|
Oxygen Storage
Methods of oxygen storage for subsequent use span many approaches, including high pressures in oxygen tanks, cryogenics, oxygen-rich compounds and reaction mixtures, and chemical compounds that reversibly release oxygen upon heating or pressure change. is the second most important industrial gas. Air Air is the most common source and reservoir of oxygen, containing 20.8% oxygen. This concentration is sufficient for many purposes, such as combustion of many fuels, corrosion of many metals, and breathing of animals. Most humans can function at rest with an oxygen level of 15% at one atmosphere pressure; a fuel such as methane is combustable down to 12% oxygen in nitrogen. A small room of 10 meter3 has 2.08 meter3 (2080 liters) or 2.99 kg of oxygen which would occupy 2.62 liters if it was liquid. High pressure Oxygen tanks containing pressures of up to 200 bar (3000 psi) are used for industrial processes including the manufacturing of steel and monel, welding and cutting, medic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen Tank
An oxygen tank is an oxygen storage vessel, which is either held under pressure in gas cylinders, referred to in the industry as high pressure oxygen cylinders, or as liquid oxygen in a cryogenic storage tank. Uses Oxygen tanks are used to store gas for: * medical breathing (oxygen therapy) at medical facilities and at home (high pressure cylinder) * breathing at altitude in aviation, either in a decompression emergency, or constantly (as in unpressurized aircraft), usually in high pressure cylinders * oxygen first aid sets, in small portable high pressure cylinders * gas blending, for mixing breathing gases such as nitrox, trimix and heliox * open-circuit scuba sets - mainly used for accelerated decompression in technical diving, in high pressure cylinders * some types of diving rebreather: oxygen rebreathers and fully closed circuit rebreathers, usually in high pressure cylinders * use in climbing, " Bottled oxygen" refers to oxygen in lightweight high pressure cylinde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Perchlorate
Potassium perchlorate is the inorganic salt with the chemical formula K Cl O4. Like other perchlorates, this salt is a strong oxidizer when the solid is heated at high temperature, although it usually reacts very slowly in solution with reducing agents or organic substances. This colorless crystalline solid is a common oxidizer used in fireworks, ammunition percussion caps, and explosive primers, and is used variously in propellants, flash compositions, stars, and sparklers. It has been used as a solid rocket propellant, although in that application it has mostly been replaced by the more performant ammonium perchlorate. KClO4 has a relatively low solubility in water (1.5 g in 100 mL of water at 25 °C). Production Potassium perchlorate is prepared industrially by treating an aqueous solution of sodium perchlorate with potassium chloride. This single precipitation reaction exploits the low solubility of KClO4, which is about 1/100 as much as the solubili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perovskite (structure)
A perovskite is a crystalline material of formula ABX3 with a crystal structure similar to that of the mineral perovskite, this latter consisting of calcium titanium oxide (CaTiO3). The mineral was first discovered in the Ural mountains of Russia by Gustav Rose in 1839 and named after Russian mineralogist L. A. Perovski (1792–1856). In addition to being one of the most abundant structural families, perovskites have wide-ranging properties and applications. Structure Perovskite structures are adopted by many compounds that have the chemical formula ABX3. 'A' and 'B' are positively charged ions (i.e. cations), often of very different sizes, and X is a negatively charged ion (an anion, frequently oxide) that bonds to both cations. The 'A' atoms are generally larger than the 'B' atoms. The ideal cubic structure has the B cation in 6-fold coordination, surrounded by an octahedron of anions, and the A cation in 12-fold cuboctahedral coordination. Additional perovskite for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature Swing Absorption
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making up a substance. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), with the third being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible to extract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure Swing Adsorption
Pressure swing adsorption (PSA) is a technique used to separate some gas species from a mixture of gases (typically air) under pressure according to the species' molecular characteristics and affinity for an adsorbent material. It operates at near-ambient temperature and significantly differs from the cryogenic distillation commonly used to separate gases. Selective adsorbent materials (e.g., zeolites, (aka molecular sieves), activated carbon, etc.) are used as trapping material, preferentially adsorbing the target gas species at high pressure. The process then swings to low pressure to desorb the adsorbed gas. Process The pressure swing adsorption (PSA) process is based on the phenomenon that under high pressure, gases tend to be trapped onto solid surfaces, ''i.e.'' to be "adsorbed". The higher the pressure, the more gas is adsorbed. When the pressure is dropped, the gas is released, or desorbed. PSA can be used to separate gases in a mixture because different gases are adsor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure Swing Absorption
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and even by industry. Further, both spellings are often used ''within'' a particular industry or country. Industries in British English-speaking countries typically use the "gauge" spelling. is the pressure relative to the ambient pressure. Various units are used to express pressure. Some of these derive from a unit of force divided by a unit of area; the SI unit of pressure, the pascal (Pa), for example, is one newton per square metre (N/m2); similarly, the pound-force per square inch (psi, symbol lbf/in2) is the traditional unit of pressure in the imperial and US customary systems. Pressure may also be expressed in terms of standard atmospheric pressure; the unit atmosphere (atm) is equal to this pressure, and the torr is defined as of this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absorption (chemistry)
Absorption is a physical or chemical phenomenon or a process in which atoms, molecules or ions enter the liquid or solid bulk phase of a material. This is a different process from adsorption, since molecules undergoing absorption are taken up by the volume, not by the surface (as in the case for adsorption). A more common definition is that "Absorption is a chemical or physical phenomenon in which the molecules, atoms and ions of the substance getting absorbed enter into the bulk phase (gas, liquid or solid) of the material in which it is taken up." A more general term is '' sorption'', which covers absorption, adsorption, and ion exchange. Absorption is a condition in which something takes in another substance. In many processes important in technology, the chemical absorption is used in place of the physical process, e.g., absorption of carbon dioxide by sodium hydroxide – such acid-base processes do not follow the Nernst partition law (see: solubility). For some examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ozonide
Ozonide is the polyatomic anion . Cyclic organic compounds formed by the addition of ozone () to an alkene are also called ozonides. Ionic ozonides Inorganic ozonides are dark red salts. The anion has the bent shape of the ozone molecule. Inorganic ozonides are formed by burning potassium, rubidium, or caesium in ozone, or by treating the alkali metal hydroxide with ozone; this yields potassium ozonide, rubidium ozonide, and caesium ozonide respectively. They are very sensitive explosives that have to be handled at low temperatures in an inert gas atmosphere. Lithium and sodium ozonide are extremely labile and must be prepared by low-temperature ion exchange starting from . Sodium ozonide, , which is prone to decomposition into NaOH and , was previously thought to be impossible to obtain in pure form. However, with the help of cryptands and methylamine, pure sodium ozonide may be obtained as red crystals isostructural to . Ionic ozonides are being investigated as sour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-contained Self-rescue Device
A self-contained self-rescue device, SCSR, self-contained self-rescuer, or air pack is a type of Self-contained breathing apparatus#Closed-circuit, closed-circuit SCBA with a portable oxygen source for providing breathable air when the surrounding atmosphere lacks oxygen or is contaminated with toxic gases, e.g. carbon monoxide. Self-rescuers are intended for use in environments such as coal mines where there is a risk of fire or explosion, and in a location where no external rescue may be available for some time – the wearer must make their own way to safety, or to some pre-equipped underground refuge. The main hazard here is from large quantities of carbon monoxide or whitedamp, often produced by an explosion of firedamp. In some industries, the hazard may be from anoxic asphyxia, or a ''lack'' of oxygen, rather than poisoning by something toxic. Self-rescuers are small, lightweight belt or harness-worn devices, enclosed in a rugged metal case. They are designed to have a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
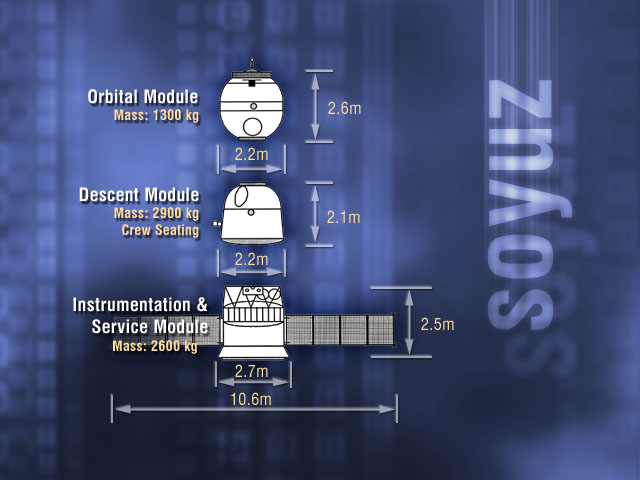
Soyuz (spacecraft)
Soyuz () is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now Energia (corporation), Energia). The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraft and was originally built as part of the Soviet crewed lunar programs. It is launched atop the similarly named Soyuz (rocket family), Soyuz rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Following the Soviet Union's dissolution, Roscosmos, the Russian space agency, continued to develop and utilize the Soyuz. Between the Space Shuttle retirement, Space Shuttle's 2011 retirement and the SpaceX Crew Dragon's 2020 debut, Soyuz was the sole means of crewed transportation to and from the International Space Station, a role it continues to fulfill. The Soyuz design has also influenced other spacecraft, including China's Shenzhou (spacecraft), Shenzhou and Russia's Progress (spacecraft), Progress cargo vehicle. The Soyu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Superoxide
Potassium superoxide is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a yellow paramagnetic solid that decomposes in moist air. It is a rare example of a stable salt of the superoxide anion. It is used as a scrubber, dehumidifier, and generator in rebreathers, spacecraft, submarines, and spacesuits. Production and reactions Potassium superoxide is produced by burning molten potassium in an atmosphere of excess oxygen. : The salt consists of and ions, linked by ionic bonding. The O–O distance is 1.28 Å. Reactivity Potassium superoxide is a source of superoxide, which is an oxidant and a nucleophile, depending on its reaction partner. Upon contact with water, it undergoes disproportionation to potassium hydroxide, oxygen, and hydrogen peroxide: : : It reacts with carbon dioxide, releasing oxygen: : : Theoretically, 1 kg of absorbs 0.310 kg of while releasing 0.338 kg of . One mole of absorbs 0.5 moles of and releases 0.75 moles of oxygen. Potass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium Perchlorate
Lithium perchlorate is the inorganic compound with the formula LiClO4. This white or colourless crystalline salt is noteworthy for its high solubility in many solvents. It exists both in anhydrous form and as a trihydrate. Applications Inorganic chemistry Lithium perchlorate is used as a source of oxygen in some chemical oxygen generators. It decomposes at about 400 °C, yielding lithium chloride and oxygen: : LiClO4 → LiCl + 2 O2 Over 60% of the mass of the lithium perchlorate is released as oxygen. It has both the highest oxygen to weight and oxygen to volume ratio of all practical perchlorate salts, and higher oxygen to volume ratio than liquid oxygen. Lithium perchlorate is used as an oxidizer in some experimental solid rocket propellants, and to produce red colored flame in pyrotechnic compositions. Organic chemistry LiClO4 is highly soluble in organic solvents, even diethyl ether. Such solutions are employed in Diels–Alder reactions, where it is proposed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |