|
Gemological
Gemology or gemmology is the science dealing with natural and artificial gemstone materials. It is a specific interdisciplinary branch of mineralogy. Some jewelers (and many non-jewelers) are academically trained gemologists and are qualified to identify and evaluate gems. History Rudimentary education in gemology for jewellers and gemologists began in the nineteenth century, but the first qualifications were instigated after the National Association of Goldsmiths of Great Britain (NAG) set up as an Education Committee for this purpose in 1908. The committee emerged as a distinct branch of NAG (named the Gemmological Association) in 1931, shortly after the incorporation of the Gemological Institute of America (GIA). In 1938 the branch was renamed as the Gemmological Association of Great Britain, before being incorporated in 1847. The organisation is now an educational charity and accredited awarding body with its courses taught worldwide. The first US graduate of Gem-A's diploma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemmological Microscopic Examination
Gemology or gemmology is the science dealing with natural and artificial gemstone materials. It is a specific interdisciplinary branch of mineralogy. Some jewellery, jewelers (and many non-jewelers) are academically trained gemologists and are qualified to identify and evaluate gems. History Rudimentary education in gemology for jewellers and gemologists began in the nineteenth century, but the first qualifications were instigated after the National Association of Goldsmiths of Great Britain (NAG) set up as an Education Committee for this purpose in 1908. The committee emerged as a distinct branch of NAG (named the Gemmological Association) in 1931, shortly after the incorporation of the Gemological Institute of America (GIA). In 1938 the branch was renamed as the Gemmological Association of Great Britain, before being incorporated in 1847. The organisation is now an educational charity and accredited awarding body with its courses taught worldwide. The first US graduate of Gem-A' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemological Institute Of America
The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) is a nonprofit institute based in Carlsbad, California. It is dedicated to research and education in the field of gemology and the jewelry arts. Founded in 1931, GIA's mission is to protect buyers and sellers of gemstones by setting and maintaining the standards used to evaluate gemstone quality. The institute does so through research, gem identification, diamond grading services, and a variety of educational programs. Through its library and subject experts, GIA acts as a resource of gem and jewelry information for the trade, the public and media outlets. In 1953 the GIA developed its International Diamond Grading System and the "four Cs" ( cut, clarity, color, and carat weight) as a standard to compare and evaluate the quality of diamonds. As of 2024, the institute is headquartered in Carlsbad, California, and operates in 13 countries, with 11 campuses, 9 laboratories, and 4 research centers. History GIA was founded in the 1920s by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
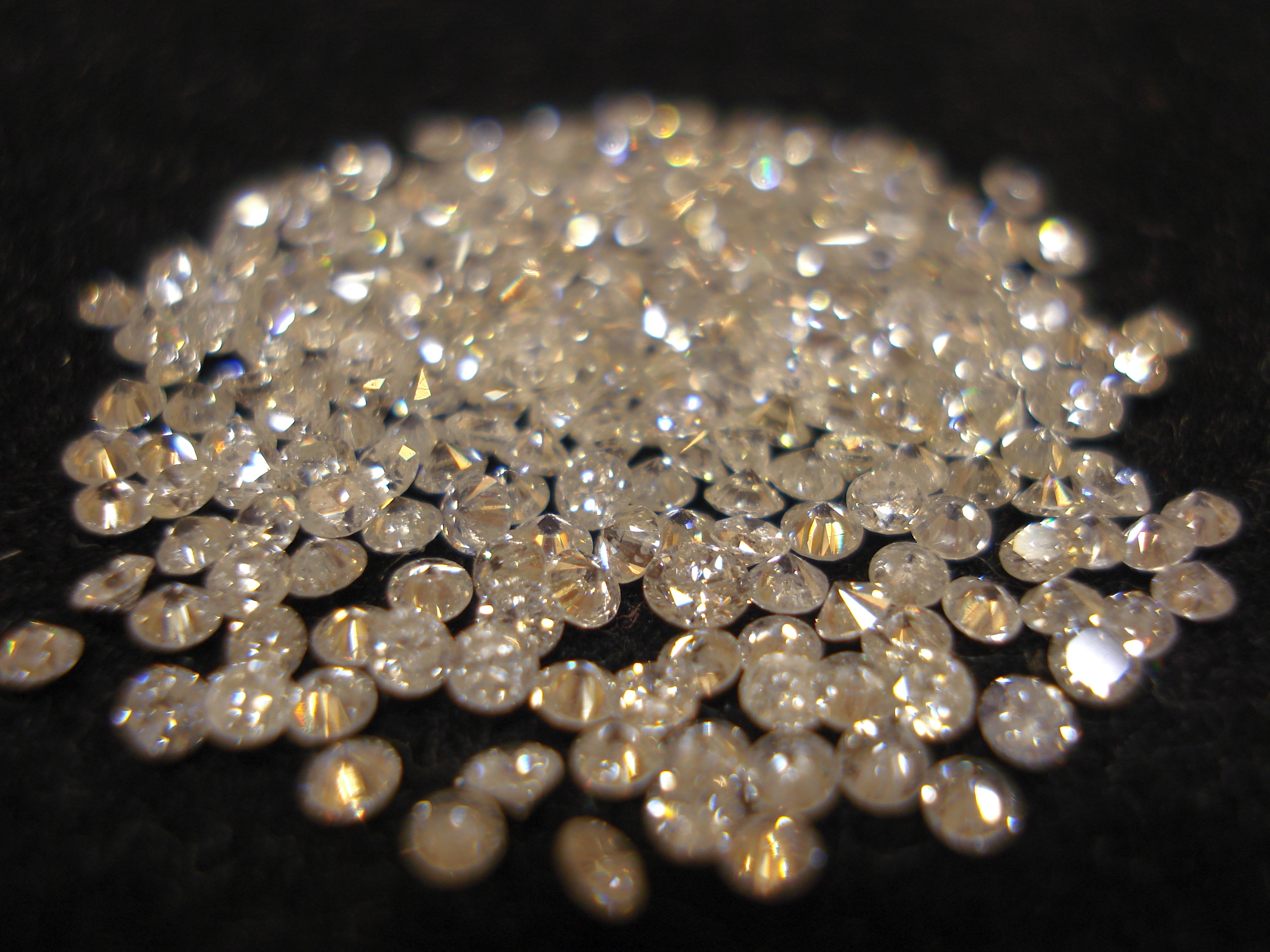
Gemstone
A gemstone (also called a fine gem, jewel, precious stone, semiprecious stone, or simply gem) is a piece of mineral crystal which, when cut or polished, is used to make jewellery, jewelry or other adornments. Certain Rock (geology), rocks (such as lapis lazuli, opal, and obsidian) and occasionally organic chemistry, organic materials that are not minerals (such as amber, Jet (gemstone), jet, and pearl) may also be used for jewelry and are therefore often considered to be gemstones as well. Most gemstones are hard, but some softer minerals such as brazilianite may be used in jewelry because of their color or Lustre (mineralogy), luster or other physical properties that have aesthetic value. However, generally speaking, soft minerals are not typically used as gemstones by virtue of their brittleness and lack of durability. Found all over the world, the industry of coloured gemstones (i.e. anything other than diamonds) is currently estimated at US$1.55billion and is projected to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
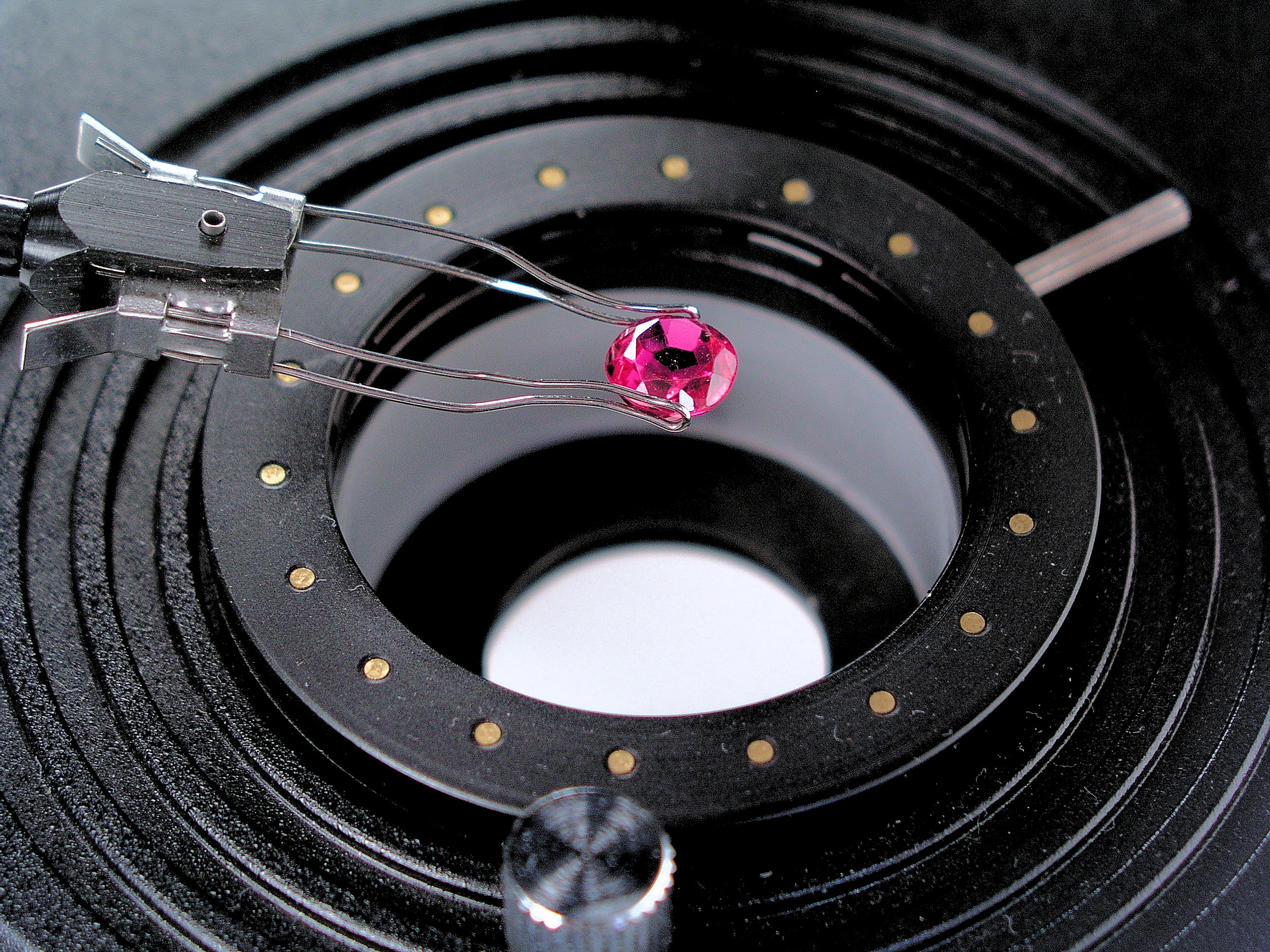
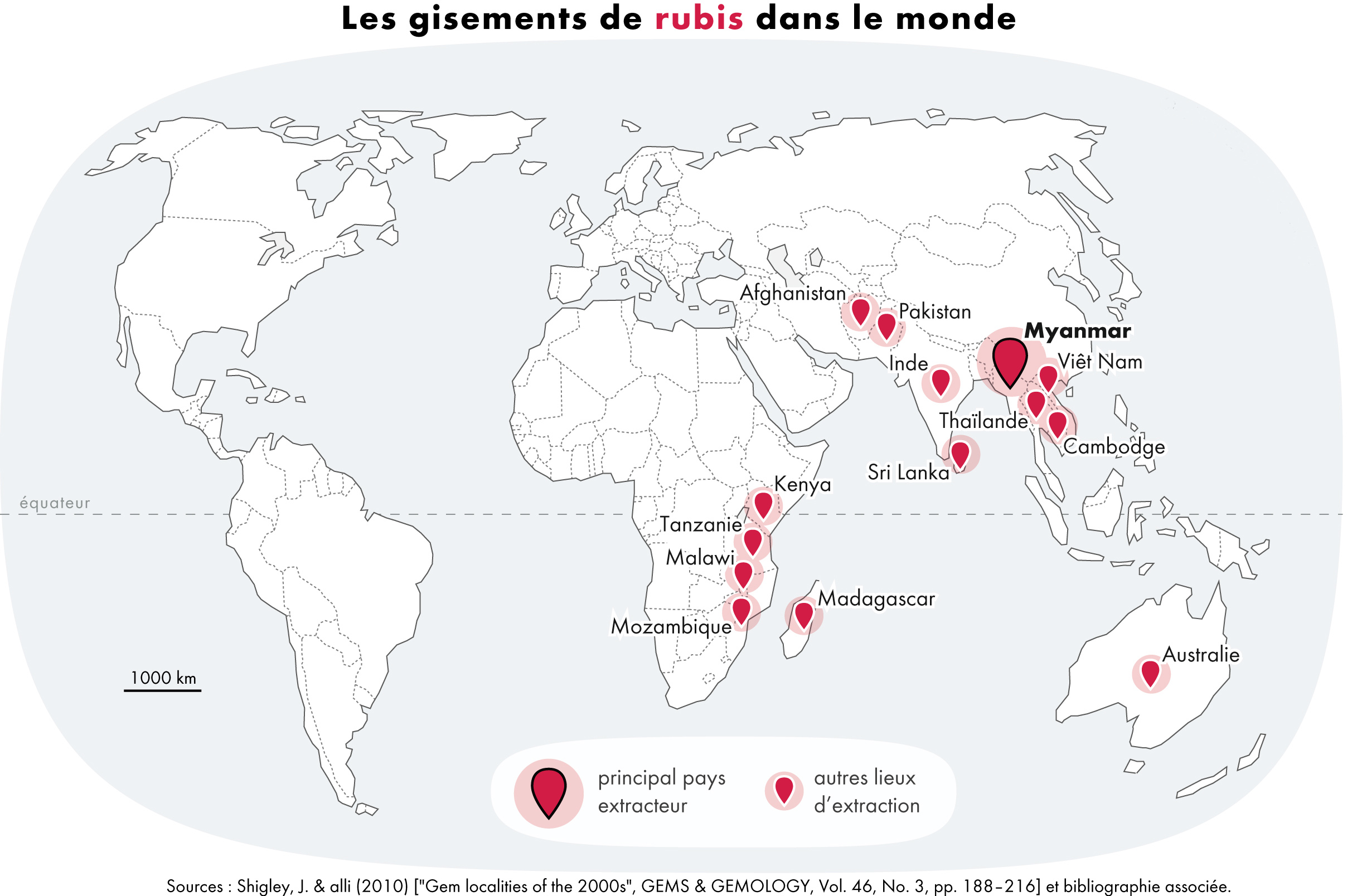
Ruby
Ruby is a pinkish-red-to-blood-red-colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum ( aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sapphires; given that the rest of the corundum species are called as such, rubies are sometimes referred to as "red sapphires". Ruby is one of the traditional cardinal gems, alongside amethyst, sapphire, emerald, and diamond. The word ''ruby'' comes from ''ruber'', Latin for red. The color of a ruby is due to the presence of chromium. Some gemstones that are popularly or historically called rubies, such as the Black Prince's Ruby in the British Imperial State Crown, are actually spinels. These were once known as "Balas rubies". The quality of a ruby is determined by its color, cut, and clarity, which, along with carat weight, affect its value. The brightest and most valuable shade of red, called blood-red or pigeon blood, commands a lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Gem Society
The American Gem Society (AGS) is a trade association of retail jewelers, independent appraisers, suppliers, and selective industry members, which was founded in 1934 by Robert M. Shipley. The Society is based in Las Vegas, Nevada, along with the affiliated American Gem Society Laboratories (AGSL) (founded in 1996) and the American Gem Society Advanced Instruments Division (founded in 2004). The Society trains and certifies jewelers, gemologists, and jewelry appraisers. Diamond grading is a specialty of the American Gem Society Laboratories and the Society has developed its own cut, color, and clarity Clarity may refer to: Music Albums * ''Clarity'' (Jimmy Eat World album) or the title song, 1999 * ''Clarity'' (Sifow album) or the title song, 2006 * ''Clarity'' (Zedd album) or the title song (see below), 2012 * ''Clarity'' (mixtape), by K ... standards. History The AGS was created by Robert M. Shipley. During the 1920s, Shipley was operating quite successfully as a jewe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractometer
A refractometer is a laboratory or field device for the measurement of an Refractive index, index of refraction (refractometry). The index of refraction is calculated from the observed refraction angle using Snell's law. For mixtures, the index of refraction then allows the concentration to be determined using mixing rules such as the Gladstone–Dale relation and Clausius–Mossotti_relation#Lorentz–Lorenz_equation, Lorentz–Lorenz equation. Refractometry Standard refractometers measure the extent of light refraction (as part of a refractive index) of transparent substances in either a liquid this is then used in order to identify a liquid sample, analyze the sample's purity, and determine the amount or concentration of dissolved substances within the sample. As light passes through the liquid from the air it will slow down and create a ‘bending’ illusion, the severity of the ‘bend’ will depend on the amount of substance dissolved in the liquid. For example, the am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubic Zirconia
Cubic zirconia (CZ) is the cubic crystalline form of zirconium dioxide (ZrO2). The synthesized material is hard and usually colorless, but may be made in a variety of different colors. It should not be confused with zircon, which is a zirconium silicate (ZrSiO4). It is sometimes erroneously called ''cubic zirconium''. Because of its low cost, durability, and close visual likeness to diamond, synthetic cubic zirconia has remained the most gemologically and economically important competitor for diamonds since commercial production began in 1976. Its main competitor as a synthetic gemstone is a more recently cultivated material, synthetic moissanite. Technical aspects Cubic zirconia is crystallographically isometric, an important attribute of a would-be diamond simulant. During synthesis zirconium oxide naturally forms monoclinic crystals, which are stable under normal atmospheric conditions. A stabilizer is required for cubic crystals (taking on the fluorite structure) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewellery
Jewellery (or jewelry in American English) consists of decorative items worn for personal adornment such as brooches, ring (jewellery), rings, necklaces, earrings, pendants, bracelets, and cufflinks. Jewellery may be attached to the body or the clothes. From a western perspective, the term is restricted to durable Ornament (art), ornaments, excluding flowers for example. For many centuries metal such as gold often combined with gemstones, has been the normal material for jewellery, but other materials such as glass, shells and other plant materials may be used. Jewellery is one of the oldest types of archaeological artefact – with 100,000-year-old beads made from ''Nassarius'' shells thought to be the oldest known jewellery. The basic forms of jewellery vary between cultures but are often extremely long-lived; in European cultures the most common forms of jewellery listed above have persisted since ancient times, while other forms such as adornments for the nose or ankle, impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
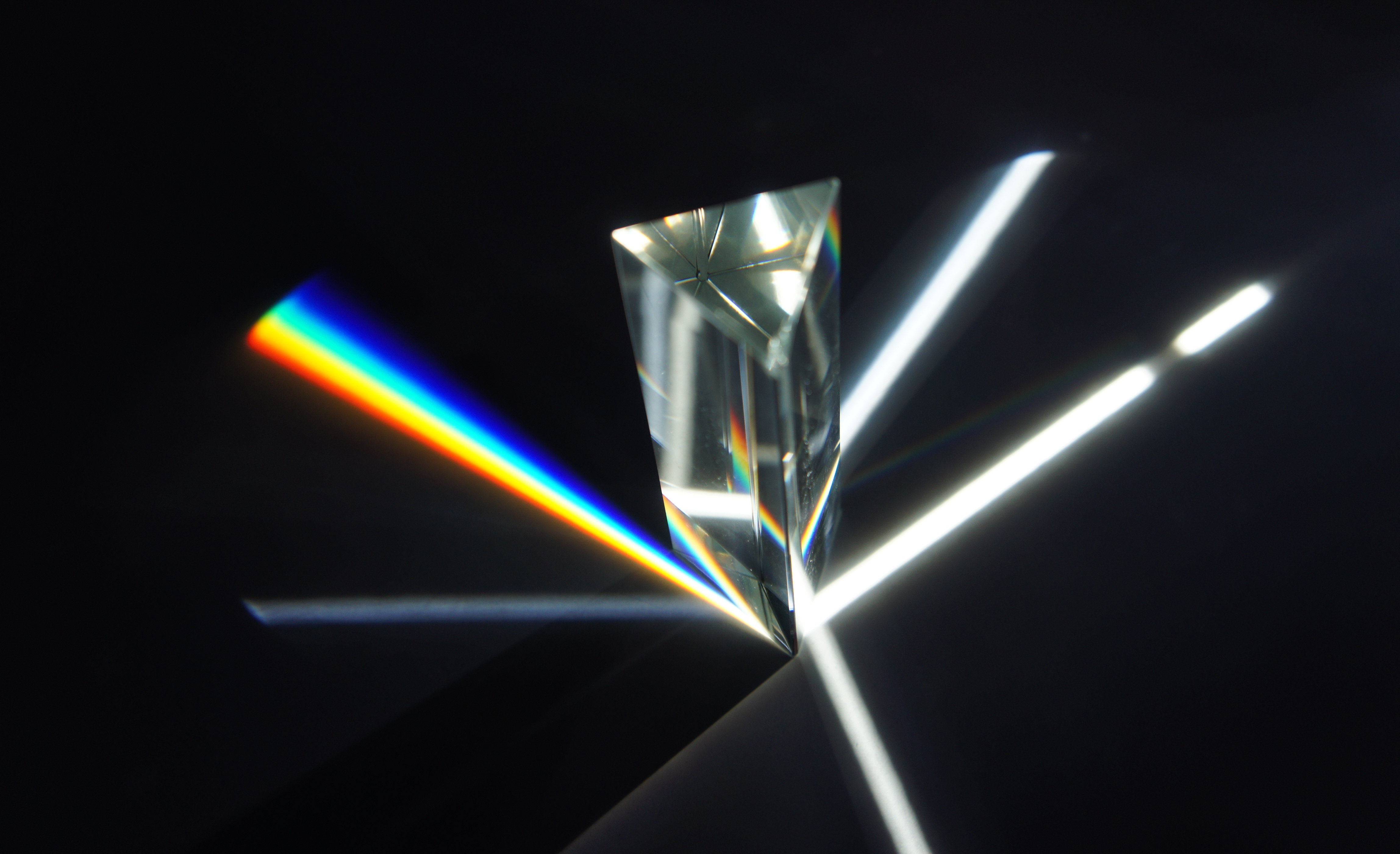
Prism (optics)
An optical prism is a transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that are designed to refract light. At least one surface must be angled—elements with two parallel surfaces are ''not'' prisms. The most familiar type of optical prism is the triangular prism, which has a triangular base and rectangular sides. Not all optical prisms are geometric prisms, and not all geometric prisms would count as an optical prism. Prisms can be made from any material that is transparent to the wavelengths for which they are designed. Typical materials include glass, acrylic and fluorite. A dispersive prism can be used to break white light up into its constituent spectral colors (the colors of the rainbow) to form a spectrum as described in the following section. Other types of prisms noted below can be used to reflect light, or to split light into components with different polarizations. Types Dispersive ''Dispersive prisms'' are used to break up light into its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Gravity
Relative density, also called specific gravity, is a dimensionless quantity defined as the ratio of the density (mass of a unit volume) of a substance to the density of a given reference material. Specific gravity for solids and liquids is nearly always measured with respect to water at its densest (at ); for gases, the reference is air at room temperature (). The term "relative density" (abbreviated r.d. or RD) is preferred in SI, whereas the term "specific gravity" is gradually being abandoned. If a substance's relative density is less than 1 then it is less dense than the reference; if greater than 1 then it is denser than the reference. If the relative density is exactly 1 then the densities are equal; that is, equal volumes of the two substances have the same mass. If the reference material is water, then a substance with a relative density (or specific gravity) less than 1 will float in water. For example, an ice cube, with a relative density of about 0.91, will float. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Critical Angle (optics)
In physics, total internal reflection (TIR) is the phenomenon in which waves arriving at the interface (matter), interface (boundary) from one Transmission medium, medium to another (e.g., from water to air) are not refraction, refracted into the second ("external") medium, but completely reflection (physics), reflected back into the first ("internal") medium. It occurs when the second medium has a higher wave speed (i.e., lower refractive index) than the first, and the waves are incident at a sufficiently oblique angle on the interface. For example, the water-to-air surface in a typical fish tank, when viewed obliquely from below, reflects the underwater scene like a mirror with no loss of brightness (Fig.1). TIR occurs not only with electromagnetic waves such as light and microwaves, but also with other types of waves, including sound and water waves. If the waves are capable of forming a narrow beam (Fig.2), the reflection tends to be described in terms of "ray (optics), rays" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |