|
Phthalo Blue
Copper phthalocyanine (CuPc), also called phthalocyanine blue, phthalo blue and many other names, is a bright, crystalline, synthetic blue pigment from the group of dyes based on phthalocyanines. Its brilliant blue is frequently used in paints and dyes. It is highly valued for its superior properties such as light fastness, tinting strength, covering power and resistance to the effects of alkalis and acids. It has the appearance of a blue powder, insoluble in most solvents including water. History The discovery of metal phthalocyanines can be traced to the observation of intensely colored byproducts from reactions of phthalic acid (benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid) or its derivatives with sources of nitrogen and metals. CuPc (copper phthalocyanine) was first prepared in 1927 by the reaction of copper(I) cyanide and ''o''-dibromobenzene, which mainly produces colorless phthalonitrile as well as an intensely blue by-product. A couple of years later, workers at Scottish Dyes obs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead(II) Phthalocyanine
Lead(II) Phthalocyanine (PbPc), also known as phthalocyanine lead, is a salt consisting of a lead ion and Pc2−, the conjugate base of pythalocyanine. It is a organolead dye and bright purple powder. It's also used as a near infared light absorber for photodetectors. It has a unique structural feature which is called and resembles a "shuttle cock." References Phthalocyanines Macrocycles Lead(II) compounds Organic pigments {{organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutile
Rutile is an oxide mineral composed of titanium dioxide (TiO2), the most common natural form of TiO2. Rarer polymorphs of TiO2 are known, including anatase, akaogiite, and brookite. Rutile has one of the highest refractive indices at visible wavelengths of any known crystal and also exhibits a particularly large birefringence and high dispersion. Owing to these properties, it is useful for the manufacture of certain optical elements, especially polarization optics, for longer visible and infrared wavelengths up to about 4.5 micrometres. Natural rutile may contain up to 10% iron and significant amounts of niobium and tantalum. Rutile derives its name from the Latin ('red'), in reference to the deep red color observed in some specimens when viewed by transmitted light. Rutile was first described in 1803 by Abraham Gottlob Werner using specimens obtained in Horcajuelo de la Sierra, Madrid (Spain), which is consequently the type locality. Occurrence Rutile is a comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Solar Cell
An organic solar cell (OSC) or plastic solar cell is a type of photovoltaic that uses organic electronics, a branch of electronics that deals with conductive organic polymers or small organic molecules, for light absorption and charge transport to produce electricity from sunlight by the photovoltaic effect. Most organic photovoltaic cells are polymer solar cells. The molecules used in organic solar cells are solution-processable at high throughput and are cheap, resulting in low production costs to fabricate a large volume. Combined with the flexibility of organic molecules, organic solar cells are potentially cost-effective for photovoltaic applications. Molecular engineering (''e.g.,'' changing the length and functional group of polymers) can change the band gap, allowing for electronic tunability. The optical absorption coefficient of organic molecules is high, so a large amount of light can be absorbed with a small amount of materials, usually on the order of hundreds of na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Electronics
Molecular electronics is the study and application of molecular building blocks for the fabrication of electronic components. It is an interdisciplinary area that spans physics, chemistry, and materials science. It provides a potential means to extend Moore's Law beyond the foreseen limits of small-scale conventional silicon integrated circuits. Molecular scale electronics Molecular scale electronics, also called single-molecule electronics, is a branch of nanotechnology that uses single molecules, or nanoscale collections of single molecules, as electronic components. Because single molecules constitute the smallest stable structures possible, this miniaturization is the ultimate goal for shrinking electrical circuits. Conventional electronic devices are traditionally made from bulk materials. Bulk methods have inherent limits, and are growing increasingly demanding and costly. Thus, the idea was born that the components could instead be built up atom by atom in a chemistry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic polymers, synthetic or Semisynthesis, semisynthetic materials composed primarily of Polymer, polymers. Their defining characteristic, Plasticity (physics), plasticity, allows them to be Injection moulding, molded, Extrusion, extruded, or Compression molding, pressed into a diverse range of solid forms. This adaptability, combined with a wide range of other properties such as low weight, durability, flexibility, chemical resistance, low toxicity, and low-cost production, has led to their widespread use around the world. While most plastics are produced from natural gas and petroleum, a growing minority are produced from renewable resources like polylactic acid. Between 1950 and 2017, 9.2 billion metric tons of plastic are estimated to have been made, with more than half of this amount being produced since 2004. In 2023 alone, preliminary figures indicate that over 400 million metric tons of plastic were produced worldwide. If global trends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is toxic, corrosive, and flammable. Trace amounts in ambient atmosphere have a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele is credited with having discovered the chemical composition of purified hydrogen sulfide in 1777. Hydrogen sulfide is toxic to humans and most other animals by inhibiting cellular respiration in a manner similar to hydrogen cyanide. When it is inhaled or its salts are ingested in high amounts, damage to organs occurs rapidly with symptoms ranging from breathing difficulties to convulsions and death. Despite this, the human body produces small amounts of this sulfide and its mineral salts, and uses it as a signalling molecule. Hydrogen sulfide is often produced from the microbial breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen, such as in swamps and sewers; this process is commonly known as anaerobic digestio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen Reduction Reaction
In chemistry, the oxygen reduction reaction refers to the reduction half reaction whereby O2 is reduced to water or hydrogen peroxide. In fuel cells, the reduction to water is preferred because the current is higher. The oxygen reduction reaction is well demonstrated and highly efficient in nature. Stoichiometry The stoichiometries of the oxygen reduction reaction, which depends on the medium, are shown: 4e− pathway in acid medium: O2 + 4 e- + 4H+ -> 2 H2O 2e− pathway in acid medium: O2 + 2e- + 2H+ -> H2O2 4e− pathway in alkaline medium: O2 + 4e- + 2H2O -> 4 OH- 2e− pathway in alkaline medium: O2 + 2e- + H2O -> HO2- + OH- 4e- pathway in solid oxide: O2 + 4e- -> 2 O^2- The 4e− pathway reaction is the cathode reaction in fuel cell especially in proton-exchange membrane fuel cells, alkaline fuel cell and solid oxide fuel cell. While the 2e− pathway reaction is often the side reaction of 4e- pathway or can be used in synthesis of H2O2. Catalysts Biocatalysts The o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
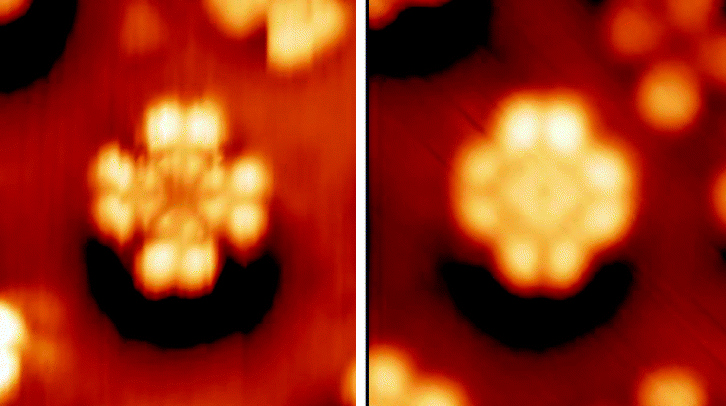
Phthalocyanine AFM
Phthalocyanine () is a large, aromatic, macrocyclic, organic compound with the formula and is of theoretical or specialized interest in chemical dyes and photoelectricity. It is composed of four isoindole units linked by a ring of nitrogen atoms. = has a two-dimensional geometry and a ring system consisting of 18 π-electrons. The extensive delocalization of the π-electrons affords the molecule useful properties, lending itself to applications in dyes and pigments. Metal complexes derived from , the conjugate base of , are valuable in catalysis, organic solar cells, and photodynamic therapy. Properties Phthalocyanine and derived metal complexes (MPc) tend to aggregate and, thus, have low solubility in common solvents. Benzene at 40 °C dissolves less than a milligram of or CuPc per litre. and CuPc dissolve easily in sulfuric acid due to the protonation of the nitrogen atoms bridging the pyrrole rings. Many phthalocyanine compounds are, thermally, very stable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper(I) Chloride
Copper(I) chloride, commonly called cuprous chloride, is the lower chloride of copper, with the formula CuCl. The substance is a white solid sparingly soluble in water, but very soluble in concentrated hydrochloric acid. Impure samples appear green due to the presence of copper(II) chloride (CuCl2). History Copper(I) chloride was first prepared by Robert Boyle and designated rosin of copper in the mid-seventeenth century from mercury(II) chloride ("Venetian sublimate") and copper metal: :HgCl2 + 2 Cu → 2 CuCl + Hg In 1799, Joseph Proust first differentiated two different chlorides of copper. He prepared CuCl (which he called white muriate of copper) by heating CuCl2 at red heat in the absence of air, causing it to lose half of its combined chlorine followed by removing residual CuCl2 by washing with water. An acidic solution of CuCl was formerly used to analyze carbon monoxide content in gases, for example in Hempel's gas apparatus where the CuCl absorbs the carbon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urea
Urea, also called carbamide (because it is a diamide of carbonic acid), is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two Amine, amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid. Urea serves an important role in the cellular metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds by animals and is the main nitrogen-containing substance in the urine of mammals. ''Urea'' is Neo-Latin, , , itself from Proto-Indo-European ''*h₂worsom''. It is a colorless, odorless solid, highly soluble in water, and practically non-toxic ( is 15 g/kg for rats). Dissolved in water, it is neither acidic nor base (chemistry), alkaline. The body uses it in many processes, most notably metabolic waste#Nitrogen wastes, nitrogen excretion. The liver forms it by combining two ammonia molecules () with a carbon dioxide () molecule in the urea cycle. Urea is widely used in fertilizers as a source of nitrogen (N) and is an important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. Originally a trading brand of the Railway Executive of the British Transport Commission, it became an independent statutory corporation in January 1963, when it was formally renamed the British Railways Board. British Railways was formed on 1 January 1948 as a result of the Transport Act 1947, which nationalised the Big Four British railway companies along with some other (but not all) smaller railways. Profitability of the railways became a pressing concern during the 1950s, leading to multiple efforts to bolster performance, including some line closures. The 1955 Modernisation Plan formally directed a process of dieselisation and electrification to take place; accordingly, steam locomotives had been entirely replaced by diesel and electric traction (except for the narrow-gauge Vale of Rheidol Railway tourist lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colour Index International
Colour Index International (CI) is a reference database jointly maintained bSDC Enterprisesand the American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists. It currently contains over 27,000 individual products listed under 13,000 Colour Index Generic Names. It was first printed in 1924 but is now published solely on the Internet. The index serves as a common reference database of manufactured colour products and is used by manufacturers and consumers, such as artists and decorators. Colourants (both dyes and pigments) are listed using a dual classification which use the Colour Index Generic Name the prime identifier and Colour Index Constitution Numbers. These numbers are prefixed with C.I. for example, C.I. Acid Orange 7 or C.I. 15510. (This abbreviation is sometimes mistakenly thought to be CL, due to the font used to display it.) The generic name lists first the class of dye (acid dye, disperse dye, etc.), then its hue (e.g., orange), followed by a number assigned by the Col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |