|
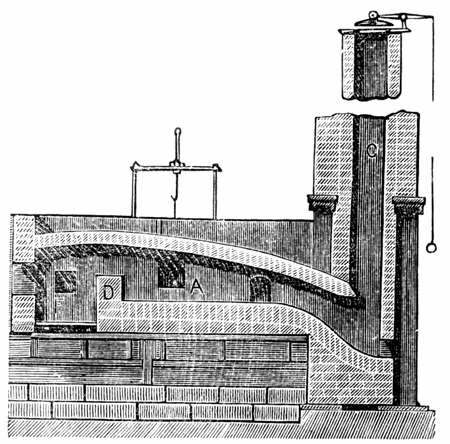
Open Hearth Furnace
An open-hearth furnace or open hearth furnace is any of several kinds of industrial Industrial furnace, furnace in which excess carbon and other impurities are burnt out of pig iron to Steelmaking, produce steel. Because steel is difficult to manufacture owing to its high melting point, normal fuels and furnaces were insufficient for mass production of steel, and the open-hearth type of furnace was one of several technologies developed in the nineteenth century to overcome this difficulty. Compared with the Bessemer process, which it displaced, its main advantages were that it did not Embrittlement, embrittle the steel from excessive nitrogen exposure, was easier to control, and permitted the melting and refining of large amounts of scrap, scrap iron and steel. The open-hearth furnace was first developed by German/British engineer Carl Wilhelm Siemens. In 1865, the French engineer Pierre-Émile Martin took out a licence from Siemens and first applied his regenerative furnace for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haya People
The Haya (or Bahaya) are a Bantu ethnic group based in Kagera Region, northwestern Tanzania, on the western side of Lake Victoria. With over one million people, it is estimated that Haya make up approximately 4% of the population of Tanzania. Historically, the Haya have had a complex kingship-based political system. Agriculture, particularly banana farming, is central to Haya economic life. They are credited with the independent development of carbon steel dating to 2000 years ago using pre-heating techniques. Etymology According to Hans Cory, the term ( Haya for fisher-people) was originally used to differentiate the Haya from the Banyambo of Karagwe. This distinction is said to be based on cultural differences, with the Haya economy predominantly oriented toward fishing and other industries on Lake Victoria and the Banyambo predominately engaged in pastoralism. Other sources on the origin of the term Haya cite oral accounts that state it derives from a goddess named Muhay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bessemer Converter
The Bessemer process was the first inexpensive industrial process for the mass production of steel from molten pig iron before the development of the open hearth furnace. The key principle is removal of impurities and undesired elements, primarily excess carbon contained in the pig iron by oxidation with air being blown through the molten iron. Oxidation of the excess carbon also raises the temperature of the iron mass and keeps it molten. Virtually all the pig iron carbon is removed by the converter and so carbon must be added at the end of the process to create steel, 0.25% carbon content is a typical value for low carbon steel which is used in construction and other low-stress applications. The modern process is named after its inventor, the Englishman Henry Bessemer, who took out a patent on the process in 1856. The process was said to be independently discovered in 1851 by the American inventor William Kelly though the claim is controversial. The process using a ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Hearth Furnace
An open-hearth furnace or open hearth furnace is any of several kinds of industrial Industrial furnace, furnace in which excess carbon and other impurities are burnt out of pig iron to Steelmaking, produce steel. Because steel is difficult to manufacture owing to its high melting point, normal fuels and furnaces were insufficient for mass production of steel, and the open-hearth type of furnace was one of several technologies developed in the nineteenth century to overcome this difficulty. Compared with the Bessemer process, which it displaced, its main advantages were that it did not Embrittlement, embrittle the steel from excessive nitrogen exposure, was easier to control, and permitted the melting and refining of large amounts of scrap, scrap iron and steel. The open-hearth furnace was first developed by German/British engineer Carl Wilhelm Siemens. In 1865, the French engineer Pierre-Émile Martin took out a licence from Siemens and first applied his regenerative furnace for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron(II) Oxide
Iron(II) oxide or ferrous oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula FeO. Its mineral form is known as wüstite. One of several iron oxides, it is a black-colored powder that is sometimes confused with rust, the latter of which consists of hydrated iron(III) oxide (ferric oxide). Iron(II) oxide also refers to a family of related non-stoichiometric compounds, which are typically iron deficient with compositions ranging from Fe0.84O to Fe0.95O. Preparation FeO can be prepared by the thermal decomposition of iron(II) oxalate. : The procedure is conducted under an inert atmosphere to avoid the formation of iron(III) oxide (). A similar procedure can also be used for the synthesis of manganous oxide and stannous oxide. Stoichiometric FeO can be prepared by heating Fe0.95O with metallic iron at 770 °C and 36 kbar.Wells A.F. (1984) ''Structural Inorganic Chemistry'' 5th edition Oxford University Press Reactions FeO is thermodynamically unstable below 575 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simplest oxocarbon, carbon oxide. In coordination complexes, the carbon monoxide ligand is called ''metal carbonyl, carbonyl''. It is a key ingredient in many processes in industrial chemistry. The most common source of carbon monoxide is the partial combustion of carbon-containing compounds. Numerous environmental and biological sources generate carbon monoxide. In industry, carbon monoxide is important in the production of many compounds, including drugs, fragrances, and fuels. Indoors CO is one of the most acutely toxic contaminants affecting indoor air quality. CO may be emitted from tobacco smoke and generated from malfunctioning fuel-burning stoves (wood, kerosene, natural gas, propane) and fuel-burning heating systems (wood, oil, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal, and a potent oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other chemical compound, compounds. Oxygen is abundance of elements in Earth's crust, the most abundant element in Earth's crust, making up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of various oxides such as water, carbon dioxide, iron oxides and silicates.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. It is abundance of chemical elements, the third-most abundant element in the universe after hydrogen and helium. At standard temperature and pressure, two oxygen atoms will chemical bond, bind covalent bond, covalently to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the chemical formula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blast Furnace
A blast furnace is a type of metallurgical furnace used for smelting to produce industrial metals, generally pig iron, but also others such as lead or copper. ''Blast'' refers to the combustion air being supplied above atmospheric pressure. In a blast furnace, fuel ( coke), ores, and flux (limestone) are continuously supplied through the top of the furnace, while a hot blast of (sometimes oxygen enriched) air is blown into the lower section of the furnace through a series of pipes called tuyeres, so that the chemical reactions take place throughout the furnace as the material falls downward. The end products are usually molten metal and slag phases tapped from the bottom, and flue gases exiting from the top. The downward flow of the ore along with the flux in contact with an upflow of hot, carbon monoxide-rich combustion gases is a countercurrent exchange and chemical reaction process. In contrast, air furnaces (such as reverberatory furnaces) are naturally aspirated, usu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batch Production
Batch production is a method of manufacturing in which products are made as specified groups or amounts, within a time frame. A batch can go through a series of steps in a large manufacturing process to make the final desired product. Batch production is used for many types of manufacturing that may need smaller amounts of production at a time to ensure specific quality standards or changes in the process. This is opposed to large mass production Mass production, also known as mass production, series production, series manufacture, or continuous production, is the production of substantial amounts of standardized products in a constant flow, including and especially on assembly lines ... or continuous production methods, where the product or process does not need to be checked or changed as frequently or periodically. Characteristics In the manufacturing batch production process, the machines are in chronological order directly related to the manufacturing process. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puddling Furnace
Puddling is the process of converting pig iron to bar (wrought) iron in a coal fired reverberatory furnace. It was developed in England during the 1780s. The molten pig iron was stirred in a reverberatory furnace, in an Redox, oxidizing environment to burn the carbon, resulting in wrought iron. It was one of the most important processes for making the first appreciable volumes of valuable and useful wrought iron, bar iron (malleable wrought iron) without the use of charcoal. Eventually, the furnace would be used to make small quantities of specialty steels. Though it was not the first process to produce bar iron without charcoal, puddling was by far the most successful, and replaced the earlier potting and stamping processes, as well as the much older charcoal finery forge, finery and bloomery processes. This enabled a great expansion of iron production to take place in Great Britain, and shortly afterwards, in North America. That expansion constitutes the beginnings of the Ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finery Forge
A finery forge is a forge used to produce wrought iron from pig iron by decarburization in a process called "fining" which involved liquifying cast iron in a fining hearth and decarburization, removing carbon from the molten cast iron through Redox, oxidation. Finery forges were used as early as the 3rd century BC in China. The finery forge process was replaced by the puddling (metallurgy), puddling process and the roller mill, both developed by Henry Cort in 1783–4, but not becoming widespread until after 1800. History A finery forge was used to refine wrought iron at least by the 3rd century BC in ancient China, based on the earliest archaeological specimens of Cast iron, cast and pig iron fined into wrought iron and steel found at the early Han dynasty (202 BC – 220 AD) site at Tieshengguo.Pigott, Vincent C. (1999). ''The Archaeometallurgy of the Asian Old World''. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology. , p. 186-187. Pigott spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |