|
Risk-loving
In accounting, finance, and economics, a risk-seeker or risk-lover is a person who has a preference ''for'' risk. While most investors are considered risk ''averse'', one could view casino-goers as risk-seeking. A common example to explain risk-seeking behaviour is; If offered two choices; either $50 as a sure thing, or a 50% chance each of either $100 or nothing, a risk-seeking person would prefer the gamble. Even though the gamble and the "sure thing" have the same expected value, the preference for risk makes the gamble's expected utility for the individual much higher. The Utility Function and Risk-Seekers Choice under uncertainty is when a person facing a choice is not certain of the possible outcomes or their probability of occurring. The standard way to model how people choose under uncertain condition, is by using expected utility. In order to calculate expected utility, a utility function 'u' is developed in order to translate money into Utility. Therefore, if a person ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accounting
Accounting, also known as accountancy, is the process of recording and processing information about economic entity, economic entities, such as businesses and corporations. Accounting measures the results of an organization's economic activities and conveys this information to a variety of stakeholders, including investors, creditors, management, and Regulatory agency, regulators. Practitioners of accounting are known as accountants. The terms "accounting" and "financial reporting" are often used interchangeably. Accounting can be divided into several fields including financial accounting, management accounting, tax accounting and cost accounting. Financial accounting focuses on the reporting of an organization's financial information, including the preparation of financial statements, to the external users of the information, such as investors, regulators and suppliers. Management accounting focuses on the measurement, analysis and reporting of information for internal use by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
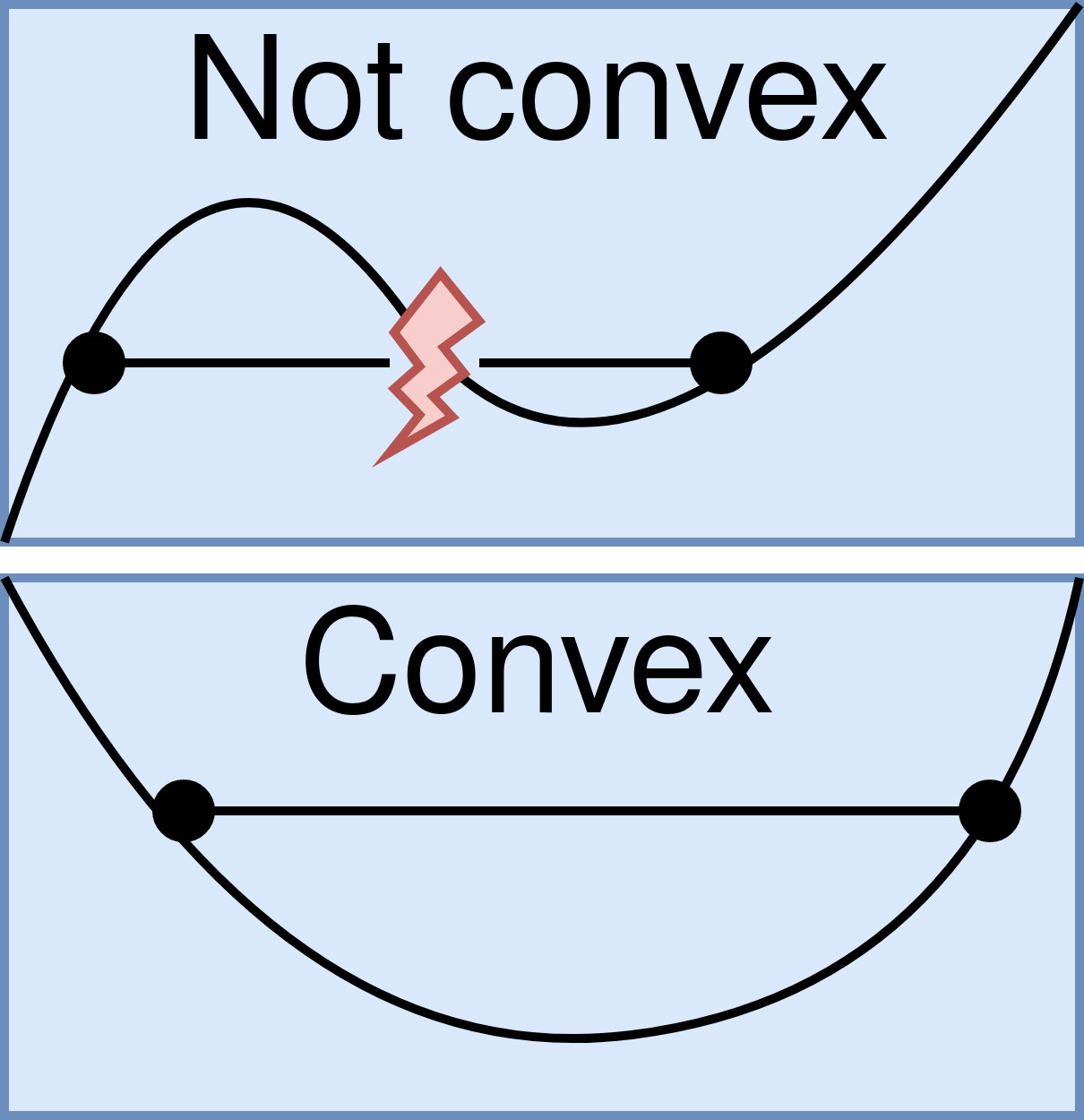
Convex Function
In mathematics, a real-valued function is called convex if the line segment between any two distinct points on the graph of a function, graph of the function lies above or on the graph between the two points. Equivalently, a function is convex if its epigraph (mathematics), ''epigraph'' (the set of points on or above the graph of the function) is a convex set. In simple terms, a convex function graph is shaped like a cup \cup (or a straight line like a linear function), while a concave function's graph is shaped like a cap \cap. A twice-differentiable function, differentiable function of a single variable is convex if and only if its second derivative is nonnegative on its entire domain of a function, domain. Well-known examples of convex functions of a single variable include a linear function f(x) = cx (where c is a real number), a quadratic function cx^2 (c as a nonnegative real number) and an exponential function ce^x (c as a nonnegative real number). Convex functions pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
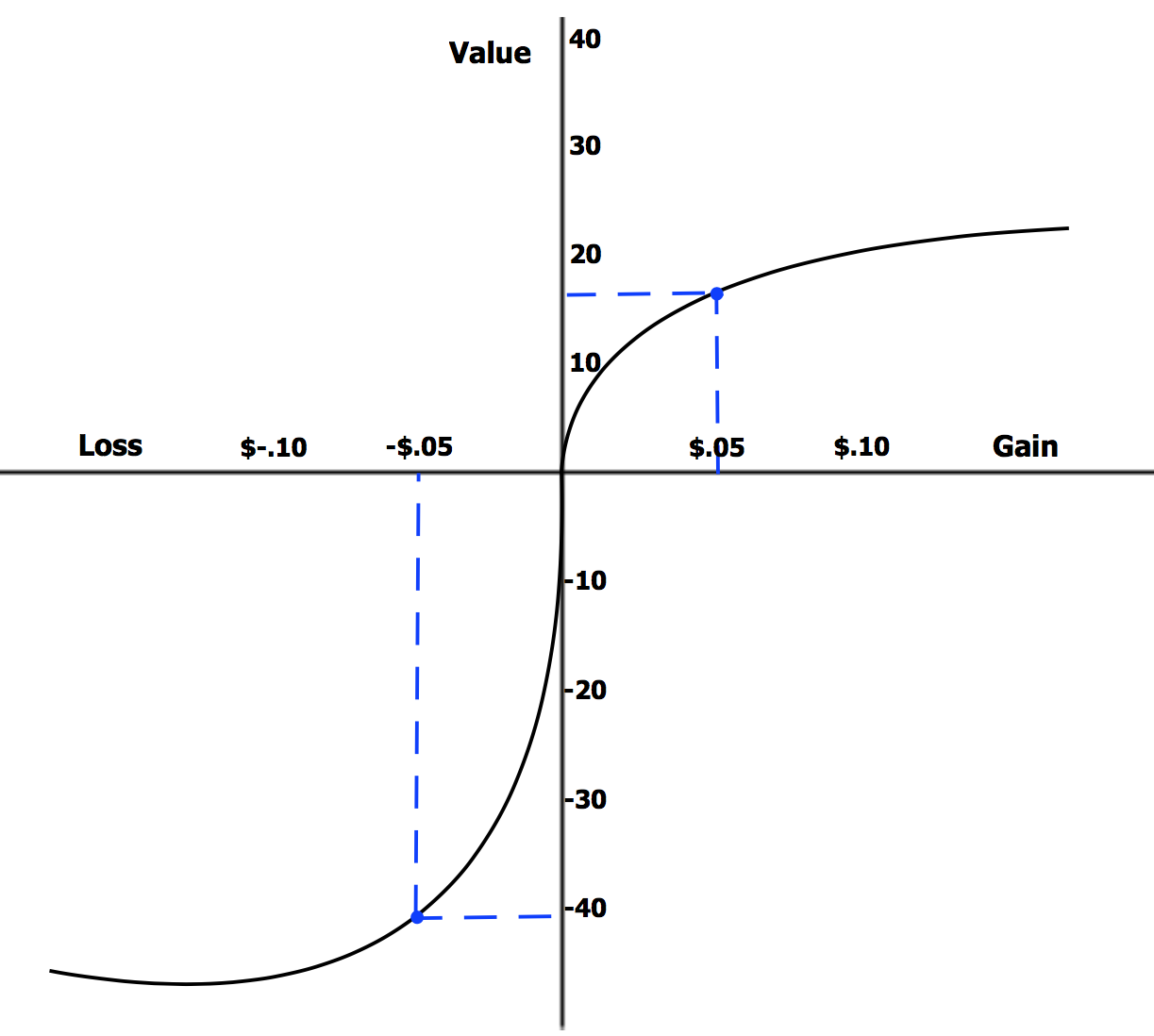
Prospect Theory
Prospect theory is a theory of behavioral economics, judgment and decision making that was developed by Daniel Kahneman and Amos Tversky in 1979. The theory was cited in the decision to award Kahneman the 2002 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economics. Based on results from controlled studies, it describes how individuals assess their loss and gain perspectives in an asymmetric manner (see loss aversion). For example, for some individuals, the pain from losing $1,000 could only be compensated by the pleasure of earning $2,000. Thus, contrary to the expected utility theory (which models the decision that perfectly rational agents would make), prospect theory aims to describe the actual behavior of people. In the original formulation of the theory, the term ''prospect'' referred to the predictable results of a lottery. However, prospect theory can also be applied to the prediction of other forms of behaviors and decisions. Prospect theory challenges the expected utility theory deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Economics
Financial economics is the branch of economics characterized by a "concentration on monetary activities", in which "money of one type or another is likely to appear on ''both sides'' of a trade".William F. Sharpe"Financial Economics", in Its concern is thus the interrelation of financial variables, such as share prices, interest rates and exchange rates, as opposed to those concerning the real economy. It has two main areas of focus:Merton H. Miller, (1999). The History of Finance: An Eyewitness Account, ''Journal of Portfolio Management''. Summer 1999. asset pricing and corporate finance; the first being the perspective of providers of Financial capital, capital, i.e. investors, and the second of users of capital. It thus provides the theoretical underpinning for much of finance. The subject is concerned with "the allocation and deployment of economic resources, both spatially and across time, in an uncertain environment".See Fama and Miller (1972), ''The Theory of Finance'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Train Surfing In Soweto
A train (from Old French , from Latin , "to pull, to draw") is a series of connected vehicles that run along a railway track and Passenger train, transport people or Rail freight transport, freight. Trains are typically pulled or pushed by locomotives (often known simply as "engines"), though some are self-propelled, such as multiple units or Railcar, railcars. Passengers and cargo are carried in railroad cars, also known as wagons or carriages. Trains are designed to a certain Track gauge, gauge, or distance between rails. Most trains operate on steel tracks with steel wheels, the low friction of which makes them more efficient than other forms of transport. Many Rail transport by country, countries use rail transport. Trains have their roots in wagonways, which used railway tracks and were Horsecar, powered by horses or Cable railway, pulled by cables. Following the invention of the steam locomotive in the United Kingdom in 1802, trains rapidly spread around the world, allo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Causative Agent
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ. The term ''pathogen'' came into use in the 1880s. Typically, the term ''pathogen'' is used to describe an ''infectious'' microorganism or agent, such as a virus, bacterium, protozoan, prion, viroid, or fungus. Small animals, such as helminths and insects, can also cause or transmit disease. However, these animals are usually referred to as parasites rather than pathogens. The scientific study of microscopic organisms, including microscopic pathogenic organisms, is called microbiology, while parasitology refers to the scientific study of parasites and the organisms that host them. There are several pathways through which pathogens can invade a host. The principal pathways have different episodic time frames, but soil has the longest or most persist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk-averse
In economics and finance, risk aversion is the tendency of people to prefer outcomes with low uncertainty to those outcomes with high uncertainty, even if the average outcome of the latter is equal to or higher in monetary value than the more certain outcome. Risk aversion explains the inclination to agree to a situation with a lower average payoff that is more predictable rather than another situation with a less predictable payoff that is higher on average. For example, a risk-averse investor might choose to put their money into a bank account with a low but guaranteed interest rate, rather than into a stock that may have high expected returns, but also involves a chance of losing value. Example A person is given the choice between two scenarios: one with a guaranteed payoff, and one with a risky payoff with same average value. In the former scenario, the person receives $50. In the uncertain scenario, a coin is flipped to decide whether the person receives $100 or nothing. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk Neutral
In economics and finance, risk neutral preferences are preference (economics), preferences that are neither risk aversion, risk averse nor risk seeking. A risk neutral party's decisions are not affected by the degree of uncertainty in a set of outcomes, so a risk neutral party is indifferent between choices with equal expected payoffs even if one choice is riskier. Theory of the firm In the context of the theory of the firm, a risk neutral firm facing risk about the market price of its product, and caring only about profit, would maximize the expected value of its profit (with respect to its choices of labor input usage, output produced, etc.). But a risk averse firm in the same environment would typically take a more cautious approach. Portfolio theory In Modern portfolio theory, portfolio choice,Merton, Robert. "An analytic derivation of the efficient portfolio frontier," ''Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis'' 7, September 1972, 1851-1872. a risk neutral investor w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concave Function
In mathematics, a concave function is one for which the function value at any convex combination of elements in the domain is greater than or equal to that convex combination of those domain elements. Equivalently, a concave function is any function for which the hypograph is convex. The class of concave functions is in a sense the opposite of the class of convex functions. A concave function is also synonymously called concave downwards, concave down, convex upwards, convex cap, or upper convex. Definition A real-valued function f on an interval (or, more generally, a convex set in vector space) is said to be ''concave'' if, for any x and y in the interval and for any \alpha \in ,1/math>, :f((1-\alpha )x+\alpha y)\geq (1-\alpha ) f(x)+\alpha f(y) A function is called ''strictly concave'' if :f((1-\alpha )x+\alpha y) > (1-\alpha ) f(x)+\alpha f(y) for any \alpha \in (0,1) and x \neq y. For a function f: \mathbb \to \mathbb, this second definition merely states that for ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utility Function
In economics, utility is a measure of a certain person's satisfaction from a certain state of the world. Over time, the term has been used with at least two meanings. * In a Normative economics, normative context, utility refers to a goal or objective that we wish to maximize, i.e., an objective function. This kind of utility bears a closer resemblance to the original Utilitarianism, utilitarian concept, developed by moral philosophers such as Jeremy Bentham and John Stuart Mill. * In a Positive economics, descriptive context, the term refers to an ''apparent'' objective function; such a function is Revealed preference, revealed by a person's behavior, and specifically by their preferences over Lottery (decision theory), lotteries, which can be any quantified choice. The relationship between these two kinds of utility functions has been a source of controversy among both Economics, economists and Ethics, ethicists, with most maintaining that the two are distinct but generally re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finance
Finance refers to monetary resources and to the study and Academic discipline, discipline of money, currency, assets and Liability (financial accounting), liabilities. As a subject of study, is a field of Business administration, Business Administration wich study the planning, organizing, leading, and controlling of an organization's resources to achieve its goals. Based on the scope of financial activities in financial systems, the discipline can be divided into Personal finance, personal, Corporate finance, corporate, and public finance. In these financial systems, assets are bought, sold, or traded as financial instruments, such as Currency, currencies, loans, Bond (finance), bonds, Share (finance), shares, stocks, Option (finance), options, Futures contract, futures, etc. Assets can also be banked, Investment, invested, and Insurance, insured to maximize value and minimize loss. In practice, Financial risk, risks are always present in any financial action and entities. Due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expected Utility
The expected utility hypothesis is a foundational assumption in mathematical economics concerning decision making under uncertainty. It postulates that rational agents maximize utility, meaning the subjective desirability of their actions. Rational choice theory, a cornerstone of microeconomics, builds this postulate to model aggregate social behaviour. The expected utility hypothesis states an agent chooses between risky prospects by comparing expected utility values (i.e., the weighted sum of adding the respective utility values of payoffs multiplied by their probabilities). The summarised formula for expected utility is U(p)=\sum u(x_k)p_k where p_k is the probability that outcome indexed by k with payoff x_k is realized, and function ''u'' expresses the utility of each respective payoff. Graphically the curvature of the u function captures the agent's risk attitude. For example, imagine you’re offered a choice between receiving $50 for sure, or flipping a coin to win $100 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |