 |
Radical Cyclization
Radical cyclization reactions are organic chemical transformations that yield cyclic products through radical intermediates. They usually proceed in three basic steps: selective radical generation, radical cyclization, and conversion of the cyclized radical to product. Introduction Radical cyclization reactions produce mono- or polycyclic products through the action of radical intermediates. Because they are intramolecular transformations, they are often very rapid and selective. Selective radical generation can be achieved at carbons bound to a variety of functional groups, and reagents used to effect radical generation are numerous. The radical cyclization step usually involves the attack of a radical on a multiple bond. After this step occurs, the resulting cyclized radicals are quenched through the action of a radical scavenger, a fragmentation process, or an electron-transfer reaction. Five- and six-membered rings are the most common products; formation of smaller and larger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Organic Reaction
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions, mechanistic organic photochemistry, photochemical reactions and organic redox reaction, redox reactions. In organic synthesis, organic reactions are used in the construction of new organic molecules. The production of many man-made chemicals such as drugs, plastics, food additives, fabrics depend on organic reactions. The oldest organic reactions are combustion of organic fuels and saponification of fats to make soap. Modern organic chemistry starts with the Wöhler synthesis in 1828. In the history of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry awards have been given for the invention of specific organic reactions such as the Grignard reaction in 1912, the Diels–Alder reaction in 1950, the Wittig reaction in 1979 and olefin metathesis in 2005. Classifications Organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
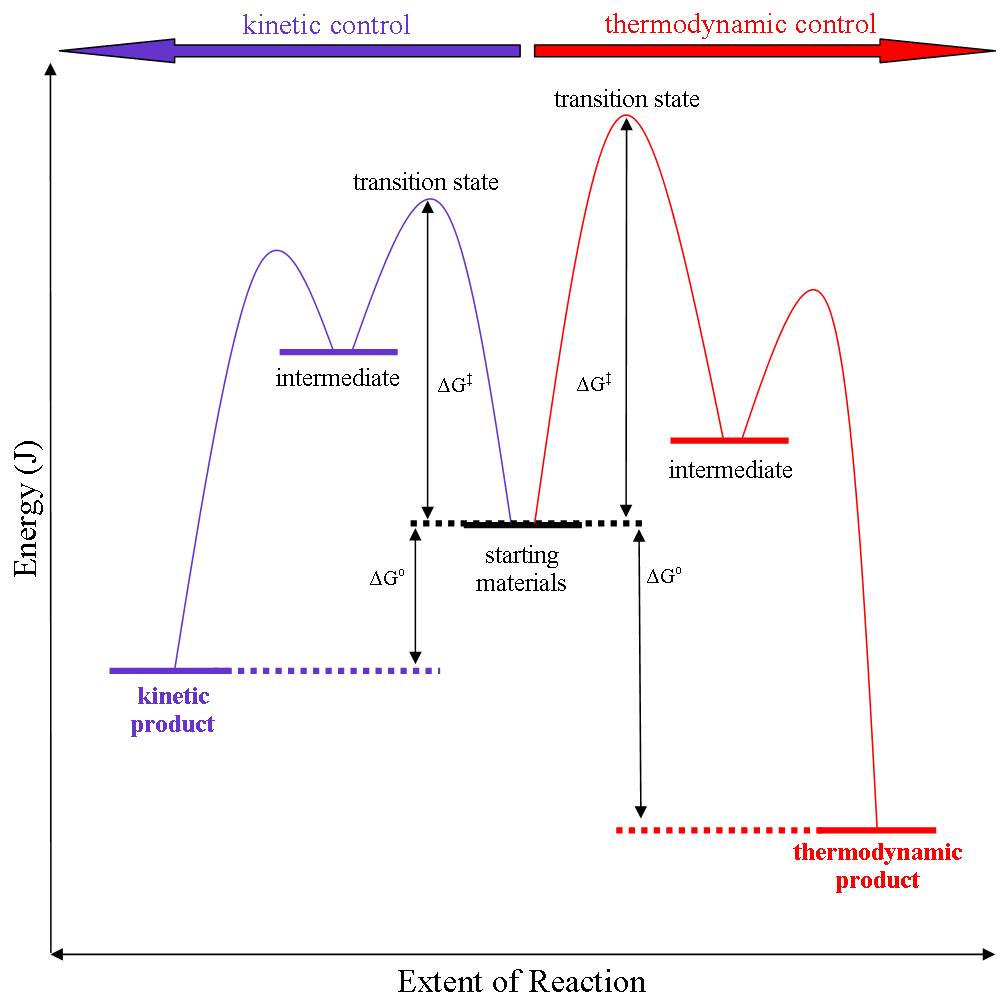 |
Thermodynamic Control
Thermodynamic reaction control or kinetic reaction control in a chemical reaction can decide the composition in a reaction product mixture when competing pathways lead to different products and the reaction conditions influence the conversion (chemistry), selectivity or stereoselectivity. The distinction is relevant when product A forms faster than product B because the activation energy for product A is lower than that for product B, yet product B is more stable. In such a case A is the kinetic product and is favoured under kinetic control and B is the thermodynamic product and is favoured under thermodynamic control.Introduction to Organic Chemistry I, Seth Robert Elsheimer, Blackwell Publishing, 2000 The conditions of the reaction, such as temperature, pressure, or solvent, affect which reaction pathway may be favored: either the kinetically controlled or the thermodynamically controlled one. Note this is only true if the activation energy of the two pathways differ, with one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is commonly known as quicksilver. A Heavy metal element, heavy, silvery d-block element, mercury is the only metallic element that is known to be liquid at standard temperature and pressure; the only other element that is liquid under these conditions is the halogen bromine, though metals such as caesium, gallium, and rubidium melt just above room temperature. Mercury occurs in deposits throughout the world mostly as cinnabar (mercuric sulfide). The red pigment vermilion is obtained by Mill (grinding), grinding natural cinnabar or synthetic mercuric sulfide. Exposure to mercury and mercury-containing organic compounds is toxic to the nervous system, immune system and kidneys of humans and other animals; mercury poisoning can result from exposure to water-soluble forms of mercury (such as mercuric chloride or methylmercury) either directly or through mechanisms of biomagnification. Mercu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic table: carbon is above it; and germanium, tin, lead, and flerovium are below it. It is relatively unreactive. Silicon is a significant element that is essential for several physiological and metabolic processes in plants. Silicon is widely regarded as the predominant semiconductor material due to its versatile applications in various electrical devices such as transistors, solar cells, integrated circuits, and others. These may be due to its significant band gap, expansive optical transmission range, extensive absorption spectrum, surface roughening, and effective anti-reflection coating. Because of its high chemical affinity for oxygen, it was not until 1823 that Jöns Jakob Berzelius was first able to p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Metal Hydride
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. These properties are all associated with having electrons available at the Fermi level, as against nonmetallic materials which do not. Metals are typically ductile (can be drawn into a wire) and malleable (can be shaped via hammering or pressing). A metal may be a chemical element such as iron; an alloy such as stainless steel; or a molecular compound such as polymeric sulfur nitride. The general science of metals is called metallurgy, a subtopic of materials science; aspects of the electronic and thermal properties are also within the scope of condensed matter physics and solid-state chemistry, it is a multidisciplinary topic. In colloquial use materials such as steel alloys are referred to as metals, while others such as polymers, wood or ceramics are nonmetallic materials. A metal conducts electricity at a temperature of absolute zero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Enantioselective
In chemistry, stereoselectivity is the property of a chemical reaction in which a single reactant forms an unequal mixture of stereoisomers during a non- stereospecific creation of a new stereocenter or during a non-stereospecific transformation of a pre-existing one. The selectivity arises from differences in steric and electronic effects in the mechanistic pathways leading to the different products. Stereoselectivity can vary in degree but it can never be total since the activation energy difference between the two pathways is finite: both products are at least possible and merely differ in amount. However, in favorable cases, the minor stereoisomer may not be detectable by the analytic methods used. An enantioselective reaction is one in which one enantiomer is formed in preference to the other, in a reaction that creates an optically active product from an achiral starting material, using either a chiral catalyst, an enzyme or a chiral reagent. The degree of selectivity is m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Chiral Auxiliaries
In stereochemistry, a chiral auxiliary is a stereogenic group or unit that is temporarily incorporated into an organic compound in order to control the stereochemical outcome of the synthesis. The chirality present in the auxiliary can bias the stereoselectivity of one or more subsequent reactions. The auxiliary can then be typically recovered for future use. Most biological molecules and pharmaceutical targets exist as one of two possible enantiomers; consequently, chemical syntheses of natural products and pharmaceutical agents are frequently designed to obtain the target in enantiomerically pure form. Chiral auxiliaries are one of many strategies available to synthetic chemists to selectively produce the desired stereoisomer of a given compound. Chiral auxiliaries were introduced by Elias James Corey in 1975 with chiral 8-phenylmenthol and by Barry Trost in 1980 with chiral mandelic acid. The menthol compound is difficult to prepare and as an alternative trans-2-phenyl-1-cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Transition State
In chemistry, the transition state of a chemical reaction is a particular configuration along the reaction coordinate. It is defined as the state corresponding to the highest potential energy along this reaction coordinate. It is often marked with the double dagger (‡) symbol. As an example, the transition state shown below occurs during the SN2 reaction of bromoethane with a hydroxide anion: The activated complex of a reaction can refer to either the transition state or to other states along the reaction coordinate between reactants and products, especially those close to the transition state. Peter Atkins and Julio de Paula, ''Physical Chemistry'' (8th ed., W.H. Freeman 2006), p.809 According to the transition state theory, once the reactants have passed through the transition state configuration, they always continue to form products. History of concept The concept of a transition state has been important in many theories of the rates at which chemical re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Diastereoselectivity
In stereochemistry, diastereomers (sometimes called diastereoisomers) are a type of stereoisomer. Diastereomers are defined as non-mirror image, non-identical stereoisomers. Hence, they occur when two or more stereoisomers of a compound have different configurations at one or more (but not all) of the equivalent (related) stereocenters and are not mirror images of each other. When two diastereoisomers differ from each other at only one stereocenter, they are epimers. Each stereocenter gives rise to two different configurations and thus typically increases the number of stereoisomers by a factor of two. Diastereomers differ from enantiomers in that the latter are pairs of stereoisomers that differ in all stereocenters and are therefore mirror images of one another. Enantiomers of a compound with more than one stereocenter are also diastereomers of the other stereoisomers of that compound that are not their mirror image (that is, excluding the opposing enantiomer). Diastereome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Carbonyl
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group with the formula , composed of a carbon atom double bond, double-bonded to an oxygen atom, and it is divalent at the C atom. It is common to several classes of organic compounds (such as aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acid), as part of many larger functional groups. A compound containing a carbonyl group is often referred to as a carbonyl compound. The term carbonyl can also refer to carbon monoxide as a ligand in an inorganic or organometallic complex (a metal carbonyl, e.g. nickel carbonyl). The remainder of this article concerns itself with the organic chemistry definition of carbonyl, such that carbon and oxygen share a double bond. Carbonyl compounds In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group characterizes the following types of compounds: Other organic carbonyls are urea and the carbamates, the derivatives of acyl chlorides, chloroformates and phosgene, carbonate esters, thioesters, lactones, lactams, Hydro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |