|
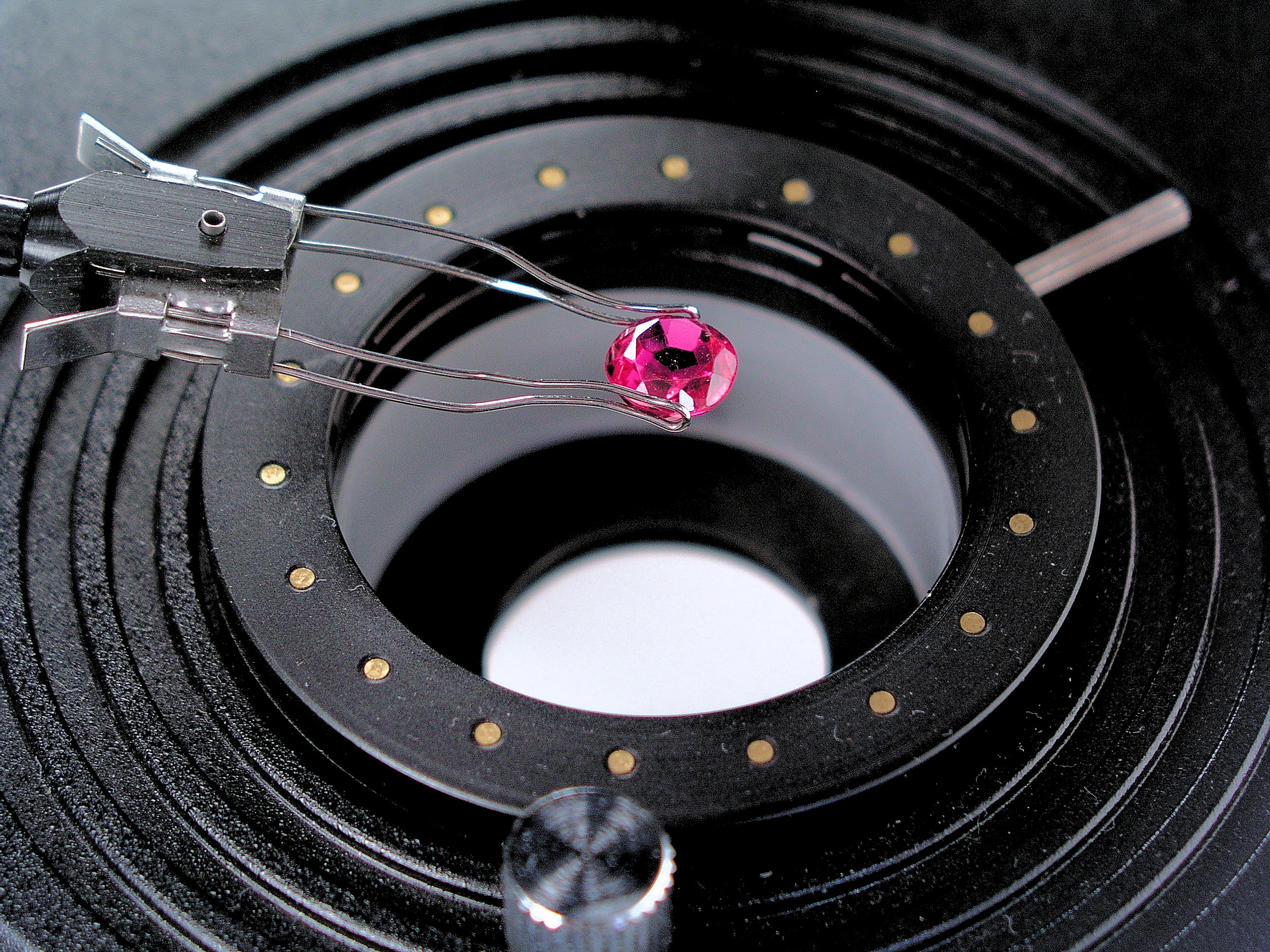
Memorial Diamonds
Memorial diamonds (also cremation diamonds) are lab-grown diamonds that are promoted as being produced from carbon extracted from human or pet animal hair or cremated remains that are provided to the producer by the customer. History The first lab-made diamonds can be dated back to the 1950s, and memorial diamonds started to appear in the market in the early 2000s. More than one company has claimed to be the first to provide memorial diamonds, and both Heart In Diamond and LifeGem have claimed to have a patent covering the growing of a "personalized gem diamond". Production process Memorial diamonds are produced using hair or ashes, often with other carbon ("lab carbon") added. In case of hair, it is subjected to heat treatment to extract carbon. Some laboratories also analyze the content of hair. A hair analysis report then serves as a client assurance. The process of unique identification of a diamond and a person based on the hair composition is described in the diamond pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lab-grown Diamond
A synthetic diamond or laboratory-grown diamond (LGD), also called a lab-grown, laboratory-created, man-made, artisan-created, artificial, or cultured diamond, is a diamond that is produced in a controlled technological process, in contrast to a naturally-formed diamond, which is created through geological processes and obtained by mining. Unlike diamond simulants (imitations of diamond made of superficially similar non-diamond materials), synthetic diamonds are composed of the same material as naturally formed diamonds—pure carbon crystallized in an isotropic 3D form—and have identical chemical and physical properties. The maximal size of synthetic diamonds has increased dramatically in the 21st century. Before 2010, most synthetic diamonds were smaller than half a carat. Improvements in technology, plus the availability of larger diamond substrates, have led to synthetic diamonds up to 125 carats in 2025.=https://www.gia.edu/gia-news-research/gems-gemology-summary-la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
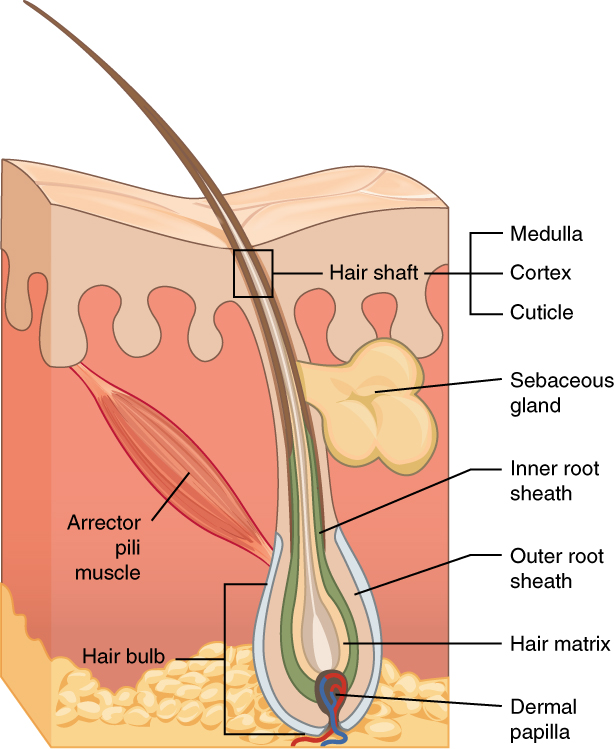
Hair
Hair is a protein filament that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals. The human body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which produce thick terminal and fine vellus hair. Most common interest in hair is focused on hair growth, hair types, and hair care, but hair is also an important biomaterial primarily composed of protein, notably alpha-keratin. Attitudes towards different forms of hair, such as hairstyles and hair removal, vary widely across different cultures and historical periods, but it is often used to indicate a person's personal beliefs or social position, such as their age, gender, or religion. Overview Meaning The word "hair" usually refers to two distinct structures: #the part beneath the skin, called the hair follicle, or, when pulled from the skin, the bulb or root. This organ is located in the dermis and maintains stem cells, which not only re-grow the hair afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cremated Remains
Cremation is a method of Disposal of human corpses, final disposition of a corpse through Combustion, burning. Cremation may serve as a funeral or post-funeral rite and as an alternative to burial. In some countries, including India, Nepal, and Syria, cremation on an Pyre, open-air pyre is an ancient tradition. Starting in the 19th century, cremation was introduced or reintroduced into other parts of the world. In modern times, cremation is commonly carried out with a Crematorium, closed furnace (cremator), at a crematorium. Cremation leaves behind an average of of remains known as ''ashes'' or ''cremains''. This is not all ash but includes unburnt fragments of bone mineral, which are commonly ground into powder. They are inorganic and inert, and thus do not constitute a health risk and may be buried, interred in a memorial site, retained by relatives or scattered in various ways. History Ancient Cremation dates from at least 17,000 years ago in the archaeological record, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Diamond
A synthetic diamond or laboratory-grown diamond (LGD), also called a lab-grown, laboratory-created, man-made, artisan-created, artificial, or cultured diamond, is a diamond that is produced in a controlled technological process, in contrast to a naturally-formed diamond, which is created through geological processes and obtained by mining. Unlike diamond simulants (imitations of diamond made of superficially similar non-diamond materials), synthetic diamonds are composed of the same material as naturally formed diamonds—pure carbon crystallized in an isotropic 3D form—and have identical chemical and physical properties. The maximal size of synthetic diamonds has increased dramatically in the 21st century. Before 2010, most synthetic diamonds were smaller than half a carat. Improvements in technology, plus the availability of larger diamond substrates, have led to synthetic diamonds up to 125 carats in 2025.=https://www.gia.edu/gia-news-research/gems-gemology-summary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemological
Gemology or gemmology is the science dealing with natural and artificial gemstone materials. It is a specific interdisciplinary branch of mineralogy. Some jewelers (and many non-jewelers) are academically trained gemologists and are qualified to identify and evaluate gems. History Rudimentary education in gemology for jewellers and gemologists began in the nineteenth century, but the first qualifications were instigated after the National Association of Goldsmiths of Great Britain (NAG) set up as an Education Committee for this purpose in 1908. The committee emerged as a distinct branch of NAG (named the Gemmological Association) in 1931, shortly after the incorporation of the Gemological Institute of America (GIA). In 1938 the branch was renamed as the Gemmological Association of Great Britain, before being incorporated in 1847. The organisation is now an educational charity and accredited awarding body with its courses taught worldwide. The first US graduate of Gem-A's diploma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |