oxygen-poor waterlogged soils. They are considered among the most biologically diverse of all ecosystems, serving as habitats to a wide range of aquatic and semi-aquatic plants and animals, with often improved water quality due to plant removal of excess nutrients such as nitrates and phosphorus. Wetlands exist on every continent, except Antarctica. The water in wetlands is either freshwater, brackish or saltwater. The main types of wetland are defined based on the dominant plants and the source of the water. For example, ''marshes'' are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
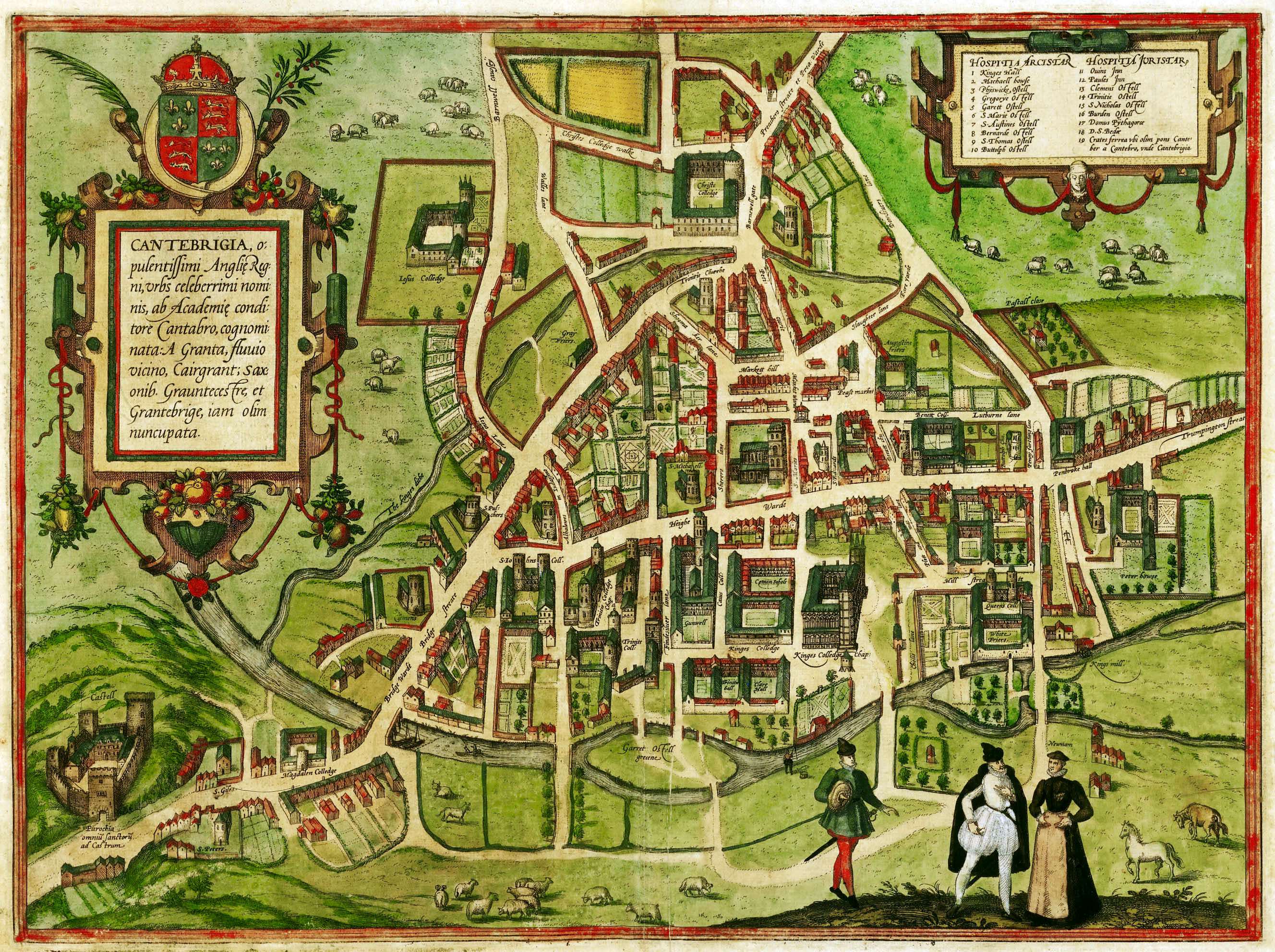
Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a List of cities in the United Kingdom, city and non-metropolitan district in the county of Cambridgeshire, England. It is the county town of Cambridgeshire and is located on the River Cam, north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of the City of Cambridge was 145,700; the population of the wider built-up area (which extends outside the city council area) was 181,137. (2021 census) There is archaeological evidence of settlement in the area as early as the Bronze Age, and Cambridge became an important trading centre during the Roman Britain, Roman and Viking eras. The first Town charter#Municipal charters, town charters were granted in the 12th century, although modern city status was not officially conferred until 1951. The city is well known as the home of the University of Cambridge, which was founded in 1209 and consistently ranks among the best universities in the world. The buildings of the university include King's College Chap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tributary
A tributary, or an ''affluent'', is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream (''main stem'' or ''"parent"''), river, or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries, and the main stem river into which they flow, drain the surrounding drainage basin of its surface water and groundwater, leading the water out into an ocean, another river, or into an endorheic basin. The Irtysh is a chief tributary of the Ob (river), Ob river and is also the longest tributary river in the world with a length of . The Madeira River is the largest tributary river by volume in the world with an average discharge of . A confluence, where two or more bodies of water meet, usually refers to the joining of tributaries. The opposite to a tributary is a distributary, a river or stream that branches off from and flows away from the main stream. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longest Rivers Of The United Kingdom
This is a list of the major rivers of the United Kingdom, as being prominent in length, flow volume (discharge rate), or both. Major rivers of the United Kingdom There seems to be little consensus in published sources as to the lengths of rivers, nor much agreement as to what constitutes a river. Thus the River Ure and River Ouse can be counted as one river system or as two rivers. If it is counted as one, the River Aire/ River Ouse/Humber system would come fourth in the list, with a combined length of ; and the River Trent/Humber system would top the list with their combined length of .http://copranet.projects.eucc-d.de/files/000165_EUROSION_Humber_Estuary.pdf Also, the Thames tributary, the River Churn, sourced at Seven Springs, adds to the length of the Thames (from its traditional source at Thames Head). The Churn/Thames' length at is therefore greater than the Severn's length of . Thus, the combined Churn/Thames river would top the list. Sue Owen et al., in their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kings Lynn
King's Lynn, known until 1537 as Bishop's Lynn and colloquially as Lynn, is a port and market town in the borough of King's Lynn and West Norfolk in the county of Norfolk, England. It is north-east of Peterborough, north-north-east of Cambridge and west of Norwich. History Toponymy The etymology of King's Lynn is uncertain. The name ''Lynn'' may signify a body of water near the town – the Welsh word means a lake; but the name is plausibly of Old English, Anglo-Saxon origin, from ''lean'' meaning a Tenure (law), tenure in fee or farm. The 1086 Domesday Book records it as ''Lun'' and ''Lenn'', and ascribes it to the Bishop of Elmham and the Archbishop of Canterbury. The Domesday Book also mentions saltings at Lena (Lynn); an area of partitioned pools may have existed there at the time. The presence of salt, which was relatively rare and expensive in the early medieval period, may have added to the interest of Herbert de Losinga and other prominent Normans in the modest parish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |