|
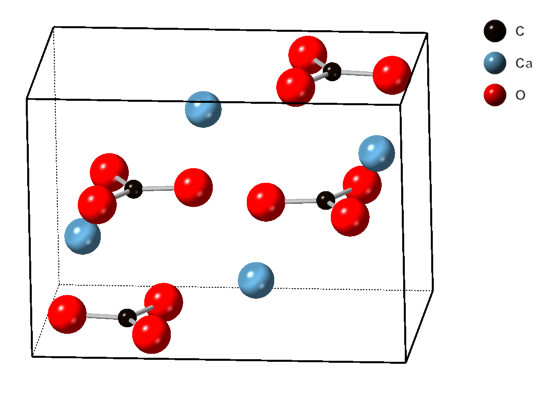
Monohydrocalcite
Monohydrocalcite is a mineral that is a hydrous form of calcium carbonate, CaCO3·H2O. It was formerly also known by the name hydrocalcite, which is now discredited by the IMA. It is a trigonal mineral which is white when pure. Monohydrocalcite is not a common rock-forming mineral, but is frequently associated with other calcium and magnesium carbonate minerals, such as calcite, aragonite, lansfordite, and nesquehonite. Monohydrocalcite has been observed in air conditioning systems, and in moonmilk deposits in caves, both probably formed from spray of carbonate rich fluids. It is well known in Robe on the Limestone Coast of South Australia as a component of beach sands of Lake Fellmongery and Lake Butler, where it is believed to be formed from algal spume. Other lacustrine deposits include Lake Issyk-Kul, Kyrgyzstan, Lake Kivu, Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Solar Lake, Sinai. It has been reported as a significant component of the decomposition of ikaite in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonate Mineral
Carbonate minerals are those minerals containing the carbonate ion, . Carbonate divisions Anhydrous carbonates *Calcite group: trigonal **Calcite CaCO3 **Gaspéite (Ni,Mg,Fe2+)CO3 **Magnesite MgCO3 **Otavite CdCO3 **Rhodochrosite MnCO3 **Siderite FeCO3 **Smithsonite ZnCO3 **Spherocobaltite CoCO3 *Aragonite group: orthorhombic **Aragonite CaCO3 **Cerussite PbCO3 **Strontianite SrCO3 **Witherite BaCO3 **Rutherfordine UO2CO3 **Natrite Na2CO3 Anhydrous carbonates with compound formulas *Dolomite group: trigonal **Ankerite CaFe(CO3)2 **Dolomite (mineral), Dolomite CaMg(CO3)2 **Huntite Mg3Ca(CO3)4 **Minrecordite CaZn(CO3)2 **Barytocalcite BaCa(CO3)2 Carbonates with hydroxyl or halogen *Carbonate with hydroxide: monoclinic **Azurite Cu3(CO3)2(OH)2 **Hydrocerussite Pb3(CO3)2(OH)2 **Malachite Cu2CO3(OH)2 **Rosasite (Cu,Zn)2CO3(OH)2 **Phosgenite Pb2(CO3)Cl2 **Hydrozincite Zn5(CO3)2(OH)6 **Aurichalcite (Zn,Cu)5(CO3)2(OH)6 Hydrated carbonates *Hydromagnesite Mg5(CO3)4(OH)2.4H2O *Ikaite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aragonite
Aragonite is a carbonate mineral and one of the three most common naturally occurring crystal forms of calcium carbonate (), the others being calcite and vaterite. It is formed by biological and physical processes, including precipitation from marine and freshwater environments. The crystal lattice of aragonite differs from that of calcite, resulting in a different crystal shape, an orthorhombic crystal system with acicular crystal. Repeated twinning results in pseudo-hexagonal forms. Aragonite may be columnar or fibrous, occasionally in branching helictitic forms called ''flos-ferri'' ("flowers of iron") from their association with the ores at the Carinthian iron mines. Occurrence The type location for aragonite is Molina de Aragón in the Province of Guadalajara in Castilla-La Mancha, Spain, for which it was named in 1797. Aragonite is found in this locality as cyclic twins inside gypsum and marls of the Keuper facies of the Triassic. This type of aragoni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Kivu
Lake Kivu is one of the African Great Lakes. It lies on the border between the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Rwanda, and is in the Albertine Rift, the western branch of the East African Rift. Lake Kivu empties into the Ruzizi River, which flows southwards into Lake Tanganyika. In 1894, German officer and colonial ruler Gustav Adolf von Götzen was the first recorded European to visit the lake. In the past, Lake Kivu drained toward the north, contributing to the White Nile. About 13,000 to 9,000 years ago, volcanism, volcanic activity blocked Lake Kivu's outlet to the watershed of the Nile. The volcanism produced mountains, including the Virunga Mountains, Virungas, which rose between Lake Kivu and Lake Edward, to the north. Water from Lake Kivu was then forced south down the Ruzizi. This, in turn, raised the level of Lake Tanganyika, which overflowed down the Lukuga River. Lake Kivu is one of three lakes in the world, along with Lake Nyos and Lake Monoun, that undergo lim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Lake
Solar Lake ( ''Birkat aš-Šams'') is a saline desert lake located on the edge of the Red Sea, about 18 km south of Eilat in the Sinai Peninsula, Taba, Egypt, close to its borders with Israel. A small lake of high salinity, it is the site of complex biochemical phenomena, linked to cycles of evaporation and of infiltration of waters. Solar Lake became isolated from the Red Sea as littoral sediments closed off an embayment between two rocky headlands.Solar Lake by Dave Grant The saline waters of the Gulf of Aqaba that seep into Solar Lake are further concentrated by evaporation in the lake. It is believed that in addition to losses from evaporation, there is a crack system a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcite
Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on Scratch hardness, scratch hardness comparison. Large calcite crystals are used in optical equipment, and limestone composed mostly of calcite has numerous uses. Other polymorphs of calcium carbonate are the minerals aragonite and vaterite. Aragonite will change to calcite over timescales of days or less at temperatures exceeding 300 °C, and vaterite is even less stable. Etymology Calcite is derived from the German , a term from the 19th century that came from the Latin word for Lime (material), lime, (genitive ) with the suffix ''-ite'' used to name minerals. It is thus a Doublet (linguistics), doublet of the word ''wikt:chalk, chalk''. When applied by archaeology, archaeologists and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Sedimentary Research
The Society for Sedimentary Geology is an international not-for-profit, scientific society based in the US state of Oklahoma. It is commonly referred to by its acronym SEPM, which refers to its former name, the Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists. The society's reason for being is to disseminate scientific information on sedimentology, stratigraphy, paleontology, environmental sciences, marine geology, hydrogeology, and related specialties. Members benefit from both gaining and exchanging information pertinent to their geologic specialties. Information is dispersed via the publication of two major scientific journals, the ''Journal of Sedimentary Research'' (JSR) and '' PALAIOS'', and the organization of technical conferences and short courses. It also publishes a monthly magazine for its members, ''The Sedimentary Record'', which is now a diamond open access Diamond open access refers to academic texts (such as monographs, edited collections, and journal artic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otolith
An otolith (, ' ear + , ', a stone), also called otoconium, statolith, or statoconium, is a calcium carbonate structure in the saccule or utricle (ear), utricle of the inner ear, specifically in the vestibular system of vertebrates. The saccule and utricle, in turn, together make the ''otolith organs''. These organs are what allows an organism, including humans, to perceive linear acceleration, both horizontally and vertically (gravity). They have been identified in both extinct and extant vertebrates. Counting the annual growth rings on the otoliths is a common technique in estimating the age of fish. Description Endolymphatic infillings such as otoliths are structures in the saccule and Utricle (ear), utricle of the inner ear, specifically in the Labyrinth (inner ear), vestibular labyrinth of all vertebrates (fish, amphibians, reptiles, mammals and birds). In vertebrates, the saccule and utricle together make the ''otolith organs''. Both statoconia and otoliths are used as gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Issyk-Kul
Issyk-Kul () or Ysyk-Köl (, ; ) is an endorheic saline lake in the western Tianshan Mountains in eastern Kyrgyzstan, just south of a dividing range separating Kyrgyzstan from Kazakhstan. It is the eighth-deepest lake in the world, the eleventh-largest lake in the world by volume (though not in surface area), the deepest lake whose deepest point is above sea level (939 meters or 3,080 feet), and the third-largest saline lake. Although it is located at a lofty elevation of and subject to severe cold during winter, it rarely freezes over due to high salinity, hence its name, which in the Kyrgyz language means "warm lake". The lake is a Ramsar site of globally significant biodiversity and forms part of the Issyk-Kul Biosphere Reserve. Geography Issyk-Kul Lake is long, up to wide and its surface area is . It is the second-largest mountain lake in the world behind Lake Titicaca in South America. It is at an altitude of and reaches in depth. About 118 rivers and streams f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiger Shark
The tiger shark (''Galeocerdo cuvier'') is a species of ground shark, and the only extant member of the genus '' Galeocerdo'' and family Galeocerdonidae. It is a large apex predator, with females capable of attaining a length of over . Populations are found in many tropical and temperate waters, especially around central Pacific islands. Its name derives from the dark stripes down its body, which resemble a tiger's pattern, but fade as the shark matures. The tiger shark is a solitary, mostly nocturnal hunter. It is notable for having the widest food spectrum of all sharks, with a range of prey that includes crustaceans, fish, seals, birds, squid, turtles, sea snakes, dolphins, and others, even smaller sharks. It also has a reputation as a "garbage eater", consuming a variety of inedible, man-made objects that linger in its stomach. Tiger sharks have only one recorded natural predator, the orca. It is considered a near-threatened species because of finning and fishing by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous territory in the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. It is by far the largest geographically of three constituent parts of the kingdom; the other two are metropolitan Denmark and the Faroe Islands. Citizens of Greenland are full Danish nationality law, citizens of Denmark and European Union citizenship, of the European Union. Greenland is one of the Special territories of members of the European Economic Area#Overseas countries and territories, Overseas Countries and Territories of the European Union and is part of the Council of Europe. It is the List of islands by area, world's largest island, and lies between the Arctic Ocean, Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Arctic Archipelago, Canadian Arctic Archipelago. It is the location of the northernmost point of land in the world; Kaffeklubben Island off the northern coast is the world's Northernmost point of land, northernmost undisputed point of land—Cape Morris Jesup on the mainland was thought to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ikaite
Ikaite is the mineral name for the hexahydrate of calcium carbonate, . Ikaite tends to form very steep or spiky pyramidal crystals, often radially arranged, of varied sizes from thumbnail size aggregates to gigantic salient spurs. It is only found in a metastable state and decomposes rapidly by losing most of its water content once removed from near-freezing water. This "melting mineral" is more commonly known through its pseudomorphs. Distribution It is usually considered a rare mineral, but this is likely due to difficulty in preserving samples. It was first discovered in nature by the Danish mineralogist Pauly in the Ikka Fjord in southwest Greenland, close to Ivittuut, the locality of the famous cryolite deposit. Here ikaite occurs in truly spectacular towers or columns (up to tall) growing out of the fjord floor towards the surface water, where they are naturally truncated by waves, or unnaturally by the occasional boat. At the Ikka Fjord, it is supposed that the ikai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |